Quality and Microstructural Changes in Salted Goose Meat Dried by Hot-Air, Infrared, and Microwave Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material and Salting Process
2.2. Drying Process with Different Techniques
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Dry Matter, Ash, Fat Content, and pH
2.5. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance (TBARS) Analysis
2.6. Color Parameters
2.7. Shrinkage Rate
2.8. Microstructural Imaging
2.9. Rehydration Rate
2.10. Modeling of Drying Data
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition and pH of Raw Material
3.2. Color and TBARS
3.3. Shrinkage and Rehydration Parameters
3.4. Microstructure
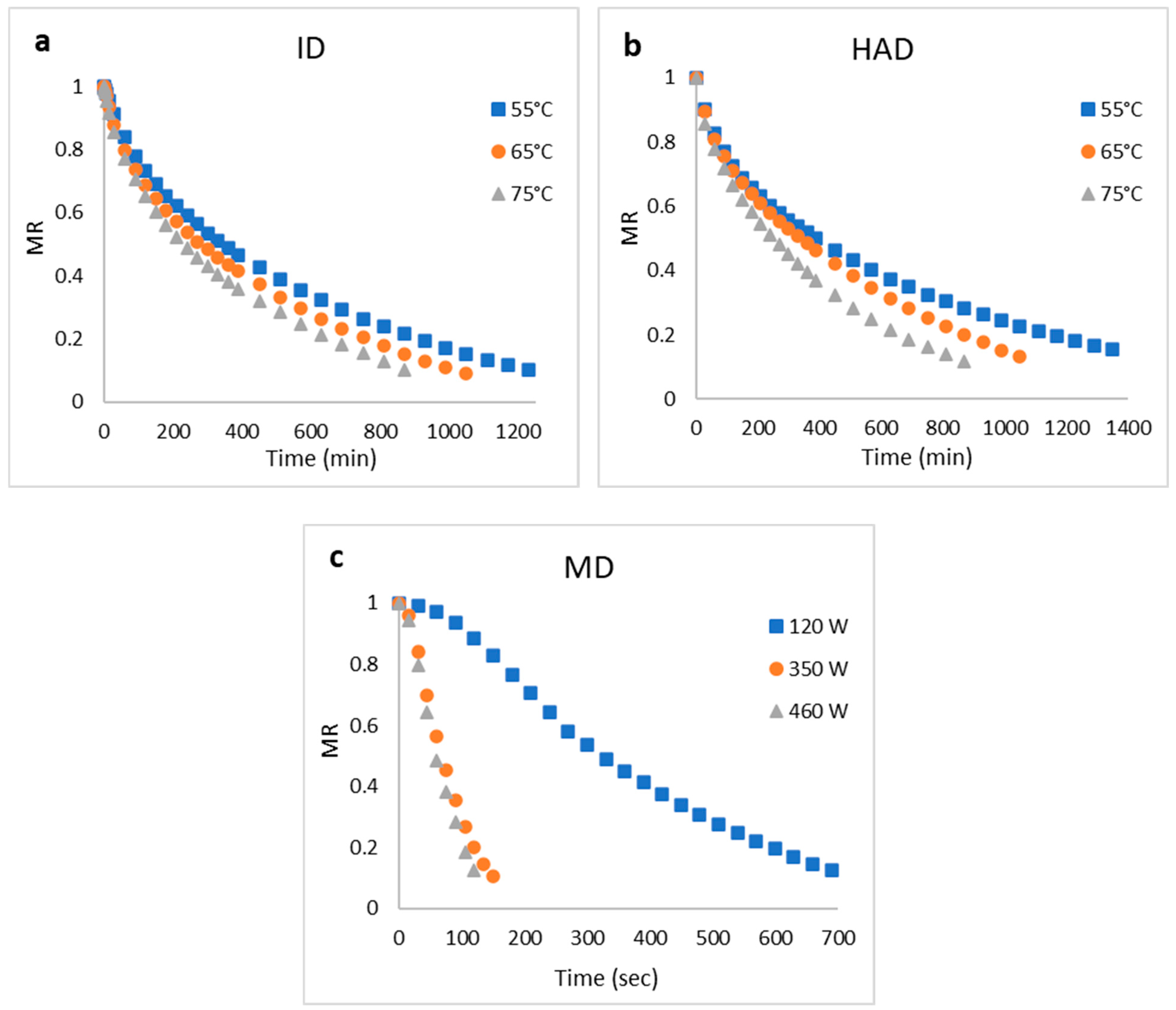
3.5. Drying Kinetics of Goose Meats
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aykın Dinçer, E.; Erbaş, M. Kurutulmuş et ürünlerinin kalite özellikleri. Gıda 2019, 44, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başlar, M.; Yalınkılıç, B.; Erol, K.F.; İrkilmez, M.Ü. Evaluation of the Use of Vacuum-Dehydrated Minced Meat in Beef Patty Production. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 1712–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, S.; Álvarez, C.; Hamill, R.; Mullen, A.M.; O’Neill, E. Drying Dynamics of Meat Highlighting Areas of Relevance to Dry-Aging of Beef. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5370–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göztok, S.P.; İçier, F. Karbon Fiber Destekli Kabin Kurutucuda Farklı Sıcaklıklarda Elma Dilimlerinin Kurutulmasının İncelenmesi: Kurutma Karakteristikleri ve Performans Değerlendirmesi. Akad. Gıda 2017, 15, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Cao, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X. Evaluation of Drying Characteristics and Quality Attributes for Microwave Vacuum Drying of Pork Skin Crisps. Foods 2024, 13, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, E.J.; Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W. Improving Drying Kinetics, Physicochemical Properties and Bioactive Compounds of Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Species) by Novel Infrared Drying. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Sun, D.W. Monitoring of Moisture Contents and Rehydration Rates of Microwave Vacuum and Hot Air Dehydrated Beef Slices and Splits Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Han, X.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, D.; Hao, J. Quality Evaluation and Drying Kinetics of Shiitake Mushrooms Dried by Hot Air, Infrared and Intermittent Microwave-Assisted Drying Methods. LWT 2019, 107, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Qin, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of Infrared Radiation Parameters on Drying Characteristics and Quality of Rice: A Systematic Review. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2025, 18, 6813–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykın Dinçer, E.; Kılıç-Büyükkurt, Ö.; Erbaş, M. Influence of Drying Techniques and Temperatures on Drying Kinetics and Quality Characteristics of Beef Slices. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 56, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.N.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, Y. Factors Affecting Energy Efficiency of Microwave Drying of Foods: An Updated Understanding. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 2618–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiray, E.; Seker, A.; Tulek, Y. Drying Kinetics of Onion (Allium cepa L.) Slices with Convective and Microwave Drying. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 53, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Jónás, G.; Felföldi, J.; Kovacs, Z.; Friedrich, L. Investigation of Salt and Water Diffusion during Dry Salting, Wet Curing, and Ultrasonic Wet Curing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalınkılıç, B.; Kaban, G.; Ertekin, Ö.; Kaya, M. Determination of Volatile Compounds of Sucuk with Different Orange Fiber and Fat Levels. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2015, 21, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalınkılıç, B.; Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Effect of Sodium Replacement on the Quality Characteristics of Pastırma (a Dry-Cured Meat Product). Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceviker, C.; Karakose, C.; Kahraman, G.; Aydin, N.; Öztürk, İ. Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties of Different Kayseri Pastirma Types. Int. J. Gastron. Res. 2025, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT: Crops and Livestock Products; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024; Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Molnár, S. Evaluation of the Hungarian and Polish goose meat production. Roczniki 2017, 2016, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, R.; Lei, M.; Guo, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, H. Reproductive Characteristics and Methods to Improve Reproductive Performance in Goose Production: A Systematic Review. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çimen, H.; Kızılkaya, P.; Sayın, B.; Baltakesmez, D.A.; Kırmacı, F. Goose Meat: Salting/Drying Effect on Nutritional Value, Physicochemical Properties, and Sensory Properties. Gıda Yem Bilim. Teknol. Derg. 2025, 33, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taste Atlas. Most Popular Goose Dishes in the World. Available online: https://www.tasteatlas.com/most-popular-goose-dishes-in-the-world (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Kaban, G.; Kızılkaya, P.; Börekçi, B.S.; Hazar, F.Y.; Kabil, E.; Kaya, M. Microbiological Properties and Volatile Compounds of Salted-Dried Goose. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, K.; Jaworska, D.; Przybylski, W.; Górska, E.; Tambor, K.; Poltorak, A. Determinants of the Sensory Quality of Półgęsek in Relation to Volatile Compounds and Chemical Composition. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülbaz, G.; Kamber, U. Experimentally Fermented Sausage from Goose Meat and Quality Attributes. J. Muscle Foods 2008, 19, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güner, A.; Doğruer, Y.; Uçar, G.; Yörük, H.D. The Possibility of Using Goose Meat in the Production of Salami. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2002, 26, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Feiner, G. Meat Products Handbook: Practical Science and Technology; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kabil, E.; Hazar Suncak, F.Y.; Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Effect of Low-Salt Processing on Lipolytic Activity, Volatile Compound Profile, Color, Lipid Oxidation, and Microbiological Properties of Four Different Types of Pastırma. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiow, T. Chemical Composition of Poultry Meat. In Handbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering; Hui, Y.H., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 32-1–32-21. [Google Scholar]
- Çakır, M.A.; Kabil, E.; Yalınkılıç, B.; Başlar, M. Investigation of Drying Kinetics of Turkey Breast Meat Using Vacuum and Ultrasound-Assisted Vacuum Drying. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Food Sci. 2025, 9, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Meng, T.; Suleman, R.; Zhang, D. Formation of Crust of Dried Meat and Its Relationship to Moisture Migration during Air Drying. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiray, E.; Özünlü, O.; Ergezer, H.; Gökçe, R. Influence of hot-air drying on drying kinetics and some quality parameters of sliced chicken breast meat. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 150, 13231–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, F.; Bodruk, A.; Köprüalan, Ö.; Arıkaya, Ş.; Koca, N.; Serdaroğlu, F.M.; Kaymak-Ertekin, F.; Koç, M. Drying Kinetics Behavior of Turkey Breast Meat in Different Drying Methods. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalp, H.Y.; Kaya, M.; Zorba, Ö.; Tülek, Y. Et Ürünlerinde Kalite Kontrolü ve Laboratuvar Uygulama Kılavuzu; Atatürk Üniversitesi Ziraat Fakültesi Ofset Tesisi: Erzurum, Türkiye, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lemon, D.W. An Improved TBA Test for Rancidity. In New Series Circular No: 51; Halifax Laboratory: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Yalınkılıç, B. Effects of Different Chloride Salts and Fat Levels on the Quality Characteristics of Beef Patties. Int. J. Gastron. Res. 2024, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doymaz, İ.; İsmail, O. Drying and Rehydration Behaviors of Green Bell Peppers. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midilli, A.; Kucuk, H.; Yapar, Z. A New Model for Single-Layer Drying. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsly, A.R.P.; Singh, D.B. Drying Kinetics of Pomegranate Arils. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadali, G.; Özbek, B. Microwave Heat Treatment of Leek: Drying Kinetic and Effective Moisture Diffusivity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başlar, M.; Kılıçlı, M.; Yalınkılıç, B. Dehydration Kinetics of Salmon and Trout Fillets Using Ultrasonic Vacuum Drying as a Novel Technique. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.M. Exposed-Layer Barley Drying: Three Models Fitted to New Data up to 150 °C. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1985, 32, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamba, P.S.; Driscoll, R.H.; Buckle, K.A. The Thin-Layer Drying Characteristics of Garlic Slices. J. Food Eng. 1996, 29, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, K.S.; Kerry, J.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Investigating the Influence of Ultrasound Pre-Treatment on Drying Kinetics and Moisture Migration Measurement in Lactobacillus sakei Cultured and Uncultured Beef Jerky. LWT 2017, 81, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.M.; Pabis, S. Grain Drying Theory II: Temperature Effects on Drying Coefficients. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1961, 6, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Karathanos, V.T. Determination of Water Content of Dried Fruits by Drying Kinetics. J. Food Eng. 1999, 39, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğrul, İ.T.; Pehlivan, D. Modelling of Drying Kinetics of Single Apricot. J. Food Eng. 2003, 58, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.M. Progress in Developing the Thin Layer Drying Equation. Trans. ASAE 1974, 17, 1167–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Singh, R.P. A Single Layer Drying Equation for Rough Rice. In ASAE Paper No. 78-3001; American Society of Agricultural Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 1978; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, L.R.; Bucklin, R.A.; Endan, J.B.; Wratten, F.T. Effects of Drying Air Parameters on Rice Drying Models. Trans. ASAE 1985, 28, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, F.; Celik, T. Proximate composition, color and nutritional profile of raw and cooked goose meat with different methods. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 2442–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbay, S.; Sariçoban, C. Effects of Different Levels of Salt and Temperature on Some Physico-Chemical and Colour Properties of Microwave-Dried Beef Round (M. semitendinosus). Br. Food J. 2021, 123, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gersdorff, G.J.; Kirchner, S.M.; Hensel, O.; Sturm, B. Impact of Drying Temperature and Salt Pre-Treatments on Drying Behavior and Instrumental Color and Investigations on Spectral Product Monitoring during Drying of Beef Slices. Meat Sci. 2021, 178, 108525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, E.; Kabil, E.; Kaya, M. The Effects of Curing Agents on the Proteolysis and Lipid Oxidation of Pastırma Produced by the Traditional Method. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, B.E.; Cumuze, T.H. Relationship between TBA Numbers and Inexperienced Panelists’ Assessments of Oxidized Flavor in Cooked Beef. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipcak, A.S.; Ismail, O. Microwave Drying of Fish, Chicken and Beef Samples. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediani, A.; Hamezah, H.S.; Jam, F.A.; Mahadi, N.F.; Chan, S.X.Y.; Rohani, E.R.; Abas, F. A Comprehensive Review of Drying Meat Products and the Associated Effects and Changes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1057366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Ya-Ting, J.; Jin-Xuan, C.; Yin-Ji, C.; Yang-Ying, S.; Xiao-Qun, Z.; Ning, G. Study on Lipolysis-Oxidation and Volatile Flavour Compounds of Dry-Cured Goose with Different Curing Salt Content during Production. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Feng, J.; An, G.; Kong, B.; Wang, H.; Pan, N.; Xia, X. Dynamics of Heat Transfer and Moisture in Beef Jerky during Hot Air Drying. Meat Sci. 2021, 182, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Karasu, S.; Akcicek, A.; Kayacan, S. Effects of Different Drying Methods on Drying Kinetics, Microstructure, Color, and the Rehydration Ratio of Minced Meat. Foods 2019, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başlar, M. From Fresh to Dried: Evaluating Drying Kinetics of Sultana and Besni Grapes. Int. J. Gastron. Res. 2023, 2, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampi, M.; Schmidt, F.C.; Laurindo, J.B. A Fast Drying Method for the Production of Salted-and-Dried Meat. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathakaranakule, A.; Kraiwanichkul, W.; Soponronnarit, S. Comparative Study of Different Combined Superheated-Steam Drying Techniques for Chicken Meat. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prothon, F.; Ahrné, L.M.; Funebo, T.; Kidman, S.; Langton, M.; Sjöholm, I. Effects of Combined Osmotic and Microwave Dehydration of Apple on Texture, Microstructure and Rehydration Characteristics. LWT 2001, 34, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, S.; Yan, L.; Li, R. Effects of microwave heating on physicochemical properties, microstructure and volatile profiles of yak meat. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2019, 47, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmat, T.; Barka, M.; Aregba, A.W.; Bruneau, D. Convective Drying Kinetics of Fresh Beef: An Experimental and Modeling Approach. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 2581–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İsmail, O.; Kocabay, O. Infrared and Microwave Drying of Rainbow Trout: Drying Kinetics and Modelling. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaei, S.; Motevali, A.; Ahmadi, E.; Azizi, H. Mathematical Models of Drying Pomegranate Arils in Vacuum and Microwave Dryers. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaee, E.; Rafiee, S.; Keyhani, A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Determining of Moisture Diffusivity and Activation Energy in Drying of Apricots. Res. Agric. Eng. 2009, 55, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model Names | Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Lewis (Newton) | MR = exp(–kt) | [41] |
| Page | MR = exp (–ktn) | [42] |
| Weibull | MR = a exp (–ktn) | [43] |
| Henderson and Pabis | MR = a exp (–(kt)) | [44] |
| Modified Henderson and Pabis | MR = a exp (–kt) + b exp (–gt) + c exp (–ht) | [45] |
| Logarithmic | MR = a exp (–(kt)) + c | [46] |
| Two-term | MR = a exp (–k0t) + b exp ((–k1t) | [47] |
| Wang and Singh | MR = 1 + at + bt2 | [48] |
| Verma | MR = a exp (–kt) + (1–a) exp (–gt) | [49] |
| Drying Method | Temperature/Power | L* | a* | b* | TBARS (mgMDA/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw meat | 39.08 ± 3.32 c | 18.04 ± 1.23 c | 5.76 ± 0.44 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | |
| Salted meat | 29.41 ± 0.93 ab | 10.73 ± 0.89 b | 9.36 ± 0.64 b | 0.49 ± 0.02 b | |
| ID | 55 °C | 27.64 ± 0.12 ab | 3.46 ± 0.40 a | 8.75 ± 0.71 b | 0.79 ± 0.02 g |
| 65 °C | 27.12 ± 0.19 a | 3.56 ± 0.20 a | 8.90 ± 0.67 b | 0.72 ± 0.07 ef | |
| 75 °C | 27.83 ± 0.40 ab | 4.40 ± 0.31 a | 8.91 ± 0.83 b | 0.64 ± 0.04 c | |
| HAD | 55 °C | 27.01 ± 0.90 a | 3.48 ± 0.37 a | 8.75 ± 0.66 b | 0.91 ± 0.03 i |
| 65 °C | 26.87 ± 0.37 a | 3.78 ± 0.29 a | 8.75 ± 1.04 b | 0.84 ± 0.02 h | |
| 75 °C | 27.83 ± 0.32 ab | 4.47 ± 0.22 a | 8.91 ± 0.6 b | 0.75 ± 0.02 f | |
| MD | 120 W | 27.33 ± 0.23 ab | 3.67 ± 0.21 a | 12.36 ± 0.49 d | 0.83 ± 0.03 gh |
| 350 W | 28.88 ± 0.79 ab | 3.88 ± 0.11 a | 11.68 ± 0.52 cd | 0.69 ± 0.02 de | |
| 460 W | 29.74 ± 0.78 b | 4.54 ± 0.21 a | 11.01 ± 0.62 c | 0.67 ± 0.09 cd |
| Drying Method | Temperature/Power | Shrinkage Rate | Rehydration Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 55 °C | 17.01 ± 0.62 a | 1.44 ± 0.03 c |
| 65 °C | 21.18 ± 0.71 c | 1.52 ± 0.02 d | |
| 75 °C | 25.95 ± 1.30 e | 1.58 ± 0.02 e | |
| HAD | 55 °C | 18.40 ± 0.86 b | 1.38 ± 0.02 b |
| 65 °C | 23.11 ± 0.43 d | 1.51 ± 0.01 d | |
| 75 °C | 29.13 ± 1.21 f | 1.62 ± 0.02 e | |
| MD | 120 W | 24.93 ± 1.01 e | 1.11 ± 0.04 a |
| 350 W | 29.49 ± 0.71 f | 1.36 ± 0.03 b | |
| 460 W | 31.00 ± 0.66 g | 1.36 ± 0.05 b |
| Model | Parameters | ID | HAD | MD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 °C | 65 °C | 75 °C | 55 °C | 65 °C | 75 °C | 120 W | 350 W | 460 W | ||
| Lewis | 0.116 | 0.141 | 0.167 | 0.099 | 0.122 | 0.160 | 8.058 | 39.904 | 45.251 | |
| 0.990 | 0.987 | 0.984 | 0.944 | 0.971 | 0.976 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 0.941 | ||
| 0.949 | 1.253 | 1.484 | 3.064 | 1.678 | 1.417 | 4.633 | 5.917 | 6.201 | ||
| RMSE | 0.03034 | 0.034799 | 0.037808 | 0.054419 | 0.040139 | 0.036776 | 0.06734 | 0.073344 | 0.07424 | |
| Page | 0.163 | 0.201 | 0.241 | 0.183 | 0.182 | 0.226 | 24.789 | 333.063 | 464.773 | |
| 0.839 | 0.817 | 0.790 | 0.727 | 0.799 | 0.807 | 1.504 | 1.565 | 1.592 | ||
| 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.995 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| 0.124 | 0.203 | 0.152 | 0.0783 | 0.266 | 0.168 | 0.166 | 0.0743 | 0.0878 | ||
| RMSE | 0.01096 | 0.013998 | 0.012091 | 0.008698 | 0.015966 | 0.012668 | 0.01276 | 0.008219 | 0.008837 | |
| Weibull | 1.001 | 0.997 | 1.001 | 0.990 | 0.976 | 0.978 | 1.024 | 1.012 | 1.007 | |
| 0.164 | 0.198 | 0.242 | 0.176 | 0.164 | 0.208 | 22.209 | 300.343 | 432.357 | ||
| 0.838 | 0.821 | 0.789 | 0.738 | 0.835 | 0.838 | 1.440 | 1.533 | 1.571 | ||
| 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.999 | ||
| 0.124 | 0.205 | 0.136 | 0.075 | 0.232 | 0.137 | 0.11 | 0.0538 | 0.0777 | ||
| RMSE | 0.01098 | 0.014092 | 0.011427 | 0.008516 | 0.014922 | 0.011424 | 0.01040 | 0.006992 | 0.008312 | |
| Henderson and Pabis | 0.111 | 0.133 | 0.157 | 0.083 | 0.107 | 0.143 | 9.444 | 44.809 | 50.480 | |
| 0.966 | 0.960 | 0.957 | 0.887 | 0.918 | 0.922 | 1.138 | 1.108 | 1.097 | ||
| 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.983 | 0.990 | 0.992 | 0.977 | 0.965 | 0.960 | ||
| 0.623 | 0.797 | 0.948 | 0.94 | 0.548 | 0.471 | 1.946 | 3.735 | 4.242 | ||
| RMSE | 0.02458 | 0.027765 | 0.030208 | 0.030148 | 0.022933 | 0.021198 | 0.04364 | 0.058274 | 0.061406 | |
| Modified Henderson and Pabis | −0.531 | 0.615 | −0.547 | 0.781 | 0.626 | 0.610 | 3.432 | −14.588 | 7.613 | |
| 5.058 | −0.908 | 4.792 | −1.643 | −1.327 | −1.290 | 2.211 | 7.091 | 5.328 | ||
| −4.532 | 0.262 | −4.253 | 0.779 | 0.628 | 0.613 | −5.564 | 7.554 | −12.896 | ||
| −0.005 | −0.005 | −0.007 | −0.004 | −0.004 | −0.005 | 0.912 | 8.964 | 2.723 | ||
| 0.300 | 0.142 | 0.496 | 0.095 | 0.108 | 0.146 | 2.846 | 8.949 | 8.108 | ||
| 0.301 | −0.005 | 0.497 | −0.004 | −0.003 | −0.005 | 2.844 | 2.948 | 8.266 | ||
| 0.999 | 0.993 | 0.999 | 0.989 | 0.991 | 0.993 | 0.994 | 0.991 | 0.992 | ||
| 0.058 | 0.67 | 0.0681 | 0.608 | 0.533 | 0.426 | 0.537 | 0.942 | 0.861 | ||
| RMSE | 0.00751 | 0.02545 | 0.008095 | 0.024234 | 0.022631 | 0.020163 | 0.02292 | 0.02926 | 0.027673 | |
| Logarithmic | 0.904 | 0.900 | 0.875 | 0.796 | 0.874 | 0.879 | 1.684 | 1.840 | 2.512 | |
| 0.133 | 0.158 | 0.200 | 0.121 | 0.124 | 0.166 | 4.501 | 18.339 | 14.144 | ||
| 0.073 | 0.070 | 0.096 | 0.130 | 0.057 | 0.059 | −0.605 | −0.784 | −1.649 | ||
| 0.995 | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.991 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.992 | ||
| 0.415 | 0.595 | 0.586 | 0.492 | 0.489 | 0.381 | 0.568 | 0.989 | 0.878 | ||
| RMSE | 0.02006 | 0.02398 | 0.023751 | 0.02181 | 0.021669 | 0.019071 | 0.02357 | 0.029986 | 0.027933 | |
| Two-term | 1.062 | 1.584 | 1.563 | 0.863 | 1.615 | 2.252 | 2.818 | 11.085 | 8.499 | |
| 0.097 | 0.116 | 0.132 | 0.072 | 0.099 | 0.133 | 2.427 | 9.845 | 7.014 | ||
| 0.131 | 0.141 | 0.165 | 0.204 | 0.137 | 0.131 | 12.583 | 18.753 | 19.006 | ||
| 0.873 | 0.863 | 0.837 | 0.796 | 0.865 | 0.869 | −11.504 | −17.697 | −17.962 | ||
| 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.992 | ||
| 0.036 | 0.0563 | 0.043 | 0.00209 | 0.0614 | 0.00885 | 0.549 | 0.982 | 0.875 | ||
| RMSE | 0.0059 | 0.007376 | 0.006433 | 0.001423 | 0.007676 | 0.002906 | 0.02318 | 0.029878 | 0.027894 | |
| Wang and Singh | −0.099 | −1.118 | −0.142 | −0.090 | −0.108 | −0.138 | −5.536 | −28.041 | −30.469 | |
| 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 5.222 | 137.166 | 99.316 | ||
| 0.997 | 0.971 | 0.969 | 0.931 | 0.952 | 0.956 | 0.985 | 0.987 | 0.988 | ||
| 2.174 | 2.705 | 2.793 | 3.788 | 2.743 | 2.623 | 1.231 | 1.432 | 1.218 | ||
| RMSE | 0.04592 | 0.051136 | 0.051864 | 0.060516 | 0.051318 | 0.050036 | 0.03471 | 0.036076 | 0.032907 | |
| Verma | 0.097 | 0.116 | 0.132 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.133 | 0.864 | 5.401 | 2.795 | |
| 0.872 | 0.862 | 0.836 | −0.429 | 0.865 | 0.869 | −10.462 | −16.853 | −17.751 | ||
| 1.002 | 1.490 | 1.511 | 0.099 | 1.594 | 2.251 | 1.288 | 6.669 | 4.267 | ||
| 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.944 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.985 | 0.986 | 0.988 | ||
| 0.038 | 0.0588 | 0.0433 | 3.066 | 0. 0618 | 0. 00885 | 1.261 | 1.493 | 1.237 | ||
| RMSE | 0.00604 | 0.007539 | 0.006461 | 0.054444 | 0.007704 | 0.002906 | 0.03514 | 0.036845 | 0.033157 | |
| Drying Method | Deff (m2/s) | Arrhenius Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | Ea (J/mol) | R2 | ||
| ID | 2.44 × 10−10 | 1.325 × 10−7 | 17,169.91 | 0.999 |
| 2.97 × 10−10 | ||||
| 3.51 × 10−10 | ||||
| HAD | 2.05 × 10−10 | 1.601 × 10−6 | 24,526.51 | 0.988 |
| 2.52 × 10−10 | ||||
| 3.38 × 10−10 | ||||
| MD | 1.71 × 10−8 | 1.802 × 10−7 | 26.98 (W/g) | 0.993 |
| 8.72 × 10−8 | ||||
| 9.74 × 10−8 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabil, E.; Çakır, M.A.; Yalınkılıç, B.; Başlar, M. Quality and Microstructural Changes in Salted Goose Meat Dried by Hot-Air, Infrared, and Microwave Techniques. Processes 2025, 13, 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103223
Kabil E, Çakır MA, Yalınkılıç B, Başlar M. Quality and Microstructural Changes in Salted Goose Meat Dried by Hot-Air, Infrared, and Microwave Techniques. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103223
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabil, Emre, Muhammet Ali Çakır, Barış Yalınkılıç, and Mehmet Başlar. 2025. "Quality and Microstructural Changes in Salted Goose Meat Dried by Hot-Air, Infrared, and Microwave Techniques" Processes 13, no. 10: 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103223
APA StyleKabil, E., Çakır, M. A., Yalınkılıç, B., & Başlar, M. (2025). Quality and Microstructural Changes in Salted Goose Meat Dried by Hot-Air, Infrared, and Microwave Techniques. Processes, 13(10), 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103223









