Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Chitosan-Coated Alginate Beads: Effects of Food Matrices (Casein, Corn Starch, and Soybean Oil) and Dynamic Gastrointestinal Conditions †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Cell Preparation
3.2. Encapsulation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG by Ionic Gelation
3.3. Viability of Encapsulated Probiotics in In Vitro Static/Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Models
3.4. Release of Encapsulated Probiotics in Static/Dynamic Intestinal Digestion Models
3.5. Effect of Food Matrices on In Vitro Gastric Digestion Models
3.6. Characterization of Probiotic Capsules
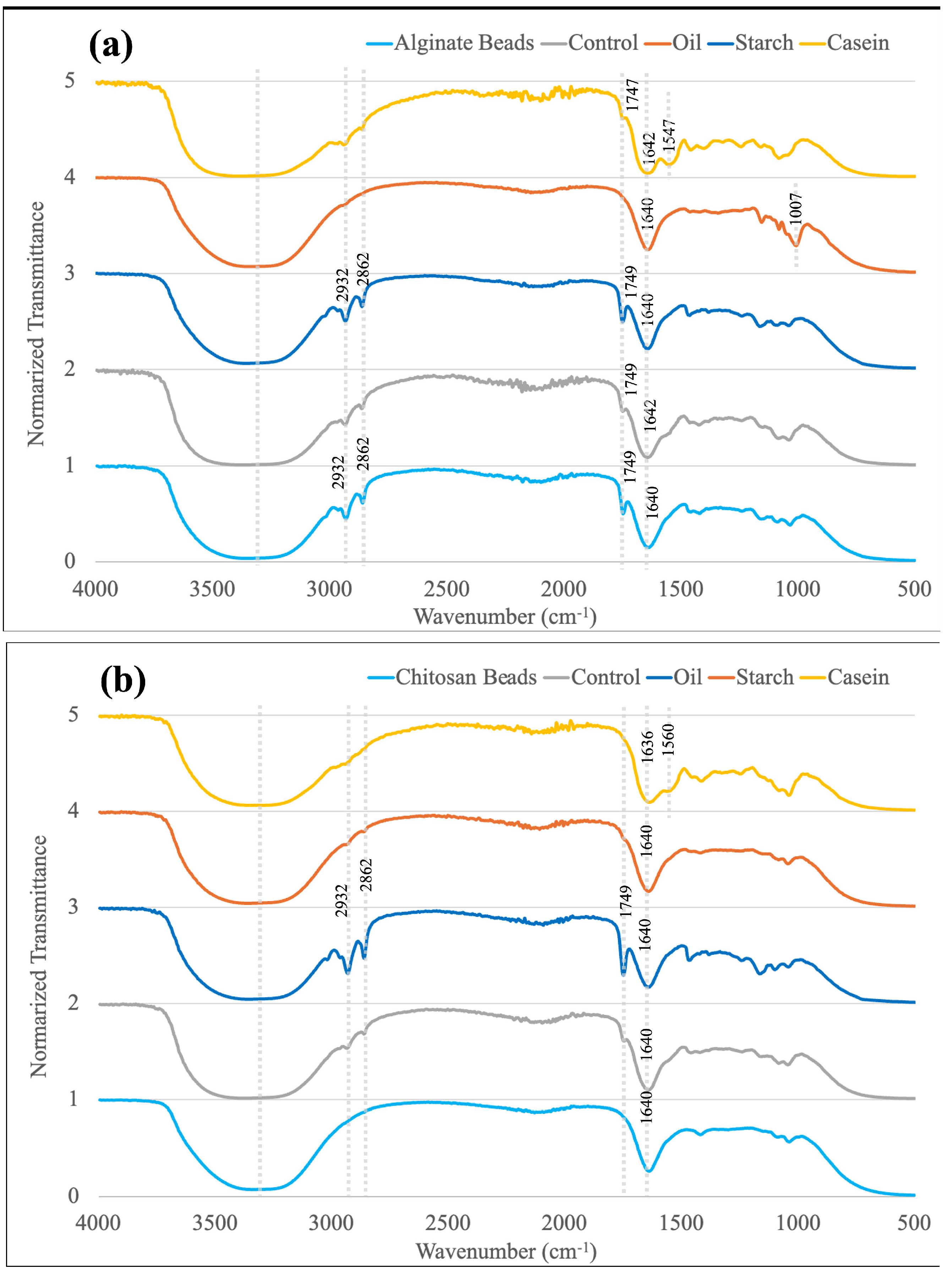
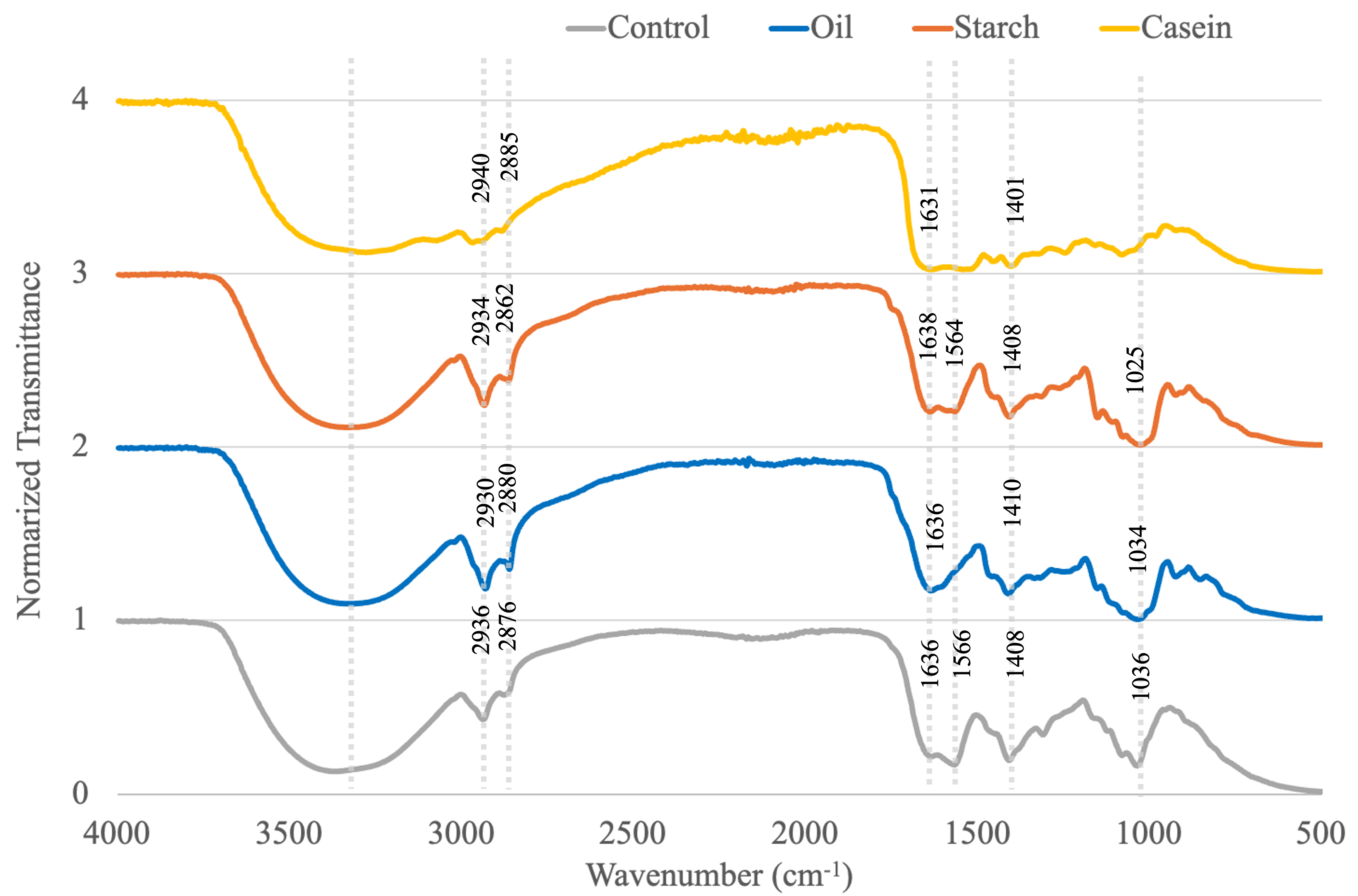
3.7. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
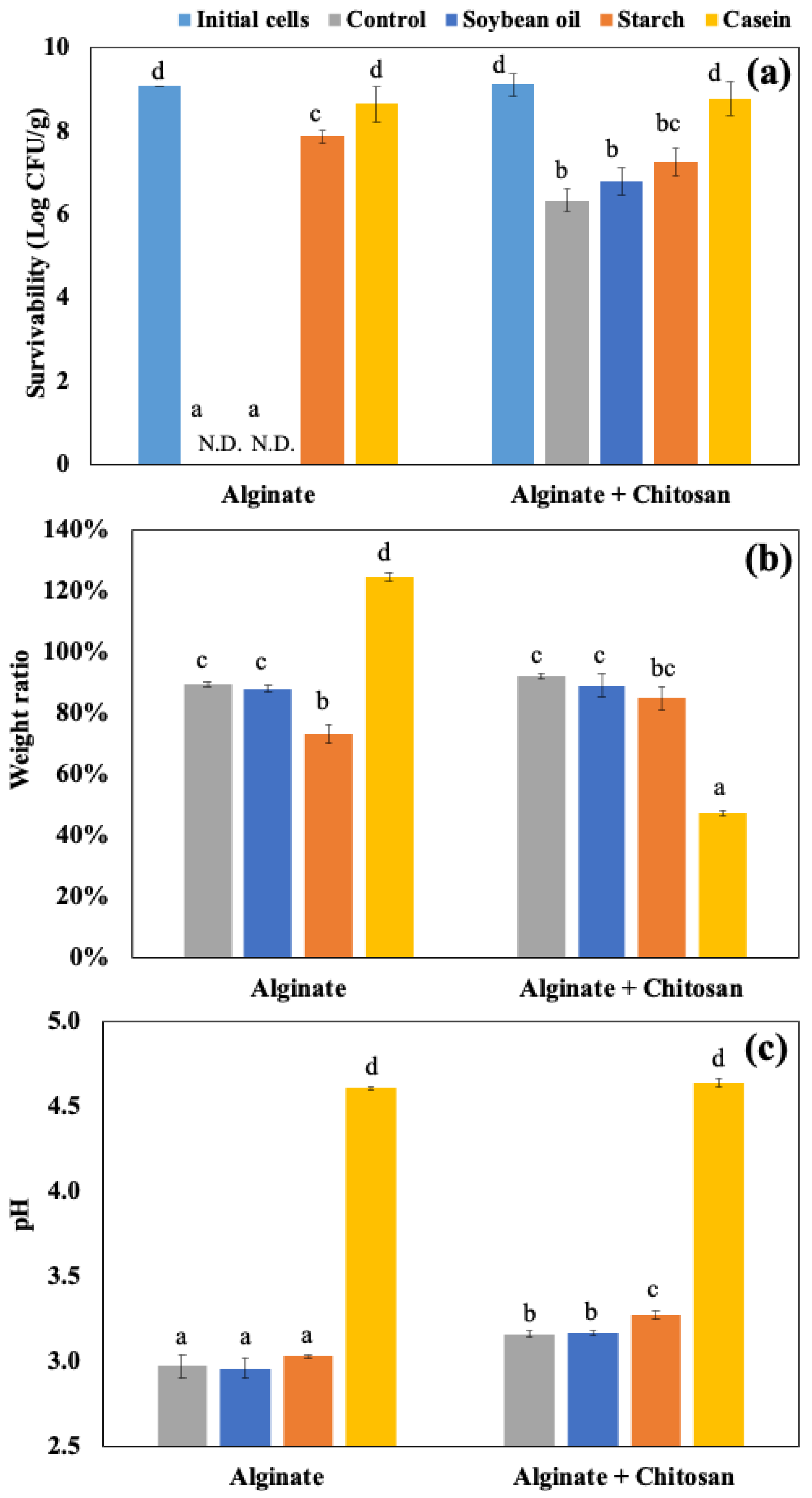
4.1. Impacts of Food Materials in Static Gastrointestinal Models
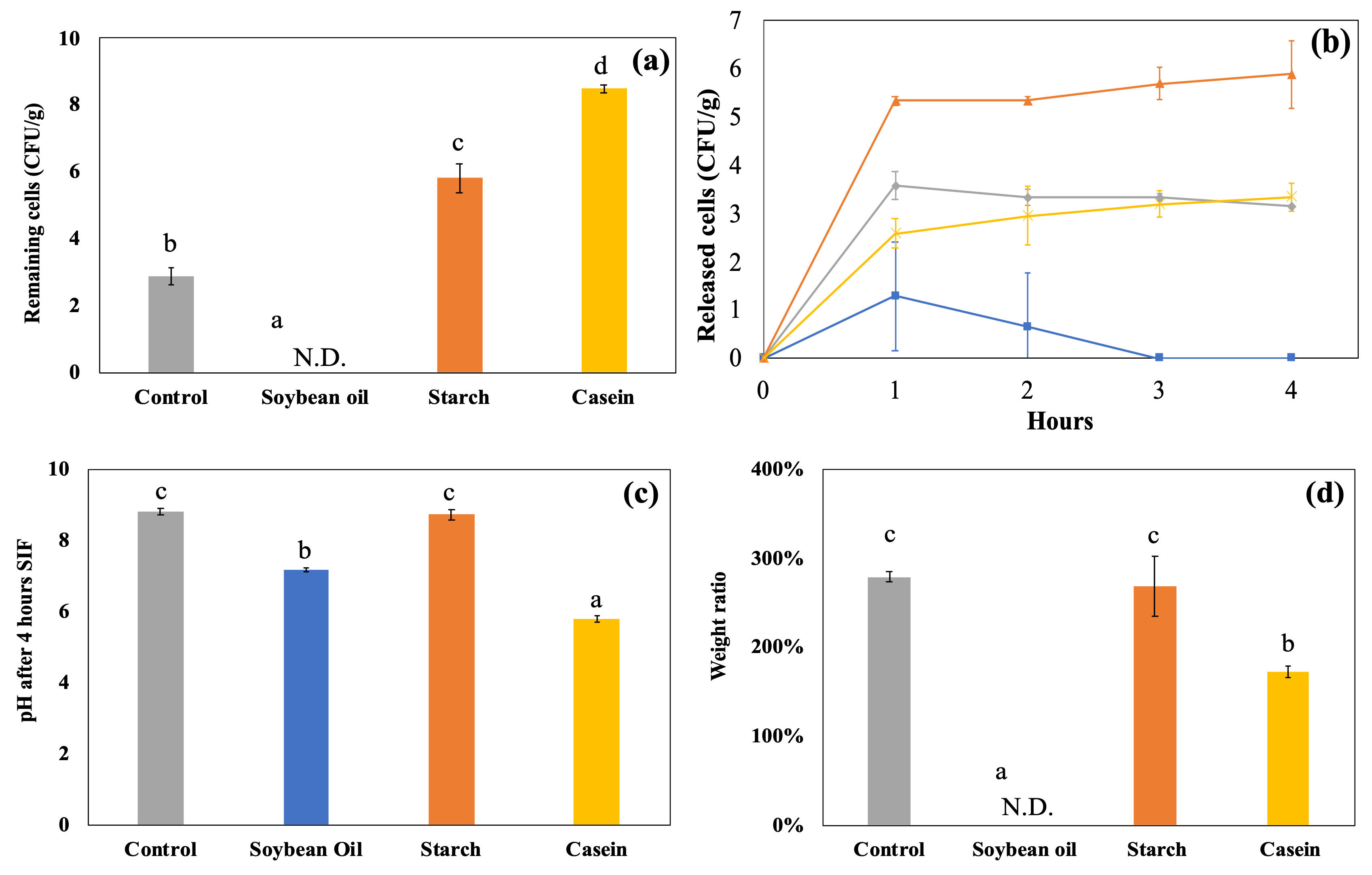
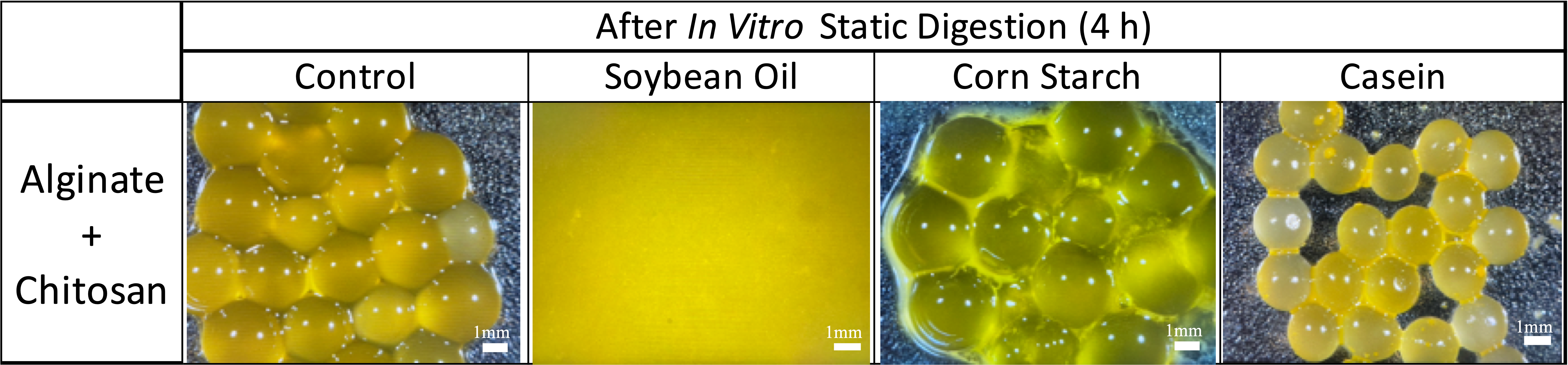
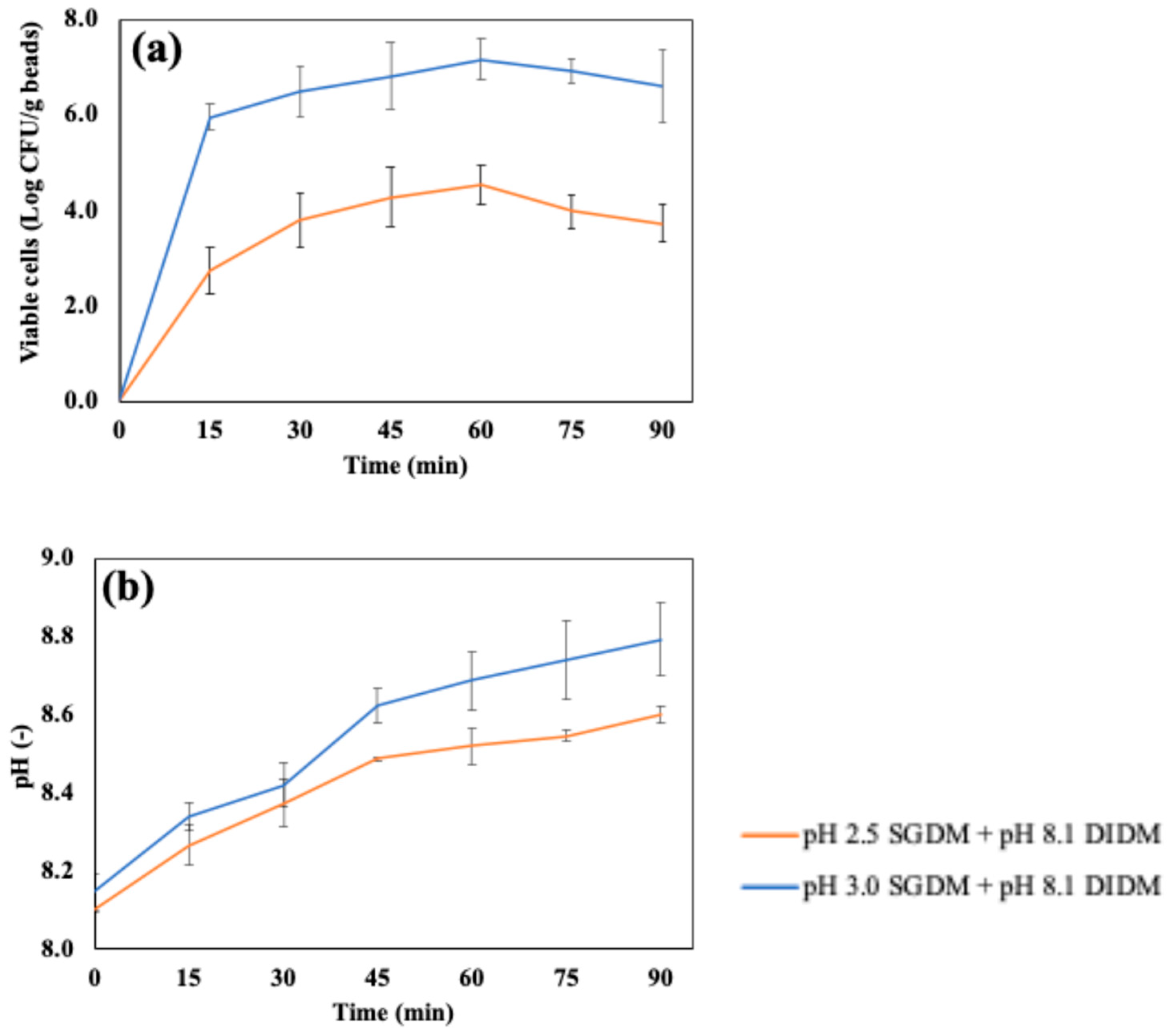
4.2. Dynamic In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion with Continuous Juice Secretion and Emptying
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LRGG | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| SGDM | Static gastric digestion model |
| DGDM | Dynamic gastric digestion model |
| SIDM | Static intestinal digestion model |
| DIDM | Dynamic intestinal digestion model |
References
- Ouwehand, A.C. A review of dose-responses of probiotics in human studies. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baral, K.C.; Bajracharya, R.; Lee, S.H.; Han, H.-K. Advancements in the Pharmaceutical Applications of Probiotics: Dosage Forms and Formulation Technology. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 7535–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.; Ai, L. Characteristics of Probiotic Preparations and Their Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringel, Y.; Quigley, E.M.; Lin, H.C. Using Probiotics in Gastrointestinal Disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 2012, 1, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, S.; Gregg, A.; Yaceczko, S.; Limketkai, B. Prebiotics and Probiotics for Gastrointestinal Disorders. Nutrients 2024, 16, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozza, M.; Laforgia, N.; Rizzo, V.; Salvatore, S.; Guandalini, S.; Baldassarre, M. Probiotics and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Pediatric Age: A Narrative Review. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 805466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, L. Thirty Years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, S1–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.I.; Reid, G.; ter Haar, J.A. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GR-1, a.k.a. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1: Past and Future Perspectives. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier-Santos, D.; Scharlack, N.K.; Pena, F.d.L.; Antunes, A.E.C. Effects of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation, via food and non-food matrices, on children’s health promotion: A scoping review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiriya, M.R.; Vekariya, Y.V.; Hati, S. Understanding the Probiotic Bacterial Responses Against Various Stresses in Food Matrix and Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Abdalla, A.K.; AlKalbani, N.S.; Baig, M.A.; Turner, M.S.; Liu, S.-Q.; Shah, N.P. Invited review: Characterization of new probiotics from dairy and nondairy products—Insights into acid tolerance, bile metabolism and tolerance, and adhesion capability. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8363–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Wu, F. Intestinal Delivery of Probiotics: Materials, Strategies, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2310174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; De Souza, C.; Ramachandran, M.; Wang, S.; Yi, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, K. Precise oral delivery systems for probiotics: A review. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajam, R.; Subramanian, P. Encapsulation of probiotics: Past, present and future. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šipailienė, A.; Petraitytė, S. Encapsulation of Probiotics: Proper Selection of the Probiotic Strain and the Influence of Encapsulation Technology and Materials on the Viability of Encapsulated Microorganisms. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Gao, M.; Du, H.; Pan, X. Next-generation probiotics delivery: Innovations and applications of single-cell encapsulation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2025, 61, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probiotics Market Size, Share & Growth Analysis Report 2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/probiotics-market (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Probiotics Market Size, Share, Industry Report, Revenue Trends and Growth Drivers, Markets and Markets. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/probiotics-market-69.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Frakolaki, G.; Giannou, V.; Topakas, E.; Tzia, C. Effect of various encapsulating agents on the beads’ morphology and the viability of cells during BB-12 encapsulation through extrusion. J. Food Eng. 2021, 294, 110423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Song, H. Advances in probiotic encapsulation methods to improve bioactivity. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, F.; Da Silva, S.; Massironi, A.; Mirpoor, S.F.; Lignou, S.; Ghawi, S.K.; Charalampopoulos, D. Silver Bionanocomposites as Active Food Packaging: Recent Advances & Future Trends Tackling the Food Waste Crisis. Polymers 2023, 15, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamdoost-Sani, N.; Khaledabad, M.A.; Amiri, S.; Khaneghah, A.M. Alginate and derivatives hydrogels in encapsulation of probiotic bacteria: An updated review. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Yun, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Microencapsulating Alginate-Based Polymers for Probiotics Delivery Systems and Their Application. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, J.; Sharma, R.K. Synbiotic formulations with microbial biofilm, animal derived (casein, collagen, chitosan) and plant derived (starch, cellulose, alginate) prebiotic polymers: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Călinoiu, L.-F.; Ştefănescu, B.E.; Pop, I.D.; Muntean, L.; Vodnar, D.C. Chitosan Coating Applications in Probiotic Microencapsulation. Coatings 2019, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, G.I.; Mafe, A.N.; Razooqi, N.F.; Umelo, E.C.; Gaaz, T.S.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Akpoghelie, P.O.; Opiti, R.A.; Essaghah, A.E.A.; et al. Advances in bio-polymer coatings for probiotic microencapsulation: Chitosan and beyond for enhanced stability and controlled release. Des. Monomers Polym. 2025, 28, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, G.; Woltering, E.J.; Mozafari, M. Applications of chitosan-based carrier as an encapsulating agent in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, S.W.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Xu, F.; Zhong, F. Protective approaches and mechanisms of microencapsulation to the survival of probiotic bacteria during processing, storage and gastrointestinal digestion: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-D.; Gan, L.; Tian, L.-Y.; Chen, G.-H. Protein/polysaccharide-based hydrogels loaded probiotic-mediated therapeutic systems: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Cui, S. Bacterial viability retention in probiotic foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokka, S.; Rantamäki, P. Protecting probiotic bacteria by microencapsulation: Challenges for industrial applications. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ban, Q.; Wang, W.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Novel nano-encapsulated probiotic agents: Encapsulate materials, delivery, and encapsulation systems. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Smith, B. Legume proteins are smart carriers to encapsulate hydrophilic and hydrophobic bioactive compounds and probiotic bacteria: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1250–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbassi, G.K.; Vandamme, T. Probiotic Encapsulation Technology: From Microencapsulation to Release into the Gut. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kong, F. Simulating human gastrointestinal motility in dynamic in vitro models. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3804–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, D.; Alric, M.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Bornhorst, G.; Cueva, C.; Deglaire, A.; Denis, S.; Ferrua, M.; Havenaar, R.; Lelieveld, J.; et al. Can dynamic in vitro digestion systems mimic the physiological reality? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1546–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoy, I. A review on the food digestion in the digestive tract and the used in vitro models. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, C.; Thévenot, J.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Denis, S.; Alric, M.; Livrelli, V.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Dynamic In Vitro Models of the Human Gastrointestinal Tract as Relevant Tools to Assess the Survival of Probiotic Strains and Their Interactions with Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 725–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almada-Érix, C.N.; Almada, C.N.; Pedrosa, G.T.S.; Lollo, P.C.; Magnani, M.; Sant’ANa, A.S. Development of a semi-dynamic in vitro model and its testing using probiotic Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 in orange juice and yogurt. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 183, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasaekoopt, W.; Bhandari, B.; Deeth, H. The influence of coating materials on some properties of alginate beads and survivability of microencapsulated probiotic bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fortner, L.; Kong, F. Development of a Gastric Simulation Model (GSM) incorporating gastric geometry and peristalsis for food digestion study. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, F.P.; Singh, R.K.; Kerr, W.L.; Pegg, R.B.; Kong, F. Total phenolics content and antioxidant capacities of microencapsulated blueberry anthocyanins during in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; El-Fotoh, W.S.A.; Elgindy, N.A. Casein-based formulations as promising controlled release drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2011, 153, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Dong, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. Improved viability of probiotics encapsulated in soybean protein isolate matrix microcapsules by coacervation and cross-linking modification. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchepare, M.d.A.; Nunes, G.L.; Nicoloso, B.R.; Barin, J.S.; Flores, E.M.M.; Mello, R.d.O.; de Menezes, C.R. Improvement of the viability of encapsulated probiotics using whey proteins. LWT 2020, 117, 108601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Harte, F. Casein maps: Effect of ethanol, pH, temperature, and CaCl2 on the particle size of reconstituted casein micelles. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, L.; Leandro, E.; Freitas, F.; de Oliveira, M.; Ferreira-Machado, A.; Borges, A.; de Moraes, C. Survival of Lactobacillus delbrueckii UFV H2b20 in fermented milk under simulated gastric and intestinal conditions. Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Tachon, S.; Eigenheer, R.A.; Phinney, B.S.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus casei Low-Temperature, Dairy-Associated Proteome Promotes Persistence in the Mammalian Digestive Tract. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3136–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Khan, A.U.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, A.; Ahmad, M.H.; Maan, A.A.; Tufail, T.; Anjum, F.M.; Hussain, S. Functional exploration of free and encapsulated probiotic bacteria in yogurt and simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3931–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, S.J.; Forssten, S.; Aakko, J.; Granlund, L.; Rautonen, N.; Salminen, S.; Viitanen, M.; Ouwehand, A.C. Probiotic cheese containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM® modifies subpopulations of fecal lactobacilli and Clostridium difficile in the elderly. AGE 2012, 34, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidzadeh, B.; Fathalipour, S.; Hosseini, S.P.; Bazazi, S. Alginate doped graphene oxide—TiO 2—Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite: Preparation, characterization, and application of sonophotocatalyst for efficient decomposition of an organic dye. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 1911–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Huang, Y. A new insight to the effect of calcium concentration on gelation process and physical properties of alginate films. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 5791–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastaj, J.; Przewłocka, A.; Rajkowska-Myśliwiec, M. Biosorption of Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) on calcium alginate beads: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies. PJCT 2016, 18, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malucelli, G.; Barbalini, M. UV-curable acrylic coatings containing biomacromolecules: A new fire retardant strategy for ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.H.D.; Chalimah, S.; Primadona, I.; Hanantyo, M.H.G. Physical and chemical properties of corn, cassava, and potato starchs. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 160, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghita, R.; Sirbu, I.-O.; Lobiuc, A.; Covasa, M. Sodium Alginate–Starch Capsules for Enhanced Stability of Metformin in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, A.L.; Deladino, L.; Martino, M. Effect of starch filler on calcium-alginate hydrogels loaded with yerba mate antioxidants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.T.; Saratoon, T.; Tzortzis, G.; Edwards, A.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. CLSM Method for the Dynamic Observation of pH Change within Polymer Matrices for Oral Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroebinger, N.; Rutherfurd, S.M.; Henare, S.J.; Hernandez, J.F.P.; Moughan, P.J. Fatty Acids from Different Fat Sources and Dietary Calcium Concentration Differentially Affect Fecal Soap Formation in Growing Pigs. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S.; Ahn, I.-S.; Jung, J.-K. Highly efficient production of monoglycerides by the continuous removal of fatty acids from lipase-catalyzed oil hydrolysis. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2009, 27, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafumi, Y.; Lairon, D.; de la Porte, P.L.; Juhel, C.; Storch, J.; Hamosh, M.; Armand, M. Mechanisms of Inhibition of Triacylglycerol Hydrolysis by Human Gastric Lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28070–28079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.F.C.; Parussulo, A.L.A.; Netto, C.G.C.M.; Andrade, L.H.; Toma, H.E. Lipase immobilized on polydopamine-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biodiesel production from soybean oil. Biofuel Res. J. 2016, 3, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruździak, P.; Panuszko, A.; Kaczkowska, E.; Piotrowski, B.; Daghir, A.; Demkowicz, S.; Stangret, J. Taurine as a water structure breaker and protein stabilizer. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Favvas, E.P.; Sapalidis, A.A.; Romanos, G.E.; Katsaros, F.K. Metal–carboxylate interactions in metal–alginate complexes studied with FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praepanitchai, O.-A.; Noomhorm, A.; Anal, A.K. Survival and Behavior of Encapsulated Probiotics (Lactobacillus plantarum) in Calcium-Alginate-Soy Protein Isolate-Based Hydrogel Beads in Different Processing Conditions (pH and Temperature) and in Pasteurized Mango Juice. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9768152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Baumann, C.; Duerr, D.; Schlegel, P.; Stoll, P.; Vergères, G.; Dupont, D.; Portmann, R. Digestion of milk proteins: Comparing static and dynamic in vitro digestion systems with in vivo data. Food Res. Int. 2019, 118, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Udo, T.; Mummaleti, G.; Qin, Z.; Chen, J.; Singh, R.K.; Jiao, Y.; Kong, F. Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Chitosan-Coated Alginate Beads: Effects of Food Matrices (Casein, Corn Starch, and Soybean Oil) and Dynamic Gastrointestinal Conditions. Foods 2025, 14, 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122094
Udo T, Mummaleti G, Qin Z, Chen J, Singh RK, Jiao Y, Kong F. Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Chitosan-Coated Alginate Beads: Effects of Food Matrices (Casein, Corn Starch, and Soybean Oil) and Dynamic Gastrointestinal Conditions. Foods. 2025; 14(12):2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122094
Chicago/Turabian StyleUdo, Toshifumi, Gopinath Mummaleti, Zijin Qin, Jinru Chen, Rakesh K. Singh, Yang Jiao, and Fanbin Kong. 2025. "Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Chitosan-Coated Alginate Beads: Effects of Food Matrices (Casein, Corn Starch, and Soybean Oil) and Dynamic Gastrointestinal Conditions" Foods 14, no. 12: 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122094
APA StyleUdo, T., Mummaleti, G., Qin, Z., Chen, J., Singh, R. K., Jiao, Y., & Kong, F. (2025). Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in Chitosan-Coated Alginate Beads: Effects of Food Matrices (Casein, Corn Starch, and Soybean Oil) and Dynamic Gastrointestinal Conditions. Foods, 14(12), 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14122094







