Abstract
Flavor compounds are key determinants of food sensory quality, originating from natural sources, processing, or artificial additives. Although physical and chemical methods can effectively enhance food flavor, microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis technology possess good potential in food flavor regulation due to their mild reaction conditions and high safety. In addition, the high efficiency and specificity of enzymes help to shorten the production cycle and accurately regulate food flavor. This review focuses on the application and regulation mechanism of bacteria, yeast, other fungi, and mixed microbe fermentation systems in flavor production. The utilization and catalytic reaction schemes of oxidoreductases, transferases, and hydrolases in flavor regulation are also deeply explored, and suggestions for the application of microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis technology in flavor regulation are discussed.
1. Introduction
Food flavor substances refer to compounds that can impart specific flavor to food. These compounds can stimulate human olfactory and taste organs to produce sensory reactions such as aroma and taste. Some raw materials themselves naturally have flavor substances [1]. For example, fruits contain a variety of volatile substances such as esters and alcohols that give them a sweet smell, while amino acids, peptides, and nucleotides in meat are important flavoring substances of meat flavor. Food also produces flavor substances during storage and processing. Fermentation is an important process used to produce flavor substances [2,3]. In the process of brewing, microorganisms such as yeast convert sugars into alcohol and produce various flavor substances such as esters and higher alcohols. In addition, the flavor of food can also be enhanced to a certain extent by artificially adding edible spices and seasonings.
Flavor substances are key factors in determining the flavor of food, and good flavor can improve the overall sensory quality of food [4]. However, some raw materials have unpleasant flavors, and adding appropriate flavor substances can improve the taste. At present, the development of plant-based meat imitations using soybean protein is hindered by the beany smell produced during extrusion processing [5]. Studies have shown that malt and flavonoids can reduce the beany flavor of the product and significantly improve its sensory quality [5,6,7]. Studies have reported that flavor substances have successfully simulated the taste of mango and Hami melon [8,9].
Some researchers have found that physical methods such as ultrasound and embedding can effectively improve the flavor of meat products, plant-based artificial meat, and other foods [10,11,12,13,14,15]. It is also a good choice to directly synthesize specific flavor substances such as esters and aldehydes through chemical reactions or directly add spices and flavor enhancers to food. Rocha et al. evaluated the ability of monosodium glutamate (MSG), disodium inosinate (IMP), disodium guanylate (GMP), and monoammonium glutamate (MAG) to enhance saltiness in aqueous solutions containing different concentrations of sodium chloride. Studies have shown that MAG and MSG have a greater ability to enhance saltiness than IMP and GMP at any sodium chloride concentration [16]. Although these methods can quickly improve food flavor, the excessive consumption of flavor enhancers is not conducive to human health, and there is also a risk of chemically synthesized flavor substances reacting with other components to produce harmful substances. The use of microorganisms or enzymes can address this problem. Microbial fermentation is a green and environmentally friendly food processing method. It uses the various metabolic activities of microorganisms to decompose macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in food to obtain different metabolites and produce unique flavors [17,18]. This method does not require the addition of artificially synthesized flavor substances, and the reaction conditions are mild, usually carried out at room temperature and pressure, which meets the requirements of green production and reduces environmental pollution. As biocatalysts, enzymes are safe and the enzymatic reaction is usually carried out under mild conditions, which helps to retain the original nutrients of food. The high efficiency and specificity of enzymes are also conducive to shortening the production cycle while avoiding unnecessary by-products and accurately regulating food flavor.
In recent years, the application of microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis technology in food flavor improvement has attracted considerable attention and has been systematically discussed in many reviews. Liu et al. reviewed the existence of probiotic Bacillus strains in the microbial composition of liquid, semi-solid, and solid-state fermented food, and statistically analyzed the single fermentation and mixed fermentation of the probiotic Bacillus as a food starter. The researchers found that the use of probiotic Bacillus strains in food fermentation enhanced the flavor and texture of the product, increased nutritional value, and improved safety. In addition, these strains contribute to the metabolism of food raw materials, shorten the fermentation time, and provide a new way to reduce the salt content in fermented foods [19]. Wang et al. reviewed the evolution of microbial community structure during food fermentation, as well as the key volatile compounds affecting food flavor and their potential relationships. They found that to improve the quality of traditional fermented foods, it is necessary to break the metabolic regulation mechanism of microorganisms and eliminate the accumulation of by-products to achieve the efficient control of certain flavor products [2]. Ye et al. reviewed the mechanism of endogenous and exogenous lipases and lipoxygenases in fermented fish products and their effects on the main volatile flavor substances in various fermented fish products. The authors found that neutral and acidic lipases mainly catalyze the hydrolysis of triglycerides to produce free fatty acids (FFAs) and other intermediate metabolites. Lipoxygenase catalyzes the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids produced during lipolysis. Lipase and lipoxygenase play a synergistic role in the fermentation process, producing a variety of volatile flavor components such as alcohols, aldehydes, esters, ketones, and acids, thereby enriching the flavor of fermented fish products [20].
Most existing studies focus on the role of single microorganisms or specific enzymes, and the synergistic mechanism of different microbial communities and enzymes in food flavor regulation has not been systematically explained. Therefore, this study focused on the application and mechanism of bacteria, yeasts, other fungi, and mixed bacteria fermentation systems in flavor regulation, as well as the application and catalytic reaction schemes of oxidoreductases, transferases, and hydrolases in flavor regulation, to provide a systematic theoretical basis for the application of microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis technology in flavor regulation.
2. Application of Microbial Fermentation in Regulation of Food Flavor
2.1. Applications of Different Microorganisms
2.1.1. Bacteria
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and Bacillus are commonly used fermentation microorganisms in the field of food flavor regulation [21,22].
LAB are a class of Gram-positive bacteria that can ferment sugars to produce lactic acid [23]. Most have no spores and are important probiotics [24]. They not only exhibit antibacterial and antioxidant activity, but also promote the decomposition of proteins and lipids, and produce flavor precursors such as free amino acids or FFAs, thus significantly affecting the flavor characteristics of food [2]. LAB improves the flavor of yogurt by producing volatile flavor substances such as lactic acid and acetaldehyde [25]. In cheese fermentation, LAB mainly decompose proteins and fats to generate free amino acids and fatty acids to form complex flavors [26]. LAB fermentation is a widely used biotechnology process. This fermentation method increases the nutritional value and flavor of food, reduces anti-nutritional compounds, promotes antioxidant and immune responses, and prolongs the shelf life of products [27,28]. Lactobacillus plantarum is one of the most commonly used LAB to improve food flavor [29,30]. Studies have shown that L. plantarum fermentation can increase the content of bioactive components such as organic acids and phenols and volatile compounds such as acids, alcohols, and ketones in lily beverages, carrot pulp, and asparagus juice; enhance the flavor of fruit juice beverages; reduce the content of terpenes, furans, and other undesirable flavor substances; and improve the overall acceptability of products [27,31,32]. Kombucha is a traditional beverage produced through the fermentation of sweet black tea by bacteria and symbiotic yeast [33,34,35]. The introduction of L. plantarum reduces the total acid and acetic acid content, promotes the production of alcohols and esters, and enriches the fruity and floral characteristics of kombucha [33]. L. plantarum was used as an enhanced starter in the post-fermentation stage of surimi products, and the ester content increased by 20%, especially ethyl caprylate, which further enhanced the flavor of surimi products. In addition, the content of biogenic amines and nitrite decreased by 17% and 37%, respectively, during fermentation [36]. Xu et al. and Zheng et al. found that the inoculation of L. plantarum can significantly shorten the fermentation cycle of radish pickles, reduce the content of nitrite and conditional pathogenic bacteria, and improve the edible safety of pickles [37,38]. In addition, the content of sweet amino acids (threonine and glycine) in pickles fermented via inoculation was low, and the content of some bitter amino acids (histidine and arginine) and volatile substances was high, which may enhance the palatability of pickles [37,39]. Zhang et al. found that the artificial inoculation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Lactobacillus paracasei rapidly fermented the production of northeast sauerkraut and promoted the catabolism and synthesis of amino acids, thereby improving the flavor and quality [40]. L. plantarum also has significant advantages in enhancing the umami flavor of mushrooms. Chen et al. found that the acidity, total free amino acid content, and total flavor nucleotides of the fermentation broth showed an upward trend throughout the fermentation process [41]. Chen et al. focused on the effect of L. plantarum fermentation on the umami flavor substances of Lentinula edodes. The results showed that except for succinic acid and fumaric acid, the content of all umami substances increased with the extension of fermentation time [42]. In addition, the researchers posited that the fermentation of L. plantarum GDM1.191 could improve the umami flavor of Lentinula edodes mainly because most of the free amino acids and 5′-nucleotides increased after fermentation had strong umami flavor characteristics [42].
Bean products generally have bitter, astringent, and beany odors [43]. LAB fermentation can reduce such odors and improve the flavor of beans. Studies have shown that Lactobacillus johnsonii, Lactobacillus fermentum, L. plantarum, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and other LAB can effectively improve the flavor of pea protein, mung bean, soybean protein isolate (SPI), and other legume foods [44,45,46,47,48,49]. During the fermentation process, these LAB increased the types and contents of bioactive substances such as amino acids and peptides, produced aroma components such as alcohols and ketones, and reduced beany flavor components such as aldehydes, thus effectively improving the overall flavor of bean products [44,45,46,47,48,49].
Bacillus is a Gram-positive spore genus that is widely found in the natural environment [2,50]. Most of the Bacillus species, such as Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis, have shown probiotic properties [19,51,52]. Probiotic Bacillus have been shown to produce cellulase, amylase, protease, and lipase [2,53]. In addition, these strains can also produce antibacterial metabolites such as bacteriocins and peptides, thereby inhibiting the growth and reproduction of harmful bacteria [19,54]. It has been found that probiotic Bacillus strains can effectively solve the problems of poor flavor and long fermentation time of fermented products caused by the lack of certain functional genes and the insufficient metabolic capacity of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and have great potential in improving the safety of fermented products [19,55]. Zou et al. inoculated B. subtilis Y4 for solid-state fermentation to improve the quality of Yibin sprouts. The results showed that the inoculation of B. subtilis Y4 could promote the growth of Lactobacillus and the dominant fungus Cystofilobasidium, and reduce the number of Bacteroides and Cryptococcus. In addition, the inoculation of B. subtilis Y4 also increased the content of esters, alkenes, and sweet amino acids in the later stage of fermentation, which helped to improve the quality of Yibin sprouts [56].
2.1.2. Yeast
Yeast is a single-celled fungus that is rich in proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and a series of enzyme systems and active compounds [2,57]. In the food industry, yeast is mainly used in the field of wine making [58]. Ma et al. found that compared with Saccharomyces cerevisiae 85#, S. cerevisiae Jiangnan 1# strain enhanced the flavor of rice wine by reducing higher alcohols and increasing acetate. The decrease in higher alcohols is related to the down-regulation of key genes in the Ehrlich pathway, amino acid metabolism, and glycolysis. The increase in acetate content may be attributed to the synergistic interaction between S. cerevisiae and other microorganisms and the fermentation environment, which together shape the fermentation kinetics [59,60]. Li et al. used the Wickerhamomyces anomalus strain YM001 to biofortify the liquor fermentation process. The results showed that the addition of W. anomalus strain YM001 increased the content of total esters in the fermentation samples to a certain extent, especially the content of ethyl acetate, acetic acid, phenylethyl ester, and other compounds, which was of great significance to the improvement of flavor substances [61]. Bian et al. found that the addition of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera significantly increased the content of alcohol, organic acid, and amino acid, which gave the yellow rice wine a new characteristic flavor and produced a stronger caramel and vinegar flavor [62]. The fermentation system of a single strain has obvious limitations, and the types and contents of volatile aroma compounds produced are limited. In recent years, researchers have tended to use mixed-strain fermentation strategies (simultaneous fermentation, sequential fermentation) to improve the flavor quality of wine products through the synergistic effect of different yeasts. A number of studies have found that the mixed fermentation of different yeast strains reduces the content of organic acids, produces a wider range of aromatic compounds (especially esters and alcohols), and improves the flavor complexity and sensory quality of fruit wine [63,64,65,66]. Gao et al. found that co-fermentation increased the production of esters and glycerol, but decreased the content of total higher alcohols in the sequential fermentation of wine using Pichia kluyveri DG2 and S. cerevisiae MT. However, the interaction between different yeast strains is not always synergistically promoted and, in some cases, may have an inhibitory effect [67]. Fu et al. found that in the process of the mixed fermentation of Candida versatilis and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii to produce soy sauce, C. versatilis had a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of Z. rouxii, and the inhibitory effect increased with the increase in the initial inoculation amount. This inhibition is likely due to the production of acidic substances by C. versatilis, which, in turn, secrete proteases and heat-sensitive substances, inhibiting the growth of Z. rouxii [68].
2.1.3. Other Fungi
In addition to yeasts, other fungi such as Eurotium cristatum and molds also play an active role in improving food flavor. For example, Song et al. used Eurotium cristatum to ferment black tea. The results showed that the bitterness and astringency of black tea were reduced, and the mellowness and floral aroma were significantly enhanced [69]. Yang et al. also used E. cristatum to ferment mulberry leaf tea. The results showed that the bitterness and astringency of mulberry leaf tea were also reduced, and the umami and salty taste characteristics were enhanced [70]. In addition, the newly formed compound 1-octen-3-one gives fermented mulberry leaf tea unique mushroom, herbaceous, and earthy flavor characteristics [70]. In terms of legume products, Zhang et al. selected four edible mushroom mycelia to ferment SPI. After the fermentation, the original grass flavor and beany flavor of SPI were reduced; the bitter and astringent characteristics were reduced; the proportion of sweet and tasteless amino acids was increased; and new flavor compounds, benzaldehyde and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, were formed [71]. Wang et al. also used four kinds of edible fungi to ferment okara in order to reduce the odor volatile compounds. The results showed that the fermentation of edible fungi not only reduced the content of odorous substances such as hexanal and cis-6-nonenal, but also produced linalool, phenylethanol, and other substances, which added new floral, tea, and fruit flavor characteristics to the system [72]. In addition, Yu et al. fermented traditional Japanese smoked and dried meat products using molds. Fermentation improved the color characteristics and taste quality of the product; promoted the production of 3-methyl-1-butanol, 2,5-dimethylpyrazine, and α-pinene; and provided the product with obvious malt, nut, and roasted flavors [73].
Table 1 provides a brief overview of the treatment objects and flavor substances produced through fermentation, and specific flavor regulation directions of several commonly used single-strain fermentations.

Table 1.
The treatment objects of the fermentation of different strains, the flavor substances produced through fermentation, and the specific direction of flavor regulation.
2.1.4. Mixed Fermentation
Compared with the simple level of flavor substances in the single-strain fermentation system, mixed-strain fermentation can form a more complex and coordinated flavor substance spectrum through multi-strain synergistic metabolic pathways [75]. Existing studies have confirmed that co-fermentation with different functional composite microbial agents is an effective way to optimize the quality and flavor of fermented food [74,76]. The mixed fermentation technology includes both bacterial and fungal fermentation systems and a mixture of the two.
Bacterial mixed fermentation technology has been widely used in many food processing fields, such as bean products, fermented meat products, pickles, fish products, dairy, and alcoholic beverages. A large number of studies have shown that this fermentation method effectively increased the content of flavor substances (such as diacetyl, 1-heptanol, 1-nonanol) in food, and inhibited the production of undesirable flavor substances (such as hexanal, methyl mercaptan). After the fermentation of bean products using mixed bacteria such as B. subtilis, the content of butyric acid and other irritating odorous substances and beany odor-related compounds such as hexanal is reduced [77,78]. In one study, the fermentation of soybean products using Bacillus bulgaricus SDL1 and L. plantarum Ly8 as starter cultures reduced the content of acetic acid and lactic acid, enhanced the synthesis of branched-chain amino acids and threonine, and increased the content of some esters, acetoin, and pyrazines, thereby significantly improving the flavor characteristics of soybean products [79]. In other research, L. plantarum was mixed with Staphylococcus and Bacillus to ferment sausage and other meat products, which strengthened the hydrolysis process of protein and lipids and promoted the formation of volatile flavor substances such as β-eudesmol, nerolidol, ethyl caproate, and citronellal [80,81,82]. In addition, researchers found that mixed fermentation enhanced the competitive ability of dominant bacteria and inhibited the growth of spoilage bacteria [80,81]. Shan et al. found that Bacillus has a general advantage in aroma production over the LAB and Staphylococcus used in traditional meat fermentation [82]. In the fermentation of ginger pickles, mixed fermentation rapidly reduced the pH, increased the content of non-volatile organic acids; promoted the formation of volatile compounds, such as olefins, alcohols, phenols, and esters; and gave the ginger pickles a floral, sweet, and sour aroma, thereby improving the overall sensory acceptability [73]. Similarly, in the fermentation of carrots, mixed fermentation not only increased the types and contents of flavor substances such as alcohols, esters, and hydrocarbons, but also reduced the accumulation of nitrite [83]. Peng et al.’s and Hu et al.’s study of the fermentation system of Chinese rice wine and fruit vinegar also confirmed that mixed fermentation can not only improve the acidity of the product, but also leads to a significant increase in volatile components and flavor compounds [84,85]. In terms of fish products, inoculation fermentation effectively inhibited the oxidation of fish fat, resulting in a significant increase in the content of umami amino acids, and some bitter amino acids were inhibited [75,86,87,88,89].
Fungal mixed fermentation is mainly used to improve the flavor characteristics of wine and vegetables. Du et al. used Monascus purpureus combined with L. plantarum or S. cerevisiae to ferment Porphyra yezoensis [90]. After fermentation, the protein, total free amino acids, and volatile substances increased significantly, and the concentration of aldehydes decreased. Finally, the mellow, fruity, and sweet aroma of P. yezoensis increased, and the fishy and seawater smell decreased [90]. In the fermentation process of yellow rice wine and highland barley wine, the content and type of volatile organic compounds also increased [91,92]. In addition, Peng et al. found that molds increased the content of bitter amino acids during the production of yellow rice wine, but Saccharomycopsis fibuligera effectively alleviated these components, thereby enhancing the alcohol body, smoothness, and balance of the beverage [91].
The mixed bacteria and fungi fermentation system is also widely used. In producing protein hydrolysates and soy foods, Cao et al. fermented soybean protein hydrolysates by co-culturing L. fermentum and Pichia fermentum. The large peptides gradually degraded with fermentation, releasing free amino acids and increasing the umami and sweetness of the protein hydrolysate [93]. Peng et al. fermented soymilk using a mixed culture of LAB and kombucha. The study showed that the mixed starter reduced the content of hexanal, a characteristic flavor substance of soymilk; increased the content of soybean isoflavones and vitamins; and produced new flavor substances, which enhanced the nutritional characteristics of the soymilk and enriched its taste [94]. Qiu et al. used mixed flora (L. plantarum, Pichia guilliermondii, and Neurospora crassa) fermentation to enrich the flavor, reduce the bitterness and beany taste, and improve the freshness and taste of Hongjun tofu [95]. Wu et al. used different halophilic bacteria and yeasts to co-inoculate fermented soy sauce, finding that yeast can promote the growth of bacteria, but bacteria inhibit the growth of yeast. The co-inoculation of L. fermentum and Z. rouxii showed outstanding performance in flavor enhancement, which strengthened the soy sauce aroma, smoke aroma, and caramel flavor, and improved the umami and bitterness of soy sauce [96,97]. In terms of sauce production, Gao et al. found that the synergistic effect of L. plantarum, Pichia fermentans, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus accelerated the fermentation process of catfish frame fish sauce. The acidity increased, the glucose content decreased, and the umami amino acid content increased, which enhanced the flavor characteristics of the fish sauce [98]. Most studies have found that mixed fermentation using bacteria and fungi (liquid fermentation and solid-state fermentation) increases the type and quantity of flavor substances in alcohol products [99,100,101,102]. Tian et al. found that the complex flora composed of L. fermentum, Rhizopus oryzae, S. cerevisiae, and W. anomalus could effectively reduce the content of the harmful substance ethyl carbamate and its precursor urea in Chinese rice wine [100]. Fang et al. and Chen et al. used the mixed fermentation of LAB and yeast to improve the flavor characteristics of sourdough and salt-free fermented wheat gluten [103,104]. The results showed that during the fermentation of sourdough, the accumulation of acetic acid increased significantly, the content of lactic acid and total polyphenols decreased, and the degradation of phytic acid was significantly enhanced [103]. In this fermentation system, the reducing sugar produced by the synergistic metabolism of LAB and yeast can be further utilized by yeast, which may promote the synthesis of flavor substances [103,105]. In addition, Chem et al. further confirmed that there was a significant synergistic effect between LAB and yeast in the biosynthesis of characteristic flavor compounds such as isoamyl acetate [104]. In addition, the mixed fermentation of bacteria and fungi also showed significant effects in improving the flavor of mutton sausage, red yeast rice, hemp seed, and coffee [106,107,108,109,110].
Table 2 presents a brief review of the common treatment objects of three mixed bacteria fermentation approaches, the flavor substances produced through fermentation, and the specific flavor regulation direction.

Table 2.
The common treatment objectives of three mixed bacteria fermentation approaches, the flavor substances produced through fermentation, and the specific flavor regulation direction.
2.2. Possible Regulatory Mechanisms of Microorganisms on Food Flavor
Although significant progress has been made in the study of microbial fermentation to regulate food flavor, there are still obvious deficiencies in current research on the interaction mechanism of strains and the formation and transformation mechanism of flavor substances in food fermentation systems. Understanding the interaction between strains and their metabolic pathways can help optimize the fermentation process parameters and effectively inhibit the reproduction of harmful microorganisms in the fermentation process. After clarifying the formation and transformation mechanism of flavor substances, we can accurately control the synthesis of flavor substances by regulating the culture conditions or genetic modification, and then optimize the whole fermentation process so that the final product presents more coordinated flavor characteristics [111]. These research results can also provide an important theoretical basis for the development of new natural food-flavoring agents.
Liang et al. studied the potential mechanism of the interaction between L. plantarum and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in regulating the fermentation process and flavor characteristics of cabbage [112]. The results showed that L. plantarum, as a dominant strain, perceives the surrounding environment through quorum sensing signals and upregulates genes related to the synthesis of key compounds, increase in product yield, and formation of biofilm to adapt to the symbiotic environment. On the contrary, R. mucilaginosa responded to the stress induced by L. plantarum by upregulating the transporters of metabolites, antioxidative-stress-related genes, and longevity regulation, and finally achieved coexistence with L. plantarum [112]. In addition, the mixed culture of these two microorganisms significantly increased the production of certain flavor compounds, including lactic acid and acetoin, and reduced bitter amino acids such as phenylalanine, which was attributed to the differentially expressed genes regulated in the proliferation and metabolic pathways of L. plantarum [112,113].
Many researchers have conducted in-depth analyses and research on the key metabolic pathways in the process of microbial fermentation. Li et al. used Schizosaccharomyces pomelo and S. cerevisiae to ferment pomelo wine sequentially. The results showed that the continuous fermentation produced a wider range of aromatic compounds, especially esters and alcohols, which were the key to the aroma of grapefruit wine. Metabolomics analysis further confirmed that amino acid metabolism is the most significant activation pathway, and continuous fermentation is conducive to regulating amino acid levels to minimize the formation of potentially harmful by-products [64]. Gao et al. co-fermented wine using P. kluyveri and S. cerevisiae, which increased the yield of esters and glycerol and enriched the aroma diversity of wine. Transcriptome analysis showed that 512 genes were differentially expressed in S. cerevisiae under co-fermentation conditions, including 318 upregulated genes (mainly related to the synthesis of wine flavor substances) and 194 downregulated genes (mainly involved in glycolysis and amino acid metabolism pathways) [67]. Jia et al. used lactic acid fermentation to improve the flavor of egg white, with the results showing that the fermentation of Streptococcus thermophilus increased the content of aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, terpenoids, and aromatic compounds. Metabolic analysis showed that leucine, isoleucine, valine, phenylalanine, glucose, and saturated fatty acids were the key metabolic substrates involved in the formation of aldehydes, alcohols, acids, esters, and ketones during fermentation. Organic acids and their derivatives and organic oxygenates are the most abundant metabolites in egg white. During the 6 h fermentation, the activities of the threonine, methionine, lysine, and isoleucine biosynthetic pathways increased, while the glycolytic pathway was inhibited [114]. Zeng et al. fermented Kuding tea (KDT) using Aspergillus neoniger (AN) and Aspergillus cristatus (AC), respectively. They found that metabolites such as lipids, phenolic acids, flavonoids, amino acids, and phenolic glycosides were significantly correlated with the flavor characteristics of KDT, and the degradation of phenolic acids and lipids, the deglycosylation of glycoside compounds, and the increase in amino acids were the key to changing the taste characteristics of KDT. In addition, during the fermentation process, AN and AC were involved in five and four metabolic pathways, respectively, and showed different regulatory mechanisms in changing the flavor of KDT. Among them, AN led to the significant deglycosylation of glycosides, while AC affected the degradation of phenolic acids and lipids [115].
In addition, some scholars have also explored the influence mechanism of the microbial fermentation process on flavor substances. Wang et al. studied the mechanism of the effect of non-Saccharomyces on the flavor of vinegar. The results showed that the addition of non-Saccharomyces during the fermentation process increased the type and content of aromatic esters, produced ethyl acetate and phenethyl acetate, and increased the content of higher alcohols such as isobutanol, phenylethanol, and isoamyl alcohol. The addition of non-Saccharomyces also enhanced the activity of esterase and β-glucosidase. In addition, the concentration of glycerol was increased while ensuring the normal production of alcohol, thus improving the taste and texture of vinegar [116]. Li et al. studied the changes in volatile compounds (VCs) and microbial composition during the co-fermentation of Lactobacillus sake with Micrococcus and Lactococcus lactis, respectively. A total of 123 VCs were identified during the co-fermentation process, of which 25 were core VCs, mainly including aldehydes, alcohols, and ketones. The abundance of most VCs, LAB, and Lactococcus increased significantly, while the abundance of Micrococcus, Acinetobacter, and Megacoccus decreased significantly. In addition, Latilactobacillus had the greatest influence on the change of core VCs, which played a key role in the improvement of the volatile flavor of fermented surimi [117]. Fan et al. deeply explored the conversion of flavor substances and the synthesis mechanism of B vitamins during the fermentation of chickpea milk using Lactobacillus. The results showed that L. plantarum FMBL L23251 increased the content of vitamin B3 and vitamin B6 through the L-aspartate acid pathway and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate-independent pathway. In addition, L. plantarum FMBL L23251 effectively removed the beany odor due to its enhanced pyruvate metabolic pathway, and the main aldehydes were converted into the corresponding alcohols or acids while reducing the content of hexanal and 2-pentylfuran [118,119].
Figure 1 is a schematic representation of the mechanisms by which some of the major microorganisms regulate the flavor of a particular food.

Figure 1.
The main substrates, metabolic pathways, and products involved in the regulation of specific food flavor by several major microorganisms.
3. Application of Enzyme Catalysis in Regulation of Food Flavor
Microbial fermentation obtains different flavor substances through various metabolic activities of microorganisms. Enzyme catalysis technology has also become another important means to regulate food flavor due to the high efficiency and specificity of enzymes. Since the enzymes found at this stage for regulating food flavor mainly comprise oxidoreductases, transferases, and hydrolases, the following will explain the application of these three types of enzymes in regulating food flavor and their respective catalytic reaction schemes.
3.1. Application of Different Enzymes
3.1.1. Oxidoreductases (EC 1)
Oxidoreductases are a class of enzymes that catalyze redox reactions and participate in the synthesis, degradation, or transformation of food flavor substances through electron transfer. Glucose oxidase is a typical oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reaction of β-D-glucose with oxygen to produce gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Existing studies have shown that the enzyme alone or in combination with other enzymes can significantly improve food flavor characteristics [120]. Luo et al. found that the hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid produced by the glucose oxidase-catalyzed reaction effectively inhibited the release of cooked odorous components in heat-treated melon juice through oxidation and hydrophobicity. In addition, these products reduced the loss of characteristic odor compounds by inhibiting the Maillard reaction, degradation reaction, and oxidation reaction during thermal processing [121]. Liu et al. used the synergistic effect of glucosidase and glucose oxidase not only to inhibit the production of 1-octen-3-one to reduce the cooking taste, but also to increase linalool, benzyl alcohol, phenylethyl alcohol, and nonanal through the metabolism of shikimic acid, glucose, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid, providing the concentrated peach puree with richer grassy and floral flavor characteristics [122]. Botezatu et al. used a complex enzyme system of glucose oxidase and catalase to quickly reduce the pH of high-pH grape juice and unfermented grape juice to the optimal level, while increasing titratable acidity, reducing alcohol content, and preventing oxidation in residual sugar wine [123].
3.1.2. Transferases (EC 2)
Transferase can catalyze the transfer of groups between molecules and affect the aroma and flavor of food by participating in the synthesis, transformation, and modification of flavor substances, which is very important for forming and improving the unique flavor of food. Transglutaminase (TGase) can catalyze the cross-linking reaction between the γ-carboxyamide group of glutamine residue (Gln) and the ε-amino group of lysine residue (Lys) in proteins or peptides to form ε-(γ-glutamyl) lysine isopeptide bonds, thereby changing the secondary structure and function of proteins [124]. The enzyme plays an active role in improving the flavor of fish, beans, and dairy products. Shan et al. found that TGase could induce conformational changes in the polypeptide structure of the Alaska pollock framework protein, which significantly increased the content of umami and sweet amino acids and reduced the content of hydrophobic bitter peptides and hydrophobic amino acids, thus effectively enhancing the umami and reducing the bitterness of the products [125]. During the treatment of hypoallergenic soy protein, the enzyme also showed a significant effect on reducing bitterness [126]. Li et al. combined the application of transglutaminase and pectin fat mimics in the processing of cheddar cheese. The results showed that the treatment not only increased the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (especially linoleic acid), but also promoted the formation of volatile flavor substances such as alcohols, acids, and methyl ketones [127].
3.1.3. Hydrolases (EC 3)
Hydrolases are a class of enzymes that can catalyze hydrolysis reactions. They are widely present in organisms and participate in physiological processes such as metabolism and digestion [128,129]. The hydrolases commonly used to improve food flavor include proteases, lipases, and amylases [130]. Protease can hydrolyze proteins in food into small molecular peptides and free amino acids, which are the core components of food flavor [131,132]. Researchers have used proteases to improve the flavor of various foods. Studies have found that the addition of enzymes can promote the hydrolysis of meat protein and contribute to the formation of key volatile compounds such as ketones, acids, and esters [133,134]. In the production of cheese [135], oysters and other aquatic products [136], soybean meal and other soybean products [137,138], and plant-based foods [139], the content of free amino acids increased, which effectively improved the umami of food and reduced the beany flavor and other bad flavors of soybean products. The addition of flavor proteases in the production of wheat bread [140] and coconut oil [141] increased the content of soluble sugars and free amino acids, which promoted the Maillard reaction and caramelization reaction and produced more volatile compounds, thereby enriching the flavor of the product. Lipase can hydrolyze fat in food into fatty acids and glycerol [142,143]. Fatty acids can be further oxidized and cleaved to produce aldehydes, ketones, acids, and other flavorful substances to improve food flavor. Chen et al. used the lipase-catalyzed modification of goat milk fat to increase ester content with sweet, floral, and fruity aromas in the final product and decrease the content of FFAs characterized by unpleasant odors, thereby improving the rancidity and tar odor of goat milk [144]. Guan et al. immobilized lipase to promote the release of FFAs in low-fat cheese and improve its flavor [145]. In addition, cellulase, pectinase, amylase, aminopeptidase, and protein glutaminase are also often used to improve the flavor characteristics of products such as fruits, beverages, and protein hydrolysates [146,147,148,149,150,151]. Several studies have confirmed that the recombinant enzyme obtained using a heterologous expression system can also effectively improve the flavor quality of food. Li et al. [152] and Zhao et al. [153] successfully expressed protein glutaminase and lipase in Escherichia coli. The former effectively reduced the beany flavor of soy protein, and the latter enhanced the release of fatty acid flavor in low-fat cheese.
The multi-enzyme synergistic catalytic system can effectively degrade the macromolecular substances in the food matrix through multi-level enzymatic reactions and promote the transformation and generation of flavor precursors, thereby significantly improving the diversity and complexity of food flavor substances. A large number of studies have shown that compound enzyme treatment can not only promote the release of various flavor substances in pea textured protein [154], Huangshan floral mushroom protein [155], rapeseed [156,157], and wine [158], but also reduce the unpleasant flavor in boiled pig trotters [159] and low-valued red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) [160], improving the overall edible quality of food.
In recent years, the synergistic application of enzyme catalysis and microbial fermentation technology has become a research hotspot in food flavor regulation. This combined strategy can utilize the high efficiency and specificity of enzyme catalysis to synthesize the key flavor substances required in a short time, and can increase the variety of flavor substances using the diversity of microbial fermentation, making the food flavor richer, more complex, and unique. It was found that this method significantly increased the types and contents of free amino acids, free fatty acids, and flavor substances in fermented foods such as grass carp [161], tartary buckwheat [162], soybean paste [163], and modified cheese [164,165]. Enzyme treatment significantly improved the substrate utilization rate during the processing of sea buckthorn juice. Schizosaccharomyces pombe cerevisiae inoculation effectively degraded organic acids and the antioxidant activity of the juice was improved, thereby improving the color quality of the juice [166]. Yan et al. found that enzymatic hydrolysis promotes the production of peptides during the fermentation of soybean meal yogurt, thereby promoting the fermentation of LAB to produce acid, resulting in a shortened fermentation time. Fermentation-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis reduced the bitterness of soybean meal yogurt and also reduced the content of beany flavor components such as 1-pentanol and benzaldehyde [167].
3.2. Enzyme Catalytic Reaction Schemes
After understanding the application of three kinds of enzymes in regulating food flavor, the molecular mechanism of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in food processing systems and their regulation of the biosynthetic pathway of characteristic flavor compounds were analyzed. This can not only clarify the essential process of food flavor formation, but also help us to accurately regulate food flavor. The catalytic reaction schemes of oxidoreductases, transferases, and hydrolases are illustrated below.
3.2.1. Possible Catalytic Reaction Schemes by Oxidoreductases (EC 1)
Studies have found that lipoxygenase helps to promote the production of flavor substances in food. Ye et al. found that lipoxygenase can specifically catalyze the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids with a cis, cis-1,4-pentadiene structure to form hydroperoxides with conjugated double bonds. The hydroperoxide is unstable and will continue to oxidize and decompose, producing volatile flavor substances such as hydrocarbons, alcohols, and aldehydes, such as 1-octene-3-ol and hexanal. These substances give fermented fish products a unique flavor [20]. Wang et al. also found a similar conclusion when treating flounder bone oil with soybean lipoxygenase. They found that soybean lipoxygenase can catalyze the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids at the ω-6 carbon position to produce specific products such as 15-hydrogen peroxide-EPA and 17-hydrogen peroxide-DHA, which are then decomposed into volatile compounds (such as 1-penten-3-one, (E)-2-hexenal and 2-pentylfuran), thereby improving the flavor of the product [168]. The reaction scheme of lipoxygenase is shown in Scheme (1):
Recent studies have shown that laccase can effectively remove the bad flavor substances in food. Spaccasassi et al. found that laccase could effectively reduce the content of the bitter compound kaempferol 3-O-(2-O-sinapoyl-β-D-sophoroside) in rapeseed protein. In addition, laccase can also catalyze the oxidative polymerization of polyphenols such as sinapic acid, change the structure and properties of polyphenols, reduce bitter and astringent substances, and thus improve the flavor of rapeseed protein [169]. The reaction scheme of laccase is shown in Scheme (2):
3.2.2. Possible Catalytic Reaction Schemes by Transferases (EC 2)
Studies have shown that transferases play an active role in improving the flavor of protein hydrolysates. Su et al. used TGase to significantly increase the umami intensity of pea protein isolate hydrolysate (PPIH) by 50% and reduce the bitterness intensity by 40%. They found that after TGase treatment, the proportion of umami amino acids (glutamic acid, aspartic acid), hydrophilic amino acids (threonine, serine, cysteine, glycine, histidine, lysine), and proline in non-free amino acids increased significantly, while the proportion of hydrophobic amino acids (alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, and phenylalanine) decreased significantly. During the TGase catalytic process, more umami/hydrophilic amino acids and proline may be involved in the formation of peptides, and the newly formed peptides have a higher binding affinity with the umami receptors T1R1-T1R3 in PPIH than the original peptides. In addition, compared with the short peptides in the untreated PPIH, TGase treatment promoted the production of long peptides, which were enriched in umami and hydrophilic amino acids, resulting in enhanced umami and reduced bitterness of the hydrolysate [170]. Shan et al. also found similar results when using TGase to improve the flavor of Alaska pollock steak hydrolysate. The increase in umami and sweet amino acids, the decrease in hydrophobic amino acids, and the change in the composition ratio in the peptide group increase the umami while reducing the bitterness, thereby improving the taste characteristics of the product and making it more palatable as a whole [125]. The reaction scheme of TGase is shown in Scheme (3):
Xia et al. enhanced the flavor of Pleurotus geesteranus protein hydrolysate by using Bacillus amyloliquefaciens γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. They found that γ-glutamyl transpeptidase can catalyze the reaction of glutamine (Gln) and receptors (free amino acids or peptides) to produce gamma-glutamyl peptides. γ-glutamyl peptide can induce kokumi taste through calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) recognition [171]. In addition, compared with the blank chicken soup model, the umami chicken soup model and the salty chicken soup model, the umami and salty taste of the chicken soup model with the γ-glutamyl hydrolyzate prepared by P. geesteranus increased significantly, which indicated that the γ-glutamyl peptide played a synergistic role with the original flavor substances of chicken soup and improved the flavor [171]. The reaction scheme of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase is shown in Scheme (4):
3.2.3. Possible Catalytic Reaction Schemes by Hydrolases (EC 3)
In a study of the flavor regulation of fish products, Wang et al. showed that the addition of lipase could significantly promote the formation of key flavor substances such as 1-octene-3-ol, hexanal, and nonanal in lightly salted large yellow croaker. The reaction scheme is that lipase can effectively catalyze the hydrolysis reaction of triacylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine, resulting in a large number of flavor precursors, including intermediate products such as lysophosphatidylcholine and diglyceride [172]. Ye et al. used lipase and lipoxygenase to treat fermented fish products and found that lipase can catalyze the hydrolysis of lipids to produce free fatty acids. These free fatty acids are oxidized by lipoxygenase to form alcohols (such as 3-methyl-1-butanol) and aldehydes (such as valeraldehyde, hexanal, heptanal, and octanal), thereby giving more flavor to fish products [20]. The reaction scheme of lipase is shown in Schemes (5) and (6):
Yang et al. found that phospholipase promoted the oxidative degradation of phospholipids by regulating the glycerophospholipid metabolic pathway, thereby increasing the content of volatile flavor substances such as aldehydes and ketones and reducing the accumulation of unpleasant flavor substances, thereby improving the overall flavor of fish [173]. The reaction scheme of phospholipase is shown in Scheme (7):
In the field of protein food flavor regulation, Liao et al. used complex enzymes to produce more of the flavor substance (E, E)-2,4-decadienal, which greatly improved the overall aroma of chicken soup [174]. Fan et al. studied the compensation mechanism of the synergistic effect of a cell-free extract and enzyme system on cheese flavor. The results showed that the combined treatment of neutral protease and flavor protease increased the content of total leucine, valine, and isoleucine, and the soluble nitrogen content reached the level of traditional 12-month mature cheese. Moreover, due to the flavor compensation effect of transaminase and decarboxylase converting leucine to 3-methylbutanal, and keto acid dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase converting 3-methylbutyrate to 3-methylbutanal, the content of volatile flavor substances in enzyme-modified cheese is close to the level of cheese matured for 12 months [175]. Chen et al. used enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation to treat egg white protein. The results showed that enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation promoted the production of lipids and umami amino acids, respectively, and both can promote protein aggregation. In addition, enzymatic hydrolysis destroyed the hydrophobic cavity bound to the off-flavor compounds, released the off-flavor compounds bound to the protein, and then removed them through fermentation to achieve the deodorization of egg white powder [176]. The reaction scheme of proteinase is shown in Scheme (8):
Figure 2 shows the substrates and products of several enzymes commonly used in improving food flavor.
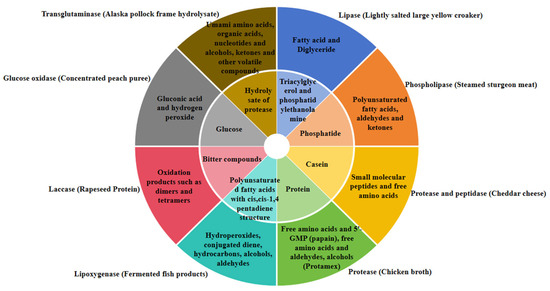
Figure 2.
Several commonly used oxidoreductases, transferases, and hydrolases catalyze substrates and corresponding products when regulating the flavor of specific products. The inner ring is the substrate and the outer ring is the product.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the application and mechanism of microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis in food flavor regulation were systematically described. Different microorganisms play a unique role in microbial fermentation. Bacteria such as LAB and Bacillus can promote the decomposition of proteins and lipids, produce flavor precursors, enhance food flavor, and enhance safety. Yeast is widely used in the field of brewing [177]. Aspergillus, mold, and other fungi can reduce unpleasant flavors in food and enhance new flavor characteristics. Mixed-strain fermentation can form a more complex and coordinated flavor profile through multi-strain synergistic metabolic pathways. The mechanism of microbial fermentation to regulate flavor mainly involves the interaction between strains and the formation and transformation of flavor substances. Different microorganisms interact with each other through quorum sensing and gene regulation, participate in metabolic pathways such as amino acids and glycolysis, and produce diverse flavor substances (such as esters, aldehydes, and ketones). Enzyme catalysis is also indispensable in the regulation of food flavor. Oxidoreductase affects food flavor by catalyzing redox reactions. Transferases are involved in the synthesis and transformation of flavor substances. For example, transglutaminase can change protein structures, enhance umami, and reduce bitterness. Hydrolases can hydrolyze the macromolecular substances in food into small molecular flavor components. The reaction scheme of enzyme catalysis is to promote the formation and transformation of flavor precursors by catalyzing specific chemical reactions, thereby improving food flavor. For oxidoreductases, lipoxygenase can catalyze the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to produce hydroperoxides, which are further oxidized and decomposed to form volatile flavor substances such as hydrocarbons and alcohols. Laccase can catalyze the oxidative polymerization of polyphenols such as sinapic acid in rapeseed protein, thereby reducing the amount of bitter and astringent substances. For transferases, transglutaminase can improve the flavor of food by catalyzing intramolecular or intermolecular cross-linking of proteins and reactions between proteins and amino acids (such as glutamic acid). γ-glutamyl transpeptidase can catalyze the reaction of glutamine with free amino acids or peptides to produce γ-glutamyl peptides. For hydrolases, lipases can catalyze the hydrolysis of lipids to produce free amino acids. Phospholipase can promote the hydrolysis of phospholipids to produce fatty acids, which can be further oxidized to aldehydes. Protease can hydrolyze proteins into peptides and amino acids, and some of the amino acids produced are umami and sweet, which can enhance the flavor of food.
Microbial fermentation and enzyme catalysis technology have shown great potential in the field of food flavor regulation due to their environmentally friendly and efficient characteristics. Future research may focus on the following suggested points to widen the application of related technologies in the food industry and meet consumer demand for high-quality food flavor.
- (1)
- Microorganisms are essential for the improvement of food flavor through fermentation. Therefore, the isolation and identification of flavor-producing microbial strains from traditional fermented food can be a potential way to enrich the microbes used in food. The construction of engineered strains for the recombinant expression of flavor-producing enzymes in food-safe microorganisms is also an alternative method.
- (2)
- Since the compounds in fermented food are complex, the identification of those compounds essential for food flavor is beneficial for quality control during food fermentation. The relationship between fermentation conditions and food flavor should also be explored in order to optimize standard protocol in food factories.
- (3)
- The enzymatic transformation of food to improve flavor is highly efficient. However, some flavor compounds are still extracted from plants or chemically synthesized. It is necessary to explore or design novel enzymes for the production of new natural flavor agents or low-cost and environmentally friendly synthesized flavors.
- (4)
- For the industrial application of enzymes in food flavor regulation, it is important to investigate food-safe, low-cost immobilization supports with good catalytic performance. The design of enzymatic reactors for food flavor improvement should also be explored.
- (5)
- Since an increasing number of flavor compounds produced by microorganisms and enzymes have been identified and their functions revealed, a database of flavor compounds, functions, producers, and transformers should be established; moreover, new flavor compounds could be designed with the assistance of AI, providing sufficient learning and training has been conducted. Further, potential pathways for the synthesis of new flavor compounds using microbial and/or enzymatic methods may also be identified by AI models based on the database.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing, F.W., M.W., L.X., X.G., Z.D. and K.C.; project administration, F.W.; writing—original draft, M.W. and L.X.; validation, L.X. and B.X.; visualization, J.Q. and B.X.; funding acquisition, K.C.; supervision, F.W. and X.G.; conceptualization, F.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172764) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2024YFD1300204).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tahir, H.E.; Zou, X.B.; Huang, X.W.; Shi, J.Y.; Mariod, A.A. Discrimination of honeys using colorimetric sensor arrays, sensory analysis and gas chromatography techniques. Food Chem. 2016, 206, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Guo, R.-R.; Ye, Q.; Zhao, H.-L.; Huang, X.-H. The regulation of key flavor of traditional fermented food by microbial metabolism: A review. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.G.; Jiao, T.H.; Adade, S.; Zhen, W.; Qin, O.Y.; Chen, Q.S. Digital twin for predicting and controlling food fermentation: A case study of kombucha fermentation. J. Food Eng. 2025, 393, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aregbe, A.Y.; Mubeen, B.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.K. Fermentation with Lactobacillus strains, Acetobacter pasteurianus, and Torulaspora delbrueckii D1-3 improves nutritional quality and volatile profile of sea buckthorn-based cereal beverage. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Chen, T.; Liu, X. Control of beany flavor from soybean protein raw material in plant-based meat analog processing. Foods 2023, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Takahashi, N.; Sasaki, R. Enzymatic improvement of food flavor II. Removal of beany flavor from soybean products by aldehyde dehydrogenase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1979, 43, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Redrejo-Rodriguez, M.; Tejeda-Cano, A.; del Carmen Pinto, M.; Macías, P. Lipoxygenase inhibition by flavonoids: Semiempirical study of the structure–activity relation. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2004, 674, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, G. The imitation and creation of a mango flavor. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e34622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhu, G.; Zheng, X. A hami melon flavor creation. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e95221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchabo, W.; Ma, Y.K.; Kwaw, E.; Zhang, H.N.; Xiao, L.L.; Tahir, H.E. Aroma profile and sensory characteristics of a sulfur dioxide-free mulberry (Morus nigra) wine subjected to non-thermal accelerating aging techniques. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Zhang, J.K.; Liu, E.M.; Yang, M.Q.; Chen, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, H.L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.T. Enhancing the taste of raw soy sauce using low intensity ultrasound treatment during moromi fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.L.; Liu, E.M.; Zhang, J.K.; Yang, M.Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Ma, H.L.; Hu, F. Effects of sonication during moromi fermentation on antioxidant activities of compounds in raw soy sauce. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 116, 108605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Lan, Y.B.; Yang, B.; Yang, J.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, M.; Xia, X.D.; Xu, W.M.; Wang, D.Y.; Zou, Y. Effect of low-frequency ultrasound pretreatment on taste substances in chicken liver by fermentation. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 218, 117458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, P. Evaluation of ultrasound-assisted tomato sour soup marination on beef: Insights into physicochemical, sensory, microstructural, and flavour characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 110, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Ni, L.; Li, H.; Xi, Y.; et al. Encapsulation of roast beef flavor by soy protein isolate/chitosan complex Pickering emulsions to improve its releasing properties during the processing of plant-based meat analogues. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.A.R.; Ribeiro, M.N.; Silva, G.A.; Rocha, L.C.R.; Pinheiro, A.C.M.; Nunes, C.A.; Carneiro, J.d.D.S. Temporal profile of flavor enhancers MAG, MSG, GMP, and IMP, and their ability to enhance salty taste, in different reductions of sodium chloride. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, M.T.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Fan, S.T.; Zhu, L.; Song, C.; Xiao, X. Recent Developments in Fermented Cereals on Nutritional Constituents and Potential Health Benefits. Foods 2022, 11, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Hu, W.W.; Su, J.; Li, H.H.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.W. Nondestructively sensing of total viable count (TVC) in chicken using an artificial olfaction system based colorimetric sensor array. J. Food Eng. 2016, 168, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, D.; Ma, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, G.; Tu, Q. Probiotic Bacillus as fermentation agents: Status, potential insights, and future perspectives. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Tan, J.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Effect of lipase and lipoxygenase on lipid metabolism and the formation of main volatile flavour compounds in fermented fish products: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.G.; Bai, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.S.; Pan, R.R.; Dong, Y.; Cui, H.L.; Xiao, X. Transcriptomics reveals the anti-obesity mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum fermented barley extract. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.S.; Lu, F.; Liu, D.D.; Zhao, X.X.; Chao, J.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Luan, Y.; Ma, H.L. The process of solid-state fermentation of soybean meal: Antimicrobial activity, fermentation heat generation and nitrogen solubility index. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 3228–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaw, E.; Ma, Y.K.; Tchabo, W.; Apaliya, M.T.; Xiao, L.L.; Wu, M. Effect of lactic acid fermentation on the phytochemical, volatile profile and sensory attributes of mulberry juice. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 56, 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, X.J.; Yagoub, A.E.; Xia, G.H.; Zhou, C.S. Effect of vacuum impregnation assisted probiotics fermentation suspension on shelf life quality of freshly cut lotus root. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Hao, G.; Yu, H.; Tian, H.; Zhao, G. Role of lactic acid bacteria on the yogurt flavour: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S316–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.A.; Ur-Rehman, S.; Anjum, F.M.; Huma, N.; Hafiz, I. Cheddar Cheese Ripening and Flavor Characterization: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Huang, S.; Xiong, T.; Peng, F. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU1546 fermentation on active components, in vitro uric acid lowering activity and flavor of Lilium. Food Biosci. 2025, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Pan, B.B.; Luo, W.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, Z.C.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, X. Role of sulfatase LPMS from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum dy-1 in releasing bound phenolic acids of barley bran dietary fiber. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, T.; Wu, F. Dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1 fermented barley suppresses body weight gain in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4907–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Shi, L.N.; Xu, T.; Wu, F. The anti-obesity effect of fermented barley extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in diet-induced obese rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Du, T.; Xiong, S.; Yuan, L.; Xiong, T.; Liu, G. Fermentation of asparagus juice using selected probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum JGS49 isolated from pickled asparagus: Microbiological, physicochemical and flavour characteristics. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 7113–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiong, S.; Hardie, W.J.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, M.; Xiong, T.; et al. Transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NCU116 fermentation on carrot flavor. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, L. Addition of lactic acid bacteria modulates microbial community and promotes the flavor profiles of Kombucha. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.D.; Dai, Y.Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.N.; Zhou, J.Z. Kombucha fermentation enhances the health-promoting properties of soymilk beverage. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazi, M.I.; Liaqat, F.; Liu, X.R.; Yan, Y.L.; Zhu, D.C. Fermentation, functional analysis, and biological activities of turmeric kombucha. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, M.; He, W.; Dai, W.; Tang, X.; Zheng, R.; Zhou, X. Flavor and nutritional characteristics of surimi product with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum as a reinforcing starter culture. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Mi, T.; Ma, S.; Yi, X.; Huang, P.; Huang, P.; Wu, C. Insight into the autochthonous lactic acid bacteria as starter culture for improving the quality of Sichuan radish paocai: Changes in microbial diversity and metabolic profiles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 425, 110877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Effects of enhanced fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WWPC on physicochemical characteristics and flavor profiles of radish paocai and dried-fermented radish. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, S.J.; Yang, F.; Hu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.J.; Yang, B.Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, L. Cold Plasma Controls Nitrite Hazards by Modulating Microbial Communities in Pickled Radish. Foods 2023, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Xin, L.; Xu, S.; Meng, X. Effect of rapid fermentation on the quality of northeastern sauerkraut analyzed based on HSSPME-GC-MS and LC-MS. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 198, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, H.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Fang, X.; Han, Y.; Mu, H. Effects of fermentation with different microbial species on the umami taste of Shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes). Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Fang, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, H.; Gao, H. Effects of fermentation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum GDM1.191 on the umami compounds in shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes). Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Ding, X.N.; Dai, C.H.; Ma, H.L. Changes in the structure and dissociation of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound-assisted acid pretreatment. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Yi, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, T.; Wen, R.; Li, C.; Reshetnik, E.I.; Gribanova, S.L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Physicochemical properties and volatile profile of mung bean flour fermented by Lacticaseibacillus casei and Lactococcus lactis. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 163, 113565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, J.-L.; Hao, Y.-P.; Zhu, M.-X.; Wang, J. Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum GD01 fermentation on the nutritional components and flavor substances of three kinds of bean milk. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 184, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Dai, J. Effect of Corynebacterium glutamicum Fermentation on the Volatile Flavors of the Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Soybean Protein Isolate. Foods 2024, 13, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccasassi, A.; Utz, F.; Dunkel, A.; Borner, R.A.; Ye, L.; De Franceschi, F.; Bogicevic, B.; Glabasnia, A.; Hofmann, T.; Dawid, C. Screening of a Microbial Culture Collection: Empowering Selection of Starters for Enhanced Sensory Attributes of Pea-Protein-Based Beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 15890–15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F. Exploring the flavor changes in mung bean flour through Lactobacillus fermentation: Insights from volatile compounds and non-targeted metabolomics analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Quan, K. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on the volatile flavors of mung beans. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 146, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Y.; Zhou, C.S.; Ma, H.L.; Li, S.J.; Yagoub, A.A.; Abdualrahman, M.A.Y. Proteomics Analyses and Morphological Structure of Bacillus subtilis Inactivated by Pulsed Magnetic Field. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Y.; Zhou, C.S.; Ma, H.L.; Li, S.J.; Yagoub, A.A.; Abdualrahman, M.A.Y. Biological Effect and Inactivation Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis Exposed to Pulsed Magnetic Field: Morphology, Membrane Permeability and Intracellular Contents. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; He, R.H.; Huang, L.R.; Zhu, S.Y.; Ding, Q.Z.; Luo, L. Improvement of nutritional value and bioactivity of soybean meal by solid-state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 86, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, J.A.; Ma, H.L.; Zabed, H.M.; Dong, Y.T.; Chen, G.; Guo, L.A.; Betchem, G.; Igbokwe, C.J. Exploring magnetic field treatment into solid-state fermentation of organic waste for improving structural and physiological properties of keratin peptides. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.S.; Dai, C.H.; Tang, Y.X.; Xing, Z.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Ding, Q.Z.; He, R.H.; Ma, H.L. Thermophilic solid-state fermentation of rapeseed meal and analysis of microbial community diversity. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 116, 108520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Jiang, H.; He, R.H.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Dai, C.H.; Sun, L.; Ma, H.L. Rapid detection model of Bacillus subtilis in solid-state fermentation of rapeseed meal. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhong, K.; Gao, H. Effects of solid-state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis Y4 on the quality of Yibin Yacai. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zabed, H.; Zhang, H.H.; Wang, X.; Yun, J.H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Yang, M.M.; Sun, W.J.; Qi, X.H. Optimization of fermentation medium for a newly isolated yeast strain (Zygosaccharomyces rouxii JM-C46) and evaluation of factors affecting biosynthesis of D-arabitol. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 99, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Z.; Chen, Z.L.; Wen, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.Y. The quality change of fig wine fermented by RV171 yeast during the six-month aging process. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 166, 113789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yuan, L.; Mao, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Han, X.; Ji, Z.; Liu, S.; Mao, J. Optimizing Huangjiu fermentation for enhanced aroma: Insights into Saccharomyces cerevisiae jiangnan1# strain. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 139, 107051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J.W.; Pan, W.X.; Chen, Q.S. Real-time monitoring of process parameters in rice wine fermentation by a portable spectral analytical system combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Du, B.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, H.; Sun, B.; Hao, J.; Li, X. Microbial community dynamics and spatial distribution of flavor compound metabolism during solid-state fermentation of Baijiu enhanced by Wickerhamomyces anomalus. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Fang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Han, B. Dynamic Changes in Physicochemical Properties, Amino Acid Content, and Flavour-Related Substances During Fortified Fermentation of Rice Wine with Saccharomycopsis fibuligera. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2024, 2024, 5581068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Li, B.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zeng, W.; Cai, W.; Wan, Y.; Fu, G. Effect of co-fermentation of non-Saccharomyces yeasts with Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the quality and flavor of blueberry wine. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Xiong, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, R.; Tu, T.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Bai, J.; Huang, Y. Enhancing the quality and flavor of pomelo wine through sequential fermentation with Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A non-targeted metabolomic analysis. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yuan, H.; Fei, Y.; Wang, H.; Qu, C.; Bai, W.; Liu, G. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Cyberlindnera fabianii Inoculation on Rice-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2024, 13, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Ji, C.; Liang, H.; Chen, Y. Effect of co-fermentation of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa with Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the quality and flavor profile of cider. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, Z.; Ma, L.; Du, L.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Yang, W. Effects of Pichia kluyveri on the flavor characteristics of wine by co-fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Co-culture relationship between Zygosaccharomyces rouxii and Candida versatilis and its effect on the flavour of soy sauce. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ma, F.; Chen, H.; Fei, Q.; Tao, G.; Wu, S.; Shi, D.; Deng, J.; Zhao, D.; Dong, X.; et al. Dynamic changes in flavor characteristics of black tea during solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yan, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, L. Effects of Fermentation with Eurotium cristatum on Sensory Properties and Flavor Compounds of Mulberry Leaf Tea. Foods 2024, 13, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, Z.; Liu, T.; Liang, J.; Liu, J. Fermentation with edible mushroom mycelia improves flavor characteristics and techno-functionalities of soybean protein. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, T.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Reduction of off-flavor volatile compounds in okara by fermentation with four edible fungi. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 155, 112941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, Z.; Yu, G.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C. Exploring the effect of mold fermentation on the taste and flavor properties of traditional Japanese smoked-dried bonito (katsuobushi). Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, H.N.; Pan, J.Y.; Dai, C.H.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Zhou, R.; He, R.H.; Ma, H.L. Mixed-Strain Fermentation Conditions Screening of Polypeptides from Rapeseed Meal and the Microbial Diversity Analysis by High-Throughput Sequencing. Foods 2022, 11, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Shang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dai, J.; Li, Z.; Xiang, W.; Tang, J. Effects of synthetic microbial community fermentation on volatile flavor and quality characteristics of ginger pickle. Food Res. Int. 2025, 207, 116077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S. Improvement of the quality and safety of low-salt fish sauce by reconstruction of microbial community through cooperative fermentation of starters. Food Res. Int. 2025, 205, 115972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wen, A.; Zeng, H.; Liu, N.; Qin, L. Effects of enhanced fermentation with high-yielding strains of Tetramethylpyrazine on flavor quality of Douchiba. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Varela, R.; Hansen, A.H.; Svendsen, B.A.; Moghadam, E.G.; Bas, A.; Kracun, S.K.; Harle, O.; Poulsen, V.K. Harnessing Fermentation by Bacillus and Lactic Acid Bacteria for Enhanced Texture, Flavor, and Nutritional Value in Plant-Based Matrices. Ferment. 2024, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Hu, X.-Y.; Liu, W.-H.; Liu, B.-Q.; Yang, J.; Tu, Z.-C.; Huang, Y.-H. Flavor improvement of fermented soybean foods by co-fermentation with Bacillus velezensis and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 186, 115257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Peng, L.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, R.; Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, X. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum C7 and Staphylococcus warneri S6 on flavor quality and bacterial diversity of fermented meat rice, a traditional Chinese food. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y. Improving the Flavor of Fermented Sausage by Increasing Its Bacterial Quality via Inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum MSZ2 and Staphylococcus xylosus YCC3. Foods 2022, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, K.; Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, M.; Ke, W.; He, H.; Li, C. Effect of probiotic Bacillus cereus DM423 on the flavor formation of fermented sausage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-N.; Yao, Q.-B.; Zhang, H.-R.; Li, W.-Q.; Nie, J.; Liang, Q.-C.; Wang, L.-H.; Zeng, X.-A.; Huang, Y.-Y. Impact of different lactic acid bacteria on nitrite degradation and quality of fermented carrot. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 6501–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, J.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Meng, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Enhancing the flavor quality of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu) through inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 211, 116935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Mai, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, B. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum cofermentation on the flavor and taste characteristics of mango vinegar. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 3744–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, S.; Shen, X.; Liang, Q.; Xu, T.; Shi, W. Effects of different fermenters on the quality and flavour of fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 4992–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.C.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.; Tian, H.Y.; Yuan, L. Effects of mixed starter cultures and exogenous L-Lys on the physiochemical and sensory properties of rapid-fermented fish paste using longsnout catfish by-products. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 108, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, F.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Gao, R.C.; Yuan, L. Suanyu fermentation strains screening, process optimization and the effect of thermal processing methods on its flavor. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, F.; Jin, W.G.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Gao, R.C. Dynamic changes and correlation analysis of protease activities, texture and flavour compounds during fish fermentation (suanyu) using mixed culture (Enterococcus rivorum and Enterococcus lactis). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2312–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Shim, S.-M.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Fu, X. Impact of Monascus purpureus combined with Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation on nutritional and flavor characteristics of Pyropia yezoensis. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, H.; Xie, G. Investigating the role of primary fungi in Huangjiu fermentation: Insights from flavor orientation and synthetic microbiomes. Food Microbiol. 2025, 129, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Feng, S. Flavor characteristics of hulless barley wine fermented with mixed starters by molds and yeasts isolated from Jiuqu. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Song, X.; Mu, Y.; Sun, W.; Su, G. Co-culturing Limosilactobacillus fermentum and Pichia fermentans to ferment soybean protein hydrolysates: An effective flavor enhancement strategy. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 100, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liao, Y.; Ren, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, A.; Tian, T.; Liao, P.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Fermentation performance, nutrient composition, and flavor volatiles in soy milk after mixed culture fermentation. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ye, S.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Xia, M.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q. Fermentation with a multi-strain to enhance the flavor of HongJun Tofu, a Chinese fermented okara food. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 189, 115495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, T.; Zhao, M.; Feng, Y. Effect of co-inoculation of different halophilic bacteria and yeast on the flavor of fermented soy sauce. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Liu, E.M.; Zhang, J.K.; Yang, L.X.; Huang, Q.R.; Chen, S.; Ma, H.L.; Ho, C.T.; Liao, L. Accelerating aroma formation of raw soy sauce using low intensity sonication. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, P.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Xia, W. Metabolomics ravels flavor compound formation and metabolite transformation in rapid fermentation of salt-free fish sauce from catfish frames induced by mixed microbial cultures. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liang, X.; Fei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liang, J.; Bai, W.; He, S. Effect of Mixed Strains on Microbial Community and Flavor Metabolites in Fermentation Process of Chi-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2024, 13, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Du, G.; Liu, Q. Effect of cultures of synthetic starters on the flavour and ethyl carbamate content of rice wine. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 5868–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, Y.; Tang, F.; Cai, W.; Hao, G.; Shan, C. Quality improvement of jujube wine through mixed fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacillus licheniformis. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.; Huang, S.; Chang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Effects of two kinds of Bacillus on flavour formation of Baijiu solid-state fermentation with pure mixed bacteria. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, W.; Dou, Z.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Cai, L.; Li, Y. Effects of mixed fermentation of different lactic acid bacteria and yeast on phytic acid degradation and flavor compounds in sourdough. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 174, 114438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Ananta, E.; Muller, J.A.; Liang, Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Liu, S.-Q. Co-Inoculation of Latilactobacillus sakei with Pichia kluyveri or Saccharomyces boulardii Improves Flavour Compound Profiles of Salt-Free Fermented Wheat Gluten. Fermentation 2024, 10, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.W.; Zhang, Y. Isolation and screening of high-quality lactic acid bacteria and yeast strains in kefir grains and preparation of kefir compound fermentation starter. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e17073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, L. Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici and Rhizopus Oryzae on protein degradation and flavor formation in fermented mutton sausages. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 213, 117075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Jiao, P.; Tang, C. Influences of lactic acid bacteria strains on the flavor profiles, metabolites and quality characteristics of red yeast rice produced by solid-state fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Effects of fermentation with Kefir grains on nutrient composition, flavor volatiles, and product physical stability of a hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) beverage. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 183, 114934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, M.H.S.; Borem, F.M.; Alves, A.P.d.C.; Pieroni, R.S.; Santos, C.M.; Nakajima, M.; Sugino, R. Fermentation of coffee fruit with sequential inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Effects on volatile composition and sensory characteristics. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, K.Y.; Guo, A.Z.; Qi, X.H.; Cai, M.H. The evaluation of kefir pure culture starter: Liquid-core capsule entrapping microorganisms isolated from kefir grains. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2016, 22, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, D. Engineering Corynebacterium crenatum for enhancing succinic acid production. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, 12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chu, C.; Yi, J.; Liu, Z. Enhancing fermented vegetable flavor with Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa. Food Res. Int. 2025, 200, 115500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Jomaa, S.A.; Abd El-Wahed, A.; El-Seedi, H.R. The Many Faces of Kefir Fermented Dairy Products: Quality Characteristics, Flavour Chemistry, Nutritional Value, Health Benefits, and Safety. Nutrients 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Duan, J.; Bao, S.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; Ye, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. Metabolomic and proteomic profiling reveals the formation mechanism of volatile flavor in egg whites during fermentation by Streptococcus thermophilus. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Song, C.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhao, M.; et al. Constituent-taste relationship of Kuding tea fermented by Aspergillus neoniger and Aspergillus cristatus: Unveiling taste characteristics through untargeted metabolomics. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, L.; Hadiatullah, H.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, G. Enhancing flavour with non-Saccharomyces during vinegar alcoholisation: A mechanism study. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Improvement mechanism of volatile flavor in fermented tilapia surimi by cooperative fermentation of Pediococcus acidilactici and Latilactobacillus sakei: Quantization of microbial contribution through influence of genus. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Dong, L.; Luo, J.; Tian, F.; Ni, Y. Omics analysis of key pathway in flavour formation and B vitamins synthesis during chickpea milk fermentation by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Tang, P.; Bai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, T.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H.; Yang, A. Anti-food allergic activity of soymilk fermented by Lactobacillus in vitro. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, S.H.; Vakili, O.; Ahmadi, N.; Soltani Fard, E.; Mousavi, P.; Khalvati, B.; Maleksabet, A.; Savardashtaki, A.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Movahedpour, A. Glucose oxidase: Applications, sources, and recombinant production. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Bi, S.; Wu, J. Effect of glucose oxidase treatment on the aroma qualities and release of cooked off-odor components from heat-treated Hami melon juice. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chen, Q.; Gou, M.; Bi, J. The potential of glucosidase and glucose oxidase for aroma improvement in concentrated peach puree based on volatilomics and metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botezatu, A.; Essary, A.; Bajec, M. Glucose Oxidase in Conjunction with Catalase—An Effective System of Wine pH Management in Red Wine. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2023, 74, 0740004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, J.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; Fu, R.; Qayum, A.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Low temperature extrusion promotes transglutaminase cross-linking of whey protein isolate and enhances its emulsifying properties and water holding capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Wu, G.; Bu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Li, X. Effect of transglutaminase cross-linking on debittering of Alaska pollock frame hydrolysate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Combining Alcalase hydrolysis and transglutaminase-cross-linking improved bitterness and techno-functional properties of hypoallergenic soybean protein hydrolysates through structural modifications. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; Yu, Y.; Song, H.; Zhu, D.; Liu, H. Effects of pectic fat mimetics and transglutaminase on the regularity of protein and fat degradation and flavour compounds in Cheddar cheese during ripening. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, L.N.; Chen, H.J.; Sun, D.W.; Deng, B.X.; Li, J.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, F. Inactivation of Lipase and Lipoxygenase of Wheat Germ with Temperature-Controlled Short Wave Infrared Radiation and Its Effect on Storage Stability and Quality of Wheat Germ Oil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, W.W.; Luo, M.; Wang, B.; Qu, W.J.; He, R.H.; Owusu, J.; Li, Y.L. Effects and mechanism of ultrasound pretreatment on rapeseed protein enzymolysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.W.; Dong, S.Y.; Chen, M.; Gao, R.C.; Chen, S.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Sun, B.W. Preparation of a fermentation solution of grass fish bones and its calcium bioavailability in rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Li, W.; Li, C.Z.; Lin, L. Intelligent release of cinnamon oil from engineered proteoliposome via stimulation of Bacillus cereus protease. Food Control 2016, 67, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.C.; Shi, T.; Liu, X.D.; Zhao, M.Q.; Cui, H.L.; Yuan, L. Purification and characterisation of a salt-stable protease fromthe halophilic archaeon Halogranum rubrum. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Sun, F.; Kong, B. Effect of the protease from Staphylococcus carnosus on the proteolysis, quality characteristics, and flavor development of Harbin dry sausage. Meat Sci. 2022, 189, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Proteolysis and quality characteristics of Harbin dry sausages caused by the addition of Staphylococcus xylosus protease. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pei, Y.; Cheng, K.; Deng, Y.; Dong, X.; Fang, R.; Chu, B.; Wei, P.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, G. Production and evaluation of enzyme-modified cheese adding protease or lipase to improve quality properties. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 135, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Yuan, C.; Huang, T.; Jia, R.; Wei, H. Effect of Neutral Protease on Freshness Quality of Shucked Pacific Oysters at Different Storage Conditions. Foods 2024, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, F.; Sui, X.; Fang, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Assessment the flavor of soybean meal hydrolyzed with Alcalase enzyme under different hydrolysis conditions by E-nose, E-tongue and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. -X 2021, 12, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbaningrum, K.; Hidayat, C.; Witasari, L.D.; Utami, T. Flavor Precursors and Volatile Compounds Improvement of Unfermented Cocoa Beans by Hydrolysis Using Bromelain. Foods 2023, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Hoz, A.; Caripan, P.; Moltedo, B.; Ferrada, N.; Contreras, R.A. A metabolomic approach of AI-driven enzymatic digestion of pumpkin seed flour for producing umami metabolites. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2025, 39, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Gu, M.; Xi, J.; Chen, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, F.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q. Effect of a commercial peptidase on volatile composition and sensory properties of wheat bread crumb and crust. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 189, 115532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chan, J.X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Pre-treatment of coconut kernels by proteases to modulate the flavour of coconut oil. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tan, X. Characterization of a Desiccation Stress Induced Lipase Gene from Brassica napus L. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.S.; Cu, D.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Chen, G.; Jia, C.S.; Feng, B. Highly Efficient Synthesis of Phytosterol Linolenate Catalyzed by Candida Rugosa Lipase through Transesterification. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Stevenson, R.J.; Ang, X.; Peng, Y.; Quek, S.Y. Lipase-catalyzed modification of milk fat: A promising way to alter flavor notes of goat milk products. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, Y. The enhanced fatty acids flavor release for low-fat cheeses by carrier immobilized lipases on O/W Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Su, L. Enzyme-Assisted Osmosis Process of Functional Sugar to Improve the Quality Characteristics of Cherry Tomatoes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 3776–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, B.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, S. Effect of cellulase on antioxidant activity and flavor of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Zhan, Q.; Zhong, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L. The critical roles of α-amylase and amyloglucosidase in improving the quality of black waxy corn beverages: Special attentions to the color and flavor. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 110, 103625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Saito, M.; Maruyama, M.; Yamanaka, S.; Tanemura, T.; Watanabe, M.; Fukumori, F.; Hayashi, K. Reduction in the bitterness of protein hydrolysates by an aminopeptidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2023, 29, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Okada, M.; Yamaguchi, S. Protein-glutaminase improves water-/oil-holding capacity and beany off-flavor profiles of plant-based meat analogs. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.R.; He, X.C.; Wu, J.C.; Ma, X.N.; Han, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The evaluation of deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids as cosolvents system for improving cellulase properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Heterologous expression of protein-glutaminase in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for improved flavor properties of soy protein and its implications on high-moisture extrudates. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, M.; Yan, X.; Zhang, G.; Xia, J.; Zeng, G.; Tian, W.; Bao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, P.; et al. Expression and characterization of a novel lipase from Bacillus licheniformis NCU CS-5 for application in enhancing fatty acids flavor release for low-fat cheeses. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Broches, N.; Okuda, K.; Okada, M.; Yamaguchi, S. Umami and saltiness enhancements of textured pea proteins by combining protease- and glutaminase-catalyzed reactions. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, J. Analysis of flavor changes in Huangshan floral mushroom hydrolysates obtained by different enzyme treatments. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Chen, C.; Cui, F.-J.; Ye, P.P.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhou, T.L.; Shi, J.-C.; Shu, X.-Q.; Chen, Z.-W. Flavor enhancement of strong fragrant rapeseed oils by enzymatic treatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betchem, G.; Dabbour, M.; Tuly, J.A.; Billong, L.F.; Ma, H.L. Optimization of fermentation conditions to improve the functional and structural characteristics of rapeseed meal with a mutant Bacillus subtilis species. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 205, 117424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, H.; Yu, H.; Shen, L.; Jiang, J.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y. Characterization of Trichoderma reesei endoglucanase displayed on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell surface and its effect on wine flavor in combination with β-glucosidase. Process Biochem. 2023, 124, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Sheng, B.; Xu, S.; Ma, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, D. The deodorising and flavouring effect of enzymatic hydrolysis and glycation on boiled pig trotters. Czech J. Food Sci. 2024, 42, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. Flavor substances of low-valued red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) hydrolysates derived from double enzymatic systems. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zheng, C.; Yin, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, W. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum and flavourzyme on protein degradation and flavor development in grass carp during fermentation. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, M. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on volatile flavor compounds of Monascus -fermented tartary buckwheat based on headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, S.; Ji, C. Impact of Enzyme-Microbe Combined Fermentation on the Safety and Quality of Soy Paste Fermented with Grass Carp By-Products. Foods 2025, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Zhong, F. Flavor precursors and flavor compounds in Cheddar-flavored enzyme-modified cheese due to pre-enzymolysis combined with lactic acid bacteria fermentation. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Wu, J.; Li, C.Z.; Lin, L. Anti-listeria effects of chitosan-coated nisin-silica liposome on Cheddar cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8598–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y. Optimization of the quality of sea buckthorn juice by enzymatic digestion and inoculation sequence. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fan, X.; Hua, D.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Effects of different enzymatic hydrolysis techniques on volatile flavor compounds and nutritional metabolites of soybean meal yogurt. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.-S.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Qin, L.; Huang, X.-H. Mechanism of differentiated and targeted catalysis in complex lipid system under lipase and lipoxygenase mediation. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccasassi, A.; Walser, C.; Nisov, A.; Sozer, N.; Frank, O.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.F. Reducing the Bitterness of Rapeseed Protein: Integrating Enzymatic Treatment, Metabolomics, and Sensory Analysis to Elucidate Underlying Mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 3657–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Xie, Y.; Liu, R.; Cui, G.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J. Effect of transglutaminase on taste characteristics of pea protein hydrolysates through altering the composition of amino acids and peptides. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Protein Hydrolysates from Pleurotus geesteranus Modified by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Exhibit a Remarkable Taste-Enhancing Effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12143–12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.-H.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Qin, L. Compensatory effect of lipase on the flavor of lightly-salted large yellow croaker: Integration of flavoromics and lipidomics. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X. Contribution of phospholipase B to the formation of characteristic flavor in steamed sturgeon meat. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.; Peng, S.; Guo, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, K.; Ma, L.; Chen, F.; Hu, X.; Liao, X.; Ji, J. The effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the flavor improvement of chicken broth by characterizing key taste and odor-active compounds. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shen, Q.; Quan, W.; Luo, J. Preparation of a novel enzyme-modified cheddar cheese: Molecular mechanism of cheese flavor compensation by synergistic action of cell-free extracts and enzyme systems. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 142281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Huo, J.; Gao, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, S. Study on the effect of enzymolysis combined fermentation on reducing the off-flavor of egg white powder. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, E.Y.; Hu, M.; Oladejo, A.; Gong, X.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhong, H. Isolation, identification and screening of high-quality yeast strains for the production of milk beer. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).