Acidic Electrolyzed Water Maintains the Storage Quality of Postharvest Wampee Fruit by Activating the Disease Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. AEW Preparation
2.2. Wampee Fruit and Postharvest Handling
2.3. Measurement of Fruit Storability
2.4. Appraisal of Pericarp Color Variations
2.5. Evaluation of Pulp Nutrients
2.6. Appraisal of Fruit Disease Index
2.7. Assay of Pericarp Lignin Content
2.8. Assay of Pericarp DREs Activities
2.9. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
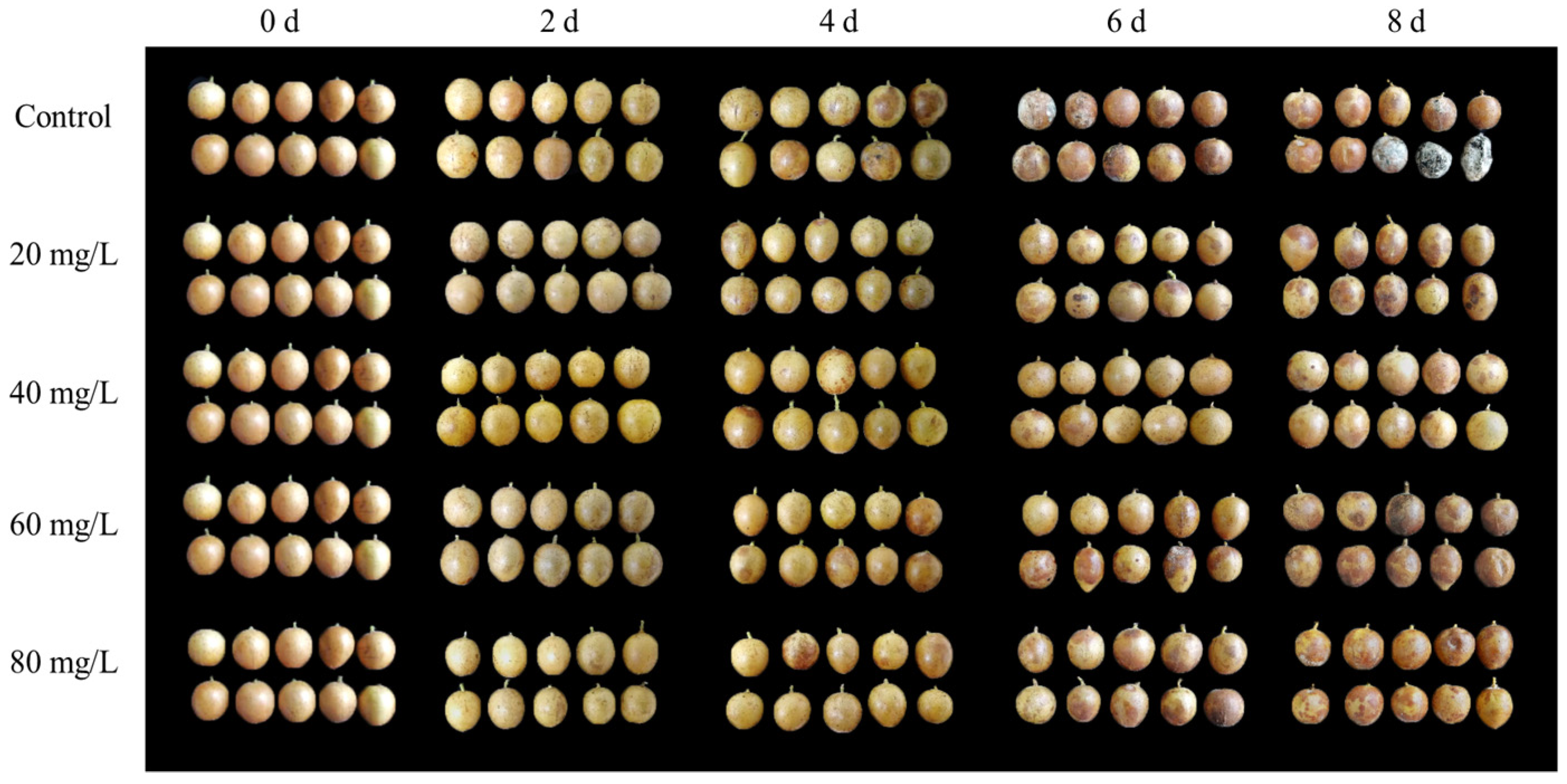
3.1. Changes in Fruit Appearance Quality
3.2. Changes in Fruit Storability
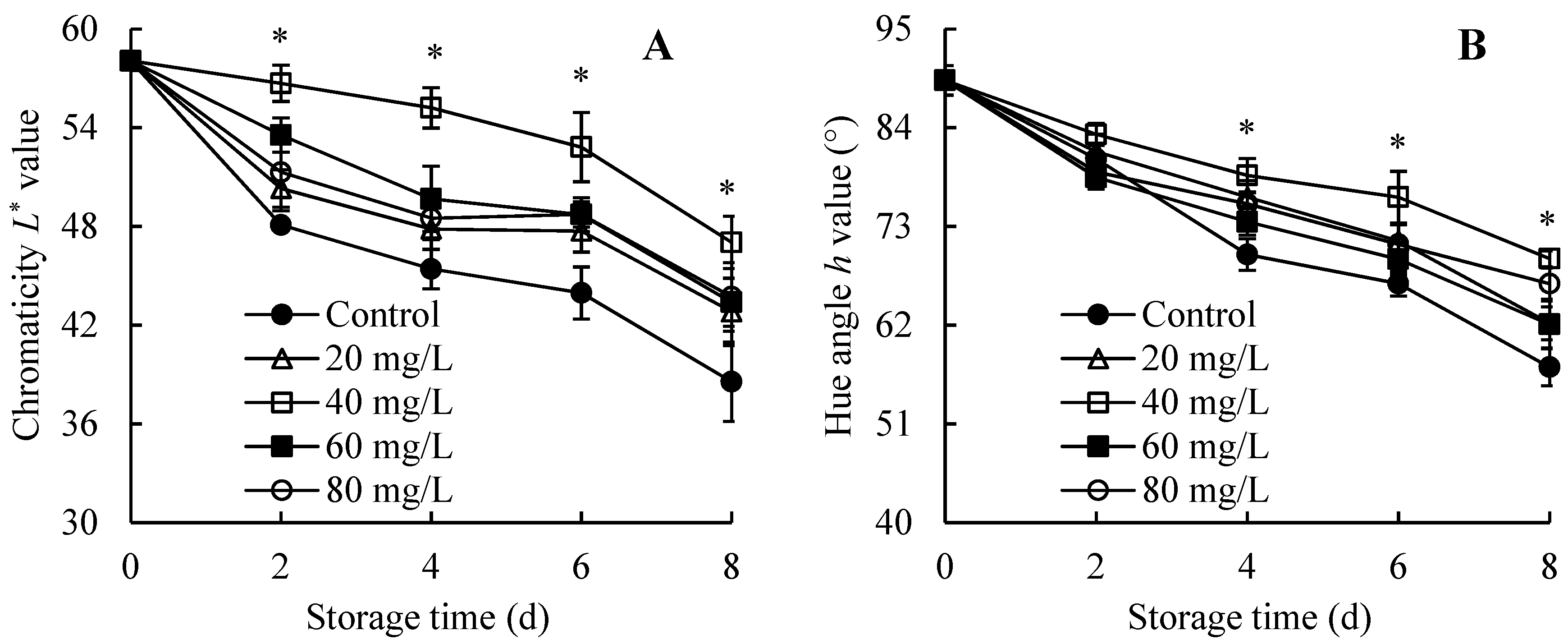
3.3. Changes in Chromaticity L* and Hue Angle h Values
3.4. Changes in Pulp Nutrient Content
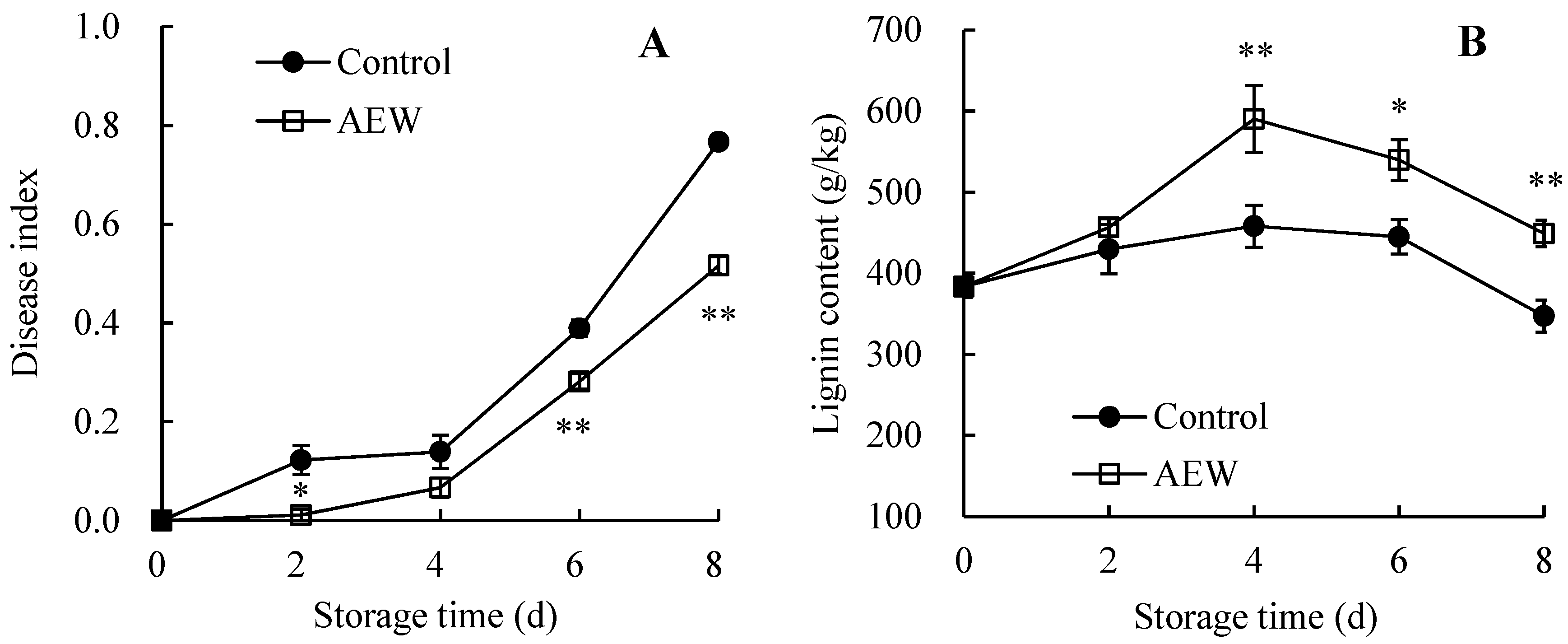
3.5. Changes in the Fruit Disease Index and Pericarp Lignin Content
3.6. Changes in Pericarp PAL, C4H, 4-CL, CAD, and PPO Activities
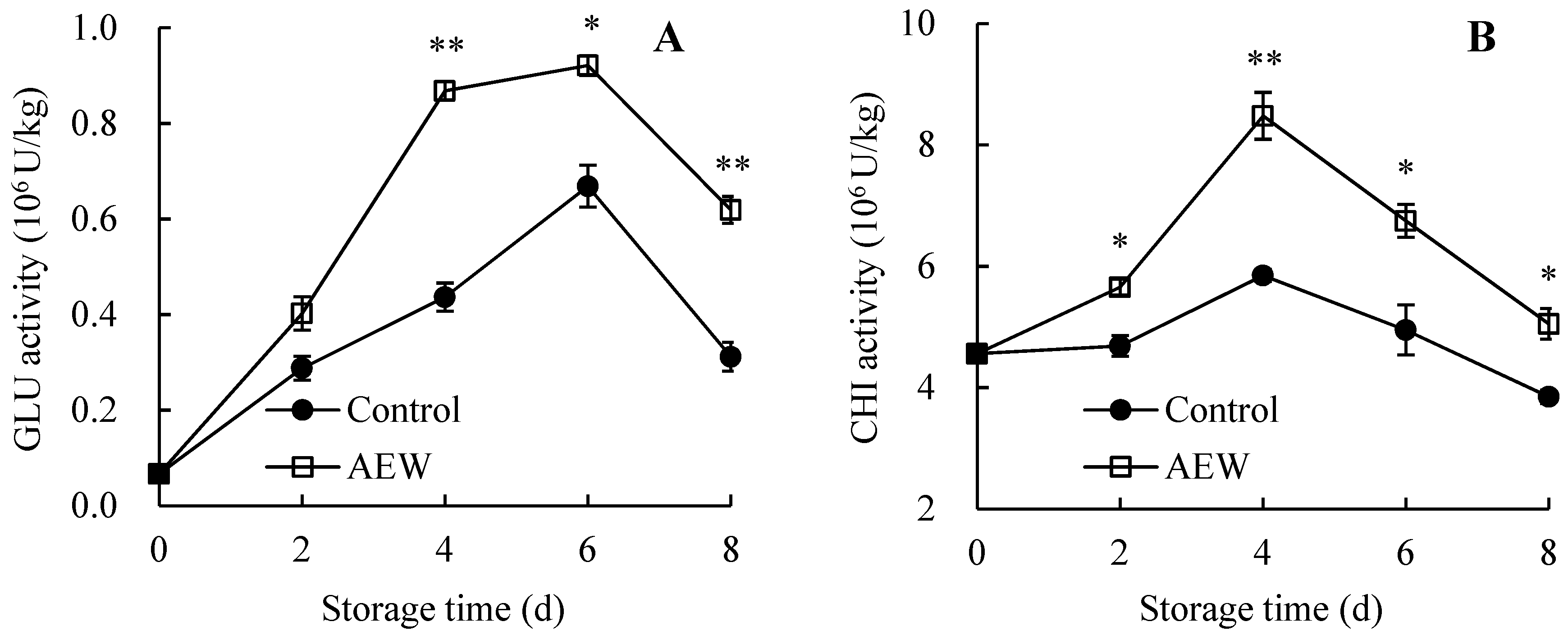
3.7. Changes in Pericarp GLU and CHI Activities
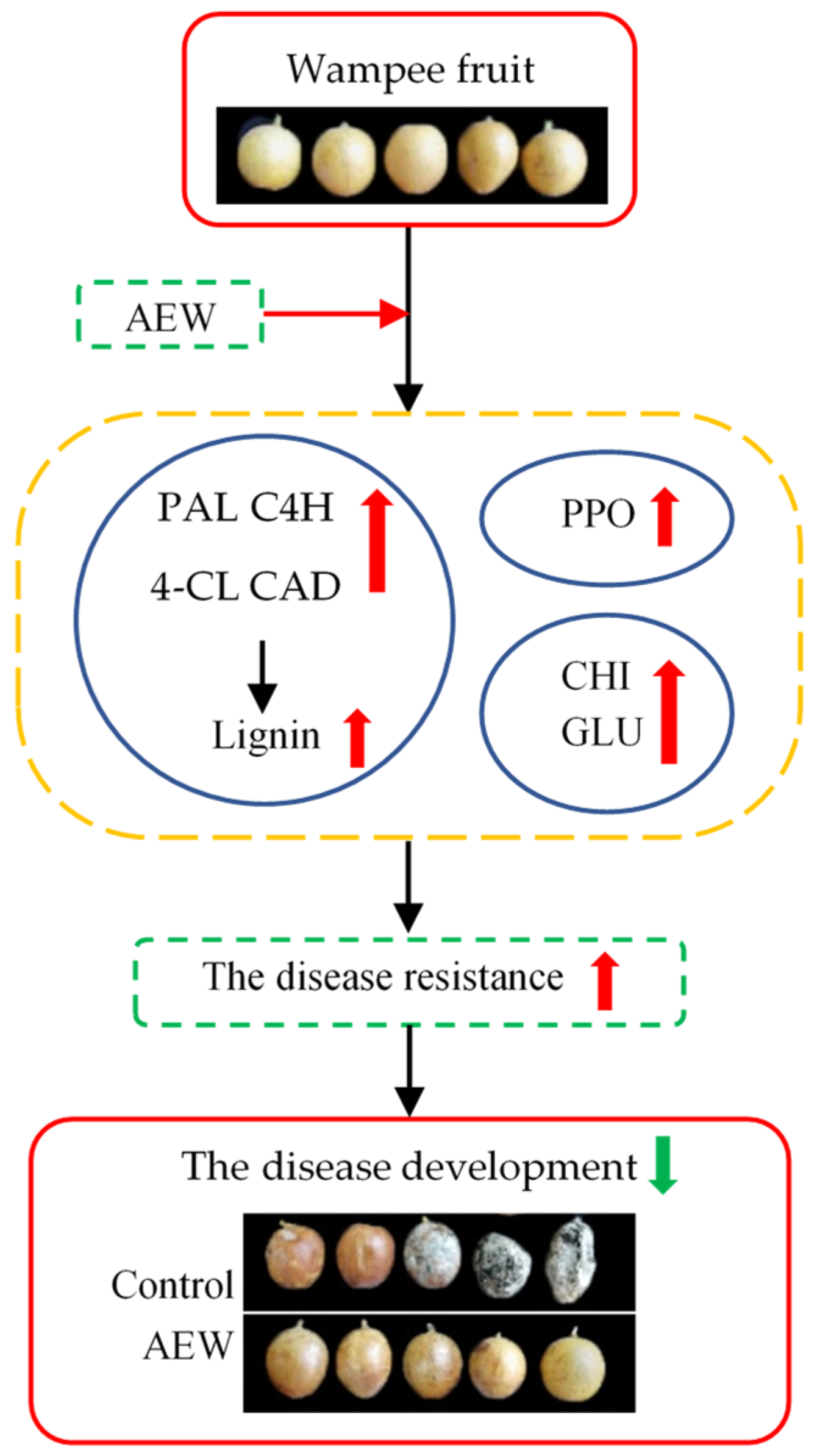
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Y.Z.; Jiang, Z.T.; Zeng, J.K.; Li, W.; Dong, Y. Effect of ethanol fumigation on pericarp browning associated with phenol metabolism, storage quality, and antioxidant systems of wampee fruit during cold storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3380–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Huang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Q.; Lei, H.; Niu, H. Characterization and prebiotic properties of pectin polysaccharide from Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.C.; Ji, J.B.; Zhang, R.H.; Duan, Z.W.; Xie, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, F.C.; Deng, H. Identification and verification of key taste components in wampee using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Bu, Z.B.; Ren, H.Y.; He, Q.; Yu, Y.S.; Xu, Y.J.; Cheng, L.N.; Li, L. Physicochemical, structural, and functional properties of wampee (Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels) fruit peel pectin extracted with different organic acids. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.G.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, R.; Liu, Y.; Huan, C.; Zheng, X.L. Preharvest spray with melatonin improves postharvest disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 193, 112055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.F.; Xue, Y.H.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.M.; Xiao, G.Y.; He, J.Y. Improvement of postharvest anthracnose resistance in mango fruit by nitric oxide and the possible mechanisms involved. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15460–15467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Z.; Fan, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Jiang, Y.J.; Lin, M.S.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, H.T. The effect of ε-poly-l-lysine treatment on molecular, physiological and biochemical indicators related to resistance in longan fruit infected by Phomopsis longanae Chi. Food Chem. 2023, 416, 135784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Lin, H.T.; Hung, Y.C.; Xie, H.L.; Chen, Y.H. Acidic electrolyzed water treatment delayed fruit disease development of harvested longans through inducing the disease resistance and maintaining the ROS metabolism systems. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 171, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F. Reduction of postharvest diseases of loquat fruit by serine protease and possible mechanisms involved. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, X.M.; Deng, B.; Chen, O.; Deng, L.L.; Zeng, K.F. Methionine enhances disease resistance of jujube fruit against postharvest black spot rot by activating lignin biosynthesis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 190, 111935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.Y.; Chen, X.R.; Xu, W.; Fan, S.S.; Wan, T.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.L. Methyl jasmonate induces postharvest disease resistance to decay caused by Alternaria alternata in sweet cherry fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 292, 110624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.R.; Zong, Y.Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhu, Y.T.; Oyom, W.; Bi, Y. Both chitosan and chitooligosaccharide treatments accelerate wound healing of pear fruit by activating phenylpropanoid metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, B.; Tang, H.M.; Zhu, D.Q.; Yao, Q.P.; Han, H.Q.; He, K.Q.; Ding, X.C. Benzothiazole treatment regulates the reactive oxygen species metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway of Rosa roxburghii fruit to delay senescence during low temperature storage. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 753261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.J.; Lin, H.T.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.X.; Shi, J.; Lin, Y.F. A novel chitosan formulation treatment induces disease resistance of harvested litchi fruit to Peronophythora litchii in association with ROS metabolism. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.L.; Wang, H.X.; Shu, C.; Chen, L.Y.; Cao, J.K.; Jiang, W.B. The combination treatment of chlorogenic acid and sodium alginate coating could accelerate the wound healing of pear fruit by promoting the metabolic pathway of phenylpropane. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Z.; Chen, H.B.; Xie, H.L.; Li, M.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, H.T. Acidic electrolyzed water treatment retards softening and retains cell wall polysaccharides in pulp of postharvest fresh longans and its possible mechanism. Food Chem X 2022, 13, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Z.; Jiang, X.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, M.S.; Tang, J.Y.; Lin, Q.; Lin, H.T. Recent trends and applications of electrolyzed oxidizing water in fresh foodstuff preservation and safety control. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, M.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, H.T. Acidic electrolyzed water treatment suppresses Phomopsis longanae Chi-induced the decreased storability and quality properties of fresh longans through modulating energy metabolism. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Xie, H.L.; Tang, J.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, H.T. Effects of acidic electrolyzed water treatment on storability, quality attributes and nutritive properties of longan fruit during storage. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.L.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.S.; He, J.G. Acidic electrolyzed water improves the postharvest quality of jujube fruit by regulating antioxidant activity and cell wall metabolism. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.E.; Khan, I.; Oh, D.H. Electrolyzed water as a novel sanitizer in the food industry: Current trends and future perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.Z.; Li, N.; Lin, H.T.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Ritenour, M.A.; Lin, Y.F. Effects of chitosan treatment on the storability and quality properties of longan fruit during storage. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.B.; Lin, H.T.; Jiang, X.J.; Lin, M.S.; Fan, Z.Q. Amelioration of chilling injury and enhancement of quality maintenance in cold-stored guava fruit by melatonin treatment. Food Chem X 2022, 14, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.J.; Lin, H.T.; Shi, J.; Neethirajan, S.; Lin, Y.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.X. Effects of a novel chitosan formulation treatment on quality attributes and storage behavior of harvested litchi fruit. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.L.; Nie, S.R.; Li, W.H.; Fan, C.; Wang, S.Q.; Wu, F.Z.; Pan, K. Wheat straw increases the defense response and resistance of watermelon monoculture to Fusarium wilt. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.B.; Guan, W.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Shao, Y.L.; Mao, L.C. Methyl jasmonate promotes wound healing by activation of phenylpropanoid metabolism in harvested kiwifruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 175, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Jiang, H.T.; Cao, J.K.; Jiang, W.B. UV-C treatment controls brown rot in postharvest nectarine by regulating ROS metabolism and anthocyanin synthesis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 180, 111613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, L.; Sun, B.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, Y.F.; Yan, X.R. Controlling effect and mechanism of burdock fructooligosaccharide against Alternaria fruit rot in blueberry during postharvest. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 196, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Gao, X.X.; Yue, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.L. Exogenous caffeic acid and epicatechin enhance resistance against Botrytis cinerea through activation of the phenylpropanoid pathway in apples. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Lin, Y.F.; Lin, M.S.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Lin, H.T. Propyl gallate postharvest treatment improves the storability of longans by regulating the metabolisms of respiratory and disease-resistance substances. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 206, 112556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Xi, P.G.; Lin, Z.M.; Huang, J.H.; Lu, S.H.; Jiang, Z.D.; Qiao, F. Efficacy and potential mechanisms of benzothiadiazole inhibition on postharvest litchi downy blight. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liu, G.S.; Gao, Z.Y.; Li, M.; Su, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.K. Inhibition on anthracnose and induction of defense response by nitric oxide in pitaya fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 245, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Jiang, H.Y.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.G.; Guo, H.L.; Meng, D.M. Antimicrobial peptide CB-M exhibits direct antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea and induces disease resistance to gray mold in cherry tomato fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 196, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, S.F.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Y.H. Effect of β-aminobutyric acid on disease resistance against Rhizopus rot in harvested peaches. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripong, K.; Jitareerat, P.; Uthairatanakij, A. UV irradiation induces resistance against fruit rot disease and improves the quality of harvested mangosteen. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 149, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, S.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y. Acidic Electrolyzed Water Maintains the Storage Quality of Postharvest Wampee Fruit by Activating the Disease Resistance. Foods 2024, 13, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101556
Lin Y, Chen H, Dong S, Chen Y, Jiang X, Chen Y. Acidic Electrolyzed Water Maintains the Storage Quality of Postharvest Wampee Fruit by Activating the Disease Resistance. Foods. 2024; 13(10):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101556
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yuzhao, Hongbin Chen, Sisi Dong, Yazhen Chen, Xuanjing Jiang, and Yihui Chen. 2024. "Acidic Electrolyzed Water Maintains the Storage Quality of Postharvest Wampee Fruit by Activating the Disease Resistance" Foods 13, no. 10: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101556
APA StyleLin, Y., Chen, H., Dong, S., Chen, Y., Jiang, X., & Chen, Y. (2024). Acidic Electrolyzed Water Maintains the Storage Quality of Postharvest Wampee Fruit by Activating the Disease Resistance. Foods, 13(10), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13101556





