Abstract
Zingiber montanum (J. Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr. (Zingiberaceae) is known as “Banada” in Bangladesh, and the rhizomes are frequently used in traditional medicines for the treatment of constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, stomach bloating, and as mosquito repellant. In this study, dried rhizomes were extracted successively with 95% and 50% ethanol and the combined extract was then subjected to various column chromatographic methods to isolate one sesquiterpenoid derivative, zerumbone (1) and five kaempferol derivatives, i.e., kaempferol 3-O-methyl ether (2), kaempferol 3-O-α-rhamnopyranoside (3), kaempferol 3-O-α-(4”-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside (4), kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside (5), and kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”,4”-di-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside (6). All compounds except 1 were isolated for the first time from the title plant.
1. Introduction
The Zingiberaceae family has about 50 genera distributed all over the world but mostly in Asia, Central America and Africa. Many plants of Zingiberaceae family are used as food, spice, and medicines [1]. The genus Zingiber consists of about 85 species [2] that are used for various purposes as food and medicine. Among them, Zingiber officinale Roscoe is the most widely used one. In Bangladesh, eight species of the genus Zingiber have been found, namely Z. capitatum Roxb., Z. montanum (J. Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr., Z. officinale Roscoe, Z. zerumbet (L.) Roscoe ex Sm., Z. roseum Roxb., Z. rubens Roxb., Z. salarkhanii Rahman et Yusuf. [3], and Z. spectabile Griff. [4].
Zingiber montanum (J. Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr. (Syns: Amomum cassumunar (Roxb.) Donn, Amomum montanum J. Koenig, Amomum xanthorhiza Roxb. ex Steud., Cassumunar roxburghii Colla, Jaegera montana (J. Koenig) Giseke, Zingiber anthorrhiza Horan., Zingiber cassumunar Roxb., Zingiber cassumunar var. palamauense Haines, Zingiber cassumunar var. subglabrum Thwaites, Zingiber cliffordiae Andrews, Zingiber luridum Salisb., Zingiber montanum (J. König ex Retz.) Theilade, Zingiber purpureum Roscoe, Zingiber purpureum var. palamauense (Haines) K.K.Khanna, Zingiber xantorrhizon Steud.) [5] is considered to be native to India and Bangladesh. It is also widely distributed in tropical countries [6] in Southeast Asia and cultivated in Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia [7]. In Bangladesh, it is commonly known as “Banada”, meaning wild ginger. The rhizomes of Z. montanum are used traditionally to treat constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, stomach bloating, and as mosquito repellant [8,9,10]. Previous pharmacological studies of Z. montanum have reported antimicrobial [11], anti-inflammatory [12,13], antioxidant [11], antihistaminic, smooth muscle relaxant [14], antifungal [15], insecticidal activity [16] and anticholinesterase activities [17]. There have been many studies on the volatile constituents of the rhizomes of Z. montanum and (E)-1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)butadiene, terpinen-4-ol and γ-terpinene [18], 1,4-bis (methoxy) triquinacene, (Z)-ocimene, terpinen-4-ol, γ;-terpinene, and β-phellandrene [19] were reported as its main constituents. A sesquiterpenoid, zerumbone as an antiulcer compound [8] and the complex curcuminoids, cassumunins A, B, C [12] and cassumunarins A, B, C [20] with potent antioxidant activities were also isolated from the rhizomes.
Various Zingiber plants including Z. montanum are reported to be used as a substitute and/or adulterant of Z. officinalis [21,22]. Recently, Z. montanum was also reported as an invasive species in many countries [22]. For the proper utilization of this plant, the detailed chemical analysis of bioactive compounds is necessary. Although there are many studies on volatile constituents of Z. montanum, very few studies have reported non-volatile constituents including phenolic compounds. Thus, in this study, we aimed for the isolation and identification of compounds from Z. montanum collected from Bangladesh.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
1H-, 13C- and 2D-NMR spectra were measured on an AVANCE 600 NMR spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) (1H-NMR: 600 MHz and 13C-NMR: 150 MHz). Chemical shift values (δH and δC) are given in ppm with reference to tetramethylsilane (TMS). Column chromatography was carried out with MCI gel CHP20P (75–150 μm, Mitsubishi Chemical Industries Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), Sephadex LH-20 (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Tokyo, Japan), and silica gel 60 (0.040–0.063 mm, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on a precoated silica gel 60 F254 (Aluminum sheet, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Structures of compounds were drawn using the software ChemBioDraw Ultra 14.0 (CambridgeSoft Corporation, PerkinElmer Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA).
2.2. Plant Materials
Fresh rhizomes of Z. montanum were collected from Gazipur central area, Gazipur district, Bangladesh in January 2018 and identified by Dr. Mohammad Sayedur Rahman, Senior Scientist, Bangladesh National Herbarium, Dhaka, Bangladesh. A voucher specimen (No. DACB-45749) is deposited at the Museum of Bangladesh National Herbarium.
2.3. Extraction and Isolation
Shade dried rhizomes of Z. montanum (1200 g) were extracted successively with 95% EtOH and 50% (8 L, two times each for 72 h) at room temperature. The filtered extracts were then combined and evaporated by using a rotary evaporator to obtain 132.5 g of dried extract. The extract was then suspended in water (1000 mL) and extracted with hexane (1000 mL, 3 times) to obtain a hexane fraction and a water-soluble fraction. The hexane fraction (28.6 g) was subjected to silica gel CC (Hex: EtOAc = 10:1) to obtain compound 1 (6412.0 mg). The water-soluble fraction (101.0 g) was subjected to MCI gel CHP20P column chromatography (CC) and eluted successively with water, 40%, 70% and 100% MeOH to give 11 fractions (1–11). Among them, fraction 5 (1.6 g), 6 (1.0 g) and 7 (1.3 g) were mixed and subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to afford 6 fractions (Fr. 5-1–5-6). Subfraction 5-2 (1.3 g) was further subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to obtain compound 6 (34.0 mg). Subfraction 5-3 (340 mg) was subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to obtain compound 5 (5.1 mg). Fraction 5-4 (170 mg) was subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to obtain seven subfractions (5-4-1~5-4-7). Subfraction 5-4-2 (65 mg) was again subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to obtain compound 4 (15.3 mg). Subfraction 5-4-5 was obtained as compound 3 (33.6 mg). Subfr. 5-5 (100 mg) was subjected to silica gel CC (CH2Cl2: MeOH: H2O = 9:1:0.1) to obtain compound 2 (13.9 mg) (Figure 1).
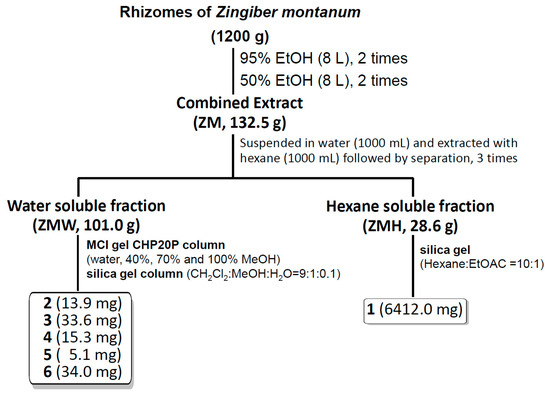
Figure 1.
Schematic flowchart of extraction and isolation of compounds from the rhizomes of Zingiber montanum.
3. Results and Discussion
The detailed chemical analysis of rhizomes of Z. montanum afforded a sesquiterpenoid derivative, zerumbone (1) [23] and five flavonoid derivatives, kaempferol 3-O-methyl ether (2) [23], kaempferol 3-O-α-rhamnopyranoside (3) [24,25], kaempferol 3-O-α-(4”-O-acetyl) rhamnopyranoside (4) [25,26], kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”-O-acetyl) rhamnopyranoside (5) [25] and kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”, 4”-di-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside (6) [23] (Figure 2). Compound 6 was obtained as a mixture with compounds 4 and 5. Structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of NMR spectral data (Table 1 for compound 1 and Table 2 for compounds 2–6) and comparison to literature values. To the best of our knowledge, all compounds except 1 were isolated for the first time from Z. montanum.
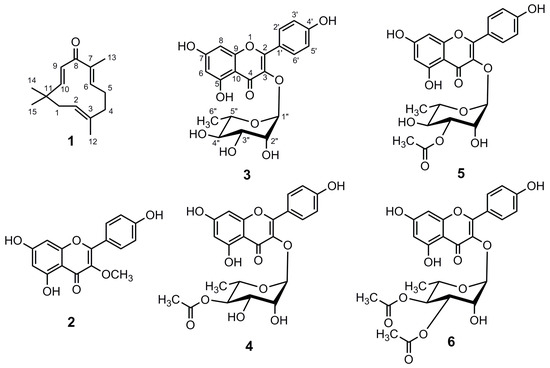
Figure 2.
Structures of compounds isolated from the rhizomes of Zingiber montanum.

Table 1.
NMR spectroscopic data of compound 1 in CDCl3.

Table 2.
NMR spectroscopic data of compounds 2–6 in CD3OD.
Zerumbone (1) was isolated in 1960 from Z. zerumbet Smith [27] and structurally characterized in 1965 [28]. Other than Z. zerumbet [25,29,30,31], it has also been reported from Z. montanum [8], Z. spectabile [4] and Z. aromaticum [31]. However, it should be noted that Dai et al. [31] reported Z. zerumbet and Z. aromaticum as separate species collected from the Philippines and Indonesia, respectively but The Plant List [5] currently includes Z. aromaticum Valeton as a synonym of Z. zerumbet (L.) Roscoe ex Sm. Thus, in the following discussion, the plant source names that authors mentioned in their articles are used irrespective of their current taxonomic classification. There have been extensive studies on zerumbone regarding various biological activities [32], including anti-inflammatory activity in acute lung injury after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration in mice [33], antiparasitic activity in protozoa [34], antioxidant, gastroprotective, antisecretory and anti- Helicobacter pylori activities [35], and protection of pancreatic β cell in high glucose induced apoptosis [36]. Similarly, it is reported to be effective in anticancer activity in human breast cancer [37], mouse skin cancer [38] and human cervical cancer cell lines [39]. It is also reported to be effective in protecting ultraviolet B-treated mice from cataractogenesis and photokeratitis [40]. As zerumbone was isolated in a large quantity from Z. montanum in our study, it may serve as a suitable source for the isolation of this bioactive compound.
Five kaempferol derivatives (2–6) isolated in this study have been reported to be present in many other plant species of the Zingibereceae family, and it showed a particularly close resemblance with Z. zerumbet. Kaempferol 3-O-methyl ether (2) was isolated previously from the rhizomes of Z. zerumbet [25,41,42], Z. spectabile [4], Z. aromaticum [43], and Roscoea purpurea [44], among others. Similarly, kaempferol 3-O-α-rhamnopyranoside (3) was isolated and identified from Z. ottensii [45], Z. aromaticum [42,43], and Z. zerumbet [30]. Kaempferol 3-O-α-(4”-O-acetyl) rhamnopyranoside (5) was isolated from Z. zerumbet [30,31,42], Z. spectabile [4,46], and Z. aromaticum [43]. Kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”-O-acetyl)rhamnopyranoside (5) was isolated from Z. zerumbet [25,30,42], Z. spectabile [4], Z. ottensii [45], and Z. aromaticum [43]. Kaempferol 3-O-α-(3”,4”-di-O-acetyl) rhamnopyranoside (6) was isolated from Z. zerumbet [23,29,30], Z. spectabile [4,46], Z. ottensii [45], and Z. aromaticum [31,43].
Recently, Jiang et al. [21] reported that Z. zerumbet and Z. montanum were closely related to Z. officinale on the basis of molecular analysis and volatile chemical constituents analysis, respectively. In this study, we observed that the major constituents (zerumbone and flavonoids) isolated form Z. montanum were isolated previously from Z. zerumbet, which showed its close resemblance with later species. Z. montanum may have the potential to be used as an alternative to Z. zerumbet as a spice and in medicines. However, further studies are necessary to provide more detailed chemotaxonomic evidences in the future.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, one sesquiterpenoid derivative, zerumbone (1) and five kaempferol derivatives (2–6) were isolated from the rhizomes of Z. montanum collected in Bangladesh. Further studies should be focused on the biological activity analysis of these compounds.
Author Contributions
T.I. and H.P.D. conceived and designed the experiments; M.M.H., A.A.-D., and H.P.D. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; M.M.H. and H.P.D. wrote the paper. All authors checked and approved the final version of manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Program for Leading Graduate Schools “HIGO” (Health Life Science: Interdisciplinary and Glocal Oriented), MEXT, Japan and Program for Building Regional Innovation Ecosystems at Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mohammad Sayedur Rahman, Senior Scientist, Bangladesh National Herbarium, Dhaka, Bangladesh for identifying the plant species.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Varoni, E.M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Matthews, K.R.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Kobarfard, F.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Mnayer, D.; Zakaria, Z.A.; et al. Plants of the genus zingiber as a source of bioactive phytochemicals: From tradition to pharmacy. Molecules 2017, 22, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabulal, B.; Dan, M.; John, A.J.; Kurup, R.; Pradeep, N.S.; Valsamma, R.K.; George, V. Caryophyllene-rich rhizome oil of Zingiber nimmonii from South India: Chemical characterization and antimicrobial activity. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2469–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Yusuf, M. Zingiber salarkhanii (Zingiberaceae), a new species from Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2013, 20, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, S.K.; Khatun, A.; Ohtsuki, T.; Ishibashi, M. First isolation of sesquiterpenes and flavonoids from Zingiber spectabile and identification of zerumbone as the major cell growth inhibitory component. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Plant List. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 19 April 2019).
- Sanatombi, R.; Sanatombi, K. Biotechnology of Zingiber montanum (Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr.: A review. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2017, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirugsa, P. Thai Zingiberaceae: Species Diversity and Their Uses. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amin, M.; Sultana, G.N.N.; Hossain, C.F. Antiulcer principle from Zingiber montanum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manochai, B.; Paisooksantivatana, Y.; Choi, H.; Hong, J.H. Variation in DPPH scavenging activity and major volatile oil components of cassumunar ginger, Zingiber montanum (Koenig), in response to water deficit and light intensity. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 2010, 126, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Kawahara, N.; Harada, M. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Zingiber cassumunar ROXB. and Its Active Principles. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2011, 39, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithayanukul, P.; Tubprasert, J.; Wuthi-Udomlert, M. In vitro antimicrobial activity of Zingiber cassumunar (Plai) oil and a 5% Plai oil gel. Phyther. Res. Int. J. Devot. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2007, 21, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Jitoe, A. Antioxidative and Antiinflammatory Compounds from Tropical Gingers: Isolation, Structure Determination, and Activities of Cassumunins A, B, and C, New Complex Curcuminoids from Zingiber cassumunar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthong, A.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Niwatananun, V.; Tuntiwachwuttikul, P.; Reutrakul, V. Anti-inflammatory activity of compounds isolated from Zingiber cassumunar. Planta Med. 1990, 56, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanapothi, D.; Soparat, P.; Panthong, A.; Tuntiwachwuttikul, P.; Reutrakul, V. A Uterine Relaxant Compound from Zingiber cassumunar. Planta Med. 2007, 53, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- bin Jantan, I.; Yassin, M.S.M.; Chin, C.B.; Chen, L.L.; Sim, N.L. Antifungal Activity of the Essential Oils of Nine Zingiberaceae Species. Pharm. Biol. 2003, 41, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, B.W.; Schwarz, B.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Insecticidal constituents from rhizomes of Zingiber cassumunar and Kaempferia rotunda. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonogi, S.; Chaiyana, W. Enhancement of anti-cholinesterase activity of Zingiber cassumunar essential oil using a microemulsion technique. Drug Discov. Ther. 2012, 6, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pongprayoon, U.; Soontornsaratune, P.; Jarikasem, S.; Sematong, T.; Wasuwat, S.; Claeson, P. Topical antiinflammatory activity of the major lipophilic constituents of the rhizome of Zingiber cassumunar. Part I: The essential oil. Phytomedicine 1997, 3, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.N.I.; Chowdhury, J.U.; Begum, J. Volatile constituents of essential oils isolated from leaf and rhizome of Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitoe, A.; Masuda, T.; Mabry, T.J. Novel Antioxidants, Cassumunarin A, B, and C, from Zingiber cassumunar. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xie, Z.; Koo, H.J.; McLaughlin, S.P.; Timmermann, B.N.; Gang, D.R. Metabolic profiling and phylogenetic analysis of medicinal Zingiber species: Tools for authentication of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.). Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invasive Species Compendium. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/ISC/datasheet/57536 (accessed on 19 April 2019).
- Nakatani, N.; Jitoe, A.; Masuda, T.; Yonemori, S. Flavonoid Constituents of Zingiber zerumbet Smith. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, K.R.; Chari, V.M. Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy of Flavonoids. In The Flavonoids; Harborne, J.B., Marby, T.J., Marby, H., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 19–134. ISBN 978-1-4899-2915-0. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Jitoe, A.; Kato, S.; Nakatani, N. Acetylated flavonol glycosides from Zingiber zerumbet. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2391–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Smith, J.A.; Lannigan, D.A.; Hecht, S.M. Three acetylated flavonol glycosides from Forsteronia refracta that specifically inhibit p90 RSK. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3974–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, S. Studies in sesquiterpenes-XVI. Zerumbone, a monocyclic sesquiterpene ketone. Tetrahedron 1960, 8, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, T.; Okamoto, T.; Hill, R.K.; Kawai, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Yonemori, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ohe, K.; Uemura, S.; Sawada, S. Chemistry of Zerumbone. 1. Simplified isolation, conjugate addition reactions, and a unique ring contracting transannular reaction of its dibromide. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2667–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, T.Y.; Chen, L.G.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, F.Y.; Wang, C.C. Anti-inflammatory constituents of Zingiber zerumbet. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslay, S.; Abas, F.; Shaari, K.; Zainal, Z.; Maulidiani; Sirat, H.; Israf, D.A.; Lajis, N.H. Characterization of the components present in the active fractions of health gingers (Curcuma xanthorrhiza and Zingiber zerumbet) by HPLC-DAD-ESIMS. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.R.; Cardellina, J.H.; McMahon, J.B.; Boyd, M.R. Zerumbone, an HIV-inhibitory and cytotoxic sesquiterpene of Zingiber aromaticum and Z. zerumbet. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1997, 10, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Moniri, M.; Moghaddam, A.B.; Rahim, R.A.; Bin Ariff, A.; Izadiyan, Z.; Mohamad, R. A Review of the biomedical applications of zerumbone and the techniques for its extraction from ginger rhizomes. Molecules 2017, 22, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.C.; Lee, S.S.; Yang, M.L.; Huang-Liu, R.; Lee, C.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Kuan, Y.H. Zerumbone reduced the inflammatory response of acute lung injury in endotoxin-treated mice via Akt-NFκB pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 271, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Singh, C.B.; Dey, S.; Mandal, S.; Ghosh, J.; Mallick, S.; Hussain, A.; Swapana, N.; Ross, S.A.; Pal, C. Induction of apoptosis by zerumbone isolated from Zingiber zerumbet (L.) Smith in protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani due to oxidative stress. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidahmed, H.M.A.; Hashim, N.M.; Abdulla, M.A.; Ali, H.M.; Mohan, S.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; Taha, M.M.E.; Fai, L.M.; Vadivelu, J. Antisecretory, gastroprotective, antioxidant and anti-Helicobcter pylori activity of zerumbone from Zingiber zerumbet (L.) smith. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zou, S.; Cui, Z.; Guo, P.; Meng, Q.; Shi, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, G.; Han, Z. Zerumbone protects INS-1 rat pancreatic beta cells from high glucose-induced apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, A.; Sakao, K.; Singh, S.V. Notch2 activation is protective against anticancer effects of zerumbone in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Ohnishi, K.; Murakami, A.; Lee, J.S.; Kundu, J.K.; Na, H.K.; Ohigashi, H.; Surh, Y.J. Zerumbone induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in mouse skin and cultured murine epidermal cells through activation of Nrf2. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, J.; Dhanya, B.P.; Greeshma, G.; Radhakrishnan, K.V.; Priya, S. Effects of a new synthetic zerumbone pendant derivative (ZPD) on apoptosis induction and anti-migratory effects in human cervical cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 278, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lin, D.P.; Su, K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Teng, M.; Tsai, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Chang, H. Dietary zerumbone prevents against ultraviolet B-induced cataractogenesis in the mouse. Mol. Vis. 2011, 723–730. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.Y.; Jang, D.S.; Han, A.; Jang, J.O.; Kwon, Y.; Seo, E.; Lee, H.J. Modulation of P-glycoprotein-Mediated Resistance by Kaempferol Derivatives Isolated from Zingiber zerumbet. Phytother. Res. 2007, 569, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subehan; Usia, T.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Constituents of Zingiber aromaticum and their CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inhibitory activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usia, T.; Iwata, H.; Hiratsuka, A.; Watabe, T.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Sesquiterpenes and flavonol glycosides from Zingiber aromaticum and their CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 inhibitory activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Devkota, H.P.; Joshi, K.R.; Malla, K.J.; Watanabe, T.; Yahara, S. Chemical constituents from the aerial parts and rhizomes of Roscoea purpurea. Jpn. J. Pharmacogn. 2014, 68, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Kikuzaki, H.; Aoki, T.; Okuda, A.; Lajis, N.H.; Nakatani, N. Terpenoids and a diarylheptanoid from Zingiber ottensii. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasothy, Y.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Mohamad, K.; Leong, K.H.; Ibrahim, H.; Sulaiman, S.F.; Ooi, K.L.; Awang, K. Spectaflavoside A, a new potent iron chelating dimeric flavonol glycoside from the rhizomes of Zingiber spectabile Griff. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3831–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).