Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related to Flavor Compounds in Douchi from the Sichuan–Chongqing Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Collection of Douchi
2.2. Determination of the Microbial Diversity in the Samples
2.3. Determination of Amino Acid Levels
2.4. Volatile Compound Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alpha Diversity in Different Fermented Douchi Products
3.2. Microbial Community Composition in Douchi Products
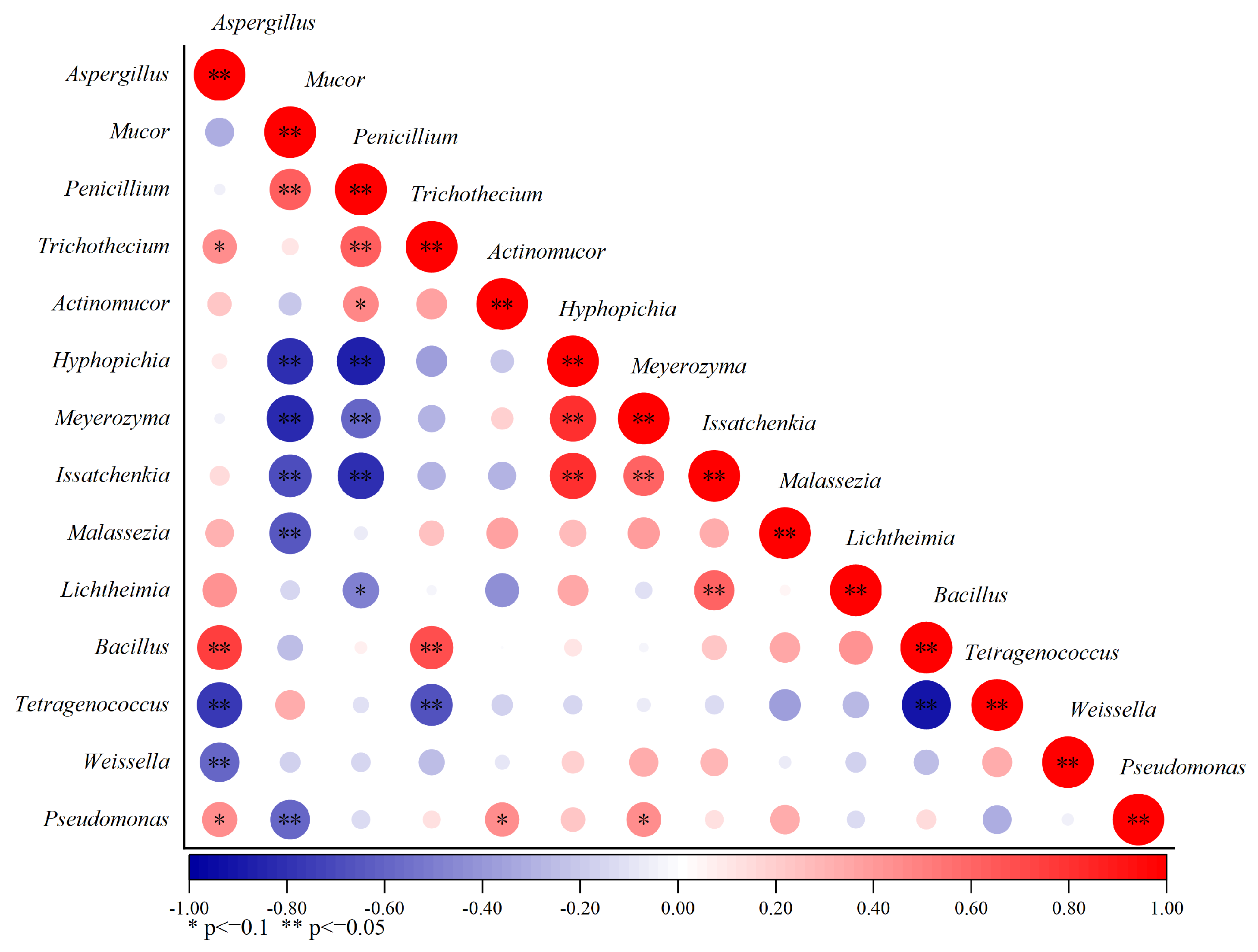
3.3. Bacterial and Fungal Interaction Analysis
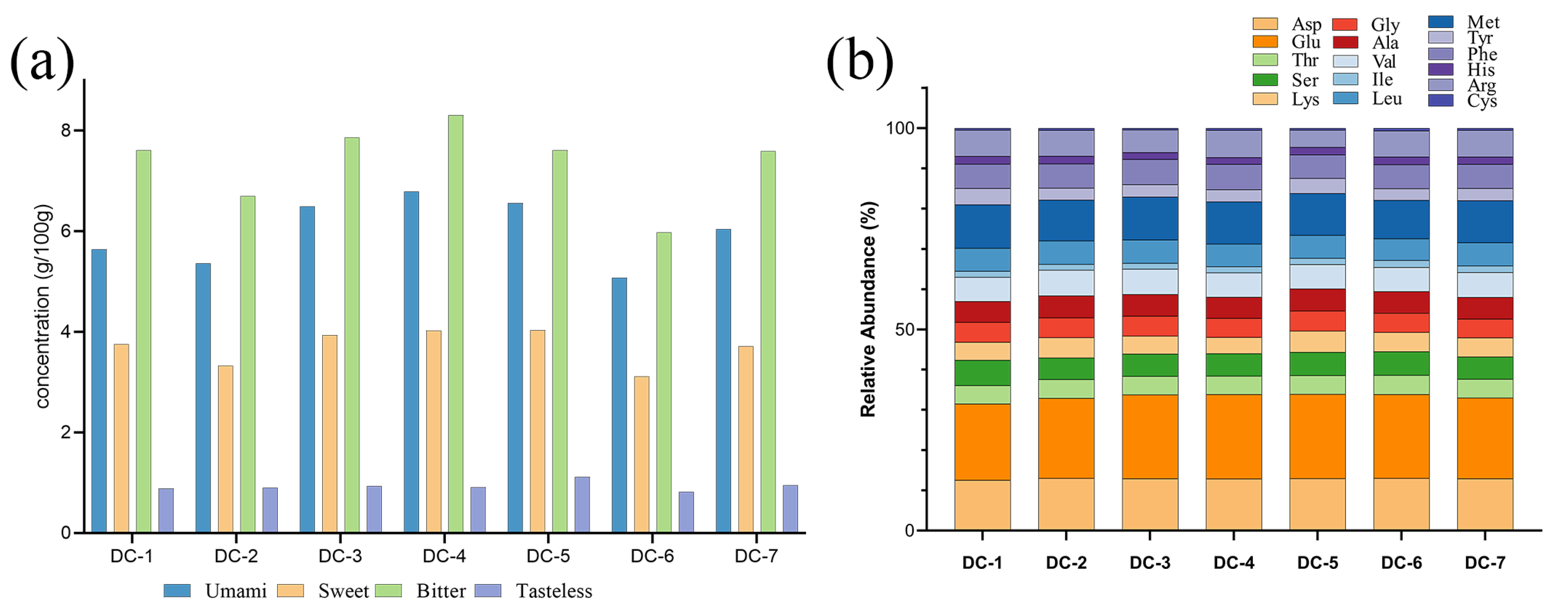
3.4. Amino Acid Analysis
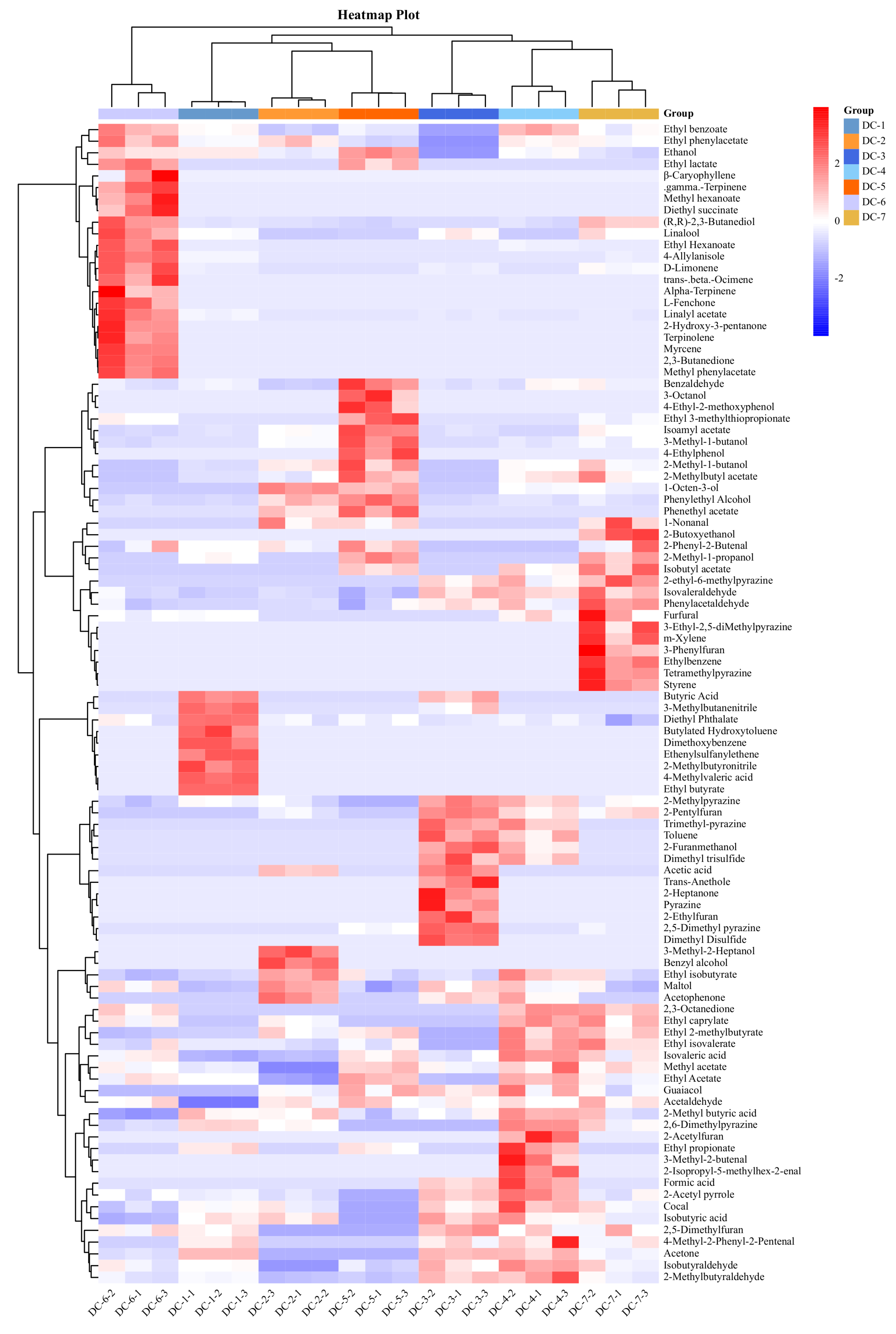
3.5. Volatile Components
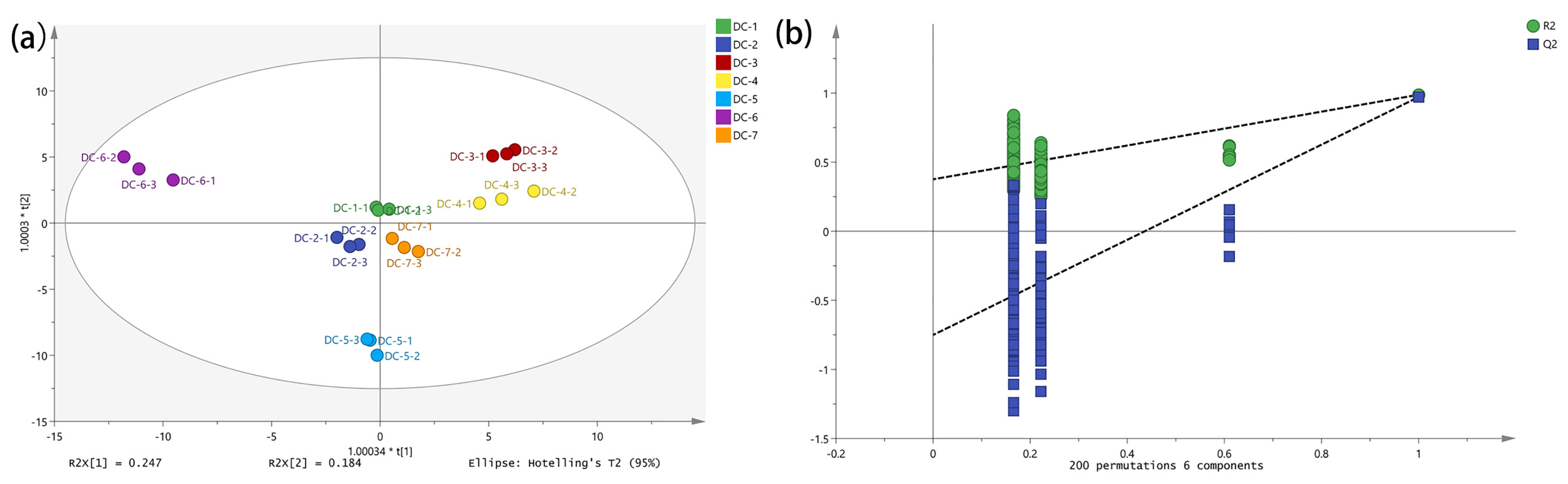
3.6. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Volatile Components and Amino Acids
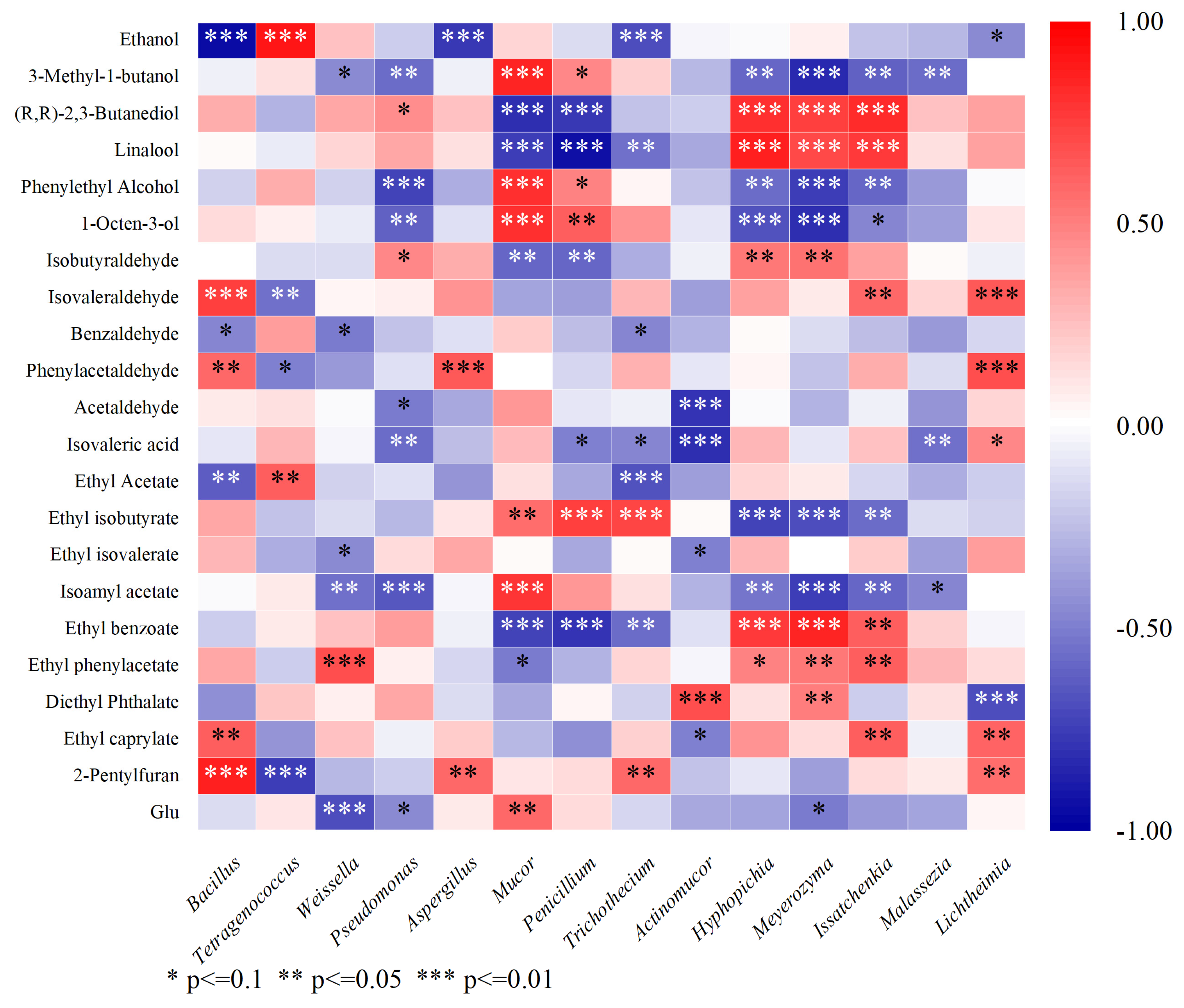
3.7. Correlation Analysis Between Flavor Compounds and Microorganisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Suo, H. Correlation between the Quality and Microbial Community of Natural-Type and Artificial-Type Yongchuan Douchi. LWT 2021, 140, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Comparative Peptidomics Analysis in the Discovery of Umami Peptides from Chinese Douchi. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, L.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characteristic Fingerprints and Volatile Flavor Compound Variations in Liuyang Douchi during Fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; He, Q.; Wei, R.; Sun, Z.; Duan, S.; Li, Y. Correlation between Microbial Community Succession and Flavor Substances during Fermentation of Yongchuan Douchi. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Liang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R. Comparing the Differences of Characteristic Flavour between Natural Maturation and Starter Culture for Mucor-Type Douchi. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiovanni, M.; Gosetti, F.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Termopoli, V. Aroma Determination in Alcoholic Beverages: Green MS-based Sample Preparation Approaches. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2024, 43, 660–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N. Comparative Analysis of Flavour Profile and Aroma Components of Shanxi Aged Vinegar from China. Flavour Fragr. J. 2025, 40, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.; António, S.B.; Sílvia, M.R.; José, S.C. Optimisation of Solid-Phase Microextraction Combined with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Based Methodology to Establish the Global Volatile Signature in Pulp and Skin of Vitis vinifera L. Grape Varieties. Talanta 2011, 85, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; You, K.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhu, D. Characterisation of Lentinus Edodes Chicken Filling Based on Their Flavour Profiles Using SPME-GC–MS, Electronic Sensory Analysis, and Fuzzy Mathematics. Flavour Fragr. J. 2025, 2025, ffj.3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S. Flavor Quality Characterization of Rapeseed Oil During Storage by Physicochemical Analysis, Sensory Evaluation, Electronic Nose, and GC–O. J. Food Biochem. 2025, 2025, 7434957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, S.O.; Colakoglu, F.; Kunili, I.E.; Ormanci, H.B. Profiling the Effects of Starter Cultures on Biochemical Compounds in Fermented Fish Sauces and Their Relationships with Sensory Perceptions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 6473–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, J.; Ji, Y.; Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Effect of Microbial Fermentation on the Quality of Soybean Meal. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; Xi, X.; Yao, T.; Yang, H.; Ma, Y. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Microbial Communities and Their Correlation with Volatile Aroma Compounds during the Fermentation of Mucor racemosus Sufu. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Fermentation Relationship Between Microorganism and Flavor Formation in Traditional Aspergillus-Type Douchi. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, A.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Correlation between Flavor Compounds and Microorganisms of Chaling Natural Fermented Red Sufu. LWT 2022, 154, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wan, L.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Tu, Z. Change of Volatile Compounds in Aspergillus-Type Douchi during Processing Evaluated by SPME-GC-MS. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Turning over Fermented Grains Elevating Heap Temperature and Driving Microbial Community Succession during the Heap Fermentation of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. LWT 2022, 172, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lapu, M.; Kang, S.; Jiang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, M. Effects of Tartary Buckwheat on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Low Salt Natural Fermented Soybean Paste. Food Control 2022, 138, 108953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hua, Q.; Tian, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, P.; Xia, W. Effect of Starter Cultures and Spices on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities of Fermented Fish (Suanyu) after Fermentation and Storage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wang, H.; Suo, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Microbial Composition and Correlation between Microbiota and Quality-Related Physiochemical Characteristics in Chongqing Radish Paocai. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Guo, R.-R.; Ye, Q.; Zhao, H.-L.; Huang, X.-H. The Regulation of Key Flavor of Traditional Fermented Food by Microbial Metabolism: A Review. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Wei, C.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, X.; Zou, J. Dynamics and Correlation between Volatile Compounds and Microbial Community in Chestnut Rice Wine Fermentation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 5155–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z. Comparative Evaluation of the Microbial Diversity and Metabolite Profiles of Japanese-Style and Cantonese-Style Soy Sauce Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 976206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Lin, X.-N.; Ji, Y.-Q.; He, H.-J.; Yang, H.-Z.; Tang, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-G. Characterization and Correlation of Dominant Bacteria and Volatile Compounds in Post-Fermentation Process of Ba-Bao Douchi. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, H. Comparison of the Microbial Community and Flavor Compounds in Fermented Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi): Three Typical Types of Chinese Fermented Mandarin Fish Products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.H.; Han, D.M.; Kim, H.M.; Park, D.; Jeong, D.M.; Kang, H.A.; Jeon, C.O. Metabolic Features of Ganjang (a Korean Traditional Soy Sauce) Fermentation Revealed by Genome-Centered Metatranscriptomics. mSystems 2021, 6, e00441-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.A.; Kim, E.; Yang, S.M.; Lee, S.; Yoon, S.R.; Jang, K.S.; Kim, H.Y. High-Throughput Sequencing of the Microbial Community Associated with the Physicochemical Properties of Meju (Dried Fermented Soybean) and Doenjang (Traditional Korean Fermented Soybean Paste). LWT 2021, 146, 111473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, M.-H.; Kim, H.-Y. Analysis of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Japanese- and Chinese-Fermented Soybean Pastes Using Nested PCR–DGGE. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Dumba, T.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, C.; Cai, C.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. Microbial Diversity and Chemical Property Analyses of Sufu Products with Different Producing Regions and Dressing Flavors. LWT 2021, 144, 111245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; He, W.; Liao, L.; Xia, B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Microbial Community and the Characterization of Aspergillus Flavus in Liuyang Douchi during Fermentation. LWT 2022, 154, 112567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Determination of the Microbial Communities of Guizhou Suantang, a Traditional Chinese Fermented Sour Soup, and Correlation between the Identified Microorganisms and Volatile Compounds. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L. Dynamic Analysis of Microbial Communities and Flavor Properties in Merlot Wines Produced from Inoculation and Spontaneous Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Guan, X.; Liu, Y.; Che, Z.; Lin, H.; Min, X.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, W. Contribution of Microbial Communities to Flavors of Pixian Douban Fermented in the Closed System of Multi-Scale Temperature and Flow Fields. LWT 2023, 173, 114188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, M.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Simultaneous Determination of Free Amino Acids in Pu-Erh Tea and Their Changes during Fermentation. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tian, T.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tao, D.; Wu, R.; Yue, X. The Dynamic Changes of Chemical Components and Microbiota during the Natural Fermentation Process in Da-Jiang, a Chinese Popular Traditional Fermented Condiment. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhao, S.; Jia, H.; Guo, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. Flavor Differences between Commercial and Traditional Soybean Paste. LWT 2021, 142, 111052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mu, Y. Correlations between Microbiota with Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Flavor Components in Black Glutinous Rice Wine Fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Association between Flavors and Microbial Communities of Traditional Aspergillus-Douchi Produced by a Typical Industrial-Scale Factory. LWT 2023, 176, 114532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Kan, J. Comparative Evaluation of Commercial Douchi by Different Molds: Biogenic Amines, Non-Volatile and Volatile Compounds. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Sun, B.; Fu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Analysis of Physicochemical Indices, Volatile Flavor Components, and Microbial Community of a Light-Flavor Daqu. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 76, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chao, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, T.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Key Aroma-Active Compounds in Different Types of Douchi Based on Molecular Sensory Science Approaches. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Qin, L.; Liu, N.; Wen, A.; Zeng, H.; Miao, S. Flavor Formation by Amino Acid Catabolism in Low-Salt Sufu Paste, a Chinese Fermented Soybean Food. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Monitoring Oxidative Stability and Changes in Key Volatile Compounds in Edible Oils during Ambient Storage through HS-SPME/GC–MS. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 20, S2926–S2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Feng, X.; Yang, G.; Peng, X.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Kan, J. Impact of Aroma-Enhancing Microorganisms on Aroma Attributes of Industrial Douchi: An Integrated Analysis Using E-Nose, GC-IMS, GC–MS, and Descriptive Sensory Evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, C.; Tang, Z.; Liu, P.; Ding, W.; Lin, H.; Tang, J. Revealing the Formation Mechanisms of Key Flavors in Fermented Broad Bean Paste. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gemert, L.J. Compilations of Odour Threshold Values in Air, Water and Other Media, 2nd ed.; China Science Publishing Media Ltd. (CSPM): Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetti, V.; Boccacci Mariani, M.; Mannino, P.; Marini, F. Volatile Fraction Analysis by HS-SPME/GC-MS and Chemometric Modeling for Traceability of Apples Cultivated in the Northeast Italy. Food Control 2017, 78, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, A.; Chen, W.; Duan, Y.; Li, K.; Tang, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. The Potential Correlation between Microbial Communities and Flavors in Traditional Fermented Sour Meat. LWT 2021, 149, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Han, B.; Chen, J. Bacterial Community Succession and Metabolite Changes during Sufu Fermentation. LWT 2018, 97, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, T.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M. Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related with Flavor Compounds in Fermented Soy Sauce from Different Sources. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Linforth, R.; Onyeaka, H.; Gkatzionis, K. Effects of Co-Inoculation and Sequential Inoculation of Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on Soy Sauce Fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Location |
|---|---|
| DC-1 | Chongqing |
| DC-2 | Chongqing |
| DC-3 | Chongqing |
| DC-4 | Sichuan |
| DC-5 | Chongqing |
| DC-6 | Sichuan |
| DC-7 | Chongqing |
| Type | Sample | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon | Ace | Goods_Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bacteria | DC-1 | 129.96 | 0.69 | 2.11 | 117.83 | 0.9999 |
| DC-2 | 141.36 | 0.44 | 1.70 | 135.80 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-3 | 256.19 | 0.53 | 1.79 | 234.57 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-4 | 106.60 | 0.54 | 2.06 | 99.57 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-5 | 143.56 | 0.77 | 2.70 | 135.87 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-6 | 200.98 | 0.53 | 1.85 | 189.83 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-7 | 112.40 | 0.59 | 2.56 | 105.93 | 0.9999 | |
| fungi | DC-1 | 120.31 | 2.13 | 0.55 | 121.56 | 0.9999 |
| DC-2 | 113.65 | 3.13 | 0.81 | 114.21 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-5 | 97.78 | 0.97 | 0.26 | 95.72 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-6 | 105.63 | 1.93 | 0.51 | 98.23 | 0.9999 | |
| DC-7 | 92.88 | 1.61 | 0.40 | 94.80 | 0.9999 |
| Compound | R.I. calc. a | R.I. Ref. b | Odor Description c | Threshold d mg/kg | DC-1 | DC-2 | DC-3 | DC-4 | DC-5 | DC-6 | DC-7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | Content (mg/kg) | OAV | |||||
| Ethanol | / | ND | Wine, Pungent Flavor | 0.62 | 11.91 ± 0.02 | 19.21 | 8.03 ± 0.41 | 12.95 | 0.56 ± 0.08 | 0.9 | 9.92 ± 0.84 | 16.01 | 19.42 ± 1.57 | 31.32 | 13.33 ± 1.64 | 21.5 | 6.36 ± 0.91 | 10.25 |
| 3-Methyl-1-butanol | 731 | 734 | Alcohol, Fruity, Banana | 0.0061 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 13.21 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 52.33 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 7.23 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 22.23 | 1.59 ± 0.31 | 259.94 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 7.21 | 0.29 ± 0.1 | 47.43 |
| 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 735 | 736 | Fish Oil, Green, Malt, Onion, Wine | 0.14 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 1.37 | ND | ND | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.38 ± 0.16 | 2.74 | ND | ND | 0.17 ± 0.1 | 1.22 |
| Linalool | 1101 | 1104 | Coriander, Floral, Lavender, Lemon, Rose | 0.0024 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 71.29 | ND | ND | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 102.8 | ND | ND | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 5.84 | 0.68 ± 0.2 | 284.78 | 0.26 ± 0.09 | 109.09 |
| Phenylethyl Alcohol | 1114 | 1114 | Fruit, Honey, Lilac, Rose, Wine | 0.012 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 6.05 | 0.72 ± 0.16 | 59.91 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 5.38 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 10.83 | 1.15 ± 0.16 | 95.9 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 7.12 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 12.1 |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 982 | 986 | Mushroom-like | 0.001 | ND | ND | 1.13 ± 0.08 | 1129.17 | ND - | ND | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 309.04 | 0.85 ± 0.11 | 852.71 | ND | ND | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 270.4 |
| Guaiacol | 1086 | 1096 | Smoky, Burning | 0.0095 | ND | ND | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 9.62 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 16.07 | 0.2 ± 0.11 | 20.64 | 0.18 ± 0.08 | 18.6 | ND | ND | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 8.08 |
| Isobutyraldehyde | / | 552 | Burnt, Caramel, Cocoa, Green, Malt | 0.001 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 178.75 | ND | ND | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 237.35 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 344.32 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 105.22 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 159.63 | 0.18 ± 0.07 | 183.12 |
| Acetaldehyde | / | / | Floral, Green Apple | 0.0027 | ND | ND | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 81 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | 75.08 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 78.69 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 97.15 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 82.45 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 95.87 |
| Isovaleraldehyde | / | 649 | Fruity, Chocolate | 0.002 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 135 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 160 | 0.68 ± 0.12 | 340 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 320 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 105 | 0.35 ± 0.07 | 175 | 0.78 ± 0.22 | 390 |
| 2-Methylbutyraldehyde | / | 659 | Fruity, Nuts, Coffee, Caramel | 0.001 | 0.58 ± 0.02 | 582.98 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 217.08 | 1.04 ± 0.13 | 1044.82 | 1.38 ± 0.42 | 1376.81 | 0.27 ± 0.06 | 270.24 | 0.45 ± 0.09 | 446.4 | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 553.57 |
| Benzaldehyde | 959 | 961 | Almond, Fruity | 0.085 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 5.09 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 2.88 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 4.22 | 0.5 ± 0.16 | 5.9 | 1.32 ± 0.27 | 15.51 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 4.34 | 0.49 ± 0.12 | 5.79 |
| Phenylacetaldehyde | 1042 | 1043 | Rose-like, Sweet | 0.00072 | 0.7 ± 0 | 968.47 | 0.73 ± 0.02 | 1007.01 | 1.06 ± 0.08 | 1465.66 | 1 ± 0.28 | 1383.37 | 0.69 ± 0.25 | 965.12 | 0.7 ± 0.14 | 975.01 | 1.59 ± 0.23 | 2209.71 |
| Isobutyric acid | 768 | 785 | Burnt, Butter, Cheese | 0.0054 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 24.75 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 28.57 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 34.35 | 0.16 ± 0.07 | 29.25 | ND | ND | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 3.64 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | 17.97 |
| Isovaleric acid | 863 | 867 | Cheese, Pungent | 0.0018 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | 258.02 | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 312.18 | 0.9 ± 0.13 | 500.67 | 1.97 ± 0.13 | 1095.58 | 1.33 ± 0.17 | 736.69 | 1.17 ± 0.17 | 648.63 | 1.25 ± 0.32 | 692.5 |
| 2-Methyl butyric acid | 871 | 873 | Butter, Cheese, Fermented, Sour | 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 12.5 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 12 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 9.73 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 17.11 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 6.29 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.62 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 9.78 |
| Ethyl Hexanoate | 996 | 998 | Brandy, Fruit Gum, Pineapple | 0.003 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 15.46 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 30.78 | ND | ND | 1.24 ± 0.22 | 413.85 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 13.51 |
| Ethyl benzoate | 1170 | 1171 | Chamomile, Celery, Fat, Flowers, Fruit | 0.0006 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 746.04 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 304.68 | ND | ND | 0.75 ± 0.08 | 1249.65 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 515.51 | 0.81 ± 0.15 | 1349.16 | 0.38 ± 0.08 | 640.72 |
| Ethyl phenylacetate | 1241 | 1244 | Floral, Fruit, Honey, Rose | 0.0033 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 160.45 | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 249.66 | ND | ND | 0.67 ± 0.05 | 202.65 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 109.25 | 1.12 ± 0.23 | 339.3 | 0.58 ± 0.07 | 176.61 |
| Diethyl Phthalate | 1587 | 1585 | NF | 0.33 | 3.61 ± 0.03 | 10.95 | 1.33 ± 0.24 | 4.04 | 1.24 ± 0.08 | 3.75 | 1.37 ± 0.11 | 4.16 | 1.49 ± 0.16 | 4.52 | 1.53 ± 0.4 | 4.64 | 0.8 ± 0.46 | 2.42 |
| Ethyl Acetate | / | 612 | Fruity, Grape, Cherry, Aromatic | 0.88 | 11.37 ± 0.02 | 12.92 | 5.47 ± 0.56 | 6.21 | 7.31 ± 0.18 | 8.31 | 15.8 ± 0.86 | 17.95 | 15.48 ± 0.97 | 17.59 | 11.89 ± 1.72 | 13.51 | 10.84 ± 1.2 | 12.32 |
| Ethyl isobutyrate | 750 | 755 | Fruity, Floral | 0.00011 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 663.92 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 2774.29 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 727.27 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 2405.92 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 1048.14 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 323.09 | 0.12 ± 0.08 | 1097.68 |
| Ethyl isovalerate | 849 | 847 | Apple, Fruit, Pineapple, Sour | 0.000069 | 0.04 ± 0 | 610.54 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 501.77 | ND | ND | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1794.81 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 701.89 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 648.76 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | 1498.87 |
| Isoamyl acetate | 873 | 876 | Fruity, Floral | 0.067 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 3.34 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.86 | ND | ND | 0.92 ± 0.16 | 13.76 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 3.79 |
| 2-Methylbutyl acetate | 875 | 877 | Apple, Banana, Pear | 0.14 | 0.04 ± 0 | 0.28 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.45 | ND | ND | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 1.57 | ND | ND | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 1.05 |
| 2-Pentylfuran | 988 | 993 | Beans, Fruit | 0.019 | ND | ND | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 4.08 | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 21.09 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 10.02 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 9.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, D.; Kang, J.; Li, Q.; Deng, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; Ming, J.; Brennan, M.; Brennan, C.; You, L. Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related to Flavor Compounds in Douchi from the Sichuan–Chongqing Region. Foods 2025, 14, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050810
Tu D, Kang J, Li Q, Deng M, Liu M, Liu W, Ming J, Brennan M, Brennan C, You L. Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related to Flavor Compounds in Douchi from the Sichuan–Chongqing Region. Foods. 2025; 14(5):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050810
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Dawei, Junhan Kang, Qingqing Li, Meilin Deng, Meiyan Liu, Wenjun Liu, Jian Ming, Margaret Brennan, Charles Brennan, and Linfeng You. 2025. "Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related to Flavor Compounds in Douchi from the Sichuan–Chongqing Region" Foods 14, no. 5: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050810
APA StyleTu, D., Kang, J., Li, Q., Deng, M., Liu, M., Liu, W., Ming, J., Brennan, M., Brennan, C., & You, L. (2025). Exploring the Core Functional Microbiota Related to Flavor Compounds in Douchi from the Sichuan–Chongqing Region. Foods, 14(5), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14050810







