Conical Annular Nozzle Pressure Prediction and Applications to 3D Food-Printing for Dysphagia Diets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
- -
- The extrusion material is incompressible.
- -
- The extrusion material is sufficiently slow for the inertial terms to be neglected.
- -
- The extrusion material in the die entry is not rotational, which is prone to being stretched.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Raw Materials
3.2. Determination of Rheological Properties
3.3. IDDSI Tests
3.4. FEM Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
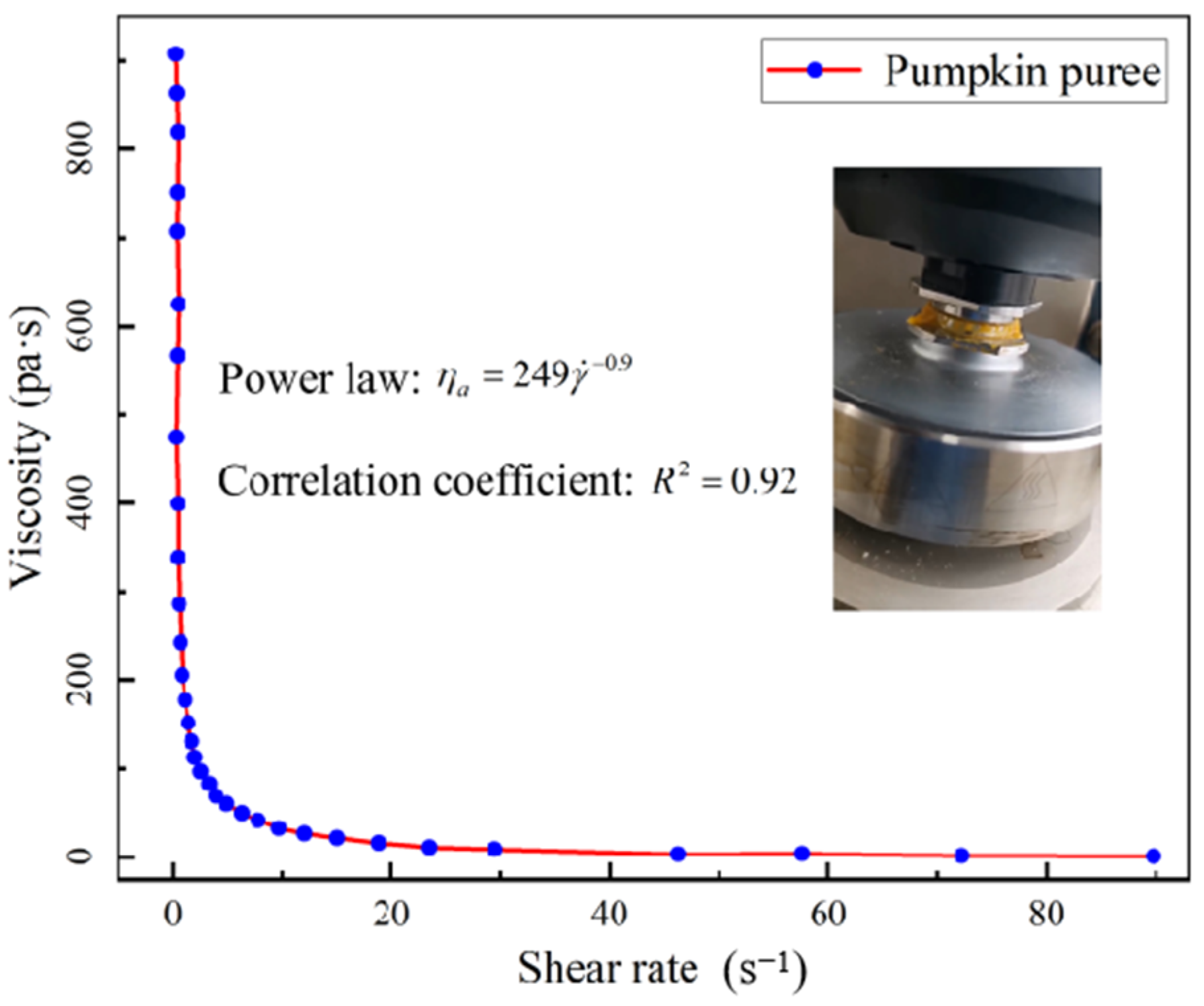
4.1. Rheological Properties
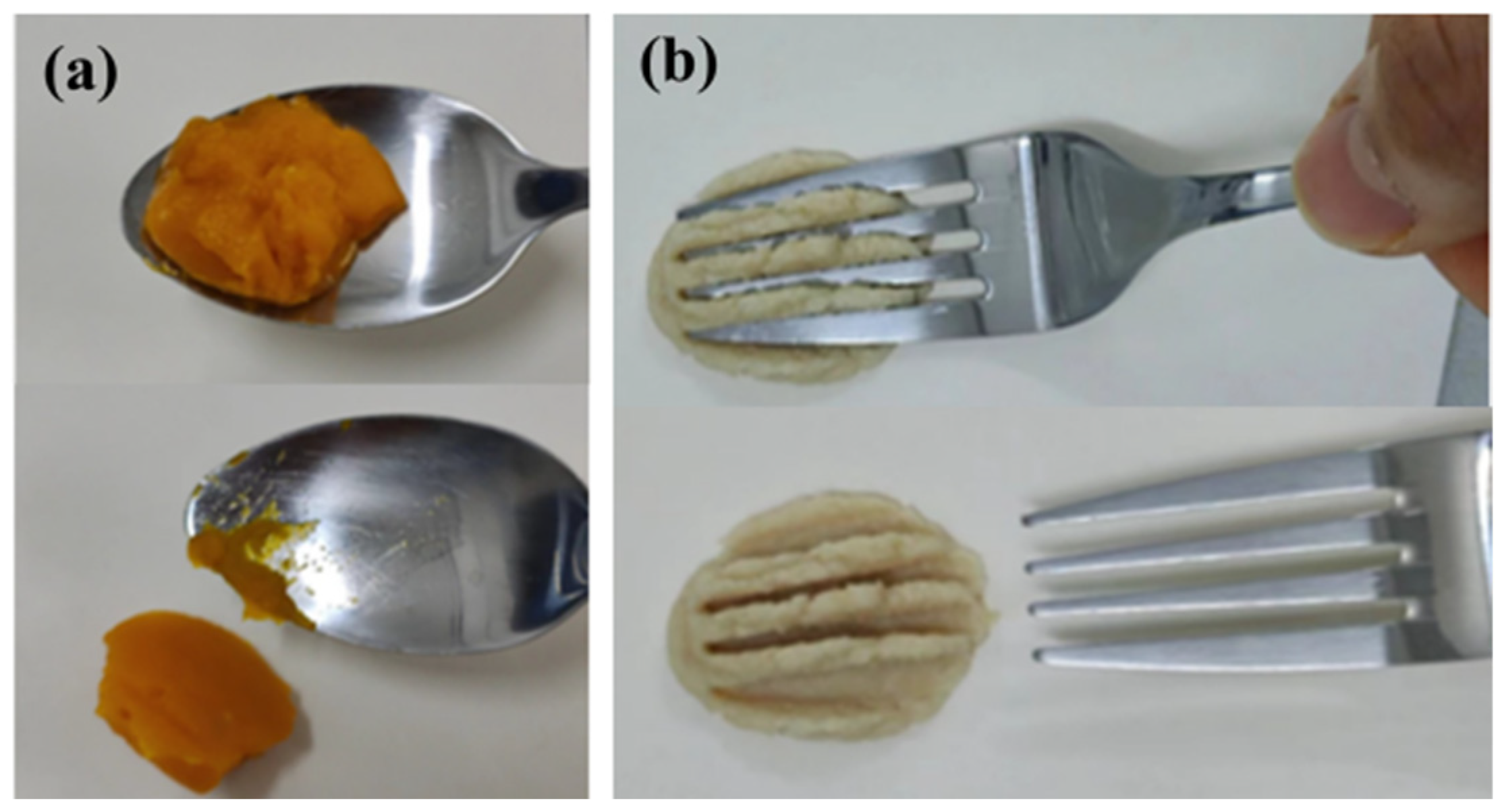
4.2. IDDSI Test
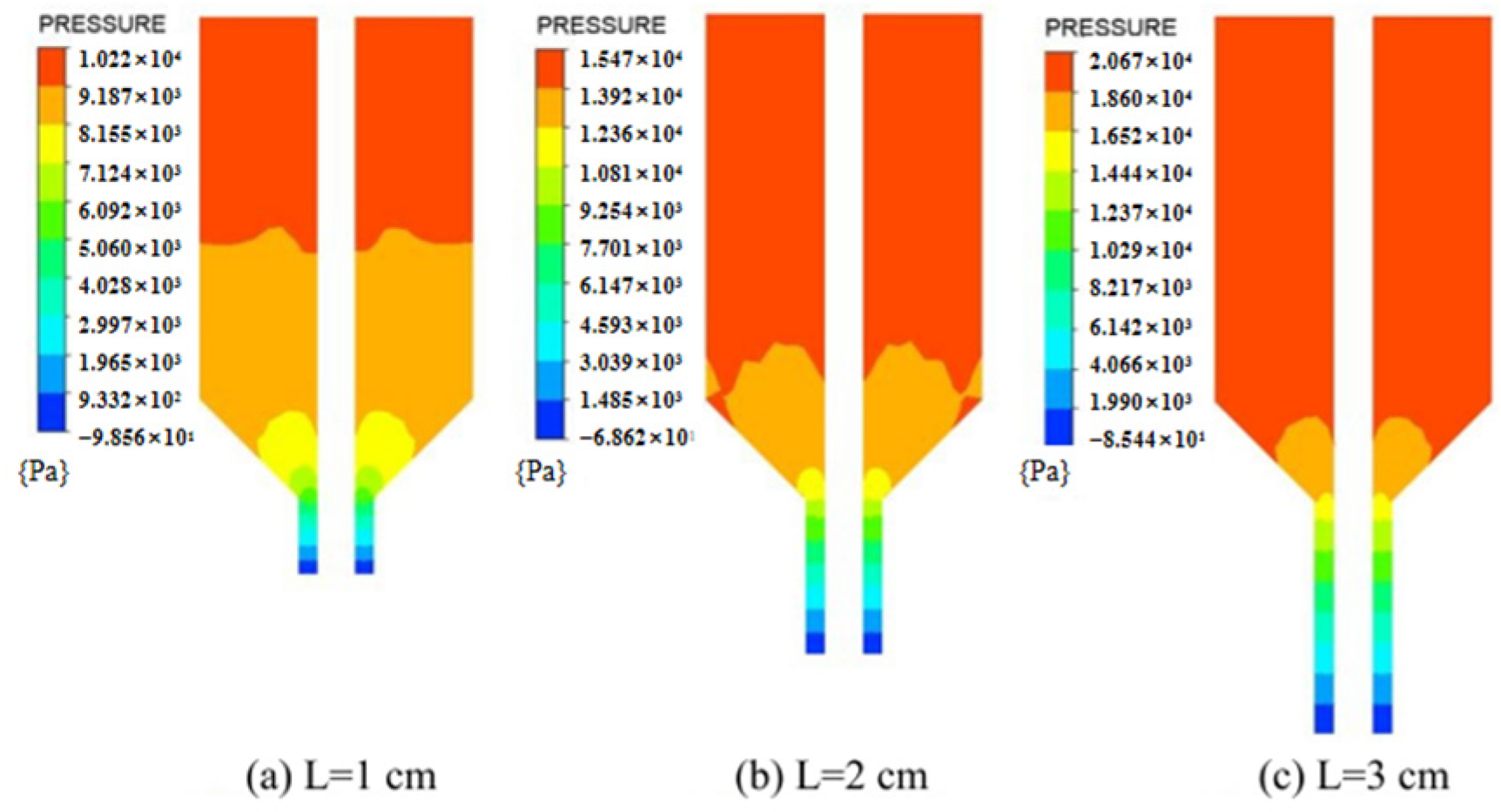
4.3. Pressure Analysis
4.4. Velocity Analysis
4.5. Characterization Parameters
5. Nozzle Design and Print Test
5.1. The Nozzle Structure
5.2. Print Test
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- A predictive model for the extrusion pressure of the conical annular nozzle is established, and the characterization parameters are determined by FEM. The error between the calculated value and the experimental value is within 15%.
- (2)
- Increasing the length of the die land is prone to increase the pressure loss within the extrusion barrel, but it has almost no effect on the flow velocity. Furthermore, the inlet volume flow rate has a significant impact on both the average velocity and the extrusion pressure positively related to it. In particular, an increase of 1 cm/s in the inlet volume flow rate leads to a corresponding increase of 1.5 cm/s in the average extrusion velocity.
- (3)
- A novel conical annular nozzle whose structural parameters were calculated by the predictive model was designed for dysphagia patients. Through the printing test, the printed food has a smooth and uniform shape, and the quality of the pork mince filling is good. Both pumpkin puree and minced pork meet IDDSI standards.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Almeida Pontes, P.V.; Shiwaku, I.A.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as potential solvent for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves: Extraction optimization and solvent characterization. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, I.; Dufresne, T.; Gray-Donald, K. A novel dysphagia diet improves the nutrient intake of institutionalized elders. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, I.W.; Choi, R.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.J. Coaxial 3D printing of chicken surimi incorporated with mealworm protein isolate as texture-modified food for the elderly. J. Food Eng. 2022, 333, 111151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Zarim, N.; Zainul Abidin, S.; Ariffin, F. Rheological studies on the effect of different thickeners in texture-modified chicken rendang for individuals with dysphagia. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4522–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargaraan, A.; Rastmanesh, R.; Fadavi, G.; Zayeri, F.; Mohammadifar, M.A. Rheological aspects of dysphagia-oriented food products: A mini review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2013, 2, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tian, H.; Chen, L.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Chen, J. Interactions between soluble soybean polysaccharide and starch during the gelatinization and retrogradation: Effects of selected starch varieties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Li, J. Easy-to-swallow mooncake using 3D printing: Effect of oil and hydrocolloid addition. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rong, L.; Shen, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, J. Rheology, texture and swallowing characteristics of a texture-modified dysphagia food prepared using common supplementary materials. Foods 2023, 12, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Khan, I.; Blundell, R.; Azzopardi, J.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni.: An updated review of its health benefits, industrial applications and safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Wang, Y. 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, T.; Iskandar, M.M.; Baeghbali, V.; Ngadi, M.O.; Kubow, S. 3D food printing applications related to dysphagia: A narrative review. Foods 2022, 11, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Li, J. Advances and application of efficient physical fields in extrusion based 3D food printing technology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 131, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Sartori, A.G.; Saliba, A.S.M.C.; Bitencourt, B.S.; Guedes, J.S.; Torres, L.C.R.; De Alencar, S.M.; Augusto, P.E.D. Anthocyanin bioaccessibility and anti-inflammatory activity of a grape-based 3D printed food for dysphagia. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Chitrakar, B.; Chang, L. Investigation of 3D printing of apple and edible rose blends as a dysphagia food. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diañez, I.; Gallegos, C.; Brito-de La Fuente, E.; Martínez, I.; Valencia, C.; Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M. Implementation of a novel continuous solid/liquid mixing accessory for 3D printing of dysphagia-oriented thickened fluids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.P.; Karyappa, R.; Hashimoto, M. 3D printing of milk-based product. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29821–29828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, T.; Kozu, H.; Kobayashi, I. Analysis of pumpkin paste printability for screw-based 3D food printer. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Εkonomou, S.Ι.; Hadnađev, M.; Gioxari, A.; Abosede, O.R.; Soe, S.; Stratakos, A.C. Advancing dysphagia-oriented multi-ingredient meal development: Optimising hydrocolloid incorporation in 3D printed nutritious meals. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Moon, K.D. Effects of isolated pea protein on honeyed red ginseng manufactured by 3D printing for patients with dysphagia. LWT 2024, 191, 115570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.P.; Ng, M.J.Y.; Chian, N.M.Y.; Hashimoto, M. Multi-material Direct Ink Writing 3D Food Printing using Multi-channel Nozzle. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, S.; Ubeyitogullari, A. Enhancing the stability of lutein by loading into dual-layered starch-ethyl cellulose gels using 3D food printing. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 69, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Lavados, C.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Rivera-Tobar, D.; Carvajal-Mena, N.; Palma-Acevedo, A.; Moreno-Osorio, L.; Pérez-Won, M. Development of bean-based emulgels for 3D printing applications: Feasibility for dysphagia diets. J. Food Eng. 2023, 358, 111687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Guo, C.; Zheng, W.; Cao, S.; Lu, H.; Mo, H.; Li, H. 3D printing of shiitake mushroom incorporated with gums as dysphagia diet. Foods 2021, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; Tu, K. Investigation of 3D printing product of powder-based white mushroom incorporated with soybean protein isolate as dysphagia diet. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.Y.; Lam, P.; Steele, C.M.; Hanson, B.; Chen, J.; Dantas, R.O.; Duivestein, J.; Kayashita, J.; Lecko, C.; Murray, J.; et al. Development of international terminology and definitions for texture-modified foods and thickened fluids used in dysphagia management: The iddsi framework. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, M.; Devahastin, S. Improvement of 3D printability of buckwheat starch-pectin system via synergistic Ca2+-microwave pretreatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Chitrakar, B.; Hati, S.; Xie, S.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Mo, H. Development of black fungus-based 3D printed foods as dysphagia diet: Effect of gums incorporation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Gelatin/polychromatic materials microgels enhanced by carnosic acid inclusions and its application in 2D pattern printing and multi-nozzle food 3D printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Phuhongsung, P.; Yu, D. Double-nozzle 3D-printed bean paste buns: Effect of filling ratio and microwave heating time. J. Texture Stud. 2023, 54, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; Khin, M.N.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Design and development of dual-extruder food 3D printer based on selective compliance assembly robot arm and printing of various inks. J. Food Eng. 2024, 370, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, N.; Freitas, C.; Ribeiro, M.; Abrantes, J.; Frade, J. Extrusion of porous cellular ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 109–110, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basterfield, A.; Dimitropoulos, G.; Bills, D.; Cullen, O.; Freeman, V.E. “I would love to have online support but I don’t trust it”: Positive and negative views of technology from the perspective of those with eating disorders in Canada. Health Soc. Care Community 2018, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, C.; Yan, M.; Ao, C. Blockage mechanism analysis and optimization design of 3D concrete printhead. J. Sustain. Cem. Based Mater. 2024, 13, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecanu, R.; Della Valle, G.; Leverrier, C.; Ramaioli, M. Predicting the gravity-driven flow of power law fluids in a syringe: A rheological map for the IDDSI classification. Rheol. Acta 2024, 63, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, Q.; Abbas, N.; Akbar, M.; Sabi, E.; Thomas, B.S.; Arshid, M.U. Influence of print speed and nozzle diameter on the fiber alignment in 3D printed ultra-high-performance concrete. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1355647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Blanco, J.C.; Galván-Chacón, V.; Patrocinio, D.; Matamoros, M.; Sánchez-Ortega, J.; Marcos, A.C.; Duarte-León, M.; Marinaro, F.; Pagador, J.B.; Sánchez-Margallo, F.M. Improving Cell Viability and Velocity in μ-Extrusion Bioprinting with a Novel Pre-Incubator Bioprinter and a Standard FDM 3D Printing Nozzle. Materials 2021, 14, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter Setting | D (cm) | D0 (cm) | L (cm) | D1 (cm) | L/(D − D1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical value | 1 | 3.6 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 0.5 | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 |
| Characterization Parameters | Pumpkin Puree |
|---|---|
| σ0 (MPa) | 0.6 |
| α (MPa sm m−m) | 1.1 |
| m | 0.21 |
| τ0 (MPa) | 0 |
| β (MPa sn m−n) | 0.52 |
| n | 0.2 |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| T (N·m) | 0.42 |
| S (cm/r) | 0.3 |
| D (cm) | 1 |
| D0 (cm) | 3.6 |
| D1 (cm) | 0.5 |
| L (cm) | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Ao, C.; Su, X.; Ren, C. Conical Annular Nozzle Pressure Prediction and Applications to 3D Food-Printing for Dysphagia Diets. Processes 2024, 12, 2747. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122747
Wang Y, Yan M, Yang K, Wang S, Ao C, Su X, Ren C. Conical Annular Nozzle Pressure Prediction and Applications to 3D Food-Printing for Dysphagia Diets. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2747. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122747
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yibo, Ming Yan, Kun Yang, Shourui Wang, Chenyang Ao, Xin Su, and Changzai Ren. 2024. "Conical Annular Nozzle Pressure Prediction and Applications to 3D Food-Printing for Dysphagia Diets" Processes 12, no. 12: 2747. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122747
APA StyleWang, Y., Yan, M., Yang, K., Wang, S., Ao, C., Su, X., & Ren, C. (2024). Conical Annular Nozzle Pressure Prediction and Applications to 3D Food-Printing for Dysphagia Diets. Processes, 12(12), 2747. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122747






