Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Starter Inoculum
2.3. Fermentation Conditions
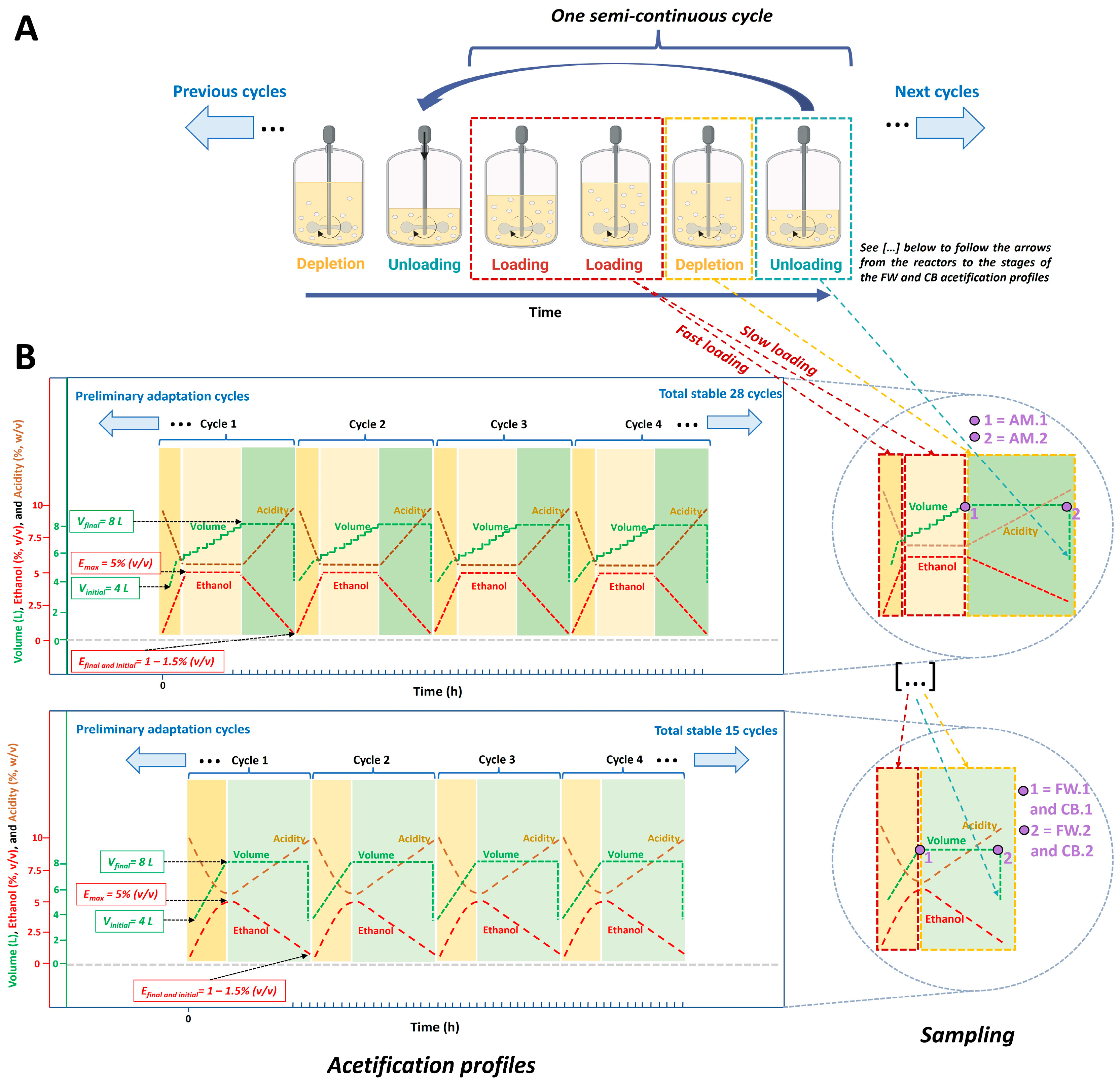
2.4. Sampling
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Metagenomics
2.6.1. Samples Processing
2.6.2. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.7. Metabolomics
2.7.1. Minor Volatile Compounds Analysis
2.7.2. Nitrogenous Compounds Analysis (HPLC)
2.8. Statistical Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Description of System Variables
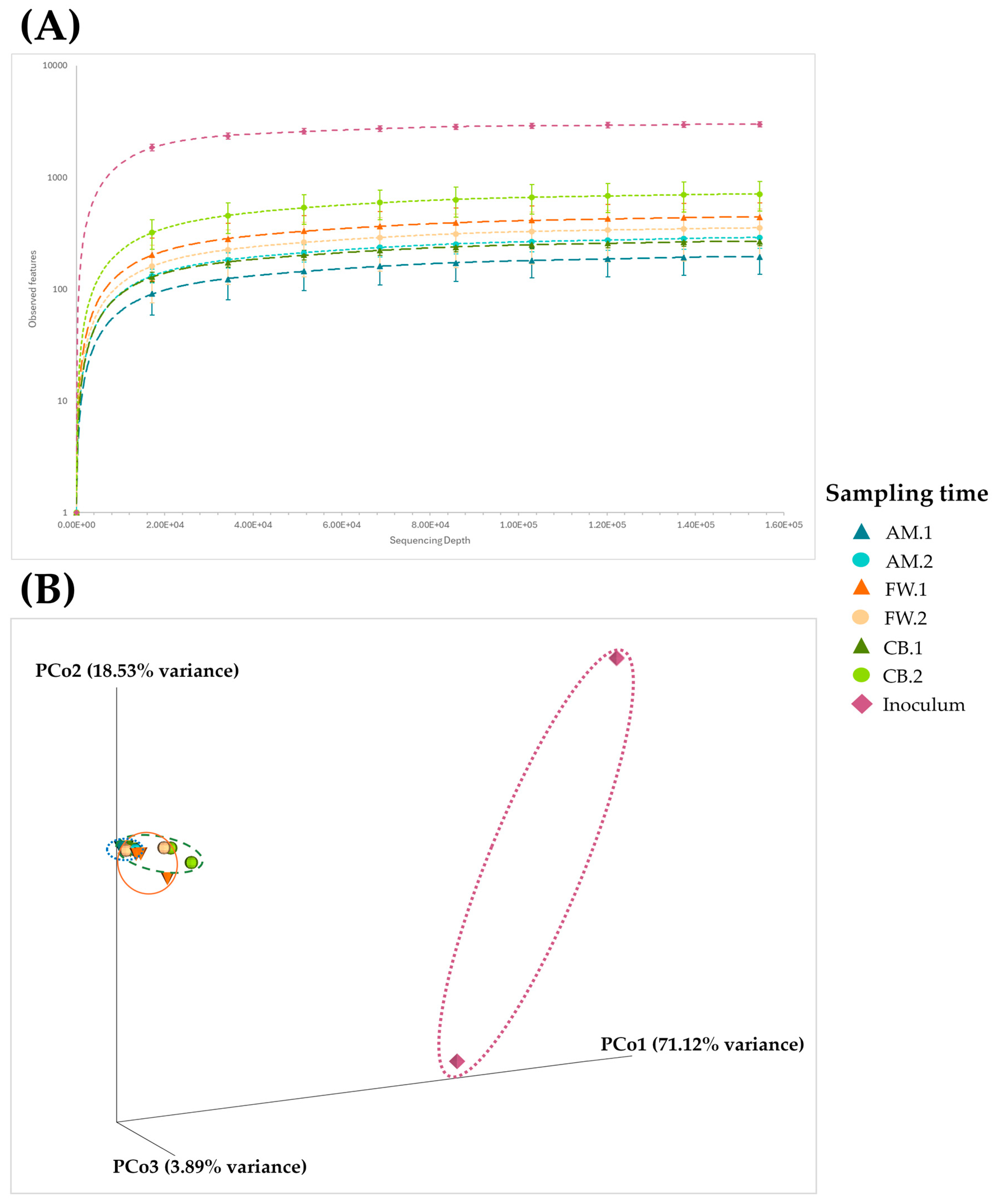
3.2. Microbial Diversity Throughout Acetification Profiles
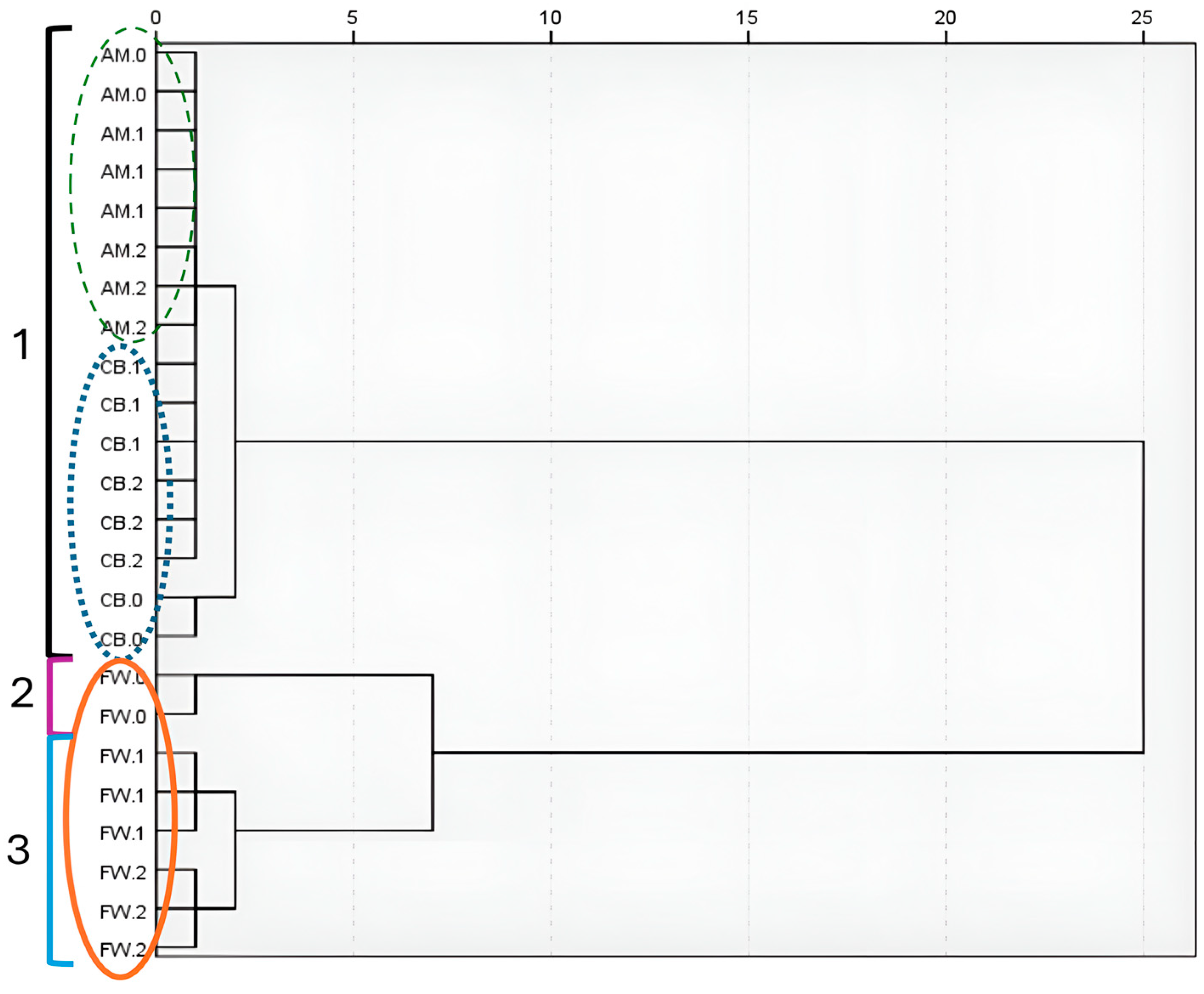
3.3. Microbial Dynamics Throughout Acetification Profiles
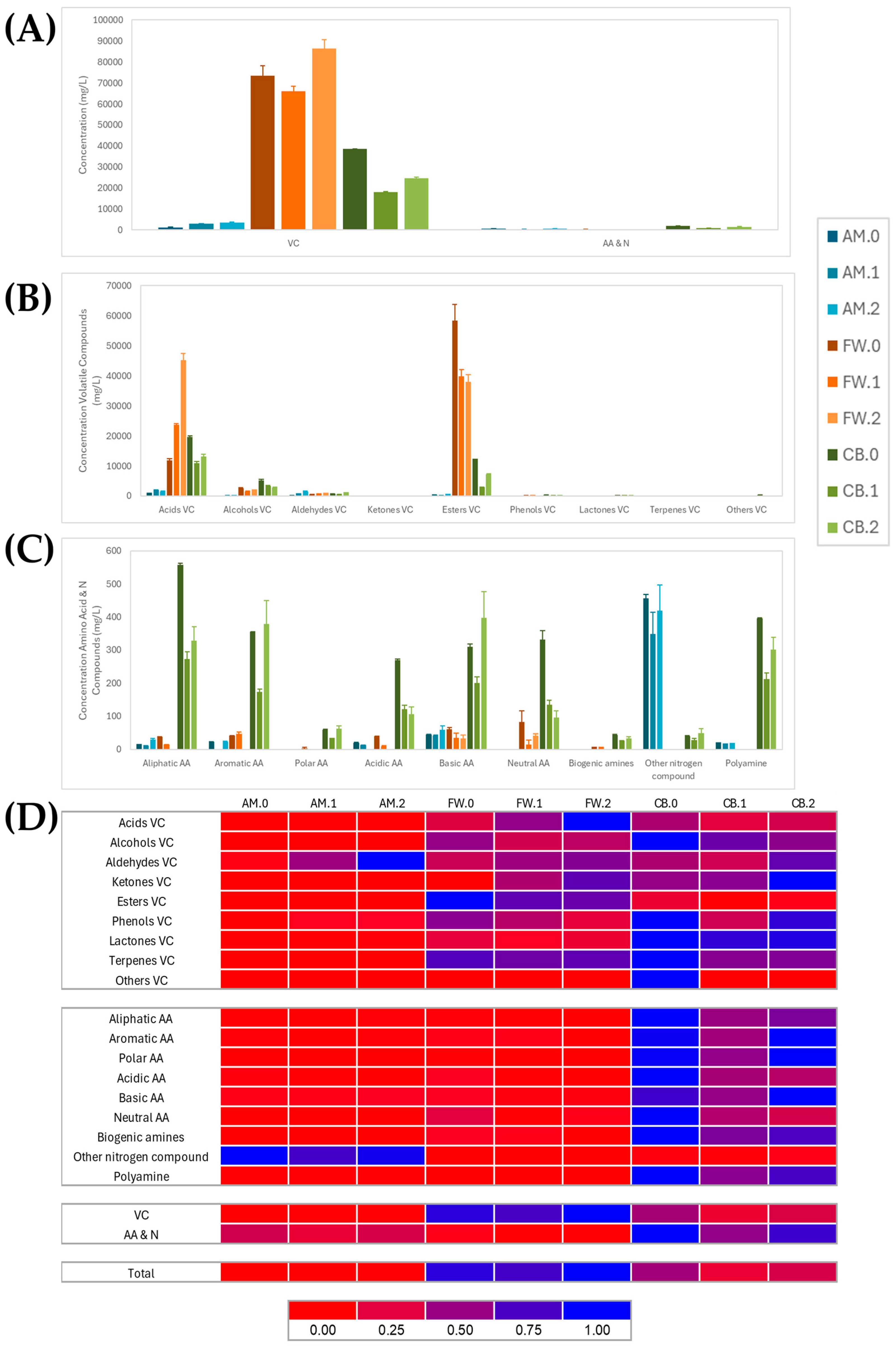
3.4. Comparison of Metabolite Profiling in Vinegar Making
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Microbiota and Metabolites in Vinegar Making
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luzón-Quintana, L.M.; Castro, R.; Durán-Guerrero, E. Biotechnological Processes in Fruit Vinegar Production. Foods 2021, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; García-García, I.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; Mauricio, J.C. Latest Trends in Industrial Vinegar Production and the Role of Acetic Acid Bacteria: Classification, Metabolism, and Applications—A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.W.; Lazim, A.M.; Fazry, S.; Zaki, U.K.H.H.; Lim, S.J. Varieties, Production, Composition and Health Benefits of Vinegars: A Review. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, M.; Verzelloni, E.; Canonico, M. Aerobic Submerged Fermentation by Acetic Acid Bacteria for Vinegar Production: Process and Biotechnological Aspects. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, H. Classification of Acetic Acid Bacteria and Their Acid Resistant Mechanism. AMB Expr. 2021, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, W.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Dynamics of Microbial Communities, Flavor, and Physicochemical Properties during Ziziphus Jujube Vinegar Fermentation: Correlation between Microorganisms and Metabolites. Foods 2022, 11, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, K.; Li, J.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Liu, A. Microbial Characterization of Sichuan Baoning Vinegar: Lactic Acid Bacteria, Acetic Acid Bacteria and Yeasts. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Vázquez, C.; Román-Camacho, J.J.; Consuegra-Rivera, R.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-García, I.; García-Martínez, T.; Mauricio, J.C. Exploring Microbial Diversity and Functionality in Verdejo Wine Vinegar Fermentation through LC-MS/MS Analysis. LWT 2024, 213, 117054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Li, Y.; Xing, J.; Chao, J.; Qin, X.; Li, Z. Comparison of Two Types of Vinegar with Different Aging Times by NMR-based Metabolomic Approach. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazim, A.M.; Lim, S.J.; Ho, C.W.; Fazry, S. Types of Vinegars. In Advances in Vinegar Production; Bekatorou, A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 19–28. ISBN 978-1-351-20847-5. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; García-García, I.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; Ehrenreich, A.; Liebl, W.; García-Martínez, T.; Mauricio, J.C. Combining Omics Tools for the Characterization of the Microbiota of Diverse Vinegars Obtained by Submerged Culture: 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing and MALDI-TOF MS. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, A.; Torija, M.J.; García-Parrilla, M.D.C.; Troncoso, A.M. Acetic Acid Bacteria and the Production and Quality of Wine Vinegar. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 394671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trček, J.; Mahnič, A.; Rupnik, M. Diversity of the Microbiota Involved in Wine and Organic Apple Cider Submerged Vinegar Production as Revealed by DHPLC Analysis and Next-Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 223, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Hornero, J.E.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-García, I. Modelling Acetification with Artificial Neural Networks and Comparison with Alternative Procedures. Processes 2020, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Cáliz, C.M.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; Jiménez-Hornero, J.E.; García-García, I. Optimization of the Acetification Stage in the Production of Wine Vinegar by Use of Two Serial Bioreactors. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gu, C.; Guo, X.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Qiu, X.; Chai, J.; Liu, F.; Feng, Z. Dynamic Changes of Microbiota and Metabolite of Traditional Hainan Dregs Vinegar during Fermentation Based on Metagenomics and Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, X. Dynamic Microbial Succession of Shanxi Aged Vinegar and Its Correlation with Flavor Metabolites during Different Stages of Acetic Acid Fermentation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, K.; Román-Camacho, J.-J.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Identification of Aroma Active Compounds in Shanxi Aged Vinegar and Tracing the Source in the Entire Production Process. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Su, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Microbial Succession and Its Effect on Key Aroma Components during Light-Aroma-Type Xiaoqu Baijiu Brewing Process. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhao, L. Microbial Succession and Its Correlation with the Dynamics of Volatile Compounds Involved in Fermented Minced Peppers. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1041608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, B.; Zeng, H. Metagenomic and Flavoromic Profiling Reveals the Correlation between the Microorganisms and Volatile Flavor Compounds in Monascus-Fermented Cheese. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, A.; Lucini, L.; Torchio, F.; Dordoni, R.; De Faveri, D.M.; Lambri, M. Metabolite Profiling and Volatiles of Pineapple Wine and Vinegar Obtained from Pineapple Waste. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I. Recent Advances in Applying Omic Technologies for Studying Acetic Acid Bacteria in Industrial Vinegar Production: A Comprehensive Review. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2300566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.-H.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yu, Y.-J.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Metagenomics Reveals Flavour Metabolic Network of Cereal Vinegar Microbiota. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinu, F.; De Carvalho-Silva, S.; Trovatti Uetanabaro, A.; Villas-Boas, S. Vinegar Metabolomics: An Explorative Study of Commercial Balsamic Vinegars Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, R.; García-Martínez, T.; Puig-Pujol, A.; Mauricio, J.C.; Moreno, J. Changes in Sparkling Wine Aroma during the Second Fermentation under CO2 Pressure in Sealed Bottle. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, H.; Guo, Y.; Jia, L.; Jing, X.; Wu, J. Subzero-Temperature Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction for the Stereoselective Determination of Chiral Triadimefon and Its Metabolite in Water, Fruit Juice, Vinegar, and Fermented Liquor by HPLC. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 5492–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Bang, E.; Na, Y.-C. Chiral Separation of Intact Amino Acids by Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry Employing a Partial Filling Technique with a Crown Ether Carboxylic Acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1586, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llaguno, C. Definición y tipos de vinagre. In El Vinagre de Vino; Llaguno, C., Polo, M.C., Eds.; Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas: Madrid, Spain, 1991; pp. 133–145. ISBN 978-84-00-07205-6. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I. Unraveling the Role of Acetic Acid Bacteria Comparing Two Acetification Profiles From Natural Raw Materials: A Quantitative Approach in Komagataeibacter europaeus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Ruano, S.; Jiménez-Ot, C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; Cantero-Moreno, D.; Barja, F.; García-García, I. Rapid Method for Total, Viable and Non-Viable Acetic Acid Bacteria Determination during Acetification Process. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved Alignments and New Tools for rRNA Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global Patterns of 16S rRNA Diversity at a Depth of Millions of Sequences per Sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Alonso, S.; Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I.; García-Romero, E. Simultaneous HPLC Analysis of Biogenic Amines, Amino Acids, and Ammonium Ion as Aminoenone Derivatives in Wine and Beer Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Virk, M.S.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F. Effects of Various Rice-Based Raw Materials on Enhancement of Volatile Aromatic Compounds in Monascus Vinegar. Molecules 2021, 26, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Segura-Borrego, M.P.; Morales, M.L.; Callejón, R.M. Characterization of the Aroma Profile and Key Odorants of the Spanish PDO Wine Vinegars. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés-Barrao, C.; Saad, M.M.; Cabello Ferrete, E.; Bravo, D.; Chappuis, M.-L.; Ortega Pérez, R.; Junier, P.; Perret, X.; Barja, F. Metaproteomics and Ultrastructure Characterization of Komagataeibacter Spp. Involved in High-Acid Spirit Vinegar Production. Food Microbiol. 2016, 55, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, T.; Zhong, X.-Z.; Chai, L.-J.; Lu, Z.-M.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Komagataeibacter Europaeus Improves Community Stability and Function in Solid-State Cereal Vinegar Fermentation Ecosystem: Non-Abundant Species Plays Important Role. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchez, A.; De Vuyst, L. Acetic Acid Bacteria in Sour Beer Production: Friend or Foe? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 957167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, K.; Dai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; et al. Metagenomics Profiling of the Microbial Community and Functional Differences in Solid-State Fermentation Vinegar Starter (Seed Pei) from Different Chinese Regions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1389737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, L.; Castro, R.; Barroso, C.G.; Durán-Guerrero, E. Characterization by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry of the Most Odour-Active Compounds in Italian Balsamic Vinegars with Geographical Indication. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Du, B.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, H.; Sun, B.; Hao, J.; Li, X. Microbial Community Dynamics and Spatial Distribution of Flavor Compound Metabolism during Solid-State Fermentation of Baijiu Enhanced by Wickerhamomyces Anomalus. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, P.; Lei, Q.; Li, B.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Lei, H.; Xie, N. Metabolic Adaptability Shifts of Cell Membrane Fatty Acids of Komagataeibacter Hansenii HDM1-3 Improve Acid Stress Resistance and Survival in Acidic Environments. JIMB 2019, 46, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankuan, X.; Cuimei, Z.; Bingqian, F.; Yu, Z.; Menglei, X.; Linna, T.; Jia, S.; Xinyi, Z.; Min, W. Metabolic Network of Ammonium in Cereal Vinegar Solid-State Fermentation and Its Response to Acid Stress. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Lu, Z.-M.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Exploring Flavour-Producing Core Microbiota in Multispecies Solid-State Fermentation of Traditional Chinese Vinegar. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Liang, X.; Peng, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, T.; Gu, J.-D.; Hu, Z. Ecological Distribution and Function of Comammox Nitrospira in the Environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, H.-G.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Oh, H.-M. Kaistia Defluvii Sp. Nov., Isolated from River Sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2878–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jeon, C.O. Kaistia Algarum Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Freshwater Green Alga Paulinella Chromatophora. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Jiménez Colmenero, F.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Muñoz, R. Biogenic Amine Production in Spanish Dry-Cured “Chorizo” Sausage Treated with High-Pressure and Kept in Chilled Storage. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnici, F.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; Riponi, C. Discrimination of Some European Vinegars with Protected Denomination of Origin as a Function of Their Amino Acid and Biogenic Amine Content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3762–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokhoijav, E.; Guba, A.; Vadadokhau, U.; Tőzsér, J.; Győri, Z.; Kalló, G.; Csősz, É. Comparative Analysis of Amino Acid and Biogenic Amine Compositions of Fermented Grape Beverages. Metabolites 2023, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J.M.; Ferrer, S.; Pardo, I. Biogenic Amine Production by Lactic Acid Bacteria, Acetic Bacteria and Yeast Isolated from Wine. Food Control 2007, 18, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Gou, L.; Fan, T.; Cai, Y. Enzymatic Properties of Ornithine Decarboxylase from Clostridium Aceticum DSM1496. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2024, 71, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhu, Y. Effects of Plant Extracts on Biogenic Amine Accumulation, Bacterial Abundance and Diversity in Fermented Sausage. CyTA—J. Food 2021, 19, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.M.; Hughes, D.J.; Fu, Q.; Abadie, M.; Hirsch, P.R. Metagenomic Approaches Reveal Differences in Genetic Diversity and Relative Abundance of Nitrifying Bacteria and Archaea in Contrasting Soils. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

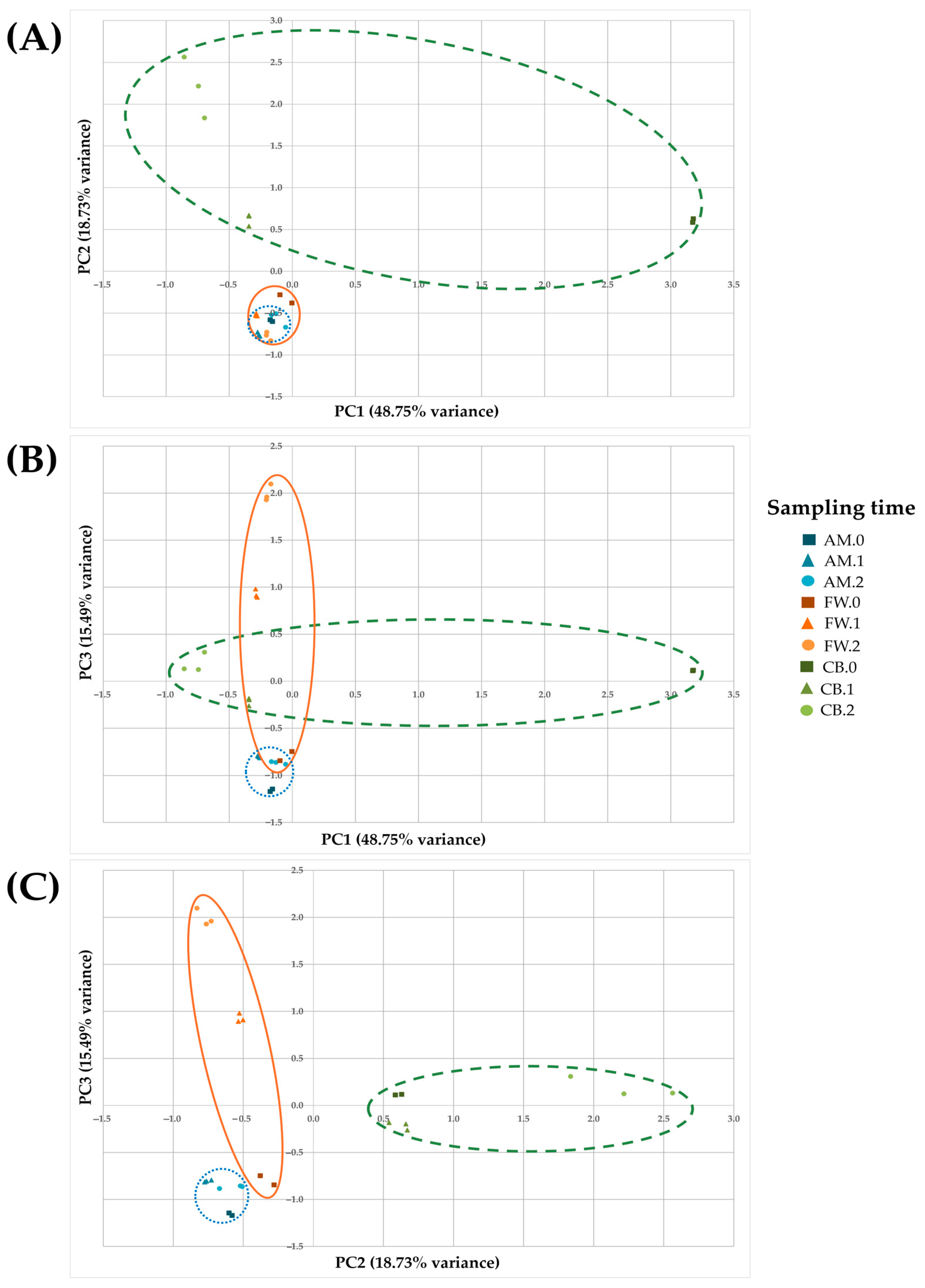
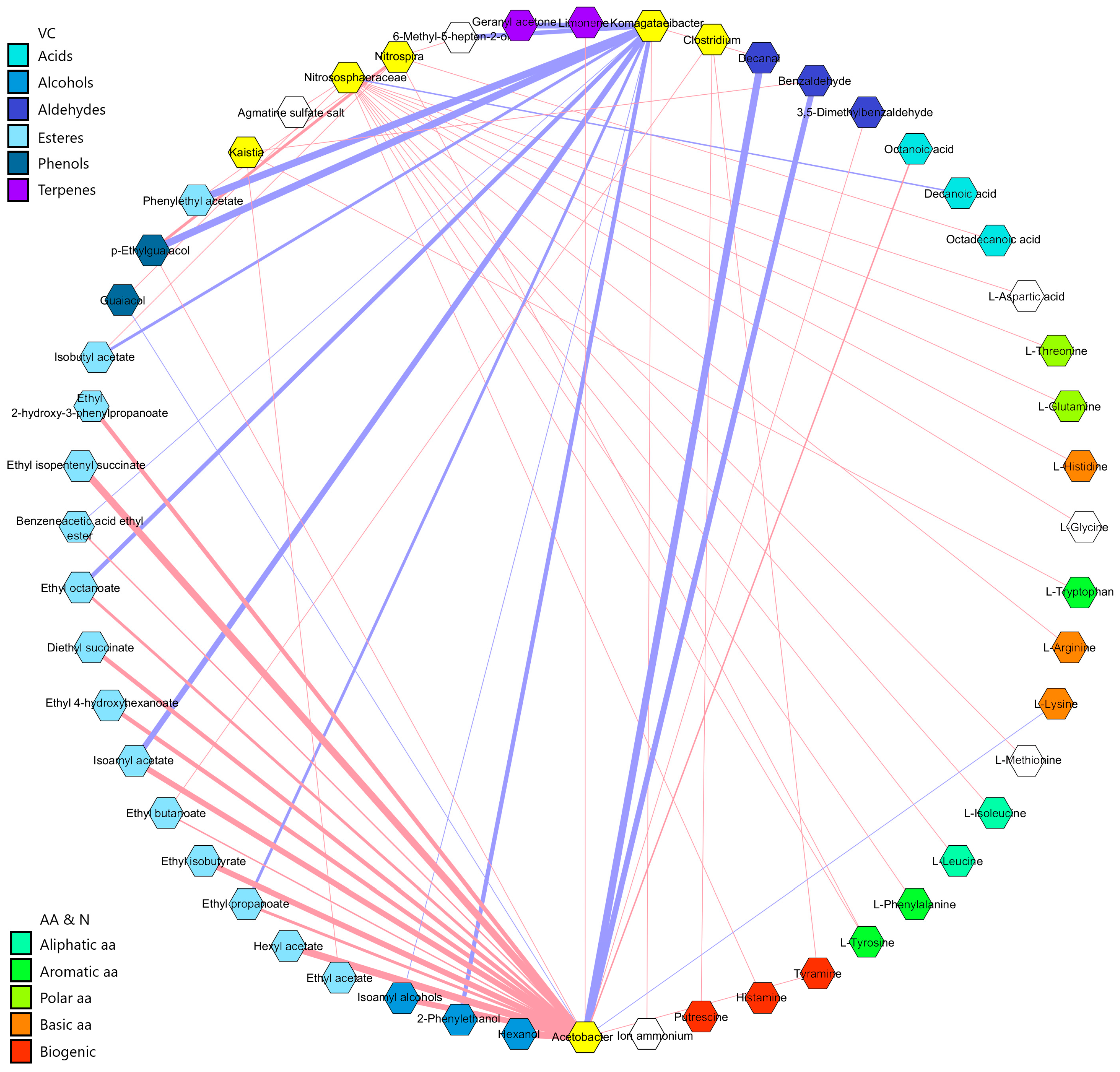
| Variable (Mean ± SD) | AM.0 | AM.1 | AM.2 | CB.0 | CB.1 | CB.2 | FW.0 | FW.1 | FW.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle time (h) | - | 8.8 ± 2.8 | 28.9 ± 2.6 | - | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 24.3 ± 1.1 | - | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 21.4 ± 0.1 |
| Volume (L) | - | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | - | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | - | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 |
| Ethanol (% v/v) | 10.0 ± 0.3 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| Total acidity (% w/v) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 6.8 ± 0.7 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 7.9 ± 0.2 |
| Viable cell (108 cell/mL) | - | 1.69 ± 0.34 | 2.30 ± 0.29 | - | 0.84 ± 0.70 | 1.05 ± 0.70 | - | 1.43 ± 0.33 | 1.47 ± 0.28 |
| AM | CB | FW | |||||||
| Mean acetification rate (rA) [g acetic acid/(L h)] | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | ||||||
| Global acidity production (pA) (g acetic acid/h) | 10.2 ± 1.0 | 11.3 ± 0.5 | 15.2 ± 0.5 | ||||||
| Sample | Observed Features | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculum | 2417 ± 784 | 3.40 ± 1.30 | 0.434 ± 0.154 |
| AM.1 | 198 ± 56 | 0.27 ± 0.10 | 0.042 ± 0.016 |
| AM.2 | 294 ± 52 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.054 ± 0.006 |
| CB.1 | 272 ± 22 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 0.056 ± 0.007 |
| CB.2 | 720 ± 197 | 0.73 ± 0.20 | 0.105 ± 0.029 |
| FW.1 | 450 ± 138 | 0.61 ± 0.19 | 0.104 ± 0.025 |
| FW.2 | 359 ± 158 | 0.50 ± 0.21 | 0.079 ± 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Román-Camacho, J.J.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-García, I.; García-Martínez, T.; Peinado, R.A.; Mauricio, J.C. Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars. Foods 2025, 14, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010056
Román-Camacho JJ, Santos-Dueñas IM, García-García I, García-Martínez T, Peinado RA, Mauricio JC. Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars. Foods. 2025; 14(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomán-Camacho, Juan J., Inés M. Santos-Dueñas, Isidoro García-García, Teresa García-Martínez, Rafael A. Peinado, and Juan C. Mauricio. 2025. "Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars" Foods 14, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010056
APA StyleRomán-Camacho, J. J., Santos-Dueñas, I. M., García-García, I., García-Martínez, T., Peinado, R. A., & Mauricio, J. C. (2025). Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars. Foods, 14(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14010056









