Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review
Abstract
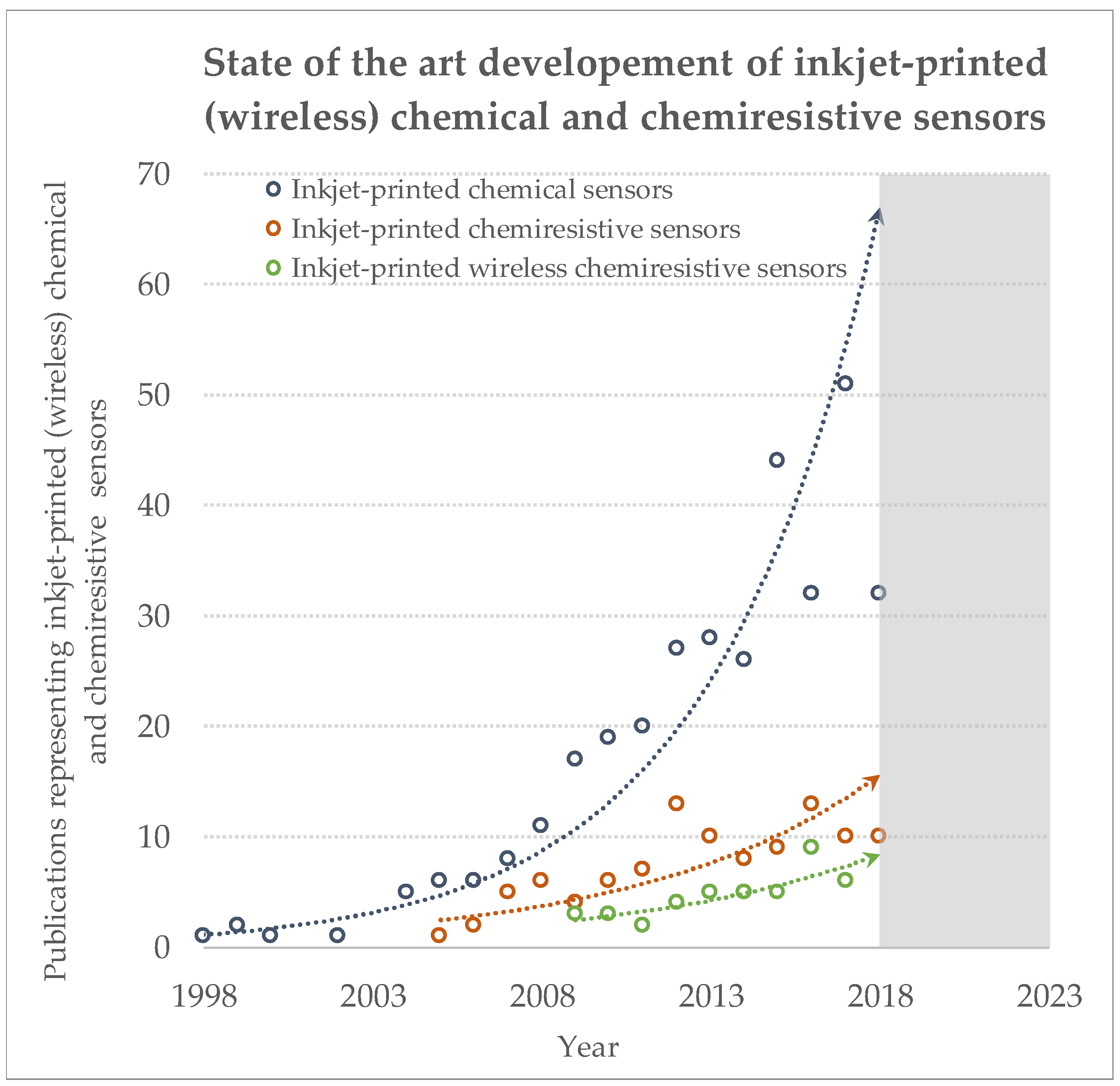
1. Introduction
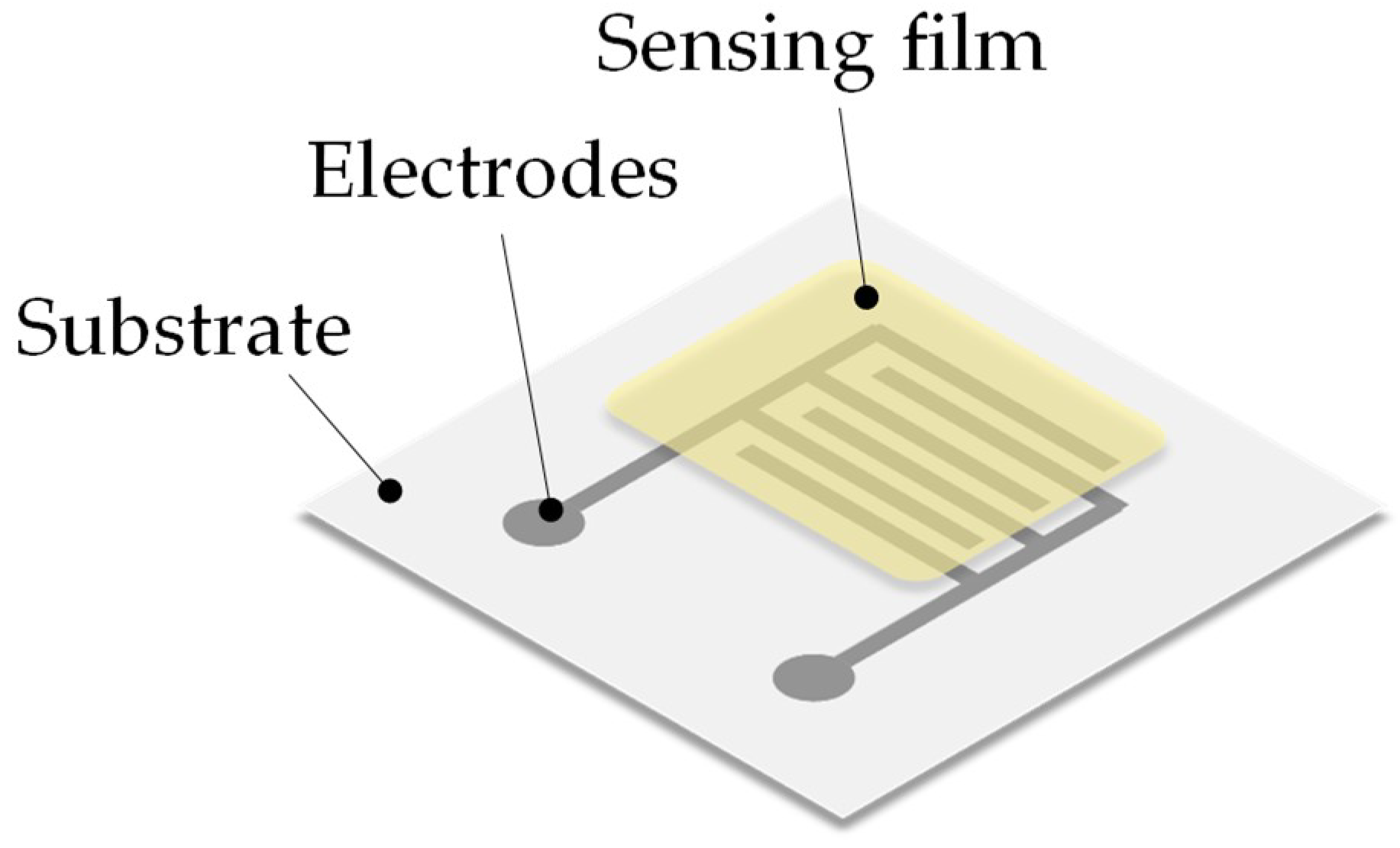
2. Structure and Transduction Mechanism
3. Inkjet-Printed Sensors
3.1. Substrate and Electrode Materials
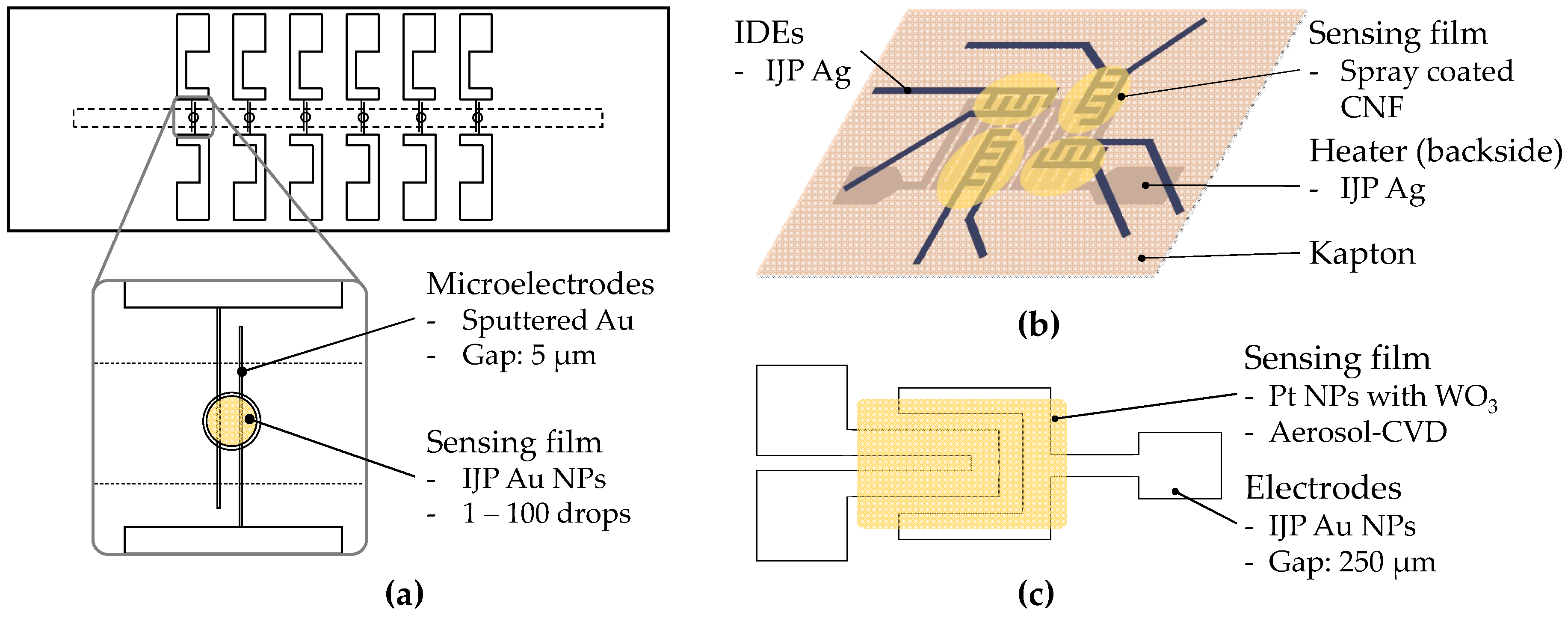
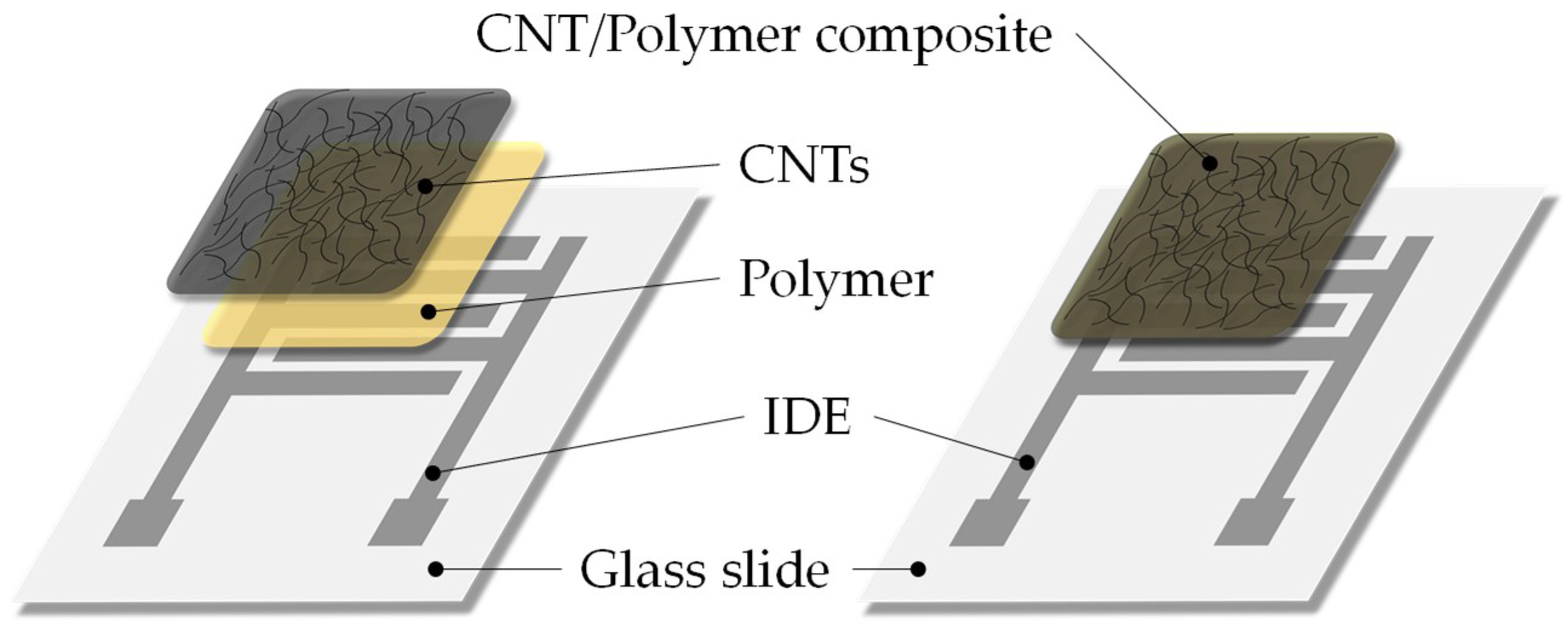
3.2. Partly Inkjet-Printed Chemiresistors
3.3. Fully Inkjet-Printed Chemiresistors
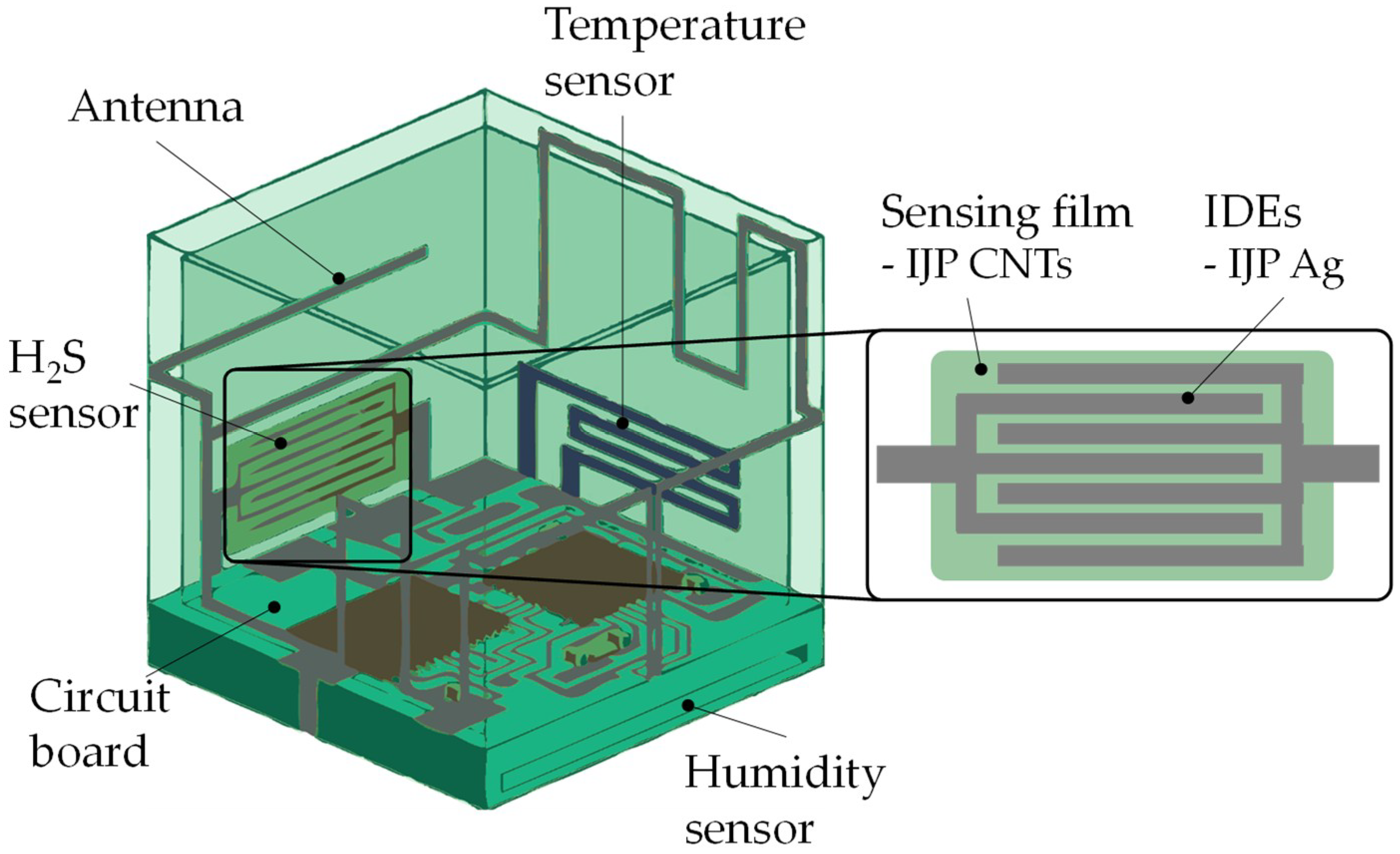
4. Integration of Inkjet-Printed Chemiresistors into Wireless Applications
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Research Nester. Chemical Sensors Market: Global Demand Analysis & Opportunity Outlook 2024. 2018. Available online: https://www.researchnester.com/reports/chemical-sensors-market-global-demand-analysis-opportunity-outlook-2024/381 (accessed on 14 December 2018).
- Wilson, D.M.; Hoyt, S.; Janata, J.; Booksh, K.; Obando, L. Chemical sensors for portable, handheld field instruments. IEEE Sens. J. 2001, 1, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Handbook of Gas Sensor Materials: Properties, Advantages and Shortcomings for Applications Volume 2: New Trends and Technologies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gründler, P. Chemical Sensors: An Introduction for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Teichler, A.; Perelaer, J.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet printing of organic electronics—Comparison of deposition techniques and state-of-the-art developments. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzik, P.; Veselý, M.; Kete, M.; Pavlica, E.; Štangar, U.L.; Neumann-Spallart, M. Properties and Application Perspective of Hybrid Titania-Silica Patterns Fabricated by Inkjet Printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16177–16190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossmeyer, T.; Jia, S.; DeIonno, E.; Diehl, M.R.; Kim, S.-H.; Peng, X.; Alivisatos, A.P.; Heath, J.R. Combinatorial approaches toward patterning nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 3664–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsara, M.; Beltsios, K.; Goustouridis, D.; Chatzandroulis, S.; Raptis, I. Sequential polymer lithography for chemical sensor arrays. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4602–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, B.J.; de Laat, A.W.M.; Hendriks, C.E.; Schubert, U.S. Inkjet-printed silver tracks: Low temperature curing and thermal stability investigation. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, J.; Hendriks, C.E.; de Laat, A.W.M.; Schubert, U.S. One-step inkjet printing of conductive silver tracks on polymer substrates. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 165303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komuro, N.; Takaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Inkjet printed (bio)chemical sensing devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5785–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, A.; Gabriel, G.; Villa, R.; Javier del Campo, F. Inkjet-printed electrochemical sensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassal, P.; Steinberg, M.D.; Steinberg, I.M. Wireless chemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.G.D.; Kimionis, J.; Tentzeris, M.M. Printed Motes for IoT Wireless Networks: State of the Art, Challenges, and Outlooks. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2017, 65, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreshaid, A.T.; Hester, J.G.; Su, W.; Fang, Y.; Tentzeris, M.M. Review—Ink-Jet Printed Wireless Liquid and Gas Sensors for IoT, SmartAg and Smart City Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, B407–B413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, W.H. Interdigitated Array Electrode Sensors: Their Design, Efficiency, and Applications. Honors Thesis, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.Y.; Yelich, S.W. Resistive and Capacitive Based Sensing Technologies. Sens. Transducers J. 2008, 90, 100–116. [Google Scholar]
- Potyrailo, R.A.; Surman, C.; Nagraj, N.; Burns, A. Materials and transducers toward selective wireless gas sensing. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7315–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukkola, J.; Mohl, M.; Leino, A.-R.; Tóth, G.; Wu, M.-C.; Shchukarev, A.; Popov, A.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Lauri, J.; Riihimäki, M.; et al. Inkjet-printed gas sensors: Metal decorated WO3 nanoparticles and their gas sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17878–17886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Sowade, E.; Dinh, T.N.; Kanoun, O.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Baumann, R.R. Inkjet printing of chemiresistive sensors based on polymer and carbon nanotube networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices (SSD), Chemnitz, Germany, 20–23 March 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Sowade, E.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Baumann, R.R. All inkjet-printed chemical gas sensors based on CNT/polymer nanocomposites: Comparison between double printed layers and blended single layer. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Hua Hin, Phetchaburi, Thailand, 16–18 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Raguse, B.; Chow, E.; Barton, C.S.; Wieczorek, L. Gold nanoparticle chemiresistor sensors: Direct sensing of organics in aqueous electrolyte solution. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7333–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.; Herrmann, J.; Barton, C.S.; Raguse, B.; Wieczorek, L. Inkjet-printed gold nanoparticle chemiresistors: Influence of film morphology and ionic strength on the detection of organics dissolved in aqueous solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.D.; Nguyen, T.N.N.; Doan, D.C.T.; Dang, T.M.D.; Dang, M.C. Fabrication of interdigitated electrodes by inkjet printing technology for apllication in ammonia sensing. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 25002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, F.; Schiattarella, C.; Polichetti, T.; Di Capua, R.; Loffredo, F.; Alfano, B.; Miglietta, M.L.; Massera, E.; Verdoliva, L.; Di Francia, G. Study of the correlation between sensing performance and surface morphology of inkjet-printed aqueous graphene-based chemiresistors for NO2 detection. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, K.; Morrin, A.; Shepherd, R.L.; in het Panhuis, M.; Wallace, G.G.; Smyth, M.R.; Killard, A.J. Fabrication of Polyaniline-Based Gas Sensors Using Piezoelectric Inkjet and Screen Printing for the Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, J.; Fogde, A.; Ihalainen, P.; Peltonen, J. The performance of inkjet-printed copper acetate based hydrogen sulfide gas sensor on a flexible plastic substrate—Varying ink composition and print density. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Baumann, R.R.; Sowade, E.; Watthanawisuth, N.; Kerdcharoen, T. A Zigbee-based wireless wearable electronic nose using flexible printed sensor array. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Nanoelectronics Conference (INEC), Singapore, 2–4 January 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 291–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lorwongtragool, P.; Sowade, E.; Watthanawisuth, N.; Baumann, R.R.; Kerdcharoen, T. A novel wearable electronic nose for healthcare based on flexible printed chemical sensor array. Sensors 2014, 14, 19700–19712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero, A.V.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Smits, E.C.P.; Danesh, E.; van den Brand, J.; Persaud, K.; Oprea, A.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U.; de Rooij, N.F.; et al. Smart RFID label with a printed multisensor platform for environmental monitoring. Flex. Print. Electron. 2016, 1, 25003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.G.D.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Fang, Y. Inkjet-printed, flexible, high performance, carbon nanomaterial based sensors for ammonia and DMMP gas detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 45th European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 7–10 September 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 857–860. [Google Scholar]
- Claramunt, S.; Monereo, O.; Boix, M.; Leghrib, R.; Prades, J.D.; Cornet, A.; Merino, P.; Merino, C.; Cirera, A. Flexible gas sensor array with an embedded heater based on metal decorated carbon nanofibres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneyra, A.; Fernández-Salmerón, J.; Agudo-Acemel, M.; López-Villanueva, J.A.; Palma, A.J.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F. A printed capacitive–resistive double sensor for toluene and moisture sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.L.; Annanouch, F.E.; Llobet, E.; Briand, D. Architecture for the efficient manufacturing by printing of heated, planar, resistive transducers on polymeric foil for gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vena, A.; Sydanheimo, L.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Ukkonen, L. A Fully Inkjet-Printed Wireless and Chipless Sensor for CO2 and Temperature Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Lakafosis, V.; Kim, S.; Cook, B.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Lin, Z.; Wong, C.-P. A novel graphene-based inkjet-printed WISP-enabled wireless gas sensor. In Proceedings of the 2012 European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October–1 November 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 412–415. [Google Scholar]
- Bahoumina, P.; Hallil, H.; Lachaud, J.-L.; Abdelghani, A.; Frigui, K.; Bila, S.; Baillargeat, D.; Zhang, Q.; Coquet, P.; Paragua, C.; et al. Chemical Gas Sensor Based on a Flexible Capacitive Microwave Transducer Associated with a Sensitive Carbon Composite Polymer Film. Proceedings 2017, 1, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quddious, A.; Yang, S.; Khan, M.M.; Tahir, F.A.; Shamim, A.; Salama, K.N.; Cheema, H.M. Disposable, Paper-Based, Inkjet-Printed Humidity and H2S Gas Sensor for Passive Sensing Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskela, J.; Sarfraz, J.; Ihalainen, P.; Määttänen, A.; Pulkkinen, P.; Tenhu, H.; Nieminen, T.; Kilpelä, A.; Peltonen, J. Monitoring the quality of raw poultry by detecting hydrogen sulfide with printed sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 218, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Lin, Z.; Wong, C.P.; Tentzeris, M.M. Enhanced-performance wireless conformal “smart skins” utilizing inkjet-printed carbon-nanostructures. In Proceedings of the IEEE 64th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Lake Buena Vista, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Stempien, Z.; Kozicki, M.; Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Owczarek, G.; Poscik, A.; Sajna, D. Ammonia gas sensors ink-jet printed on textile substrates. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS 2016, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–2 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Myers, A.; Malhotra, A.; Lin, F.; Bozkurt, A.; Muth, J.F.; Zhu, Y. A Wearable Hydration Sensor with Conformal Nanowire Electrodes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Borgne, B.; Jacques, E.; Harnois, M. The Use of a Water Soluble Flexible Substrate to Embed Electronics in Additively Manufactured Objects: From Tattoo to Water Transfer Printed Electronics. Micromachines 2018, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltman, D.; Subramanian, V. Inkjet-printed line morphologies and temperature control of the coffee ring effect. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2008, 24, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, J.; Derby, B. Formation and stability of lines produced by inkjet printing. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2010, 26, 10365–10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, B. Inkjet Printing of Functional and Structural Materials: Fluid Property Requirements, Feature Stability, and Resolution. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Le Borgne, B.; Mohammed-Brahim, T.; Jacques, E.; Harnois, M. Spreading and drying impact on printed pattern accuracy due to phase separation of a colloidal ink. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelaer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Mager, D.; Soltman, D.; Volkman, S.K.; Subramanian, V.; Korvink, J.G.; Schubert, U.S. Printed electronics: The challenges involved in printing devices, interconnects, and contacts based on inorganic materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8446–8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Lopez, F.; Briand, D.; de Rooij, N.F. Inkjet Printing of Interdigitated Capacitive Chemical Sensors with Reduced Size by the Introduction of a Dielectric Interlayer. Procedia Eng. 2012, 47, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, S.; Pykari, L.; Mantysalo, M. Electrical Performance Characterization of an Inkjet-Printed Flexible Circuit in a Mobile Application. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manufact. Technol. 2013, 3, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.S.; Alenezi, M.R.; Lai, K.T.; Silva, S.R.P. Inkjet printing of polymer functionalized CNT gas sensor with enhanced sensing properties. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed graphene–PEDOT: PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Lopez, F.; Briand, D.; de Rooij, N.F.; Smolander, M. Fully inkjet-printed parallel-plate capacitive gas sensors on flexible substrate. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2012 IEEE, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Altenberend, U.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Oprea, A.; Briand, D.; Bârsan, N.; de Rooij, N.F.; Weimar, U. Towards fully printed capacitive gas sensors on flexible PET substrates based on Ag interdigitated transducers with increased stability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbard, T.; Crowley, K.; Killard, A.J. Direct measurement of ammonia in simulated human breath using an inkjet-printed polyaniline nanoparticle sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 779, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, C.; Llobet, E.; Ivanov, P.; Correig, X.; Vilanova, X.; Brezmes, J.; Hubalek, J.; Malysz, K.; Pireaux, J.J.; Calderer, J. Influence of the doping method on the sensitivity of Pt-doped screen-printed SnO2 sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 97, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Al-Milaji, K.N.; Zhao, H. Inkjet Printing of Silver Nanowires for Stretchable Heaters. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.J.; Scanaill, C.N. (Eds.) Sensor Technologies: Healthcare, Wellness, and Environmental Applications; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.-H.; Tang, K.-T. A review of sensor-based methods for monitoring hydrogen sulfide. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Naishadham, K.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Shaker, G. A novel highly-sensitive antenna-based “smart skin” gas sensor utilizing carbon nanotubes and inkjet printing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1593–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Shaker, G.; Naishadham, K.; Song, X.; McKinley, M.; Wagner, B.; Tentzeris, M. Carbon-Nanotube Loaded Antenna-Based Ammonia Gas Sensor. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2011, 59, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Dios, A.S.; Díaz-García, M.E. Multifunctional nanoparticles: Analytical prospects. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 666, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hecht, D.S.; Grüner, G. Carbon nanotube thin films: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5790–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Inkjet printing of conductive materials: A review. Circuit World 2012, 38, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Chou, Y.-H.; Hsieh, T.-W.; Wang, M.-W.; Shu, Y.-Y.; Ger, M.-D. Interdigitated electrode fabricated by integration of ink-jet printing with electroless plating and its application in gas sensor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 402, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiattarella, C.; Polichetti, T.; Villani, F.; Loffredo, F.; Alfano, B.; Massera, E.; Miglietta, M.L.; Di Francia, G. Inkjet Printed Graphene-Based Chemiresistive Sensors to NO2. In Sensors, Proceedings of the Third National Conference on Sensors, Rome, Italy, 23–25 February 2016; Andò, B., Baldini, F., Di Natale, C., Marrazza, G., Siciliano, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 431, pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Navarro, C.; Weitz, R.T.; Bittner, A.M.; Scolari, M.; Mews, A.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K. Electronic transport properties of individual chemically reduced graphene oxide sheets. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3499–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, Y. Chemiresistor coatings from Pt- and Au-nanoparticle/nonanedithiol films: Sensitivity to gases and solvent vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 98, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, Y.; Besnard, I.; Rosenberger, M.; Guse, B.; Nothofer, H.-G.; Wessels, J.M.; Wild, U.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Su, D.; Schlögl, R.; et al. Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticle/Alkanedithiol Films: Preparation, Electron Microscopy, XPS-Analysis, Charge Transport, and Vapor-Sensing Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7406–7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, Y.; Guse, B.; Vossmeyer, T.; Yasuda, A. Gold Nanoparticle/Organic Networks as Chemiresistor Coatings: The Effect of Film Morphology on Vapor Sensitivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12507–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, Y.; Peić, A.; Chen, X.; Michl, J.; Vossmeyer, T.; Yasuda, A. Vapor Sensitivity of Networked Gold Nanoparticle Chemiresistors: Importance of Flexibility and Resistivity of the Interlinkage. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12855–12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diéguez, A.; Vilà, A.; Cabot, A.; Romano-Rodrı́guez, A.; Morante, J.R.; Kappler, J.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U.; Göpel, W. Influence on the gas sensor performances of the metal chemical states introduced by impregnation of calcinated SnO2 sol–gel nanocrystals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 68, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvan, M.; Pijolat, C. Selectivity improvement of SnO2 films by superficial metallic films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 58, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Colozza, N.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Polomoshnov, M.; Sowade, E.; Baumann, R.R.; Arduini, F. Electroanalysis moves towards paper-based printed electronics: Carbon black nanomodified inkjet-printed sensor for ascorbic acid detection as a case study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.S.; Shkunov, M.; Silva, S.R.P. Inkjet printed PEDOT:PSS/MWCNT nano-composites with aligned carbon nanotubes and enhanced conductivity. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2014, 8, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.; Staiculescu, D.; Wong, C.P.; Tentzeris, M.M. A Novel Conformal RFID-Enabled Module Utilizing Inkjet-Printed Antennas and Carbon Nanotubes for Gas-Detection Applications. Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2009, 8, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentzeris, M.; Nikolaou, S. RFID-enabled ultrasensitive wireless sensors utilizing inkjet-printed antennas and carbon nanotubes for gas detection applications. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronic Systems, Tel Aviv, Israel, 9–11 November 2009; Staff, I., Ed.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Orecchini, G.; Shaker, G.; Lee, H.; Tentzeris, M. Battery-free RFID-enabled wireless sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–28 May 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Farooqui, M.F.; Karimi, M.A.; Salama, K.N.; Shamim, A. 3D-Printed Disposable Wireless Sensors with Integrated Microelectronics for Large Area Environmental Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, M.F.; Shamim, A. 3D inkjet printed disposable environmental monitoring wireless sensor node. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honololu, HI, USA, 4–9 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1379–1382. [Google Scholar]
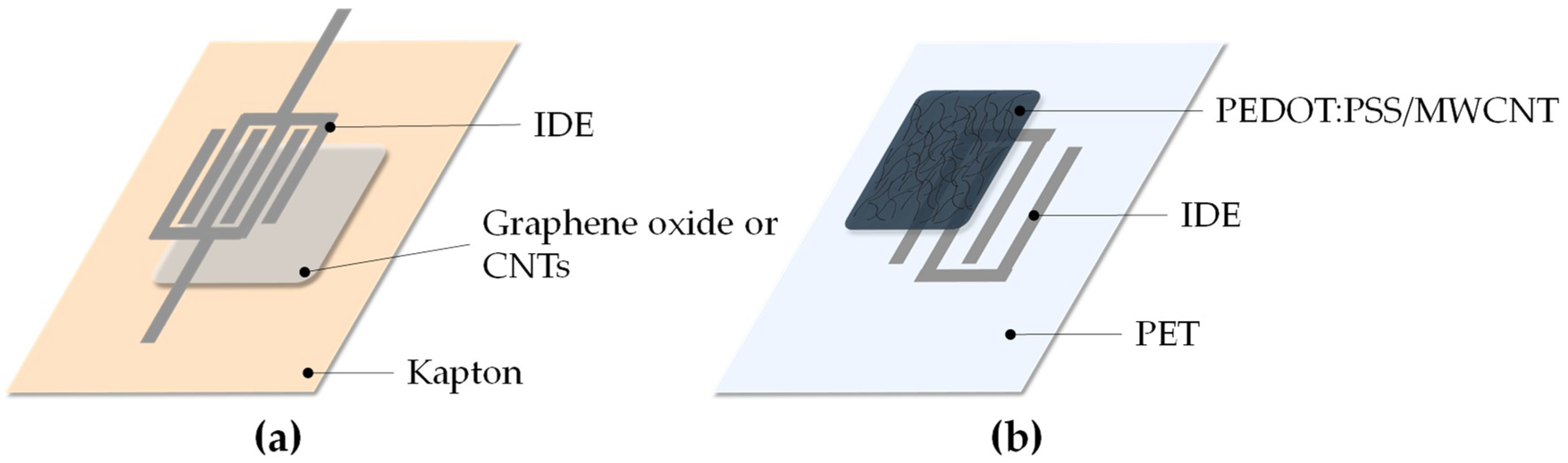
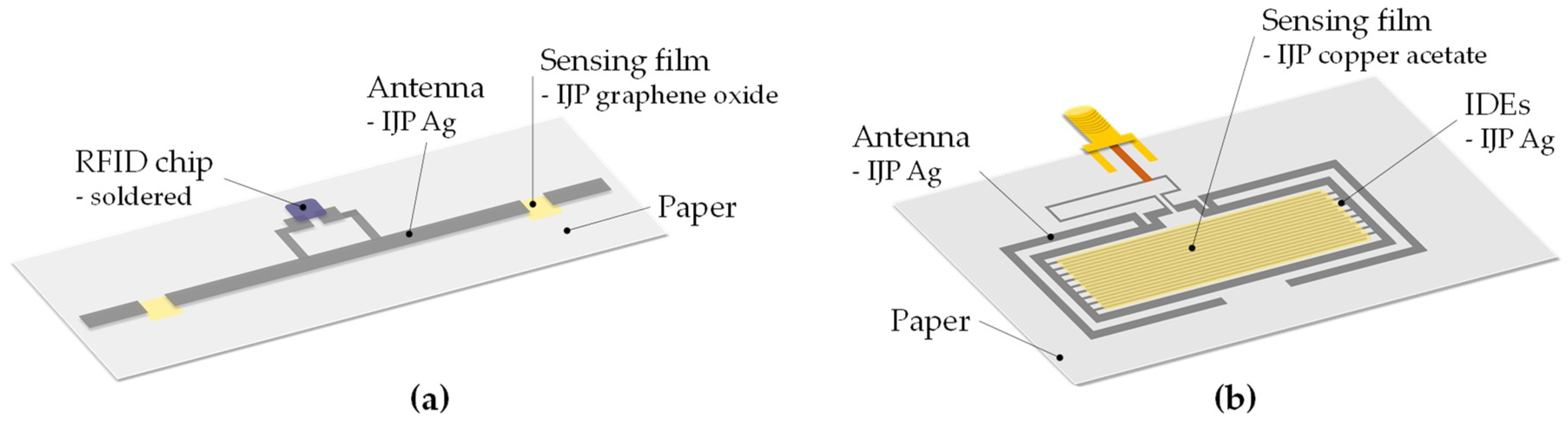
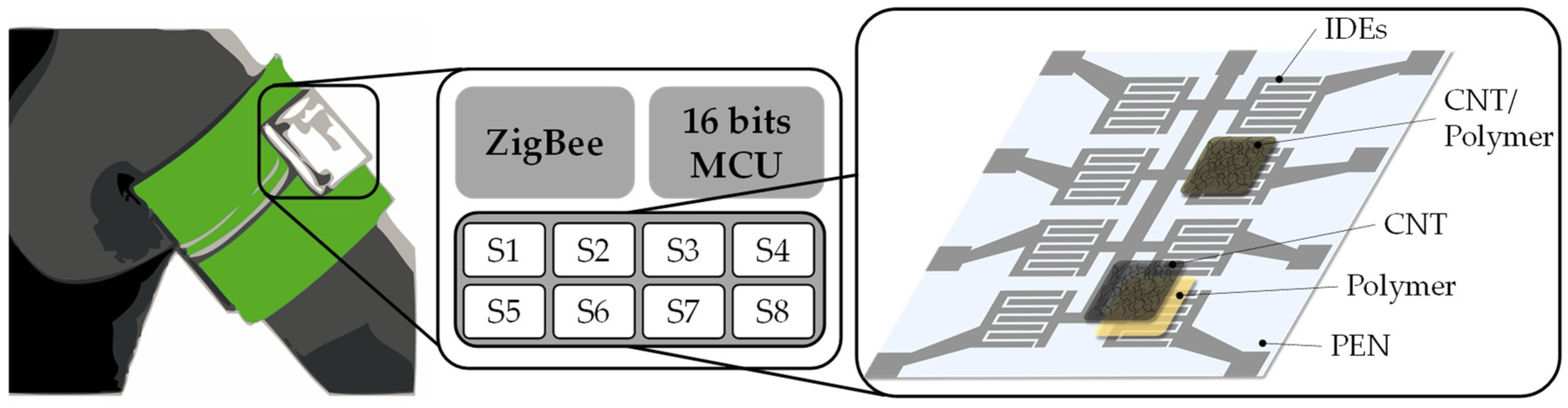
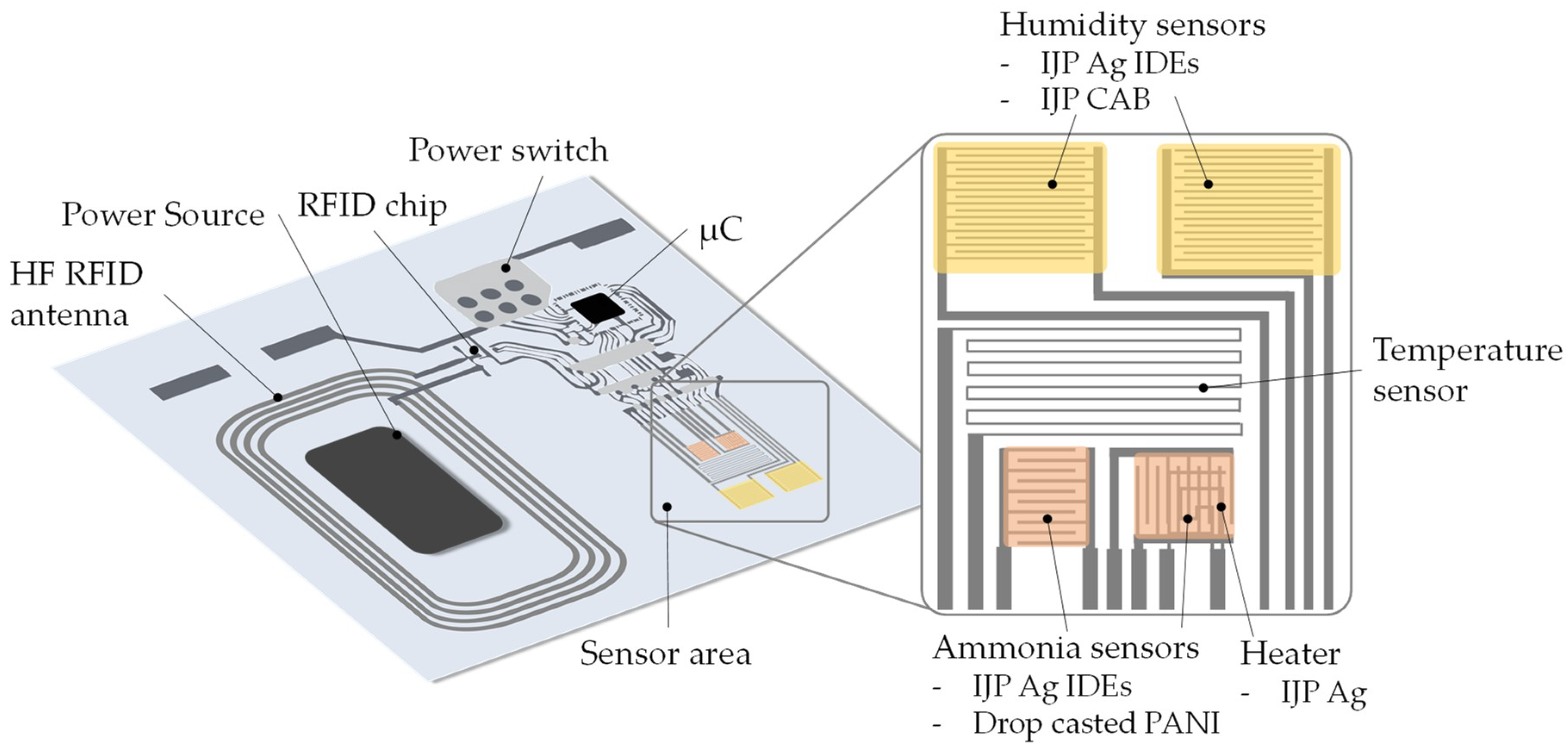
| Analyte | Technology | Substrate | Interdigitated Electrode, Gap | Sensing Material, Thickness | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium Hydroxide, Ethanol, Acetone, Triethylamine, Tetrahydrofuran | Inkjet | Glass | IJP (DMP 2831) Ag, 200 µm | IJP (Microdrop) CNTs, 70.5–385 nm | [20,21] |
| Ammonia | Screen, Inkjet | Flexible, transp. | Screen printed Ag, 1 mm | IJP (Office printer) graphene-PEDOT:PSS, 402–407 nm | [52] |
| Ammonia | Inkjet, Drop casting | Silicon wafer | IJP (DMP 2800) Ag, 72–335 µm | Drop casted PANI | [24] |
| Ammonia | Inkjet, Spray coating | Kapton | IJP (Xenjet 4000) Ag | Spray coated carbon nano fibres, 300 nm | [31,32] |
| Ammonia, Dimethylmethyl-phosphonat | Inkjet | Kapton | IJP (DMP 2831) Ag, 350 µm | IJP graphene oxide, CNTs | [31] |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | Screen, Inkjet | PET | Screen printed Ag and carbon, 200 µm | IJP (DMP 2811) PANI, PANI-copper chloride | [26,27] |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | Lithograph, Inkjet | PET | Etched copper, 300 µm | IJP (DMP 2831) copper acetate | [27] |
| Toluene, Dichloromethane, Ethanol | Sputtering, Inkjet | Glass | Sputtered Au, 5 µm | IJP (Microdrop) Au NP, 600 nm | [22] |
| Hydrogen | Inkjet, AA-CVD | Kapton | IJP Au NP (DMP 2800), 250 µm | AA-CVD, Pt NP decorated WO3 | [34] |
| Nitrogen dioxide | E-beam evaporation Inkjet | Paper Silicium Aluminum | Evaporated Au, 350, 860 µm | IJP (DMP 2831) graphene, ~50–225 nm | [25,66] |
| Ethanol | Inkjet | PET | IJP Ag, ~25 µm | IJP (DMP 2831) PEDOT:PSS/MWCNT, 40 nm | [51,76] |
| Toluene | Inkjet, Screen | Kapton | IJP (DMP 2831) Ag, 57–163 µm | Screen printed graphite-polystyrene, 7 µm | [33] |
| Analyte | Technology | Substrate | Interdigitated Electrode | Sensing Material | Wireless System | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen sulfide | Inkjet (DMP 2831) | Photo Paper | IJP Ag | IJP copper acetate | RFID | [38] |
| 3D printed polymer | IJP Ag | IJP CNTs | ZigBee | [80,81] | ||
| Coated paper | IJP Ag | IJP copper acetate | RFID | [39] | ||
| Ammonia | Inkjet (DMP 2800) | Kapton | IJP Ag | IJP graphene oxide | RFID | [36,40] |
| Carbon dioxide | Inkjet (DMP 2831) | Kapton | IJP Ag | IJP SWCNTs | RFID | [35] |
| Ammonia, acetic acid, acetone, ethanol | Inkjet (DMP 2831 Microdrop) | PEN | IJP Ag | IJP CNTs | ZigBee | [28,29] |
| Humidity, ammonia | Inkjet (DMP 2831), Drop Casting | PEN | IJP Ag | IJP CAB, drop casted PANI | RFID | [30] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hartwig, M.; Zichner, R.; Joseph, Y. Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040066
Hartwig M, Zichner R, Joseph Y. Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(4):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040066
Chicago/Turabian StyleHartwig, Melinda, Ralf Zichner, and Yvonne Joseph. 2018. "Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review" Chemosensors 6, no. 4: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040066
APA StyleHartwig, M., Zichner, R., & Joseph, Y. (2018). Inkjet-Printed Wireless Chemiresistive Sensors—A Review. Chemosensors, 6(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040066





