Abstract
This work is devoted to the study of the effect of small Bi additives on the functional properties of Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts in the selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. The catalysts obtained by the joint impregnation method were characterized (TEM) by high dispersion of bimetallic nanoparticles with a median diameter of 4–5 nm. The structure of the Pd-Bi solid solution was confirmed via XPS and showed a change in the valence state of Pd and Bi depending on the Bi content, as well as the fraction of the oxidized state of Bi. TPR-H2 revealed various forms of Pd, including PdO and mixed Pd-O-Bi structures. The Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 catalyst demonstrated the highest efficiency (77.2% glucose conversion, 96% sodium gluconate selectivity), which is due to the optimal ratio between Pd and Bi, ensuring the stabilization of metallic Pd and preventing its oxidation.
1. Introduction
The development of highly efficient and selective catalysts is one of the key tasks of modern chemistry [1]. Among the variety of catalytic systems, nanoscale bimetallic catalysts based on Pd attract considerable attention due to the possibility of a synergistic effect, manifested in the improvement of catalytic characteristics compared to monometallic catalysts [2,3,4]. Pd, known for its high catalytic activity in various processes, in combination with a second promoter metal, which has the ability to modify the electronic structure of Pd, allows the creation of catalytic systems with unique properties [5]. Modification of Pd with Bi leads to a change in its adsorption and catalytic properties, which opens up new possibilities for selective reactions. In this context, supported Pd-Bi (Pd-Bi) catalysts are of particular interest, demonstrating high efficiency and selectivity in various oxidation and redox processes involving hydrogen transfer [6,7,8].
Pd-Bi systems are being investigated as electrocatalysts in fuel cells and electrochemical sensors [9,10,11,12,13]. Studies have shown that Pd-Bi catalysts are effectively used in the conversion of polyols (e.g., glycerol) into valuable chemicals such as lactic acid, glyceraldehyde, dihydroxyacetone, glyceric acid, tartaric acid, mesoxalic acid, glycolic acid, oxalic acid, formic acid and others [14,15,16]. Pd-Bi catalysts can be active in the selective oxidation of various alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones [17,18,19]. Experimental work was carried out on the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene alcohol and the hydrogenation of acetylene [20,21]. The most common application of Pd-Bi catalysts is for the process of selective glucose oxidation with gluconic acid formation [22,23]. Gluconic acid is a valuable biodegradable and biocompatible substance with a wide range of applications [24]. Its “green” properties make it increasingly in demand in various industrial fields, including pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, chemical, cement, textile, metalworking, water purification and other important areas [25,26].
However, for the most efficient production of gluconic acid, Pd-Bi catalysts must have an optimal concentration of the modifier (i.e., Bi), which will ensure maximum activity and selectivity in the formation of the desired product [27,28]. The key role of Bi in the structure of Pd-Bi catalysts is its ability to protect the active centers of Pd. Studying the promoting effect of Bi, Wenkin et al. [29] came to the conclusion that special bimetallic Pd-Bi active centers are formed in which Bi is able to protect Pd from three main deactivation factors in the process: chemical poisoning by reaction products, overoxidation of active sites and corrosion of the noble metal, leading to surface restructuring. In addition, the authors stated that Bi is additionally stabilized with the formation of an adsorbed Bi-glucose complex. The advantage of Bi is that it has a higher oxophilic property compared to Pd, as well as a higher surface energy, which allows it to coat Pd particles in the catalysts [30,31]. However, a significant amount of introduced Bi can lead to aggregation of bimetallic particles, reducing the overall surface area and, consequently, the activity of the catalyst in the reaction [32]. An excess of Bi also leads to blocking of Pd active sites [33]. In addition, Bi does not have its own catalytic effect in the process of glucose oxidation. The above-mentioned facts demonstrate the necessity to find optimal Pd/Bi ratios at which the negative effect of excess Bi on the activity of Pd-Bi catalysts is absent with the maximum possible promotional effect. The optimal concentration promotes the formation of highly dispersed Pd particles with high surface activity.
Despite the comprehensive study of the glucose oxidation process in the presence of supported Pd-Bi catalysts, the optimal Bi content, as well as the limits of the promoting effect of the modifier, have not yet been established. Thus, determining the optimal Bi concentration requires not only careful control during the synthesis of catalysts, but also a comprehensive study of the functional properties of catalyst samples using various surface characterization methods, as well as catalytic investigations in the glucose oxidation reaction. In previous studies, much attention was given to the consideration of the structure and effectiveness of Pd-Bi catalysts with a high addition of Bi in the range from 25.0 to 66.7 at. % of the total amount of metals deposited [23,33]. Despite certain success in deepening the understanding of the principles of Pd-Bi catalysts, studies have shown that a decrease in Bi content inevitably leads to an increase in the efficiency of the catalyst. On the other hand, the monometallic Pd catalyst demonstrated much lower catalytic activity compared to Pd-Bi. This gap in research has not been filled and the optimal Pd/Bi ratio remains unknown.
The aim of this work was to study the effect of small Bi additives below 16.7 at. % of the total amount of metals deposited on the efficiency of Pd-Bi catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3 in the process of selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. It was shown that the maximum efficiency of the catalysts was achieved in the Pd/Bi range from 5 to 10. We also paid great attention to the morphology of the observed metal particles. The demonstrated changes in the crystal and electronic structure of the particles allowed us to confirm the formation of a bimetallic Pd-Bi alloy.
2. Results and Discussion
Microscopy methods are powerful tools for analyzing surface morphology in the synthesis of supported catalysts. The micrographs obtained by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for pure γ-Al2O3 (Figure 1a) and the prepared catalyst sample Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (Figure 1b) demonstrate significant destruction of the support granules. Most likely, the granules lose their shape during the preparation of the catalysts due to prolonged mixing and high-temperature treatment, during which the catalysts are subjected to cyclic prolonged heating followed by cooling. The initial fraction of spherical γ-Al2O3, equal to 125–250 μm, is destroyed to form fine crumbs with an irregular shape with rare inclusions of granules reaching sizes up to 80 μm. This pattern is representative of all the studied samples prepared by the method used. The distribution of Pd and Bi over the catalyst support surface was studied using SEM in combination with the energy-dispersion spectrometer (EDS). The results showed the homogeneous and uniform distribution of the metal nanoparticles over the entire studied support surface both in powder (Figure 1c) and on a separate granule (Figure 1d). This means that no clusters or aggregates of Pd and Bi were observed in any specific areas in the micrographs obtained in the SEM mode. On the contrary, the nanoparticles of both metals were distributed sufficiently and uniformly without the formation of large clusters or zones with an increased concentration of one of the components.
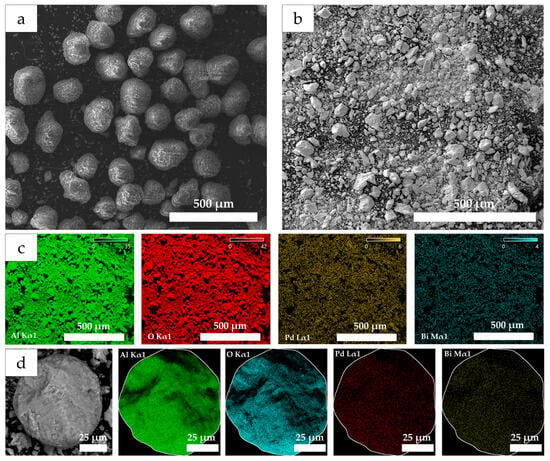
Figure 1.
SEM micrographs for γ-Al2O3 (a) and Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (b) and element maps for Pd Lα1 and Bi Mα1 obtained by the SEM-EDS on powder (c) and a separate granule (d) of the Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 sample.
Such uniform distribution is an extremely important factor that provides high catalytic activity since it improves the adsorption characteristics of the reacting agents at the active sites of the catalyst. The uniform distribution also indicates a high efficiency of the method, which is used for the synthesis and application of the metal particles on the support.
A much more important factor in the synthesis of nanoscale deposited catalysts than the morphology of the support is the morphology of nanoparticles supported on its surface. First of all, it concerns the size of the active nanoparticles. The smaller the size of the nanoparticles, the larger the active surface, and, as a result, the greater the catalytic activity of these catalysts demonstrate [34]. To study the morphology and size of the studied particles, micrographs were obtained for all samples using the transmission electron microscope (TEM) (Figure 2a–d).
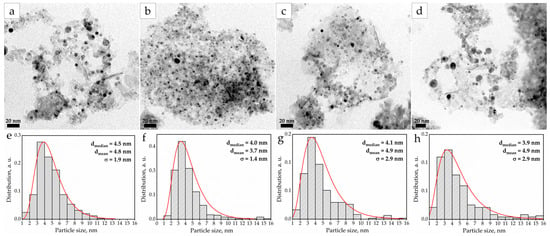
Figure 2.
TEM micrographs and PSD for catalyst samples: Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 (a,e), Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (b,f), Pd15:Bi1/Al2O3 (c,g) and Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3 (d,h).
To measure the size of the observed nanoparticles, particle size distribution (PSD) was performed for all the samples (Figure 2e–h). The distribution patterns obey the log-normal distribution law. The average and median diameters of the catalyst particles were 4–5 nm. All the samples exhibit a relatively narrow particle size distribution in the range from 2 to 8 nm. A negligible number of larger nanoparticles (>10 nm) are present in all the samples, which indicates some degree of particle aggregation during the synthesis [35]. However, their contribution to the average particle diameter is insignificant. Consequently, the influence of the particles of such a size on the overall catalytic activity will be minimal, due to the very low active surface of such particles [36]. The high dispersion of small particles suggests a more developed specific surface area of the catalyst, which, as a rule, has a positive effect on its catalytic activity.
To estimate the distribution of metals in nanoparticles, the areas with the largest particles present in the samples were examined by TEM-EDS (Figure 3). The data obtained demonstrate the close proximity of Bi and Pd atoms on the surface of the γ-Al2O3 support. Elemental mapping has shown that metal particles are mainly composed of Pd. The Bi is located in the same areas as the Pd, and as the intensity of the Pd increases, the intensity of the Bi signal also increases. No areas have been found on the elemental maps in which a significant amount of any metal would be located separately from the second metal. These observations allow us to assume that Pd and Bi have certain tendencies towards mutual localization in the studied catalysts. The observed proximity of Pd and Bi atoms leads to the appearance of an electronic intermetallic interaction between them (confirmed further by XPS study) [37]. This also suggests the formation of bimetallic Pd-Bi nanoparticles [38]. To confirm this hypothesis, the spot composition of a random sample of 40 particles from the surface of the Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 sample was measured and the atomic ratio Pd/Bi was calculated (Figure 4a). This showed the absence of monometallic formations in the catalyst, and also demonstrated the fact that the largest number of particles of all these types of particles is in the Pd/Bi ratio of 8–10. This fits well with the theoretical and the measured by X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) ratios.
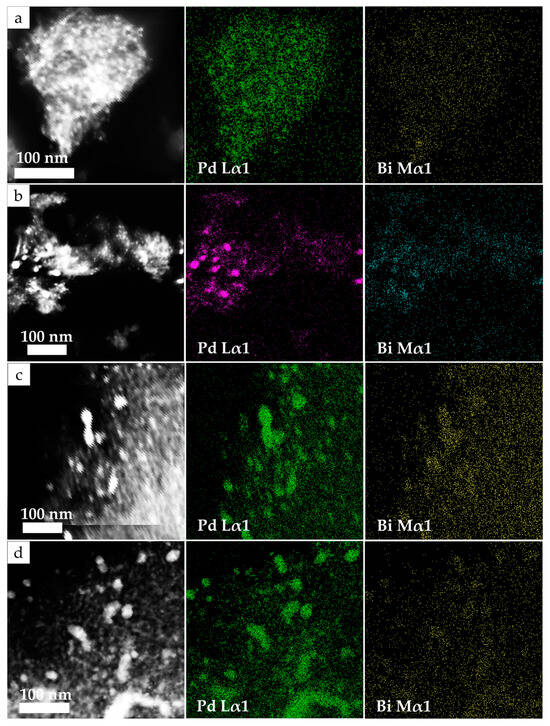
Figure 3.
Element maps for Pd Lα1 and Bi Mα1 obtained by the TEM-EDS for catalyst samples: Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 (a), Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (b), Pd15:Bi1/Al2O3 (c) and Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3 (d).
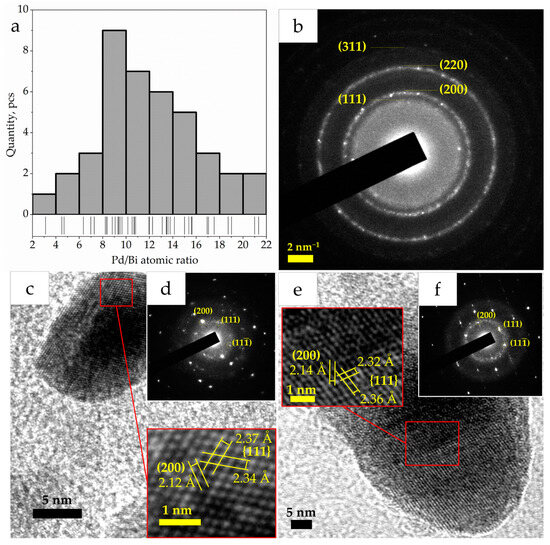
Figure 4.
Distribution of Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 particles by Pd/Bi atomic ratio (a), SAED pattern Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (b), HRTEM micrographs of individual particles of Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 (c) and Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3 (e) and SAED patterns obtained from these particles (d,f).
However, the TEM-EDS data are insufficient to confirm the formation of a bimetallic alloy. An analysis of the literature has shown that the formation of a Pd-Bi alloy is possible, and there are a number of works confirming this fact [38,39,40,41]. On the pattern (Figure 4b), obtained by the selected-area electron diffraction method (SAED), there are reflexes of (111), (200), (220) and (311) lattice planes that can be clearly observed, which obviously correspond to the structure of Pd fcc Fm-3m (PDF: 00-046-1043; a = 0.3890 nm). There are no reflexes that could be attributed to Bi. The Pd-Bi alloy, depending on the synthesis method, can form on the surface of a Pd particle, forming a “core–shell” structure with a Bi shell and an alloy at the phase boundary between Pd and Bi [38]. The second option, which is more likely for cases when both components are mixed homogeneously and, as a result, is more likely in current work, is the formation of a solid solution in the whole particle volume [42]. It should be noted that, with the limited functionality of the electron microscope, unfortunately, we did not have the opportunity to study particles using the high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) method, or to obtain «zoom-in» images of a single particle, which would confirm or deny the structure of the “core–shell”. Instead, we tried to obtain valuable information from the high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) images for individual large particles in the samples with the highest and lowest concentrations of Bi—Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 (Figure 4c) and Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 (Figure 4e), respectively. The images clearly show the boundaries of the crystal lattice of both particles and the lattice spacings are available for measurement. Due to the fact that the orientation of the crystals is unknown, the lattice spacings and angles between the planes were measured and compared with the standard values for Pd fcc Fm-3m noted earlier. Measured values 2.34 Å and 2.37 Å for Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 and 2.32 Å and 2.36 Å for Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 are equivalent if we take into account the measurement error (±0.5 Å) and correspond the family of {111} planes. Values 2.12 Å and 2.14 Å correspond to the (200) plane. It is obvious that the crystal structure in both cases is close identical to Pd fcc Fm-3m, but the measurement results significantly exceed the standard values for Pd (PDF: 00-046-1043; d(111) = 2.15 Å, d(200) = 1.95 Å). This effect is observed due to the substitution of Pd atoms (atomic radius 1.37 Å) with larger Bi atoms (atomic radius 1.70 Å), due to which the boundaries of the crystal lattice expanding. Thus, the observed particles are a bimetallic solid solution of Pd-Bi. The structure of fcc Fm-3m is also confirmed by SAED patterns from individual particles, which, in addition, demonstrate their pronounced monocrystallinity. We also report that attempts to detect mono-Bi particles in order to examine their crystal structure have not been successful.
The structure of the samples was additionally confirmed using the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) method. The obtained diffractograms (Figure 5), unfortunately, are not informative for us, since the Pd and Bi reflexes we are interested in are mainly in the regions where the γ-Al2O3 reflexes, which have a high degree of amorphousness and sufficiently wide peaks, are found. Nevertheless, the most intense Pd (111) reflex is observed at 39.4°, and its intensity increases with increasing Pd content. It is also interesting that although the Bi additive is quite small, the region in which we could expect its most intense peak (COD 1539906; (200); 2θ = 28.5°) is not characterized by any reflexes (including γ-Al2O3) [43]. This may also further indicate that Bi forms a solid solution with Pd, the particles of which crystallize in the fcc structure of Pd.
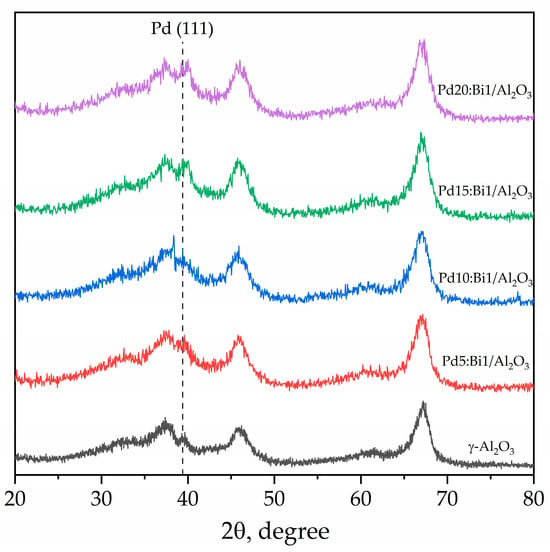
Figure 5.
XRD diffractograms of Pd-Bi catalyst and γ-Al2O3.
The above given facts indicate a high efficiency of the method for applying catalytically active components and the adequate mixing of Pd and Bi with the support during joint impregnation of γ-Al2O3 with acetous acid solutions of Pd(C5H7O2)2 and Bi(CH3COO)3 precursors. The possible formation of a Pd-Bi alloy phase with the electron interaction between Pd and Bi at the atomic level can significantly influence the catalytic properties of the material. This interaction can lead to a change in the electronic structure of both metals, which in turn will affect their adsorption properties and catalytic activity during the primary reaction [44]. Additional studies were used, such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and the method of temperature-programmed reduction with hydrogen (TPR-H2), for a more accurate confirmation of the formation of the alloy phase or bimetallic nanoparticles. These methods allowed the structure and the composition of the obtained material to be studied at the atomic level in more detail and the assumption about the formation of an alloy or other bimetallic structures to be confirmed.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a powerful surface-sensitive method for studying the surface properties of solids. As mentioned before, the close proximity of Pd and Bi atoms, as well as the formation of a Pd-Bi solid solution, leads to a change in the electronic properties of the surface of these metals. To detect changes in the electronic structure of metals, monometallic Pd/Al2O3 and Bi/Al2O3 samples prepared according to the method used were used as standard samples. This allowed us to ignore the effect of the γ-Al2O3 carrier on metals during data interpretation.
XPS was used to study the valence state of the metal particles on the surface of Pd-Bi catalyst samples (Figure 6). The spectra deconvolution was performed to interpret the obtained results. The XPS profiles for monometallic Pd/Al2O3 consist of two peaks related to the Pd 3d3/2 and Pd 3d5/2 states with the binding energies of 340.4 eV and 334.9 eV, respectively. The XPS profile for the Pd 3d5/2 core level contains lines at 337.8 eV and 334.9 eV that correspond to the PdII and Pd0 states, respectively (Table 1) [45,46]. The XPS spectrum of the monometallic Bi/Al2O3 of the Bi 4f7/2 core level consists of two peaks related to the BiIII and Bi0 states with binding energies of 158.7 eV and 156.9 eV, respectively [47,48]. The presence of the oxidized form of Pd and Bi in both monometallic samples and, as will be shown later, in bimetallic ones is inevitable due to the strong adsorption of metals on the surface of the oxygen-containing support γ-Al2O3 during synthesis [49]. In addition, both metals can undergo partial oxidation under the influence of X-ray radiation in the XPS analysis chamber.
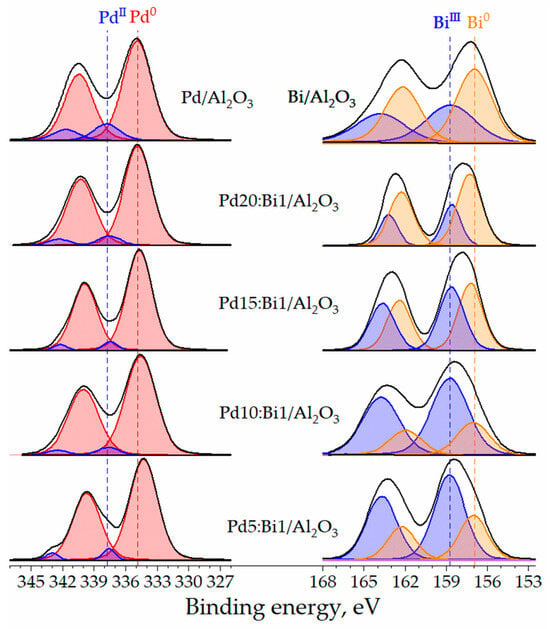
Figure 6.
XPS-spectra of Pd-Bi and monometallic Pd and Bi catalyst samples at Pd 3d and Bi 4f core levels.

Table 1.
Binding energies and the values of contributions from various Pd 3d5/2 and Bi 4f7/2 states in Pd-Bi catalyst samples.
The introduction of Bi into the electronic structure of Pd introduces noticeable changes in the valence states of metals, which are observed on the XPS spectra. The changes can be divided into three main groups. First, an increase in the proportion of Bi in the catalysts leads to a shift of the Pd0 3d5/2 line towards lower binding energies from 334.9 eV in Pd/Al2O3 to 334.8, 334.7, 334.6 and 334.3 eV in Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3, Pd15:Bi1/Al2O3, Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 and Pd5: Bi1/Al2O3, respectively. This indicates a redistribution of charge and the formation of electron-rich Pd states. The second noticeable change is the shift of the Bi0 4f7/2 lines towards larger binding energies, and this shift is inversely proportional to the addition of Bi and becomes more obvious with a decrease in the proportion of Bi in the catalysts. The shift occurs from 156.9 eV in Bi/Al2O3 to 157.0, 157.0, 157.2 and 157.3 eV in Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3, Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3, Pd15:Bi1/Al2O3 and Pd20: Bi1/Al2O3, respectively. The shift of the Bi0 lines towards greater binding energy proves the transfer of electrons from Pd to Bi. The fact that a decrease in the Bi content leads to a greater shift clearly demonstrates that in this case, a greater number of Pd atoms interact with Bi atoms. The third noticeable change is a significant change in the ratio of Bi0/BiIII states with a change in the Bi content. When Bi is incorporated in a significant amount (Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3), most of it is in the oxidized state. When the amount of Bi introduced is reduced to a minimum (Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3), a noticeable increase in the metallic state of Bi0 is observed, which confirms the strong inter-metallic interaction between Pd and Bi.
Temperature-programmed reduction with hydrogen (TPR-H2) profiles of Pd-Bi catalysts along with the corresponding reference Pd/Al2O3 sample are shown in Figure 7. In the TPR profile of the monometallic Pd/Al2O3 sample, there is a single peak of reduction of the oxidized state of PdOx at 100 °C [23]. In the case of Pd-Bi catalysts, the peaks of H2 absorption of an uneven shape are observed in the temperature range of 50–150 °C [50]. The peaks at ≈92 °C are associated with the reduction of PdO due to hydrogen absorption. However, the appearance of the additional absorption peaks at 120–135 °C is probably related to the reduction of the mixed form of Pd-O-Bi. The “humped” shape of the curves at 50–150 °C indicates different dispersion of the nanoparticles and different contributions of both larger particles and smaller ones. A similar pattern was found for active gold centers of different types: gold clusters and gold nanoparticles with different sizes and effective charges [51]. Owing to the small amount of the introduced Bi in the samples in the temperature range from 300 to 400 °C, there are low-intensity bands of reduction of monometallic Bi species, which indirectly confirm the presence of monometallic Bi particles in an extremely small amount.
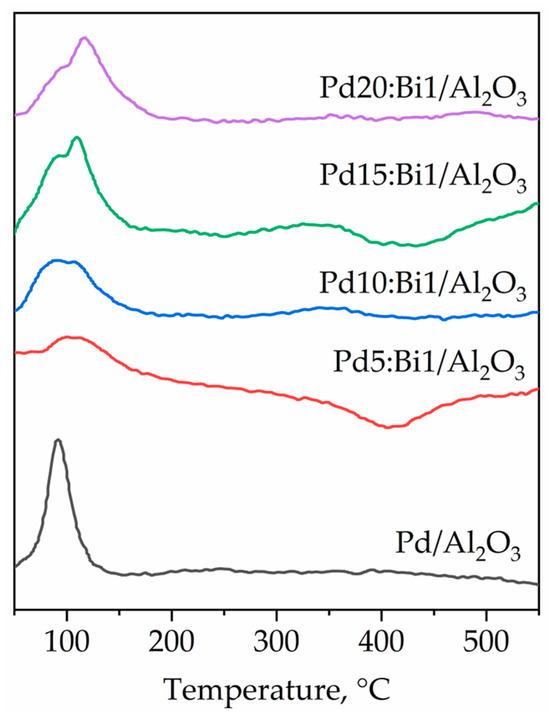
Figure 7.
TPR profiles of samples Pd-Bi and monometallic Pd catalyst samples.
Speaking about the mechanism of the reaction of catalytic oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid on Pd-Bi catalysts, the mechanism proposed by Besson et al. [52] is generally accepted and most often used for description. (Figure 8). According to this mechanism, Bi acts as a promoter protecting active Pd sites from deactivation, while Pd0 has catalytic activity in this process. The active sites of metallic Pd (1) are targets for glucose adsorption (2) through H- and OH-groups (3, 4), and Bi (5), which has a higher affinity for oxygen than Pd, is an acceptor of the oxygen molecule (6). The interaction of adsorbed hydrogen and oxygen leads to the release of hydrogen peroxide molecules into the reaction media (7), and glucose is transformed into an intermediate product, glucono-δ–lactone (8), which is subsequently destroyed by an added solution of sodium hydroxide to form a molecule of sodium gluconate (9).
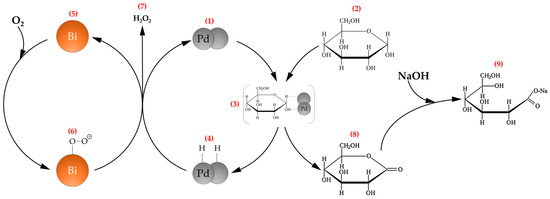
Figure 8.
The mechanism of selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid on Pd-Bi catalysts, proposed by Besson [52].
Previously, the catalytic systems of the Pdx:Biy/Al2O3 composition (where x:y = 3:1; 5:2; 2:1; 1:1; 1:2) were studied in the reaction of the selective catalytic oxidation of glucose into gluconic acid (sodium gluconate). The catalyst with the lowest Bi content of the Pd3:Bi1/Al2O3 composition was found to have the highest efficiency (glucose conversion 56.6%) and the sample with the highest Bi content of Pd1:Bi2/Al2O3 demonstrated the lowest conversion of glucose (glucose conversion 27.8%) into the product due to the aggregation of nanoparticles particles, their leaching into a reaction medium and the blocking of active sites. Therefore, the authors of this paper observed a tendency to increase the catalytic activity with a decrease in the amount of the introduced Bi. Hence, in this work, the authors focused on studying the promoting effect of Bi when it is introduced in smaller quantities. Catalytic experiments were conducted using Pdx:Biy/Al2O3, where x:y = 5:1; 10:1; 15:1; 20:1 at a molar ratio of Glu:Pd = 5000:1. The rate constant and the initial reaction rate were calculated at the first sampling (20 min after the start of the reaction) on the assumption that the reaction proceeds according to the first order, since the solubility of oxygen in water at 60 degrees and a pressure of 1 bar is much lower than the concentration of glucose in 50 mL of solution (CGlu = 0.03 mol/50 mL, CO2 = 3.56 × 10−5 mol) [53]. The conversion in the presence of Pdx:Biy/Al2O3 catalysts depending on the atomic ratio is shown in Figure 9.
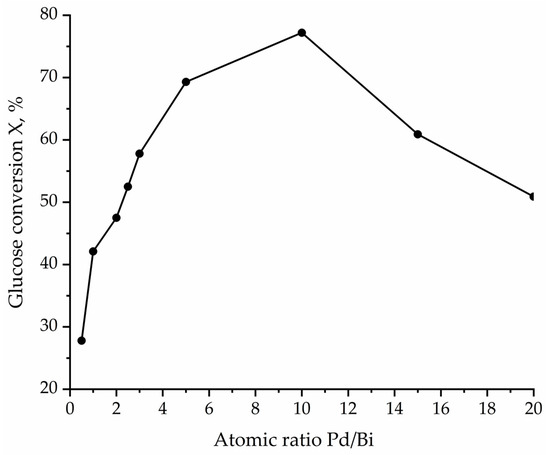
Figure 9.
The dependence of the glucose conversion on the Pd/Bi ratio.
It was established that increasing the Pd proportion (i.e., decreasing the amount of the introduced Bi) to Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 led to a significant increase in the glucose conversion up to 77.2% with a selectivity for sodium gluconate that is equal to 96%. It is worth noting that the only by-product was fructose, which is a product of glucose isomerization in an alkaline medium. The samples with a lower Bi content (Pd15:Bi1/Al2O3 and Pd20:Bi1/Al2O3) demonstrated a decrease in the glucose conversion in the presence of these catalysts up to 60.9% and 50.9%, respectively (Table 2) while maintaining the selectivity for sodium gluconate of ~95%. Samples of catalysts with a Pd/Bi ratio of 5 and 10 show almost identical values of the initial reaction rate and the rate constant. Indeed, according to the kinetic curves of the process (Figure 10), both catalysts show the same efficiency for up to 40 min of the reaction. This tells us that the range of atomic Pd/Bi ratios from 5 to 10 is optimal to ensure the highest efficiency of the reaction. However, 60 min after the start of the reaction, deactivation of the Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 sample is stronger than Pd10:Bi1. Taking this fact into account, we suggested that the “ideal” exact ratio should lie in the range between Pd/Bi, equal from 5 to 10, preferably closer to Pd/Bi = 10.

Table 2.
Catalytic parameters of the glucose oxidation reaction in the presence of the Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts.
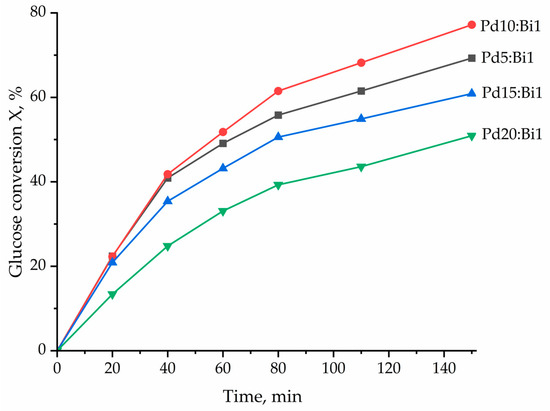
Figure 10.
Kinetic curves of the process of glucose to gluconic acid oxidation over Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts.
Studies have shown that the optimal ratio of metals in Pd-Bi catalysts deposited on γ-Al2O3 for the process of selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid is achieved in the Pd/Bi range between 5 and 10, and among the studied samples, Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 demonstrated the best results. In this case, the amount of Bi is sufficient to demonstrate the maximum promotional effect. Bi acts as a promoter and has a positive effect on the functional properties of Pd-Bi catalysts, preventing the degradation of Pd and modifying its morphological and electronic properties, which leads to an increase in its catalytic properties. It has been shown that a further increase in the proportion of Bi (Pd/Bi > 10) leads to a decrease in catalytic activity.
The presence of Bi in the amount corresponding to the Pd10:Bi/Al2O3 composition was sufficient to prevent the complete oxidation of Pd up to PdII during the catalytic reaction of glucose oxidation to sodium gluconate. This phenomenon indicates the protective role of Bi, which prevents catalyst deactivation by oxidation of the active sites of Pd. In view of this, Bi not only promotes effective conversion, but also ensures the stability of the active phase of Pd under reaction conditions, allowing high catalytic activity to be maintained. The mechanism of this protective action may be associated with the modification of the electronic properties of Pd under the influence of Bi, as well as with the formation of bimetallic structures that are resistant to oxidation.
Therefore, it is possible to conclude that a certain amount of Bi is necessary for the effective modification of Pd and optimization of catalytic properties. An excessively low Bi content does not provide a sufficient promoting influence, which leads to a decrease in the catalyst efficiency. The revealed regularities denote the existence of an optimal Pd:Bi ratio, at which the maximum efficiency is achieved during selective oxidation of glucose.
Thus, the catalyst particles obtained by this method have high dispersibility with a size of 4–5 nm. The data on glucose conversion obtained in the presence of the catalyst composition Pd10:Bi/Al2O3 (77.2%) exceed the results for the previously obtained composition Pd3:Bi/Al2O3 [33]. Moreover, the synthesis of catalysts by joint impregnation of the support with acetylacetonates and acetates can be easily adapted to obtain other catalyst compositions. The identified patterns will provide a basis for the design of new catalytic materials. A deep understanding of the relation between composition, structure, and catalytic properties will allow the targeted synthesis of catalysts with specified characteristics optimized for specific processes and reaction conditions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Catalyst Samples
Shredded granules of the γ-Al2O3 support (SKTB Katalizator, Novosibirsk, Russia) with a fraction of 125–250 μm were pre-dried to remove moisture in a VAC-52 vacuum cabinet (Stegler, China, Russian representative office: Moscow, Russia) at 120 °C for 24 h. Further, the catalysts were prepared by joint impregnation of the support with acetic acid (Ecos-1, Moscow, Russia, 99.5%, 200 mL) solutions of precursors Pd(C5H7O2)2 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, 99%) and Bi(CH3COO)3 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, 99.99%) with constant stirring (500 rpm) using a 1500S magnetic stirrer (ULAB, Nanjing, China) for 18 h. The solvent was then removed using a rotary evaporator (Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany) in a water bath (55 °C, 60–80 rpm). The catalyst powders were then dried at 80 °C in a vacuum oven for 24 h. The dried samples underwent successive three-stage heat treatment in an atmosphere of Ar (500 °C, heating rate 0.7 °C/min), O2 (350 °C, heating rate 1 °C/min) and H2 (500 °C, heating rate 1 °C/min) and held at a constant temperature for 2 h at each stage of pretreatment. Samples of the composition Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 were obtained, where (x = 5; 10; 15; 20). The ratio between Pd and Bi was close to the theoretically specified one during the synthesis of the catalysts. The total content of Pd and Bi was ~5 wt. %. The textural characteristics and composition of the catalysts are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Composition of catalysts and textural characteristics.
3.2. Catalytic Experiment
Catalytic oxidation of glucose (0.6 M) was carried out in a three-necked reactor at 60 °C, atmospheric pressure and pH 9 (controlled by adding 3 M NaOH), where 50 mL of glucose solution contained 5.4 g of glucose. The reaction mixture was continuously stirred (1500 rpm) and bubbled with oxygen (10 mL/min) for 150 min. Gluconic acid was formed as sodium gluconate.
3.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
The analysis of glucose oxidation products was carried out by HPLC-RID on an Agilent 1200 liquid chromatograph (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a refractometric detector using a Rezex ROA Organic Acid column (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA). The isocratic elution mode with 0.05% phosphoric acid solution at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min was selected. The injection volume was 2 μL, the thermostat temperature was 45 °C, and the cell temperature was 45 °C. The analysis time was 20 min.
3.4. Low-Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption
The specific surface area of the samples was studied using a TriStar 3020 automatic gas adsorption analyzer (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) based on nitrogen adsorption data at a temperature of −196 °C. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) multipoint method was used to determine the specific surface area (Ssp) in the range of relative nitrogen pressure P/P0 from 0.05 to 0.35. The Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method was used to determine the total pore volume (V) and average pore diameter (D). Before measuring the specific surface area, the samples were pre-degassed (200 °C, vacuum) for 2 h.
3.5. X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis (XRF)
For qualitative and quantitative analysis of catalysts, an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer Lab Center XRF-1800 Lab Center XRF-1800 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a 4 kW X-ray tube with a rotation capability of up to 60 rpm was used. The device error was ±1%.
3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
To evaluate the morphology and size of the particles of the obtained samples, as well as their distribution on the surface of the carrier, the method of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with the use of energy-dispersive analysis was used. To obtain images of the particles, a JEM-2100F (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) transmission electron microscope was used. The microscope was equipped with an electron gun with field emission of the cathode, a high-resolution pole piece (dot resolution of 0.19 nm) and a JEOL JED-2300 Analysis Station spectrometer. Scanning to obtain high-resolution images was performed at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV.
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
To study the grain structure of the catalyst samples by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using energy-dispersive analysis, SEM images of the studied catalyst samples were taken. An EVO50 scanning electron microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) with a tungsten hot cathode equipped with INCA ENERGY 350 X (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) was used.
3.8. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) was performed on an XRD-6000 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a Cu X-ray tube with a long fine focus and a power of 2.2 kW at a step of 1°/min according to the Bragg–Brentano scheme. The obtained data were deciphered using the International Center for Diffraction Data (ICDD) database, version PDF-4+.
3.9. Temperature-Programmed Reduction (TPR-H2)
The reactivity of the samples towards hydrogen was studied using the temperature-programmed reduction (TPR-H2) method. AutoChem 2950 HP (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) automated chemisorption analyzer system with a thermal conductivity detector was used to measure the TPR-H2. In addition, 0.05 g of each sample was collected for analysis. The catalyst samples to be studied were preliminarily oxidized in an O2 flow at 350 °C for 10 min, heating them from room temperature to 350 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min. Then, by increasing the temperature from 50 °C to 550 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min, the surface of the catalyst powders was reduced with a gas flow consisting of 10% H2 in argon.
3.10. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
To study the chemical composition and electronic state of the surface atoms of the catalyst samples, the method of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used. The measurements were carried out using a 100-micron X-ray beam on a PHI 5000 VersaProbe-II (ULVAC-PHI, Chigasaki, Kanagawa, Japan) instrument equipped with argon and electron guns, which were used to neutralize the charge arising in the analysis of non-conducting samples (double beam charge neutralization method). The accuracy of measurements of the binding energy was ±0.1 eV for all the samples. The C 1s line at 284.6 eV was used as an internal standard. When analyzing the XPS spectra, peak deconvolution was performed using a mixed Gaussian–Lorentzian distribution by simultaneously subtracting the background caused by secondary electrons and photoelectrons losing energy, according to the Shirley algorithm. The obtained XPS spectra were processed using the standard CasaXPS software (version 2.3.22PR1.0, 2018).
4. Conclusions
Key findings from the comprehensive study of Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts:
- During the preparation of catalysts, the granules of the γ-Al2O3 carrier are destroyed from a fraction of 125–250 μm to fine crumbs with rare inclusions of granules up to 80 μm.
- Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts obtained by the method of joint impregnation of γ-Al2O3 with Pd(C5H7O2)2 and Bi(CH3COO)3 precursors have a high degree of dispersion with average sizes from 3.9 to 4.5 nm. The average size decreases with decreasing Bi fraction, but the contribution from single inclusions of larger particles (>10 nm) increases. A small amount of larger particles (>10 nm) does not have a significant effect on the overall activity.
- Pd and Bi demonstrate close proximity on the surface of the support. No monometallic particles were found. An analysis of the composition of a random sample of individual particles showed that all particles contain both Pd and Bi in their composition. For Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3, the largest contribution is made by particles with an atomic Pd/Bi ratio of 8–10, which corresponds to the theoretically calculated value and the results of the XRF elemental analysis.
- Analysis of the particle structure in the catalysts showed the presence of signals (111), (200), (220), (311) of Pd fcc Fm-3m, and the absence of any signals that correspond to Bi. The measured values of the lattice spacings are increased in comparison with the standard values for Pd, which indicates the formation of a Pd-Bi solid solution with an fcc structure.
- The addition of a significant amount of Bi leads to a shift in the Pd0 state towards a lower binding energy, which leads to the formation of electron-rich Pd active centers. An increase in the Bi additive also increases the proportion of oxidized BiIII up to 72.5%, while a minimal Bi additive leads to the opposite effect, reducing the proportion of the oxidized state to 29.8%. With minimal addition of Bi, there is also a Bi0 shift towards greater binding energy. These dependences are explained by the strong intermetallic electronic interaction of Pd and Bi.
- It is shown that PdII can take the form of both PdOx and Pd-O-Bi. which reduced at different temperatures. Moreover, with a decrease in the Bi additive, the catalysts have a greater tendency to form a mixed Pd-O-Bi oxide. TPR analysis showed that Pdx:Bi/Al2O3 catalysts contain various forms of Pd, including PdO and mixed Pd-O-Bi structures, which are reduced in different temperature ranges.
- The Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 catalyst demonstrated the highest efficiency in the reaction of selective oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid (77.2% glucose conversion, 96% selectivity for sodium gluconate). However, both Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3 and Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 have almost identical rate constants and initial reaction rates, and the first 40 min proceed the same for both samples. However, the deactivation of Pd5:Bi1/Al2O3 begins a little earlier than that of Pd10:Bi1/Al2O3, which indicates that the exact optimal atomic ratio of Pd/Bi is between 5 and 10 (presumably closer to 10).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.K., A.K.K. and M.P.S.-S.; methodology, M.P.S.-S., S.A.G. and R.K.; formal analysis, E.P.M., A.K.S. and S.S.; investigation, S.A.G., K.I.K. and A.V.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P.S.-S. and S.A.G.; writing—review and editing, E.P.M. and A.N.P.; visualization, M.P.S.-S. and S.A.G.; supervision, I.A.K. and R.K.; project administration, I.A.K.; funding acquisition I.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (MSHE) of the Russian Federation (Grant No. 075-15-2023-468) and the Government of India (Grant No. DST/INT/MSHE/P-02/2022(G)) within the framework of international cooperation between Russia and India.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Malcolmson, S.J.; Meek, S.J.; Sattely, E.S.; Schrock, R.R.; Hoveyda, A.H. Highly Efficient Molybdenum-Based Catalysts for Enantioselective Alkene Metathesis. Nature 2008, 456, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.; Lo, T.W.B.; Tsang, S.C.E. Recent Developments in Pd-Based Bimetallic Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 1998–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Feng, J. Recent Progress on Rational Design of Bimetallic Pd Based Catalysts and Their Advanced Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13560–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellert, O.G.; Tsodikov, M.V.; Nikolaev, S.A.; Novotortsev, V.M. Bimetallic Nanoalloys in Heterogeneous Catalysis of Industrially Important Reactions: Synergistic Effects and Structural Organization of Active Components. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 718–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.E.; Haque, N.; Northey, S.A.; Giddey, S. Platinum Group Metals: A Review of Resources, Production and Usage with a Focus on Catalysts. Resources 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüsi, M.; Erikson, H.; Piirsoo, H.-M.; Paiste, P.; Aruväli, J.; Kikas, A.; Kisand, V.; Tamm, A.; Tammeveski, K. Oxygen Reduction Reaction on PdM/c (M = Pb, Sn, Bi) Alloy Nanocatalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 917, 116391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witońska, I.A.; Walock, M.J.; Dziugan, P.; Karski, S.; Stanishevsky, A.V. The Structure of Pd–M Supported Catalysts Used in the Hydrogen Transfer Reactions (M=In, Bi and Te). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odularu, A.T. Bi as Smart Material and Its Application in the Ninth Principle of Sustainable Chemistry. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 9802934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.K.; Dey, S.; Basu, S. Investigation on Borohydride Oxidation Performance of Activated Charcol Supported Pd-Bi Nanoparticles Electrocatalyst for Fuel Cell Application. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2025, 55, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, F.S.; Fontes, E.H.; Nandenha, J.; de Souza, R.F.B.; Neto, A.O. Addition of Bi to Pt and Pd for Electric Power Generation with Selective Cogeneration of Acetate from Ethanol in a Fuel Cell Type Reactor. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.S.; Saleem, J.; Alwi, A.; Al-Odail, F.A.; Hossain, M.M. Recent Advances in Anode Electrocatalysts for Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells—Part I—Fundamentals and Pd Based Catalysts. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202200045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zheng, L.; Wei, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, D. Pd/Bi Nanowires with Rough Surface for Stable Hydrogen Sensing at Low Temperatures. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qin, X.; Deng, C.; Cai, W.-B.; Jiang, K. Electrocatalytic CO2 and HCOOH Interconversion on Pd-Based Catalysts. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2022, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten, S.A.; Kurmanova, M.D.; Kurmanbayeva, K.; Torbina, V.V.; Stonkus, O.A.; Vodyankina, O.V. Base-Free Cascade Glycerol Conversion to Lactic Acid over Pd-Bi Nanoparticles Immobilized in Metal-Organic Framework Zr-UiO-66. Appl. Catal. A 2024, 674, 119603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Santos, J.B.; Vieira, C.; Crisafulli, R.; Linares, J.J. Promotional Effect of Auxiliary Metals Bi on Pt, Pd, and Ag on Au, for Glycerol Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 45, 25658–25671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalineeva, A.; Serov, A.; Padilla, M.; Martinez, U.; Artyushkova, K.; Baranton, S.; Coutanceau, C.; Atanassov, P. Self-Supported PdxBi Catalysts for the Electrooxidation of Glycerol in Alkaline Media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3937–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Gao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Reaction Induced Robust PdxBiy/SiC Catalyst for the Gas Phase Oxidation of Monopolistic Alcohols. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 42564–42569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y. Bi-Modified Pd/c Catalyst via Irreversible Adsorption and Its Catalytic Activity for Ethanol Oxidation in Alkaline Medium. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 99, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Q. Rational Design of PdBi Nanochains with Grain Boundaries for Enhanced Ethanol Oxidation Reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 14859–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dou, K.; Xie, D.; Zhang, F. Semi-Hydrogenation of Acetylenic Alcohol to Olefinic Alcohol Catalyzed by Pd Nanoparticles Embedded in Nitrogen-Enriched Porous Carbon Derived from ZIF-8. Appl. Catal. O 2024, 191, 206917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Wu, J.; Lou, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zou, S.; Fan, J. Controllable Deposition of Bi onto Pd for Selective Hydrogenation of Acetylene. Molecules 2023, 28, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Chen, L.-C. A Binary Pd–Bi Nanocatalyst with High Activity and Stability for Alkaline Glucose Electrooxidation. J. Power Sources 2015, 287, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, M.P.; Sidelnikov, V.S.; Geraskin, A.A.; Chernyavskii, A.V.; Kurzina, I.A. Influence of the Method of Preparation of the Pd-Bi/Al2O3 Catalyst on Catalytic Properties in the Reaction of Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Glucose into Gluconic Acid. Catalysts 2020, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiadis, S.; Morgunov, I.G. Gluconic Acid Production. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete-Rodríguez, A.M.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; Jiménez-Hornero, J.E.; Ehrenreich, A.; Liebl, W.; García-García, I. Gluconic Acid: Properties, Production Methods and Applications—An Excellent Opportunity for Agro-Industrial By-Products and Waste Bio-Valorization. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Nair, S.; Larroche, C.; Pandey, A. Gluconic Acid. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Su, D.S.; Prati, L. New Challenges in Gold Catalysis: Bimetallic Systems. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karski, S. Activity and Selectivity of Pd–Bi/SiO2 Catalysts in the Light of Mutual Interaction between Pd and Bi. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 253, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkin, M.; Ruiz, P.; Delmon, B.; Devillers, M. The Role of Bi as Promoter in Pd–Bi Catalysts for the Selective Oxidation of Glucose to Gluconate. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 180, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wu, F.; Cheng, L.; Bao, H.; Gao, W.; Duan, J.; Niu, W.; Xu, G. Maneuvering the Peroxidase-like Activity of Palladium-Based Nanozymes by Alloying with Oxophilic Bismuth for Biosensing. Small 2022, 19, 2205997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shcherbakova-Sandu, M.P.; Saraev, A.A.; Knyazev, A.S.; Kurzina, I.A. Pd-Bi-Based Catalysts for Selective Oxidation of Glucose into Gluconic Acid: The Role of Local Environment of Nanoparticles in Dependence of Their Composition. Catalysts 2024, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkin, M.; Renard, C.; Ruiz, P.; Delmon, B.; Devillers, M. Promoting Effects of Bi in Carbon-Supported Bimetallic Pd-Bi Catalysts for the Selective Oxidation of Glucose to Gluconic Acid. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1997, 110, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, M.P.; Kovtunov, M.A.; Baturin, V.S.; Oganov, A.R.; Kurzina, I.A. Influence of the Pd : Bi Ratio on Pd–Bi/Al2O3 Catalysts: Structure, Surface and Activity in Glucose Oxidation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 2021, 23, 14889–14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Somorjai, G.A. Size and Shape Control of Metal Nanoparticles for Reaction Selectivity in Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ren, Y.; Jin, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Sun, T.; Tian, J.; Zhu, Y. Icosahedral Pd Nanocrystal Catalysts with Dispersed Bi Atoms via Photochemical Route for Enhanced Formic Acid Oxidation Reaction. ChemNanoMat 2023, 9, e202300127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, E.W. Relation between Catalytic Activity and Size of Particle. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1939, 31, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yiu, Y.M.; Wang, Z.; Covelli, D.; Sammynaiken, R.; Finfrock, Y.Z.; Sham, T.-K. Elucidating the Many-Body Effect and Anomalous Pt and Ni Core Level Shifts in X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Pt–Ni Alloys. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chu, M.; Wang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, M.; Yang, H.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; et al. Unveiling the Local Structure and Electronic Properties of PdBi Surface Alloy for Selective Hydrogenation of Propyne. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16869–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Livi, K.J.T.; Wang, C.; Luo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Alghamdi, H.; Li, C.; An, F.; Gaskey, B.; et al. Ordered Intermetallic Pd3Bi Prepared by an Electrochemically Induced Phase Transformation for Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10818–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, G.; Bai, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, F.; Chen, R. General synthesis and atomic arrangement identification of ordered Bi-Pd intermetallics with tunable electrocatalytic CO2 reduction selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Kang, J.; Ma, D.; Chu, K. Single-Atom Bi Alloyed Pd Metallene for Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2209890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Dong, Q.; Qin, Q.; Li, H.; Xie, J.; Yu, G.; Chen, H. PdBi Alloy Nanoparticle-Enhanced Catalytic Activity toward Formic Acid Oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 19900–19907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Li, G.; Xiao, H.; Lu, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, R. Large-Scale Synthesis of Bismuth Hollow Nanospheres for Highly Efficient Cr(VI) Removal. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, X.; Yang, M.; Sheng, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Pang, M.; Fu, A.; Li, H.; Guo, P. Monodisperse PdBi Nanoparticles with a Face-Centered Cubic Structure for Highly Efficient Ethanol Oxidation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 5, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, M.C.; Simko, S.J. Elemental Pd by XPS. Surf. Sci. Spectra 1994, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery, D.L.; Graboski, M.S.; Ohno, T.R.; McCormick, R.L. Deactivation of PdO–Al2O3 Oxidation Catalyst in Lean-Burn Natural Gas Engine Exhaust: Aged Catalyst Characterization and Studies of Poisoning by H2O and SO2. Appl. Catal. B 1999, 21, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Pu, Y. Conductivity of ZnO Nanomaterials Measured by Terahertz Time-Domain. SPIE Proc. 2011, 8195, 81950P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, T.; Pan, H.; Fu, D.; Han, Y. Change of the Short-Range Scattering in the Graphene Covered with Bi2O3 Clusters. Physica E 2015, 78, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.C.; Raybaud, P.; Sautet, P. Interplay between Molecular Adsorption and Metal–Support Interaction for Small Supported Metal Clusters: CO and C2H4 Adsorption on Pd4/γ-Al2O3. J. Catal. 2007, 247, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witońska, I.; Królak, A.; Karski, S. Bi modified Pd/support (SiO2, Al2O3) catalysts for hydrodechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 331, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanchikova, N.; Pestryakov, A.; Tuzovskaya, I.; Zepeda, T.A.; Farias, M.H.; Tiznado, H.; Martynyuk, O. Effect of Redox Treatments on Activation and Deactivation of Gold Nanospecies Supported on Mesoporous Silica in CO Oxidation. Fuel 2012, 110, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, M.; Lahmer, F.; Gallezot, P.; Fuertès, P.; Flèche, G. Catalytic Oxidation of Glucose on Bismuth-Promoted Palladium Catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 152, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromans, D. Temperature and Pressure Dependent Solubility of Oxygen in Water: A Thermodynamic Analysis. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).