An Immunomodulating Peptide with Potential to Promote Anticancer Immunity Without Compromising Immune Tolerance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Peptide Synthesis
2.3. Isolation and In Vitro Culture of Human PBMC and Immune Cell Subsets for Functional Analysis
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. ELISA Assays
2.6. Proliferation Assay Comparing Effects of Peptide and Doxorubicin on B16F10 Melanoma Cell Growth In Vitro
2.7. Murine Melanoma Study
2.8. IMQ-P Study
2.9. Data Analyses
3. Results
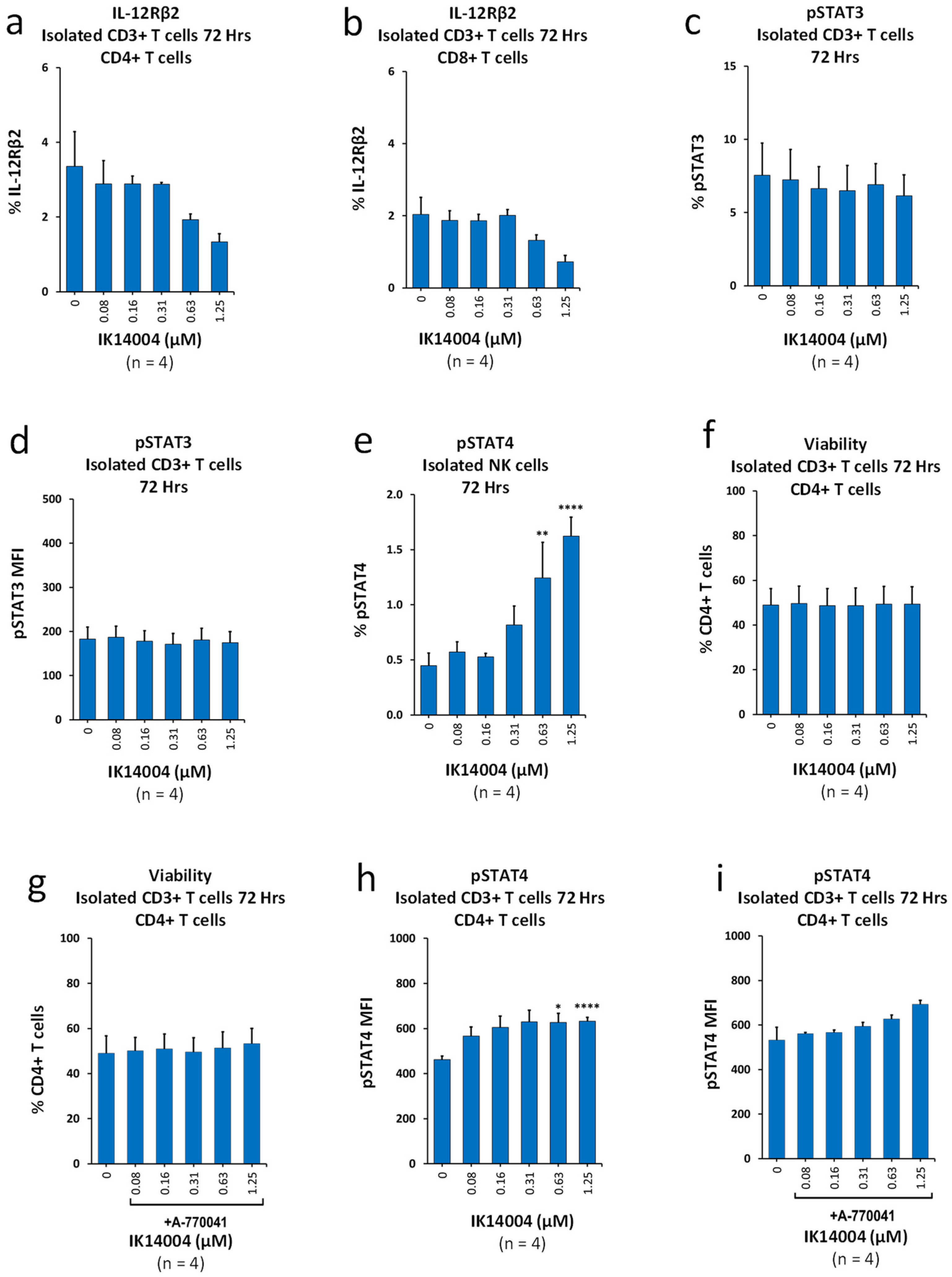
3.1. IK14004 Suppresses Expression of IL-12Rβ2 in Isolated T Cell Cultures and Differentially Activates STAT3/STAT4
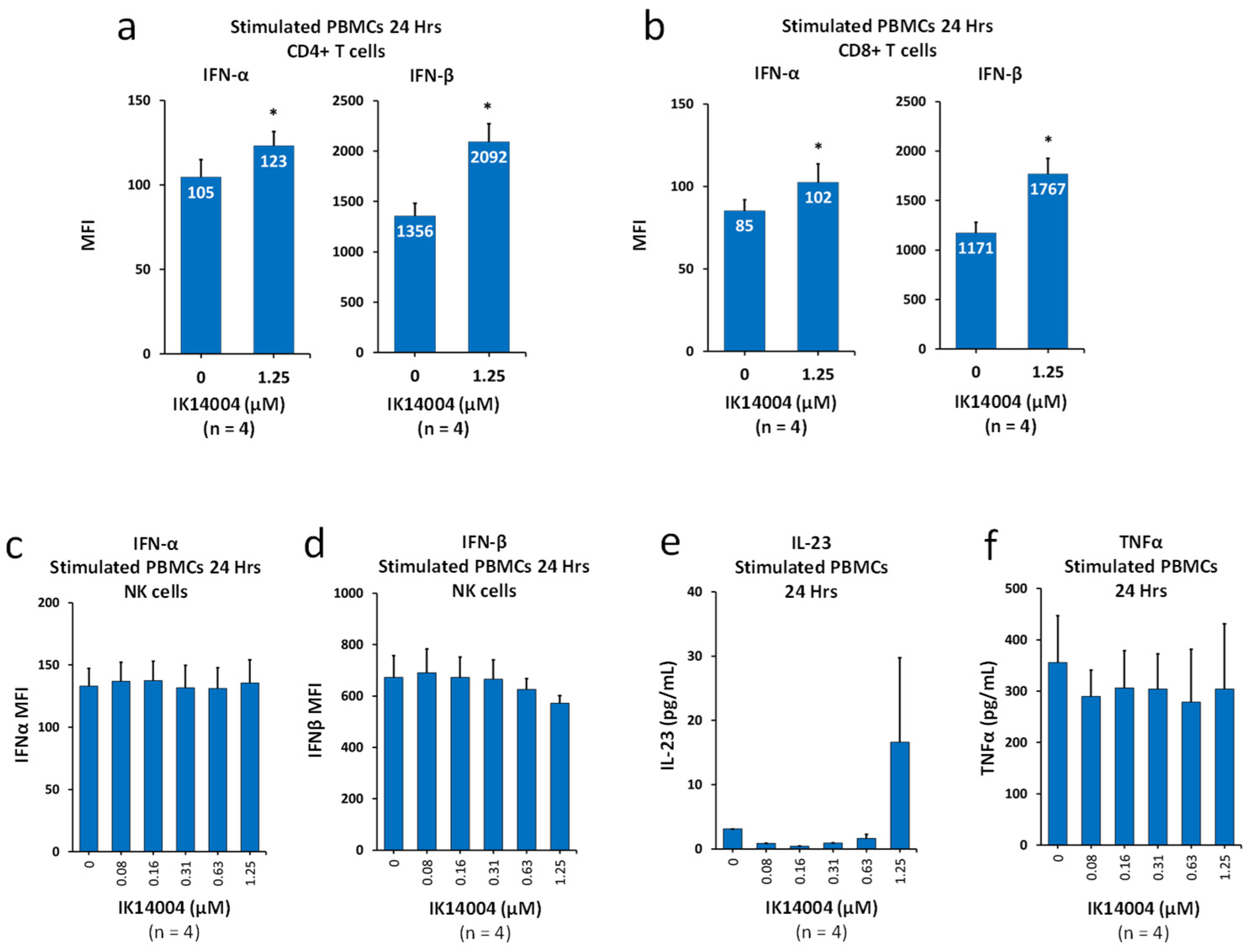
3.2. IK14004 Lowers the IFN-α:IFN-β Ratio in T Cells, but Not NK Cells, and Does Not Induce Production of IL-23 or Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α)
3.3. IK14004 Differentially Affects Expression of IL-15 and IL-2 Receptors in CD3+ T and NK Cells
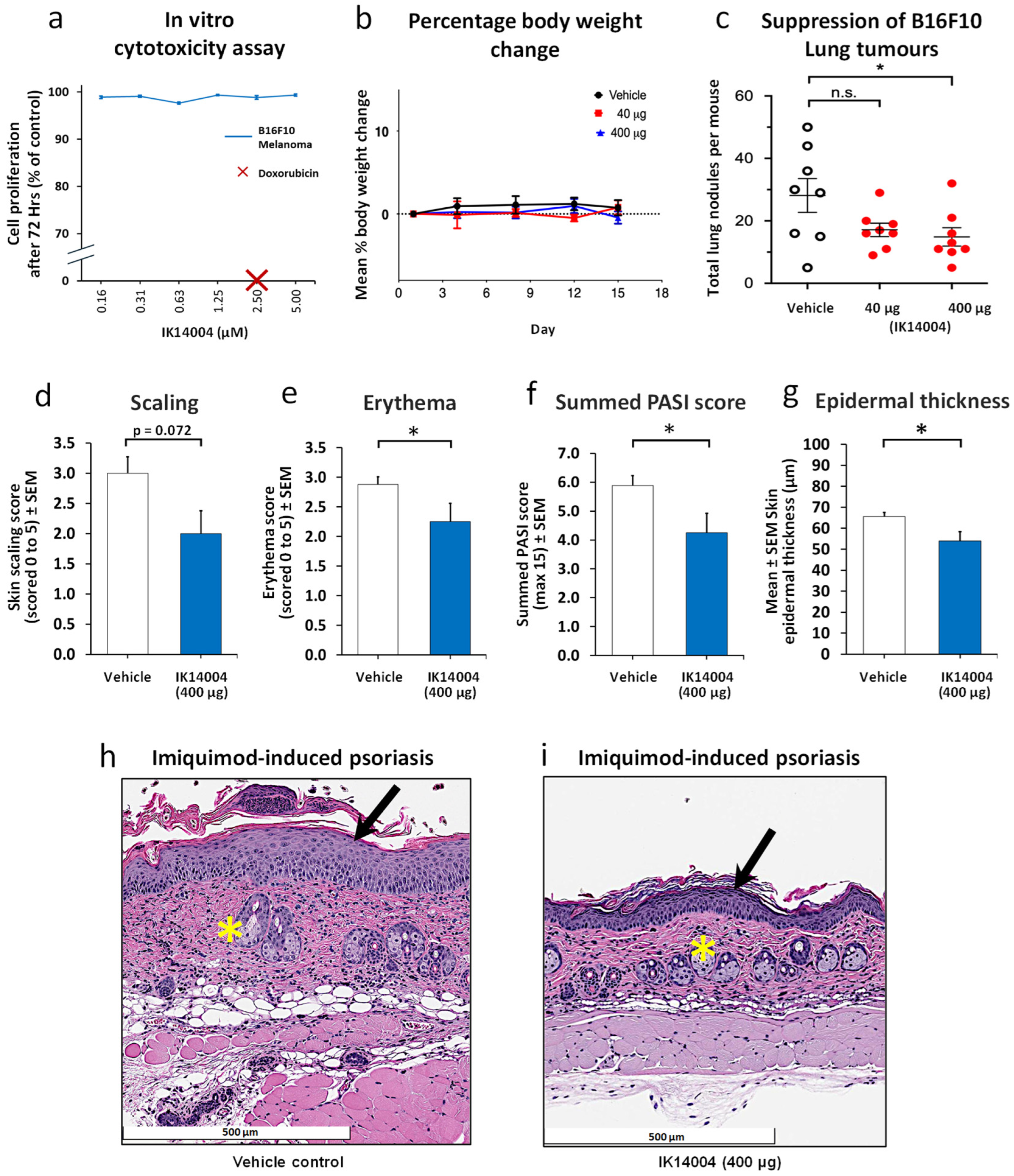
3.4. IK14004 Inhibits Melanoma Growth and Psoriasis in Murine Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.; Shilkrut, M.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Batty, N.; Barber, B. Autoimmune comorbidities in patients with metastatic melanoma: A retrospective analysis of us claims data. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.C.; Egbukichi, N.; Erwin-Cohen, R.A. Autoimmunity and cancer, the paradox comorbidities challenging therapy in the context of preexisting autoimmunity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.C.; Stefanova, I.; Cha, Y.; Elsolh, K.; Zereshkian, A.; Gaafour, N.; McWhirter, E. Chronic immune-related adverse events in patients with cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubchenko, T.; Leung, D.Y.; Goleva, E. Why are immune adverse events so common with checkpoint inhibitor therapy? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, M.A.; Dastoli, S.; d’Apolito, M.; Staropoli, N.; Tassone, P.; Tagliaferri, P.; Barbieri, V. Pembrolizumab-induced psoriasis in metastatic melanoma: Activity and safety of apremilast, a case report. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 579445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthay, A. How do regulatory T cells work? Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralainirina, N.; Poli, A.; Michel, T.; Poos, L.; Andrès, E.; Hentges, F.; Zimmer, J. Control of NK cell functions by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Leucoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulai, G.; Oleinik, E. Targeting regulatory T cells in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 cancer immunotherapy. Scand. J. Immunol. 2022, 95, e13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Han, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Ke, S.; Zhu, F.; Lu, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, C.; et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cell perturbation mediated by the IFNγ-STAT1-IFITM3 feedback loop is essential for anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, K.; Singh, N.J. Making many from few: IL-12p40 as a model for the combinatorial assembly of heterodimeric cytokines. Cytokine 2015, 76, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmachari, S.; Pahan, K. Suppression of regulatory T cells by IL-12p40 homodimer via nitric oxide. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.D.; Hall, B.M.; Plain, K.M.; Robinson, C.M.; Boyd, R.; Tran, G.T.; Wang, C.; Bishop, G.A.; Hodgkinson, S.J. Interleukin-12 (IL-12p70) promotes induction of highly potent Th1-like CD4+ CD25+ T regulatory cells that inhibit allograft rejection in unmodified recipients. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDyer, J.F.; Goletz, T.J.; Thomas, E.; June, C.H.; Seder, R.A. CD40 ligand/CD40 stimulation regulates the production of IFN-gamma from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in an IL-12- and/or CD28-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaka, A.S.; Foster, A.E.; Weiss, H.E.; Rooney, C.M.; Leen, A.M. Using dendritic cell maturation and IL-12 producing capacity as markers of function: A cautionary tale. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nandagopal, N.; Ali, A.K.; Komal, A.K.; Lee, S.H. The critical role of IL-15–PI3K–mTOR pathway in natural killer cell effector functions. Front. Ιmmunol. 2014, 5, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Basse, P.H. NK cells in the tumor microenvironment. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2014, 19, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koka, R.; Burkett, P.R.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Chan, F.; Lodolce, J.P.; Boone, D.L.; Ma, A. Interleukin (IL)-15Rα–deficient natural killer cells survive in normal but not IL-15Rα–deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Yu, J. Harnessing IL-15 signaling to potentiate NK cell-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rosa, M.; Rutz, S.; Dorninger, H.; Scheffold, A. Interleukin-2 is essential for CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Ma, Y.; Jin, H. Low-dose Interleukin-2 for psoriasis therapy based on the regulation of Th17/Treg cell balance in peripheral blood. Inflammation 2023, 46, 2359–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, H.F.; Li, S. PD-1-mediated inhibition of T cell activation: Mechanisms and strategies for cancer combination immunotherapy. Cell Insight 2024, 3, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Gadina, M.; Wang, K.; O’Shea, J.; Seder, R.A. Cytokine regulation of IL-12 receptor β2 expression: Differential effects on human T and NK cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuzoglu, E.; Phillips, R.A.; Dai, R.; Graniello, C.; Gogal, R.M., Jr.; Ahmed, S.A. Signal transducer and activation of transcription (STAT) 4β, a shorter isoform of interleukin-12-induced STAT4, is preferentially activated by estrogen. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agrez, M.; Rzepecka, J.; Turner, D.; Knox, G.; Chandler, C.; Howard, C.B.; Fletcher, N.; Thurecht, K.; Parker, S.; Gooding, H.; et al. A novel lipidic peptide with potential to promote balanced effector-regulatory T cell responses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrez, M.; Chandler, C.; Thurecht, K.J.; Fletcher, N.L.; Liu, F.; Subramaniam, G.; Howard, C.B.; Blyth, B.; Parker, S.; Turner, D.; et al. An immunomodulating peptide with potential to suppress tumour growth and autoimmunity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasset, F.; Dayer, J.M.; Chizzolini, C. Type I interferons in systemic autoimmune diseases: Distinguishing between afferent and efferent functions for precision medicine and individualized treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 633821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, D.; Moudgil, K.D. Interferons in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: Regulation and roles. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, M.; Martinez, A.D.; Gallo, R.L.; Hata, T.R. Induction and exacerbation of psoriasis with Interferon-alpha therapy for hepatitis C: A review and analysis of 36 cases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Deng, S.; Liu, X.; Hutton, G.J.; Hong, J. IFN-β induces the proliferation of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells through upregulation of GITRL on dendritic cells in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 242, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueyo-González, F.; McGinty, M.; Ningoo, M.; Anderson, L.; Cantarelli, C.; Angeletti, A.; Demir, M.; Llaudó, I.; Purroy, C.; Marjanovic, N.; et al. Interferon-β acts directly on T cells to prolong allograft survival by enhancing regulatory T cell induction through Foxp3 acetylation. Immunity 2022, 55, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Shibuya, A. Interferon-β promotes the survival and function of induced regulatory T cells. Cytokine 2022, 158, 156009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerfordt, I.M.; Framke, E.; Windfeld-Mathiasen, J.; Mogensen, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Magyari, M.; Horwitz, H. Reevaluating the role of interferon-beta in psoriasis pathogenesis: A registry-based self-controlled study. J. Dermatol. 2024, 51, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Nie, H.; Zhang, X.; Niu, X.; Zang, Y.C.; Skinner, S.M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Killian, J.M.; Hong, J. Regulatory effects of IFN-β on production of osteopontin and IL-17 by CD4+ T Cells in MS. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, A.; Fujimura, T.; Furudate, S.; Kambayashi, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Yagita, H.; Aiba, S. Immunomodulatory effect of peritumorally administered interferon-beta on melanoma through tumor-associated macrophages. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1047584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, U.A.; Finocchiaro, L.M.; Glikin, G.C. Interferon-β gene transfer inhibits melanoma cells adhesion and migration. Cytokine 2017, 89, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.S.; Arlauckas, S.P.; Kohler, R.H.; Trefny, M.P.; Garren, S.; Piot, C.; Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Siwicki, M.; Gungabeesoon, J.; et al. Successful anti-PD-1 cancer immunotherapy requires T cell-dendritic cell crosstalk involving the cytokines IFN-γ and IL-12. Immunity 2018, 49, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Adamopoulos, I.E. Psoriatic arthritis under the influence of IFNγ. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, C.L.; Aria, N.; Toichi, E.; McCormick, T.S.; Cooper, K.D.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Everitt, D.E.; Frederick, B.; Zhu, Y.; Graham, M.A.; et al. A phase I study evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical response of a human IL-12p40 antibody in subjects with plaque psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Toomey, C.B.; Morris, K.V.; Kono, D.H. Interferon-γ and systemic autoimmunity. Discov. Med. 2013, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.A.; Abdel-Hamid, M.F.; Kotb, A.M.; Mabrouk, E.A. Serum interferon-g is a psoriasis severity and prognostic marker. Cutis 2009, 84, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bacon, C.M.; Petricoin, E.F., 3rd; Ortaldo, J.R.; Rees, R.C.; Larner, A.C.; Johnston, J.A.; O’Shea, J.J. Interleukin 12 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of STAT4 in human lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7307–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calautti, E.; Avalle, L.; Poli, V. Psoriasis: A STAT3-centric view. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacaflores, A.; Chapman, N.M.; Harty, J.T.; Richer, M.J.; Houtman, J.C. Exposure of human CD4 T cells to IL-12 results in enhanced TCR-induced cytokine production, altered TCR signaling, and increased oxidative metabolism. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llavero, F.; Artaso, A.; Lacerda, H.M.; Parada, L.A.; Zugaza, J.L. Lck/PLCγ control migration and proliferation of interleukin (IL)-2-stimulated T cells via the Rac1 GTPase/glycogen phosphorylase pathway. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, N.O.; Ahmad, S.F.; Almutairi, M.; Alanazi, A.Z.; Ibrahim, K.E.; Alqarni, S.A.; Alqahtani, F.; Alhazzani, K.; Alharbi, M.; Alasmari, F.; et al. Lck signaling inhibition causes improvement in clinical features of psoriatic inflammation through reduction in inflammatory cytokines in CD4+ T cells in imiquimod mouse model. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 376, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerholm, R.; Rizk, J.; Viñals, M.T.; Bekiaris, V. STAT 3 but not STAT 4 is critical for γδT17 cell responses and skin inflammation. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachlewitz, R.F.; Hart, M.A.; Bettencourt, B.; Kebede, T.; Schwartz, A.; Ratnofsky, S.E.; Calderwood, D.J.; Waegell, W.O.; Hirst, G.C. A-770041, a novel and selective small-molecule inhibitor of Lck, prevents heart allograft rejection. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.H.; Cantrell, D.A. Signaling and function of interleukin-2 in T lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, W.E.; Giri, J.G.; Lindemann, M.; Linett, M.L.; Ahdieh, M.; Paxton, R.; Anderson, D.; Eisenmann, J.; Grabstein, K.; Caligiuri, M.A. Interleukin (IL) 15 is a novel cytokine that activates human natural killer cells via components of the IL-2 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bock, M.; Hulstaert, E.; Kruse, V.; Brochez, L. Psoriasis vulgaris exacerbation during treatment with a PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor: Case report and literature review. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2018, 10, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, B.R.; Warner, A.B.; Zaman, F.Y.; Haydon, A.; Bhave, P.; Dewan, A.K.; Ye, F.; Irlmeier, R.; Mehta, P.; Kurtansky, N.R.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with pre-existing psoriasis: Safety and efficacy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Mei, X.; Liu, Y. Exacerbation of psoriasis induced by Nivolumab in a patient with stage IIIc gastric adenocarcinoma: A case report and literature review. J. Transl. Autoimm. 2023, 6, 100193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Ayithan, N.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Hwang, S.T. Cutting edge: PD-1 regulates imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis through inhibition of IL-17A expression by innate γδ-low T cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logotheti, S.; Pützer, B.M. STAT3 and STAT5 targeting for simultaneous management of melanoma and autoimmune diseases. Cancers 2019, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; McSharry, M.; Bullock, B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kwak, J.; Poczobutt, J.M.; Sippel, T.R.; Heasley, L.E.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.; Clambey, E.T.; et al. The tumor microenvironment regulates sensitivity of murine lung tumors to PD-1/PD-L1 antibody blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Dai, W.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Z. DPP inhibition enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade by remodeling the tumor microenvironment in lewis lung carcinoma model. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrez, M.; Garg, M.; Dorahy, D.; Ackland, S. Synergistic anti-tumor effect of cisplatin when combined with an anti-Src kinase integrin-based peptide. J. Cancer Ther. 2011, 2, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, L.S.; Wang, Q.W.; Chen, F.; Wei, D.Z.; Han, Z.G. Nuclear localization signal of ING4 plays a key role in its binding to p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, A.J.; Chodisetti, S.B.; Bricker, K.N.; Choi, N.M.; Chroneos, Z.C.; Kaplan, M.H.; Rahman, Z.S. STAT4 Is Largely Dispensable for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus–like Autoimmune-and Foreign Antigen–Driven Antibody-Forming Cell, Germinal Center, and Follicular Th Cell Responses. ImmunoHorizons 2021, 5, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeger, L.K.; McKinney, J.; Salvekar, A.; Hoey, T. Identification of a STAT4 binding site in the interleukin-12 receptor required for signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupov, I.P.; Voiles, L.; Han, L.; Schwartz, A.; De La Rosa, M.; Oza, K.; Pelloso, D.; Sahu, R.P.; Travers, J.B.; Robertson, M.J.; et al. Acquired STAT4 deficiency as a consequence of cancer chemotherapy. Blood 2011, 118, 6097–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, Y.; Tilborghs, S.; Jacobs, J.; De Waele, J.; Quatannens, D.; Deben, C.; Prenen, H.; Pauwels, P.; Trinh, X.B.; Wouters, A.; et al. The potential and controversy of targeting STAT family members in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, G.; Qiao, H.; Leng, Z.; et al. Chrysin enhances antitumour immunity response through the IL-12-STAT4 signal pathway in the B16F10 melanoma mouse model. Scand. J. Immunol. 2022, 96, e13177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, A.; Zhang, D.; Zou, T.; Xiao, M.; Chen, J.; Wen, B.; Wen, Q.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; et al. Molecular profiling of core immune-escape genes highlights LCK as an immune-related prognostic biomarker in melanoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1024931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommhardt, U.; Schraven, B.; Simeoni, L. Beyond TCR signaling: Emerging functions of Lck in cancer and immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.J.; Hu, X.X.; Wei, W. New insights into the Lck-NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1120747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Hiam-Galvez, K.J.; Mowery, C.T.; Herold, K.C.; Gitelman, S.E.; Esensten, J.H.; Liu, W.; Lares, A.P.; Leinbach, A.S.; Lee, M.; et al. The effect of low-dose IL-2 and Treg adoptive cell therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e147474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßhoff, H.; Comdühr, S.; Monne, L.R.; Müller, A.; Lamprecht, P.; Riemekasten, G.; Humrich, J.Y. Low-dose IL-2 therapy in autoimmune and rheumatic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.H.; Yeoh, E.; Tay, A.; Brenner, S.; Venkatesh, B. STAT4 is a target of the hematopoietic zinc-finger transcription factor Ikaros in T cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4470–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.S.; Ritz, J.; Frank, D.A. IL-2 induces STAT4 activation in primary NK cells and NK cell lines, but not in T cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mai, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, B.; Hou, J.; Jiang, D. STAT4: An immunoregulator contributing to diverse human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaghi, A.; Durand-Dubief, M.; Brusselaers, N.; Björnstedt, M. Combining PD-1/PD-L1 blockade with type I interferon in cancer therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1249330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, A.; Rosen, A.; Petri, M.; Akhter, E.; Andrade, F. Interferon-alpha regulates the dynamic balance between human activated regulatory and effector T cells: Implications for antiviral and autoimmune responses. Immunology 2010, 131, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overacre-Delgoffe, A.E.; Chikina, M.; Dadey, R.E.; Yano, H.; Brunazzi, E.A.; Shayan, G.; Horne, W.; Moskovitz, J.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Sander, C.; et al. Interferon-γ drives Treg fragility to promote anti-tumor immunity. Cell 2017, 169, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Seventer, J.M.; Nagai, T.; van Seventer, G.A. Interferon-β differentially regulates expression of the IL-12 family members p35, p40, p19 and EBI3 in activated human dendritic cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 133, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, A.J.; Robins, R.A.; Constantinescu, C.S. Reciprocal effects of IFN-β and IL-12 on STAT4 activation and cytokine induction in T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipi, M.; Jack, S. Interferons in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: A clinical efficacy, safety, and tolerability update. Int. J. MS Care 2020, 22, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinski, P.; Vieira, P.L.; Schuitemaker, J.H.; de Jong, E.C.; Kapsenberg, M.L. Prostaglandin E2 is a selective inducer of interleukin-12 p40 (IL-12p40) production and an inhibitor of bioactive IL-12p70 heterodimer. Blood 2001, 97, 3466–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulig, P.; Musiol, S.; Freiberger, S.N.; Schreiner, B.; Gyülveszi, G.; Russo, G.; Pantelyushin, S.; Kishihara, K.; Alessandrini, F.; Kündig, T.; et al. IL-12 protects from psoriasiform skin inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, N.L.; Welsing, P.M.; Silva-Cardoso, S.C.; Bekker, C.P.; Lopes, A.P.; Olde Nordkamp, M.; Leijten, E.F.; Radstake, T.R.; Angiolilli, C. Suppression of IL-12/IL-23 p40 subunit in the skin and blood of psoriasis patients by Tofacitinib is dependent on active interferon-γ signaling in dendritic cells: Implications for the treatment of psoriasis and interferon-driven diseases. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.E.; Turk, M.J. Th1-like Treg cells are dressed to suppress anti-tumor immunity. Immunity 2023, 56, 1437–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Shibata, F.; Miyasaka, N.; Miura, O. The human perforin gene is a direct target of STAT4 activated by IL-12 in NK cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Feng, J.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Opposing effect of IFNγ and IFNα on expression of NKG2 receptors: Negative regulation of IFNγ on NK cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2005, 5, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietra, G.; Manzini, C.; Rivara, S.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Petretto, A.; Balsamo, M.; Conte, R.; Benelli, R.; Minghelli, S.; et al. Melanoma cells inhibit natural killer cell function by modulating the expression of activating receptors and cytolytic activity. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.; Potempa, M.; Gotthardt, D.; Lanier, L.L. Cutting edge: IL-2–induced expression of the amino acid transporters SLC1A5 and CD98 is a prerequisite for NKG2D-mediated activation of human NK cells. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouirand, V.; Habrylo, I.; Rosenblum, M.D. Regulatory T cells and inflammatory mediators in autoimmune disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, L.; Romano, M.; McGregor, R.; Correa, I.; Pavlidis, P.; Grageda, N.; Hoong, S.J.; Yuksel, M.; Jassem, W.; Hannen, R.F.; et al. An atlas of human regulatory T helper-like cells reveals features of Th2-like Tregs that support a tumorigenic environment. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, M.; Tada, Y. Dendritic cells and macrophages in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, L.; Chen, Y.L.; Ogg, G.S. Role of regulatory T cells in psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-W.; Jacek, T.; Jacek, R. Dendritic cells heterogeneity and its role in cancer immunity. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2006, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Belhadj Hmida, N.; Moes, N.; Buyse, S.; Abdeladhim, M.; Louzir, H.; Cerf-Bensussan, N. IL-15 renders conventional lymphocytes resistant to suppressive functions of regulatory T cells through activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6763–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, O.M.; Peterson, M.E.; Hollander, M.J.; Dorward, D.W.; Arora, G.; Traba, J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Snapp, E.L.; Garcia, K.C.; Waldmann, T.A.; et al. Trans-endocytosis of intact IL-15Rα–IL-15 complex from presenting cells into NK cells favors signaling for proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nausch, N.; Cerwenka, A. NKG2D ligands in tumor immunity. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5944–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwinn, N.; Vokhminova, D.; Sucker, A.; Textor, S.; Striegel, S.; Moll, I.; Nausch, N.; Tuettenberg, J.; Steinle, A.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. Interferon-γ down-regulates NKG2D ligand expression and impairs the NKG2D-mediated cytolysis of MHC class I-deficient melanoma by natural killer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsamo, M.; Vermi, W.; Parodi, M.; Pietra, G.; Manzini, C.; Queirolo, P.; Lonardi, S.; Augugliaro, R.; Moretta, A.; Facchetti, F.; et al. Melanoma cells become resistant to NK-cell-mediated killing when exposed to NK-cell numbers compatible with NK-cell infiltration in the tumor. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Michel, T.; Thérésine, M.; Andrès, E.; Hentges, F.; Zimmer, J. CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: An important NK cell subset. Immunology 2009, 126, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canter, R.J.; Murphy, W.J. A possible new pathway in natural killer cell activation also reveals the difficulty in determining human NK cell function in cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sentman, C.L. Mouse tumor vasculature expresses NKG2D ligands and can be targeted by chimeric NKG2D-modified T cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne-Hoffman, C.N.; Deng, W.; McGrath, O.; Wang, P.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Klinke, D.J. Interleukin-12 elicits a non-canonical response in B16 melanoma cells to enhance survival. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, S.; Komlódi, R.; Perkecz, A.; Pintér, E.; Gyulai, R.; Kemény, Á. Methodological refinement of Aldara-induced psoriasiform dermatitis model in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubago-Rodríguez, A.; Quiñones-Vico, M.I.; Sánchez-Díaz, M.; Sanabria-de la Torre, R.; Sierra-Sánchez, Á.; Montero-Vílchez, T.; Fernández-González, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Challenges in Psoriasis Research: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Models. Dermatology 2024, 240, 620–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Fu, X.Y.; Gao, H.Y.; Ma, Y.N.; Yao, J.F.; Du, S.S.; Qi, Y.K.; Wang, K.W. Design, synthesis and anticancer evaluation of novel oncolytic peptide-chlorambucil conjugates. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 138, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Chen, X.T.; Chi, Q.N.; Ma, Y.N.; Fu, X.Y.; Du, S.S.; Qi, Y.K.; Wang, K.W. The hybrid oncolytic peptide NTP-385 potently inhibits adherent cancer cells by targeting the nucleus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, X.T.; Yao, J.F.; Ma, Y.N.; Song, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, Q.Y.; Du, S.S.; Qi, Y.K.; et al. Three rounds of stability-guided optimization and systematical evaluation of oncolytic peptide LTX-315. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 3885–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Gupta, K.; Kumar, D.; Lofland, G.; Sharma, A.K.; Solnes, L.B.; Rowe, S.P.; Forde, P.M.; Pomper, M.G.; Gabrielson, E.W.; et al. Non-invasive PD-L1 quantification using [18F]DK222-PET imaging in cancer immunotherapy. J. ImmunoTher. Cancer 2023, 11, e007535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tianyu, E.; Zhou, M.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.; Miao, R.; Dong, C.; Gao, H.; Jing, C.; Liang, B. Integrin αvβ6 mediates the immune escape through regulation of PD-L1 and serves as a novel marker for immunotherapy of colon cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 2608–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huel Huelsboemer, L.; Knoedler, L.; Kochen, A.; Yu, C.T.; Hosseini, H.; Hollmann, K.S.; Choi, A.E.; Stögner, V.A.; Knoedler, S.; Hsia, H.C.; et al. Cellular therapeutics and immunotherapies in wound healing–on the pulse of time? Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, B.; Ge, H.; Zhen, Q.; Mao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; et al. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV promotes imiquimod-induced psoriatic inflammation via macrophages and keratinocytes in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, K.; Juang, Y.T.; Crispín, J.C.; Kis-Toth, K.; Tsokos, G.C. Suppression of autoimmunity and organ pathology in lupus-prone mice upon inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowska, J.; Arcimowicz, Ł.; Jankowiak, M.; Papak, I.; Markiewicz, A.; Dziubek, K.; Kurkowiak, M.; Kote, S.; Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Połom, K.; et al. Autoimmunity and Cancer—Two Sides of the Same Coin. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 793234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, E.; Canter, R.J.; Grossenbacher, S.K.; Mac, S.; Chen, M.; Smith, R.C.; Hagino, T.; Perez-Cunningham, J.; Sckisel, G.D.; Urayama, S.; et al. NK cells preferentially target tumor cells with a cancer stem cell phenotype. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4010–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythema | None | Faint Pink | Definite Pink | Pinkish-Reddish | Definite Red | Redness with Bleeding |
| Scaling | None | 1–20% | 21–40% | 41–60% | 61–80% | ≥81% |
| 0 | Normal, no hyperplasia, mean measure is ≤30 µm |
| 0.5 | Very minimal epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is 31–45 µm |
| 1 | Minimal epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is 46–60 µm |
| 2 | Mild epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is 61–75 µm |
| 3 | Moderate epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is 76–90 µm |
| 4 | Marked epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is 91–115 µm |
| 5 | Severe epidermal hyperplasia, mean measure is >115 µm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agrez, M.; Chandler, C.; Johnson, A.L.; Sorensen, M.; Cho, K.; Parker, S.; Blyth, B.; Turner, D.; Rzepecka, J.; Knox, G.; et al. An Immunomodulating Peptide with Potential to Promote Anticancer Immunity Without Compromising Immune Tolerance. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081908
Agrez M, Chandler C, Johnson AL, Sorensen M, Cho K, Parker S, Blyth B, Turner D, Rzepecka J, Knox G, et al. An Immunomodulating Peptide with Potential to Promote Anticancer Immunity Without Compromising Immune Tolerance. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081908
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgrez, Michael, Christopher Chandler, Amanda L. Johnson, Marlena Sorensen, Kirstin Cho, Stephen Parker, Benjamin Blyth, Darryl Turner, Justyna Rzepecka, Gavin Knox, and et al. 2025. "An Immunomodulating Peptide with Potential to Promote Anticancer Immunity Without Compromising Immune Tolerance" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081908
APA StyleAgrez, M., Chandler, C., Johnson, A. L., Sorensen, M., Cho, K., Parker, S., Blyth, B., Turner, D., Rzepecka, J., Knox, G., Nika, A., Hall, A. M., Gooding, H., & Gallagher, L. (2025). An Immunomodulating Peptide with Potential to Promote Anticancer Immunity Without Compromising Immune Tolerance. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081908






