Abstract
This article introduces the aptamer affinity column (AAC) with nucleic acid aptamer as an affinity ligand for the extraction of four aminoglycoside antibiotics (AGs). The AAC was prepared by loading the aptamer functionalized Sepharose into an extraction column, which was conjugated by covalent binding between NHS-activated Sepharose and amino-modified aptamers with a coupling time of 2 h. After the sample solution flowed through the AAC, the AGs were retained because of the affinity between the AGs and aptamer, then AGs were eluted and analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS. Under the optimized conditions, the maximum adsorption of AGs on the AAC could reach 8.0 μg. Moreover, the proposed AAC could be reused more than 20 times. The resultant AAC that conjugated with the aptamer was successfully applied in the enrichment and purification of four AGs in a milk sample and good recovery results in the range of 83.3–98.8% were obtained (with RSD in the range of 0.6–5.8%). The proposed AAC for recognition of multi-target AGs exhibited good enrichment and purification effects, showing great application potential for targets with their related aptamers.
1. Introduction
Aminoglycoside antibiotics (AGs), as a kind of broad-spectrum antibiotics, are made up of one or more amino sugar molecules and amino cyclic alcohol linked by glycosidic bonds [1]. With a lot of amino groups and hydroxyl groups, AGs exhibit high polarity and strong hydrophilicity, and are slightly soluble in methanol and insoluble in non-polar organic reagents. AGs mainly include Kanamycin (KANA), Kanamycin B (KANB), Amikacin (AMI), Streptomycin (STR), Neomycin (NEO), Tobramycin (TOB), Gentamicin (GEN), and Amikacin (AMK). AGs are mainly used in the treatment of moderate and severe respiratory tract infections, intestinal infections, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and so on. It inhibits bacterial growth and reproduction by binding to bacterial ribosomes and destroying bacterial cell membrane structure [2]. However, the unreasonable use of drugs and the abuse of antibiotics cause severe residues in food. AGs have a high affinity to human tissues and cannot be metabolized for a long time, which results in potential damage to humans [3]. Thus, the Ministry of Agriculture of China, the FDA of the United States, and the European Union have all established clear regulations on the maximum residue limits of AGs [4], to minimize the risk of drug residues, as shown in Table 1. Therefore, it is necessary to establish an easily operable and effective way for the enrichment and purification of AGs in foods.

Table 1.
Maximum residue limits (MRLs) of some aminoglycosides in various countries.
At present, the analysis of AGs is focused on the following three techniques: instrumental, immunoassay [5], and microbiological assays. Immunoassay and microbiological methods are relatively simple, but the detection time is long, the accuracy of the experiment is low, and the antibiotics with similar structures may interfere with the test results causing false positive results. Instrumental methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to a UV detector [6,7], capillary electrophoresis coupled to tandem mass spectrometry [8], ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) [9,10]. AGs are highly polar compounds with poor retention in traditional reverse phase liquid chromatography, and because of lack of chromophore and fluorophore [11], results for AGs cannot be detected directly by UV or fluorescence detectors unless dispensed by a derivative method [12]. However, such derivatives lead the HPLC instrument conditions more complex, and additional processing steps result in the loss of analytical substances, excessive reagents, and other uncertain factors in analytical results. UPLC-MS shows advantages in screening, identifying, and quantifying AGs due to its high accuracy and sensitivity. Due to the special properties of AGs, some sample pretreatment processes are needed before UPLC-MS detection. In the traditional pretreatment method-solid-phase extraction (SPE), poor recognition of the SPE column may lead to poor purification effect, poor detection sensitivity, and poor recovery caused by the influence of miscellaneous peaks in sample matrix [13]. In general, immunoaffinity columns (IAC) are also used for extraction and separation prior to sample analysis, where the target is identified by antigen–antibody interaction, showing superior performance in recognition specificity. However, as an important part of IAC, antibody synthesis is affected by many conditions, such as temperature, pH, ion environment, resulting in large differences between batches and poor stability. Additionally, AGs as small molecule semi-antigen, which cannot stimulate the body to produce corresponding antibodies, resulting in much more difficult for highly sensitive antibodies preparation.
An aptamer, which is called a “chemical antibody”, refers to the short single-stranded oligonucleotides (DNA or RNA) selected from the combinatorial library by Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) [14]. Additionally, it can bind with different targets ranging from small molecules, and metal ions, to macromolecular proteins, polypeptides, and even cells, bacteria, and tissues. Aptamers may fold into secondary and tertiary structures in the presence of a target and bind to it with high affinity and specificity [15]. It not only has the function of an antibody but also overcomes the defects of antibodies, showing good stability, easy synthesis, and costlessness. The aptamer is a good substitute for an antibody with wide application prospects. Furthermore, it has been widely used in sample pretreatment, biosensing, drug delivery, and immune therapy. In this work, taking advantage of an aptamer that can be easily modified with different groups to achieve coupling with other materials [16], we developed an aptamer-based affinity column (AAC) for the recognition of multi-target AGs for the first time. The aptamer we used was selected by Song and co-workers [17], which had a good affinity to KANA, KNANB, and TOB. Based on this result, we developed AAC for the recognition of multi-target AGs. AAC was prepared by the conjugation of -NH2 modified aptamer and N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-modified agarose, and finally was successfully used in the extraction of AGs in milk substrates. Such AAC exhibits great application potential for various targets with their related aptamers in the diverse complex sample matrix.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
Xevo TQ-S UPLC-MS/MS (Waters Company, MA, USA); 0.22-μm polytetrafluoroethylene syringe filter (Tianjin JinTeng Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd., Tianjin, Chia), DHM200 scroll oscillator (Ningbo Luoshan Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China); FE28 pH meter (Shanghai Mettler-Toledo instrument Co., Ltd., Ihanghai, China); 3–30 K table freezing centrifuge (Sigma centrifuge Co., Ltd., MO, USA). Empty reversible cartridges with 1 mL capacity and its sieve plate with a 10-μm aperture (1 mL with flange column, Tianjin Eger Fenome Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China).
All oligonucleotides (TGGGGGTTGAGGCTAAGCCGA [17]) were synthesized, modified, and then HPLC-purified by Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). TOB, KANA, KANB, AMI (all from Dr. Ehrenstorfer Co., Ltd., Augsburg, Germany), NHS-activated Sepharose (90 μm, GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK), methanol of HPLC grade was provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Ultra-pure water is prepared by the Milli-Q system (American Millipore Company, MA, USA).
Reaction buffer contains 100.0 mM MES,150.0 mM NaCl (pH 6.0); blocking buffer contains 150.0 mM NaCl and 0.2% BSA (pH 6.0); washing buffer contains 50.0 mM Tris-HCl and 150.0 mM NaCl (pH 7.2); binding buffer contains 20.0 mM Tris-HCl, 50.0 mM NaCl, 5.0 mM KCl, 5.0 mM MgCl2 (pH 7.5); elution buffer contains acetonitrile:water:formic acid (40:55:5); and the phosphate extract buffer contains 1 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.4 mM Na2EDTA and 0.15% trichloroacetic acid. All other reagents were at least of analytical grade, without further purification.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Conditions of Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
Chromatographic conditions: ACQUITY UPLC ®BEH Amide column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm, Waters Company, MA, USA), injection volume 5.0 μL, column temperature 40 °C, mobile phase: 5.0 mM ammonium acetate containing 0.2% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile (B). The gradient elution procedure is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Gradient elution procedure for UPLC.
Mass spectrometry conditions: the triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was used as the detector and the detection mode was multi-reaction monitoring (MRM), positive ion scanning. The conditions are as follows: electrospray ion source, electrospray ion source temperature: 150 °C, capillary voltage: 3.5 kV, atomizer temperature: 500 °C, atomizer flow rate: 800 L/h. The mass spectrometry conditions such as qualitative and quantitative ion pair (M/Z), conical hole voltage (Cone), and collision energy (CE) are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
MRM transitions and mass spectrometric condition parameters of four compounds.
2.2.2. AAC Preparation
Compared with the traditional agarose gel activated by streptavidin and hydrogen bromide, the amino group can covalently bind to NHS with a coupling time of only 2 min, which is much quicker than that of most reported AAC coupling methods [18,19]. AAC is highly stable and can be stable for two months. First, 1 OD 3′-NH2 modified aptamer dissolved in 500 μL reaction buffer was heated at 95 °C for 5 min and left to stand at room temperature. Then, 300 μL NHS activated agarose was washed with 1 mL anhydrous ethanol two times to remove isopropanol [20]. Then the aptamer and agarose solutions were mixed and incubated for 2 h. The supernatant was removed through centrifugation and then 1.0 mL of blocking buffer was added to block the unreacted NHS for two hours. Finally, the suspension was loaded into a 1.0 mL SPE column and washed with 5.0 mL cleaning buffer. The as-prepared AAC was stored at 4 °C and activated with 5 mL binding buffer before use.
2.2.3. Sample Extraction and Purification
A 5.0 mL milk sample and 45.0 mL phosphate extract were mixed and then centrifuged for 5 min at 10,000 rpm, and subsequently, the pH of the supernatant was adjusted to 6.5. After the AAC was balanced with 5.0 mL binding buffer in advance, a 10.0 mL sample was passed through the AAC at the rate of 1–2 drops per second. After the sample dropping was finished, the column was then washed with 1.0 mL binding buffer and flushed with 2.0–3.0 mL air. Then AGs were desorbed from AAC with 1.0 mL elution buffer. After flushing with air, the eluted AGs were collected, which were subsequently dried in nitrogen at 40 °C, redissolved in 1.0 mL 70% acetonitrile solution, and filtered by 0.22-μm microporous membrane before being analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Principle of AAC for AGs Extraction
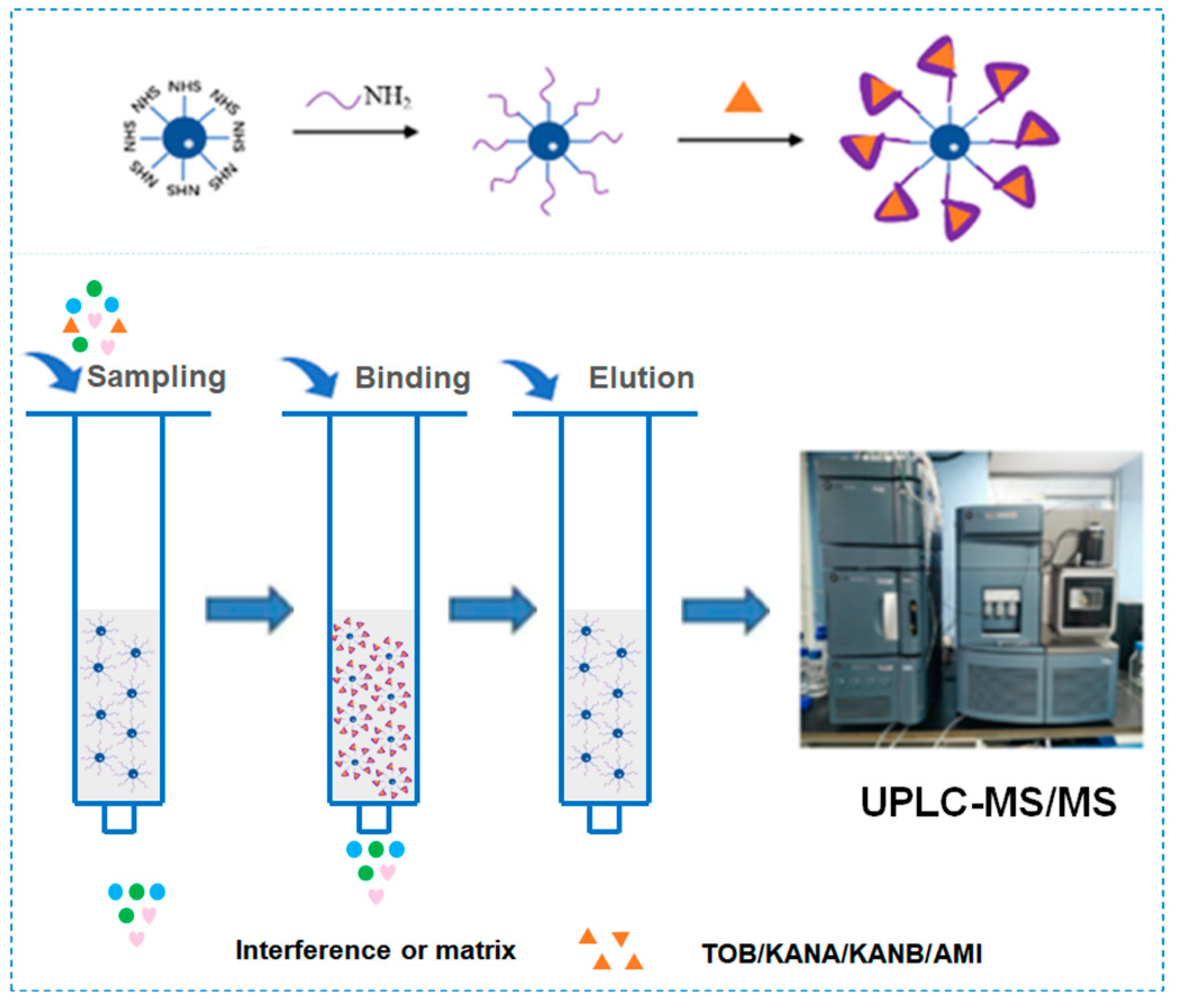
Amino-modified AGs aptamers were covalently coupled to NHS-activated agarose to prepare AAC for 4 AGs extraction in milk prior to analysis by UPLC-MS/MS (Figure 1). Due to the good affinity of AGs aptamer to AGs, AGs could be selectively adsorbed on aptamer–agarose surface during sample loading. Non-specific adsorbed impurities or interfering compounds could be easily removed in the washing step. Finally, the solution recovered by elution was analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS.
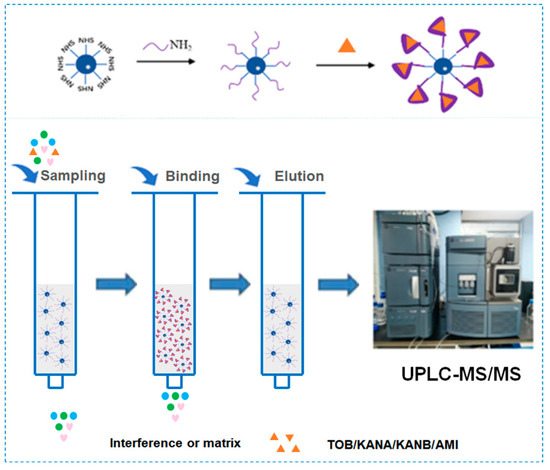
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of aptamer and agarose coupling and AAC working principle.
3.2. Optimization of Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometry Conditions
3.2.1. Chromatographic Column Optimization
AGs with multiple amino groups and hydroxyl groups are highly polar and have almost no retention on the commonly used reversed-phase chromatography C18 column [21]. In order to realize the retention on the reversed-phase chromatographic column for determination, heptafluorobutyric acid and trifluoroacetic acid were added into the mobile phase by the researchers [22]. However, the ion pair reagents irreversibly damage the chromatographic column, which greatly reduces the use time of the chromatographic column and increases the difficulty of instrument maintenance [23]. With the development of hydrophilic interaction chromatography, more and more researchers tend to use hydrophilic columns for the analysis of aminoglycosides. In this study, the separation behavior of two hydrophilic chromatographic columns, HILIC related column with unbounded silica [24] and the Amide column with hybrid particle substrate with amide groups, were studied. It was found that when using the HILIC column for AGs separation, the chromatographic peak tailing of each compound was more serious. The long equilibrium time of the HILIC column and the high proportion of organic solvents in the mobile phase leads to poor solubility of AGs [25]. While when there was 100-200 mM buffer salt in mobile phase, better separation and peak shape could be obtained. However, such a high concentration of salt would bring some pollution to mass spectrometry detector and reduce the sensitivity. Therefore, in this study, an amide amino column with good chromatographic peak shape of AGs was selected.
3.2.2. Selection of Mobile Phase
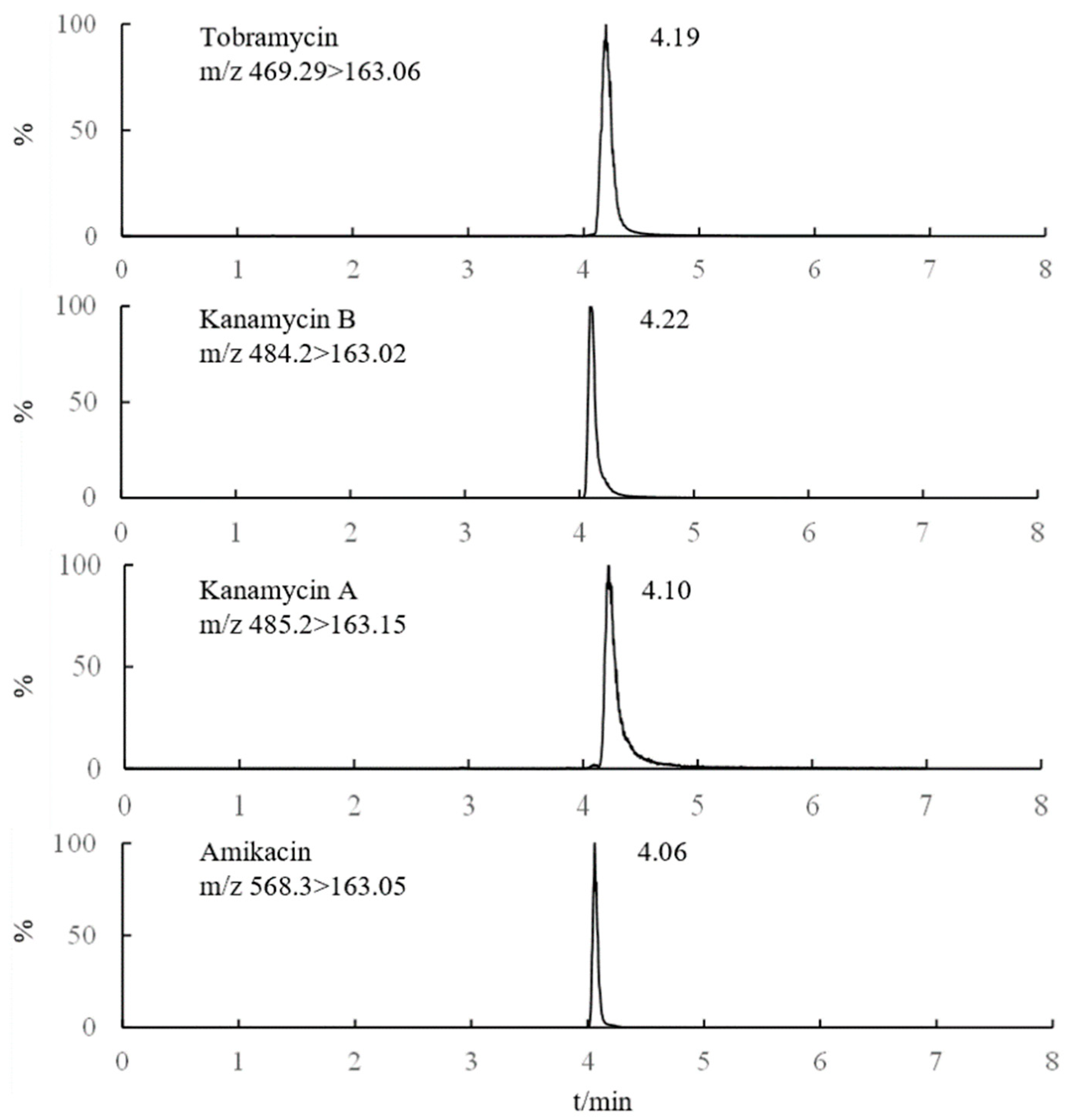
The retention time of AGs was longer with a high proportion of organic solvent in the mobile phase when analyzed by the Amide column. Therefore, the separation of AGs or impurities and AGs in the matrix could be realized by the use of a high proportion of organic phase in the initial stage of the gradient elution procedure, and gradually increase the proportion of the aqueous phase in the later stage. Thus, the influence of various mobile phases such as methanol-water, acetonitrile-water, methanol-formic acid solution, and acetonitrile-formic acid solution (the volume fraction of formic acid was 0.1–0.5%, respectively) on the AGs separation was investigated. The results showed that when methanol was used as the organic phase, the retention time and reproducibility of AGs were poor, which might be induced by the esterification of carboxyl on the surface of silica gel [26]. When only pure water was used as the aqueous phase, there was almost no peak in AGs. While obvious chromatographic peak could be observed, when formic acid was added in the aqueous phase. The addition of formic acid was helpful to the positive ionization of MS. Excellent peak shape could be observed when the volume fraction of formic acid was 0.2%. Furthermore, the response value and peak shape of the four AGs drugs were better when acetonitrile was used as the organic phase. Moreover, different concentrations of ammonium acetate (2.0-20.0 mM) in the aqueous phase were beneficial for the separation of AGs, and it was found that improved separation efficiency and relatively short retention time could be obtained with 5.0 mM ammonium acetate in the aqueous phase. Therefore, 0.2% formic acid (containing 5.0 mM ammonium acetate)–acetonitrile was used as the mobile phase. Under optimized conditions, the MRM chromatograms of the representative AGs are shown in Figure 2.
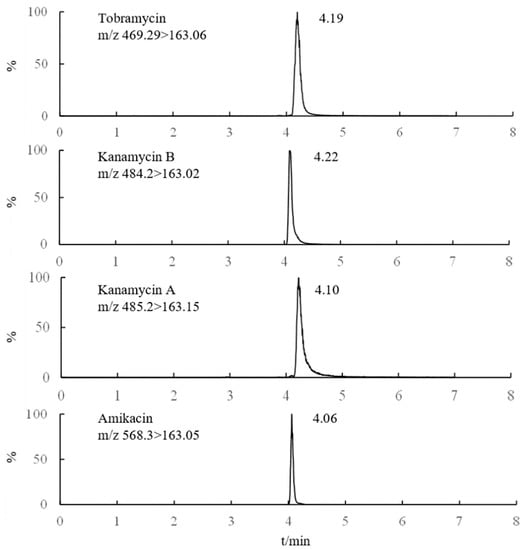
Figure 2.
MRM chromatograms of 4 Ags (1 μg/mL).
3.3. AAC Condition Optimization
3.3.1. Binding Buffer pH Optimization
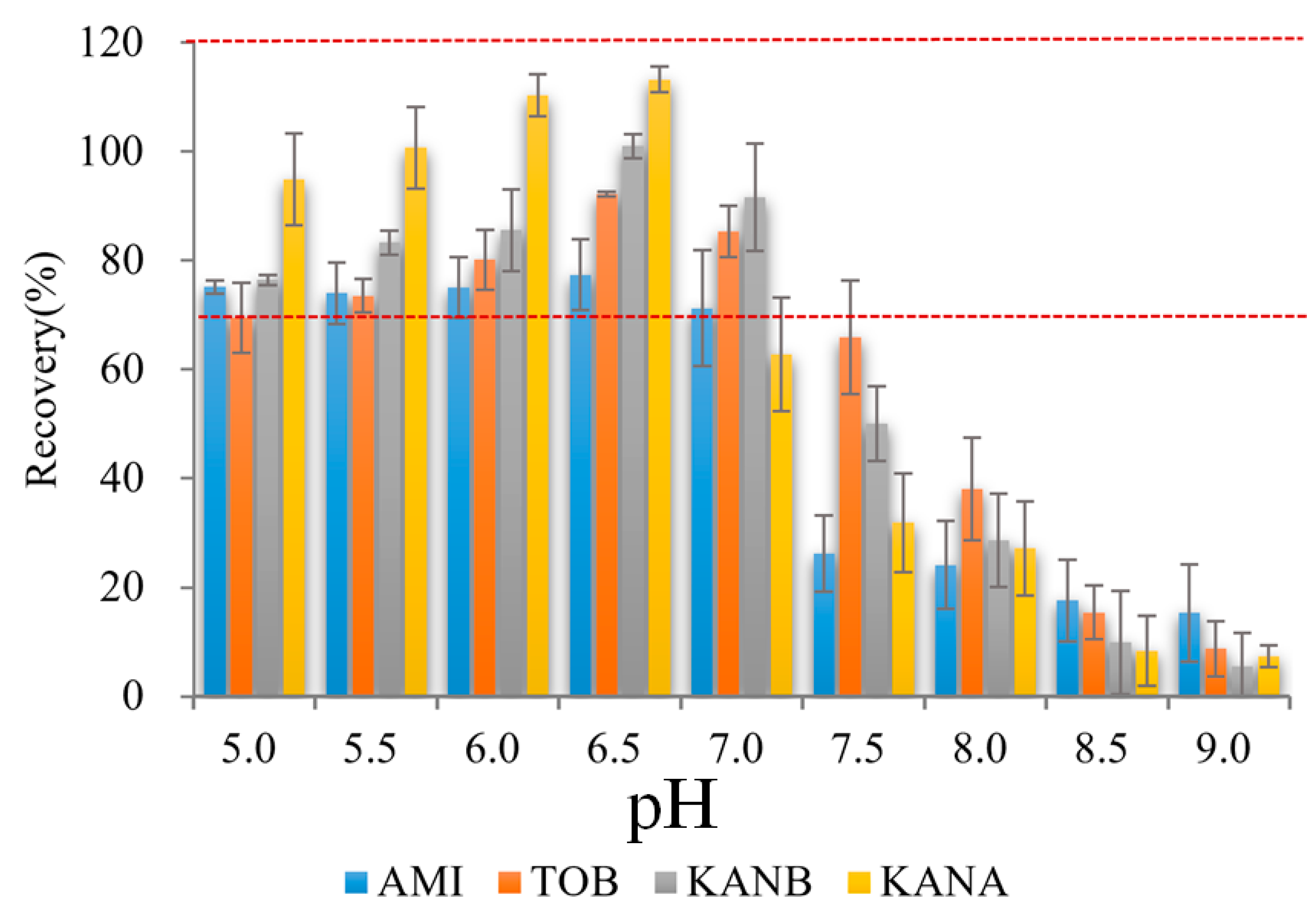
Binding buffer pH was important for AGs adsorption on AAC, which influenced the binding between the aptamer and AGs [27]. Thus, the effect of binding buffer pH on AAC adsorption was optimized. As shown in Figure 3, different pH of binding buffers (5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0) were prepared, and used as diluent to prepare 500.0 ng/mL mixed AGs solutions. After AGs loading, binding, and elution, the eluate was collected for UPLC-MS/MS detection. The recoveries of 4 AGs were the highest when the pH value was 6.5. Therefore, pH 6.5 was used as the best sample solution pH in this experiment.
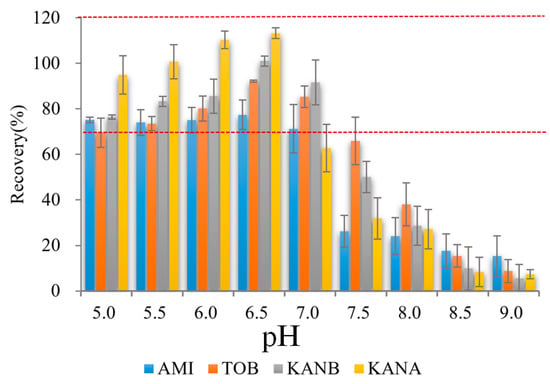
Figure 3.
Effect on analytes recoveries of binding buffer pH (n = 3) (Red dash lines reprensents the recoveries form 70% to 120%).
3.3.2. Optimize Eluent Composition
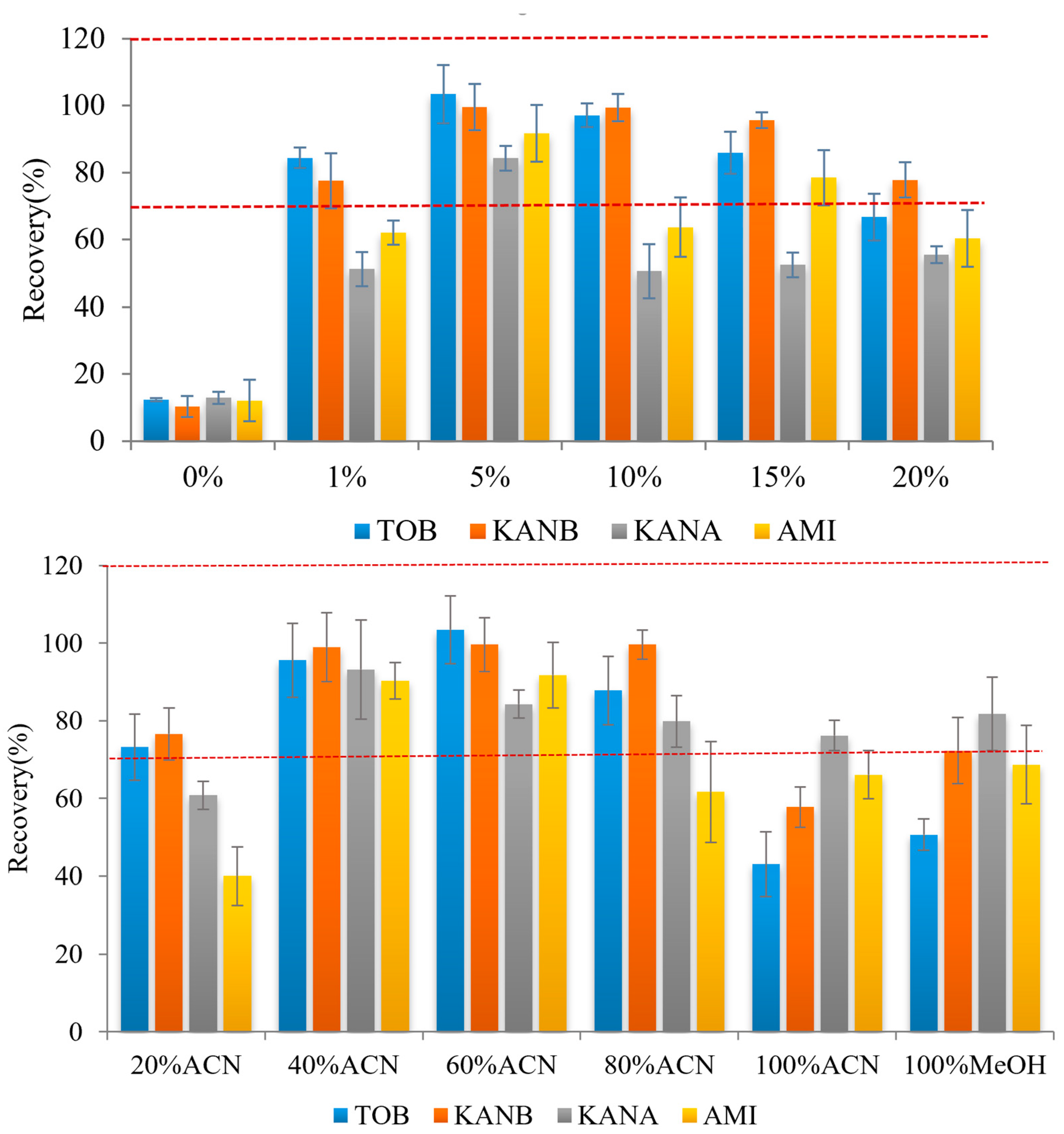
Ags are very soluble in water and insoluble in non-polar organic solvents. Direct use of organic solvents for elution leads to poor elution effects. Therefore, in this study, a different ratio of organic solvents with formic acid was added to adjust the eluent pH was optimized. Firstly, the ratio of formic acid was investigated, 1%, 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% formic acid were added into 40% acetonitrile as eluent for the AGs elution. The results showed that the target could not be completely eluted when the volume fraction of formic acid is too low (0% or 1%) or too high (10%, 15%, and 20%), and the four targets have the highest recoveries when the volume fraction of formic acid was 5% (Figure 4 top). Then the ratio of organic solvents was studied. Briefly, 1.0 mL 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100% acetonitrile and 100% methanol with 5% formic acid were used as eluent, respectively. It was found that when the concentration of acetonitrile in the eluent is 40%, all four kinds of AGs can be eluted, and the recovery is higher than 90% (Figure 4 bottom). Therefore, acetonitrile:water:formic acid (40:55:5) was selected as the eluent in this experiment.
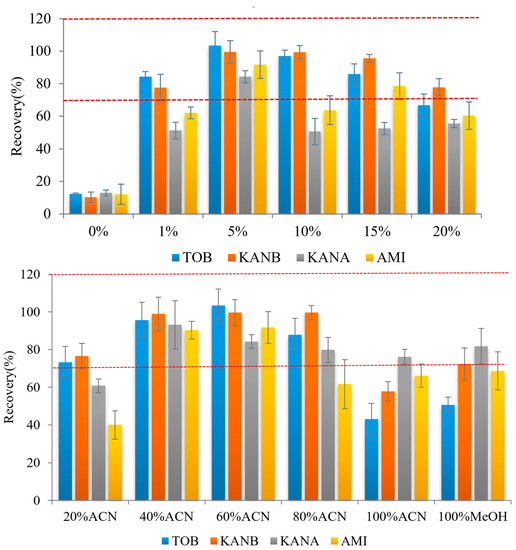
Figure 4.
Effect on analyte recoveries of formic acid (top) and ACN content (bottom) in the elution mixture (n = 3) (Red dash lines reprensents the recoveries form 70% to 120%).
3.3.3. Capacity of AAC
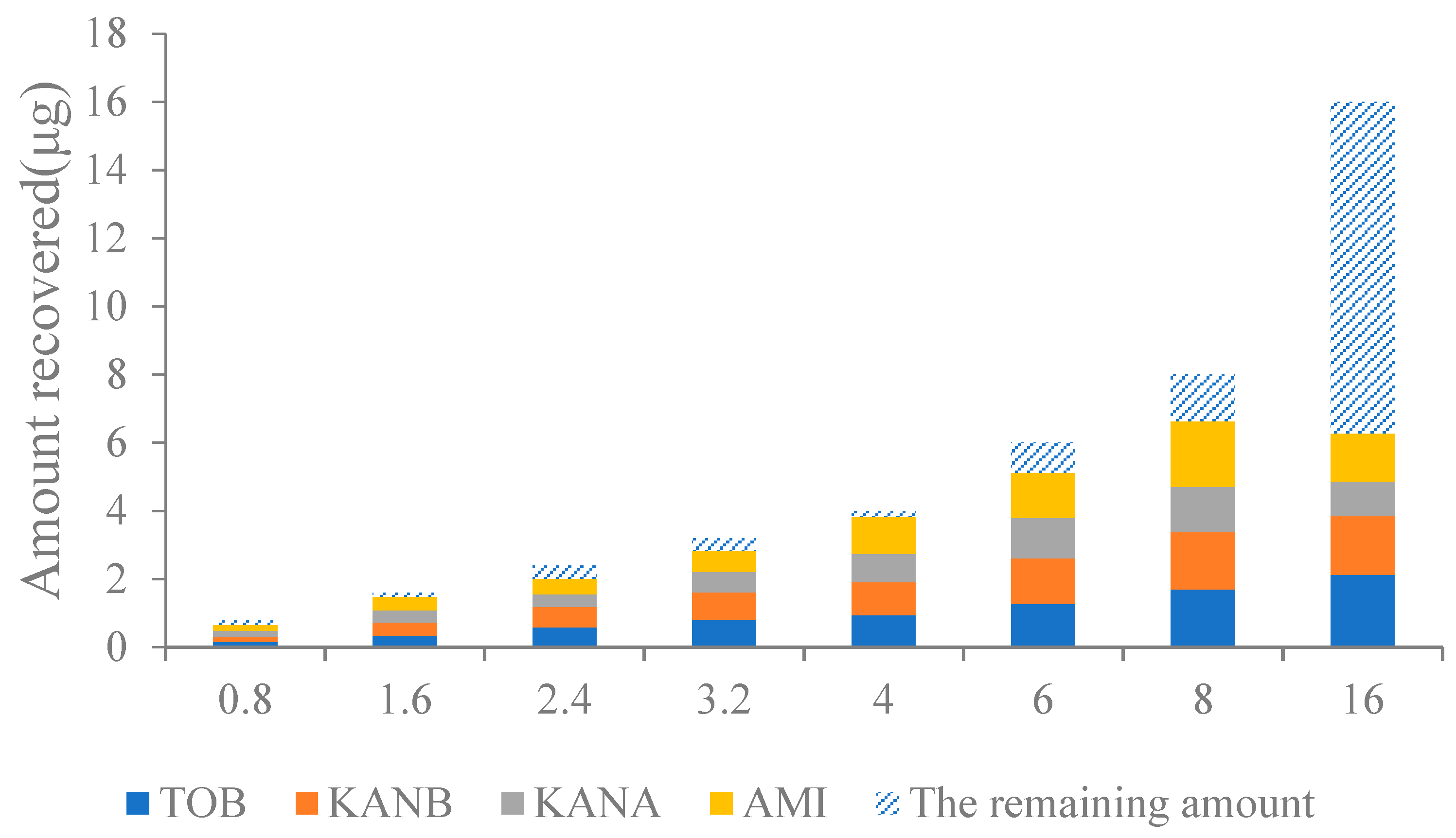
In this work, four kinds of AGs standards mixture (ranging from 0.8 to 16.0 μg) were loaded on the AAC, and the column capacity was investigated. As shown in Figure 5, when the total amount of AGs loaded in the column was 0.8–8.0 μg, the AAC could effectively retain almost all the targets, and the column capacity reached the maximum; when the total amount exceeded 8.0 μg, a large part of the targets could not be completely captured by the AAC, and the amount of recovery became reduced. Therefore, the maximum column capacity of the AAC is 8.0 μg.
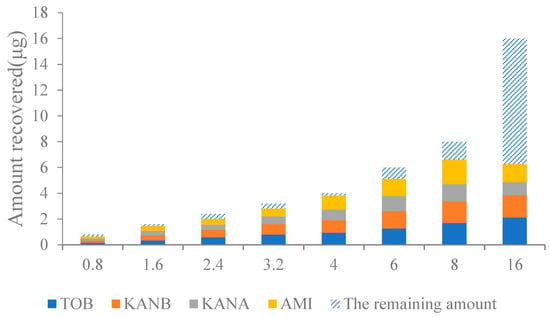
Figure 5.
Effect on analyte recoveries of the capacity of AAC column.
3.3.4. Regeneration and Reusability of AAC
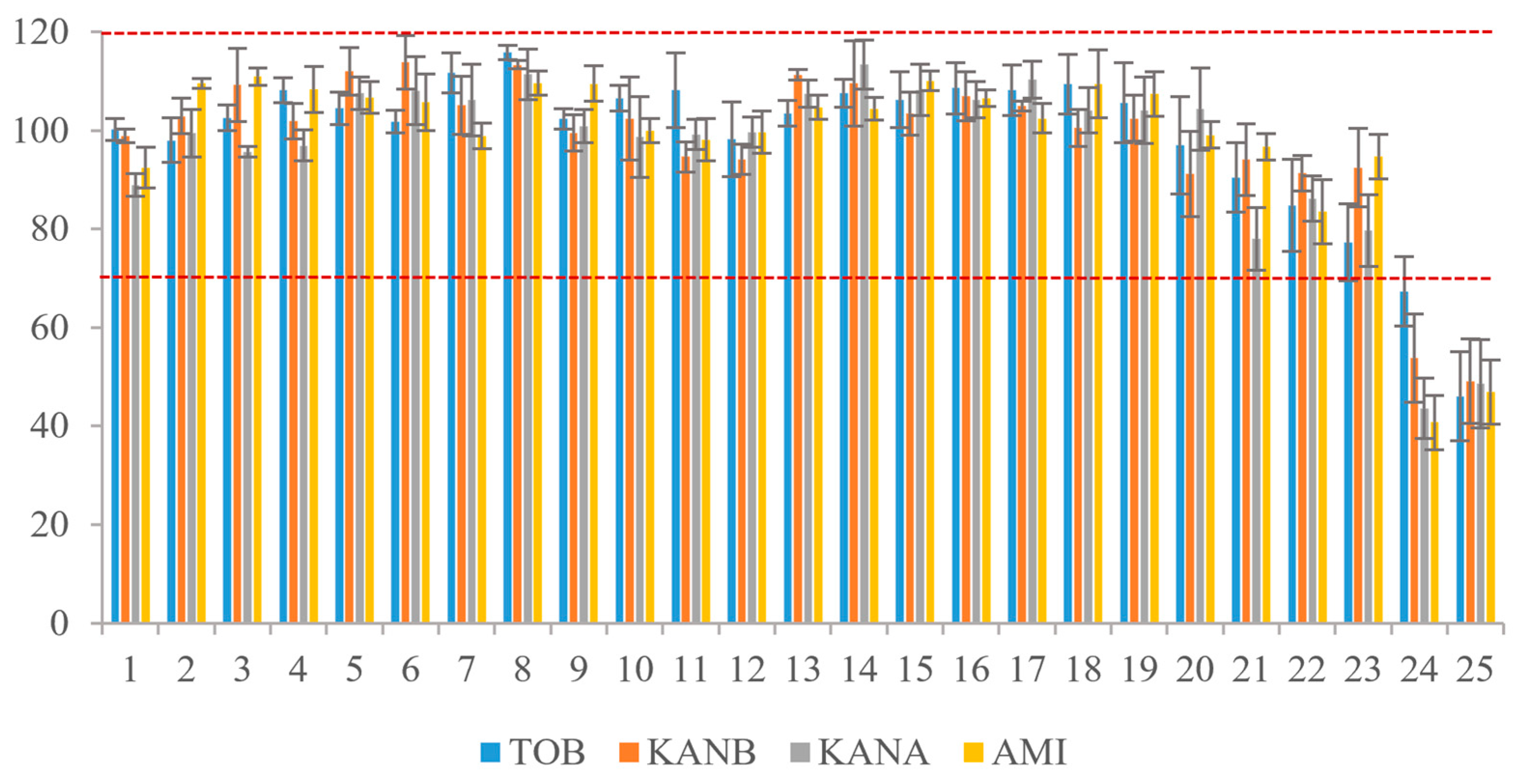
The AGs mixture was loaded on the affinity column for 25 consecutive times of extraction and purification. After each enrichment and purification, the 5.0 mL binding buffer was added to regenerate the AAC. After AAC repeated-use of 23 times, the recoveries of the four kinds of AGs were in the range of 77.3–113.4%, RSD was 0.8–9.9% (Figure 6). The results showed that the AAC could be reused more than 20 times without affecting the affinity of the aptamer to the target.
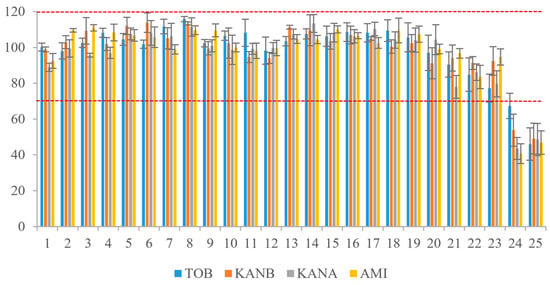
Figure 6.
Reuse times of AAC. (Red dash lines reprensents the recoveries form 70% to 120%).
3.3.5. Selectivity
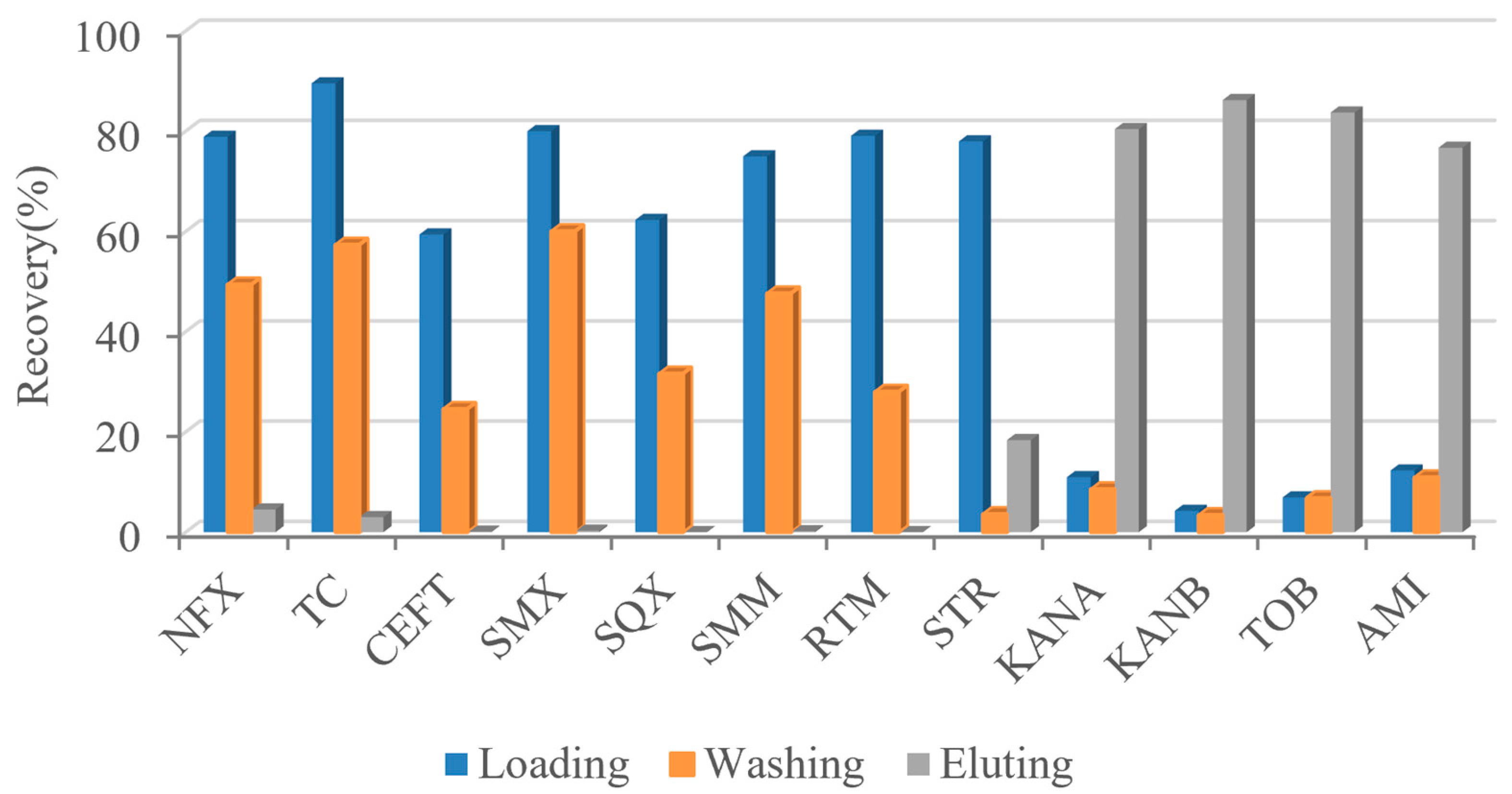
There are many kinds of antibiotics, which can be divided into β-lactam, macrolide, tetracycline, quinolone, aminoglycoside, and so on. Aminoglycoside antibiotics are glycoside antibiotics linked by amino sugars and amino cyclic alcohols through glycoside bonds. They have a common core structure (2-deoxystreptomycin cyclohexanol). Except for streptomycin, streptomycin contains streptavidin (cyclohexanol substituted with 2 amino groups). In order to investigate the specificity of AAC to AGs class, several representative antibiotics were loaded into AAC. Samples of 500 ng/mL norfloxacin (NFX), tetracycline (TC), cefoxitin (CEFT), sulfaparadimethoxine (SMX), sulfaquinoxazoline (SQX), sulfadimethoxine (SMM), roxithromycin (RTM), STR, KANA, KANB, TOB, and AMI were loaded into AAC, respectively. After loading, washing, and eluting, the eluting solutions were collected for the recovery determination of each component. As shown in Figure 7, all antibiotics except AGs were detected in the loading and washing part, that is, they could not be effectively captured by the AAC. STR did not retain in the AAC that well, because it did not have the mother nuclear structure recognized by aptamers. The other four kinds of AGs displayed high recoveries in the eluent. Therefore, it could be concluded that AAC has good specificity for AGs.
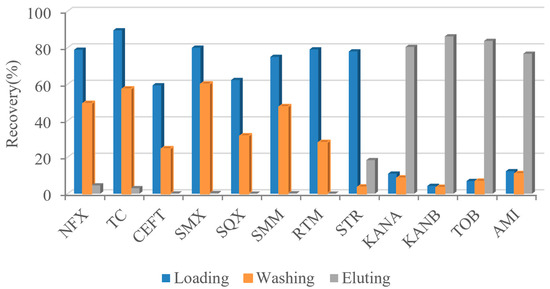
Figure 7.
Specificity of AAC to AGs.
3.4. Method Validation
In order to evaluate the feasibility of the proposed AAC for the 4 AGs adsorption in real samples, it was applied in AGs adsorption of AGs spiked milk samples. The amounts of AGs in milk samples were detected through UPLC-MS/MS method. The stock solutions of TOB, KANA, KANB, and AMI were prepared with 70% acetonitrile solution to form a series of standard working solutions with a mass concentration of 100.0–1000.0 ng/mL, which were tested by UPLC-MS/MS. The results are shown in Table 4. The four AGs showed a good linear relationship in the range of 100.0–1000.0 ng/mL with R2 all greater than 0.999, and the LODs were in the range of 4.0–11.3 ng/mL. The standard solution of low concentration was added to the blank sample, and the retention time and peak area were recorded after treatment according to the above method.

Table 4.
Linear equations of four kinds of AGs.
Blank milk samples were added with standard working solutions of TOB, KANA, KANB, and AMI equivalent to 100.0, 200.0, and 500.0 ng/mL, respectively. Three parallel samples were prepared in each group. The samples were treated and determined according to the established method, and the recoveries and RSDs were calculated. In Table 5, the average recovery of the four target substances in milk was 83.3–98.8%, and the RSD was 0.6–5.8%. It is proved that the method had good accuracy and precision and could meet the requirements for the detection of four kinds of AGs in milk. Compared with other methods (Table 6), the proposed AAC exhibited high affinity and specificity, was easily operated, and could be used for the purification and adsorption of other targets only through changing its related aptamer.

Table 5.
Results of standard recovery of 4 kinds of AGs samples (n = 3).

Table 6.
Comparison with other methods.
4. Conclusions
With the improvement of people’s living quality, environmental and food safety issues have attracted more and more attention. The threat of antibiotic residues in the environment and food to people has aroused more people to pay attention to how to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of AGs detection. In this paper, AAC was prepared with aptamers-conjugated-agarose instead of antibodies. The prepared AAC could not only overcome the inherent poor stability of IAC on the market but also realize the enrichment and purification of four AGs including TOB, KANA, KANB, and AMI at the same time, which greatly reduces the cost of the experiment. After the optimization of purification conditions of AAC, good recoveries in the range of 83.3–98.8% could be achieved in the analysis of milk samples. The column with good column capacity, selectivity, and repeatability showed great potential in enrichment and purification of different targets in various complex matrices by changing the type of aptamer.
Author Contributions
Methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, L.Z.; methodology, formal analysis, investigation, X.J., X.X., and N.W.; data curation, software, X.W.; supervision, funding acquisition, R.Y.; investigation, X.L.; resources, Z.L.; project administration, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and technology innovation special construction funded program of Beijing academy of agriculture and forestry sciences (KJCX20220140), Distinguished Young Scientists Program of Beijing Natural Science Foundation (JQ19023), Beijing Agricultural Forestry Academy Youth Foundation (QNJJ201903) and the Science and technology project of Beijing (Z211100007021006).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yue, F.L.; Li, F.L.; Kong, Q.Q.; Guo, Y.M.; Sun, X. Recent advances in aptamer-based sensors for aminoglycoside antibiotics detection and their applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Lu, A. Advances in the Application of Aptamer Biosensors to the Detection of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, F.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; Niessen, W.M.A. Challenges in the determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics, a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 890, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Wei, D.; Zeng, K.; Huang, z.; Du, D. Research progress on rapid analysis methods of aminoglycoside antibiotics in food. Jiangsu Agric. Sci 2019, 47, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Jiang, W.X.; Zhou, J.; Wen, K.; Wang, Z.H.; Jiang, H.Y.; Ding, S.Y. Production of Monoclonal Antibody and Development of a New Immunoassay for Apramycin in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3108–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchaert, B.; Huang, S.; Wach, K.; Adams, E.; Van Schepdael, A. Assay Development for Aminoglycosides by HPLC with Direct UV Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, F. Microwave-assisted derivatization-ionic liquid dispersion liquid-liquid microextraction-high performance liquid chromatography for determination of aminoglycoside antibiotic residues in milk. Mod. Food Technol 2014, 30, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-González, D.; Lara, F.J.; Jurgovská, N.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.M. Determination of aminoglycosides in honey by capillary electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry and extraction with molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Lightfield, A.R. Simultaneous analysis of aminoglycosides with many other classes of drug residues in bovine tissues by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using an ion-pairing reagent added to final extracts. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chai, T.; Mu, P.; Xu, N.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, Q.; Qiu, J. Multi-residue determination of 210 drugs in pork by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1463, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Tang, Y.; Fang, C.; Kong, C.; Yu, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, D. Simultaneous determination of ten aminoglycoside antibiotics in aquatic feeds by high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry with pass-through cleanup. Chirality 2020, 32, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, S. Determination of Ampramycin Sulfate in Premix by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Pre-column Derivatization. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 35, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Mastovska, K.; Lightfield, A.R.; Nuñez, A.; Dutko, T.; Ng, C.; Bluhm, L. Rapid analysis of aminoglycoside antibiotics in bovine tissues using disposable pipette extraction and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1313, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C.B.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Chen, Y.; Phang, W.-M.; Hashim, U. Aptamer-based ‘point-of-care testing’. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.I.; Alshaer, W. Therapeutic aptamers in discovery, preclinical and clinical stages. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röthlisberger, P.; Hollenstein, M. Aptamer chemistry. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-M.; Cho, M.; Jo, H.; Min, K.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, T.; Han, M.S.; Ku, J.K.; Ban, C. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 415, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, D.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z. Preparation and evaluation of highly hydrophilic aptamer-based hybrid affinity monolith for on-column specific discrimination of ochratoxin A. Talanta 2019, 200, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Luan, Y.; Lu, A.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, J. An oligosorbent-based aptamer affinity column for selective extraction of aflatoxin B2 prior to HPLC with fluorometric detection. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kong, W.; Hu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.; Ouyang, Z. Aptamer-affinity column clean-up coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection for the rapid determination of ochratoxin A in ginger powder. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z.; Cai, N. Immunoaffinity column purification-UPLC-MS/MS determination of three aminoglycoside antibiotics in fish and shrimp meat. Food Sci 2018, 39, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.; Ding, L.; Zhu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Fu, S.; Wang, L. Determination of 10 aminoglycoside antibiotic residues in dairy products by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chromatography 2012, 30, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, P.; Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Kong, X.; He, H. Simultaneous determination of 10 antibiotics in pharmaceutical wastewater by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chromatography 2015, 33, 722–729. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-González, D.; Hamed, A.M.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Evaluation of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and extraction with molecularly imprinted polymers for determination of aminoglycosides in milk and milk-based functional foods. Talanta 2017, 171, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, C. Optimization and application of parallel solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 11 aminoglycoside residues in honey and royal jelly. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1542, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Analysis and Determination of Aminoglycoside Drugs in Feed and Environmental Water; South China Agricultural University: Guangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.; Wei, J.; Yan, J.; Jin, G.; Ding, J.; Yang, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liang, X. Two-dimensional solid-phase extraction strategy for the selective enrichment of aminoglycosides in milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L. Synthesis of dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for solid phase extraction of aminoglycosides antibiotics from environmental water samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. A polyvinyl alcohol-functionalized sorbent for extraction and determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics in honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1403, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Ji, S. A polyvinyl alcohol-coated core-shell magnetic nanoparticle for the extraction of aminoglycoside antibiotics residues from honey samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokh, S.; El Hawari, K.; Nassar, R.; Budzinski, H.; Al Iskandarani, M. Optimization of a solid-phase extraction method for the determination of 12 aminoglycosides in water samples using LC–ESI–MS/MS. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).