The Effects of Thermal Pasteurisation, Freeze-Drying, and Gamma-Irradiation on the Antibacterial Properties of Donor Human Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Donor Human Milk Handling
2.3. Freeze-Drying
2.4. Holder Pasteurisation
2.5. Gamma-Irradiation
2.6. Reconstitution of Freeze-Dried Donor Human Milk
2.7. Bacterial Stock Preparation
2.8. Gamma-Irradiation of Freeze-Dried Milk for Pathogen Control
2.9. Bacterial Proliferation Assays
2.10. Preparation of Bacteria for Growth Curve Analysis and Flow Cytometry
2.11. Flow Cytometry Assay Preparation
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
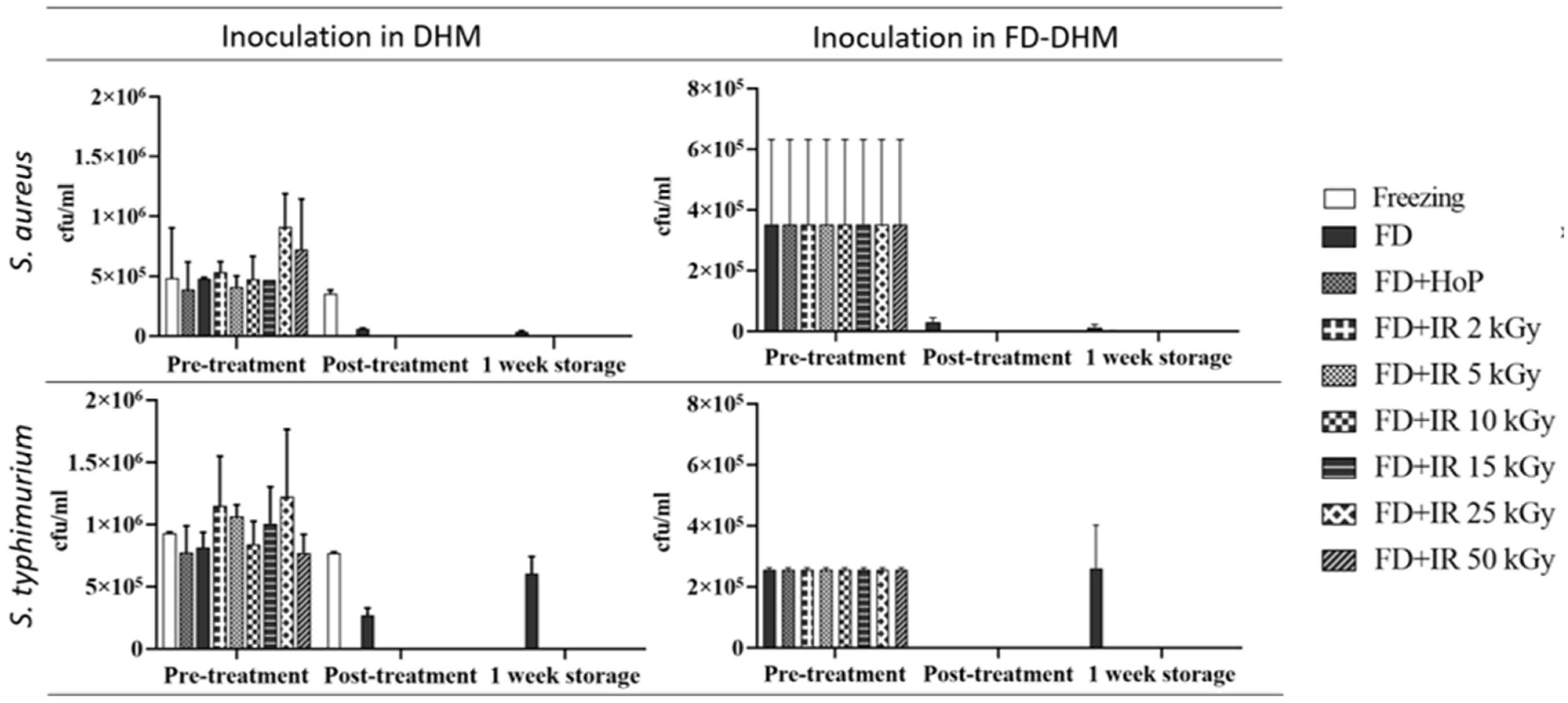
3.1. Efficacy of Pathogen Control Methods Prior to Freeze-Drying of Donor Human Milk
3.2. Efficacy of Gamma-Irradiation in Reducing Bacterial Inoculants Added to Freeze-Dried Donor Human Milk Powder
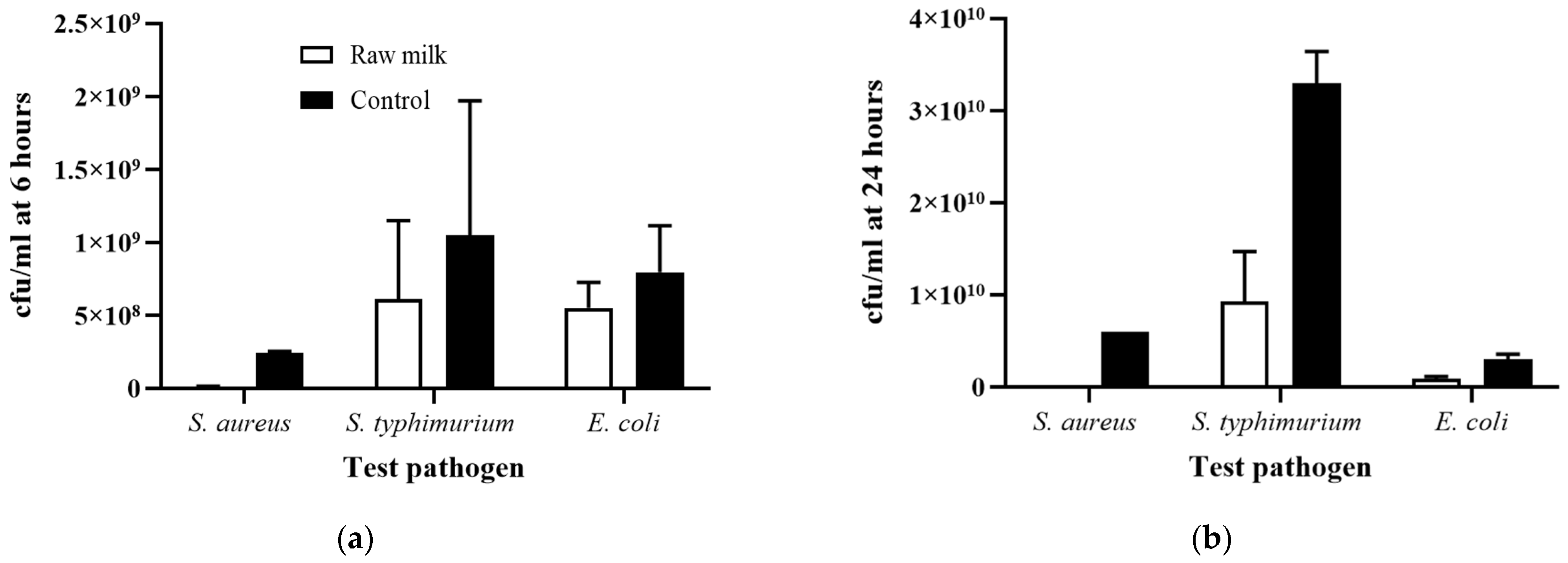
3.3. Growth Inhibition of Pathogens by Raw Donor Human Milk
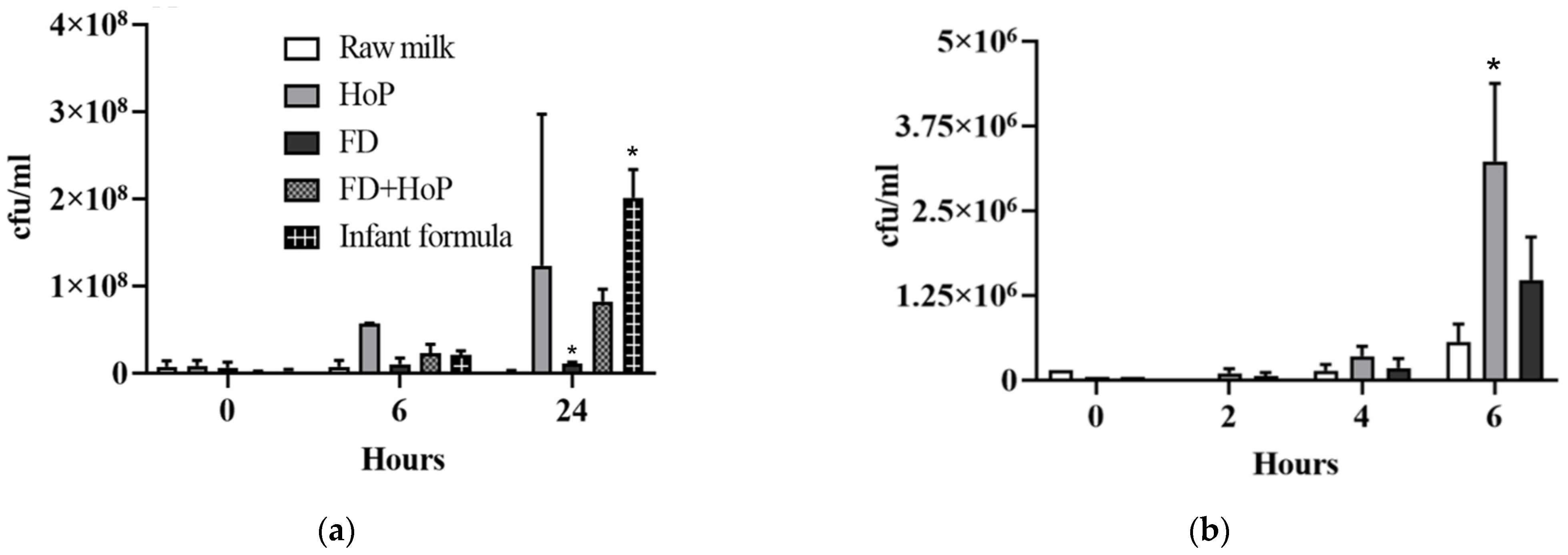
3.4. Freeze-Drying Does Affect Antimicrobial Activity in DHM
3.5. Growth Inhibition of Gram-Negative Bacteria
3.6. Flow Cytometry Results
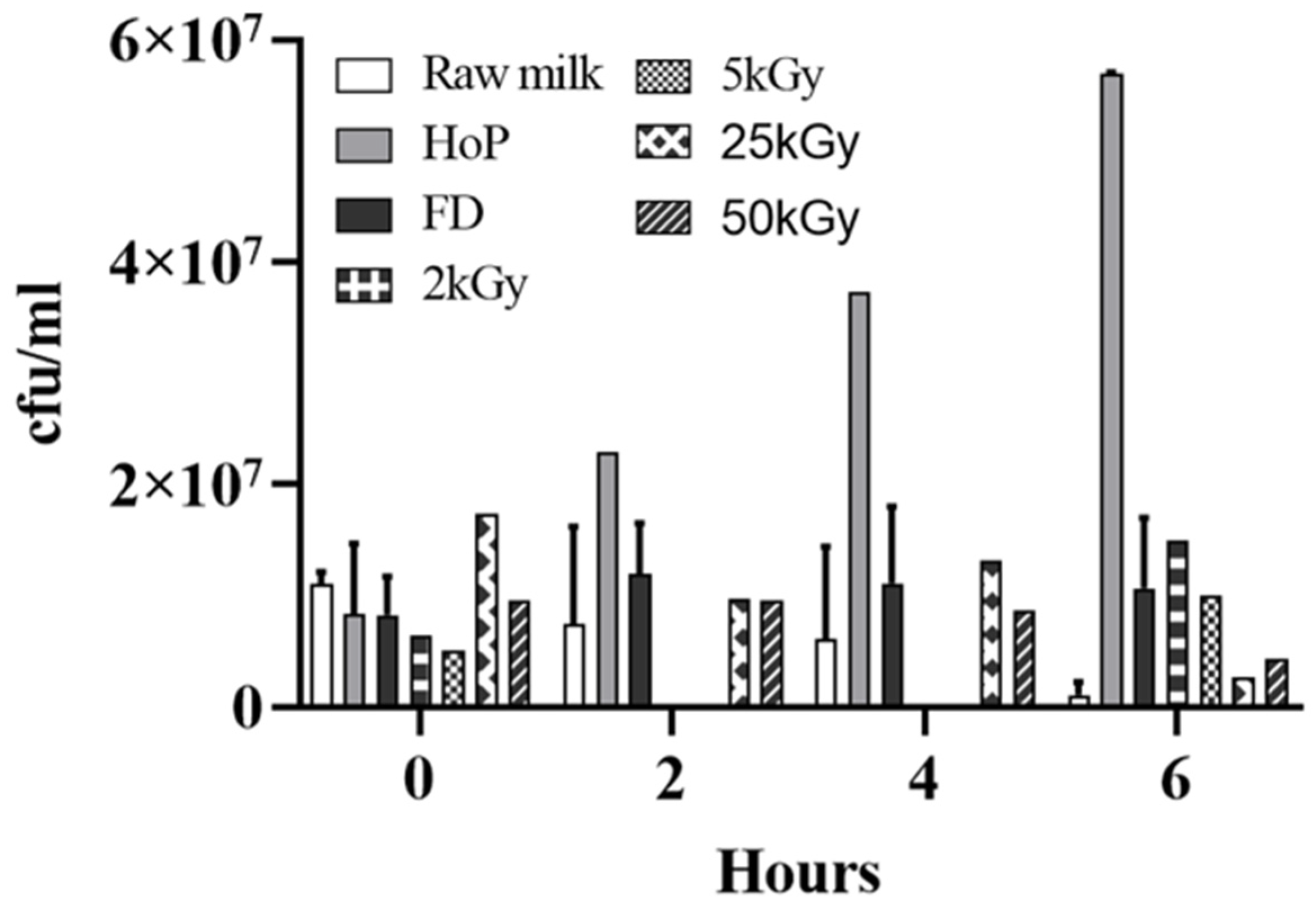
3.7. Gamma-Irradiation Increases the Antimicrobial Activity of FD-DHM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fugate, K.; Hernandez, I.; Ashmeade, T.; Miladinovic, B.; Spatz, D.L. Improving human milk and breastfeeding practices in the NICU. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2015, 44, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Embleton, N.D.; McGuire, W. Formula versus donor breast milk for feeding preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.; Schanler, R.J.; Kim, J.H.; Patel, A.L.; Trawöger, R.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Chan, G.M.; Blanco, C.L.; Abrams, S.; Cotten, C.M. An exclusively human milk-based diet is associated with a lower rate of necrotizing enterocolitis than a diet of human milk and bovine milk-based products. J. Pediatrics 2010, 156, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel-Ballard, K. Strengthening systems to ensure all infants receive human milk: Integrating human milk banking into newborn care and nutrition programming. Breastfeed. Med. 2018, 13, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NICE. Donor Breast Milk Banks: The Operation of Donor Milk Bank Services; National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Updegrove, K.H. Donor human milk banking: Growth, challenges, and the role of HMBANA. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czank, C.; Prime, D.K.; Hartmann, B.; Simmer, K.; Hartmann, P.E. Retention of the immunological proteins of pasteurized human milk in relation to pasteurizer design and practice. J. Hum. Lact. 2009, 66, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.; Ryley, H.; Neale, L.; Dodge, J.; Lewarne, V. Effect of storage and heat on antimicrobial proteins in human milk. Arch. Dis. Child. 1978, 53, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, Á.; Diniz, E.M.d.A.; Barbosa, S.F.C.; Vaz, F.A.C. Immunologic factors in human milk: The effects of gestational age and pasteurization. J. Hum. Lact. 2005, 21, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska, A.; Sinkiewicz-Darol, E.; Barbarska, O.; Bernatowicz-Lojko, U.; Borszewska-Kornacka, M.K.; van Goudoever, J.B. Innovative techniques of processing human milk to preserve key components. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gysel, M.; Cossey, V.; Fieuws, S.; Schuermans, A. Impact of pasteurization on the antibacterial properties of human milk. Eur. J. Pediatrics 2012, 171, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazos-Garduño, A.; Serrano-Niño, J.; Solís-Pacheco, J.; Gutierrez-Padilla, J.; González-Reynoso, O.; García, H.; Aguilar-Uscanga, B. Effect of pasteurization, freeze-drying and spray drying on the fat globule and lipid profile of human milk. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 4, 296–302. [Google Scholar]
- Schuck, P.; Jeantet, R.; Bhandari, B.; Chen, X.D.; Perrone, Í.T.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Fenelon, M.; Kelly, P. Recent advances in spray drying relevant to the dairy industry: A comprehensive critical review. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1773–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbondo, N.N.; Owino, W.O.; Ambuko, J.; Sila, D.N. Effect of drying methods on the retention of bioactive compounds in African eggplant. Food Sci. 2018, 6, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvankhah, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G. Encapsulation and delivery of bioactive compounds using spray and freeze-drying techniques: A review. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.; Daoussi, R.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.-P.; De Beer, T. Freeze-drying of live virus vaccines: A review. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.-H.; Kim, J.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Kang, N.M. The human milk oligosaccharides are not affected by pasteurization and freeze-drying. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.-H.; Bae, S.P.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Seo, J.-B.; Kang, N.M. The freeze-drying does not influence the proteomic profiles of human milk. J. Matern. FetaNeonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martysiak-Żurowska, D.; Rożek, P.; Puta, M. The effect of freeze-drying and storage on lysozyme activity, lactoferrin content, superoxide dismutase activity, total antioxidant capacity and fatty acid profile of freeze-dried human milk. Dry. Technol. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins, R.A. Food Irradiation: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova, R.; Vasilev, N.V.; Spassov, S.L. Irradiation of food, current legislation framework, and detection of irradiated foods. Food Anal. Methods 2010, 3, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. High-Dose Irradiation: Wholesomeness of Food Irradiatied with Doses above 10 kGy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; Volume 890. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.; Bettelheim, K.; Luke, R.; Goldwater, P. Serotypes of Escherichia coli in sudden infant death syndrome. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, B.M.; Salgado, C.D.; Karchmer, T.B.; Sherertz, R.J. Can antibiotic-resistant nosocomial infections be controlled? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackshaw, K.; Valtchev, P.; Koolaji, N.; Berry, N.; Schindeler, A.; Dehghani, F.; Banati, R.B. The risk of infectious pathogens in breast-feeding, donated human milk and breast milk substitutes. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 24, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; McGoverin, C.; Vanholsbeeck, F.; Swift, S. Optimisation of the protocol for the LIVE/DEAD® BacLightTM bacterial viability kit for rapid determination of bacterial load. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, A.; Fernandez, M.; Sanchez, J. A death round affecting a young compartmentalized mycelium precedes aerial mycelium dismantling in confluent surface cultures of Streptomyces antibioticus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 151, 3689–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Erdmann, P.; Thakkar, S.K.; Sauser, J.; Destaillats, F. Longitudinal evolution of true protein, amino acids and bioactive proteins in breast milk: A developmental perspective. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahani, S.; Shakiba, A.; Jahani, L. The Antimicrobial effect of lactoferrin on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Int. J. Infect. 2015, 2, e27954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Dufour, J.C.; Lagier, J.C.; Dubourg, G.; Raoult, D.; Million, M. Repertoire of human breast and milk microbiota: A systematic review. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela, D.A.; Mills, D.A. Nursing our microbiota: Molecular linkages between bifidobacteria and milk oligosaccharides. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1537S–1543S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanoglu, S.; Bertino, E.; Tonetto, P.; De Nisi, G.; Ambruzzi, A.M.; Biasini, A.; Profeti, C.; Spreghini, M.R.; Moro, G.E. Guidelines for the establishment and operation of a donor human milk bank: Italian Association of Human Milk Banks Associazione Italiana Banche del Latte Umano Donato (AIBLUD: www.aiblud.org). J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 23, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Aquino, K.A. (Ed.) Sterilization by Gamma Irradiation; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Volume 9, pp. 172–202. [Google Scholar]
- Shawrang, P.; Mortaheb, M.; Motamedi-sede, F.; Askari, H. Application of Gamma Irradiation for Eliminating Bacterial Contamination of Bovine Colostrums. Res. Anim. Prod. 2018, 9, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Oh, S.H.; Byun, E.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Woon, J.H.; Byun, M.W. Inactivation of Enterobacter sakazakii of dehydrated infant formula by gamma-irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2007, 76, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, N.J.; Al-Khalidi, A.; Jaiteh, M.; Clarke, E.; Hyde, M.J.; Modi, N.; Holmes, E.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le Doare, K. Role of human milk oligosaccharides in Group B Streptococcus colonisation. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, N.; Saraiva, M.A.F.; Duarte, E.A.A.; de Carvalho, E.A.; Vieira, B.B.; Evangelista-Barreto, N.S. Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from human milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, D.; Ruiz, P.; Martinez-Costa, C.; Plaza, A.; Lopez, M. Effect of pasteurization on the bactericidal capacity of human milk. J. Hum. Lact. 2008, 24, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.H.; Bae, S.P.; Lee, H.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Kang, N.M. The impact of freeze-drying on the glycoproteomic profiles of human milk. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 33, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Odueke, O.B.; Farag, K.W.; Baines, R.N.; Chadd, S.A.J.F. Irradiation applications in dairy products: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashisaka, A.; Matches, J.; Batters, Y.; Hungate, F.; Dong, F. Effects of Gamma Irradiation at −78 °C on Microbial Populations in Dairy Products. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.; Victor, A.F.; Howell, M.L.; Yeo, J.G.; Qu, Y.; Selover, B.; Waite-Cusic, J.; Dallas, D.C. Bile Salt-Stimulated Lipase Activity in Donor Breast Milk Influenced by Pasteurization Techniques. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 552362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentainer, J.V.; Santos, O.O.; Maldaner, L.; Zappielo, C.; Neia, V.; Visentainer, L.; Pelissari, L.; Pizzo, J.; Rydlewski, A.; Silveira, R.J.B. Lipids and Fatty Acids in Human Milk: Benefits and Analysis; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Batovska, D.I.; Todorova, T.; Tsvetkova, V.; Najdenski, H.M. Antibacterial study of the medium chain fatty acids and their 1-monoglycerides: Individual effects and synergistic relationships. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Neyts, J.; Kristmundsdottir, T.; De Clercq, E.; Thormar, H. Hydrogels containing monocaprin prevent intravaginal and intracutaneous infections with HSV-2 in mice: Impact on the search for vaginal microbicides. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 61, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsue, M.; Mori, Y.; Nagase, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Hirano, R.; Ogai, K.; Ogura, K.; Kurihara, S.; Okamoto, S. Measuring the antimicrobial activity of lauric acid against various bacteria in human gut microbiota using a new method. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.J. The immunological components of human milk and their effect on immune development in infants. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, C.E.; Thormar, H. The role of milk-derived antimicrobial lipids as antiviral and antibacterial agents. In Immunology of Milk and the Neonate; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sprong, R.C.; Hulstein, M.F.; Van der Meer, R. Bactericidal activities of milk lipids. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundele, M.O. Cytotoxicity by stored human breast-milk: Possible contribution of complement system. Cell Biol. Int. 1999, 23, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.L. Antimicrobial activity of host-derived lipids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thormar, H.; Hilmarsson, H. The role of microbicidal lipids in host defense against pathogens and their potential as therapeutic agents. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 150, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchward, C.P.; Alany, R.G.; Snyder, L.A. Alternative antimicrobials: The properties of fatty acids and monoglycerides. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecgel, U.; Gumus, T.; Tasan, M.; Daglioglu, O.; Arici, M. Determination of fatty acid composition of γ-irradiated hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds, and pistachios. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2011, 80, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, T.R.; Fay, T.N.; Hamosh, M. Effect of pasteurization on long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid levels and enzyme activities of human milk. J. Pediatrics 1998, 132, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Ménard, O.; Etienne, J.; Ossemond, J.; Durand, A.; Buffin, R.; Loizon, E.; Meugnier, E.; Deglaire, A.; Dupont, D. Human milk pasteurisation reduces pre-lipolysis but not digestive lipolysis and moderately decreases intestinal lipid uptake in a combination of preterm infant in vitro models. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 126927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkilä, M.P.; Saris, P. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Percentage of Live Bacteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 24 h | |
| Raw milk | 95.3 | 92.2 |
| Freeze-dried | 79.9 | 11.3 |
| Holder pasteurised | 99.0 | 93.9 |
| Freeze-dried + Holder pasteurised | 85.0 | 0.3 |
| Infant formula | 91.4 | 95.5 |
| Positive control | 99.2 | 99.2 |
| Negative control | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Raw | HoP | FD | FD + HoP | Infant Formula | 2 kGy | 5–50 kGy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 94.9 ± 0.8 | 67.7 ± 12.5 | 97.8 ± 1.0 | 90.7 ± 4.2 | 91.4 ± 2.0 | 99.7 ± 0.3 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| 24 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 96.3 ± 1.4 | 99.9 ± 0.0 | 98.6 ± 0.2 | 96.7 ± 0.5 | 100 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blackshaw, K.; Wu, J.; Valtchev, P.; Lau, E.; Banati, R.B.; Dehghani, F.; Schindeler, A. The Effects of Thermal Pasteurisation, Freeze-Drying, and Gamma-Irradiation on the Antibacterial Properties of Donor Human Milk. Foods 2021, 10, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092077
Blackshaw K, Wu J, Valtchev P, Lau E, Banati RB, Dehghani F, Schindeler A. The Effects of Thermal Pasteurisation, Freeze-Drying, and Gamma-Irradiation on the Antibacterial Properties of Donor Human Milk. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092077
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlackshaw, Katherine, Jiadai Wu, Peter Valtchev, Edwin Lau, Richard B. Banati, Fariba Dehghani, and Aaron Schindeler. 2021. "The Effects of Thermal Pasteurisation, Freeze-Drying, and Gamma-Irradiation on the Antibacterial Properties of Donor Human Milk" Foods 10, no. 9: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092077
APA StyleBlackshaw, K., Wu, J., Valtchev, P., Lau, E., Banati, R. B., Dehghani, F., & Schindeler, A. (2021). The Effects of Thermal Pasteurisation, Freeze-Drying, and Gamma-Irradiation on the Antibacterial Properties of Donor Human Milk. Foods, 10(9), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092077







