Effect of Radio-Frequency Drying on the Physicochemical Properties and Isoflavone Contents of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Black Bean Dregs and Fermentation of Their Products
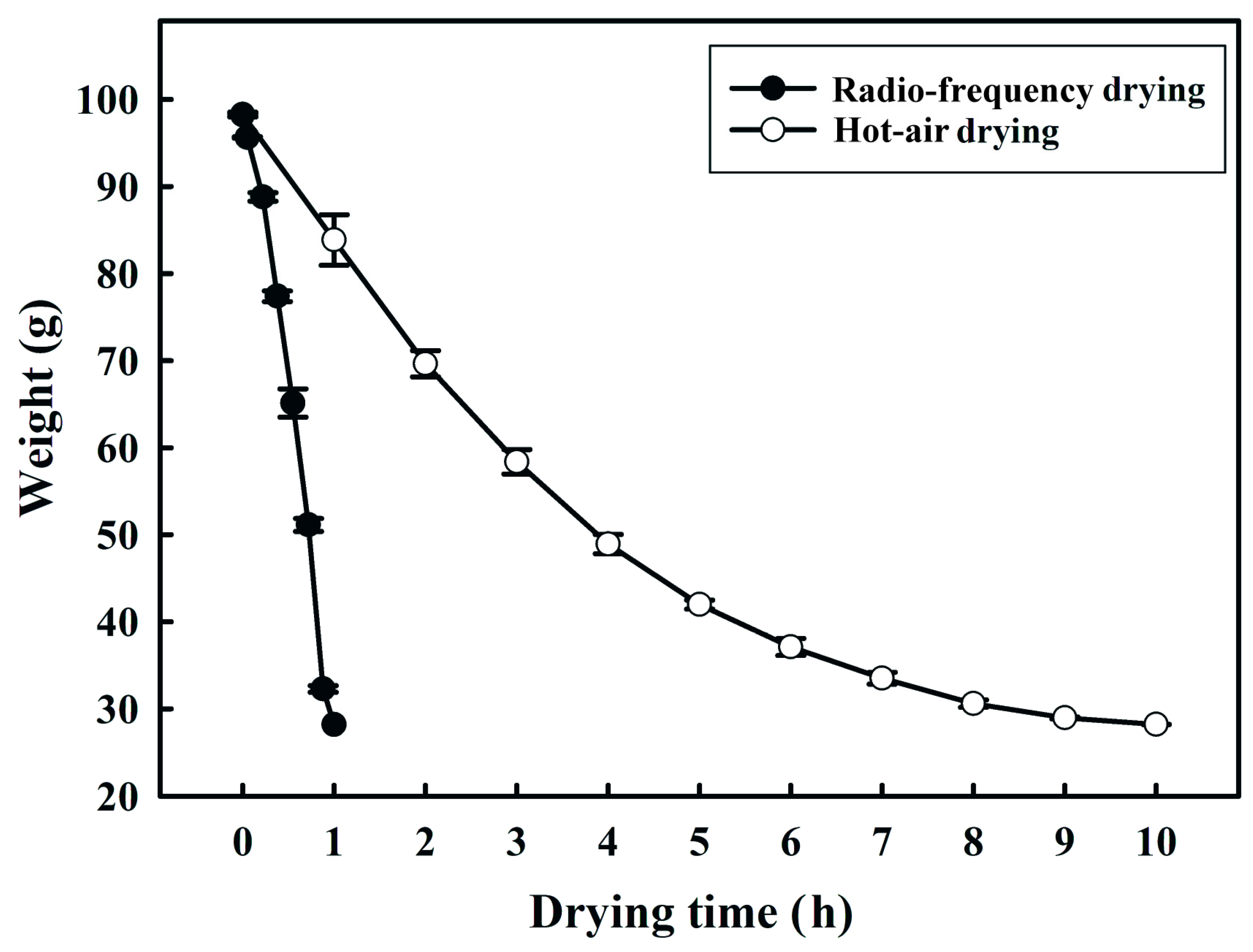
2.2. Effect of Hot-Air and RF Drying on the Weight of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
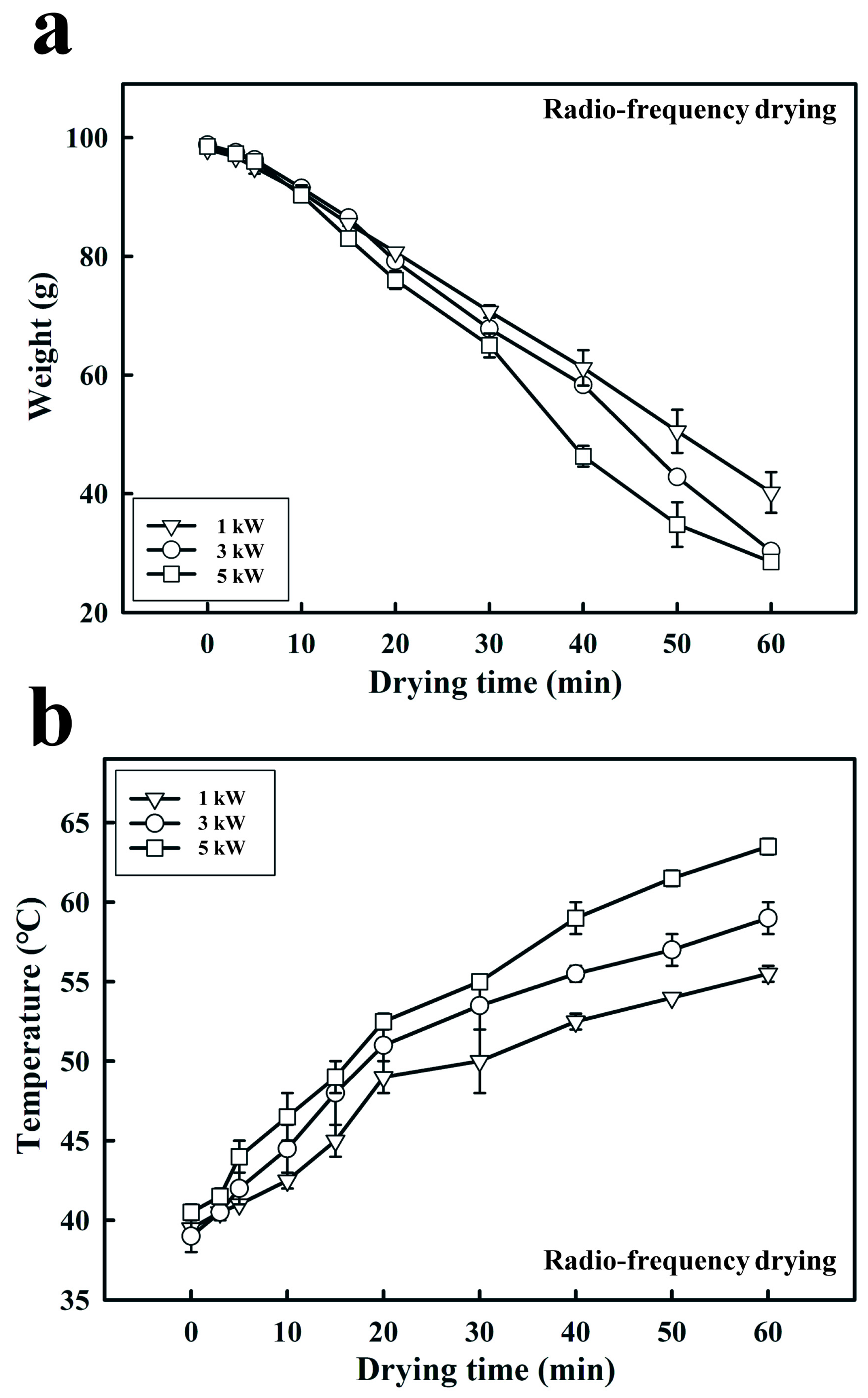
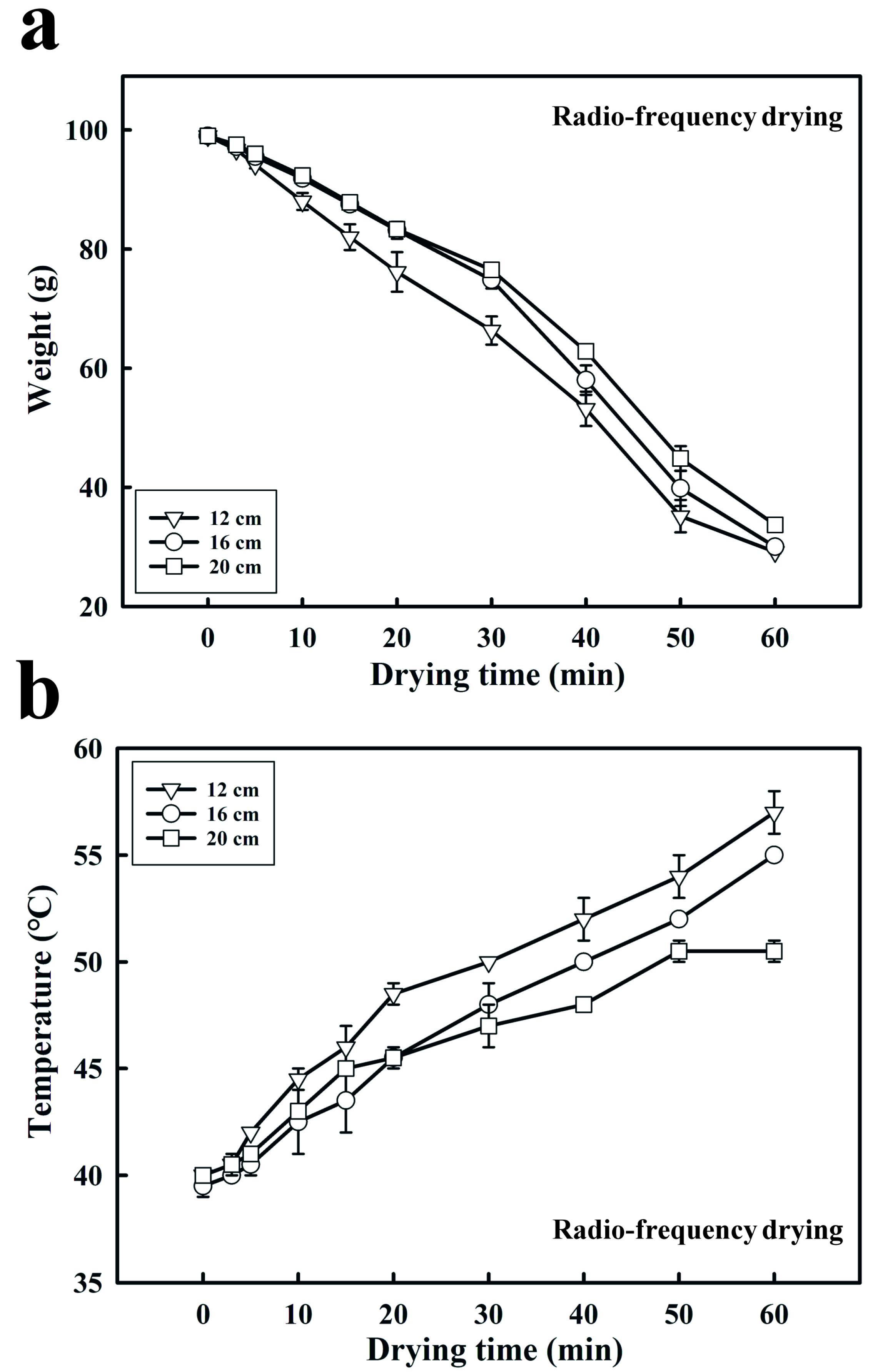
2.3. Effect of RF Output Power and Electrode Gap on the Weight of Dried Fermented Black Bean Dregs
2.4. Determination of Water Activity and Color of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
2.5. Determination of Fermented Black Bean Dreg Solubility
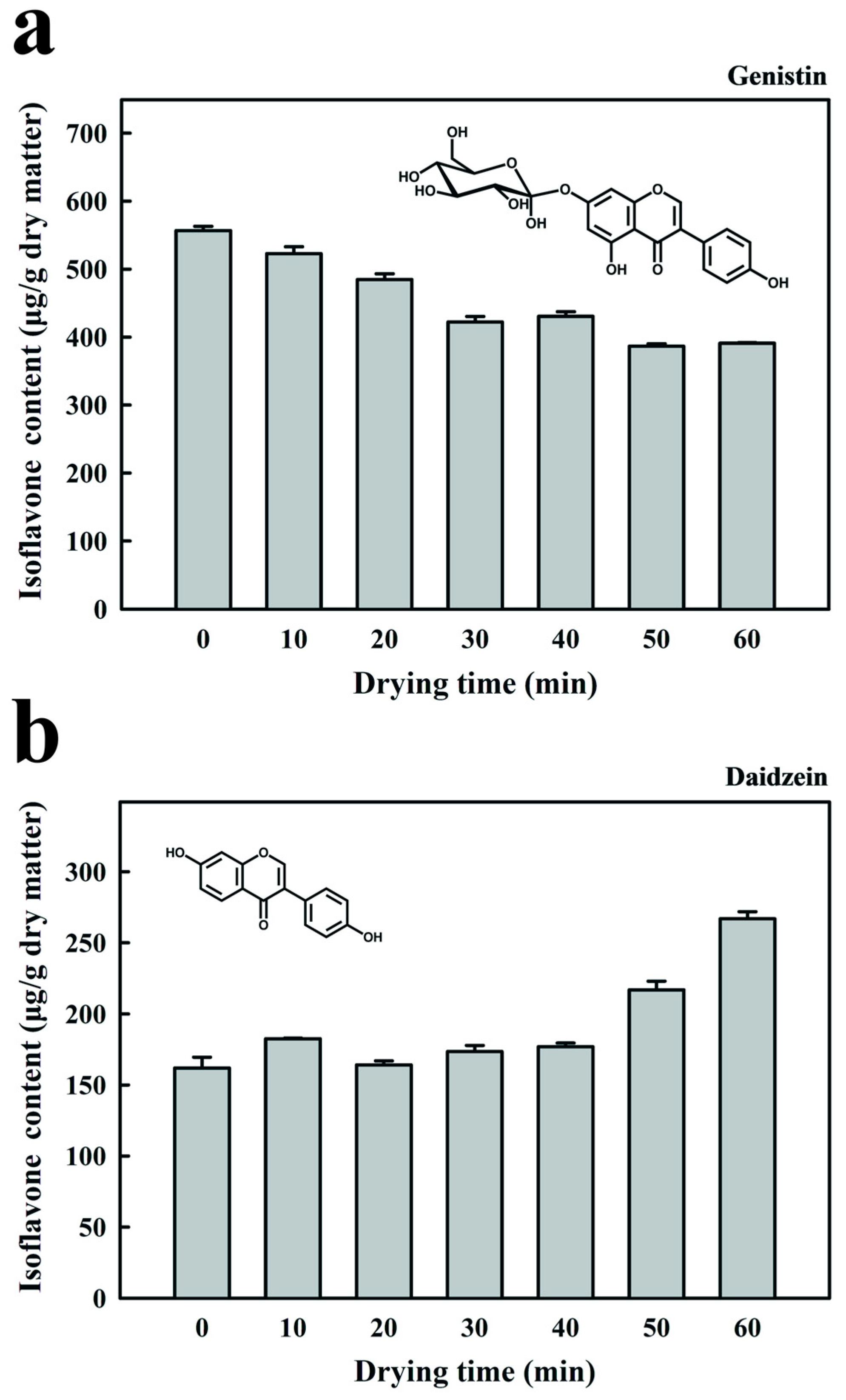
2.6. Determination of Isoflavone Contents in Fermented Black Bean Dregs
2.7. Determination of the Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Hot-Air and RF Drying on the Weight of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
3.2. Effects of the RF Output Power and Electrode Gap on Fermented Black Bean Dreg Drying
3.3. Effect of RF Drying Time on the Water Activity, Appearance, Color, and Solubility of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
3.4. Effect of RF Drying Time on the Isoflavone Content and Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Black Bean Dregs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Changrue, V.; Raghavan, V.G.; Orsat, V.; Vijaya Raghavan, G. Microwave drying of fruits and vegetables. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2006, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, F. Recent applications and potential of infrared dryer systems for drying various agricultural products: A review. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 20, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S. Recent developments in radio frequency drying of food and agricultural products: A review. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Zhang, L.; Lyng, J.G. Radio frequency treatment of foods: Review of recent advances. J. Food Eng. 2009, 91, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Gu, Y.; Li, W.; Zheng, J.; Jiang, H. Physicochemical characteristics, antioxidant capacity and thermodynamic properties of purple-fleshed potatos dried by radio frequency energy. Dry. Technol. 2020, 38, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhen, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Evaluation of strawberries dried by radio frequency energy. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, C.; Wang, X.; Liao, M.; Yue, J.; Jiao, S. Application of hot air-assisted radio frequency as second stage drying method for mango slices. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yen, Y.; Chen, S. Study of radio frequency drying on soybean residue. Taiwan. J. Agric. Chem. Food Sci. 2017, 55, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, R. Effect of drying methods on functional properties of bean curd dregs. J. Henan Inst. Sci. Technol. 2008, 36, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mateos-Aparicio, I.; Redondo-Cuenca, A.; Villanueva-Suárez, M.J.; Zapata-Revilla, M.A.; Tenorio-Sanz, M.D. Pea pod, broad bean pod and okara, potential sources of functional compounds. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnan-Winarno, A.D.; Cordeiro, L.; Winarno, F.G.; Gibbons, J.; Xiao, H. Tempeh: A semicentennial review on its health benefits, fermentation, safety, processing, sustainability, and affordability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1717–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, W.C.; Hua, X.Y.; Liu, S.Q. Solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus oligosporus and Yarrowia lipolytica improved nutritional and flavour properties of okara. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, R.; Azi, F.; Jiao, L.; Wang, H.; He, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Lu, B. Solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus oligosporus RT-3 enhanced the nutritional properties of soybeans. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 972860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Fan, J.F.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Li, L.T. Improvement of the antioxidant activity of Chinese traditional fermented okara (Meitauza) using Bacillus subtilis B2. Food Control 2008, 19, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andayani, S.N.; Lioe, H.N.; Wijaya, C.H.; Ogawa, M. Umami fractions obtained from water-soluble extracts of red oncom and black oncom-Indonesian fermented soybean and peanut products. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, R.; Romulo, A. Antioxidant profile of red oncom, an Indonesian traditional fermented soyfood. Food Res. 2023, 7, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Li, J.; Ruan, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, D. Process for increasing soluble dietary fiber content of soybean meals. Trans. CSAE 2007, 23, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.M.; Ma, C.Y. Acid modification of proteins from soymilk residue (okara). Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiao, M.; Lu, F. Composition, nutrition, and utilization of okara (soybean residue). Food Rev. Int. 2012, 28, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, B.Y. Response surface methodology-optimized co-fermentation of pigeon pea okara by Rhizopus oligosporus and Yarrowia lipolytica and its application for vegetable paste. JSFA Rep. 2022, 2, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tong, X.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xie, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Xu, J.; et al. Effect of spray-drying and freeze-drying on the properties of soybean hydrolysates. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 9201457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, I.; Laranjo, M.; Potes, M.E.; Agulheiro-Santos, A.C.; Ricardo-Rodrigues, S.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Oliveira, M.; Elias, M. Staphylococcus spp. and Lactobacillus sakei starters with high level of inoculation and an extended fermentation step improve safety of fermented sausages. Fermentation 2022, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lin, J.H.; Chang, S.Y. Physicochemical properties of waxy and normal corn starches treated in different anhydrous alcohols with hydrochloric acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.H.; Hsieh, J.F. The conversion and deglycosylation of isoflavones and anthocyanins in black soymilk process. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.L.; Yu, Y.P.; Hsieh, J.F.; Kuo, M.I.; Ma, Y.S.; Lu, C.P. Effect of germination on composition profiling and antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide-protein conjugate in black soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, B.M.; Lyng, J.; Brunton, N.; Shirsat, N. Advances in radio frequency and ohmic heating of meats. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.K.; Yang, L.; Fang, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J. Effects of intermittent radio frequency drying on structure and gelatinization properties of native potato flour. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewale, S.R.; Rajoriya, D.; Bhavya, M.L.; Hebbar, H.U. Application of radiofrequency heating and low humidity air for sequential drying of apple slices: Process intensification and quality improvement. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shi, L.; Qi, H.; Xie, Y.; Cai, L. Effect of radio frequency (RF) drying technology on dehydration rate and energy consumption of Australia lignite. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Marra, F.; Subbiah, J.; Wang, S. Computer simulation for improving radio frequency (RF) heating uniformity of food products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1033–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, J.; Gao, M.; Tang, J.; Powers, J.R.; Wang, S. Developing hot air-assisted radio frequency drying for in-shell macadamia nuts. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M. A new look at models of the combined effect of temperature, pH, water activity, or other factors on microbial growth rate. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yen, Y.F.; Chen, S.D. Effects of radio frequency heating on the stability and antioxidant properties of rice bran. Foods 2021, 10, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, S.N.; Prakash, J. Nutritional and sensory quality of buns enriched with soy fiber (Okara). J. Eng. Process. Manag. 2018, 10, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Tatol, M. Colour difference ∆ E-A survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Subbiah, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of radio frequency heating treatment on structure changes of soy protein isolate for protein modification. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutsinas, L.P.; Cheung, E.; Nakai, S. Relationships of hydrophobicity to emulsifying properties of heat denatured proteins. J. Food Sci. 1983, 48, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.B.; Pawelzik, E.; von Hoersten, D. Effect of radio frequency heating on nutritional quality and protein solubility of corn. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.F.; Chen, S.D. Influence of radio frequency heating on the pasteurization and drying of solid-state fermented Wolfiporia cocos products. Foods 2022, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoli, M.C.; Anese, M.; Parpinel, M. Influence of processing on the antioxidant properties of fruit and vegetables. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Wu, D.; Dai, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, W. Effect of radio frequency-assisted hot-air drying on drying kinetics and quality of Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum maxim). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Gou, M.; Xia, T.; Li, W.; Song, X.; Jiang, H. Characteristics of pitaya after radio frequency treating: Structure, phenolic compounds, antioxidant, and antiproliferative activity. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| RF Drying Time | Colorimetric Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (min) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* |
| 0 | 21.13 ± 0.15 a | 4.24 ± 0.04 a | 7.96 ± 0.06 a | 0 ± 0 a |
| 10 | 21.84 ± 0.24 a | 4.26 ± 0.02 a | 7.94 ± 0.04 a | 0.71 ± 0.29 a |
| 20 | 22.48 ± 0.40 a | 4.32 ± 0.02 a | 8.06 ± 0.11 ab | 1.35 ± 0.71 a |
| 30 | 25.91 ± 0.93 b | 4.47 ± 0.04 ab | 8.72 ± 0.09 bc | 4.83 ± 1.30 b |
| 40 | 26.81 ± 0.88 b | 4.67 ± 0.08 bc | 9.15 ± 0.14 cd | 5.81 ± 1.21 b |
| 50 | 26.58 ± 0.38 b | 4.79 ± 0.10 bc | 9.31 ± 0.21 cd | 5.63 ± 0.51 b |
| 60 | 26.62 ± 1.08 b | 4.85 ± 0.13 c | 9.51 ± 0.27 d | 5.73 ± 2.71 b |
| RF Drying Time (min) | Mean Solubility (%) | EC50 of Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24.5 ± 0.3 a | 43.6 ± 0.9 a |
| 10 | 27.6 ± 0.4 b | 52.1 ± 0.6 c |
| 20 | 28.1 ± 1.2 b | 52.5 ± 1.7 c |
| 30 | 28.2 ± 0.6 b | 55.0 ± 1.0 d |
| 40 | 28.6 ± 0.6 b | 47.6 ± 1.0 b |
| 50 | 28.9 ± 0.1 b | 50.7 ± 1.5 c |
| 60 | 28.84 ± 0.1 b | 51.7 ± 0.7 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Kuo, M.-I.; Chen, B.-Y.; Lu, C.-P.; Yeh, C.-C.; Jao, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-C.; Hsieh, J.-F. Effect of Radio-Frequency Drying on the Physicochemical Properties and Isoflavone Contents of Fermented Black Bean Dregs. Processes 2024, 12, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071294
Huang C, Kuo M-I, Chen B-Y, Lu C-P, Yeh C-C, Jao C-H, Lai Y-C, Hsieh J-F. Effect of Radio-Frequency Drying on the Physicochemical Properties and Isoflavone Contents of Fermented Black Bean Dregs. Processes. 2024; 12(7):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071294
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Cheng, Meng-I Kuo, Bang-Yuan Chen, Chun-Ping Lu, Chien-Cheng Yeh, Cheng-Hsun Jao, Yi-Chung Lai, and Jung-Feng Hsieh. 2024. "Effect of Radio-Frequency Drying on the Physicochemical Properties and Isoflavone Contents of Fermented Black Bean Dregs" Processes 12, no. 7: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071294
APA StyleHuang, C., Kuo, M.-I., Chen, B.-Y., Lu, C.-P., Yeh, C.-C., Jao, C.-H., Lai, Y.-C., & Hsieh, J.-F. (2024). Effect of Radio-Frequency Drying on the Physicochemical Properties and Isoflavone Contents of Fermented Black Bean Dregs. Processes, 12(7), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12071294









