Tabletop 3D Display with Large Radial Viewing Angle Based on Panoramic Annular Lens Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
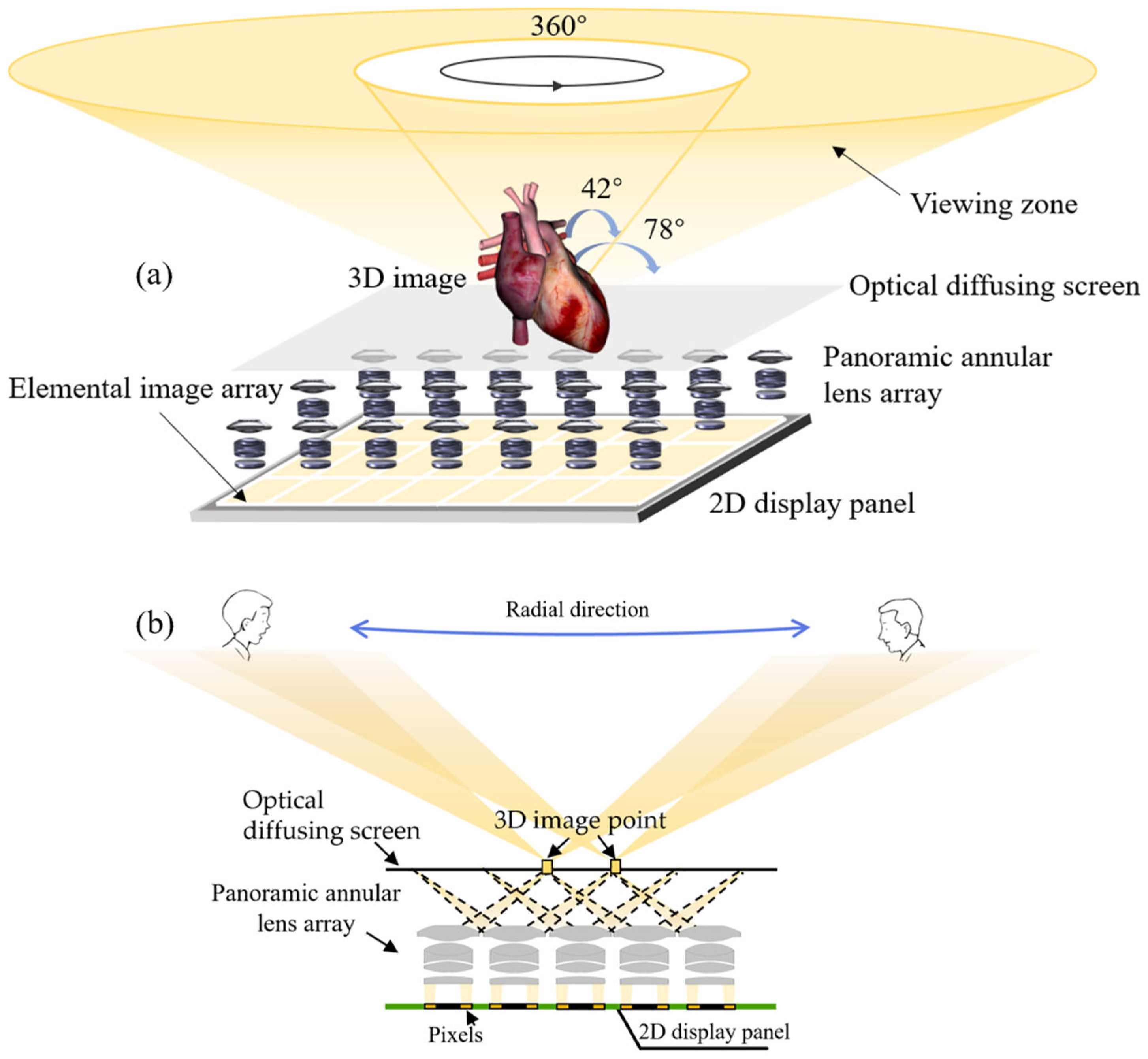
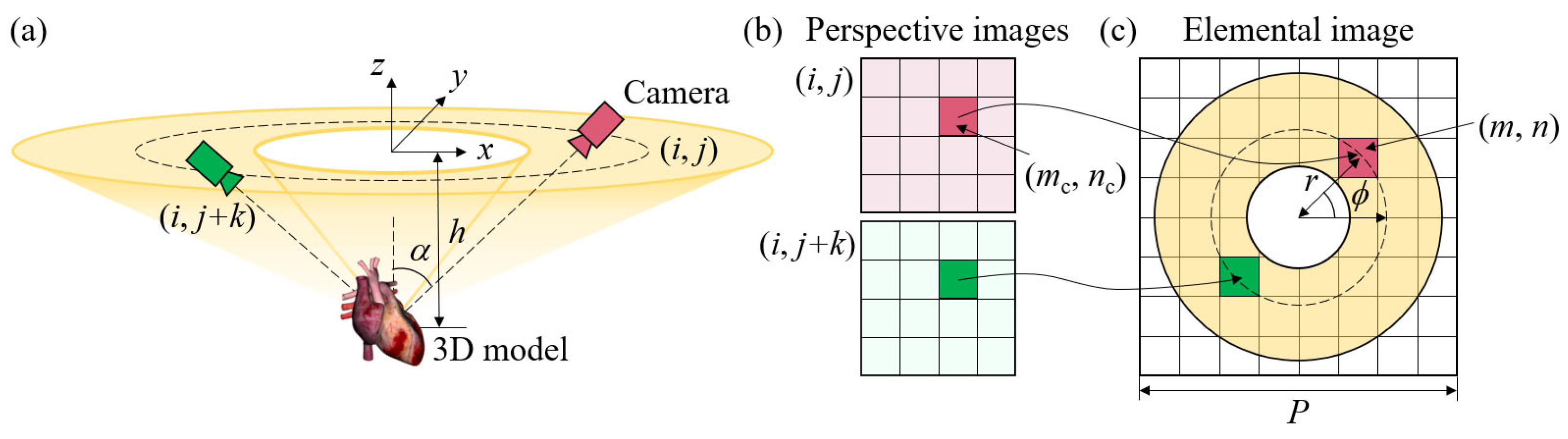
2.1. Configuration of the Tabletop 3D Display
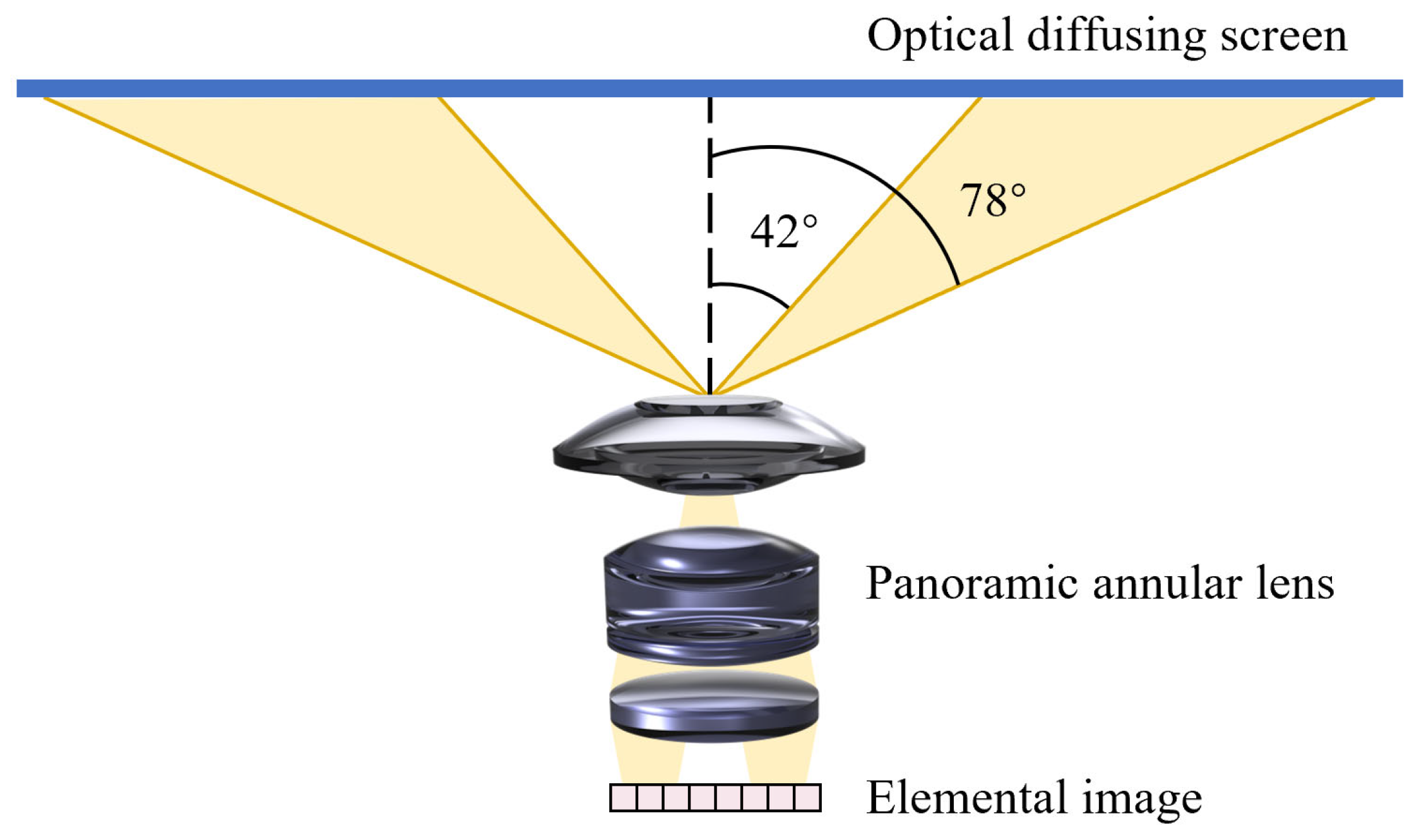
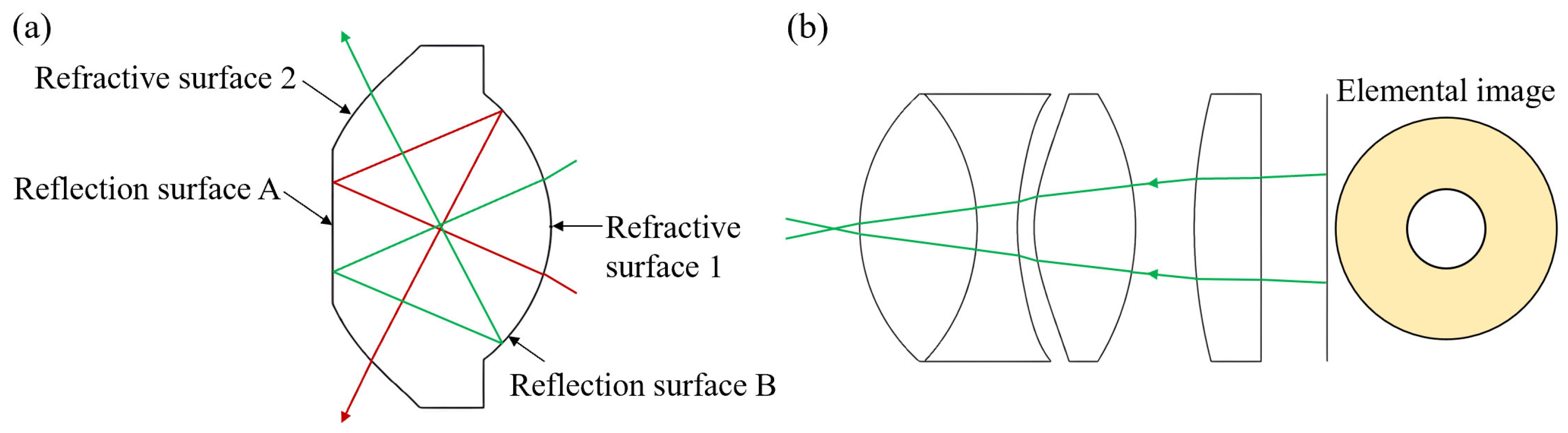
2.2. Design of Panoramic Annular Lens Array
2.3. Characteristics of Optical Diffusing Screen
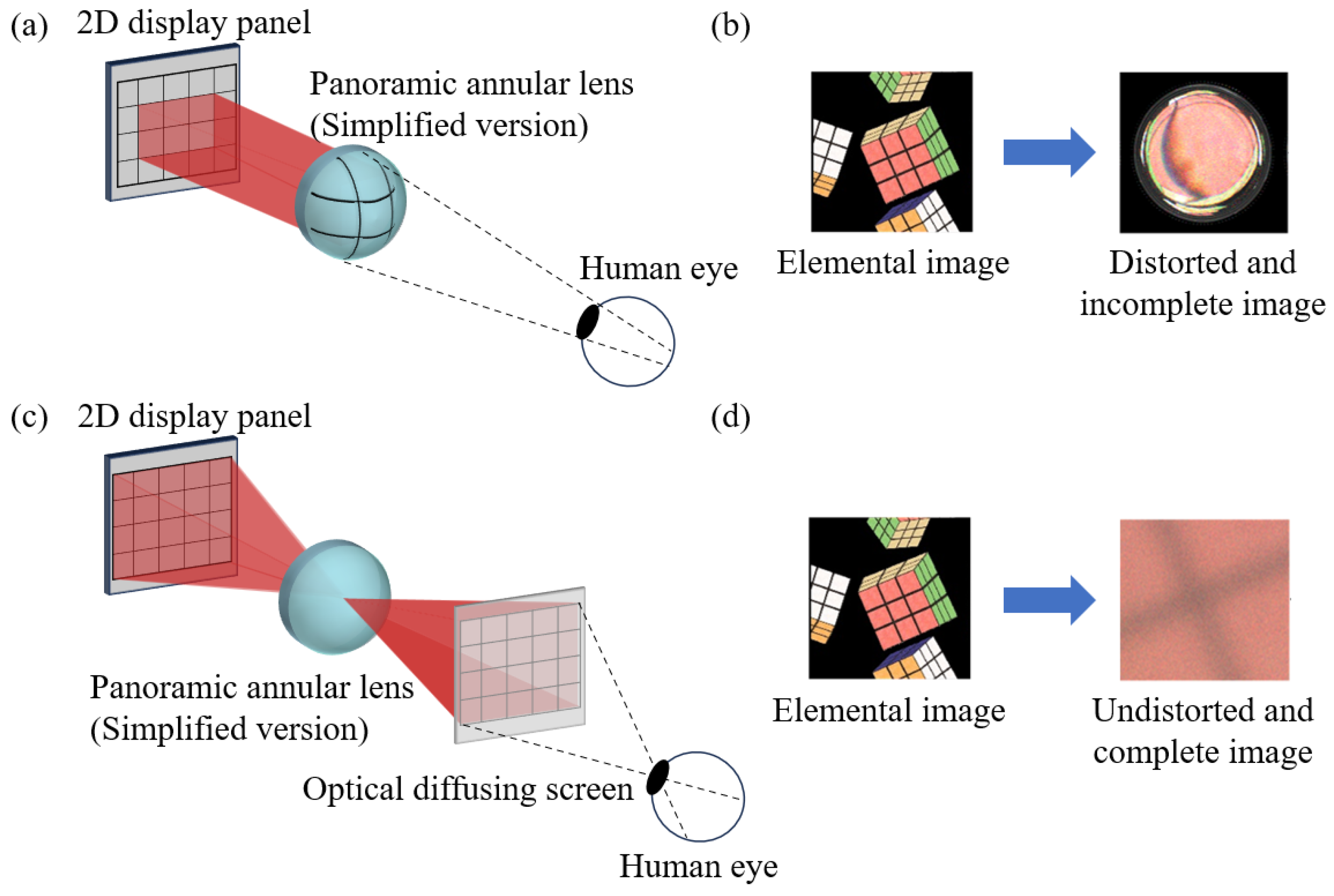
2.4. Generation of the Elemental Image Array
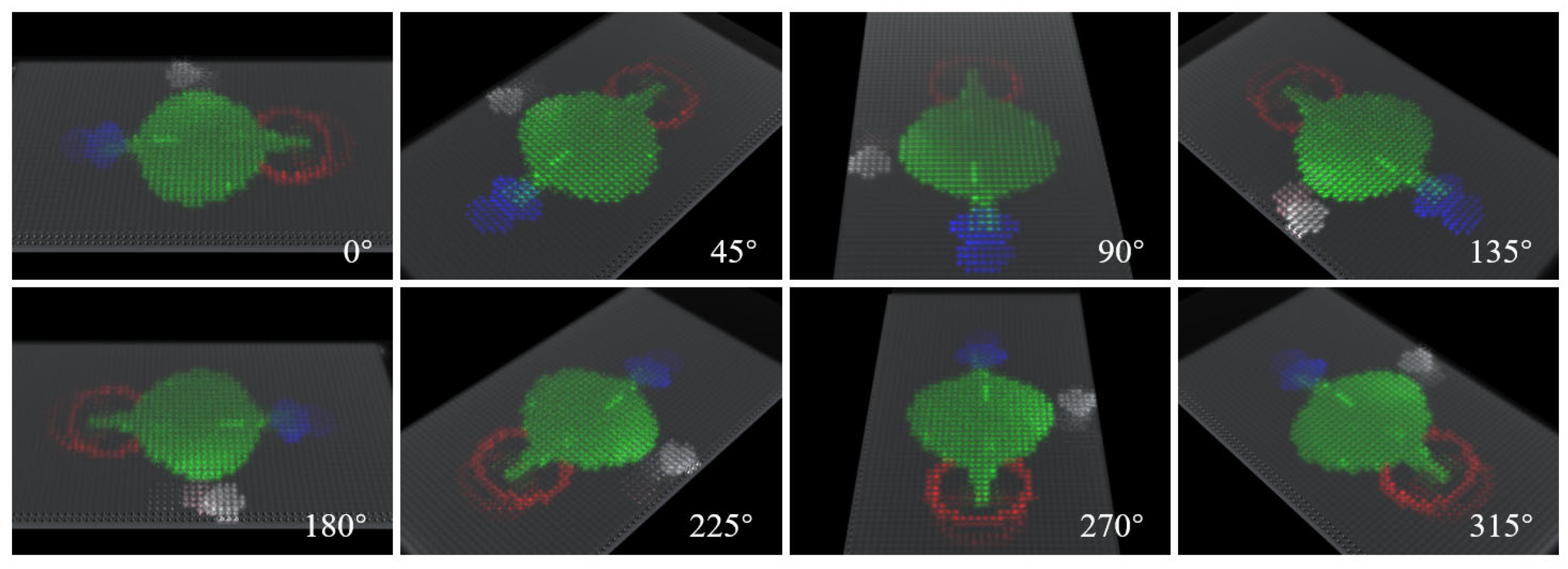
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, A.; McDowall, I.; Yamada, H.; Bolas, M.; Debevec, P. Rendering for an interactive 360° light field display. ACM Trans. Graph. 2007, 20, 40-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, R.; Hoshino, T.; Horry, Y. Transpost: 360 deg-viewable three-dimensional display system. Proc. IEEE 2006, 94, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S. fVisiOn: 360-degree viewable glasses-free tabletop 3D display composed of conical screen and modular projector arrays. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 13194–13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Shen, W. A 360-degree floating 3D display based on light field regeneration. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 11237–11247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Qiao, W. 56-2: Tabletop 3D display with triple viewing zones. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2019, 50, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Dong, H.; Gao, X.; Fu, B.; Pei, X.; Zhao, S.; Yan, B.; Sang, X. 360-degree directional micro prism array for tabletop flat-panel light field displays. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 32273–32286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, Y.; Uchida, S. Table screen 360-degree three-dimensional display using a small array of high-speed projectors. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 8848–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiguchi, M.; Sakamoto, D.; Takada, H.; Honda, K.; Ono, T. Interactive 360-degree glasses-free tabletop 3D display. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Sapporo, Japan, 20–23 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Takaki, Y.; Nakamura, J. Generation of 360-degree color three-dimensional images using a small array of high-speed projectors to provide multiple vertical viewpoints. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 8779–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Yan, Z.; Jing, T.; Zhang, P.; Lin, M.; Li, P.; Jiang, X.Y. Enhancement of effective viewable information in integral imaging display systems with holographic diffuser: Quantitative characterization, analysis, and validation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 161, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Deng, H.; Yang, C.N.; Chen, Y.A.; Zhao, C.J.; Tang, J. Sub-pixel marking and depth-based correction methods for the elimination of voxel drifting in integral imaging display. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 12243–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Guo, Z.D.; Deng, H.; Yang, C.N.; Bai, Y.C. Integral imaging three-dimensional display system with anisotropic backlight for the elimination of voxel aliasing and separation. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 29132–29144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, J.; Son, Y.; Choi, K. Crosstalk reduction in voxels for a see-through holographic waveguide by using integral imaging with compensated elemental images. Photonics 2021, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Chu, F.; Lin, F.C.; Hu, Y.X.; Li, Y.L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.H. Wide-viewing-angle color holographic 3D display system with high brightness encoding. PhotoniX 2025, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Qiao, W.; Chen, L. Recent advances in planar optics based glasses-free 3D displays. Front. Nanotechnol. 2022, 4, 829011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Hua, E.; Zhou, F.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Duan, H.; Hu, Y.Q.; Qiao, W.; Chen, L. Foveated glasses-free 3D display with ultrawide field of view via a large-scale 2D-metagrating complex. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, F.; Zhanghu, M.Y.; Yuan, Z.N.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, K.; Kwok, H.S.; Liu, Z.J. Ultra-low-defect homoepitaxial micro-LEDs with enhanced efficiency and monochromaticity for high-PPI AR/MR displays. PhotoniX 2024, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Yan, B.; Yu, C. 360 light field 3D display system based on a triplet lenses array and holographic functional screen. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2017, 15, 121201. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Xia, Y.P.; Zhang, H.L.; Cui, H.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, T.Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Integral imaging-based tabletop light field 3D display with large viewing angle. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2023, 6, 220178-1–220178-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sang, X.; Gao, X.; Yan, B.; Chen, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, P. 360-degree tabletop 3D light-field display with ring-shaped viewing range based on aspheric conical lens array. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 26738–26748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xia, Y.P.; Li, S.; Ren, H.; Wang, Q.H. Annular sector elemental image array generation method for tabletop integral imaging 3D display with smooth motion parallax. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 34706–34716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.P.; Li, S.; Ren, H.; Deng, H.; Xing, Y. High-efficient rendering to generate annular sector elemental image array for tabletop integral imaging three-dimensional display. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2021, 29, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Bai, J.; Wang, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, K. Comparison of two panoramic front unit arrangements in design of a super wide angle panoramic annular lens. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhu, R.; Gao, F.; Li, Z. Extremely wide-angle lens with transmissive and catadioptric integration. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T. Design of a panoramic annular lens with ultrawide angle and small blind area. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 5737–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wen, X.R.; Li, W.Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, Q.H. P-123: Analysis of light shaping diffuser in integral imaging based light field display. SID Symp. Digest Tech. Papers 2014, 55, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yan, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, P. Characteristics of the holographic diffuser in integral imaging display systems: A quantitative beam analysis approach. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 139, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Conic | 6.266 |
| Index of refraction | 1.497 | |
| 4th order term | −5.697 × 10−4 | |
| 6th order term | 2.079 × 10−5 | |
| 8th order term | −2.73 × 10−7 | |
| S2 | Conic | −5.666 |
| 4th order term | 4.752 × 10−4 | |
| 6th order term | −2.171 × 10−6 | |
| 8th order term | 8.093 × 10−8 | |
| S3 | Conic | 7.099 |
| Index of refraction | 1.497 | |
| 2nd order term | −1.802 | |
| 4th order term | 1.537 × 10−4 | |
| S4 | Conic | −7.733 |
| Index of refraction | 1.626 | |
| 2nd order term | 6.132 | |
| 4th order term | 4.752 × 10−4 | |
| S5 | Conic | 8.833 |
| 4th order term | 1.210 × 10−4 | |
| 6th order term | 3.174 × 10−6 | |
| 8th order term | 4.578 × 10−7 | |
| S6 | Conic | 5.799 |
| Index of refraction | 1.497 | |
| 4th order term | 1.701 × 10−5 | |
| 6th order term | −3.447 × 10−6 | |
| 8th order term | 2.064 × 10−8 | |
| S7 | Conic | −10.066 |
| S8 | Conic | 21.199 |
| Index of refraction | 1.626 | |
| 6th order term | 2.170 × 10−6 | |
| 8th order term | 1.093 × 10−8 | |
| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| 2D display panel | Pixel size | 0.09 mm |
| Dimension | 698.11(W)mm × 392.69(H)mm | |
| Resolution | 7680 × 4320 pixels | |
| Elemental image array | Number of elemental images | 64 × 36 |
| Size of elemental image (D) | 7.8 mm × 7.8 mm | |
| Panoramic annular lens array | Pitch | 7.8 mm × 7.8 mm |
| Thickness | 27.8 mm | |
| Number of lenses | 64 × 36 | |
| Lens layout | Rectangle | |
| Optical diffusing screen | Diffusion angle (θ) | 10° |
| Thickness of the diffusion layer (d) | 0.25 mm | |
| PC for generation of the elemental image array | CPU | Intel(R) Core™ i9-13900K |
| Main memory | 64 GB | |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX GeForce 4090 Laptop | |
| Main memory | 16 GB | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, M.-Y.; Zhao, C.-B.; Wen, X.-R.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, Q.-H.; Xing, Y. Tabletop 3D Display with Large Radial Viewing Angle Based on Panoramic Annular Lens Array. Photonics 2025, 12, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050515
He M-Y, Zhao C-B, Wen X-R, Liu Y-J, Wang Q-H, Xing Y. Tabletop 3D Display with Large Radial Viewing Angle Based on Panoramic Annular Lens Array. Photonics. 2025; 12(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Min-Yang, Cheng-Bo Zhao, Xue-Rui Wen, Yi-Jian Liu, Qiong-Hua Wang, and Yan Xing. 2025. "Tabletop 3D Display with Large Radial Viewing Angle Based on Panoramic Annular Lens Array" Photonics 12, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050515
APA StyleHe, M.-Y., Zhao, C.-B., Wen, X.-R., Liu, Y.-J., Wang, Q.-H., & Xing, Y. (2025). Tabletop 3D Display with Large Radial Viewing Angle Based on Panoramic Annular Lens Array. Photonics, 12(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050515





