Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Release and Biotransformation of Bound Phenolics in Ma Bamboo Shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Fermented Bamboo Shoot Samples
2.3. Determination of Polyphenol Content
2.4. Determination of Polyphenol Fractions
2.5. Determination of pH and Total Acid (TA) Content
2.6. Enzyme Activity Assay
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.7.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.7.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.10. Inverted Fluorescence Microscope (IFM)
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
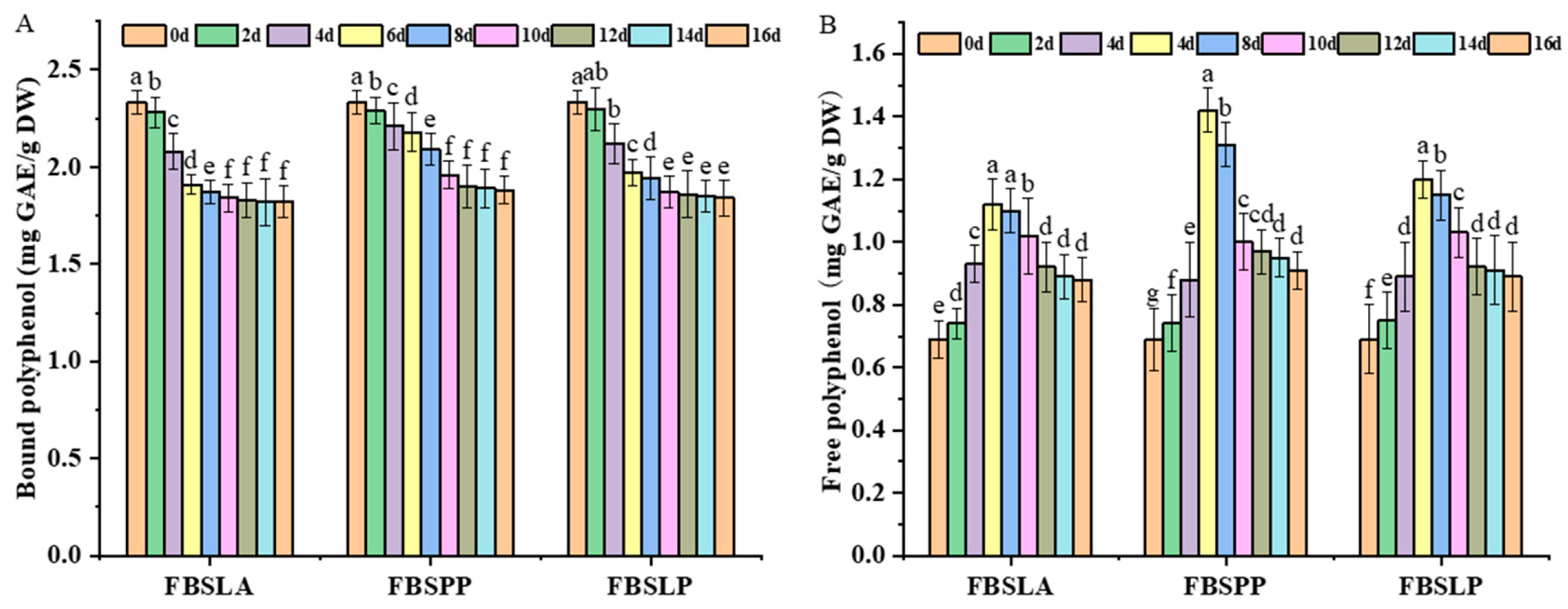
3.1. Impact of LAB Fermentation on Polyphenol Content in Bamboo Shoots
3.2. Effect of LAB Fermentation on the Polyphenol Composition in Bamboo Shoots
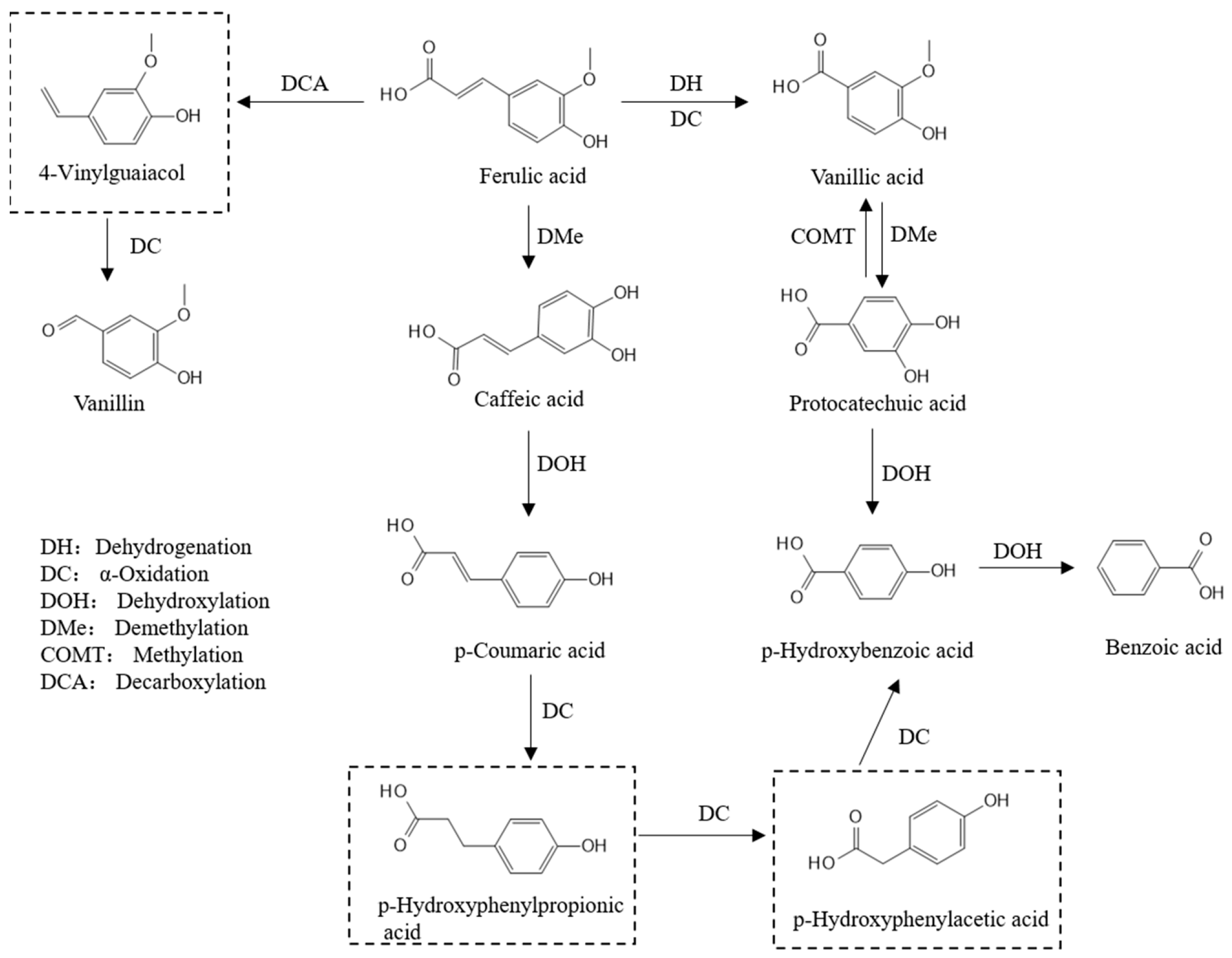
3.3. Biotransformation Among Polyphenol Components in Fermented Bamboo Shoots
3.4. Effects of LAB Fermentation on pH, TA, and Enzyme Activity in Bamboo Shoots
3.5. Comparative Antioxidant Activity of Free and Bound Phenol Extracts in Fermented Bamboo Shoots
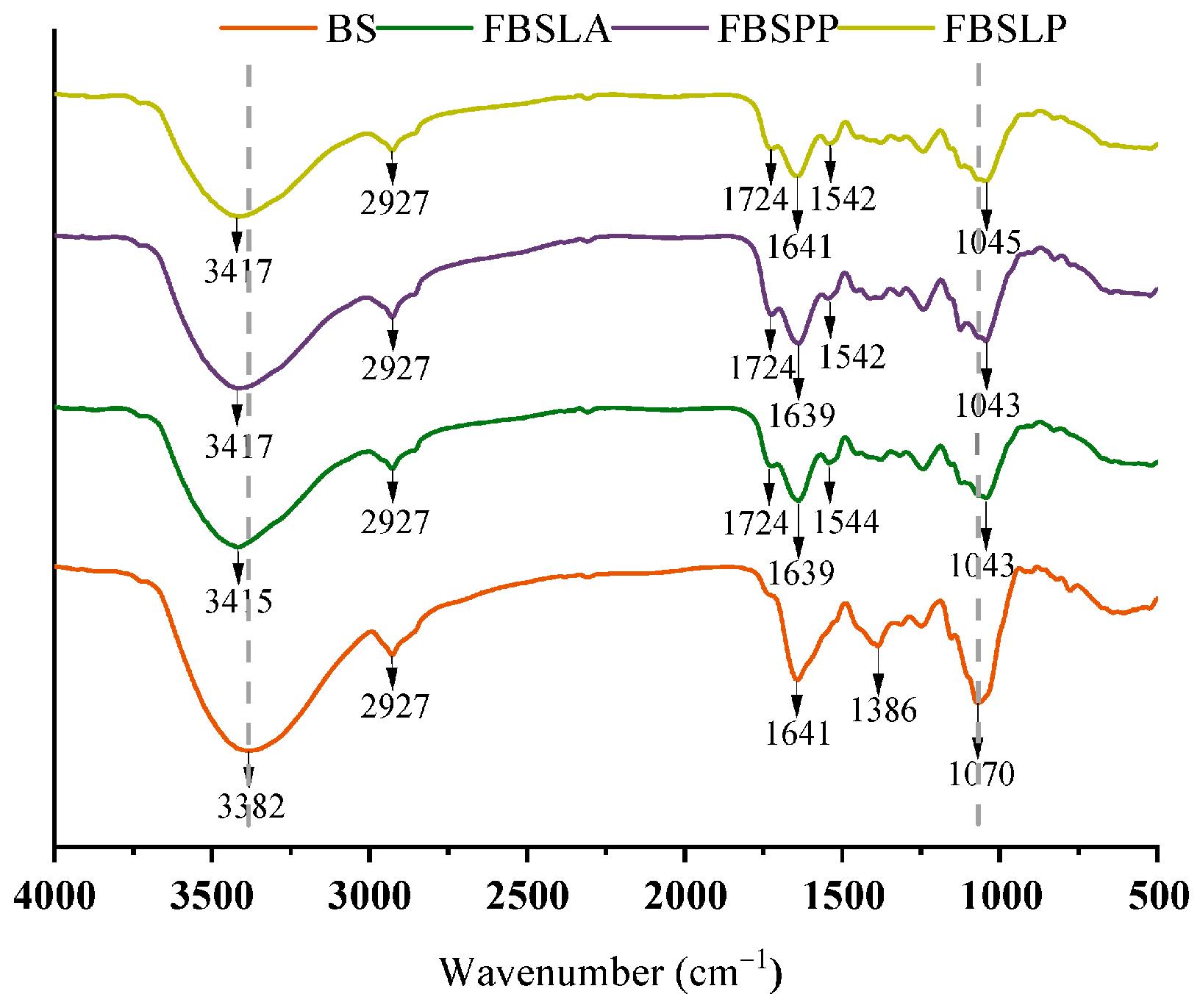
3.6. FTIR Analysis of Bamboo Shoots Samples Before and After LAB Fermentation
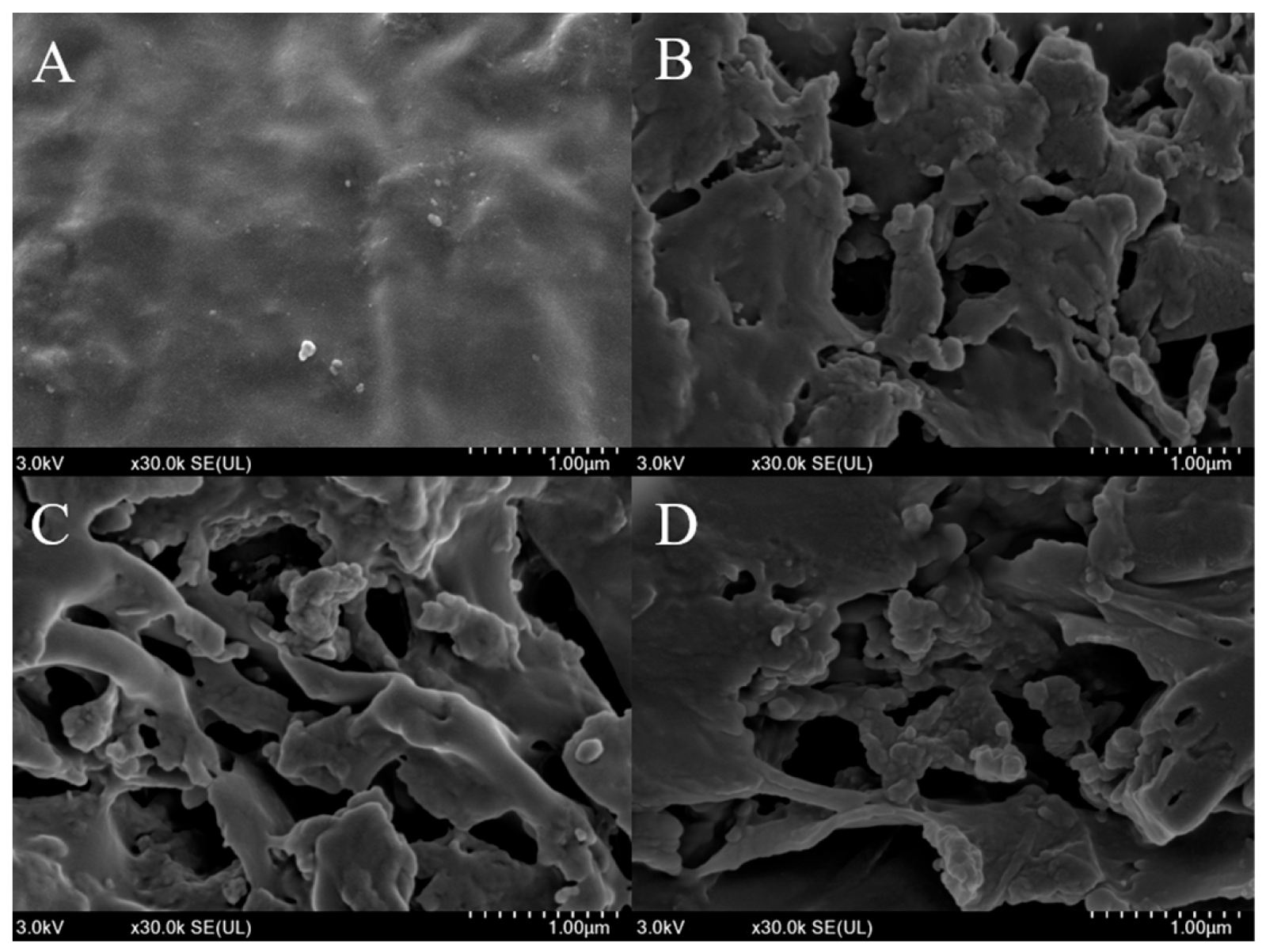
3.7. SEM Analysis of Bamboo Shoot Samples Before and After LAB Fermentation
3.8. IFM of Bamboo Shoot Samples Before and After LAB Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhury, D.; Sahu, J.K.; Sharma, G.D. Value Addition to Bamboo Shoots: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Deng, T.; Zhao, X.; Shi, S.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, X.; Li, W. The Effects of Drying Methods on Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of Two Cultivars of Psidium Guajava Fruits. LWT 2020, 118, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.; Balaji, S. Health Benefits of Fermented Bamboo Shoots: The Twenty-First Century Green Gold of Northeast India. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Mao, B.; Zhang, H.; Cui, S. Characterization of Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profiles of Fermented Chinese Bamboo Shoots (Suansun) from Liuzhou and Guilin. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Du, W.; Chen, Q.; Hu, S. Dynamic Changes in Flavor and Microbiota in Traditionally Fermented Bamboo Shoots (Chimonobambusa Szechuanensis (Rendle) Keng f.). Foods 2023, 12, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant Characteristics of Bound and Free Phenolics from Rosa Roxburghii Tratt. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, M.; Wen, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; McClements, D.J.; Nemli, E.; Bener, M.; Apak, R.; Capanoglu, E. Recent Progress in Promoting the Bioavailability of Polyphenols in Plant-Based Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 2343–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Remize, F.; Poucheret, P. Fruits and Vegetables, as a Source of Nutritional Compounds and Phytochemicals: Changes in Bioactive Compounds during Lactic Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razola-Díaz, M.d.C.; De Montijo-Prieto, S.; Guerra-Hernández, E.J.; Jiménez-Valera, M.; Ruiz-Bravo, A.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Verardo, V. Fermentation of Orange Peels by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Impact on Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity. Foods 2024, 13, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X. Influence of Fermentation with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria and in Vitro Digestion on the Change of Phenolic Compounds in Fermented Kiwifruit Pulps. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2670–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J. Influence of Fermentation by Lactic Acid Bacteria and in Vitro Digestion on the Biotransformations of Blueberry Juice Phenolics. Food Control 2022, 133, 108603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Omedi, J.O.; Huang, W.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, L.; Li, N.; Gao, T.; et al. Antioxidant, flavor profile and quality of wheat dough bread incorporated with kiwifruit fermented by β-glucosidase producing lactic acid bacteria strains. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and storage temperature on the fermentation quality, in vitro digestibility and phenolic acid extraction yields of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) silage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, D.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Mo, R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of Free, Esterified and Bound Phenolic Compounds in Walnut Kernel. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Li, A.; Tang, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, P.; Cheng, H. Bound Phenolics Release from Dried Bamboo Shoots Prepared by Different Processes during in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion: Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7047–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 12456-2021; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Total Acid in Foods. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, X.; Guo, Q.; Yue, Y.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. The Bioaccessibility, Bioavailability, Bioactivity, and Prebiotic Effects of Phenolic Compounds from Raw and Solid-Fermented Mulberry Leaves during in Vitro Digestion and Colonic Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar-Sümer, E.N.; Verheust, Y.; Özçelik, B.; Raes, K. Impact of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation Based on Biotransformation of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Mushrooms. Foods 2024, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.; Albuquerque, T.; Santos, A.; Massa, N.; Alves, J. Potential Interactions among Phenolic Compounds and Probiotics for Mutual Boosting of Their Health-Promoting Properties and Food Functionalities—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C. Effect of Lactobacillus (L. Acidophilus NCIB1899, L. Casei CRL 431, L. Paracasei LP33) Fermentation on Free and Bound Polyphenolic, Antioxidant Activities in Three Chenopodium Quinoa Cultivars. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Sui, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, J.; Cai, S.; Xiong, T.; Cai, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.; Mei, X. Phenolic Profile and Bioactivity Changes of Lotus Seedpod and Litchi Pericarp Procyanidins: Effect of Probiotic Bacteria Biotransformation. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, G.; Gänzle, M.G. Conversion of (Poly) Phenolic Compounds in Food Fermentations by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Novel Insights into Metabolic Pathways and Functional Metabolites. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Chao, C.; Derang, N.; Yubo, Y.; Jinhu, T.; Yuanyi, L.; Shiguo, C.; Xingqian, Y.; Li, W. Effects of Fermentation on Bioactivity and the Composition of Polyphenols Contained in Polyphenol-Rich Foods: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, B.; Chakraborty, D.; Kumar, B. Phenolic Biotransformations during Conversion of Ferulic Acid to Vanillin by Lactic Acid Bacteria. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 590359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Tran, M.H.; Lee, E.Y. Co-Upgrading of Ethanol-Assisted Depolymerized Lignin: A New Biological Lignin Valorization Approach for the Production of Protocatechuic Acid and Polyhydroxyalkanoic Acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 338, 125563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.P.G.; Sganzerla, W.G.; John, O.D.; Marchiosi, R.A. Comprehensive Review of the Classification, Sources, Biosynthesis, and Biological Properties of Hydroxybenzoic and Hydroxycinnamic Acids. Phytochem. Rev. 2023, 24, 1061–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Liao, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Chang, X.; Peng, G.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; Yu, Q. Release Characteristic and Mechanism of Bound Polyphenols from Insoluble Dietary Fiber of Navel Orange Peel via Mixed Solid-State Fermentation with Trichoderma Reesei and Aspergillus Niger. LWT 2022, 161, 113387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, S.; Dong, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Xie, J.; Xue, P.; Feng, L.; Yu, Q. Mixed Solid-State Fermentation for Releasing Bound Polyphenols from Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Carrots via Trichoderma Viride and Aspergillus Niger. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, R.; Khorsandi, K.; Hemmaty, S. Study of the Effect of Surfactants on Extraction and Determination of Polyphenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruits Extracts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Fermentation and Complex Enzyme Hydrolysis for Improving the Total Soluble Phenolic Contents, Flavonoid Aglycones Contents and Bio-Activities of Guava Leaves Tea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, N.; Teng, J.; Wei, B.; Huang, L. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on Extractable and Non-Extractable Polyphenols of Soybean Milk: Influence of β-Glucosidase and Okara. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Kong, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, X. Comparison of Enzyme Secretion and Ferulic Acid Production by Escherichia Coli Expressing Different Lactobacillus Feruloyl Esterases. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 568716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Campos, F.M.; Hogg, T.; Couto, J.A. Wine Phenolic Compounds Influence the Production of Volatile Phenols by Wine-Related Lactic Acid Bacteria: Production of Volatile Phenols by LAB. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C. Improved Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Dietary Fiber from Millet Bran Fermented by Bacillus Natto. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Dong, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Peng, G.; Liao, W.; Xue, P.; Feng, L.; Yu, Q. Bound Polyphenols from Insoluble Dietary Fiber of Defatted Rice Bran by Solid-State Fermentation with Trichoderma Viride: Profile, Activity, and Release Mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5026–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Kiefer, J.; Santini, A.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Souto, E.; Romani, A.; Lampe, A.; Ferrari Nicoli, S.; Gabrielli, P.; et al. Grape Seeds: Chromatographic Profile of Fatty Acids and Phenolic Compounds and Qualitative Analysis by FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy. Foods 2019, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Olejar, K.J.; Parpinello, G.P.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Versari, A. Application of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy in the Characterization of Tannins. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 407–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fangel, J.U.; Willats, W.G.T.; Vivier, M.A.; Moore, J.P. Dissecting the Polysaccharide-Rich Grape Cell Wall Changes during Winemaking Using Combined High-Throughput and Fractionation Methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.N.; Mancini, M.C.; Oliveira, F.C.S.D.; Passos, T.M.; Quilty, B.; Thiré, R.M.D.S.M.; McGuinness, G.B. FTIR Analysis and Quantification of Phenols and Flavonoids of Five Commercially Available Plants Extracts Used in Wound Healing. Matéria 2016, 21, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Estrada, B.A.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O. Bound Phenolics in Foods, a Review. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ying, D.; Sanguansri, L.; Cai, Y.; Le, X. Adsorption of Catechin onto Cellulose and Its Mechanism Study: Kinetic Models, Characterization and Molecular Simulation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Phenolic Content | BS | FBSLA | FBSPP | FBSLP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bound | Protocatechuic acid | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 23.84 ± 0.94 d | 101.80 ± 4.68 b | 108.96 ± 5.86 a | 91.79 ± 3.16 c | |
| Vanillic acid | 66.75 ± 7.15 a | 4.30 ± 0.14 d | 8.03 ± 0.22 b | 7.98 ± 0.18 c | |
| Vanillin | 8.78 ± 0.23 d | 13.05 ± 0.16 c | 21.43 ± 2.23 a | 18.12 ± 0.08 b | |
| p-Coumaric acid | 173.52 ± 5.79 b | 136.32 ± 8.07 d | 208.28 ± 9.42 a | 165.58 ± 8.89 c | |
| Ferulic acid | 504.01 ± 10.20 a | 458.93 ± 9.26 b | 404.20 ± 6.94 c | 400.25 ± 7.77 c | |
| Free | Protocatechuic acid | 0.01 ± 0.00 d | 23.52 ± 1.06 c | 32.26 ± 1.57 a | 26.78 ± 1.12 b |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | ND | 3.95 ± 0.08 c | 7.11 ± 0.06 a | 6.44 ± 0.08 b | |
| Vanillic acid | 83.21 ± 3.29 c | 107.13 ± 9.26 b | 119.57 ± 8.69 a | 118.17 ± 9.23 a | |
| Vanillin | 0.72 ± 0.04 c | 0.64 ± 0.07 d | 2.21 ± 0.07 a | 0.76 ± 0.12 b | |
| p-Coumaric acid | 0.67 ± 0.07 d | 0.87 ± 0.07 c | 20.83 ± 0.08 a | 14.36 ± 0.17 b | |
| Ferulic acid | 7.33 ± 0.20 d | 22.19 ± 0.62 c | 33.63 ± 1.13 a | 25.82 ± 1.46 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Li, A.; Liu, H.; Mo, Q.; Zhong, Z. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Release and Biotransformation of Bound Phenolics in Ma Bamboo Shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Foods 2025, 14, 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152573
Zhang L, Li A, Liu H, Mo Q, Zhong Z. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Release and Biotransformation of Bound Phenolics in Ma Bamboo Shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Foods. 2025; 14(15):2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152573
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liangshi, Anping Li, Hemei Liu, Qifeng Mo, and Zhengchang Zhong. 2025. "Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Release and Biotransformation of Bound Phenolics in Ma Bamboo Shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro)" Foods 14, no. 15: 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152573
APA StyleZhang, L., Li, A., Liu, H., Mo, Q., & Zhong, Z. (2025). Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Release and Biotransformation of Bound Phenolics in Ma Bamboo Shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro). Foods, 14(15), 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152573






