Environmental and Food Safety Assessment of Pre-Harvest Activities in Local Small-Scale Fruit and Vegetable Farms in Northwest Portugal: Hazard Identification and Compliance with Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
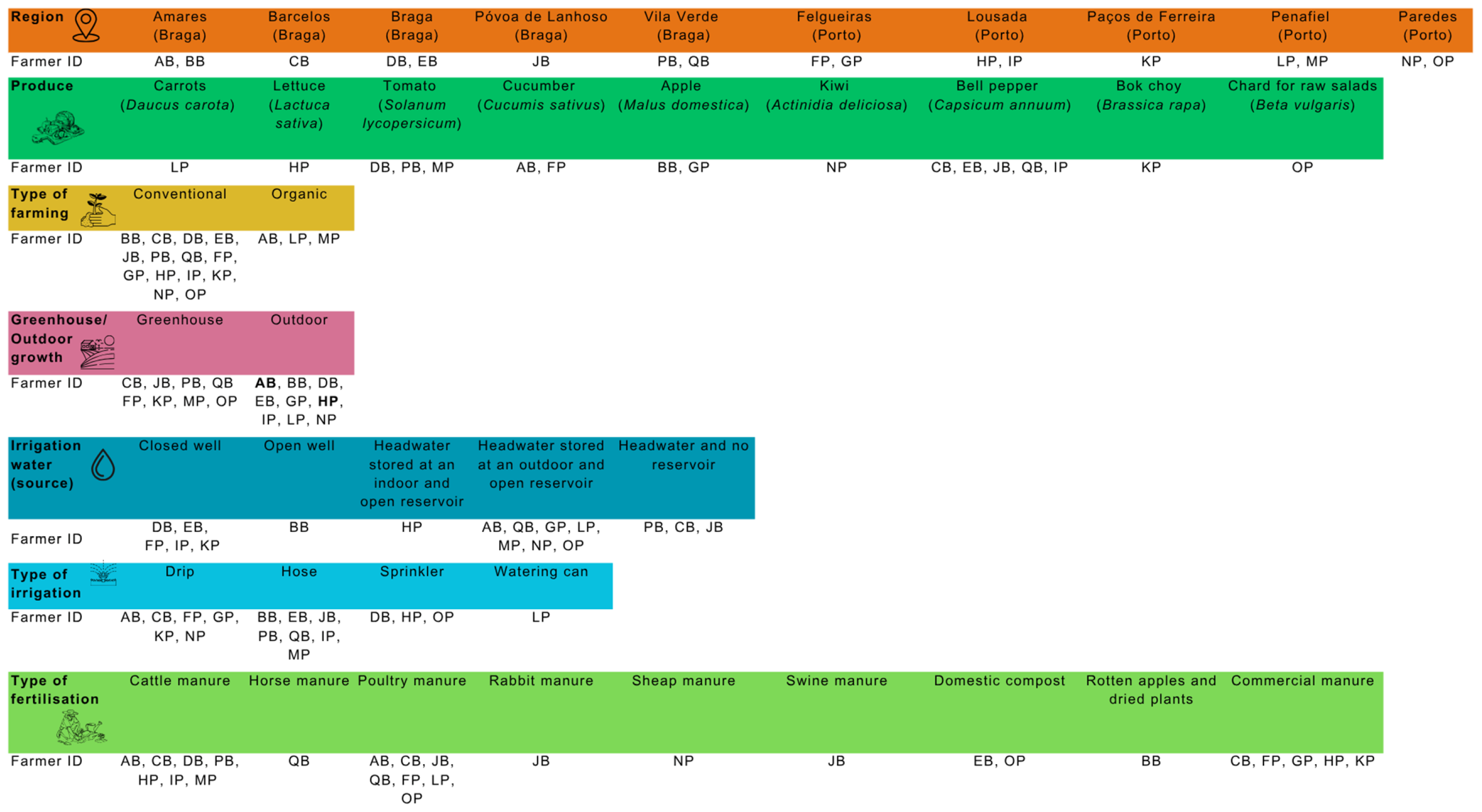
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Microbiological Analysis
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3.1. Pesticide, PCBs, and Flame Retardants Compounds
2.3.2. Nitrate
2.3.3. Heavy Metals
2.4. Evaluation of Farmers’ Behaviour Regarding GAPs Before and After Training
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
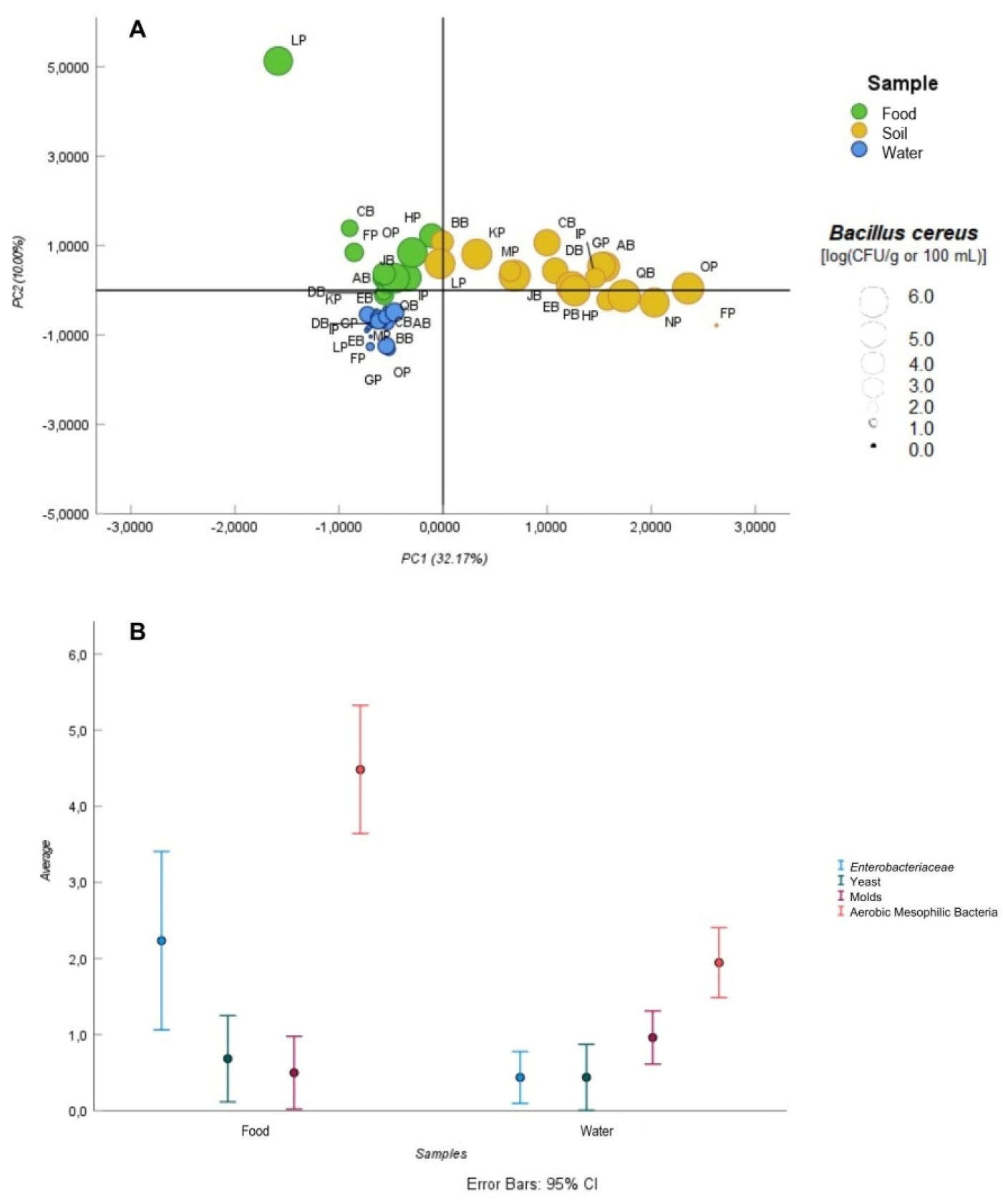
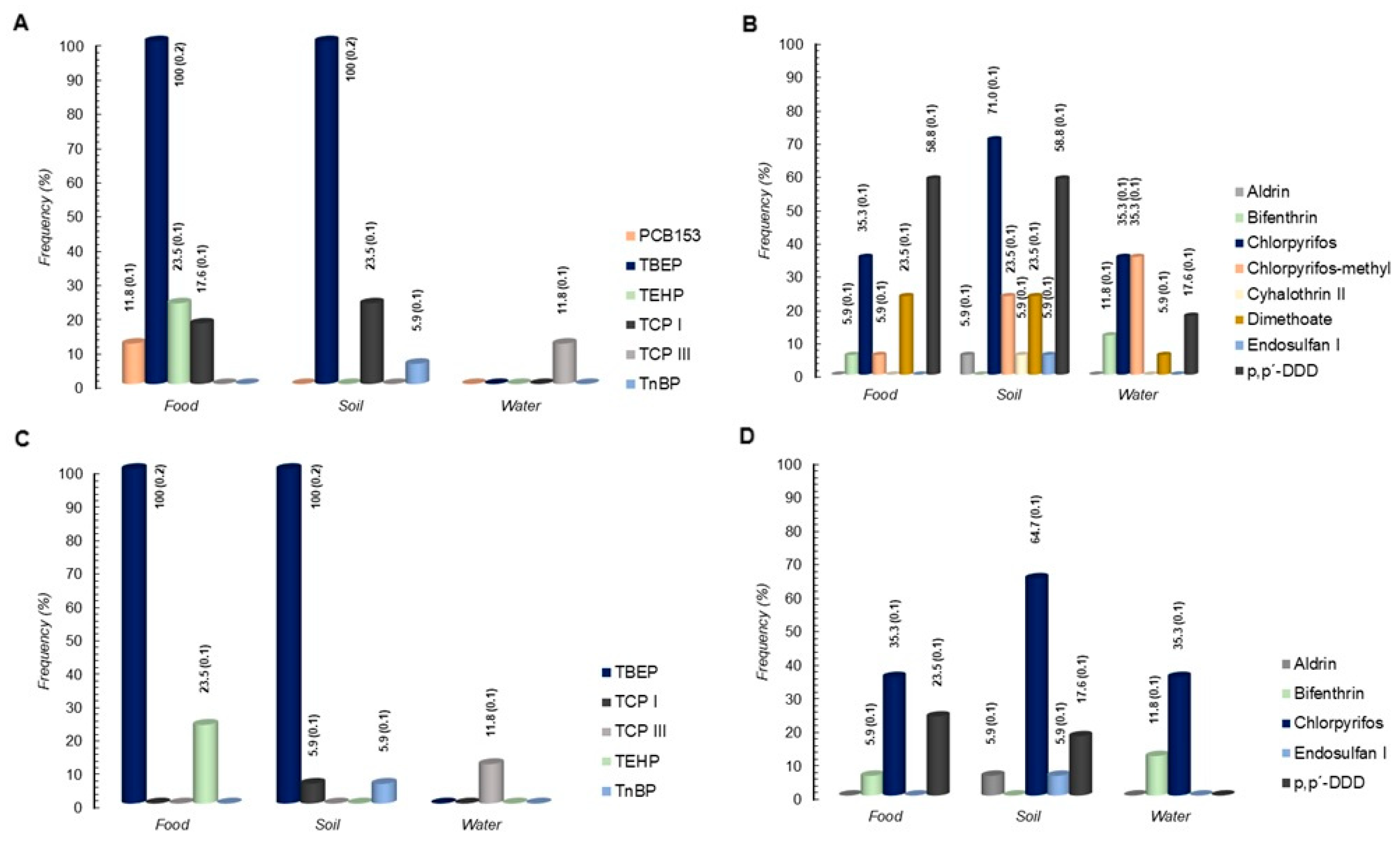
3.1. Assessment of Microbiological and Chemical Hazards
3.2. Impact of Training on Farmers’ Adherence to Good Agricultural Practices
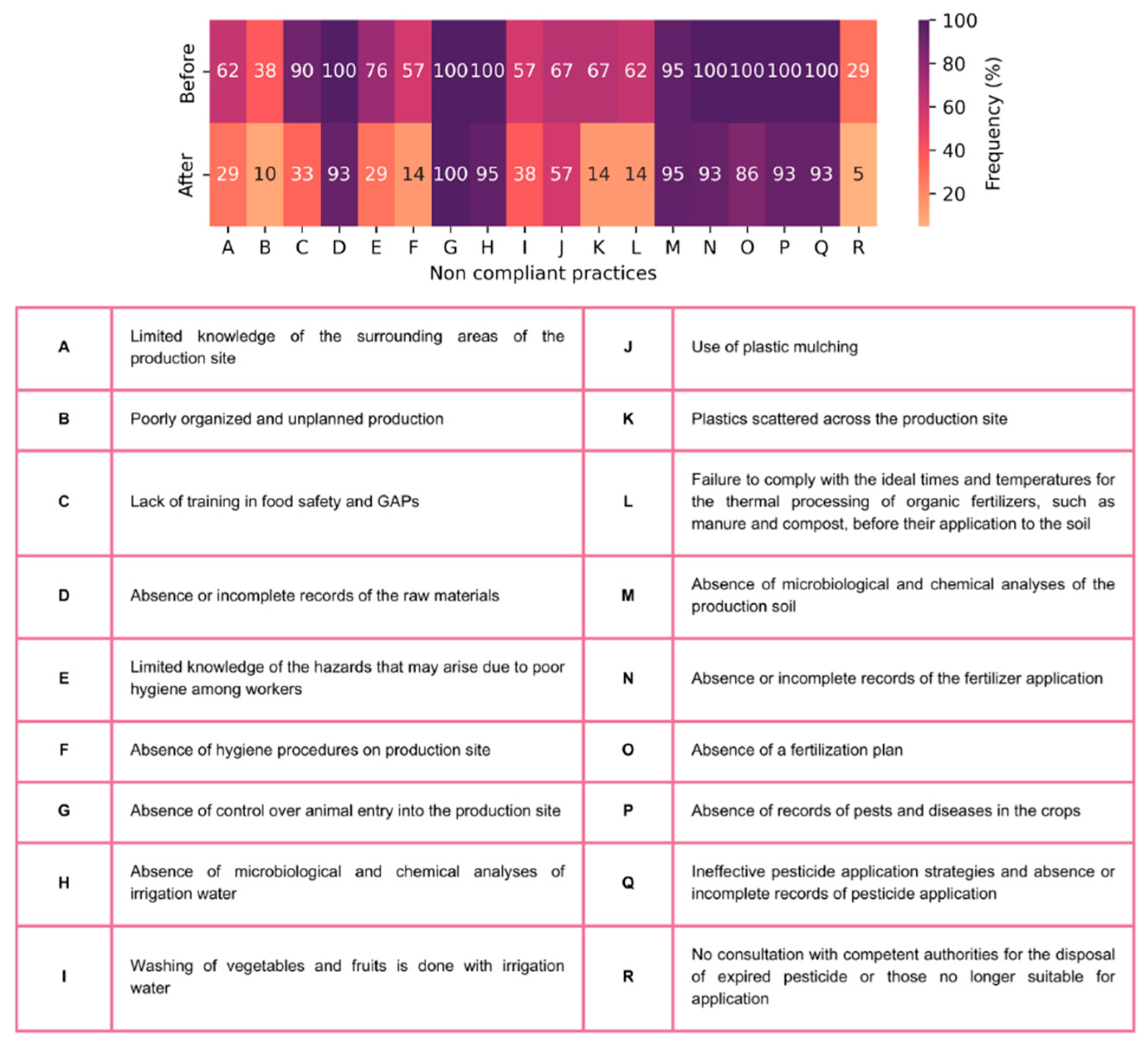
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Talwar, S.; Murphy, M.; Kaur, P.; Dhir, A. A behavioural reasoning perspective on the consumption of local food. A study on REKO, a social media-based local food distribution system. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 93, 104264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mritunjay, S.K.; Kumar, V. Fresh farm produce as a source of pathogens: A review. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 9, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, S.C.; Mauad, J.R.C.; Domingues, C.H.F.; Borges, J.A.R.; Silva, J.R. The importance of local food products’ attributes in Brazilian consumers’ preferences. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.D.; Christensen, T.; Denver, S.; Ditlevsen, K.; Lassen, J.; Teuber, R. Heterogeneity in consumers’ perceptions and demand for local (organic) food products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 73, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, S.B.; Akoglu, A. Assessment of local food use in the context of sustainable food: A research in food and beverage enterprises in Izmir, Turkey. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 20, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; Galli, F.; Menozzi, D.; Maye, D.; Touzard, J.; Marescotti, A.; Six, J.; Brunori, G. Comparing the sustainability of local and global food products in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, R.B.; Neill, C.L.; Lelekacs, J.; Velandia, M.; Woods, T.A.; Goodwin, H.L.; Rainey, R.L. A local food system glossary: A rose by any other name. Choices 2018, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Skallerud, K.; Wien, A.H. Preference for local food as a matter of helping behavior: Insights from Norway. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 67, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Grunert, K.G.; Zhou, Y. A values–beliefs–attitude model of local food consumption: An empirical study in China and Denmark. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaimat, A.N.; Holley, R.A. Factors influencing the microbial safety of fresh produce: A review. Food Microbiol. 2012, 32, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, J.W.; Walcott, R.R.; Beuchat, L.R. Recent trends in microbiological safety of fruits and vegetables. Plant Health Prog. 2003, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłapeć, T.; Wójcik-Fatla, A.; Cholewa, A.; Cholewa, G.; Dutkiewicz, J. Microbiological characterization of vegetables and their rhizosphere soil in Eastern Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macieira, A.; Barbosa, J.; Teixeira, P. Food safety in local farming of fruits and vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinberg, J.A.; Dudley, E.G.; Campbell, J.; Roberts, B.; DiMarzio, M.; Debroy, C.; Cutter, C.N. Prevalence and phylogenetic characterization of Escherichia coli and hygiene indicator bacteria isolated from leafy green produce, beef, and pork obtained from farmers’ markets in Pennsylvania. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.; Simonne, A.; House, L.; Ahn, S. Microbiological analysis of fresh produce sold at Florida farmers’ markets. Food Control 2018, 92, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Singleton, I.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Sources and contamination routes of microbial pathogens to fresh produce during field cultivation: A review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikankuba, V.L.; Mwanyika, G.; Ntwenya, J.E.; James, A.; Yildiz, F. Pesticide regulations and their malpractice implications on food and environmental safety. Cogent Food Agric. 2019, 5, 1601544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P. Environmental pollution and the burden of food-borne diseases. In Foodborne Disease; Holban, A.M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 15, pp. 473–500. [Google Scholar]
- Bempah, C.K.; Agyekum, A.A.; Akuamoa, F.; Frimpong, S.; Buah-Kwofie, A. Dietary exposure to chlorinated pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from Ghanaian markets. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 46, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebelo, K.; Malebo, N.; Mochane, M.J.; Masinde, M. Chemical contamination pathways and the food safety implications along the various stages of food production: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Regulation (EC) N° 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 February 2005 on Maximum Residue Levels of Pesticides in or on Food and Feed of Plant and Animal Origin and Amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC. 2005. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/eur50711.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Guo, W.; Pan, B.; Sakkiah, S.; Yavas, G.; Ge, W.; Zou, W.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Persistent organic pollutants in food: Contamination sources, health effects and detection methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, O.S. Evaluation of selected polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) congeners and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) in fresh root and leafy vegetables using GC-MS. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D.O. Health effects of persistent organic pollutants: The challenge for the Pacific Basin and for the world. Rev. Environ. Health 2011, 26, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.R.; Mortimer, D.; Rose, M.; Smith, F.; Steel, Z.; Panton, S. Recently listed Stockholm convention POPs: Analytical methodology, occurrence in food and dietary exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, S.; Delcourt, N. Studying the impact of persistent organic pollutants exposure on human health by proteomic analysis: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment Programme. Flame Retardants. 2022. Available online: www.unep.org/explore-topics/chemicals-waste/what-we-do/persistent-organic-pollutants/flame-retardants (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Van der Veen, I.; Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrae, N.J. Durable and Environmentally Friendly Flame Retardants for Synthetics. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2007. Available online: http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/1904 (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- EFSA. Nitrate in vegetables: Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) 2023/915 of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. 2023. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023R0915 (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Ozdestan, O.; Uren, A. Development of a cost-effective method for nitrate and nitrite determination in leafy plants and nitrate and nitrite contents of some green leafy vegetables grown in the Aegean region of Turkey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5235–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano, L.; Yusà, V.; Font, G.; McAllister, C.; Torres, C.; Pardo, O. Risk assessment and monitoring programme of nitrates through vegetables in the Region of Valencia (Spain). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, R.; Thakur, M.U.; Uddin, M.Z.; Islam, G.M.R. Study of nitrate levels in fruits and vegetables to assess the potential health risks in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, A.; Alehashem, M. Heavy metal contamination of vegetables in Isfahan, Iran. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, P.; Handley, H.; Taylor, M. Identification of the sources of metal (lead) contamination in drinking waters in north-eastern Tasmania using lead isotope compositions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12276–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massadeh, A.M.; El-Rjoob, A.O.; Gharaibeh, S.A. Analysis of selected heavy metals in tap water by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry after pre-concentration using Chelex-100 ion exchange resin. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafidi, M.; Sanjabi, M.R.; Shirkhan, F.; Zahedi, M.T. A review of recent trends in the development of the microbial safety of fruits and vegetables. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.; Trevizam, A.R.; Muraoka, T.; Marcante, N.C.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G. Heavy metals in vegetables and potential risk for human health. Sci. Agric. 2012, 60, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stančić, Z.; Vujević, D.; Gomaz, A.; Bogdan, S.; Vincek, D. Detection of heavy metals in common vegetables at Varaždin City Market, Croatia. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2016, 67, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Good Agricultural Practices—A Working Concept Background Paper for the FAO Internal Workshop on Good Agricultural Practices. 2004. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/ag856e/ag856e00.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Guidelines Good Agricultural Practices for Family Agriculture. 2007. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/a1193e/a1193e00.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Painter, J.; Hoekstra, R.; Ayers, T.; Tauxe, R.; Braden, C.; Angulo, F. Attribution of foodborne illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths to food commodities by using outbreak data, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, I.P. (INIAV). Colheita de Amostras de Terra Antes da Instalação das Culturas (Ar Livre). 2021. Available online: https://www.iniav.pt/images/Servicos-Laboratoriais/solos-nutricao-vegetal-fertilizantes/colheita-amostras/Mod-LQARS083_Colheita-amostras-terra-antes-instalacao-culturas_vs26-05-2021.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- ISO 16649-2; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Beta-Glucuronidase-Positive Escherichia coli—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique at 44 °C Using 5-Bromo-4-Chloro-3-Indolyl Beta-D-Glucuronide. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- ISO 11290-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 13720; Meat and Meat Products—Enumeration of Presumptive Pseudomonas spp. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 7932; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Presumptive Bacillus cereus—Colony-Count Technique at 30 Degrees C. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- ISO 7937; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Clostridium perfringens—Colony-Count Technique. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- ISO 6888-1; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and Other Species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 11290-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 2: Enumeration Method. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 6579-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 21528-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 21527-1; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Molds—Part 1: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Greater Than 0.95. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 4833-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 2: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Surface Plating Technique. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 9308-1:20147/Amd 1; Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 1: Membrane Filtration Method for Waters with Low Bacterial Background Flora. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 16266; Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa—Method by Membrane Filtration. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14189; Water Quality—Enumeration of Clostridium perfringens—Method Using Membrane Filtration. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 19250; Water Quality—Detection of Salmonella spp. The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Fernandes, V.C.; Lehotay, S.J.; Geis-Asteggiante, L.; Kwon, H.; Mol, H.G.J.; van der Kamp, H.; Mateus, N.; Domingues, V.F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Analysis of pesticide residues in strawberries and soils by GC-MS/MS, LC-MS/MS and two-dimensional GC-time-of-flight MS comparing organic and integrated pest management farming. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.C.; Domingues, V.F.; Mateus, N.; Delerue-Matos, C. Organochlorine pesticide residues in strawberries from integrated pest management and organic farming. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7582–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragança, I.; Lemos, P.C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Domingues, V.F. Assessment of pyrethroid pesticides in topsoils in northern Portugal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosh, O.; Fernandes, V.C.; Moreira, M.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Occurrence of pesticides and environmental contaminants in vineyards: Case study of Portuguese grapevine canes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.C.; Freitas, M.; Pacheco, J.P.G.; Oliveira, J.M.; Domingues, V.F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Magnetic dispersive micro solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography determination of organophosphorus pesticides in strawberries. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1566, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongsibsong, S.; Polyiem, W.; Narksen, W.; Kerdnoi, T.; Prapamontol, T. Determination of nitrate in the edible part of vegetables from markets around Chiang Mai city, northern Thailand by using high performance liquid chromatography. Asian J. Agric. Res. 2014, 8, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, N.T.; Capel, P.D. Environmental Factors that Influence the Location of Crop Agriculture in the Conterminous United States: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2011, 2011–5108. 2011. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2011/5108/pdf/SIR2011_5108.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente (APA). Solos Contaminados—Guia Técnico: Valores de Referência Para o Solo. 2022. Available online: https://sniambgeoviewer.apambiente.pt/GeoDocs/geoportaldocs/AtQualSolos/Guia_Tecnico_Valores%20de%20Referencia_2019_01.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- DL n.° 236/98. Estabelece Normas, Critérios e Objectivos de Qualidade com a Finalidade de Proteger o Meio Aquático e Melhorar a Qualidade das águas em Função Dos Seus Principais Usos. Revoga o Decreto-Lei n.° 74/90, de 7 de Março.1998, Número 176/98. Portugal, 48pp. Available online: https://diariodarepublica.pt/dr/detalhe/decreto-lei/236-1998-430457 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Rajwar, A.; Srivastava, P.; Sahgal, M. Microbiology of fresh produce: Route of contamination, detection methods, and remedy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisiana Department of Health. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Section. Enterobacteriaceae. 2018. Available online: https://ldh.la.gov/assets/oph/Center-PHCH/Center-CH/infectious-epi/EpiManual/EnterobacteriaceaeManual.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2021).
- Donhauser, J.; Niklaus, P.A.; Rousk, J.; Larose, C.; Frey, B. Temperatures beyond the community optimum promote the dominance of heat-adapted, fast growing and stress resistant bacteria in alpine soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, H.; Korfanty, G.; Xu, J. Isolation of culturable yeasts and molds from soils to investigate fungal population structure. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 183, e63396. [Google Scholar]
- Paramithiotis, S.; Drosinos, E.H.; Skandamis, P.N. Food recalls and warnings due to the presence of foodborne pathogens—A focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, dairy, and eggs. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L. Inhibitory effect against pathogenic and spoilage bacteria of Pseudomonas strains isolated from spoiled and fresh fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Nacional de Saúde Doutor Ricardo Jorge (INSA). Interpretação de Resultados de Ensaios Microbiológicos em Alimentos Prontos para Consumo e em Superfícies do Ambiente de Preparação e Distribuição Alimentar: Valores-Guia. 2019. Available online: https://www.insa.min-saude.pt/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/INSA_Valores-guia.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Tango, C.N.; Wei, S.; Khan, I.; Hussain, M.S.; Kounkeu, P.N.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.H. Microbiological quality and safety of fresh fruits and vegetables at retail levels in Korea. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Gu, O.; Xue, L.; et al. Bacillus cereus isolated from vegetables in China: Incidence, genetic diversity, virulence genes, and antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, J.M.; Brazier, A.K.M.; Wallace, C.A. Determining common contributory factors in food safety incidents—A review of global outbreaks and recalls 2008–2018. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.; Strawn, L.K.; Chapman, B.J.; Dunn, L.L. A systematic review of Listeria species and Listeria monocytogenes prevalence, persistence, and diversity throughout the fresh produce supply chain. Foods 2021, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leff, J.W.; Fierer, N. Bacterial communities associated with the surfaces of fresh fruits and vegetables. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Thai, P.; Li, Z.; Baduel, C.; Mueller, J.F. Concentrations of organophosphate esters and their specific metabolites in food in southeast Queensland, Australia: Is dietary exposure an important pathway of organophosphate esters and their metabolites? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12765–12773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, T.; Beggio, G.; Pivato, A.; Piazza, R. Maize plant (Zea mays) uptake of organophosphorus and novel brominated flame retardants from hydroponic cultures. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Mei, W.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Environmental fate and effects of organophosphate flame retardants in the soil-plant system. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, L.C.; Piazza, G.D.; Dujardin, B.; Pastor, P.M.; EFSA. The 2021 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J. 2021, 21, 7939. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. EU Pesticides Database. 2023. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/start/screen/active-substances (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- European Commission. EU Pesticides Database. 2023. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/start/screen/mrls (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Shen, L.; Xia, B.; Dai, X. Residues of persistent organic pollutants in frequently-consumed vegetables and assessment of human health risk based on consumption of vegetables in Huizhou, South China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpyrka, E.; Kurdziel, A.; Matyaszek, A.; Podbielska, M.; Rupar, J.; Słowik-Borowiec, M. Evaluation of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the region of south-eastern Poland. Food Control 2014, 48, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano, L.; Yusa, V.; Font, G.; Pardo, O. Chronic cumulative risk assessment of the exposure to organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid and pyrethrin pesticides through fruit and vegetables consumption in the region of Valencia (Spain). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Geissen, V. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Nondietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Pesticides in Groundwater. 2018. Available online: www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/pesticides-groundwater#:~:text=Pesticides%20can%20reach%20water%2Dbearing,injection%20waste%20material%20into%20wells (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation (Queensland). Soil Health for Vegetable Production in Australia—Part 4: Measuring Soil Health. 2010. Available online: http://era.daf.qld.gov.au/id/eprint/2479/1/Soil-health-vegetable-production.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Gerke, H.H.; Arning, M.; Stöppler-Zimmer, H. Modelling long-term compost application effects on nitrate leaching. Plant Soil 1999, 213, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H. Too much of a good thing? Nitrate from nitrogen fertilizers and cancer. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G.; Song, Y.; Muminov, M.A. Advances of organic products over conventional production with respect to nutritional quality and food security. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S. Synthetic fertilizer increases denitrifier abundance and depletes subsoil total N in a long-term fertilization experiment. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2006/118/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 December 2006 on the Protection of Groundwater Against Pollution and Deterioration. 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006L0118 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Atidégla, S.C.; Huat, J.; Agbossou, E.K.; Saint-Macary, H.; Glèlè Kakai, R. Vegetable contamination by the fecal bacteria of poultry manure: Case study of gardening sites in Southern Benin. Int. J. Food Sci. 2016, 2016, 4767453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Mamphweli, S.N.; Meyer, E.L.; Makaka, G.; Simon, M.; Okoh, A.I. An overview of the control of bacterial pathogens in cattle manure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyakuwaire, M.; Olupot, G.; Amoding, A.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Basamba, T.A. How safe is chicken litter for land application as an organic fertilizer? A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, X.M.; Hu, H.; Guo, N.; Xu, X.T.; Li, J.L. Effects of cow manure application on soil microbial community in farmland. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2023, 44, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, M.C. Overview: Foodborne pathogens in wildlife populations. In Food Safety Risks from Wildlife; Jay-Russell, M., Doyle, M.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzlerland, 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, P.P.; Springer, M. Management of Wildlife and Cooperative Extension Service Domestic Animals on Your Farm. In Good Agriculture Practices. In Good Agriculture Practices. University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment. 2016. Available online: https://publications.ca.uky.edu/sites/publications.ca.uky.edu/files/ID243.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Health Guidelines for the Use of Wastewater in Agriculture and Aquaculture; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Banach, J.L.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Microbiological reduction strategies of irrigation water for fresh produce. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, I.M. Manual de Horticultura no Modo de Produção Biológico; Escola Superior Agrária de Ponte de Lima/IPVC: Ponte de Lima, Portugal, 2007; p. 198. [Google Scholar]
- Bayissa, L.D.; Gebeyehu, H.R. Vegetables contamination by heavy metals and associated health risk to the population in Koka area of central Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, D.A. Public health implications of heavy metals in foods and drinking water in Ethiopia (2016 to 2020): Systematic review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, N.; Jahangeer, M.; Bouyahya, A.; El Omari, N.; Ghchime, R.; Balahbib, A.; Aboulaghras, S.; Mahmood, Z.; Akram, M.; Ali Shah, S.M.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of natural foods is a serious health issue: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrios, G.N. Control of plant diseases. In Plant Pathology, 5th ed.; Agrios, G.N., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 293–353. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, E.S.; Santos, A.A.; Carmo, D.G.; Melo, J.B.; Picanço, M.C. Lethal and antifeedant effects of Bordeaux mixture on the marsh slug (Deroceras laeve). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2021, 56, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, A.; Qi, H. Concentration, uptake and human dietary intake of novel brominated flame retardants in greenhouse and conventional vegetables. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, S.; Otani, T.; Motoki, Y.; Seike, N.; Iwafune, T. Differential uptake and translocation of organic chemicals by several plant species from soil. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Silva, V.; Lwanga, E.H.; Beriot, N.; Oostindie, K.; Bin, Z.; Pyne, E.; Busink, S.; Zomer, P.; Mol, H.; et al. Cocktails of pesticide residues in conventional and organic farming systems in Europe—Legacy of the past and turning point for the future. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandanayake, S.; Hettithanthri, O.; Buddhinie, P.K.C.; Vithanage, M. Plant uptake of pesticide residues from agricultural soils. In Pesticides in Soils, 1st ed.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S., Sánchez-Martín, M.J., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 113, pp. 197–223. [Google Scholar]
- Sweetman, A.J.; Valle, M.D.; Prevedouros, K.; Jones, K.C. The role of soil organic carbon in the global cycling of persistent organic pollutants (POPs): Interpreting and modelling field data. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, A.; Fernandes, V.C.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Teixeira, P. A global perspective of synthetic agrochemicals in local farmers’ markets. In One Health Implications of Agrochemicals and Their Sustainable Alternatives, 1st ed.; Ogwu, M.C., Izah, S.C., Eds.; Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 34, pp. 461–483. [Google Scholar]
- Pesticide Action Network Europe. Pesticide Atlas. Facts and Figures About Toxic Chemicals in Agriculture. 2022. Available online: https://pan-europe.info/EU-Pesticide-Atlas-2022 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Dufault, R.J.; Hester, A.; Ward, B. Influence of organic and synthetic fertility on nitrate runoff and leaching, soil fertility, and sweet corn yield and quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 1858–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, R.; Malin’ska, K.; Marfà, O. Nitrification within composting: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.A.; McDonald, M.D.; Burke, J.; Robertson, I.; Coker, H.; Gentry, T.J.; Lewis, K.L. Influence of fertilizer and manure inputs on soil health: A review. Soil Secur. 2024, 16, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, R.; Moncur, Q. Small-scale farming: A review of challenges and potential opportunities offered by technological advancements. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibane, Z.; Soni, S.; Phali, L.; Mdoda, L. Factors impacting sugarcane production by small-scale farmers in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosona, T.; Gebresenbet, G. Food traceability as an integral part of logistics management in food and agricultural supply chain. Food Control 2013, 33, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macieira, A.; Teixeira, P. Food safety and traceability in local farming of fruits and vegetables in the North of Portugal. In Back to the Future EurSafe 2024, 1st ed.; Giersberg, M.F., Bovenkerk, B., Meijboom, F.L.B., Eds.; Brill|Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mdluli, F.; Thamaga-Chitja, J.; Schmidt, S.; Shimelis, H. Production hygiene and training influences on rural small-scale organic farmer practices: South Africa. J. Fam. Ecol. Consum. Sci. 2014, 42, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Schmit, T.M.; Wall, G.L.; Newbold, E.J.; Bihn, E.A. Assessing the costs and returns of on-farm food safety improvements: A survey of Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) training participants. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, S.S.; Oko, A.A.; Oduntan, F.T. Adoption of appropriate Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) technologies among smallholder farmers in Nigeria. Int. J. Agric. Res. Sustain. Food Suffic. 2020, 7, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
| Food (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Soil (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Water (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy metals | ||||||
| Zn | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, HP, JB, KP, LP, MP, OP, PB, QB, | 82.4 | AB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 82.4 | EB | 5.9 |
| Cd | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 94.1 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | JB | 5.9 |
| Pb | AB, BB, EB, HP, IP, KP, LP, MP OP | 52.9 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | CB, DB, FP, JB, HP, KP, LP, MP, OP | 52.9 |
| Ni | IP, JB, QB, KP, LP, OP, AB, FP, NP, HP, HP, PB | 70.6 | AB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 88.2 | NP | 5.9 |
| Cu | BB, CB, EB, IP, JB, QB, KP, LP, AB, FP, NP, HP, DB, MP, PB | 88.2 | AB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 82.4 | ||
| Cr | LP, OP | 11.8 | AB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 88.2 | ||
| PCBs and flame retardant compounds | ||||||
| PCB153 | LP | 5.9 | ||||
| TBEP | AB, BB,CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | --- | --- |
| TCPI | CB, LP, OP | 17.6 | AB, GP, KP, MP | 5.9/ 23.5 | ||
| TCPIII | LP, OP | 11.8 | ||||
| TEHP | CB, LP, FP, HP | 23.5 | ||||
| TnBP | KP | 5.9 | ||||
| Pesticide residues | ||||||
| Aldrin | CB, KP | 5.9/5.9 | ||||
| Bifenthrin | LP | 5.9 | JB, KP | 11.8 | ||
| Chlorpyrifos | GP, CB, IP, JB, FP, HP | 35.3 | AB, CB, DB, GP, IP, JB, KP, LP, OP, PB, QB | 58.8/ 5.9 | AB, BB, GP, KP, LP, NP | 35.3 |
| Chlorpyrifos-methyl | CB, AB, NP, EB | 23.5 | BB, CB IP | 17.6 | AB, BB, CB, HP, LP, QB | 35.3 |
| Cyhalothrin II | LP | 5.9 | ||||
| p,p’-DDD | GP, CB, JB, QB, LP, AB, FP, NP, DB, PB | 23.5/ 35.3 | AB, BB, DB, IP, JB, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB | 17.6/ 41.2 | EB, GP, PB | 17.6 |
| Dimethoate | CB, IP, JB, PB | 23.5 | BB, CB, DB, IP | 23.5 | EB | 5.9 |
| Endosulfan I | BB | 5.9 | ||||
| Food (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Soil (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Water (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | IP, HP | 11.8 | AB, EB, FP, GP, HP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 52.9 | GB, HP, JB, OP | 23.5 |
| Listeria spp. | IP, HP, LP | 17.6 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | AB, CB, DB, JB, LP, OP, PB, QB | 47.1 |
| B. cereus | AB, BB, CB, DB, FP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, NP, OP, QB | 76.5 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, GP, HP, IP, JB KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 94.1 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB KP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 94.1 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 88.2 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 |
| Coagulase-positive Staphylococci | HP | 5.9 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | QB | 5.9 |
| C. perfringens | LP, OP | 11.8 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | AB, BB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, JB, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 82.4 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | DB, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, OP, PB, QB | 52.9 | --- | --- | AB, DB, GP, HP, JB, OP | 35.3 |
| Yeasts | HP, IP, JB, KP, OP | 29.4 | --- | --- | CB, JB, MP, PB | 23.5 |
| Moulds | CB, IP, KP, HP | 23.5 | --- | --- | BB, CB, DB, EB, GP, HP, IP, KP, LP, MP, NP, PB, QB | 76.5 |
| Aerobic mesophilic bacteria | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 | --- | --- | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB KP, LP, MP, NP, OP, PB, QB | 100 |
| Detection of L. monocytogenes | --- | --- | --- | --- | FP, GP | 11.8 |
| Food a (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Soil b (Farmers ID) | % of Positives | Water c (Farmers ID) | % of Positives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB, HP, KP, LP, OP, PB | 35.3 | AB, BB, CB, DB, EB, FP, GP, HP, IP, JB, KP, MP, NP, OP, QB | 88.2 | BB, JB | 11.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macieira, A.; Fernandes, V.C.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Teixeira, P. Environmental and Food Safety Assessment of Pre-Harvest Activities in Local Small-Scale Fruit and Vegetable Farms in Northwest Portugal: Hazard Identification and Compliance with Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs). Foods 2025, 14, 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122129
Macieira A, Fernandes VC, Brandão TRS, Delerue-Matos C, Teixeira P. Environmental and Food Safety Assessment of Pre-Harvest Activities in Local Small-Scale Fruit and Vegetable Farms in Northwest Portugal: Hazard Identification and Compliance with Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs). Foods. 2025; 14(12):2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122129
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacieira, Ariana, Virgínia Cruz Fernandes, Teresa R. S. Brandão, Cristina Delerue-Matos, and Paula Teixeira. 2025. "Environmental and Food Safety Assessment of Pre-Harvest Activities in Local Small-Scale Fruit and Vegetable Farms in Northwest Portugal: Hazard Identification and Compliance with Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs)" Foods 14, no. 12: 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122129
APA StyleMacieira, A., Fernandes, V. C., Brandão, T. R. S., Delerue-Matos, C., & Teixeira, P. (2025). Environmental and Food Safety Assessment of Pre-Harvest Activities in Local Small-Scale Fruit and Vegetable Farms in Northwest Portugal: Hazard Identification and Compliance with Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs). Foods, 14(12), 2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122129








