Abstract
The swift progression of nanotechnology has transformed the food and dairy industries through the facilitation of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and antimicrobial systems. This review examines the environmentally friendly synthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) through the utilization of microorganisms, offering a sustainable and biocompatible alternative to traditional physical and chemical approaches. This study primarily aims to investigate the contemporary trends, mechanisms, and microbial species associated with NP biosynthesis, as well as to evaluate NPs’ techno-functional applications in food and dairy processing. The specific objectives encompass analysis of the synthesis pathways—both intracellular and extracellular—utilized by bacteria, fungi, yeasts, and algae. Additionally, an evaluation of the physicochemical properties and biological activities (including antibacterial, antioxidant, and antifungal effects) of synthesized NPs will be conducted, alongside the identification of their potential applications in food preservation, packaging, and fortification. The review emphasizes notable advancements in laboratory-scale applications, especially concerning yogurt fortification, biofilm suppression, and antimicrobial food coatings. Nonetheless, commercial application is constrained by issues related to scalability, purification, stability, regulatory adherence, and toxicity evaluation. Future investigations ought to focus on enhancing bioreactor systems, leveraging microbial consortia, utilizing food and agricultural waste as substrates, and implementing omics technologies to elucidate biosynthetic mechanisms. Furthermore, the standardization of synthesis protocols and the improvement of regulatory frameworks will be crucial in closing the divide between experimental achievements and NPs’ application in industry. In a nutshell, the microbial-mediated green synthesis of NPs offers a promising pathway for the advancement of safe, sustainable, and functional innovations within the food and dairy sectors.
1. Introduction
Nanotechnology has significant potential to revolutionize food systems by enabling the development of innovative products and expanding their range of applications, including bioactive compounds (BACs), nutraceuticals, functional food and dairy products, and pharmaceutical foods [,,,,,,,,]. This technology offers advanced methods for detecting pathogens in milk and milk products, thereby enhancing the quality and safety standards of dairy products [,,,,]. In the domain of food and dairy processing, nanoencapsulation is utilized to incorporate nano-sized elements and nutritional supplements, including proteins and antioxidants, along with additives such as flavors and colors, into functional foods [,]. This methodology effectively masks undesirable tastes and off-flavors, creates protective barriers, facilitates controlled release, and improves the bioavailability of various vitamins and their precursors.
Additionally, nanotechnology is being utilized to address food-related health challenges, including diabetes and obesity, and to develop specialized nutritional diets tailored for specific demographic groups, especially older people and individuals with diverse lifestyles [,,,,]. Furthermore, it enhances the sustainability of food production systems []. This technology facilitates the creation of devices designed for precise nutrient delivery through nutritional nano therapy [,,], as well as the development of advanced systems for controlled nutrient release via nanoencapsulation []. The development of nanoscale enzymatic reactors signifies a novel application, enabling the incorporation of new food products via fortification [,,]. Furthermore, electrospun nanofibers are garnering significant interest as materials for packaging and encapsulation, offering structured polymeric films with improved functionality [,,,,]. Thus, nanotechnology represents a multidisciplinary domain that investigates innovative approaches to address issues at the molecular and atomic scale through the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale [,,,,]. Nanotechnology involves the investigation, creation, production, and incorporation of intricate and accurately defined structures. The increasing prevalence of nanotechnology has led to significant advancements in sectors such as agriculture [,,], food production [,,,], and healthcare [,,]. The emergence of antibiotic resistance in bacterial populations represents a significant challenge within global health systems.
Within the last decade, nanoparticles (NPs) have come to represent highly effective nanomaterials utilized in the earlier specified fields [], exhibiting significantly enhanced biological properties such as antioxidant [,,], antibacterial [,,,,,,], antifungal [,,,], antiviral [,], and anticancer [,,] effects. Additionally, NP formulations enhance the delivery and dispersion of BACs and water-insoluble components []. The synthesis of green NPs using biological extracts is being increasingly recognized for its environmentally sustainable and economically viable processing methods, scalability, and, crucially, its applications in various fields, including the food [,,,], environment [,,], biological [,,], and healthcare and medical sectors [,,,,,,]. The green synthesis of NPs employs various biological sources, including bacteria [,,], yeast [,,,,], fungi [,,], algae [,,,,], plants [,,,,], and agro-industrial waste [,]. The characteristics of the NPs generated from these biological sources are subsequently examined in terms of size, morphology, chemical composition, and stability within a medium.
NPs are materials with minuscule dimensions, generally ranging from 1 to 100 nm in diameter, and display distinct properties when contrasted with their micron-scale counterparts (1–100 μm) [,,,,]. The nanoscale dimensions and high surface-area-to-volume ratio of NPs provide significant benefits, such as heightened chemical reactivity, improved energy absorption, and enhanced biological mobility [,,,]. A range of established methodologies are utilized for the synthesis of NPs, encompassing chemical, physical, and environmentally sustainable (green) synthesis techniques [,,]. This last method is frequently favored because of its ability to attain elevated purity levels, a manageable morphology, and a significant yield. The techniques employed include plasma chemical processes [], vapor deposition [,,], microwave irradiation [], pulsed laser techniques [,], sonochemical reduction [,,], ultrasound irradiation [], and gamma radiation [,].
The techniques developed for NP synthesis present distinct advantages and limitations, contingent upon the specific physicochemical properties of the NPs and their intended applications. Plasma chemical processes facilitate the generation of NPs that are both highly pure and uniformly sized via ionized gas-phase reactions []. However, scalability poses a challenge due to the intricate requirements of the instrumentation involved [,]. Vapor deposition techniques, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical vapor deposition (PVD), offer atomic-level precision and are widely utilized in the semiconductor and coating industries [,,,]. Nevertheless, their elevated costs and reliance on vacuum processes restrict their use in the synthesis of bulk NPs. Microwave irradiation provides a swift and energy-efficient method that improves reaction kinetics and crystalline quality; however, achieving uniform scalability continues to pose challenges [,]. Pulsed laser techniques, including pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL), enable the surfactant-free production of ultrapure NPs [,]. However, their limited yield and elevated operational costs confine their use to specialized applications [,,]. Sonochemical reduction, facilitated by acoustic cavitation, enables straightforward synthesis under ambient conditions while providing a degree of control over morphology; however, the reproducibility and uniformity of particles may fluctuate between different batches [,,]. Gamma radiation techniques employ ionizing energy for the synthesis of NPs without the need for reductants, presenting benefits in biomedical and sterile contexts. Nonetheless, issues pertaining to radiation safety and necessary infrastructure limit their application to regulated environments []. Consequently, the choice of synthesis method must be methodically aligned with the targeted characteristics of the NPs, the scale of production, and the particular industrial or biomedical application.
In contrast, chemical synthesis, a commonly employed technique, utilizes reducing agents in various environments, including polyol, microemulsions, thermal decomposition, and electrochemical reactions [,,,]. Nonetheless, both physical and chemical synthesis methodologies encounter obstacles, such as the necessity for high-purity materials, strict compliance with procedural protocols, significant financial expenditure, and possible biological risks associated with toxic byproducts. In contrast, green synthesis methods offer a sustainable and biocompatible alternative by utilizing natural reducing agents sourced from nonpathogenic or non-toxic microorganisms, such as bacteria [,,,], fungi [,,], yeast [,], and extracts derived from plants [,,]. Green synthesis presents significant benefits in terms of environmental impact and technical efficiency, as it reduces reliance on the toxic chemicals and harsh synthetic conditions traditionally used in NP fabrication [,,,].
In recent years, the synthesis of metallic NPs through eco-friendly methods has been increasingly incorporated food waste, especially in regions like West Asia. West Asia is commonly known as the Middle East. Turkey, Iran, Israel, Jordan, and Lebanon represent West Asian nations where such research and applications are presumably taking place, informed by the regional agricultural context and existing evidence [,,,]. These regions generate significant quantities of agricultural and food waste, thus providing a substantial and sustainable source of natural reducing agents for the synthesis of NPs. For example, extracts obtained from botanical sources, such as fruit peels, leaves, seeds, and vegetable byproducts, have effectively enabled the production of various metallic NPs [,,,,]. In a comparable context, various tropical countries with significant agricultural waste have utilized substances like papaya leaves, orange peels, and coffee grounds for the eco-friendly production of metallic NPs [,]. These organic sources contain a wealth of BACs, such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidants, which facilitate the reduction of metal ions and contribute to the stabilization of the resulting NPs.
Through the critical discussion in the preceding paragraphs based on the integration of results and findings from the previously published scientific literature, it can be inferred that there exist specific research gaps and a deficiency of consolidated papers presented on a singular platform. Such a compilation could provide valuable information aimed at aiding scientists in improving their critical thinking and analytical perspectives concerning their scientific projects and experimental endeavors. Consequently, this review paper aims to address various aspects to fill these research gaps and fulfill the requirements identified by the scientific community in the preceding discussion. This study seeks to outline current trends in the use of green nanotechnology, with a particular emphasis on the development of functional dairy products utilizing NPs produced via environmentally sustainable techniques. This study aims to thoroughly examine the synthesis of NPs utilizing biological sources, including bacteria, fungi, yeast, algae, and agro-industrial waste, highlighting their environmentally friendly and sustainable characteristics in contrast to conventional physical and chemical approaches. Furthermore, the review emphasizes the utilization of agricultural and food waste, especially in areas such as West Asia, as viable sources of natural reducing agents for the synthesis of metallic NPs. The paper further investigates the role of microbially synthesized NPs in improving food safety, quality, shelf life, and functionality within food packaging, preservation, nutrient delivery, pathogen detection, and quality enhancement in dairy products such as milk, yogurt, cheese, and meat. The discussion encompasses potential risks such as toxicity, environmental impacts, and consumer perception, while emphasizing the necessity for regulatory frameworks and safety assessments to guarantee safe implementation. Additionally, the paper aims to delineate future research developments, encompassing progress in synthetic biology, cohesive bioreactor systems, AI-enhanced optimization, and the utilization of waste-derived substrates to enhance the scalability, safety, and sustainability of NP applications within food systems.
2. Synthesis of Green Nanoparticles
NPs undergo comprehensive investigation through various physical and chemical methodologies (Figure 1); however, they exhibit unpredictability, high costs, and the potential to produce hazardous byproducts. Table 1 presents a comparative analysis of the high-cost factors associated with using physical and chemical methodologies for NP synthesis, emphasizing aspects such as equipment, energy consumption, material requirements, scalability, and operational complexity. Each method undergoes an assessment focused on its cost determinants, accompanied by estimated cost ranges where relevant and substantiated. A variety of synthetic methodologies have been employed to produce NPs with diverse morphologies and dimensions. As a result, the primary principle directing this research initiative is to carefully synthesize nanostructured particles using a methodology that is both efficient and mindful of environmental sustainability []. The literature has extensively documented that resources linked to green synthesis can function as bioresearch centers, enabling the synthesis of metallic and metal oxide NPs via a biomimetic approach that emulates natural processes [,,]. A diverse array of microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes [,,,,,,], as well as extracts obtained from plants [,,,,], have been recognized as effective and environmentally sustainable precursors for the successful synthesis of NPs aimed at particular applications [,,,,,,,]. Figure 2 demonstrates that biological sources such as plants and microorganisms (including bacteria, fungi, algae, and yeast), along with various waste materials, are utilized for the environmentally sustainable synthesis of green NPs. These biological agents provide a sustainable and non-toxic alternative to traditional chemical and physical methods for NP synthesis, in accordance with the principles of green chemistry and environmental sustainability [,,,].
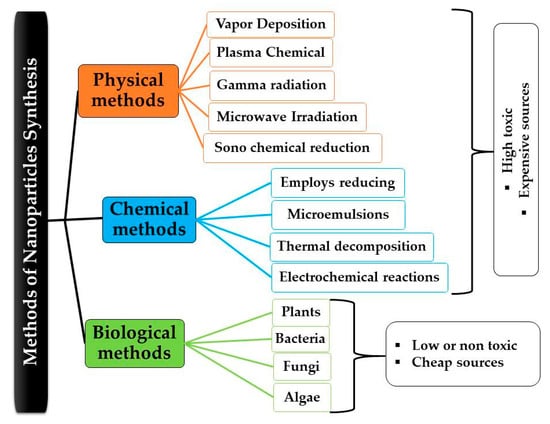
Figure 1.
Overview of nanoparticle synthesis techniques ranging from conventional physical and chemical approaches to eco-friendly biological methods employing microorganisms and plant extracts for reduced toxicity and environmental impact.

Table 1.
Comparative cost analysis of physical and chemical methods for nanoparticle synthesis.
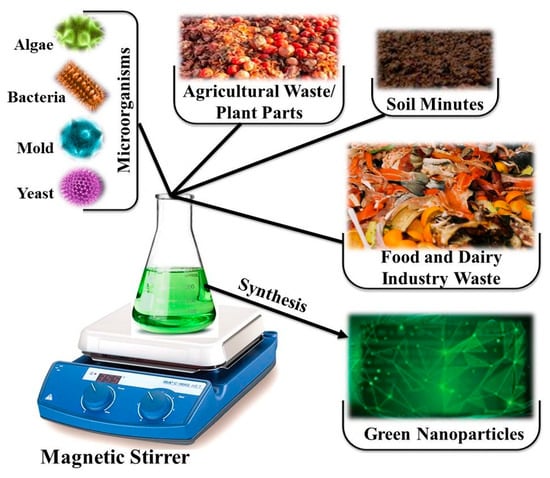
Figure 2.
Various biological sources such as plants, microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, algae, and yeast), and different wastes are utilized for the eco-friendly synthesis of green nanoparticles, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional chemical methods.
The mechanism of green synthesis for NPs primarily takes place in aqueous solutions, rather than employing other chemical solvents [], thus entirely eliminating the introduction of hazardous substances that may present considerable threats to environmental and human health (Figure 1). To enhance the stability of NPs synthesized via green methodologies, various capping agents are utilized [,,,]. A prominent example is polysaccharides like dextran, which is composed of glucose molecules that can differ in length []. These agents are recognized for their affordability, intrinsic stability, biodegradability, and non-toxic properties. Amino cellulose fiber was utilized in the synthesis of zinc oxide NPs (ZnO-NPs), serving effectively as both a reducing agent and a stabilizing agent in the process []. The nitrogen group in the amino cellulose acted as a functional group that was indirectly involved in the formation of NPs, especially during the crucial reduction phase of the synthesis process. A significant advantage associated with the utilization of biological molecules as stabilizing agents in the NP synthesis process is the enhancement of biocompatibility, especially when compared to NPs generated through other methods []; this characteristic renders biocompatible NPs suitable for a variety of important applications across multiple fields, including the agriculture, food, health, and biomedical sectors [,,,,,].
3. Formation of Nanoparticles
The biogenic synthesis of NPs through the utilization of bacteria [,,], fungi (molds) [,], yeast [], and algae [,,] represents a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach compared to traditional methods. This process harnesses microbial metabolic processes to synthesize biocompatible NPs suitable for various applications. Recent developments highlight the utilization of various microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, in the synthesis of metallic NPs (Ag and Au), metal oxide NPs (TiO2 and ZnO), and semiconductor NPs [,,,,,,,]. Recent investigations emphasize the synthesis of NPs using microalgae, the implementation of sustainable purification techniques, and the utilization of renewable resources. Advancements in technology encompass both intracellular and extracellular synthesis mechanisms, where extracellular methods facilitate the collection of NPs [,,,]. The process of purification is complex, necessitating several stages, including centrifugation, filtration, dialysis, and chromatography, to eliminate biological contaminants such as proteins and polysaccharides [,,]. Innovative approaches, including magnetic separation, NP immobilization on solid substrates, and enzyme optimization, effectively tackle challenges related to scalability and purity [,,]. Utilizing advanced characterization techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) facilitates accurate quality control of NPs [,].
Furthermore, various challenges arise, including intricate purification processes, especially for intracellular NPs, necessitating multiple stages (centrifugation, dialysis, and chromatography) to eliminate biological contaminants [,,]. The scalability of such processes is adversely affected by the variability in NP size and shape, as well as fluctuations in microbial growth at the industrial scale [,]. NP aggregation, potential toxicity to non-target organisms, insufficient mechanistic insights, and the elevated costs associated with enzymes and equipment present significant challenges to widespread adoption [,,]. In order to address the challenges outlined previously, a range of solutions can be considered, including the prioritization of extracellular synthesis, the implementation of advanced separation techniques such as magnetic separation and nanofiltration, and the automation of purification processes to improve overall efficiency [,,,,]. Enhancements in scalability can be achieved via the optimization of bioreactors, the utilization of microbial consortia, and the implementation of standardized protocols [,,]. The stability of NPs is examined through the use of polymeric matrices, natural stabilizers, and surface functionalization [,,]. The mitigation of toxicity can be achieved through the application of biodegradable NPs and controlled release systems [,,,,]. Additionally, the utilization of omics technologies and waste-based media contributes to cost reduction and enhances mechanistic understanding [,,]. A comprehensive summary in Table 2 delineates the challenges and corresponding solutions associated with the biosynthesis of NPs utilizing bacteria, fungi, yeast, and algae, with a particular emphasis on the complex purification process and other pertinent issues involved.

Table 2.
Challenges and solutions in the microbial biosynthesis of nanoparticles concerning purification, scalability, and stability for sustainable applications.
A critical discussion in the following sections presents the biosynthesis of NPs utilizing bacteria, fungi (molds), yeast, and algae as sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to conventional methods.
3.1. By Bacteria
There are two methodologies for synthesizing NPs utilizing bacterial cells, as follows: intracellular and extracellular processes. Nonetheless, the precise mechanical process underlying the production of NPs remains unidentified [,,,,]. However, it is hypothesized that their formation occurs through the initial entrapment of metal ions either on the bacterial cell surface or within its interior [,,,,,]. Secondly, the ion is subjected to multiple enzymatic processes (reduction reactions) facilitated by bacterial enzymes [,,,,]. The extracellular production method is typically favored due to its more straightforward purification process and higher yield in comparison to intracellular synthesis []. Bacteria function as a reducing agent in the presence of ionic solutions, such as those containing silver or gold, during the synthesis of NPs [,,,]. The bacterial metabolic enzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen (NADPH) facilitate the transfer of an electron to the metal atom, thereby enhancing its stability [,,]. Following the proliferation of bacterial cells, the synthesis of NPs commences. The synthesis of NPs during the reduction phase of silver metal ions is critically dependent on a key enzyme. This process involves the electron transfer mechanism facilitated by NADH and NADH-dependent nitrate reductase (NADH-DNR) present in Bacillus spp., highlighting the complex biochemical interactions at play [,].
The bacterial-mediated biosynthesis of metallic NPs through a pathway reliant on the enzyme nitrate reductase [] is illustrated in Figure 3. Nitrate ions (NO3+) are taken up by the bacterial cell, prompting the activation of nitrate reductase, an intracellular enzyme that employs NADH as an electron donor, transforming it into NAD+ while releasing electrons (e−) [,]. These electrons are subsequently transferred through NADH-DNR to facilitate the reduction of metal ions (M+) into their zero-valent metallic state (M0), resulting in the formation of metallic NPs [,,]. This method exemplifies an environmentally sustainable approach for the synthesis of NPs, utilizing bacterial enzymatic systems under standard conditions []. The NPs produced may be classified as either intracellular or extracellular, contingent upon the specific bacterial species and metal precursor utilized [].
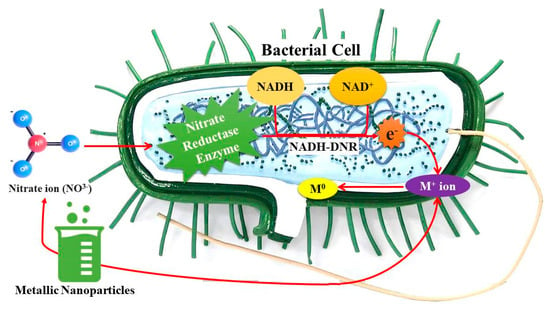
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of bacterial nanoparticle synthesis. During bacterial growth, metal ions (M+) are reduced to their elemental form (M0) through microbial redox reactions, leading to the formation and accumulation of metallic nanoparticles around or within the cells.
In 1999, Ps. stutzeri was utilized for the production of NPs through the accumulation and aggregation of silver ions on the bacterial outer membranes []. Silver ions aggregated within the bacterial cell membrane due to their interaction with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) generated by the bacteria [,,]. This reaction transformed the gas into a non-toxic compound suitable for bacterial utilization. Nitrate reduction enzymes and cofactors are integral to the process of reducing silver NPs (Ag-NPs) in bacterial systems. Certain proteins have been identified as participants in the reduction of silver nitrate (AgNO3), resulting in the formation of Ag-NPs [,,,,,,].
Cell-free culture supernatants obtained from seven bacterial strains, namely Phaeocystis antarctica, Ps. proteolytica, Ps. meridiana, Arthrobacter kerguelensis, A. gangotriensis, Bacillus indicus, and Bhargavaea cecembensis, were utilized for the biosynthesis of Ag-NPs with sizes ranging from approximately 6 to 13 nm (refer to Table 3). The NPs demonstrated stability for a duration of eight months when stored in a dark environment. The synthesis and subsequent stability of the Ag-NPs were found to be affected by variables including temperature, pH, and the particular bacterial species from which the supernatant originated [,,,]. It was observed that the supernatant of A. kerguelensis did not promote the production of Ag-NPs at the temperature optimal for the synthesis of these NPs by Phaeocystis antarctica [,,,]. As a result, this study presents substantial evidence indicating that the components found in cell-free culture supernatants that facilitate the synthesis of Ag-NPs differ among various bacterial species.

Table 3.
Important studies on different bacterial species as biological nanofactories to produce metal nanoparticles for different applications in food and dairy products.
The synthesis of NPs by bacteria represents a novel technological advancement that yields a significant quantity of NPs. However, this approach encounters several challenges, including the purification process, which is intricate, necessitating multiple steps and considerable effort to achieve pure particles. Furthermore, there is a limitation in the ability to regulate the size of the NPs produced. The primary obstacle lies in the production and purification of these particles at an industrial scale. To address the previously identified challenges, several strategic solutions have been proposed (Table 2). Emphasis on extracellular synthesis, along with the adoption of advanced separation techniques, such as magnetic separation and nanofiltration, and the automation of purification processes, can significantly enhance overall process efficiency. Scalability improvements can be achieved through the optimization of bioreactors, incorporation of microbial consortia, and implementation of standardized protocols. To enhance NP stability, approaches such as the use of polymeric matrices, natural stabilizers, and surface functionalization are commonly employed. Toxicity reduction is facilitated through the development of biodegradable NPs and the incorporation of controlled release systems. Moreover, the integration of omics technologies and the utilization of waste-derived media will contribute to cost reduction while simultaneously providing deeper mechanistic insights.
3.2. By Fungi (Molds)
The formation of NPs through fungal processes closely resembles the particle synthesis mechanisms employed by bacteria, encompassing both intracellular and extracellular methodologies []. NPs are synthesized through the combination of metallic precursors and fungal metabolites, which encompass various compounds, including cyclosporine, griseofulvin, lovastatin, and mevastatin, as well as oxidation-reduction enzymes such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCases), NADH, NADPH, and peroxidases [,,]. Metabolic products facilitate the conversion of metal ions into a reduced state, resulting in the synthesis of NPs (Figure 4).
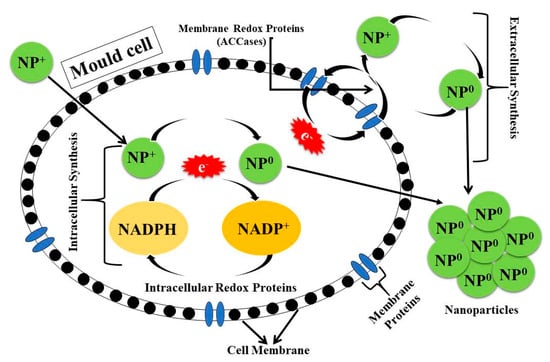
Figure 4.
Biosynthesis of nanoparticles by molds via intracellular and extracellular routes offers an eco-friendly, cost-effective, and scalable approach for producing metal nanoparticles with potential applications in food, medicine, and environmental sectors.
In the intracellular approach, metallic precursors are introduced into the fungal growth medium, where the activity of reducing enzymes facilitates the synthesis of NPs []. In both methodologies, the synthesized NPs can be isolated from metabolites through centrifugation, chemical washing, and filtration techniques. Fungi exhibit significant resistance to agitation and flow forces within bioreactors, thereby enhancing their application in the production of NPs ((A) in Table 4). A variety of fungal species have been utilized for the synthesis of NPs, including A. flavus [,,], A. fumigatus [,], A. niger [,,,], Fusarium pseudonygamai [], Penicillium solitum [], P. citrinum [], Rhizopus arrhizus [], and Trichoderma viride [,].

Table 4.
Important studies on metal nanoparticle synthesis from diverse fungal species, including molds (A) and yeasts (B), which show wide-ranging applications, with emphasis on food and dairy products due to their biocompatibility and eco-friendly production methods.
The synthesis of Ag-NPs utilizing the fungus Macrophomina phaseolina has been reported. The reduction of silver ions was facilitated by the exoenzymes located on the surface of the mold cells [,,]. In another investigation, extracellular proteins and polysaccharides facilitated the reduction of gold ions (Au+3) present in AuCl4 via electrostatic interactions, aided by the presence of positively charged lysine. The transport of Au+3 ions into the cell was observed to occur via ionic pathways across the cell membrane, followed by reduction facilitated by cytoplasmic oxidation-reduction enzymes [,]. M. phaseolina exhibited elevated oxidation-reduction enzyme activity compared to other fungi, facilitating the synthesis of Au-NPs and Ag-NPs. This characteristic is economically advantageous, as it requires a reduced amount of enzymes to produce Au-NPs and Ag-NPs [,,]. The production of NPs through fungal methods is hindered by challenges related to low yield, necessitating purification processes to achieve pure particles. These processes elevate production expenses.
3.3. By Fungi (Yeasts)
Yeasts, classified as unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms, exhibit a notable capacity to absorb and concentrate considerable amounts of hazardous metallic cations from their environment [,,,]. This ability is linked to their extensive cell surface area and substantial cytosolic volume, which, together, enhance the efficient uptake of these toxic elements []. These eukaryotic organisms demonstrate a wide range of advanced detoxification processes, such as chelation, bioprecipitation, and biosorption, which, together, make them highly effective as bio-factories for the production of metal NPs from metallic precursors via different biochemical pathways [,,]. The inherent differences in the detoxification mechanisms utilized by various yeast species significantly influence the production of bio-metal NPs, which exhibit a diverse array of tunable characteristics, such as particle size, morphology, and chemical composition [,]. These variations result in a range of physicochemical properties that can be customized for specific applications. As a result, the capacity of these microorganisms to modify their detoxification mechanisms not only increases the adaptability of the synthesized metal NPs, but also creates a wide range of opportunities for their application across various domains, such as nanotechnology and environmental remediation []. Baker’s yeast (Sa. cerevisiae) was employed to synthesize highly stable Ag-NPs, utilizing yeast extract as both a reducing and coating agent for the synthesized nanoparticles due to the presence of numerous reducing enzymes within the yeast extract [,,]. Lead NPs (Pb-NPs) were synthesized through the adsorption technique on the external surfaces of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa in acidic conditions, resulting in particle sizes ranging from 10 to 20 nm [,]. Various yeast strains were employed to synthesize NPs from a range of metal ions, including lead, silver, gold, and others ((B) in Table 4).
3.4. By Algae
Algae are eukaryotic organisms characterized by their significant ability to absorb and concentrate heavy metals, subsequently transforming them into various forms. Due to these unique characteristics, algae have been employed in the synthesis of NPs composed of various metals [,,,]. The biosynthesis of NPs commences with the formulation of an initial metal ion solution that is subsequently combined with algal extracts [,]. The BACs found in algae extracts, including pigments, fats, starches, unsaturated oils, and proteins, effectively neutralize the charge of the ionic solution to a state of zero valence [,,,]. The biosynthesis of natural products by algae occurs in three distinct stages. The initial phase, referred to as the activation stage, involves the reduction of metal ions facilitated by oxidation-reduction enzymes that are secreted by algal cells []. This phase induces a modification in the chromatic properties of the solution. The second stage involves the growth phase, during which metal ions aggregate to produce NPs of various geometries and dimensions that exhibit stability. During the third stage, the NPs are acquired in their definitive configuration [,,,,]. The biosynthesis of particles is influenced by variables such as temperature, pH, solution concentration, and the method of stirring [,]. The biosynthesis of NPs from algae can take place either within the cells (intracellularly) or outside the cells (extracellularly) [,,,]. The intracellular approach is contingent upon the concentration of ion dosage in the growth medium and the production of NADH or NADPH-dependent reductase enzymes during metabolic activities, including nitrogen fixation, respiration, and photosynthesis (Figure 5).
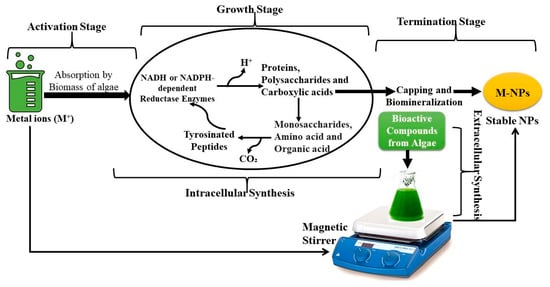
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram illustrating the dual mechanism of metal nanoparticle synthesis by algae through intracellular and extracellular pathways. In intracellular synthesis, metal ions penetrate algal cell walls and are reduced by intracellular biomolecules, leading to nanoparticle formation inside the cells. In extracellular synthesis, algal-secreted enzymes and metabolites in the surrounding medium reduce metal ions externally, resulting in the formation of nanoparticles outside the cells.
The algae-mediated green synthesis of metal NPs offers an eco-friendly, sustainable, and cost-effective alternative to conventional chemical methods [,,,]. The biosynthesis process is depicted in Figure 5, which typically involves the following three sequential stages: activation, growth, and termination []. During the activation stage, metal ions (M+) are absorbed by the algal biomass through interactions with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amino groups present on the cell surface [,]. In the growth stage, intracellular enzymes—particularly NADH or NADPH-dependent reductases—facilitate the reduction of metal ions to their zero-valent forms (M0) [,,,]. A variety of algal-derived biomolecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, carboxylic acids, amino acids, and tyrosinated peptides, contribute to reduction and stabilization processes []. This intracellular transformation is complemented by the termination stage, wherein BACs such as polysaccharides, phenolics, and pigments act as capping agents, promoting biomineralization and ensuring NP stability [,,]. Additionally, extracellular synthesis pathways also play a significant role, wherein metabolites secreted by algae reduce and cap metal ions outside the cell, a process that can be optimized using magnetic stirring for an enhanced dispersion and yield [,,]. This dual mechanism of intracellular and extracellular synthesis not only enhances NP stability and functionality, but also supports broad applicability in the biomedical, agricultural, and environmental domains due to the biocompatibility and low toxicity of the synthesized metal NPs [,,,].
The intracellular synthesis of gold NPs (Au-NPs) was accomplished by incubating chloroauric acid with Rhizoclonium fontinale algae at a temperature of 20 °C for a duration of 72 h []. A noticeable change in the coloration of the algal thallus from green to purple indicated the successful biosynthesis of Au-NPs. Furthermore, incubation of the gold metal solution with the biomass did not lead to any change in color, indicating the absence of intracellular enzymes or metabolites participating in the bio-reduction process [,]. In another experiment, gold/cellulose NPs (Au/cellulose-NPs) were synthesized using Chlorella vulgaris []. The synthesized Au/cellulose NPs were evaluated using UV–Vis spectroscopy, TEM, zeta potential analysis, and FTIR. Au/cellulose NPs have been employed in the treatment of lung cancer cells, leading to a notable enhancement in the relative expression of tumor suppressor genes when compared to control cells [].
The extracellular synthesis pathway occurs when metal ions bind to the surfaces of algal cells, where a range of metabolites—such as proteins, lipids, RNA, DNA, polysaccharides, pigments, and enzymes—aid in their reduction at these surfaces []. The extra-cellular synthesis pathway offers significant benefits, particularly in the ease of purifying NPs [,]. Nonetheless, it is crucial to perform specific preliminary treatments, including the washing and homogenization of algal biomass, to ensure optimal results. The dimensions, morphology, and aggregation of NPs are influenced by several variables, such as pH, temperature, and metal concentration. An elevated pH level inhibits the agglomeration of NPs by augmenting the reductive capacity of functional groups present in metals [,,]. An elevated pH level (greater than 7) enhances the stability of NPs generated externally to the cell by facilitating the interaction between metal ions and the amino acids located in the cell wall []. The extracellular synthesis of Au-NPs utilizing Spirulina maxima polysaccharides at different concentrations of chloroauric acid H[AuCl4] was evidenced by the detection of a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at 530 nm, suggesting the participation of proteins, enzymes, and biomolecules in the algal-mediated formation of NPs []. Algae, as photosynthetic organisms, exhibit a remarkable capacity to thrive across diverse aquatic environments [,]. Their significance in nanotechnology is underscored by their exceptional ability to facilitate the biosynthesis of various metal NPs and metal oxides []. This capability is primarily due to their rapid growth rates, ease of cultivation and manipulation, and a biomass accumulation rate that is, on average, ten times more accelerated than that of higher terrestrial plant species []. A diverse array of algal strains have undergone extensive investigation and analysis regarding their capacity for the eco-friendly synthesis of various NPs, thereby underscoring the adaptability and prospective applications of these organisms in the progression of sustainable nanomaterials production (Table 5).

Table 5.
Some key studies reporting on the involvement of algal species in the biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles, emphasizing their distinct properties and various applications with emphasis on food and dairy products.
4. Analytical Techniques for Confirming Microbially Synthesized Nanoparticles
The confirmation of NPs produced through microbial approaches depends on a range of complementary analytical techniques (Table 6), with each of them providing distinct information regarding their physicochemical properties.

Table 6.
Comparative overview of analytical techniques for characterizing microbially synthesized nanoparticles.
UV–Vis spectroscopy is frequently the first technique utilized, identifying SPR peaks—generally observed at approximately 420–450 nm for Ag-NPs and 520–550 nm for Au-NPs [,]. This method offers a swift, economical, and non-invasive initial confirmation of NP formation [,]. Nonetheless, it exhibits a lack of specificity attributed to possible spectral overlap with microbial biomolecules and provides restricted insights regarding morphology or composition [,].
TEM provides high-resolution imaging that is essential for assessing NP size, shape, and crystallinity, frequently enhanced by selected area electron diffraction (SAED) [,]. This method is regarded as optimal for conducting detailed morphological analysis, such as confirming the presence of spherical AgNPs synthesized by Bacillus species [,]. Its limitations encompass elevated operational costs, complex sample preparation processes, and the analysis of limited sample areas, which may not adequately represent the overall heterogeneity of the sample [].
SEM, often integrated with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), offers three-dimensional surface imaging alongside elemental composition analysis [,]. This method is especially effective for visualizing NP distribution on microbial cells or within biofilms []. SEM provides a wider field of view in comparison to TEM; however, it exhibits a reduced resolution for NPs that are smaller than 5–10 nm [,,]. Furthermore, the necessity for sample coating could lead to the introduction of imaging artifacts.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) evaluates the hydrodynamic size and polydispersity index (PDI) of NPs within colloidal suspension [,]. This method is a non-invasive and rapid approach that is appropriate for assessing the size distribution of NPs and their colloidal stability, specifically for Ag-NPs derived from Escherichia coli [,]. Nonetheless, DLS frequently presents an overestimation of particle size as a result of solvation shells and is prone to interference from leftover microbial debris.
XRD is utilized to ascertain the crystalline characteristics and phase composition of NPs, such as determining the face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of AgNPs [,,]. This non-destructive technique provides comprehensive structural information; however, it necessitates larger sample quantities and demonstrates a reduced efficacy in characterizing amorphous NPs [,,]. Morphological data are supplied.
FTIR serves as a method for identifying surface functional groups that play a role in the stabilization of NPs, including proteins or polysaccharides that cap AgNPs synthesized by F. oxysporum [,,]. While qualitative in nature, FTIR provides insights into the mechanisms of capping and stabilization [,]. The interpretation of complex spectra resulting from microbial biomolecules can present significant challenges.
EDS, when combined with SEM or TEM, facilitates qualitative and semi-quantitative elemental analysis, confirming the existence of particular elements (e.g., silver in AgNPs) [,,]. EDS delivers a high specificity; however, it exhibits a limited sensitivity for trace elements and does not provide insights into crystalline structure or morphology.
Therefore, a critical conclusion can be drawn regarding several aspects of these analytical techniques, including resolution and detail, cost and accessibility, sample preparation, and their complementary nature. TEM provides the highest resolution for morphological and crystallographic analysis, establishing it as the benchmark for NP characterization. SEM offers additional surface imaging capabilities; however, its effectiveness diminishes when analyzing very small NPs. DLS and UV–Vis spectroscopy provide less comprehensive information but are highly effective for swift, solution-based analysis. Regarding cost and accessibility, UV–Vis spectroscopy and DLS are the most economical and readily available options, making them suitable for routine monitoring. The utilization of TEM, SEM, and XRD is constrained by the necessity for costly equipment and specialized knowledge, thereby restricting their application to laboratories with substantial financial resources. Sample preparation for UV–Vis spectroscopy and DLS involves minimal steps, making it suitable for the analysis of NPs in microbial media. TEM and SEM require intricate preparation processes, which may introduce artifacts, whereas XRD and FTIR are non-destructive techniques that necessitate adequate sample quantities. In terms of complementary nature, no single technique offers complete characterization. TEM can ascertain size and morphology, XRD validates crystallinity, FTIR detects the presence of capping agents, and EDS establishes compositional elements. A variety of techniques are commonly utilized for thorough NP characterization, including UV–Vis spectroscopy for preliminary screening, TEM/SEM for imaging, XRD for assessing crystallinity, and FTIR/EDS for conducting chemical analysis.
5. Nanomaterial Applications in Food and Dairy Products
The integration of nanotechnology within the food and dairy industry represents a significant transformation in this domain. NPs are utilized in the processing of food and dairy products to yield high-quality and health-safe outcomes [,,,,,,]. Table 7 delineates the various types of nanomaterials used, the microorganisms utilized in their synthesis, and their specific applications within food and dairy products. Furthermore, the characteristics of the active compounds present in dairy products may be altered as a result of the diminutive scale of NPs. Nonetheless, various issues have been highlighted regarding the possible risks associated with the application of nanotechnology in food and dairy products, underscoring the necessity of verifying the safety of these products prior to their commercialization [,,,,,,].

Table 7.
Applications of microbial-synthesized nanomaterials in enhancing food and dairy product quality, safety, and shelf life.
The improvement of food product and dairy functionality via the incorporation of functional food components has become a significant trend in the market [,,,,]. The incorporation of these functional food components can serve to inhibit unwanted microbial proliferation, enhance the taste, color, and flavor of a product, and, most importantly, confer health-promoting benefits [,,,,]. A significant proportion of these functional food components demonstrate incompatibility with food matrices as a result of their low solubility in water, restricted oral bioavailability, undesirable sensory characteristics, and vulnerability to chemical degradation [,,,].
The utilization of contemporary technologies, including nanocomposites and metal NPs, is essential to address the growing demand for food and dairy products in international markets [,,,,,]. These technologies encompass the enhancement of nutritional value [], the facilitation of active ingredient delivery [,], the improvement of quality [,], the innovation of novel packaging technologies [,,], the detection of harmful contaminants [], the inhibition of detrimental bacteria [,,], and the extension of product shelf life [,].
5.1. In Functional Foods
Functional foods are defined as those that, beyond their nutritional value, serve a specific physiological role within the body and may facilitate the delivery or transmission of various BACs, including phenols, short-chain fatty acids, bacteriocins, and other relevant substances [,,,,,]. Functional foods produced through nanotechnology have the capability to alter the sensory characteristics of food products []. For instance, they can decrease the volume of fat emulsion in ice cream, augment its surface area, improve the biological efficacy of the emulsification process, and consequently minimize the quantity of emulsifier incorporated into the ice cream mixture [,]. Furthermore, a nano-capsule was engineered to encapsulate phytosterols such as β-carotene and lycopene, serving as a substitute for detrimental cholesterol []. Additionally, the development of certain nano-plant oils aims to provide an alternative to cholesterol, thereby mitigating the absorption and accumulation of harmful cholesterol in the bloodstream and the associated health complications [].
5.2. In Milk
Ag-NPs were synthesized using extracts from the following three species of red algae: Caulerpa racemosa, Jania rubens, and Padina pavonica. The application of these particles served to inhibit the growth of Listeria monocytogenes bacteria []. The findings demonstrated the significant effectiveness of Ag-NPS from P. pavonica extract. Following a storage period of 28 days, L. monocytogenes bacteria were entirely inactivated in dairy products, including cheese and whey []. The enzyme laccase derived from Trametes versicolor was utilized to synthesize NPs incorporating various metals and chitosan. The produced particles were employed to eliminate aflatoxin M1 from milk samples. The findings indicated that laccase-NPs exhibited the greatest adsorption efficiency in relation to M1. The synthesized Fe3O4/Cs/MoS2/laccase NPs achieved the highest removal rate of M1 (68.5%) in milk samples after 1 h of treatment []. Selenium NPs (Se-NPs) were synthesized using Lactaseibacillus paracasei bacteria derived from human milk, with a particle diameter ranging from 3.0 to 50.0 nm. The particles demonstrated significant efficacy as an anti-Candida and Fusarium species, effectively targeting pathogenic fungi isolated from animal sources []. Nisin derived from Lactococcus lactis was utilized in conjunction with MgO ions for the synthesis of magnesium NPs (Mg-NPs). The particles demonstrated inhibitory effects on pathogenic bacteria found in milk, including E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus []. ZnO-NPs were synthesized using the T. harzianum mold and employed for antibacterial and antitumor applications [,]. The particles were utilized in soy milk as antimicrobial agents targeting a species of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The maximum inhibition observed was 14.3 mm for Enterococcus faecalis and 11.6 mm for E. coli [].
5.3. In Yogurt
With the increasing awareness among consumers about the health-promoting attributes of their dietary selections, the idea of incorporating functional food elements into a range of food and dairy products has come to light [,,]. Yogurt is considered a suitable medium for the integration of functional ingredients due to various factors [,]. Methodology for augmenting yogurt with functional components is firmly entrenched in the dairy industry. Nonetheless, the prospective uses of nano-scale functional ingredients in yogurt continue to be a subject of active research []. In total, 200 μg/mL of Fe-NPs, synthesized using B. subtilis ML6, was incorporated as a fortifying agent in yogurt. The incorporation of these particles enhanced the sensory characteristics of the resultant yogurt. The incorporation of 200–400 μg/mL of Fe-NPs was observed to enhance the shelf life of yogurt []. Nisin derived from Lc. lactis was utilized in the synthesis of NPs. A concentration of 0.125 mg/mL of nisin NPs exhibited significant antibacterial efficacy against methicillin-resistant St. aureus and E. coli O157:H7. Yogurt that was inoculated with nisin NPs exhibited an extended shelf life compared to yogurt produced without the incorporation of these NPs []. In another investigation, ZnO-NPs were synthesized utilizing Lactobacillus gasseri. The particles exhibited significant antibacterial efficacy. The incorporation of these particles into yogurt resulted in an enhanced total solids content, as well as improvements in its chemical, physical, and microbial characteristics. The sensory attributes exhibited greater consumer acceptability over a 28-day period of refrigerated storage [].
5.4. In Cheese
The production of cheese represents a significant sector within the global dairy industry. All varieties of cheese produced exhibit elevated concentrations of solid constituents, encompassing proteins, fats, and carbohydrates [,]. Cheese serves as an appropriate substrate for the proliferation of diverse microorganisms [,,]. Nanotechnology has been integrated into the cheese industry to inhibit microbial growth and enhance the shelf life of cheese. A significant number of investigations focus on the development of nano-coatings intended for the encapsulation of produced cheeses [,,]. This research was conducted to investigate the inhibitory effects of both pure nisin derived from Lc. lactis and nisin NPs against A. flavus via inoculation in laboratory-produced Ras cheese. The nisin NPs employed in our investigation exhibited a remarkable biocompatibility and safety for applications in food preservation. Moreover, the sensory characteristics of the Ras cheese treated with nisin and nisin NPs demonstrated a significant degree of overall acceptability []. NPs were synthesized utilizing a yogurt starter culture comprising Lb. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, and nickel oxide ions to enhance the preservation of Domiati cheese against enterotoxigenic St. aureus. The findings indicated that a concentration of 35 µg/mL of the particles effectively inhibited St. aureus for a duration of 21 days throughout the cheese ripening process []. The prior study aimed to assess the presence of L. monocytogenes during the maturation period at temperatures of 5, 10, and 20 °C for artisanal Canastra cheeses utilizing a packaging system based on Ag-NPs. The assessed packaging methodology did not influence the initial pH levels (approximately 5.0) or water activity (aw) (approximately 0.95) during the entire storage period. As a result, the active packaging system being studied failed to demonstrate effectiveness in inactivating L. monocytogenes throughout the storage period of artisanal Canastra cheeses [].
5.5. In Meat Production
Meat products of diverse varieties represent a significant proportion of food products prevalent in international markets, facing numerous challenges such as a limited shelf life and susceptibility to microbial contamination [,]. The application of nanotechnology in the production and preservation of meat represents a groundbreaking advancement [,,]. The previous research focused on examining the impacts of dietary Zn-NPs in conjunction with B. licheniformis on the growth performance, carcass characteristics, blood metabolite levels, and population of specific cecal microorganisms in broiler chickens. In summary, the incorporation of Zn-NPs with B. licheniformis resulted in enhanced weights of broilers, improved carcass characteristics, and superior meat quality attributes, along with favorable alterations in certain blood indices and a reduction in cecal microbial load []. Minced beef exhibits a high rate of perishability attributed to its extensive surface area, which is susceptible to spoilage, coupled with elevated aw levels. Nisin synthesized by Lc. lactis was utilized in conjunction with Zn ions to generate NPs. The microbial population decreased from approximately 2 to 4 log CFU/cm2 in packed minced beef during a storage period of 15 days at 4 °C []. This detailed analysis aimed to investigate the progress of films containing NPs designed to improve the preservation of meat products via advanced packaging techniques. Throughout the film development process, extensive research underscored the application of natural polymers, with a particular emphasis on chitosan. The literature predominantly examines polymeric NPs, with metallic NPs following in frequency, while chicken and beef emerge as the primary products of interest in these studies. The main analyses performed on these products focused on lipid oxidation and the evaluation of antimicrobial effectiveness. Most research findings demonstrate that these films significantly mitigate lipid oxidation, consequently prolonging the shelf life of meat products []. A bilayer membrane was developed consisting of chitosan/zein in conjunction with a layer of nisin produced by Lc. lactis, incorporating nano Zn ions for the preservation of carp fillets []. The coating procedure demonstrated a reduction of 1.8–2.3 log CFU/g following the tenth day of storage. Additionally, Pseudomonas bacteria represent the predominant fraction of bacterial contamination in the fillets, while the membranes played a role in inhibiting the proliferation of this bacterial species []. Synthetic NPs have been employed in conjunction with microorganisms as a facilitator in the production of various types of meat, including beef, poultry, and fish, to enhance preservation and extend shelf life through their roles as antimicrobial agents or antioxidants. The incorporation of these particles into meat products, their integration into biofilm manufacturing, and their application in packaging materials serve to enhance the shelf life of these products.
6. Potential Risks and Threats Associated with the Implementation of Nanotechnology
NPs are synthesized in substantial volumes and subsequently discharged into the ecosystem. During the stages of the manufacturing, processing, transportation, environmental remediation, and disposal of NPs, various potential risks may emerge [,,,,]. These particles influence the health of the human body, as well as that of animals, impacting every organ system within the body [,,,,]. Nonetheless, the ultimate outcome of NPs remains uncertain. To thoroughly assess the detrimental impacts of nanotechnology on public health, extensive scientific investigations concentrating on bioavailability, absorption, and in vivo accumulation are necessary [,].
Currently, the application of nanotechnology is more prevalent in food packaging than in food processing [,,]. This trend is attributed to the favorable perception of employing nanotechnology in surface packaging, as it does not involve the introduction of NPs into the food system, thereby alleviating concerns associated with this technology [,,,]. Recent studies suggest that NPs may migrate from packaging materials into food, subsequently entering the bloodstream and accumulating within the body’s systems, thereby presenting a potential risk to public health [,]. ZnO-NPs and TiO2-NPs have been observed to induce genotoxic effects in intestinal epithelial cells [,,]. The toxicity of NPs is influenced by various parameters such as the size of the NPs, the viscosity of the solution, the temperature at which they are stored, and the length of the storage period []. Furthermore, in fermented dairy products, particularly those that include probiotic bacteria, a detrimental impact of NPs on viable cells is noted, as the majority of these particles impede the growth of microorganisms, resulting in a reduction in the population of these bacteria and a decline in their metabolic byproducts [].
Considering the numerous uncertainties associated with the applications of nanotechnology, it is essential to perform genotoxicity studies and precise risk assessments. Researchers may identify novel approaches to assess and mitigate the risks associated with nanotechnology, thereby safeguarding both consumers and the environment, through the examination of the behavior, transport pathways, and potential long-term effects of NPs.
6.1. Regulatory Frameworks and Challenges
Microbially synthesized NPs such as Ag-NPs, ZnO-NPs, and TiO2-NPs are being increasingly utilized in food and dairy applications, especially in the areas of packaging and preservation [,,]. Regulatory frameworks worldwide are designed to ensure safety, although they vary in their scope and implementation methods. Within the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) offers directives regarding the safety evaluation of NPs utilized in food additives, contact materials, and novel foods, emphasizing the importance of physicochemical characterization [,,,]. Nevertheless, the standardization of testing methodologies for toxicity and migration is still constrained. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States oversees NPs under general food safety regulations, lacking specific legislation for nanotechnology. This absence of targeted regulation leads to ambiguities concerning the long-term health implications of these materials [,,]. Australia, via Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ), performs risk assessments for NPs, including TiO2-NPs, although frameworks for compliance specific to nanotechnology are still in development [,]. Significant global challenges encompass the lack of standardized definitions for nanofoods, the inadequacy of methods for migration testing, and the scarcity of data regarding chronic toxicity, bioaccumulation, and genotoxicity [,]. To address these regulatory gaps, it is essential to establish harmonized protocols for safety, toxicity, and environmental risk assessments.
6.2. Consumer Perception
The perception of consumers regarding microbially synthesized NPs in food and dairy products is notably shaped by their awareness, perceived advantages, and concerns related to safety.
6.2.1. Benefits Driving Acceptance
Microbially synthesized NPs provide various functional benefits in food systems, particularly through their antimicrobial properties, which improve food safety, extend shelf life, and enhance overall product quality [,,,,,]. For example, Ag-NPs are being progressively integrated into packaging materials due to their effectiveness in inhibiting microbial growth []. In a similar vein, smart packaging technologies that incorporate nanosensors are capable of detecting spoilage and contamination in real time [,,,]. Consumers place significant importance on concrete advantages, including enhanced nutrition and safety, particularly within premium categories such as dairy products [,,]. Studies demonstrate that acceptance tends to rise notably when the perceived advantages, particularly those associated with health, nutrition, and safety, are clearly greater than the potential risks involved [].
6.2.2. Concerns and Mistrust
Despite their potential, consumer mistrust continues to pose a significant obstacle to the adoption of NP-based food technologies. A considerable segment of the population possesses a limited understanding of nanotechnology, frequently leading to widespread skepticism []. In addition to scientific risk data, numerous consumers take into account wider ethical, moral, and social implications when assessing the use of nanomaterials in food. Concerns encompass possible nanotoxicity effects, including oxidative stress, DNA damage, and bioaccumulation within organs. Regulatory actions in specific regions, including the prohibition of certain NPs in various parts of Europe, contribute to increased consumer apprehension [,]. The lack of clear and transparent labeling, along with inconsistencies in international regulatory frameworks, leads to a decline in public trust.
6.2.3. Strategies for Enhancing Acceptance
To promote public acceptance, it is crucial to adopt strategies that emphasize transparency and education. This encompasses engaging consumers in the product development process, ensuring the transparent and accurate labeling of NP content, and enhancing public awareness about both the advantages and potential risks []. Surveys carried out in nations such as Switzerland highlight the significance of collaboration among multiple stakeholders—including industry, regulators, and academia—to guarantee that NP applications meet consumer expectations and values.
6.3. Environmental Impacts
As an environmentally acceptable substitute for traditional chemical synthesis, NPs produced by microbes such as bacteria, fungus, or plant extracts are a viable option. According to Chavez-Hernandez et al. [], these environmentally friendly synthesis techniques are in line with sustainability principles and lessen reliance on harmful chemicals. By producing less waste than conventional plastics made from petrochemicals, biodegradable nanocomposites like starch and polylactic acid (PLA) further improve environmental friendliness [,,]. There have been encouraging results in the field of environmental remediation using certain NPs, such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and iron oxide (Fe2O3). Contributing to cleaner ecosystems and sustainable resource management, these materials efficiently adsorb heavy metals and remove microbiological contaminants from polluted water sources [,]. There is, nevertheless, cause for concern about the bioaccumulation and environmental persistence of NPs, even though they have advantages. Soil and water are possible entry points for NPs into the food chain. For example, as shown with copper oxide NPs (CuO-NPs), they can cause pollution and oxidative stress in plants as they degrade, because they release harmful ions such heavy metals []. In addition to potentially interfering with biological processes in exposed organisms, non-biodegradable NPs add to particle pollution. Researchers must immediately begin collecting data on the environmental impacts, distribution routes, and ultimate destinations of NPs produced by microbes. Environmental risks can only be fully understood by life cycle assessments (LCAs) and eco-toxicological testing with model organisms (such as plants, soil microorganisms, and aquatic species) [,]. Guaranteeing safe and sustainable deployment will need the development of strong regulatory frameworks, as well as standardized processes for NP disposal, monitoring, and risk assessment.
7. Future Perspectives and Directions
To enhance the synthesis of biogenic NPs utilizing bacteria, fungi, yeasts, and algae, researchers must explore novel approaches to address challenges related to purification, scalability, contamination, toxicity, and aggregation. Future directions should focus on utilizing synthetic biology to design microbes for accurate NP synthesis and self-purification. Additionally, the development of integrated bioreactor systems that combine synthesis and purification processes is essential. Employing artificial intelligence to enhance microbial selection and purification workflows is also recommended. The integration of nanotechnology, including lab-on-chip devices and nanostructured supports, has the potential to improve the precision of synthesis and the efficiency of purification processes. Utilizing waste-derived substrates and recyclable purification media represents a sustainable approach that is consistent with the principles of a circular economy. Standardized protocols, interdisciplinary collaboration, and the investigation of novel microbes, such as extremophiles and marine species, will facilitate scalability and foster innovation. Application-specific NP design, concentrating on biomedical or environmental requirements, guarantees customized solutions, underpinned by stringent regulatory frameworks to promote commercialization.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology have led to notable developments within the food and dairy sectors, facilitating the emergence of innovative solutions designed to enhance food safety, quality, and functionality. One of its notable applications includes the detection and analysis of mycotoxins, pesticide residues, and chemical contaminants within food matrices. Advanced nanoscale sensors and detection platforms enable rigorous quality control and adherence to regulatory standards, thereby ensuring consumer safety and confidence. Notwithstanding these developments, the extensive deployment of nanotechnology within food systems is still in its early phases, requiring additional investigation, risk evaluation, and technological enhancement for widespread application.
One of the most rapidly evolving domains of investigation is food packaging utilizing nanotechnology. The advancement of intelligent packaging systems, utilizing nano-membranes derived from biodegradable, carbon-neutral nanocomposites, and silica-based materials, presents significant potential. Nano-enabled coatings significantly enhance barrier properties, thereby reducing microbial contamination and prolonging product shelf life. Furthermore, the incorporation of nano-sensors into packaging materials facilitates the immediate identification of spoilage, contamination, or chemical alterations, thus reducing food waste and providing significant advantages to both producers and consumers.
The future indicates a trajectory towards the advancement of green nanotechnology, which prioritizes environmentally sustainable methodologies. The utilization of advantageous microorganisms, such as lactic acid bacteria and probiotic yeasts, for the synthesis of NPs presents a promising approach to address potential toxicity issues linked to traditional nanomaterials. These biological nanofactories are capable of synthesizing functional nanostructures that exhibit an enhanced biocompatibility, safety, and efficiency. These advancements are expected to significantly impact food preservation, especially in the realm of fermented dairy products.
Moreover, nanotechnology is anticipated to transform the manufacturing processes of functional foods and enhance precision in drug delivery systems. The application of probiotic bacteria as starter cultures, in conjunction with nanocarriers, will improve the delivery of BACs and probiotics in fermented dairy products. Furthermore, the integration of nanofibers and their customized interactions with food constituents offers significant opportunities for post-processing, enhancements in texture, and the precise release of nutrients and BACs.
The comprehensive modification and optimization of nanotechnology applications within the food sector is crucial to fully harness this potential. Addressing safety, environmental implications, regulatory structures, and consumer acceptance will be crucial. Should these challenges be addressed, nanotechnology is set to emerge as a significant influence in the food and dairy sectors, revolutionizing food processing, preservation, packaging, and the development of functional foods in the foreseeable future.
8. Conclusions
The utilization of green nanotechnology, which involves the microbial synthesis of NPs by various microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, yeast, and algae, signifies a significant advancement in food and dairy systems. This approach provides sustainable and innovative solutions aimed at improving safety, quality, and functionality. This review highlights the diverse capabilities of microbially synthesized NPs, including Ag-NPs, ZnO-NPs, and TiO2-NPs, which demonstrate significant antimicrobial, antioxidant, antifungal, and antiviral activities. The aforementioned attributes facilitate sophisticated applications such as antimicrobial packaging, nanoencapsulation to enhance the bioavailability of BACs, pathogen detection, and the extension of shelf life in dairy products (e.g., milk, yogurt, and cheese) and meat. The utilization of biological resources, such as agro-industrial byproducts from areas like West Asia, is consistent with the principles of a circular economy. This approach minimizes environmental consequences and lowers production expenses in comparison to traditional chemical and physical synthesis techniques.
Notwithstanding these advancements, considerable challenges remain, particularly concerning scalability and purification. Intricate purification methodologies, especially concerning intracellular NPs, along with the variability in NP dimensions and morphology, as well as challenges related to aggregation, hinder production at an industrial scale. The proposed solutions encompass the prioritization of extracellular synthesis, the application of advanced separation techniques such as magnetic separation and nanofiltration, and the optimization of bioreactors through the implementation of standardized protocols. Furthermore, potential hazards including the migration of NPs from packaging into food, bioaccumulation, and genotoxicity (for instance, ZnO-NPs and TiO2-NPs causing damage to intestinal cells) require comprehensive safety evaluations. Global regulatory frameworks, such as those established by the EU’s EFSA and the US FDA, exhibit a deficiency in specific guidelines pertaining to nanotechnology. This absence results in inconsistencies that obstruct the process of commercialization. The acceptance of consumers is additionally hindered by a lack of awareness and apprehensions regarding nanotoxicity, highlighting the necessity for clear labeling, public education initiatives, and collaboration among stakeholders.
The environmental implications of green NPs are twofold. Biodegradable nanocomposites and waste-derived substrates contribute to sustainability; however, issues regarding the persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity of NPs, such as CuO-NPs inducing oxidative stress in plants, necessitate thorough life cycle assessments and eco-toxicological investigations. Future research avenues encompass the utilization of synthetic biology for the accurate synthesis of nanoparticles, the incorporation of artificial intelligence for the selection of microbial strains, and the advancement of sustainable bioreactor systems. Advancements including intelligent packaging integrated with nanosensors, dairy products enhanced with probiotics, and strategies for waste valorization hold the potential to tackle challenges related to food security and nutritional requirements. Nonetheless, the realization of this potential is contingent upon the establishment of cohesive global regulations, the implementation of standardized testing protocols, and collaborative interdisciplinary initiatives aimed at ensuring safety, scalability, and consumer confidence.
In a nutshell, NPs synthesized through microbial processes present significant potential to transform food and dairy systems by improving safety, nutritional content, and sustainability. Addressing technical, regulatory, and societal obstacles through ongoing research and collaboration will establish green nanotechnology as a fundamental component of advanced food technologies, tackling worldwide issues related to food security and environmental sustainability.
Author Contributions
A.K.N., S.T.G.A.-S., D.K.V., S.S., and A.R.P. have conceptualized, interpreted, corrected, and compiled literature and technically sound final versions of the manuscript; A.K.N., M.T., S.S., and P.P. have compiled the tables for manuscripts; A.K.N., S.T.G.A.-S., D.K.V., P.P., M.T., S.S., and A.R.P. have read the manuscript and provided suggestions and corrections for the final submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors, A.K.N. and S.T.G.A.-S. would like to acknowledge the financial assistance of the Food and Dairy Lab., Department of Food Science, College of Agriculture, University of Basrah.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACCases | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| Ag2O | Silver oxide |
| AgNO3 | Silver nitrate |
| Ag | Silver |
| AOT | Sodium bis-2-ethylhexyl-sulfosuccinate |
| Au | Gold |
| BACs | Bioactive compounds |
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| CuO | Copper oxide |
| CVD | Chemical vapor deposition |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| E551 | Silicon dioxide |
| EDX | Energy dispersive X-ray |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EU | European Union |
| FCC | Face-centered cubic |
| Fe2O3 | Iron oxide |
| Fe3O4/Cs/MoS2/laccase-NPs | Iron oxide/Chitosan/Molybdenum disulfide/laccase nanoparticles |
| Fe | Iron |
| FESEM | Field emission scanning electron microscopy |
| FE–SEM–EDX | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy |
| FSANZ | Food Standards Australia New Zealand |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared |
| GRAS | Generally Recognized as Safe |
| H[AuCl4] | Chloroauric acid |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| HRTEM | High-resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| Lb. | Lactobacillus |
| Lc. | Lactococcus |
| LCAs | Life cycle assessments |
| Mg | Magnesium |
| MgO | Magnesium Oxide |
| NADH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NADH-DNR | NADH-dependent nitrate reductase |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen |
| NC-AFM | Non-contact atomic force microscopy |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| Pb | Lead |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| Pd | Palladium |
| PdO | Palladium oxide |
| PECVD | Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition |
| PL spectrometer | Photoluminescence spectroscopy |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PLAL | Pulsed laser ablation in liquid |
| Ps. | Pseudomonas |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| PVD | Physical vapor deposition |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| RF Plasma | Radio Frequency Plasma |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| Sa. | Saccharomyces |
| SAED | Selected area electron diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| Se | Selenium |
| SnO2 | Tin oxide |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| St. | Staphylococcus |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| US FDA | United States Food and Drug Administration |
| UV–Vis spectroscopy | Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
References
- Santillán-Urquiza, E.; Ruiz-Espinosa, H.; Angulo-Molina, A.; Ruiz, J.F.V.; Méndez-Rojas, M.A. Applications of nanomaterials in functional fortified dairy products: Benefits and implications for human health. In Nutrient Delivery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 293–328. [Google Scholar]
- Vélez, M.A.; Perotti, M.C.; Santiago, L.; Gennaro, A.M.; Hynes, E. Bioactive compounds delivery using nanotechnology: Design and applications in dairy food. In Nutrient Delivery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 221–250. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, N.R.; Chen, H.; Cui, H. Nanotechnology Applications and Implications of Agrochemicals toward Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6451–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.K.; Goyal, M.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. Nanotechnology and Nanomaterial Applications in Food, Health and Biomedical Sciences; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Apple Academic Press: Burlington, CA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781771887649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Sitohy, M.Z.; Ramadan, M.F.; Saad, A.M. Green Nanotechnology for Preserving and Enriching Yogurt with Biologically Available Iron (II). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 69, 102645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, B.; Du, Q.; Liu, D.; Shi, X.; Tu, J.; Xia, X. A review on synthesis and antibacterial potential of bio-selenium nanoparticles in the food industry. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1229838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramani, A.; Taherabbas, S.; Saji, R.; Bumbadiya, M.; Gandhi, K.; Seth, R. Nanotechnology: An Emerging Trend in the Dairy Industry-Applications and Future Challenges. Food Humanit. 2024, 3, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Patel, A.R.; Tripathy, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Singh, S.; Shah, N.; Utama, G.L.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Zongo, K.; Banwo, K.; et al. Processing and formulation technology of nutritional and functional food products by utilizing cheese and/or paneer whey: A critical review. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptan, B. Nanotechnological Applications in Current Innovative Approaches in Dairy Technology—A review. J. Agric. Sci. 2025, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, M.; Firouzabadi, F.B. Reduction of Listeria monocytogenes and Bacillus cereus in milk by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Iran. J. Pathol. 2015, 10, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Mirhosseini, M.; Afzali, M. Investigation into the Antibacterial Behavior of Suspensions of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles in Combination with Nisin and Heat against Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus in Milk. Food Control. 2016, 68, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, W.M.; Hassanien, A.A.; Zayed, G.M.; Kamal, S.M. Natural Approach of Using Nisin and Its Nanoform as Food Bio-Preservatives against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and E. Coli O157:H7 in Yoghurt. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Verma, D.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Srivastav, P.P.; Patel, A.R.; González, M.L.C.; Utama, G.L.; Aguilar, C.N. Nanoencapsulation of biofunctional components as a burgeoning nanotechnology-based approach for functional food development: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 102890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorraquín-Peña, I.; Cueva, C.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Silver nanoparticles against foodborne bacteria. Effects at intestinal level and health limitations. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Bogdanovich, M.; Harter, R.; Milosevic, A.; Petri-Fink, A. Use of nanoparticles in food industry: Current legislation, health risk discussions and public perception with a focus on Switzerland. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2021, 103, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmous, I.; Tlahig, S.; Loumerem, M.; Lachiheb, B.; Bouhamda, T.; Mabrouk, M.; Debouba, M.; Chaoui, A. Assessment of the risks of copper-and zinc oxide-based nanoparticles used in Vigna radiata L. culture on food quality, human nutrition and health. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 4045–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Ju, Z.; Skonieczna, M.; Zhou, P.K.; Huang, R. Nanoparticles-Induced Potential Toxicity on Human Health: Applications, Toxicity Mechanisms, and Evaluation Models. MedComm 2023, 4, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Saleem, S.; Ahamed, M.; Ahmad, J. Survival of probiotic bacteria in the presence of food grade nanoparticles from chocolates: An in vitro and in vivo study. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6689–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, V.K.; Shakya, A.; Aggarwal, M.; Gothandam, K.M.; Bohn, T.; Pareek, S. Fate of Β-carotene within Loaded Delivery Systems in Food: State of Knowledge. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, P.; Ray, P.R.; Chatterjee, P.N.; Mahato, A.; Haldar, L. Potential of zinc oxide nanoparticle for dietary fortification in yoghurt: Physicochemical, microbiological, rheological and textural analysis. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2022, 39, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, P.E.; Abidin, Z.; Arief, I.I.; Budiman, C. Characteristics and antibacterial activity of zno nanoparticle-fortified probiotic yogurt. Bul. Peternak. 2024, 48, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primožič, M.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. (Bio)Nanotechnology in Food Science—Food Packaging. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, M.S.; Schlogl, A.E.; Estanislau, F.R.; Souza, V.G.L.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; Santos, I.J.B. Nanotechnology in Packaging for Food Industry: Past, Present, and Future. Coatings 2023, 13, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, F.; Duman, H.; Akdaşçi, E.; Bolat, E.; Sarıtaş, S.; Karav, S.; Witkowska, A.M. A Comprehensive Review of Nanoparticles: From Classification to Application and Toxicity. Molecules 2024, 29, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mandal, R.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Roy, S. Nanotechnology in the manufacturing of sustainable food packaging: A review. Discov. Nano 2025, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, G.; Zane, D.; Dragone, R. Microbial nanotechnology: Challenges and prospects for green biocatalytic synthesis of nanoscale materials for sensoristic and biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Verma, D.K. Nanomaterials: Fundamental Principle and Applications. In Nanotechnology and Nanomaterial Applications in Food, Health and Biomedical Sciences; Verma, D.K., Goyal, M.R., Suleria, H.A.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Apple Academic Press: Burlington, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 163–194. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, V.; Asthir, B.; Mohan, M.; Srivastav, P.P. Nano-Particle-Based Delivery Systems: Applications in Agriculture. In Engineering Interventions in Agricultural Processing; Goyal, M.R., Verma, D.K., Eds.; as part of book series on Innovations in Agricultural and Biological Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Apple Academic Press: Burlington, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 107–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Suman, K.; Karmakar, S.; Mishra, V.; Lakra, S.G.; Saurav, G.K.; Mahto, B.K. Regulation and safety measures for nanotechnology-based agri-products. Front. Genome Ed. 2023, 5, 1200987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagda, G.; Rai, N.; Jaya Shakshi Bhalothia, C.; Singh, N.A. Nanoparticles Synthesis Using Extremophilic Microbes and their Potential Agricultural Applications. In Extremophiles for Sustainable Agriculture and Soil Health Improvement; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 455–483. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, M.M.; Mohammad, N.; Banerjee, S.; Khanna, P.K. Synthesis and food packaging application of silver nano-particles: A review. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 6, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, F.; Hosseini, S.S.; Mahuti Safai, S.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Hatami, M. New insights into the role of nanotechnology in microbial food safety. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Mobaraki, K.; Jounaki, K.; Sadeghian-Abadi, S.; Vahidi, H.; Jahani, R.; Noqani, H.; Hosseini, O.; Ashouri, F.; Amidi, S. Exploring the biological application of Penicillium fimorum-derived silver nanoparticles: In vitro physicochemical, antifungal, biofilm inhibitory, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic performance. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Long, H.; Cheng, H.; Liang, M.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Guo, Z.; Shi, H.; Sun, M.; He, S. Highly-efficient synthesis of biogenic selenium nanoparticles by Bacillus paramycoides and their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1227619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, R.A.; Aljohani, E.S. Assessment of silver nanoparticles derived from brown algae sargassum vulgare: Insight into antioxidants, anticancer, antibacterial and hepatoprotective effect. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamouda, R.A.; Alharbi, A.A.; Al-Tuwaijri, M.M.; Makharita, R.R. The Antibacterial Activities and Characterizations of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles, and Their Coated with Alginate Derived from Fucus Vesiculosus. Polymers 2023, 15, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbol, H.; AlYahya, S.; Ameen, F.; Alsamhary, K.; Alwakeel, S.; Al-Otaibi, S.; Korany, S. Bioinspired Synthesize of CuO Nanoparticles Using Cylindrospermum Stagnale for Antibacterial, Anticancer and Larvicidal Applications. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Jadhav, N.D.; Lonikar, V.V.; Kulkarni, A.N.; Zhang, H.; Sankapal, B.R.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.B.; Pathan, H.M.; Ma, Y.; et al. An overview of green synthesized silver nanoparticles towards bioactive antibacterial, antimicrobial and antifungal applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 323, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Maksoud, G.; Abdel-Nasser, M.; Hassan, S.E.D.; Eid, A.M.; Abdel-Nasser, A.; Fouda, A. Biosynthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Probiotic Bacterial Strain, Lactobacillus Rhamnosus, and Evaluate of Their Biocompatibility and Antifungal Activity. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 14, 23961–23983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, S.E.; Hashem, A.H.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Attia, M.S. Antifungal activity of myco-synthesized bimetallic ZnO-CuO nanoparticles against fungal plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 25395–25409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachaiappan, R.; Ponce, L.C.; Manavalan, K.; Awad, F.; Rajan, V.F. Nanoparticles as an exotic antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral agents. In Advances in Nanotechnology for Marine Antifouling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 231–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.J.; Abdelaziz, A.E.; Mekky, A.E.; Mahmoud, N.N.; Sharaf, M.; Al-Habibi, M.M.; Khairy, N.M.; Al-Askar, A.A.; Youssef, F.S.; Gaber, M.A.; et al. Biomedical promise of Aspergillus flavus-biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles: A green synthesis approach to antiviral, anticancer, anti-biofilm, and antibacterial applications. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaraman, P.; Balasubramanian, B.; Kaliannan, D.; Durai, M.; Kamyab, H.; Park, S.; Chelliapan, S.; Lee, C.T.; Maluventhen, V.; Maruthupandian, A. Phyco-Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated from Marine Algae Sargassum Myriocystum and Its Potential Biological and Environmental Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5255–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, J.; Ummalyma, S.B.; Pandey, A.; Bhaskar, T. Recent trends in microbial nanoparticle synthesis and potential application in environmental technology: A comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 49362–49382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafran, M.; Razavi, M.M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, K. A review on synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles from plant extracts for applications in agriculture, biomedicine, and environment. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2025, 18, 2488237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Masood, A.; Ali, K.; Farid, N.; Bashir, A.; Dar, M.S. Green synthesis of silver, starch, and zinc oxide mediated nanoparticles with probiotics and plant extracts, their characterization and anti-bacterial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 196, 107012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, R.; Nawaz, K.; Khan, A.K.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Anjum, S. An Overview of the Algae-mediated Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, G. Recent developments in the use of gold and silver nanoparticles in biomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Panda, J.; Chakrabartty, I.; Sarma, B.; Panda, S.K.; Chopra, H.; Zengin, G.; Moloney, M.G.; Sharifi-Rad, M. Promising applications of phyto-fabricated silver nanoparticles: Recent trends in biomedicine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 688, 149126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Ismail, M.; Ullah, B.; Khan, M.M.; Hussein, M.; Khan, J.U.; Ahmad, B.; Bashar, N.U.; Baseer, A.; Munir, S. The Role of Bacillus Species in the Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications: A Mini Review. Nanomed. J. 2023, 10, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kalairaj, A.; Rajendran, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Panda, R.C.; Senthilvelan, T. A Comprehensive Review on Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles from a Bacteriocin for the Natural Preservation of Food Products. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 197, 1419–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Reddy, A.; Abraham, J. Biosynthesis of Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Pichia Fermentans JA2 and Their Antimicrobial Property. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agressott, E.V.; de Moura, T.A.; Marinho, N.L.; Vasconcelos, T.D.L.; Cunha, F.A.; Fechine, P.B.A.; de Souza Filho, A.G.; Paschoal, A.R. Tip-Enhanced Raman spectroscopy investigations of core-shell Ag-proteins nanoparticles synthesized by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa and Rhodotorula glutinis fungi. Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 110, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachheti, R.K.; Abate, L.; Bachheti, A.; Madhusudhan, A.; Husen, A. Algae-, fungi-, and yeast-mediated biological synthesis of nanoparticles and their various biomedical applications. In Handbook of Greener Synthesis of Nanomaterials and Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 701–734. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, S.S. Bio-fabrication of selenium nanoparticles using Baker’s yeast extract and its antimicrobial efficacy on food borne pathogens. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 1898–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fath-Alla, A.A.; Khalil, N.M.; Mohamed, A.S.; Abd El-Ghany, M.N. Antiradical and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae-Mediated Selenium Nanoparticles. Egypt. J. Bot. 2024, 64, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieb, M.M.; Soliman, A.M.; Omara, M.S. Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Potential Endophytic Fungi Penicillium Citrinum and Rhizopus Arrhizus: Characterization and Maximization. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 15, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Marine Algae Ecklonia Cava. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Mechouet, M.; Wijesekera, K.; Filipe, C.D.; Sicard, C.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Jeffryes, C. Algae-mediated biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials as a promising route in nanobiotechnology—A review. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 552–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.; Yadav, T.; Masih, S.C. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles from algae and its various applications. In Algae and Sustainable Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Ranjani, S.; Hemalatha, S. Synthesis and characterization of Kappaphycus alvarezii derived silver nanoparticles and determination of antibacterial activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 282, 125985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L.V. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles–a review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadidargah, M.; Pedram, P.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Delattre, C.; Nesic, A.; Santagata, G.; Cerruti, P.; Moeini, A. Biomimetic synthesis of nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on green synthesis of nanoparticles with a focus on Prosopis farcta plant extracts and biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 332, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, L.; Lam, N.N.; Tran, K.; Huynh, K.G. Fruit Derived Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis for Beginners—A Review. Nanocomposites 2025, 11, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyliev, G.; Vorobyova, V. Valorization of Food Waste to Produce Eco-Friendly Means of Corrosion Protection and “Green” Synthesis of Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6615118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Razak, N.A.; Othman, N.H.; Mat Shayuti, M.S.; Jumahat, A.; Sapiai, N.; Lau, W.J. Agricultural and Industrial Waste-Derived Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Review on Chemical Synthesis Route. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyaraj, S.P.; Verma, D.K.; Bakrudeen, H.B.; Prabhu, Y.A.; Vaidevi, S.; Ramiya, B.; Monika, V.; Kartik, J.P.M.; Chandraraj, K. Characterization Techniques for Nanomaterials: Research and Opportunities for Potential Biomedical Applications. In Nanotechnology and Nanomaterial Applications in Food, Health and Biomedical Sciences; Verma, D.K., Goyal, M.R., Suleria, H.A.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Apple Academic Press: Burlington, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 195–229. [Google Scholar]
- Gudikandula, K.; Charya Maringanti, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical and biological methods and their antimicrobial properties. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faried, M.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Hajalilou, A.; Kalantari, K.; Zakaria, Z.; Hara, H.; Khairudin, N.B.A. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles via Green Method Using Ultrasound Irradiation in Seaweed Kappaphycus Alvarezii Media. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 7991–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.A.; Niamah, A.K.; Hannosh, W.S. Isolation, Preparation and Characterization of Polylactic Acid Film Reinforced with Nano Silica. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2063, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masoodi, A.H.H.; Al-Masoodi, A.H.; Goh, B.T.; Abd Majid, W.H.B. Plasma-assisted growth of nanomaterials. In Energy From Plasma; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2025; pp. 243–269. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, J.O.; Martin, P.M. Chemical vapor deposition. In Handbook of Deposition Technologies for Films and Coatings; William Andrew Publishing: Kansas City, MO, USA, 2010; pp. 314–363. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, C.; Islam, M.S.; Groza, J.R. Physical and Chemical Vapor Deposition Processes. In Materials Processing Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, T.I.; Afsheen, S.; Kausar, S. Advanced Deposition Techniques. In Thin Film Deposition Techniques: Thin Film Deposition Techniques and Its Applications in Different Fields; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 161–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kustov, L.; Vikanova, K. Synthesis of metal nanoparticles under microwave irradiation: Get much with less energy. Metals 2023, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisbiers, G.; Lara, H.H.; Mendoza-Cruz, R.; Naranjo, G.; Vincent, B.A.; Peralta, X.G.; Nash, K.L. Inhibition of Candida albicans biofilm by pure selenium nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Theerthagiri, J.; Lee, S.J.; Muthusamy, G.; Ashokkumar, M.; Choi, M.Y. Integrated technique of pulsed laser irradiation and sonochemical processes for the production of highly surface-active NiPd spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Jiménez, B.; Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Pereira Reyes, R.; Paniagua, S.A.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Novel pathway for the sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles with near-spherical shape and high stability in aqueous media. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Gamma Irradiators for Radiation Processing; International Atomic Energy Agency, Industrial Applications and Chemistry Section: Vienna, Austria, 2006; Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/records/517fx-exh85 (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Flores-Rojas, G.G.; López-Saucedo, F.; Bucio, E. Gamma-irradiation applied in the synthesis of metallic and organic nanoparticles: A short review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 169, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaras, K.; Lombardi, G.; Hassouni, K. Nanoparticles synthesis in microwave plasmas: Peculiarities and comprehensive insight. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, H.O. Handbook of Chemical Vapor Deposition: Principles, Technology and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Obaidullah, M.; Bahadur, N.M.; Furusawa, T.; Sato, M.; Sakuma, H.; Suzuki, N. Microwave assisted rapid synthesis of Fe2O3@ SiO2 core-shell nanocomposite for the persistence of magnetic property at high temperature. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 572, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, M.; Naddeo, J.J.; Griepenburg, J.C.; O’Malley, S.M.; Bubb, D.M.; Klein, E.A. Production of metal nanoparticles by pulsed laser-ablation in liquids: A tool for studying the antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 124, 55416. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, F.; Musselman, K.P. Synthesis of low dimensional nanomaterials by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. APL Mater. 2024, 12, 050602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, L.; Blanco, M.C.; López-Quintela, M.A. Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 9683–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.M.; Hassan, A.I. Synthesis and characterization of nanomaterials for application in cost-effective electrochemical devices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.M.; Fouda, A.; Eid, A.M.; Fahmy, N.M.; Elsayed, A.M.; Khalil, A.M.A.; Alzahrani, O.M.; Ahmed, A.F.; Soliman, A.M. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Their Activity against Pathogenic Microbes and Common House Mosquito, Culex Pipiens. Materials 2021, 14, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Belely, E.F.; Farag, M.M.S.; Said, H.A.; Amin, A.S.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Arthrospira Platensis (Class: Cyanophyceae) and Evaluation of Their Biomedical Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, N.S.; Mohamed, M.E.; El Semary, N.A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by the Cyanobacteria Synechocystis Sp.: Characterization, Antimicrobial and Diabetic Wound-Healing Actions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, M.; Fatima, N.; Iqbal, J.; Chalgham, W.; Mumtaz, A.S.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Tavafoghi, M. Oscillatoria Limnetica Mediated Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) Nanoparticles and Their Diverse In Vitro Bioactivities. Molecules 2023, 28, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Basu, A.; Kundu, S. Green Synthesis of Protein Capped Silver Nanoparticles from Phytopathogenic Fungus Macrophomina Phaseolina (Tassi) Goid with Antimicrobial Properties against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgorban, A.M.; Al-Rahmah, A.N.; Sayed, S.R.; Hirad, A.; Mostafa, A.A.F.; Bahkali, A.H. Antimicrobial Activity and Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Trichoderma Viride. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2016, 30, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, L.; Dong, C. Penicillium Polonicum-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Unveiling Antimicrobial and Seed Germination Advancements. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafghi, M.H.; Darroudi, M.; Zargar, M.; Zarrinfar, H.; Nazari, R. Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Aspergillus Flavus and Candida Albicans for Antifungal Applications. Micro. Nano Lett. 2021, 16, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechyen, C.; Tangnorawich, B.; Toommee, S.; Marks, R.; Parcharoen, Y. Green Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles, Characterization, and Biosensing Applications. Sens. Int. 2024, 5, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseingholian, A.; Gohari, S.D.; Feirahi, F.; Moammeri, F.; Mesbahian, G.; Moghaddam, Z.S.; Ren, Q. Recent advances in green synthesized nanoparticles: From production to application. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 24, 100500. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.R.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.B.; JPoinern, G.E. Production of High-Value Nanoparticles via Biogenic Processes Using Aquacultural and Horticultural Food Waste. Materials 2017, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraketi, S.; Khwaldia, K. Nanoparticles from Agri-Food by-Products: Green Technology Synthesis and Application in Food Packaging. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 49, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejene, B.K. Eco-friendly synthesis of metallic nanoparticles from agri-food waste extracts: Applications in food packaging and healthcare–A critical review. Mater. Today Chem. 2025, 45, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Khan, S.S.; Kumari, S.; Singh, S.; Khan, R.T.; Kumari, C.; Kumari, S.; Dasila, H.; Kour, H.; Kaur, M.; et al. Microbial nanotechnology for agriculture, food, and environmental sustainability: Current status and future perspective. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Ghany, M.N.; Hamdi, S.A.; Korany, S.M.; Elbaz, R.M.; Emam, A.N.; Farahat, M.G. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Soil Rare Actinomycetes and Their Significant Effect on Aspergillus-Derived Mycotoxins. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshan, K. Handbook of Thin Film Deposition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, M.A.; Lichtenberg, A.J. Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.K.; Li, L. Characterization of Plasma-enhanced CVD processes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Nishizawa, Y.; Kubokawa, M.; Tsuji, T. Microwave-assisted synthesis of metallic nanostructures in solution. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2005, 11, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilecka, I.; Niederberger, M. Microwave chemistry for inorganic nanomaterials synthesis. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1358–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Price, G.J. Applications of ultrasound to materials chemistry. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, M.; Kiely, C.J. Some recent advances in nanostructure preparation from gold and silver particles: A short topical review. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 202, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, V.G.; Srivastava, D.N.; Palchik, O.; Palchik, V.; Slifkin, M.A.; Weiss, A.M.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical deposition of silver nanoparticles on silica spheres. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3352–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, V.G.; Gedanken, A.; Calderon-Moreno, J. Deposition of gold nanoparticles on silica spheres: A sonochemical approach. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, I. Preparation of metal nanoparticles in water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 110, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, J.; Hollamby, M.J.; Hudson, L. Recent advances in nanoparticle synthesis with reversed micelles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Müller, A.; Cheetham, A.K. (Eds.) The Chemistry of Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Niederberger, M. Nonaqueous sol–gel routes to metal oxide nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Bandopadhyay, R. Use of Dextran Nanoparticle: A Paradigm Shift in Bacterial Exopolysaccharide Based Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y. Amino Modified Cellulose Fibers Loaded Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles via Paper-Making Wet-Forming for Antibacterial Materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, M.A.; Abd-Elhalim, B.T. Biosynthesis and biocompatibility evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared using Priestia megaterium bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Sadiq, M.B.; Ali, I.; Muhammad, N.; Rehman, Z.; Khan, M.N.; Muhammad, J.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, F.U.; Anal, A.K. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Yusof, H.; Mohamad, R.; Zaidan, U.H.; Abdul Rahman, N.A. Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Eid, A.M.; Selim, S.; Ejaz, H.; Alruwaili, M.; Manni, E.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Hassan, S.E.D. Investigating the Potential of Green-Fabricated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles to Inhibit the Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Spoiled Fruits. Catalysts 2024, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen, G.G.; Mirsafi, F.S.; Leißner, T.; Akan, T.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kışla, D. Zinc oxide nanomaterials: Safeguarding food quality and sustainability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Otoni, C.G.; Soares, N.F.F. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for food packaging applications. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.S.; Chen, G. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms and their applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 270974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.A.; Cunha Mda, C.S.O.; da Frota, S.M.; Mallmann, E.J.J.; Freire, T.M.; Costa, L.S.; Paula, A.J.; Menezes, E.A.; Fechine, P.B.A. Biogenic Synthesis of Multifunctional Silver Nanoparticles from Rhodotorula Glutinis and Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa: Antifungal, Catalytic and Cytotoxicity Activities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, R.T.; Salvadori, M.R.; Rafatullah, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Khan, M.A.; Alshareef, S.A. Exploration of microbial factories for synthesis of nanoparticles–a sustainable approach for bioremediation of environmental contaminants. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 658294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ahmad, R.; Zeyaullah, M.; Khare, S.K. Microbial nano-factories: Synthesis and biomedical applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 626834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y.; Ali, S.S. Microalgae-based bioremediation of refractory pollutants: An approach towards environmental sustainability. Microb. Cell Factories 2025, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. ZnO nanoparticles inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Kumbhakar, D.V.; Sana, S.S.; Ravinder, D.; Lakshmi, B.V.; Kalangi, S.K.; Pawar, S.C. Role of Biosynthesized Ag-NPs Using Aspergillus Niger (MK503444.1) in Antimicrobial, Anti-Cancer and Anti-Angiogenic Activities. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 812474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Poonia, A.K.; Yadav, D.; Jin, J.O. Microbe-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Applications and future prospects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Dakshinamoorthi, B.M.; Jagadeesan, M.; Sekaran, S.; Somasundaram, A.; Jagadeeswari, S.; Ramasamy, P. Current state and future prospects of microbiologically produced nanoparticles: A narrative review. Process Biochem. 2024, 147, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, I.; Geiser, A.; Somborn-Schulz, A. Innovations in nanotechnology for water treatment. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.; Sherkar, R.; Shirsathe, C.; Sonwane, R.; Varpe, N.; Shelke, S.; More, M.P.; Pardeshi, S.R.; Dhaneshwar, G.; Junnuthula, V.; et al. Biofabrication of nanoparticles: Sources, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1159193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K. How nanotechnology-enabled concepts could contribute to the prevention, diagnosis and therapy of bacterial infections. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, M.P.; Aswathi, M.; Priyadarshini, E.; Rajamani, P. Recent innovations of nanotechnology in water treatment: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abady, M.M.; Mohammed, D.M.; Soliman, T.N.; Shalaby, R.A.; Sakr, F.A. Sustainable synthesis of nanomaterials using different renewable sources. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2025, 49, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, L.S.; Fallone, C.; Noble, A.J.; Veinot, J.; Ma, G.; Goss, G.G.; Burrell, R.E. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles against bacteria, yeast, and algae. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, M.P.; Rajamani, P. Nanotechnology for water purification–current trends and challenges. J. Nanotechnol. Nanomater. 2021, 2, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Bairwan, R.D.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Mistar, E.M.; Abdullah, C.K. Microbial treatment for nanocellulose extraction from marine algae and its applications as sustainable functional material. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 16, 100811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, M.; Abbriano, R.M.; Pernice, M.; Sutherland, D.L.; Commault, A.S.; Hall, C.C.; Labeeuw, L.; McCauley, J.I.; Kuzhiuparambil, U.; Ray, P.; et al. Emerging technologies in algal biotechnology: Toward the establishment of a sustainable, algae-based bioeconomy. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsha, V.S.; Boreda, T.; Pailla, S.R.; Kambhampati, Y.; Gourav, T.; Yadavalli, R.; Vijaya Laxmi, G.; Nadimpalli, S.; Nagendranatha Reddy, C. Nanotechnology and Microbes: Revolutionizing Water Management. In Nano-Microbiology for Sustainable Development; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 293–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Białkowska, A.M. Enzymatic functionalization of bacterial nanocellulose: Current approaches and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuye, B.; Abera, B. Nanomaterials: An overview of synthesis, classification, characterization, and applications. Nano Sel. 2023, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Varjani, S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Thamarai, P.; Abirami, B.; George, C.S. A review on algal-bacterial symbiotic system for effective treatment of wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nighojkar, A.; Varma, P.; Prakash, N.J.; Kandasubramanian, B.; Zimmermann, K.; Dixit, F. Algal mediated intervention for the retrieval of emerging pollutants from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elayaraja, S.; Liu, G.; Zagorsek, K.; Mabrok, M.; Ji, M.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, S.; Rodkhum, C. TEMPO-oxidized biodegradable bacterial cellulose (BBC) membrane coated with biologically-synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) as a potential antimicrobial agent in aquaculture (In vitro). Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Khan, F.; Alshehri, S.; Khan, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Wu, H.F.; Taha, E.I.; Elbagory, I. Unique properties of surface-functionalized nanoparticles for bio-application: Functionalization mechanisms and importance in application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Khalil, A.T.; Ayaz, M.; Ahmad, I.; Nethi, S.K.; Mukherjee, S. Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles via microbial enzymes: A mechanistic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, O.; Harvey, A.; Ledesma, M.T.O.; Velasquez-Orta, S. Bioremediation of waste by yeast strains. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 69, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Madhu, S.; Singh, S. Extracellular Synthesis of Antibacterial Silver Nanoparticles Using Psychrophilic Bacteria. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.H.; Rather, M.A. Intracellular and extracellular microbial enzymes and their role in nanoparticle synthesis. In Microbial Nanotechnology: Green Synthesis and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.; Ali, N.; Wang, L.; Waseem, H.; Pan, G. Revisiting the mechanistic pathways for bacterial mediated synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 159, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altammar, K.A. A review on nanoparticles: Characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1155622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Basumatary, I.B.; Sudhani, H.P.; Bajpai, V.K.; Chen, L.; Shukla, S.; Mukherjee, A. Plant extract mediated silver nanoparticles and their applications as antimicrobials and in sustainable food packaging: A state-of-the-art review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheershwal, A.; Singh, A.; Sharma, V.; Trivedi, B. Microbial synthesis of nanoparticles for sustainable agricultural advancements: A comprehensive review. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2025, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abada, E.; Galal, T.; Ismail, I. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Nocardiopsis sp.-MW279108 and its antimicrobial activity. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawadi, S.; Katuwal, S.; Gupta, A.; Lamichhane, U.; Thapa, R.; Jaisi, S.; Lamichhane, G.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Parajuli, N. Current research on silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 6687290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Luo, J.; Qi, X.; Naz, A.; Khan, I.A.; Liu, H.; Yu, S.; Wei, J. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, structure, properties and applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, V.K.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Singh, A. Hydrogen Sulfide in Physiology and Pathogenesis of Bacteria and Viruses. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, X.; Wei, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Gong, J.; He, Y.; Dong, X.; Gao, C.; et al. Optimization of fermentation parameters to improve the biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles by Bacillus licheniformis F1 and its comprehensive application. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.S.; Batista, J.G.; Rodrigues, M.Á.; Thipe, V.C.; Minarini, L.A.; Lopes, P.S.; Lugão, A.B. Advances in silver nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on their potential as antimicrobial agents and their mechanisms of action elucidated by proteomics. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1440065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Santhoshkumar, T.; Bagavan, A.; Gaurav, K.; Karthik, L.; Rao, K.V.B. Novel Microbial Route to Synthesize ZnO Nanoparticles Using Aeromonas Hydrophila and Their Activity against Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, Ö. Safety and regulatory issues of nanomaterials in foods. In Handbook of Food Nanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 655–703. [Google Scholar]
- Kumawat, G.; Rajpurohit, D.; Vyas, D.; Bhojiya, A.A.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Jain, D. Characterization of green-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles and its influence on post-harvest shelf-life of garlic against black mold disease caused by Aspergillus niger. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1532593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligaj, M.; Tichoniuk, M.; Cierpiszewski, R.; Foltynowicz, Z. Efficiency of novel antimicrobial coating based on iron nanoparticles for dairy products’ packaging. Coatings 2020, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maliki, Q.A.; Taj-Aldeen, W.R. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity of Bacteria Mediated Synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles Using Bacillus Coagulans. J. Nanostructures 2021, 11, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Daramola, O.B.; Torimiro, N.; George, R.C. Colorimetric-Based Detection of Enteric Bacterial Pathogens Using Chromogens-Functionalized Iron Oxide-Gold Nanocomposites Biosynthesized by Bacillus Subtilis. Discov. Biotechnol. 2025, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.B.; Silva, P.L.A.P.A.; Silva, A.C.A.; Dantas, N.O.; De Paula, A.T.; Olivieri, O.C.L.; Beletti, M.E.; Rossi, D.A.; Goulart, L.R. Nanocomposite of Ag-Doped ZnO and AgO nanocrystals as a preventive measure to control biofilm formation in eggshell and Salmonella spp. Entry into eggs. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmaraj, D.; Krishnamoorthy, M.; Rajendran, K.; Karuppiah, K.; Annamalai, J.; Durairaj, K.R.; Santhiyagu, P.; Ethiraj, K. Antibacterial and Cytotoxicity Activities of Biosynthesized Silver Oxide (Ag2O) Nanoparticles Using Bacillus Paramycoides. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahem, K.H.; Ali, F.A.; Abdulla Surchee, S.M. Biosynthesis and Characterization with Antimicrobial Activity of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Probiotic Bifidobacterium Bifidum. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.S.; El-Sayed, S.M.; Youssef, A.M. Novel Approach for Biosynthesizing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Lactobacillus Gasseri and Their Influence on Microbiological, Chemical, Sensory Properties of Integrated Yogurt. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Dou, X.; Song, X.; Xu, C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles by probiotics and their application. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 119, 83–128. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri Poroj, S.; Larypoor, M.; Fazeli, M.R.; Shariatmadari, F. The synergistic effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and yeast isolated from fermented foods in reduction of aflatoxin B1. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7109–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nasser, A.; Fathy, H.M.; Badr, A.N.; Barakat, O.S.; Hathout, A.S. Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with Lactobacillus rhamnosus bioactive metabolites: Preparation, characterization, and antifungal activity. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nabulsi, A.; Osaili, T.; Sawalha, A.; Olaimat, A.N.; Albiss, B.A.; Mehyar, G.; Ayyash, M.; Holley, R. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan coating containing ZnO nanoparticles against E. coli O157: H7 on the surface of white brined cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 334, 108838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Athinarayanan, J.; Periyasamy, V.S.; Alshuniaber, M.A.; Alshammari, G.; Hakeem, M.J.; Ahmed, M.A.; Alshatwi, A.A. Antibacterial mechanisms of zinc oxide nanoparticle against bacterial food pathogens resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. Molecules 2022, 27, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Senthilkumar, K.; Sivakumar, K.; Kim, S.K. Biosynthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles using a novel Nocardiopsis sp. MBRC-1. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 287638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanaraj, S.; Thirunavukkarasu, S.; John, H.A.; Pandian, S.; Salmen, S.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A. Novel marine Nocardiopsis dassonvillei-DS013 mediated silver nanoparticles characterization and its bactericidal potential against clinical isolates. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.A.; El-Shanshoury, A.E.R.R.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Alsalmi, F.A.; Mohamed, S.F.; Sun, J.; Ali, S.S. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Marine Actinobacterium Nocardiopsis Dassonvillei and Exploring Their Therapeutic Potentials. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 705673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arserim-Uçar, D.K.; Çabuk, B. Emerging antibacterial and antifungal applications of nanomaterials on food products. In Nanotoxicity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 415–453. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, M.; Ali, N.; Imran, M.; Hussain, A.; Hassan, S.W.; Haroon, U.; Kamal, A.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Munis, M.F.H. Spherical Fe2O3 nanoparticles inhibit the production of aflatoxins (B1 and B2) and regulate total soluble solids and titratable acidity of peach fruit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 410, 110508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, G.; Gohil, J.; Gohil, N.; Chaudhari, H.; Gangapuram, B.; Khambhati, K.; Maurya, R.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Singh, V. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Serratia Marcescens Derived Silver Nanoparticles: Investigating Its Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm Potency and Molecular Docking Analysis with Biofilm-Associated Proteins. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 365, 120094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baráti-Deák, B.; Da Costa Arruda, G.C.; Perjéssy, J.; Klupács, A.; Zalán, Z.; Mohácsi-Farkas, C.; Belák, Á. Inhibition of foodborne pathogenic bacteria by excreted metabolites of Serratia marcescens strains isolated from a dairy-producing environment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherednichenko, Y.; Batasheva, S.; Akhatova, F.; Fakhrullin, R.; Rozhina, E. Antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles-halloysite nanocomposite in Serratia marcescens. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2024, 26, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygar, T.; Ugur, A. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial and antibiofilm potentials of silver nanoparticles biosynthesised by Streptomyces griseorubens. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Hassan, S.E.D.; Abdo, A.M.; El-Gamal, M.S. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Larvicidal Activities of Spherical Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Endophytic streptomyces spp. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksma, J.; Misset, T.; Wever, C.; Kemmink, J.; Kruijtzer, J.; Versluis, K.; Liskamp, R.M.J.; Boons, G.J.; Heck, A.J.R.; Boekhout, T.; et al. A New Perspective on Fungal Metabolites: Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Fungi Using Zebrafish Embryogenesis as Read-Out. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaraki, M.T.; Zahed Nasab, S.; Zare, I.; Dahri, M.; Moein Sadeghi, M.; Koohi, M.; Tan, Y.N. Biomimetic Metallic Nanostructures for Biomedical Applications, Catalysis, and Beyond. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 7547–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamed, E.Y.; El-Bassiony, T.A.E.R.; Elsherif, W.M.; Shaker, E.M. Enhancing Ras Cheese Safety: Antifungal Effects of Nisin and Its Nanoparticles against Aspergillus Flavus. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, E.S.H.; Bazina, W.K.; Abd El-Aziz, Y.M.; Abd Elghany, N.A.; Tawfik, W.A.; Mossa, M.I.; Abd El Megeed, O.H.; Abd El-Hamed, N.N.; El-Saeed, A.F.; El-Haroun, E.; et al. Nano-selenium impacts on growth performance, digestive enzymes, antioxidant, immune resistance and histopathological scores of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus against Aspergillus flavus infection. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 1587–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareib, M.; Abdallah, W.; Tahon, M.; Tallima, A. Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using the preformed biomass of Aspergillus fumigatus and their antibacterial and photocatalytic activities. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures (DJNB) 2019, 14, 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Shahzad, A.; Saeed, H.; Iqtedar, M.; Hussain, S.Z.; Kaleem, A.; Abdullah, R.; Sharif, S.; Naz, S.; Saleem, F.; Aihetasham, A.; et al. Size-Controlled Production of Silver Nanoparticles by Aspergillus Fumigatus BTCB10: Likely Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 5168698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Kataru, B.A.S.; Sravani, N.; Vigneshwari, T.; Panneerselvam, A.; Rajeswari, V.D. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using culture filtrates of Aspergillus niger: Antimicrobial textiles and dye degradation studies. OpenNano 2018, 3, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.A.; Hanif, E.; Khan, U.H.; Tanoli, A.K. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles from Aspergillus niger. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, M.A.; Eid, A.M.; Elsheikh, T.M.; Al-Faifi, Z.E.; Saad, N.; Sultan, M.H.; Selim, S.; Al-Khalaf, A.A.; Fouda, A. Mycosynthesis, characterization, and mosquitocidal activity of silver nanoparticles fabricated by Aspergillus niger strain. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.K.Y.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Salem, S.S.; Azab, M.S. Multifunctional Properties of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Synthesis by Fusarium Pseudonygamai. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 28253–28270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Shan, X.; Baig, S.; Zhao, H.; Ismail, B.; Shahzadi, I.; Majeed, Z.; Nawazish, S.; Siddique, M.; Baig, A. First Identification of Potato Tuber Rot Caused by Penicillium Solitum, Its Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis, Characterization and Use against Harmful Pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1255480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo-Tayo, B.C.; Ogunleye, G.E.; Ogbole, O. Biomedical application of greenly synthesized silver nanoparticles using the filtrate of Trichoderma viride: Anticancer and immunomodulatory potentials. Polym. Med. 2019, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-García, J.J.; Hernández-Díaz, J.A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; León-Morales, J.M.; Guerrero-Guzmán, A.; Sánchez-Chiprés, D.R.; López-Velázquez, J.C.; García-Morales, S. The role of selenium nanoparticles in agriculture and food technology. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2528–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Lakhan, M.N.; Hanan, A.; Soomro, I.A.; Ahmed, M.; Bibi, F.; Zehra, I. Recent progress on green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles—A review. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 23, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantorová, V.; Krausová, G.; Hyršlová, I.; Loula, M.; Mestek, O.; Kaňa, A. Determination of selenium nanoparticles in fermented dairy products. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2023, 199, 106592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Shivani Bhojiya, A.A.; Singh, H.; Daima, H.K.; Singh, M.; Mohanty, S.R.; Stephen, B.J.; Singh, A. Microbial fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of their antimicrobial and photocatalytic properties. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinika, I.; Verma, D.K.; Balia, R.; Utama, G.L.; Patel, A.R. Potential of cheese whey bioactive proteins and peptides in the development of antimicrobial edible film composite: A review of recent trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandy, M.; Muneeswaran, T.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Quero, F.; Anand, M.; Song, J.-M. Biologically synthesized copper and zinc oxide nanoparticles for important biomolecules detection and antimicrobial applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 100766. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoor, S.; Zahoor, I.; Baba, T.R.; Padder, S.A.; Bhat, Z.A.; Koul, A.M.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles against fungal pathogens. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 679358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.N.; Naqvi, S.M.A.; Raza, A.; Jaiswal, A.; Singh, A.K.; Dixit, M.; Barnwal, A.; Gambhir, S.; Ahmad, A. Mycosynthesis of Highly Fluorescent Selenium Nanoparticles from Fusarium Oxysporum, Their Antifungal Activity against Black Fungus Aspergillus Niger, and in-Vivo Biodistribution Studies. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Bandi, R. Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by using microorganisms and agri-based products. In Agri-Waste and Microbes for Production of Sustainable Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 655–683. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Qi, M.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Tang, D.; Li, Q. Recent research progress on the synthesis and biological effects of selenium nanoparticles. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1183487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, H.C.; Suter, M.; Naegeli, H. Critical review of the safety assessment of nano-structured silica additives in food. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, G.K.; Soni, R.; Rishi, P.; Soni, S.K. Optimization of the biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Penicillium oxalicum GRS-1 and their antimicrobial effects against common food-borne pathogens. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulikkalparambil, H.; Phothisarattana, D.; Promhuad, K.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Effect of silicon dioxide nanoparticle on microstructure, mechanical and barrier properties of biodegradable PBAT/PBS food packaging. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ahari, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jafari, S.M. Role of silica (SiO2) nano/micro-particles in the functionality of degradable packaging films/coatings and their application in food preservation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabo, H.E.; Saied, E.; Hassan, S.E.D.; Mahdy, H.M.; Sultan, M.H. Penicillium Oxalicum-Mediated the Green Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles: Characterization and Environmental Applications. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 15, 5229–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethu, S.; Midhun, S.J.; Sunil, M.A.; Soumya, S.; Radhakrishnan, E.K.; Jyothis, M. Efficient visible light induced synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Penicillium polonicum ARA 10 isolated from Chetomorpha antennina and its antibacterial efficacy against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 180, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, M.; Kumar, R.S.; Nagaraja, S.K.; Hiremath, H.; Gunagambhire, P.V.; Almansour, A.I.; Perumal, K.; Nayaka, S. Myco-nanofabrication of silver nanoparticles by Penicillium brasilianum NP5 and their antimicrobial, photoprotective and anticancer effect on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Kumar, P.; Dahiya, P.; Dang, A.S.; Suneja, P. Biogenic synthesis of zinc nanoparticles, their applications, and toxicity prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 824427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Gowtham, H.G.; Shilpa, N.; Singh, S.B.; Aiyaz, M.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Shivamallu, C.; Achar, R.R.; Silina, E.; Stupin, V.; et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared through microbial mediated synthesis for therapeutic applications: A possible alternative for plants. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1227951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobha, B.; Ashwini, B.S.; Ghazwani, M.; Hani, U.; Atwah, B.; Alhumaidi, M.S.; Basavaraju, S.; Chowdappa, S.; Ravikiran, T.; Wahab, S.; et al. Trichoderma-Mediated ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Antibiofilm and Antibacterial Activities. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumaran, M.D.; Ramachandran, R.; Balashanmugam, P.; Mukeshkumar, D.J.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Mycosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles: Optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity against human pathogens. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 182, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E.; Hendi, A.A. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma longibrachiatum and their effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamal, D.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, G.; Kumar, M.; Singh, M.; Rani, N.; Mundlia, P.; Sehrawat, A.R. Silver nanoparticles biosynthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activities, applications, cytotoxicity and safety issues: An updated review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thipe, V.C.; Lima, C.S.; Nogueira, K.M.; Batista, J.G.; Ferreira, A.H.; Katti, K.V.; Lugão, A.B. Silver nanoparticles applications and ecotoxicology for controlling mycotoxins. In Silver Nanomaterials for Agri-Food Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 549–575. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, D.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xia, W.; Yu, D. Changes in Quality and Microbial Diversity of Refrigerated Carp Fillets Treated by Chitosan/Zein Bilayer Film with Curcumin/Nisin-Loaded Pectin Nanoparticles. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Safety of selenium-enriched biomass of Yarrowia lipolytica as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 5992. [Google Scholar]
- Lashani, E.; Moghimi, H.; Turner, R.J.; Amoozegar, M.A. Characterization and Biological Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesized by Yarrowia Lipolytica. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnwal, A.; Kumar Sachan, R.S.; Devgon, I.; Devgon, J.; Pant, G.; Panchpuri, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Hossain, K.; Kumar, G. Gold nanoparticles in nanobiotechnology: From synthesis to biosensing applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 29966–29982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stałanowska, K.; Railean, V.; Pomastowski, P.; Pszczółkowska, A.; Okorski, A.; Lahuta, L.B. Seeds Priming with Bio-Silver Nanoparticles Protects Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seedlings Against Selected Fungal Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-fekaiki, D.F.; Thyab Gddoa Al-Sahlany, S.; Verma, D.K.; Patel, A.R.; Singh, S. Investigating the Effect of Addition of Probiotic Microorganisms (Bacteria or Yeast) to Yoghurt on the Viability and Volatile Aromatic Profiles. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5463–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, A.; Ranade, T.N.; Mali, S.N.; Ahmad Yasin, H.K.; Pratap, A. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs): Comprehensive Insights into Bio/Synthesis, Key Influencing Factors, Multifaceted Applications, and Toxicity—A 2024 Update. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 7549–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kthiri, A.; Hamimed, S.; Othmani, A.; Landoulsi, A.; O’Sullivan, S.; Sheehan, D. Novel Static Magnetic Field Effects on Green Chemistry Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Nong, Y.; Tang, L.; Gu, T.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Application of Pb(II) to Probe the Physiological Responses of Fungal Intracellular Vesicles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Kaur, A.; Goyal, D. Algae-based metallic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 163, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Thu Thao, N.T.; Wijerathna, H.M.S.M.; Lee, J.; Edussuriya, M.; Choi, D.; Saravana Kumar, R. In Vitro and in Vivo Anticandidal Efficacy of Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles Using Spirulina maxima Polysaccharide. Process Biochem. 2020, 92, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFadhly, N.K.; Alhelfi, N.; Altemimi, A.B.; Verma, D.K.; Cacciola, F. Tendencies affecting the growth and cultivation of genus Spirulina: An investigative review on current trends. Plants 2022, 11, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFadhly, N.K.; Alhelfi, N.; Altemimi, A.B.; Verma, D.K.; Cacciola, F.; Narayanankutty, A. Trends and technological advancements in the possible food applications of Spirulina and their health benefits: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, A.; Suresh, A.; Benor, S. Phycoremediation of heavy metals, factors involved and mechanisms related to functional groups in the algae cell surface—A review. In Strategies and Tools for Pollutant Mitigation: Avenues to a Cleaner Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 269–289. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Sana, A.; Maryam, A.; Naveed, M. Exploring How Microbial Extracellular Metabolites Drive Nanoparticle Synthesis: A Bioinformatics Approach. BioNanoScience 2025, 15, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parial, D.; Patra, H.K.; Dasgupta, A.K.R.; Pal, R. Screening of Different Algae for Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Phycol. 2012, 47, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, R.A.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I.; Wageed, M.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Elebeedy, D.; Khalil, H.; Hassan, A.; Abdella, A. Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Biosynthesized Au/Cellulose Nanocomposite from Chlorella Vulgaris. Polymers 2021, 13, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuluxan, S.; Thavaranjit, A.C.; Prabagar, S.; De Silva, R.C.L.; Prabagar, J. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Turbinaria Ornata and Its Antibacterial Activity against Water Contaminating Bacteria. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gebory, L.; Mengüç, M.P. The Effect of PH on Particle Agglomeration and Optical Properties of Nanoparticle Suspensions. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 219, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godymchuk, A.; Papina, I.; Karepina, E.; Kuznetsov, D.; Lapin, I.; Svetlichnyi, V. Agglomeration of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: PH Effect Is Stronger than Amino Acid Acidity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2019, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Sayadi, M.; Heidari, A. Green biosynthesis of palladium oxide nanoparticles using dictyota indica seaweed and its application for adsorption. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2018, 3, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaqarbeh, M.; Adil, S.F.; Ghrear, T.; Khan, M.; Bouachrine, M.; Al-Warthan, A. Recent progress in the application of palladium nanoparticles: A review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryška, L.; Jindřichová, B.; Siegel, J.; Záruba, K.; Burketová, L. Impact of palladium nanoparticles on plant and its fungal pathogen. A case study: Brassica napus–Plenodomus lingam. AoB Plants 2023, 15, plad004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Surendran, L.; Sudhagar, B.; Ranjith Santhosh Kumar, D.S. Facile Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Marine Algae Gelidiella Acerosa and Evaluation of Its Biological Potential. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, G. Gold nanoparticles: From synthesis, properties to their potential application as colorimetric sensors in food safety screening. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidari, S.; Ibrahim, S.A. Potential application of gold nanoparticles in food packaging: A mini review. Gold Bull. 2021, 54, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Gold Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis and Potential of Biomedical Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbulakshmi, A.; Durgadevi, S.; Anitha, S.; Govarthanan, M.; Biruntha, M.; Rameshthangam, P.; Kumar, P. Biogenic gold nanoparticles from Gelidiella acerosa: Bactericidal and photocatalytic degradation of two commercial dyes. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 4033–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiurunavukkarau, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Subramanian, K.; Pandi, P.; Muralitharan, G.; Arokiarajan, M.; Kasinathan, K.; Sivaraj, A.; Kalyanasundaram, R.; AlOmar, S.Y.; et al. Silver nanoparticles synthesized from the seaweed Sargassum polycystum and screening for their biological potential. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, S.R.; Santhiyagu, P.; Singamuthu, M.; Kumari Ahila, N.; Jayaraman, R.; Ethiraj, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Seaweed, Turbinaria Conoides, and Their Antimicrofouling Activity. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 938272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, M.G.; Rosa, C.H.; Rosa, G.R.; Dias, D. Biogenic synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles used in environmental applications: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.; Raj, S.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, D.P. Bibliometric analysis on exploitation of biogenic gold and silver nanoparticles in breast, ovarian and cervical cancer therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1035769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothai, R.; Arul, B.; Anbazhagan, V. Anti-Dengue Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles of Crude Fucoidan from Brown Seaweed S. marginatum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 3747–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Tettey, F.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, K.R.; Parajuli, N.; Bhattarai, N. Bioinspired synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles and assessment of their cytotoxicity and antimicrobial efficacy. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, E.A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Alqhtani, A.H.; Pokoo-Aikins, A.; Yosri, M. Estimation of the Antibacterial and Anti-Tumor Impacts of Soy Milk and Ecofriendly Myco-Manufactured Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials. In Vitro Appraisal. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.; Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Anjali, R.; Kumar, P.; Pandi, B.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Prabhu, N.M. Bioengineered gold nanoparticles from marine seaweed Acanthophora spicifera for pharmaceutical uses: Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 2231–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteon, C.E.A.; Silva, L.B.; Ccana-Ccapatinta, G.V.; Silva, T.S.; Ambrosio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Bastos, J.K.; Marcato, P.D. Biosynthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Brazilian red propolis and evaluation of its antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisha Sachan, R.S.K.; Singh, A.; Karnwal, A.; Shidiki, A.; Kumar, G. Plant-mediated gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Exploring anti-cancer mechanisms, drug delivery applications, and future prospects. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 1490980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeswari, V.; Yamini, S.; Pavithra, P.; Papitha, A.S.; Lakshmi, D. Study of Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities of Ag-Co Bimetallic Nanoparticles Biosynthesized from Red Alga (Amphiroa sp.). Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 17, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreslassie, Y.T.; Gebretnsae, H.G. Green and cost-effective synthesis of tin oxide nanoparticles: A review on the synthesis methodologies, mechanism of formation, and their potential applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Oladzadabbasabadi, N. Recent advances in synthesis, modification, and potential application of tin oxide nanoparticles. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ameen, F.; Alsamhary, K.; Dawoud, T.; Al-Khattaf, F.; AlNadhari, S. Tin Oxide Nanoparticles (SnO2-NPs) Synthesis Using Galaxaura Elongata and Its Anti-Microbial and Cytotoxicity Study: A Greenery Approach. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbanda, J.; Priya, R. Synthesis and applications of tin oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastardo-Fernández, I.; Chekri, R.; Oster, C.; Thoury, V.; Fisicaro, P.; Jitaru, P.; Noireaux, J. Assessment of TiO2 (nano) particles migration from food packaging materials to food simulants by single particle ICP-MS/MS using a high efficiency sample introduction system. NanoImpact 2024, 34, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, A.; Fouda, A.; Kishk, R.M.; El Kazzaz, W.M. Unlocking the potential of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: An insight into green synthesis, optimizations, characterizations, and multifunctional applications. Microb. Cell Factories 2024, 23, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabakar, D.; Jacob, J.M.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saratale, R.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Gelidium Amansii and Its Antimicrobial Property against Various Pathogenic Bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, A.; Saini, P.; Kokkiligadda, A.; Vij, S. Use of silicon dioxide nanoparticles for β-galactosidase immobilization and modulated ethanol production by co-immobilized K. marxianus and S. cerevisiae in deproteinized cheese whey. LWT 2018, 87, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahawar, L.; Ramasamy, K.P.; Suhel, M.; Prasad, S.M.; Živčák, M.; Brestic, M.; Rastogi, A.; Skalický, M. Silicon nanoparticles: Comprehensive review on biogenic synthesis and applications in agriculture. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanimuthu, V.; Periakaruppan, R.; Romanovski, V.; Bharathi, A.; Vijai Selvaraj, K.S.; Anukeerthana, S.; Nishanthi, R.; Vanajadevi, G. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of SiO2 Nanoparticles Using Extract of Gracilaria Crassa Via Green Chemistry Approach. ChemistryOpen 2024, 14, e202400356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Nayak, D.; Patra, B.; Bratovcic, A.; Avula, S.K.; Mohanta, T.K.; Murugan, K.; Saravanan, M. Exploring Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity Profile of Gracilaria Edulis-Mediated Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles against MDA-MB-231 Breast Carcinoma. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 3863138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Purkayastha, D.D.; Hazra, S.; Thajamanbi, M.; Bhattacharjee, C.R.; Ghosh, N.N.; Rout, J. Biosynthesis of Fluorescent Gold Nanoparticles Using an Edible Freshwater Red Alga, Lemanea fluviatilis (L.) C.Ag. and Antioxidant Activity of Biomatrix Loaded Nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammami, I.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Al Jomaa, A.; Kamoun, M. Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis Properties and Applications. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, I.; Aziz, N.; Zaki, A.; Fatma, T. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Anabaena variabilis as a potential antimicrobial agent. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, G.A.; Allam, N.G.; El-Gemizy, W.M.; Salem, M.A. The role of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by Anabaena variabilis and Spirulina platensis cyanobacteria for malachite green removal from wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 4475–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeaka, H.; Passaretti, P.; Miri, T.; Al-Sharify, Z.T. The safety of nanomaterials in food production and packaging. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, R.; Castenmiller, J.; Chaudhry, Q.; Cubadda, F.; Daskaleros, T.; Franz, R.; Gott, D.; Mast, J.; Mortensen, A.; Oomen, A.G.; et al. Regulatory safety assessment of nanoparticles for the food chain in Europe. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, N.; Ahmad, R.; Fatima, S.; Shehzadi, S.; Siddiqui, T.; Zaki, A.; Fatma, T. Toxicological Assessment of Phormidium Sp. Derived Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Its Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.L.P.A.; Bovo, F.; Baptista, R.C.; Kamimura, B.A.; Magnani, M.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Active Packaging on the Behavior of Listeria Monocytogenes and Other Microbial Groups during Ripening and Storage of Canastra Cheeses. Food Control 2024, 166, 110742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A. Bacterial Synthesis and Applications of Nanoparticles; Scholars’ Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. ‘Green’synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrulolum, H.; Nooraei, S.; Javanshir, N.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Mirbagheri, V.S.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using microorganisms and their application in the agrifood sector. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Sheikh, H.I.; Sarkar, T.; Edinur, H.A.; Pati, S.; Ray, R.R. Microbiologically-synthesized nanoparticles and their role in silencing the biofilm signaling cascade. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Salem, D.R.; Sani, R.K. Spectroscopy, microscopy, and other techniques for characterization of bacterial nanocellulose and comparison with plant-derived nanocellulose. In Microbial and Natural Macromolecules; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 419–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, A.; Goel, A. Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles by Micro-organisms and its Applications. J. Young Pharm. 2023, 15, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Min, S.C. Roles of polysaccharides-based nanomaterials in food preservation and extension of shelf-life of food products: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, S.S.; Rajput, V.D.; Gorovtsov, A.V.; Minkina, T.M.; Sushkova, S.N. (Eds.) Microbial Synthesis of Nanomaterials; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Banwo, K.; Olojede, A.O.; Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.; Patel, A.R.; Gupta, A.K.; Aguilar, C.N.; et al. Functional importance of bioactive compounds of foods with Potential Health Benefits: A review on recent trends. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Patel, A.R.; Srivastav, P.P.; Singh, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Chavez-Gonzalez, M.L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Chakravorty, N.; et al. Curcumin extraction, isolation, quantification and its application in functional foods: A review with a focus on immune enhancement activities and COVID-19. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 747956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandhi, S.; Mahato, D.K.; Kumar, A. Overview of Green Nanofabrication Technologies for Food Quality and Safety Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezagholizade-shirvan, A.; Ghasemi, A.; Mazaheri, Y.; Shokri, S.; Fallahizadeh, S.; Alizadeh Sani, M.; Mohtashami, M.; Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Sarafraz, M.; Darroudi, M.; et al. Removal of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Using Magnetic Laccase/MoS2/Chitosan Nanocomposite as an Efficient Sorbent. Chemosphere 2024, 365, 143334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Shah, N.; Verma, D.K. Lactic Acid Bacteria (Lab) Bacteriocins: An Ecologicaland Sustainable Biopreservativeapproach to Improve the Safety and Shelf Life of Foods. In Microorganisms in Sustainable Agriculture, Food, and the Environment; Apple Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 197–257. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Singh, S.; Tripathy, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Baranwal, D.; Patel, A.R.; Shah, N.; Utama, G.L.; Niamah, A.K.; et al. Bacteriocins as antimicrobial and preservative agents in food: Biosynthesis, separation and application. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Verma, D.K.; Shukla, R.M.; Patel, A.R.; Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.; Baranwal, D.; Singh, A.K.; Utama, G.L.; et al. Emerging lactic acid bacteria bacteriocins as anti-cancer and anti-tumor agents for human health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zamkan, M.A.; Hendy, B.A.; Diab, H.M.; Marraiki, N.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Saber, H.; Younis, W.; Thangamani, S.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Ahmed, A.S. Control of Virulent Listeria Monocytogenes Originating from Dairy Products and Cattle Environment Using Marine Algal Extracts, Silver Nanoparticles Thereof, and Quaternary Disinfectants. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Taha, T.F.; Najjar, A.A.; Zabermawi, N.M.; Nader, M.M.; AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Salama, A. Selenium Nanoparticles from Lactobacillus Paracasei HM1 Capable of Antagonizing Animal Pathogenic Fungi as a New Source from Human Breast Milk. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6782–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Al-Kaabi, W.J.; Al-Manhel, A.J.A.; Niamah, A.K.; Altemimi, A.B.; Al-Wafi, H.; Cacciola, F. Effects of β-Glucan Extracted from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae on the Quality of Bio-Yoghurts: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 3607–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Khassaf, W.H.; Niamah, A.K.; Al-Manhel, A.J. Date Juice Addition to Bio-Yogurt: The Effects on Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties during Storage, as Well as Blood Parameters in Vivo. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2022, 22, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, J.; Fang, S.; Zuo, X. Fabrication of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Films for Cheese Packaging Containing Gliadin-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles Co-Encapsulating Natamycin and Theaflavins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 246, 125685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.H.; Maharik, N.; Valero, A.; Elsherif, W.; Kamal, S.M. Effect of Yoghourt Starter Culture and Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles on the Activity of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus Aureus in Domiati Cheese. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, É.F.; Favarin, F.R.; Ourique, A.F. The Use of Nanostructured Films in the Development of Packaging for Meat and Meat Products: A Brief Review of the Literature. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Verma, D.K.; Singh, S.; Tripathy, S.; Thakur, M.; Patel, A.R.; González, M.L.C.; Aguilar, C.N.; Srivastav, P.P. Enzymes for meat and meat processing industry: Current trends, technological development, and future prospects. In Enzymatic Processes for Food Valorization; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Alaidaroos, B.A.; Farsi, R.M.; Abou-Kassem, D.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Shafi, M.E.; Albaqami, N.M.; Taha, A.E.; Ashour, E.A. Impacts of Supplementing Broiler Diets with Biological Curcumin, Zinc Nanoparticles and Bacillus Licheniformis on Growth, Carcass Traits, Blood Indices, Meat Quality and Cecal Microbial Load. Animals 2021, 11, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.K.; Elsabagh, R.; Trinetta, V. Evaluation of Novel Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Nisin, Lysozyme, EDTA Nanoparticles, and/or ZnO Nanoparticles to Control Foodborne Pathogens on Minced Beef. Food Control 2018, 92, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, W.M.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Li, Y.; Qin, M.; Hou, D. Environmental Fate, Toxicity and Risk Management Strategies of Nanoplastics in the Environment: Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 401, 123415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, S.; Kumar, S.; Jain, S.; Radhika Sharma, N.; Batra, K. Toxicological perspectives and environmental risks of consumer nanoproducts. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1253–1275. [Google Scholar]
- FOODGRADS. Consumer Mistrust in Food Nanoparticles: Benefits, Risks & the Future. Available online: https://foodgrads.com/2025/02/09/consumer-mistrust-in-food-nanoparticles-benefits-risks-the-future/ (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Zijno, A.; De Angelis, I.; De Berardis, B.; Andreoli, C.; Russo, M.T.; Pietraforte, D.; Scorza, G.; Degan, P.; Ponti, J.; Rossi, F.; et al. Different Mechanisms Are Involved in Oxidative DNA Damage and Genotoxicity Induction by ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles in Human Colon Carcinoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikiciuk, J.; Mikiciuk, E.; Wrońska, A.; Szterk, A. Antimicrobial Potential of Commercial Silver Nanoparticles and the Characterization of Their Physical Properties toward Probiotic Bacteria Isolated from Fermented Milk Products. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2016, 51, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.; Rauscher, H.; Gottardo, S.; Hoekstra, E.; Schoonjans, R.; Peters, R.; Aschberger, K. Regulatory status of nanotechnologies in food in the EU. In Nanomaterials for Food Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 381–410. [Google Scholar]
- FSA (Food Standards Agency). Potential use of Nanomaterials as Food Additives or Food Ingredients in Relation to Consumer Safety and Regulatory Controls. Available online: https://www.food.gov.uk/research/chemical-hazards-in-food-and-feed/potential-use-of-nanomaterials-as-food-additives-or-food-ingredients-in-relation-to-consumer-safety-and-regulatory-controls (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Kuzma, J.; Grieger, K.; Cimadori, I.; Cummings, C.L.; Loschin, N.; Wei, W. Parameters, practices, and preferences for regulatory review of emerging biotechnology products in food and agriculture. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1256388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Hernandez, J.A.; Velarde-Salcedo, A.J.; Navarro-Tovar, G.; Gonzalez, C. Safe nanomaterials: From their use, application and disposal to regulations. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 1583–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, M. Unveiling the vital role of soil microorganisms in selenium cycling: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1448539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).