Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Green-Synthesized Graphene–Silver Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms and Growth Media
2.2. Cell Surface Hydrophobicity Assay
2.3. Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.4. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene–Ag Nanocomposites (GO-AgNPs)
2.4.1. Preparation of GO
2.4.2. Preparation of AgNPs on GO
2.4.3. Characterization of GO-Ag NPs
2.5. In Vitro Antimicrobial Study of Graphene–Ag-Nanocomposite
2.5.1. Agar-Well Diffusion Assay
2.5.2. Microbroth Dilution Assay
2.5.3. Quantitative Biofilm Inhibition Assays
2.5.4. Functionalization of the Catheters with GO-AgNPs
2.5.5. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy of Microbial Biofilms on GO-AgNP-Functionalized Catheters
2.6. Hemocompatibility of GO-AgNP-Functionalized Catheters
2.7. Biocompatibility of Nanocomposite-Impregnated Catheters
3. Results and Discussion
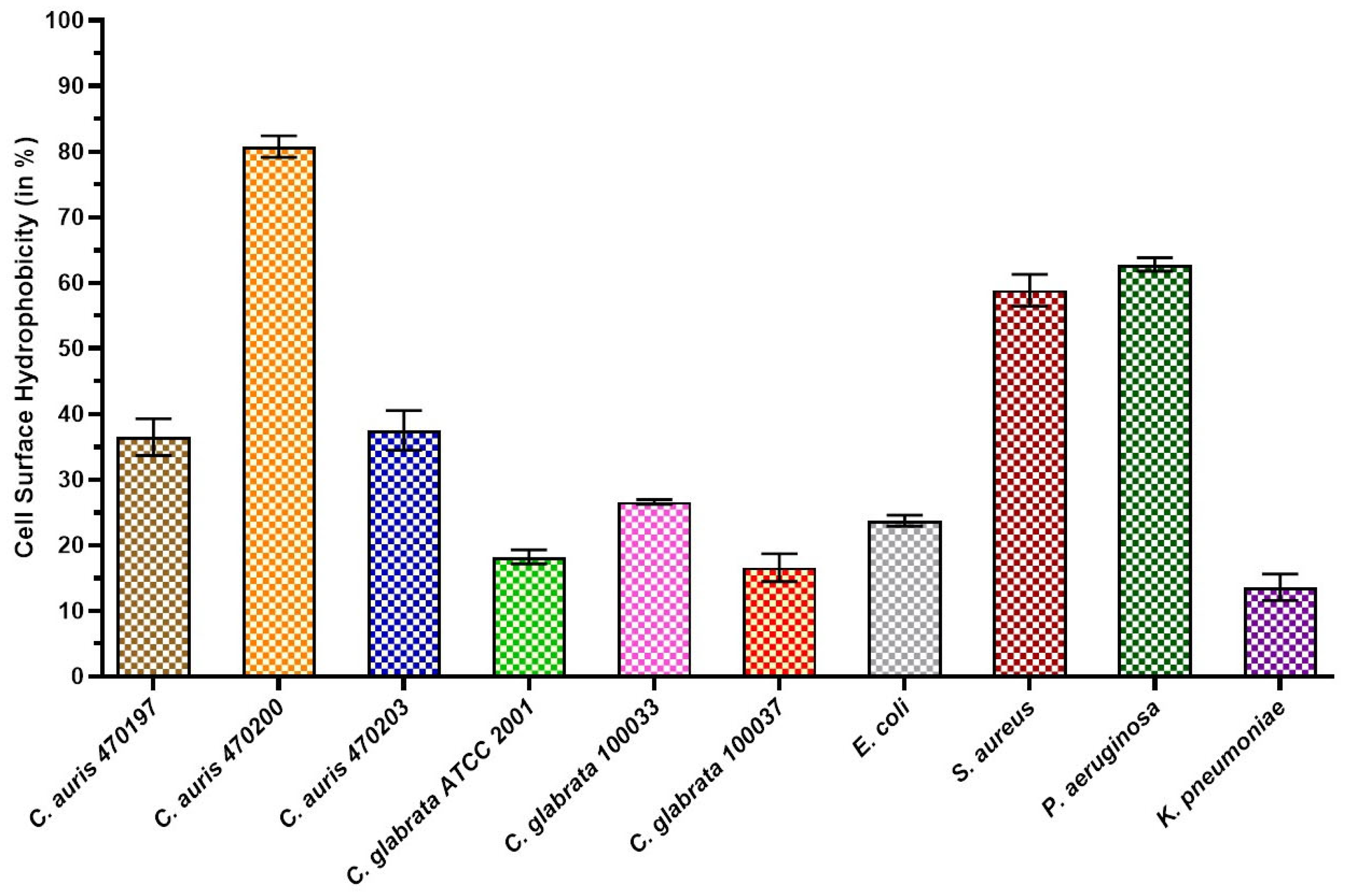
3.1. Cell Surface Hydrophobicity
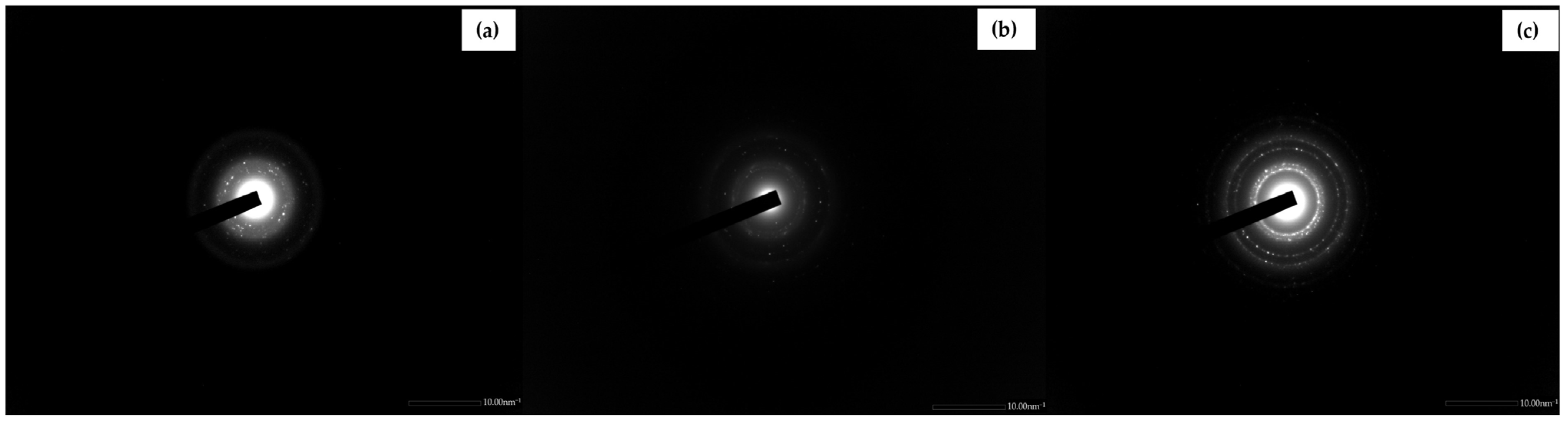
3.2. Characterization of Biosynthesized Go-AgNPs
3.2.1. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
3.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
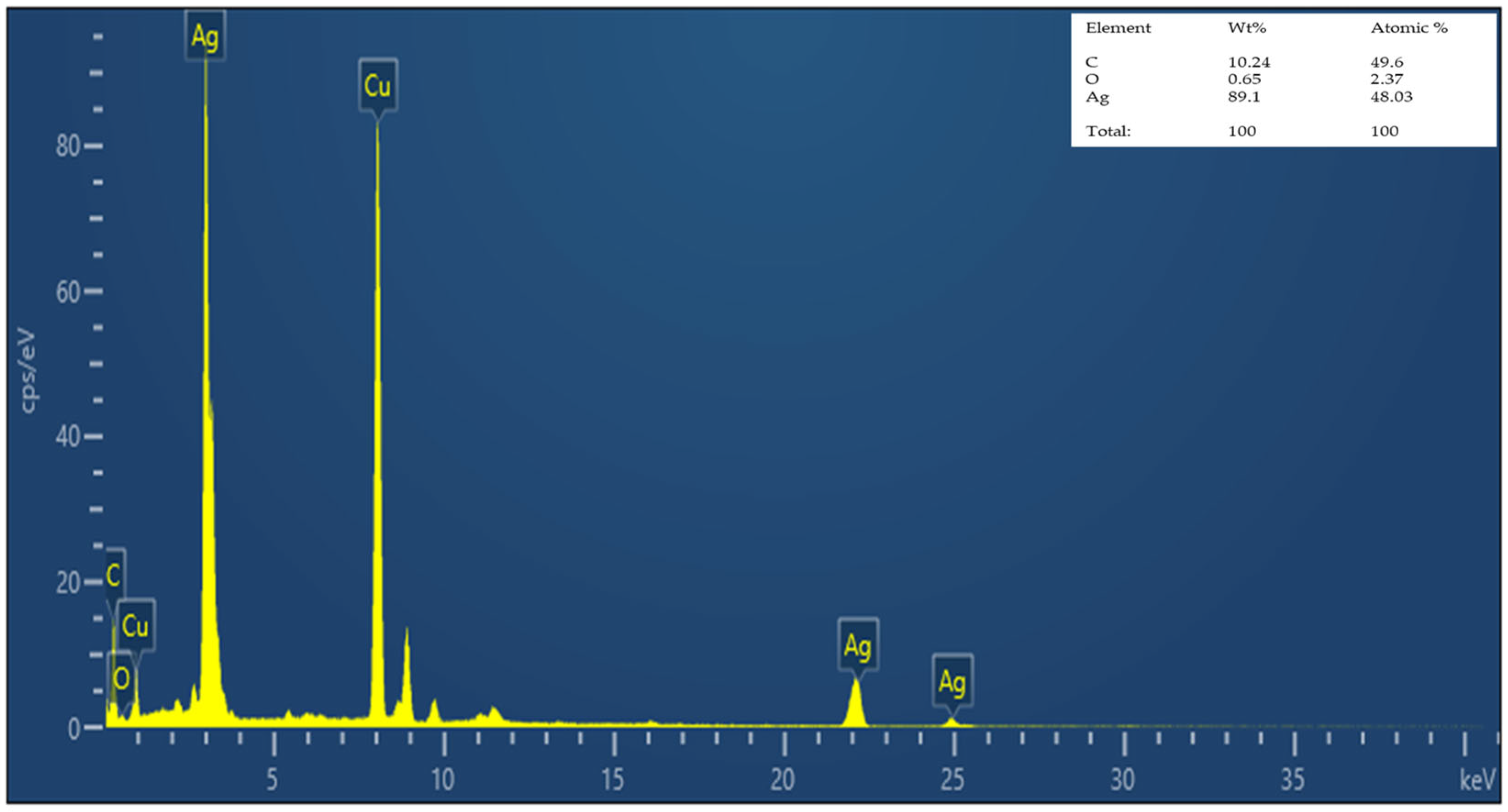
3.2.3. EDS Analysis of Nanocomposite
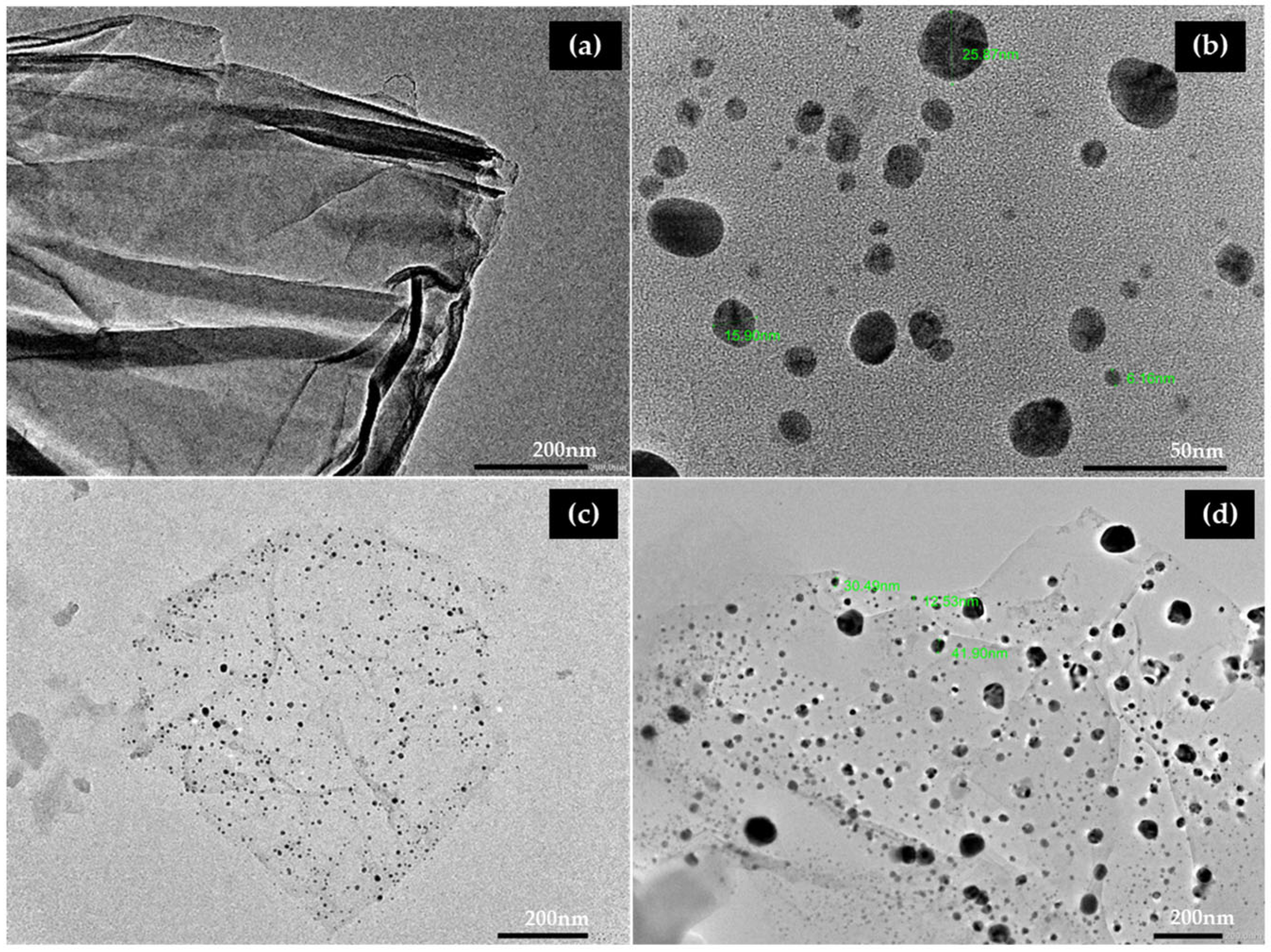
3.2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of GO-AgNPs
3.3. In Vitro Antimicrobial Efficacy of GO-Ag Nanocomposites
Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Lethal Concentration (MLC)
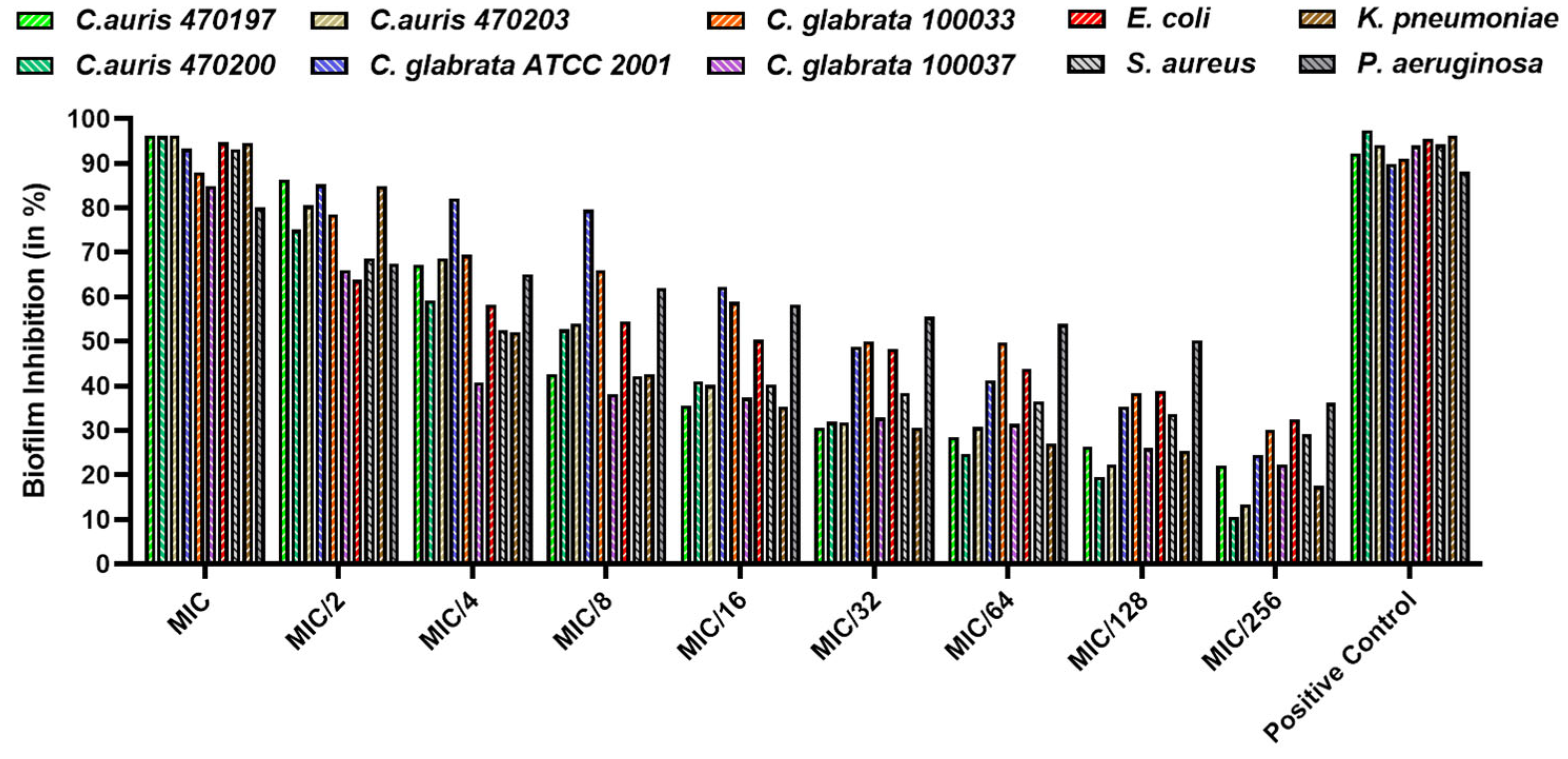
3.4. Biofilm Inhibition
3.5. GO-AgNP-Functionalized Catheters Avert Biofilm Formation by C. auris and P. aeruginosa
3.6. GO-AgNP-Functionalized Catheters Demonstrate Hemocompatibility and Biocompatibility In Vitro
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oni, O.; Orok, E.; Lawal, Z.; Ojo, T.; Oluwadare, T.; Bamitale, T.; Jaiyesimi, B.; Akinjisola, A.; Apara, T. Knowledge and Perception of Nosocomial Infections among Patients in a Nigerian Hospital. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Report on the Burden of Endemic Health Care-Associated Infection Worldwide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 978-92-4-150150-7.
- Perlroth, J.; Choi, B.; Spellberg, B. Nosocomial Fungal Infections: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, H.; Nguyen, P. First Case of COVID-19 Complicated with Burkolderia cepacia Pneumonia and Bacteremia. Chest 2020, 158, A544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nori, P.; Cowman, K.; Chen, V.; Bartash, R.; Szymczak, W.; Madaline, T.; Katiyar, C.P.; Jain, R.; Aldrich, M.; Weston, G. Bacterial and Fungal Coinfections in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized during the New York City Pandemic Surge. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariyawasam, R.M.; Julien, D.A.; Jelinski, D.C.; Larose, S.L.; Rennert-May, E.; Conly, J.M.; Dingle, T.C.; Chen, J.Z.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Ronksley, P.E.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (November 2019–June 2021). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Ghosh, N.N.; Das, M.; Adhikary, R.; Mandal, V.; Chattopadhyay, A.P. Green Synthesis of Antibacterial and Antifungal Silver Nanoparticles Using Citrus Limetta Peel Extract: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussin, J.; Robles-Botero, V.; Casañas-Pimentel, R.; Rojas, F.; Angiolella, L.; San Martin-Martinez, E.; Giusiano, G. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Green Synthesis Silver Nanoparticles Targeting Skin and Soft Tissue Infectious Agents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Tapwal, A.; Kumar, D.; Puri, S. Antimicrobial Potential and Phytochemical Profiling of Ethnomedicinal Plant Trillium govanianum Wall. Ex D. Don in Western Himalaya. J. Herb. Med. 2021, 29, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz-Zaman, K.; Bakht, J.; Malikovna, B.K.; Elsharkawy, E.R.; Khalil, A.A.; Bawazeer, S.; Rauf, A. Trillium govanianum Wall. Ex. Royle Rhizomes Extract-Medicated Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-ur-Rahman; Ismail, M.; Shah, M.R.; Adhikari, A.; Anis, I.; Ahmad, M.S.; Khurram, M. Govanoside A, a New Steroidal Saponin from Rhizomes of Trillium govanianum. Steroids 2015, 104, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, K.; Lone, J.F.; Bhushan, A.; Gupta, P.; Gairola, S. Morpho-Anatomical, Molecular, and Chemical Standardization of Trillium govanianum Wall. Ex D. Don: An Endangered Medicinal Herb Native to the Himalayas. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2023, 19, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Muñoz, R.; Borrego, B.; Juárez-Moreno, K.; García-García, M.; Mota Morales, J.D.; Bogdanchikova, N.; Huerta-Saquero, A. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Biological Systems: Does the Complexity of Biological Systems Matter? Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 276, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, M.; Jaworski, S.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Stobiński, L.; Małolepszy, A.; et al. Graphene Oxide in a Composite with Silver Nanoparticles Reduces the Fibroblast and Endothelial Cell Cytotoxicity of an Antibacterial Nanoplatform. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Jang, J. Antibacterial Properties of Novel Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) Nanofiber Containing Silver Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhi, X.; Wang, K.; Cui, D. The Antifungal Activity of Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, V.; Ansari, M.O. Antimicrobial Activity of Graphene-Based Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Applications for Human Welfare. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuța, V.; Talianu, M.-T.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.-E.; Ghica, M.V.; Prisada, R.M.; Albu Kaya, M.G.; Popa, L. Molecular Mapping of Antifungal Mechanisms Accessing Biomaterials and New Agents to Target Oral Candidiasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Chadha, J.; Harjai, K.; Verma, G.; Saini, A. Synthetic Peptide (DP1) Functionalized Graphene Oxide: A Biocompatible Nanoformulation with Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity. FlatChem 2024, 44, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Chang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Antibacterial Properties and Mechanism of Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites as Bactericidal Agents for Water Disinfection. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 604, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M. Bacterial Adherence to Hydrocarbons: A Useful Technique for Studying Cell Surface Hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1984, 22, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J.; Gupta, M.; Nagpal, N.; Sharma, M.; Adarsh, T.; Joshi, V.; Tiku, V.; Mittal, T.; Nain, V.K.; Singh, A. Antibacterial Potential of Indigenous Plant Extracts against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains Isolated from New Delhi Region. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 14, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.I.; Foo, K.L.; Hashim, U.; Tan, S.J.; Liu, W.W.; Voon, C.H. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide Using Modified Hummers Method: Solvent Influence. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vi, T.T.T.; Kumar, S.R.; Rout, B.; Liu, C.H.; Wong, C.B.; Chang, C.W.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. The Preparation of Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites: The Effect of Silver Loads on Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, J.; Khullar, L.; Gulati, P.; Chhibber, S.; Harjai, K. Repurposing Albendazole as a Potent Inhibitor of Quorum Sensing-Regulated Virulence Factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel Prospects of a Classical Drug. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rex, J.H. M27-A2 Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts. In Approved Standard, 2nd ed.; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, H.H.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Jose Yacaman, M.; Lopez-Ribot, J. Inhibition of Candida auris Biofilm Formation on Medical and Environmental Surfaces by Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21183–21191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J.; Ravi; Singh, J.; Chhibber, S.; Harjai, K. Gentamicin Augments the Quorum Quenching Potential of Cinnamaldehyde in Vitro and Protects Caenorhabditis Elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 899566. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, L.E.; Hook, A.L.; Ashraf, W.; Yousef, A.; Barrett, D.A.; Scurr, D.J.; Chen, X.; Smith, E.F.; Fay, M.; Parmenter, C.D. Biomaterial Modification of Urinary Catheters with Antimicrobials to Give Long-Term Broadspectrum Antibiofilm Activity. J. Control. Release 2015, 202, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, J.; Singh, J.; Harjai, K. α-Terpineol Synergizes with Gentamicin to Rescue Caenorhabditis Elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Attenuating Quorum Sensing-Regulated Virulence. Life Sci. 2023, 313, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisang, S.; Boongird, A.; Ungsurungsie, M.; Wanasawas, P.; Nasongkla, N. Biocompatibility and Stability during Storage of Foley Urinary Catheters Coated Chlorhexidine Loaded Nanoparticles by Nanocoating: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Shahisaraee, S.A.; Tavajjohi, A.; Pournoori, N.; Muhammadnejad, S.; Mohammadi, S.R.; Poursalehi, R.; Hamid Delavari, H. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Zingiber Officinale and Thymus Vulgaris Extracts: Characterisation, Cell Cytotoxicity, and Its Antifungal Activity against Candida albicans in Comparison to Fluconazole. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, J. In Vitro Effects of Sub-inhibitory Concentrations of Amoxicillin on Physiological Responses and Virulence Determinants in a Commensal Strain of Escherichia Coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Dias, A.; Miranda, I.M.; Branco, J.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. Adhesion, Biofilm Formation, Cell Surface Hydrophobicity, and Antifungal Planktonic Susceptibility: Relationship among Candida spp. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tene, T.; Guevara, M.; Palacios, F.B.; Barrionuevo, T.P.M.; Gomez, C.V.; Bellucci, S. Optical Properties of Graphene Oxide. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1214072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvaney, P. Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy of Nanosized Metal Particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulingam, T.; Thong, K.L.; Appaturi, J.N.; Lai, C.W.; Leo, B.F. Mechanistic Actions and Contributing Factors Affecting the Antibacterial Property and Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Todd, A.D.; Bielawski, C.W. Harnessing the Chemistry of Graphene Oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5288–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, P.P.A.; Kala, M.S.; Joseph, A.V.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Reduced Graphene Oxide/Silver Nanohybrid as a Multifunctional Material for Antibacterial, Anticancer, and SERS Applications. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Qin, J.; Siraleartmukul, K.; Siriwongrungson, V. Graphene Oxide/Silver Nanoparticle Coating Produced by Electrophoretic Deposition Improved the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of NiTi Alloy for Biomedical Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3804–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.W.; Dong, A.; Li, Y. 2D Graphdiyne Oxide Serves as a Superior New Generation of Antibacterial Agents. iScience 2019, 19, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, R.; Pemmaraju, S.C.; Sharma, A.K.; Pruthi, V. Efficacy of Ferulic Acid Encapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles against Candida albicans Biofilm. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 95, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witika, B.A.; Makoni, P.A.; Matafwali, S.K.; Chabalenge, B.; Mwila, C.; Kalungia, A.C.; Nkanga, C.I.; Bapolisi, A.M.; Walker, R.B. Biocompatibility of Biomaterials for Nanoencapsulation: Current Approaches. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wei, G.; Su, Z. Graphene Film Doped with Silver Nanoparticles: Self-Assembly Formation, Structural Characterizations, Antibacterial Ability, and Biocompatibility. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Verma, G.; Saini, A. Green Synthesis of Peptide Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) Nano Bioconjugate with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



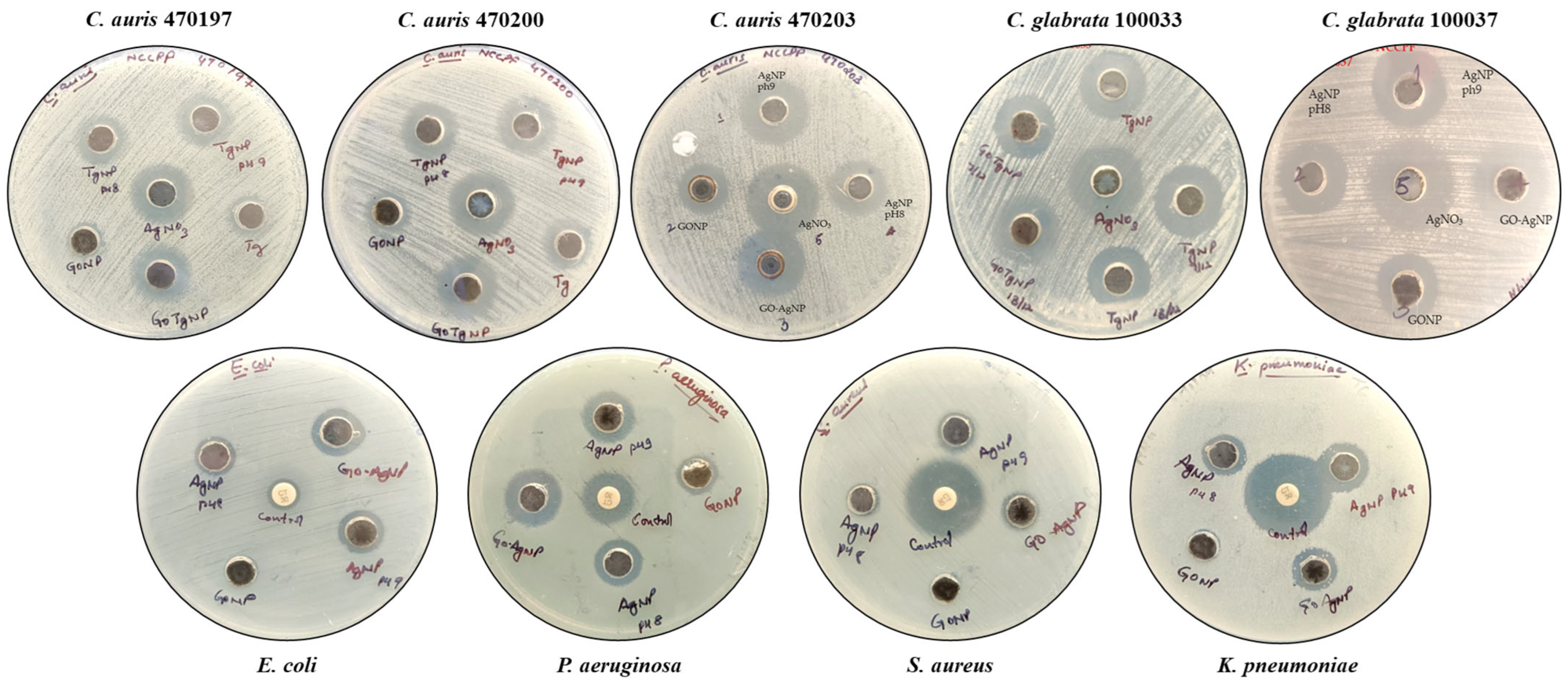


| Test Microorganism | Zone of Inhibition (mm) Obtained with | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GO-AgNPs | AgNO3 | Distilled Water | |
| C. glabrata ATCC 2001 | 16.0 ± 0.2 | 12.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| C. glabrata NCCPF 100033 | 18.0 ± 0.2 | 12.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| C. glabrata NCCPF 100037 | 17.0 ± 0.2 | 13.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| C. auris NCCPF 470197 | 17.5 ± 0.2 | 14.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| C. auris NCCPF 470200 | 18.0 ± 0.2 | 14.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| C. auris NCCPF 470203 | 17.0 ± 0.2 | 13.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| E. coli | 10.0 ± 0.2 | 8.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| S. aureus | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| K. pneumoniae | 8.5 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| P. aeruginosa | 9.0 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | ND |
| Microorganisms | MIC (µg/mL) | MLC (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNP | GO-AgNP | AgNP | GO-AgNP | |
| C. glabrata ATCC 2001 | 62.5 | 31.25 | 125 | 250 |
| C. glabrata NCCPF 100033 | 250 | 125 | 500 | 250 |
| C. glabrata NCCPF 100037 | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| C. auris NCCPF 470197 | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| C. auris NCCPF 470200 | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| C. auris NCCPF 470203 | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| E. coli | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| S. aureus | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
| K. pneumoniae | 250 | 125 | 500 | 250 |
| P. aeruginosa | 125 | 62.5 | 250 | 125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negi, P.; Chadha, J.; Harjai, K.; Gondil, V.S.; Kumari, S.; Raj, K. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Green-Synthesized Graphene–Silver Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051104
Negi P, Chadha J, Harjai K, Gondil VS, Kumari S, Raj K. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Green-Synthesized Graphene–Silver Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051104
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegi, Preeti, Jatin Chadha, Kusum Harjai, Vijay Singh Gondil, Seema Kumari, and Khem Raj. 2024. "Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Green-Synthesized Graphene–Silver Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051104
APA StyleNegi, P., Chadha, J., Harjai, K., Gondil, V. S., Kumari, S., & Raj, K. (2024). Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Potential of Green-Synthesized Graphene–Silver Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Biomedicines, 12(5), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051104






