Not Just PA28γ: What We Know About the Role of PA28αβ in Carcinogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. UPS and Cancer
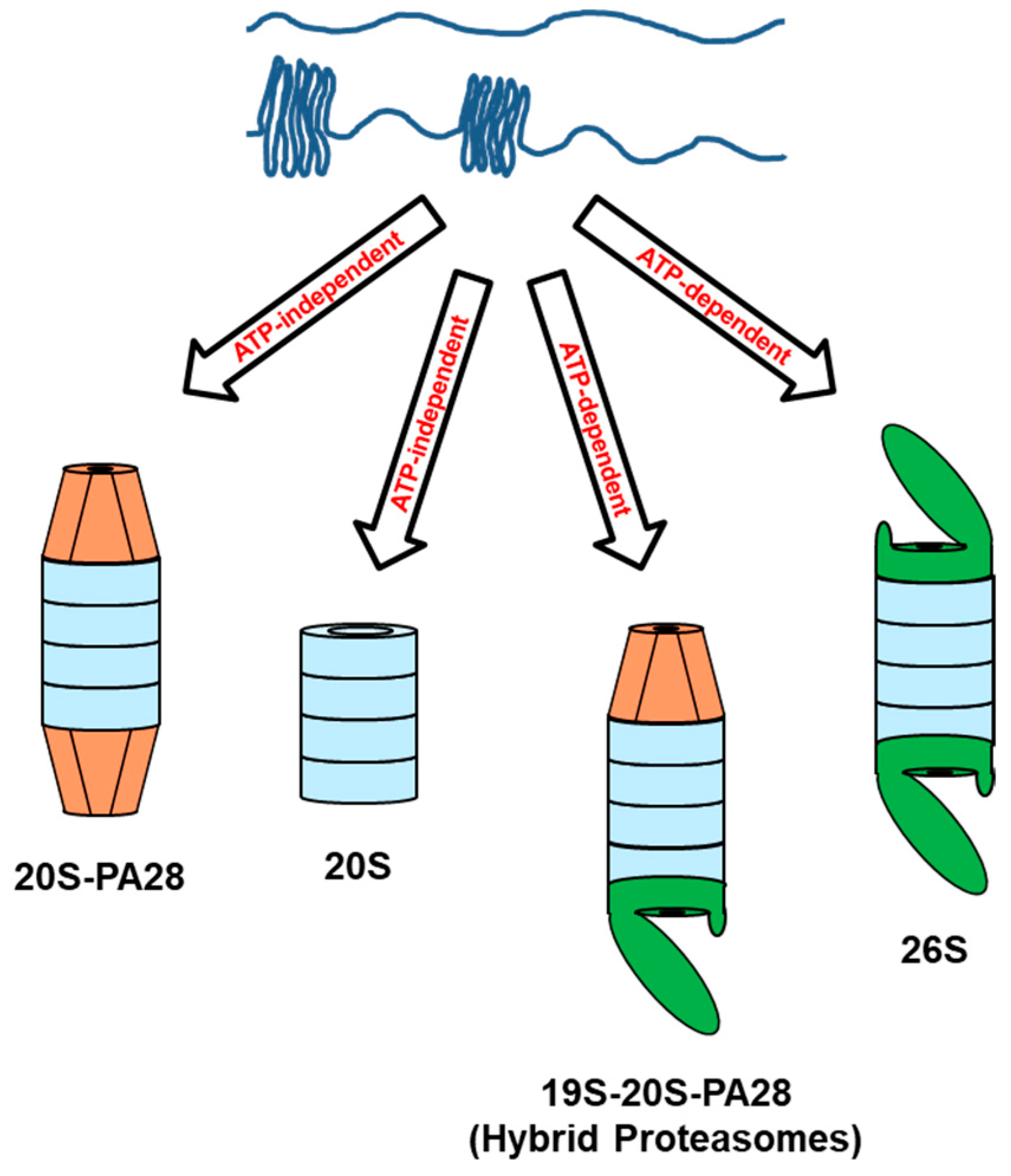
1.2. The PA28 Family of Proteasome Activators
1.3. Biological Functions of PA28 Activators
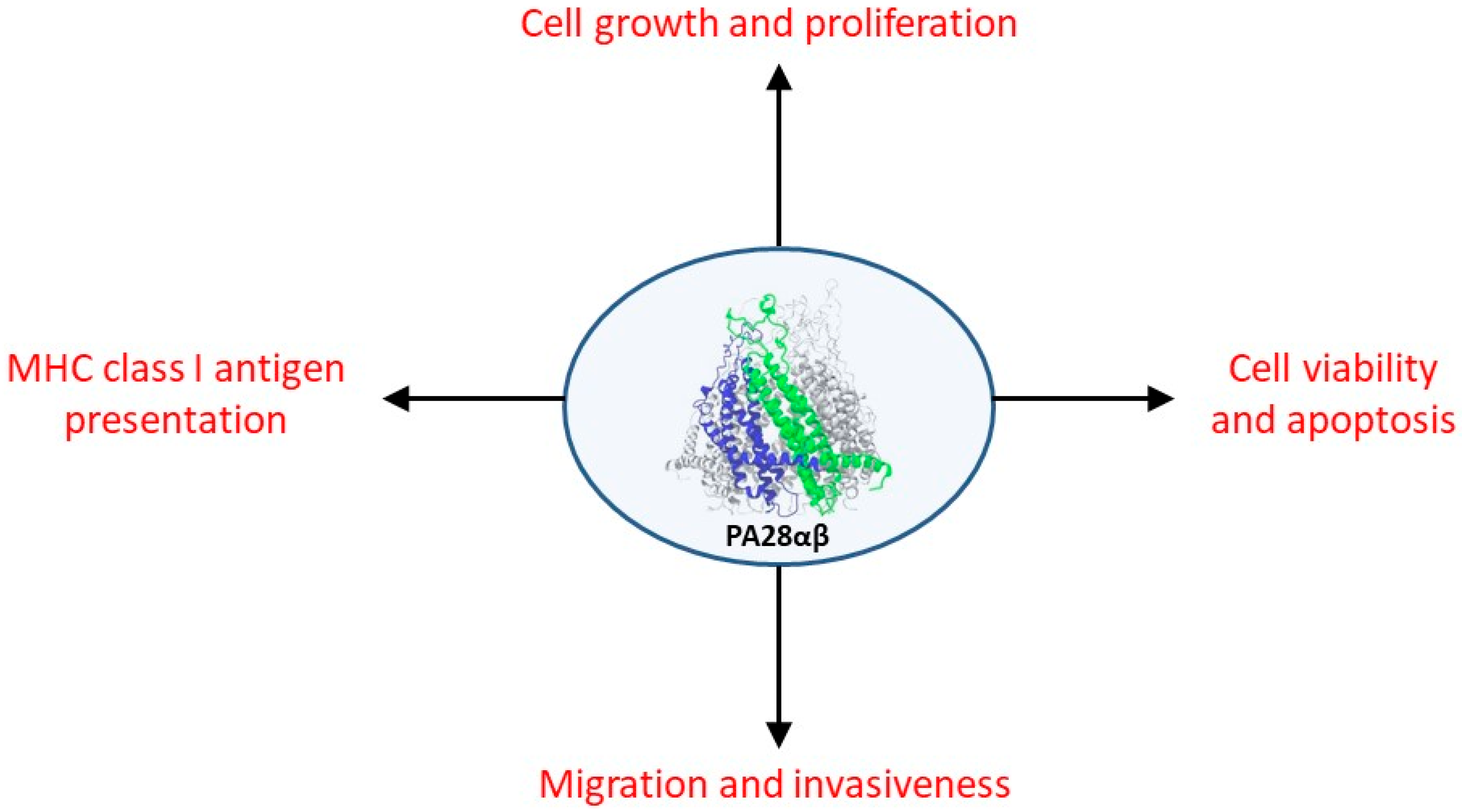
2. PA28αβ and Cancer
2.1. Role of PA28αβ in the Anti-Tumor Immune Response
2.2. Non-Immunological Role of PA28αβ in Neoplastic Transformation and Tumor Development
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tundo, G.R.; Cascio, P.; Milardi, D.; Santoro, A.M.; Graziani, G.; Lacal, P.M.; Bocedi, A.; Oddone, F.; Parravano, M.; Coletta, A.; et al. Targeting Immunoproteasome in Neurodegeneration: A Glance to the Future. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 241, 108329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y. Structure, Dynamics and Function of the 26S Proteasome. In Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer Science and Business Media B.V.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 96, pp. 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, J.A.M.; Goodall, E.A.; Greene, E.R.; Jonsson, E.; Dong, K.C.; Martin, A. Structure and Function of the 26S Proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 697–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, E.; Eisele, M.R.; Baumeister, W. Molecular and Cellular Dynamics of the 26S Proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, E.R.; Dong, K.C.; Martin, A. Understanding the 26S Proteasome Molecular Machine from a Structural and Conformational Dynamics Perspective. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2020, 61, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkinson, C.; Dong, K.C.; Gee, C.L.; Martin, A. Mechanisms and Regulation of Substrate Degradation by the 26S Proteasome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2025, 26, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayssinhes, J.-Y.A.; Cerruti, F.; Laulin, J.; Cattaneo, A.; Bachi, A.; Apcher, S.; Coux, O.; Cascio, P. PA28γ-20S Proteasome Is a Proteolytic Complex Committed to Degrade Unfolded Proteins. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 79, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaros, Y.; Raiff, A.; Timms, R.T.; Wagh, A.R.; Gueta, M.I.; Bekturova, A.; Guez-Haddad, J.; Brodsky, S.; Opatowsky, Y.; Glickman, M.H.; et al. Ubiquitin-Independent Proteasomal Degradation Driven by C-Degron Pathways. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 1921–1935.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, I.; Mali, S.M.; Sulkshane, P.; Xu, C.; Rozenberg, A.; Morag, R.; Sahoo, M.P.; Singh, S.K.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. The 20S as a Stand-Alone Proteasome in Cells Can Degrade the Ubiquitin Tag. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Olender, T.; Savidor, A.; Levin, Y.; Reuven, N.; Shaul, Y. The Disordered Landscape of the 20S Proteasome Substrates Reveals Tight Association with Phase Separated Granules. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1800076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, J.M.; Viktorova, E.G.; Pilipenko, E.V. Proteasomes Can Degrade a Significant Proportion of Cellular Proteins Independent of Ubiquitination. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskiewicz, M.J.; Sussman, J.L.; Silman, I.; Shaul, Y. Context-Dependent Resistance to Proteolysis of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurov, A.; Kuzina, E.; Kudriaeva, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Kovalchuk, S.; Surina, Y.; Smirnov, I.; Lomakin, Y.; Bacheva, A.; Stepanov, A.; et al. Ubiquitin-Independent Proteosomal Degradation of Myelin Basic Protein Contributes to Development of Neurodegenerative Autoimmunity. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Myers, N.; Moscovitz, O.; Sharon, M.; Prilusky, J.; Shaul, Y. Thermo-Resistant Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Are Efficient 20S Proteasome Substrates. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisselev, A.F.; Akopian, T.N.; Woo, K.M.; Goldberg, A.L. The Sizes of Peptides Generated from Protein by Mammalian 26 and 20 S Proteasomes. Implications for Understanding the Degradative Mechanism and Antigen Presentation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, P.; Hilton, C.; Kisselev, A.F.; Rock, K.L.; Goldberg, A.L. 26S Proteasomes and Immunoproteasomes Produce Mainly N-Extended Versions of an Antigenic Peptide. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raule, M.; Cerruti, F.; Cascio, P. Enhanced Rate of Degradation of Basic Proteins by 26S Immunoproteasomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raule, M.; Cerruti, F.; Benaroudj, N.; Migotti, R.; Kikuchi, J.; Bachi, A.; Navon, A.; Dittmar, G.; Cascio, P. PA28αβ Reduces Size and Increases Hydrophilicity of 20S Immunoproteasome Peptide Products. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erales, J.; Coffino, P. Ubiquitin-Independent Proteasomal Degradation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariel-Encontre, I.; Bossis, G.; Piechaczyk, M. Ubiquitin-Independent Degradation of Proteins by the Proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1786, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Deshmukh, F.; Yaffe, D.; Olshina, M.A.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Sharon, M. The Contribution of the 20S Proteasome to Proteostasis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Nissan, G.; Sharon, M. Regulating the 20S Proteasome Ubiquitin-Independent Degradation Pathway. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 862–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, I.; Glickman, M.H. Structural Insights into Substrate Recognition and Processing by the 20S Proteasome. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, P.; Dittmar, G. Regulating Proteasome Activity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagde, P.H.; Kandpal, M.; Rani, A.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, A.; Jha, H.C. Proteasomal Dysfunction in Cancer: Mechanistic Pathways and Targeted Therapies. J. Cell Biochem. 2025, 126, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, W.; Manton, C.; Miller, C.P.; Khatua, S.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Chandra, J. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway in Adult and Pediatric Brain Tumors: Biological Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.H. Regulation of Protein Degradation by Proteasomes in Cancer. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 23, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Breast Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Cong, M.; Yin, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Tang, J. Role of Protein Degradation Systems in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, T. The Role of Proteasomes in Tumorigenesis. Genes. Dis. 2024, 11, 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, R.Z.; Kuhn, D.J. Proteasome Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Lessons from the First Decade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasanch, E.E.; Orlowski, R.Z. Proteasome Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.; Palombella, V.J.; Sausville, E.A.; Johnson, J.; Destree, A.; Lazarus, D.D.; Maas, J.; Pien, C.S.; Prakash, S.; Elliott, P.J. Proteasome Inhibitors: A Novel Class of Potent and Effective Antitumor Agents. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, J. The Development of Proteasome Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J. The Proteasome: Structure, Function, and Role in the Cell. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.L. Development of Proteasome Inhibitors as Research Tools and Cancer Drugs. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoreva, T.A.; Tribulovich, V.G.; Garabadzhiu, A.V.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.A. The 26S Proteasome Is a Multifaceted Target for Anti-Cancer Therapies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24733–24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra-García, P.; Martini, F.; Auner, H.W. Proteasome Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: Lessons for Other Cancers. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C451–C462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fhu, C.W.; Ali, A. Dysregulation of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Human Malignancies: A Window for Therapeutic Intervention. Cancers 2021, 13, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogbein, O.; Paul, P.; Umar, M.; Chaari, A.; Batuman, V.; Upadhyay, R. Bortezomib in Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Side Effects, and Future Proteasome Inhibitors. Life Sci. 2024, 358, 123125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, F.; Sohrabi, B.; Mostafavi, E.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Webster, T.J. Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and the Role of Its Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisselev, A.F. Site-Specific Proteasome Inhibitors. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubiel, W.; Pratt, G.; Ferrell, K.; Rechsteiner, M. Purification of an 11 S Regulator of the Multicatalytic Protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22369–22377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu-Ping, M.; Slaughter, C.A.; DeMartino, G.N. Identification, Purification, and Characterization of a Protein Activator (PA28) of the 20 S Proteasome (Macropain). J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10515–10523. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Tanahashi, N.; Akiyama, K.; Hisamatsu, H.; Noda, C.; Tanaka, K.; Chung, C.H.; Shibmara, N.; Willy, P.J.; Mott, J.D.; et al. Primary Structures of Two Homologous Subunits of PA28, a γ-Interferon-Inducible Protein Activator of the 20S Proteasome. FEBS Lett. 1995, 366, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Erlander, M.; Leturcq, D.; Peterson, P.A.; Früh, K.; Yang, Y. In Vivo Characterization of the Proteasome Regulator PA28 *. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18237–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honoré, B.; Leffers, H.; Madsen, P.; Celis, J.E. Interferon-Gamma up-Regulates a Unique Set of Proteins in Human Keratinocytes. Molecular Cloning and Expression of the cDNA Encoding the RGD-Sequence-Containing Protein IGUP I-5111. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 218, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Monaco, J.J. Sequence and Expression of Mouse Proteasome Activator PA28 and the Related Autoantigen Ki. Immunogenetics 1997, 46, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, C.; Dubiel, W.; Pratt, G.; Ferrell, K.; Rechsteiner, M. Molecular Cloning and Expression of a Gamma-Interferon-Inducible Activator of the Multicatalytic Protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20727–20732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, N.; Yokota, K.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Chung, C.H.; Fujiwara, T.; Takahashi, E.I.; DeMartino, G.N.; Slaughter, C.A.; Toyonaga, T.; Yamamura, K.I.; et al. Molecular Properties of the Proteasome Activator PA28 Family Proteins and γ-Interferon Regulation. Genes. Cells 1997, 2, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, P.; Andersson, O.; Petersen, U.M.; Young, P. Identification and Characterization of a Drosophila Nuclear Proteasome Regulator. A Homolog of Human 11 S REGγ (PA28γ). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paesen, G.C.; Nuttall, P.A. A Tick Homologue of the Human Ki Nuclear Autoantigen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1309, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, C.S.; Morais, E.R.; Magalhães, L.G.; Machado, C.B.; de Moreira, É.B.C.; Teixeira, F.R.; Rodrigues, V.; Yoshino, T.P. Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Putative PA28γ Proteasome Activator Orthologue in Schistosoma Mansoni. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2013, 189, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, P.; Lundin, D.; Söderbom, F.; Young, P. Characterization of a REG/PA28 Proteasome Activator Homolog in Dictyostelium Discoideum Indicates That the Ubiquitin- and ATP-Independent REGgamma Proteasome Is an Ancient Nuclear Protease. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.C.; Metcalfe, R.D.; Hanssen, E.; Yang, T.; Gillett, D.L.; Leis, A.P.; Morton, C.J.; Kuiper, M.J.; Parker, M.W.; Spillman, N.J.; et al. The Structure of the PA28–20S Proteasome Complex from Plasmodium Falciparum and Implications for Proteostasis. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, P.; Kajava, A.V.; Delsuc, F.; Coux, O. Evolution of Proteasome Regulators in Eukaryotes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, C.; Jensen, C.C.; Zhang, Z.G.; Johnston, S.C.; Knowlton, J.R.; Hill, C.P.; Rechsteiner, M. Characterization of Recombinant REGα, REGβ, and REGγ Proteasome Activators. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25483–25492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Sahashi, H.; Kurimoto, E.; Takata, S.I.; Yagi, H.; Kanai, K.; Sakata, E.; Minami, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kato, K. Spatial Arrangement and Functional Role of α Subunits of Proteasome Activator PA28 in Hetero-Oligomeric Form. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lonard, D.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Malovannaya, A.; Feng, Q.; Qin, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O’Malley, B.W. The SRC-3/AIB1 Coactivator Is Degraded in a Ubiquitin- and ATP-Independent Manner by the REGγ Proteasome. Cell 2006, 124, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Amazit, L.; Long, W.; Lonard, D.M.; Monaco, J.J.; O’Malley, B.W. Ubiquitin- and ATP-Independent Proteolytic Turnover of P21 by the REGγ-Proteasome Pathway. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W.; Zhai, W.; Chen, H.; Li, K.; Tong, L.; Gao, X.; Amjad, A.; et al. REGγ 3 Is Critical for Skin Carcinogenesis by Modulating the Wnt/β 2-Catenin Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriishi, K.; Mochizuki, R.; Moriya, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Mori, Y.; Abe, T.; Myrata, S.; Tanaka, K.; Miyamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Critical Role of PA28γ in Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Steatogenesis and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Furuya, F.; Zhao, L.; Araki, O.; West, B.L.; Hanover, J.A.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Aberrant Accumulation of PTTG1 Induced by a Mutated Thyroid Hormone β Receptor Inhibits Mitotic Progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2972–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, P. PA28γ: New Insights on an Ancient Proteasome Activator. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowlton, J.R.; Johnston, S.C.; Whitby, F.G.; Realini, C.; Zhang, Z.; Rechsteiner, M.; Hill, C.P. Structure of the Proteasome Activator REGα (PA28α). Nature 1997, 390, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, E.M.; Groll, M. The Mammalian Proteasome Activator PA28 Forms an Asymmetric A4β3 Complex. Structure 2017, 25, 1473–1480.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Krutchinsky, A.; Endicott, S.; Realini, C.; Rechsteiner, M.; Standing, K.G. Proteasome Activator 11S REG or PA28: Recombinant REG Alpha/REG Beta Hetero-Oligomers Are Heptamers. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5651–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Makhija, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Muralidharan, M.; Huang, B.; Cheng, Y. Structural Insights into the Human PA28-20S Proteasome Enabled by Efficient Tagging and Purification of Endogenous Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207200119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Yin, Y.; Peng, C.; Ding, Z.; Cong, Y. Cryo-EM of Mammalian PA28αβ-iCP Immunoproteasome Reveals a Distinct Mechanism of Proteasome Activation by PA28αβ. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, S.; Chen, W.E.; Magnusson, R.P. Properties of the Nuclear Proteasome Activator PA28γ (REGγ). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 383, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, X.; Ortega, J.; Nazif, T.; Joss, L.; Bogyo, M.; Steven, A.C.; Rechsteiner, M. Lysine 188 Substitutions Convert the Pattern of Proteasome Activation by REGγ to That of REGs α and β. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.A.; Smith, D.M. Proteasome Activator 28γ (PA28γ) Allosterically Activates Trypsin-like Proteolysis by Binding to the α-Ring of the 20S Proteasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-D.; Hao, J.; Shen, C.-H.; Deng, X.-M.; Yun, C.-H. Atomic Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of Human Proteasome Activator PA28γ. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, P. PA28αβ: The Enigmatic Magic Ring of the Proteasome? Biomolecules 2014, 4, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, C.W.; Slaughter, C.A.; DeMartino, G.N. PA28 Activator Protein Forms Regulatory Caps on Proteasome Stacked Rings. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Clawson, A.; Realini, C.; Jensen, C.C.; Knowlton, J.R.; Hill, C.P.; Rechsteiner, M. Identification of an Activation Region in the Proteasome Activator REGα. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2807–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, X.; Joss, L.; Rechsteiner, M. The Proteasome Activator 11 S REG or PA28: Chimeras Implicate Carboxyl-Terminal Sequences in Oligomerization and Proteasome Binding but Not in the Activation of Specific Proteasome Catalytic Subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.P.; Willy, P.J.; Slaughter, C.A.; DeMartino, G.N. PA28, an Activator of the 20 S Proteasome, Is Inactivated by Proteolytic Modification at Its Carboxyl Terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 22514–22519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Mott, J.D.; von Kampen, J.; Pramanik, B.; Tanaka, K.; Slaughter, C.A.; DeMartino, G.N. A Model for the Quaternary Structure of the Proteasome Activator PA28*. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26410–26417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtmueller, B.M.; Hill, C.P. Proteasome Activators. Mol. Cell 2011, 41, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitby, F.G.; Masters, E.I.; Kramer, L.; Knowlton, J.R.; Yao, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Hill, C.P. Structural Basis for the Activation of 20S Proteasomes by 11S Regulators. Nature 2000, 408, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, J.; Stock, D.; Jap, B.; Zwickl, P.; Baumeister, W.; Huber, R. Crystal Structure of the 20S Proteasome from the Archaeon T. Acidophilum at 3.4 A Resolution. Science 1995, 268, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M.; Ditzel, L.; Löwe, J.; Stock, D.; Bochtler, M.; Bartunik, H.D.; Huber, R. Structure of 20S Proteasome from Yeast at 2.4 A Resolution. Nature 1997, 386, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, A.; Cascio, P.; Leggett, D.S.; Woo, K.M.; Goldberg, A.L.; Finley, D. The Axial Channel of the Proteasome Core Particle Is Gated by the Rpt2 ATPase and Controls Both Substrate Entry and Product Release. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M.; Bajorek, M.; Köhler, A.; Moroder, L.; Rubin, D.M.; Huber, R.; Glickman, M.H.; Finley, D. A Gated Channel into the Proteasome Core Particle. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesne, J.; Locard-Paulet, M.; Parra, J.; Zivković, D.; Menneteau, T.; Bousquet, M.-P.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Marcoux, J. Conformational Maps of Human 20S Proteasomes Reveal PA28- and Immuno-Dependent Inter-Ring Crosstalks. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschak, A.M.; Kay, L.E. Proteasome Allostery as a Population Shift between Interchanging Conformers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3454–E3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennella, E.; Huang, R.; Yu, Z.; Kay, L.E. Exploring Long-Range Cooperativity in the 20S Proteasome Core Particle from Thermoplasma Acidophilum Using Methyl-TROSY–Based NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5298–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, F.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Coffino, P.; Cheng, Y. Allosteric Coupling between α-Rings of the 20S Proteasome. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Salcedo-Tacuma, D.; Smith, D.M. Structure, Function, and Allosteric Regulation of the 20S Proteasome by the 11S/PA28 Family of Proteasome Activators. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, C.; Tanahashi, N.; Shimbara, N.; Hendil, K.B.; Tanaka, K. Tissue Distribution of Constitutive Proteasomes, Immunoproteasomes, and PA28 in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, T.; Shimada, K.; Shibata, M.; Hata, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Takasaki, Y.; Sato, C.; Takahashi, T.; Nishida, Y. Cloning and Nucleotide Sequence of cDNA for Ki Antigen, a Highly Conserved Nuclear Protein Detected with Sera from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 79, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, S.; Kawahara, H.; Tohma, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kasahara, M.; Nabeshima, Y.I.; Tanaka, K.; Chiba, T. Growth Retardation in Mice Lacking the Proteasome Activator PA28γ. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 38211–38215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, L.F.; Runnels, H.A.; Schell, T.D.; Cho, Y.; Gibbons, R.; Tevethia, S.S.; Deepe, G.S.; Monaco, J.J. Immune Defects in 28-kDa Proteasome Activator γ-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3948–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioce, M.; Boulon, S.; Matera, A.G.; Lamond, A.I. UV-Induced Fragmentation of Cajal Bodies. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonik-Nowak, B.; Menneteau, T.; Fesquet, D.; Baldin, V.; Bonne-Andrea, C.; Méchali, F.; Fabre, B.; Boisguerin, P.; De Rossi, S.; Henriquet, C.; et al. PIP30/FAM192A Is a Novel Regulator of the Nuclear Proteasome Activator PA28γ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6477–E6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldin, V.; Militello, M.; Thomas, Y.; Doucet, C.; Fic, W.; Boireau, S.; Jariel-Encontre, I.; Piechaczyk, M.; Bertrand, E.; Tazi, J.; et al. A Novel Role for PA28γ-Proteasome in Nuclear Speckle Organization and SR Protein Trafficking. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannini, L.; Lecis, D.; Buscemi, G.; Carlessi, L.; Gasparini, P.; Fontanella, E.; Lisanti, S.; Barton, L.; Delia, D. REGγ Proteasome Activator Is Involved in the Maintenance of Chromosomal Stability. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Barda, A.; Lerenthal, Y.; Davis, A.J.; Chung, Y.M.; Essers, J.; Shao, Z.; Van Vliet, N.; Chen, D.J.; Hu, M.C.T.; Kanaar, R.; et al. Involvement of the Nuclear Proteasome Activator PA28γ in the Cellular Response to DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4300–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Jia, C.; Zhang, S.; Fan, G.; Li, Y.; Shan, P.; Sun, L.; Xiao, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. The REGγ Proteasome Regulates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism through Inhibition of Autophagy. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Shen, S.; Wang, Q.; Clement, T.M.; Deskin, B.J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; et al. The REGγ-Proteasome Regulates Spermatogenesis Partially by P53-PLZF Signaling. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 13, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Haratake, K.; Miyahara, H.; Chiba, T. Proteasome Activators, PA28γ and PA200, Play Indispensable Roles in Male Fertility. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Zhou, L.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Meng, T.; Xue, Y.; Ma, X.; Shah, A.S.; et al. The Proteasome Activator REGγ Counteracts Immunoproteasome Expression and Autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulpicante, M.; Darrigrand, R.; Pierson, A.; Salgues, V.; Rouillon, M.; Gaudineau, B.; Khaled, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Bachi, A.; Cascio, P.; et al. Tumors Escape Immunosurveillance by Overexpressing the Proteasome Activator PSME3. OncoImmunology 2020, 9, 1761205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, P. PA28γ, the Ring That Makes Tumors Invisible to the Immune System? Biochimie 2024, 226, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, B.; Lambour, T.; Garrigues, L.; Ducoux-Petit, M.; Amalric, F.; Monsarrat, B.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Bousquet-Dubouch, M.P. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Dynamics of Proteasome Complexes Composition and Stoichiometry in a Wide Range of Human Cell Lines. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3027–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Bai, H.; Sun, S.; Xin, C.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. PA28γ, an Accomplice to Malignant Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, S. Role of Oncogenic REGγ in Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funderburk, K.E.; Kang, J.; Li, H.J. Regulation of Life & Death by REGγ. Cells 2022, 11, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechsteiner, M.; Realini, C.; Ustrell, V. The Proteasome Activator 11 S REG (PA28) and Class I Antigen Presentation. Biochem. J. 2000, 345, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Powell, S.R.; Wang, X. Enhancement of Proteasome Function by PA28α Overexpression Protects against Oxidative Stress. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A.M.; Davies, K.J.A. Differential Roles of Proteasome and Immunoproteasome Regulators Pa28αβ, Pa28γ and Pa200 in the Degradation of Oxidized Proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 523, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, A.M.; Koop, A.L.; Teoh, C.Y.; Ermak, G.; Grune, T.; Davies, K.J.A. The Immunoproteasome, the 20S Proteasome and the PA28αβ Proteasome Regulator Are Oxidative-Stress-Adaptive Proteolytic Complexes. Biochem. J. 2010, 432, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelöf, J.; Wiseman, J.; Zetterberg, M.; Hernebring, M. PA28α Overexpressing Female Mice Maintain Exploratory Behavior and Capacity to Prevent Protein Aggregation in Hippocampus as They Age. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, A.L.; Cascio, P.; Saric, T.; Rock, K.L. The Importance of the Proteasome and Subsequent Proteolytic Steps in the Generation of Antigenic Peptides. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macagno, A.; Gilliet, M.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Nestle, F.O.; Groettrup, M. Dendritic Cells Up-Regulate Immunoproteasomes and the Proteasome Regulator PA28 during Maturation. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 4037–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossendorp, F.; Fu, N.; Camps, M.; Granucci, F.; Gobin, S.J.P.; van den Elsen, P.J.; Schuurhuis, D.; Adema, G.J.; Lipford, G.B.; Chiba, T.; et al. Differential Expression Regulation of the Alpha and Beta Subunits of the PA28 Proteasome Activator in Mature Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7815–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Lutshumba, J.; Chen, K.C.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Sa, Q.; Ochiai, E. IFN-γ Production by Brain-Resident Cells Activates Cerebral mRNA Expression of a Wide Spectrum of Molecules Critical for Both Innate and T Cell-Mediated Protective Immunity to Control Reactivation of Chronic Infection with Toxoplasma Gondii. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1110508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nil, A.; Firat, E.; Sobek, V.; Eichmann, K.; Niedermann, G. Expression of Housekeeping and Immunoproteasome Subunit Genes Is Differentially Regulated in Positively and Negatively Selecting Thymic Stroma Subsets. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, T.; Murata, S.; Shimbara, N.; Tanaka, N.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yui, K.; Udono, H. Two Distinct Pathways Mediated by PA28 and Hsp90 in Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Antigen Processing. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sijts, A.J.A.M.; Song, M.; Janek, K.; Nussbaum, A.K.; Kral, S.; Schirle, M.; Stevanovic, S.; Paschen, A.; Schild, H.; et al. Expression of the Proteasome Activator PA28 Rescues the Presentation of a Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope on Melanoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar]
- van Hall, T.; Sijts, A.; Camps, M.; Offringa, R.; Melief, C.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Ossendorp, F. Differential Influence on Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope Presentation by Controlled Expression of Either Proteasome Immunosubunits or PA28. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, S.; Udono, H.; Tanahashi, N.; Hamada, N.; Watanabe, K.; Adachi, K.; Yamano, T.; Yui, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Kasahara, M.; et al. Immunoproteasome Assembly and Antigen Presentation in Mice Lacking Both PA28alpha and PA28beta. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5898–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, N.; van Helden, M.J.G.; Textoris-Taube, K.; Chiba, T.; Topham, D.J.; Kloetzel, P.-M.; Zaiss, D.M.W.; Sijts, A.J.A.M. PA28 and the Proteasome Immunosubunits Play a Central and Independent Role in the Production of MHC Class I-Binding Peptides in Vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groettrup, M.; Soza, A.; Eggers, M.; Kuehn, L.; Dick, T.P.; Schild, H.; Rammensee, H.G.; Koszinowski, U.H.; Kloetzel, P.M. A Role for the Proteasome Regulator PA28alpha in Antigen Presentation. Nature 1996, 381, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.; van Den Broek, M.; Kostka, S.; Kraft, R.; Soza, A.; Schmidtke, G.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Groettrup, M. Overexpression of the Proteasome Subunits LMP2, LMP7, and MECL-1, but Not PA28 Alpha/Beta, Enhances the Presentation of an Immunodominant Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus T Cell Epitope. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijts, A.; Sun, Y.; Janek, K.; Kral, S.; Paschen, A.; Schadendorf, D.; Kloetzel, P.-M. The Role of the Proteasome Activator PA28 in MHC Class I Antigen Processing. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respondek, D.; Voss, M.; Kühlewindt, I.; Klingel, K.; Krüger, E.; Beling, A. PA28 Modulates Antigen Processing and Viral Replication during Coxsackievirus B3 Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, T.; Sugahara, H.; Mizukami, S.; Murata, S.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yui, K.; Udono, H. Allele-Selective Effect of PA28 in MHC Class I Antigen Processing. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, B. Molecular Mechanisms of MHC Class I Abnormalities and APM Components in Human Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoli, M.; Ferrone, S. HLA Antigen Changes in Malignant Cells: Epigenetic Mechanisms and Biologic Significance. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5869–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Wargo, J.A.; Ribas, A. Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincola, F.M.; Jaffee, E.M.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ferrone, S. Escape of Human Solid Tumors from T-Cell Recognition: Molecular Mechanisms and Functional Significance. Adv. Immunol. 2000, 74, 181–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, U.; Momburg, F.; Pilch, H.; Huber, C.; Maeurer, M.J.; Seliger, B. Deficient Expression of Components of the MHC Class I Antigen Processing Machinery in Human Cervical Carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerruti, F.; Martano, M.; Petterino, C.; Bollo, E.; Morello, E.; Bruno, R.; Buracco, P.; Cascio, P. Enhanced Expression of Interferon-Gamma-Induced Antigen-Processing Machinery Components in a Spontaneously Occurring Cancer. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirina, L.V.; Kondakova, I.V.; Koval’, V.D.; Kolomiets, L.A.; Chernyshova, A.L.; Choinzonov, E.L.; Sharova, N.P. Proteasome Activity and Their Subunit Composition in Endometrial Cancer Tissue: Correlations with Clinical Morphological Parameters. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 153, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Horiuchi, S.; Oki, M.; Adachi, Y.; Imai, K.; Shinomura, Y. Characterization of the Immune Escape Phenotype of Human Gastric Cancers with and without High-Frequency Microsatellite Instability. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, D.; Martínez-Torrecuadrada, J.; Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Alvarez-Cienfuegos, A.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; Fernández-Periáñez, R.; Martín, M.T.; Molina-Privado, I.; Ruppen-Cañás, I.; et al. Proteasome Activator Complex PA28 Identified as an Accessible Target in Prostate Cancer by in Vivo Selection of Human Antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13791–13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhov, P.A.; Kulikov, A.M.; Karpova, Y.D.; Rodoman, G.V.; Sumedi, I.R.; Goncharov, A.L.; Razbirin, D.V.; Gorelova, V.S.; Sharova, N.P.; Astakhova, T.M. Proteasomes in Patient Rectal Cancer and Different Intestine Locations: Where Does Proteasome Pool Change? Cancers 2021, 13, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qi, B.; Shen, C.; Xie, W. Downregulation of HLA Class I Molecules in Primary Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Cell Lines. Arch. Med. Res. 2009, 40, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Ikeda, M.; Akatsuka, T. High Expression of HLA-A2 on an Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with down-Regulated Transporter for Antigen Presentation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, B.; Wollscheid, U.; Momburg, F.; Blankenstein, T.; Huber, C. Characterization of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Deficiencies in B16 Melanoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vertegaal, A.C.O.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Houweling, A.; Verlaan, M.; van der Eb, A.J.; Zantema, A. Differential Expression of Tapasin and Immunoproteasome Subunits in Adenovirus Type 5- versus Type 12-Transformed Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, T.; Tatsumi, T.; Takehara, T.; Kanto, T.; Kuzushita, N.; Sugimoto, Y.; Jinushi, M.; Kasahara, A.; Sasaki, Y.; Hori, M.; et al. Impaired Expression of Proteasome Subunits and Human Leukocyte Antigens Class I in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliger, B.; Wollscheid, U.; Momburg, F.; Blankenstein, T.; Huber, C. Coordinate Downregulation of Multiple MHC Class I Antigen Processing Genes in Chemical-Induced Murine Tumor Cell Lines of Distinct Origin. Tissue Antigens 2000, 56, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, A.; France, J.; Sy, M.S.; Harding, C.V. Down-Regulation of the Transporter for Antigen Presentation, Proteasome Subunits, and Class I Major Histocompatibility Complex in Tumor Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3660–3667. [Google Scholar]
- Delp, K.; Momburg, F.; Hilmes, C.; Huber, C.; Seliger, B. Functional Deficiencies of Components of the MHC Class I Antigen Pathway in Human Tumors of Epithelial Origin. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000, 25 (Suppl. S2), S88–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisan, T.; Levitsky, V.; Masucci, M.G. Variations in Proteasome Subunit Composition and Enzymatic Activity in B-Lymphoma Lines and Normal B Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 88, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, G.M.; Kaur, P.; Neumann, W.; Asea, E.E.; Bausero, M.A.; Multhoff, G.; Asea, A. Silencing Hsp25/Hsp27 Gene Expression Augments Proteasome Activity and Increases CD8+ T-Cell-Mediated Tumor Killing and Memory Responses. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.; Lehr, H.-A.; Drexler, I.; Sutter, G.; Hengstler, J.; Wollscheid, U.; Seliger, B. HER-2/Neu-Mediated Regulation of Components of the MHC Class I Antigen-Processing Pathway. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Hisaeda, H.; Shen, J.; Tu, L.; Imai, T.; Chou, B.; Murata, S.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Fehling, H.J.; et al. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Plays Essential Roles in Presenting an 8-Mer CTL Epitope Expressed in APC to Corresponding CD8+ T Cells. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Obata, C.; Hisaeda, H.; Ishii, K.; Murata, S.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Li, Y.; Furue, M.; Chou, B.; et al. A Novel DNA Vaccine Based on Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway Targeting ‘Self’-Antigens Expressed in Melanoma/Melanocyte. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ishii, K.; Hisaeda, H.; Murata, S.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Li, Y.; Obata, C.; Furue, M.; Himeno, K. Ubiquitin-fusion Degradation Pathway Plays an Indispensable Role in Naked DNA Vaccination with a Chimeric Gene Encoding a Syngeneic Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope of Melanocyte and Green Fluorescent Protein. Immunology 2004, 112, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, C.; Zhang, M.; Moroi, Y.; Hisaeda, H.; Tanaka, K.; Murata, S.; Furue, M.; Himeno, K. Formalin-Fixed Tumor Cells Effectively Induce Antitumor Immunity Both in Prophylactic and Therapeutic Conditions. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2004, 34, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lora, A.; Martinez, M.; Algarra, I.; Gaforio, J.J.; Garrido, F. MHC Class I-Deficient Metastatic Tumor Variants Immunoselected by T Lymphocytes Originate from the Coordinated Downregulation of APM Components. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuckelkorn, U.; Ferreira, E.A.; Drung, I.; Liewer, U.; Kloetzel, P.-M.; Theobald, M. The Effect of the Interferon-Gamma-Inducible Processing Machinery on the Generation of a Naturally Tumor-Associated Human Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope within a Wild-Type and Mutant P53 Sequence Context. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.P.; Ruppert, T.; Groettrup, M.; Kloetzel, P.M.; Kuehn, L.; Koszinowski, U.H.; Stevanović, S.; Schild, H.; Rammensee, H.G. Coordinated Dual Cleavages Induced by the Proteasome Regulator PA28 Lead to Dominant MHC Ligands. Cell 1996, 86, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Ebstein, F.; Bürger, E.; Textoris-Taube, K.; Gorny, X.; Urban, S.; Zhao, F.; Dannenberg, T.; Sucker, A.; Keller, C.; et al. The Proteasome Immunosubunits, PA28 and ER-Aminopeptidase 1 Protect Melanoma Cells from Efficient MART-126-35 -Specific T-Cell Recognition. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 3257–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, S.; Lévy, F.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Brasseur, F.; Probst-Kepper, M.; Peitrequin, A.L.; Monsarrat, B.; Van Velthoven, R.; Cerottini, J.C.; Boon, T.; et al. Processing of Some Antigens by the Standard Proteasome but Not by the Immunoproteasome Results in Poor Presentation by Dendritic Cells. Immunity 2000, 12, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.S.; Ignatz-Hoover, J.J.; Guo, C.; Mosley, A.L.; Malek, E.; Federov, Y.; Adams, D.J.; Driscoll, J.J. Immunoproteasome Activation Expands the MHC Class I Immunopeptidome, Unmasks Neoantigens, and Enhances T-Cell Anti-Myeloma Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024, 23, 1743–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inholz, K.; Bader, U.; Mundt, S.; Basler, M. The Significant Role of PA28αβ in CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Graft Rejection Contrasts with Its Negligible Impact on the Generation of MHC-I Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Overexpression of Proteasomal Activator PA28α Serves as a Prognostic Factor in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Barwick, B.G.; Shanmugam, M.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Kaufman, J.; Nooka, A.; Gupta, V.; Dhodapkar, M.; Boise, L.H.; Lonial, S. Downregulation of PA28α Induces Proteasome Remodeling and Results in Resistance to Proteasome Inhibitors in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Horak, K.M.; Su, H.; Sanbe, A.; Robbins, J.; Wang, X. Enhancement of Proteasomal Function Protects against Cardiac Proteinopathy and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3689–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanova, E.S.; Finkelstein, S.; Li, J.; Travis, A.M.; Hao, Y.; Klingeborn, M.; Skiba, N.P.; Deshaies, R.J.; Arshavsky, V.Y. Increased Proteasomal Activity Supports Photoreceptor Survival in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, W.; Yue, G.; Tang, Y.; Kim, I.-M.; Weintraub, N.L.; Wang, X.; Su, H. Cardiac Proteasome Functional Insufficiency Plays a Pathogenic Role in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2017, 102, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A.M.; Linder, R.A.; Zhang, H.; Forman, H.J.; Davies, K.J.A. Nrf2-Dependent Induction of Proteasome and Pa28αβ Regulator Are Required for Adaptation to Oxidative Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10021–10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, V.; Zhao, M.; Reddy, S.; Fajardo, G.; Wang, X.; Dewey, S.; Gomes, A.V.; Bernstein, D. Altered Ubiquitin-Proteasome Signaling in Right Ventricular Hypertrophy and Failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H551–H562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khodor, B.F.; Kholodilov, N.G.; Yarygina, O.; Burke, R.E. The Expression of mRNAs for the Proteasome Complex Is Developmentally Regulated in the Rat Mesencephalon. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2001, 129, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Lin, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, X. Potential Roles for PA28beta in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Development and Diagnosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.-L.; Huang, Q.-L.; Zhou, F.; Huang, Q.-J.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lin, X. PA28β Regulates Cell Invasion of Gastric Cancer via Modulating the Expression of Chloride Intracellular Channel 1. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Xu, L.; Fang, W.-M.; Han, J.-Y.; Wang, K.; Zhu, K.-S. Identification of PA28β as a Potential Novel Biomarker in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317719780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Dai, X.; Gong, K.; Song, K.; Tai, F.; Shi, J. PA28α/β Promote Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis via Down-Regulation of CDK15. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Qu, L.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, Y.; Meng, L.; Jin, H.; Shou, C. N-α-Acetyltransferase 10 Protein Is a Negative Regulator of 28S Proteasome through Interaction with PA28β. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, L.; Dahlmann, B. Proteasome Activator PA28 and Its Interaction with 20 S Proteasomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 329, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernebring, M.; Fredriksson, Å.; Liljevald, M.; Cvijovic, M.; Norrman, K.; Wiseman, J.; Semb, H.; Nyström, T. Removal of Damaged Proteins during ES Cell Fate Specification Requires the Proteasome Activator PA28. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, P.; Goldberg, A.L. Preparation of Hybrid (19S-20S-PA28) Proteasome Complexes and Analysis of Peptides Generated during Protein Degradation. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 398, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, P.; Call, M.; Petre, B.M.; Walz, T.; Goldberg, A.L. Properties of the Hybrid Form of the 26S Proteasome Containing Both 19S and PA28 Complexes. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendil, K.B.; Khan, S.; Tanaka, K. Simultaneous Binding of PA28 and PA700 Activators to 20 S Proteasomes. Biochem. J. 1998, 332, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, N.; Murakami, Y.; Minami, Y.; Shimbara, N.; Hendil, K.B.; Tanaka, K. Hybrid Proteasomes. Induction by Interferon-γ and Contribution to ATP- Dependent Proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14336–14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Takai, S.; Osada, H.; Yamamoto, L.; Furukawa, M.; Gullans, S.R. Novel Function of the C-Terminal Region of the Hsp110 Family Member Osp94 in Unfolded Protein Refolding. J Cell Sci 2022, 135, jcs258542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Minami, M.; Tanahashi, N.; Tanaka, K.; Yahara, I. A Critical Role for the Proteasome Activator PA28 in the Hsp90-Dependent Protein Refolding. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9055–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Suzuki, M.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Minami, Y. The Proteasome Activator PA28 Functions in Collaboration with Hsp90 in Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PA28αβ | PA28γ | |
|---|---|---|
| Subunit stoichiometry | 3α4β or 4α3β | 7γ |
| Central channel diameter (top-base) | 20 Å–30 Å | 22 Å–32 Å |
| Homolog specific insert (i.e., loop between α-helices 1 and 2 that constitute the most divergent portion between α, β, and γ monomers) [58] | Shorter | Longer |
| Subcellular localization | Cytoplasmic and nuclear | Predominantly nuclear (not in nucleolus) |
| Constitutive expression | Lymphoid cells and immunological organs | Every organ (high levels in brain and spleen) |
| Effect of interferon-γ and other pro-inflammatory cytokines on protein levels | Up-regulation | None |
| Evolutionary distribution | Jawed vertebrates (no birds) [56] | Jawless and jawed vertebrates (orthologs in invertebrates and unicellular eukaryotes) |
| Effect on the enzymatic properties of the 20S proteasome | Stimulation of short peptides hydrolysis | Stimulation of peptides and unfolded proteins hydrolysis |
| Effect on sizes distribution of peptide products released by 20S | Reduced | Unaffected or only marginally affected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cascio, P. Not Just PA28γ: What We Know About the Role of PA28αβ in Carcinogenesis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060880
Cascio P. Not Just PA28γ: What We Know About the Role of PA28αβ in Carcinogenesis. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060880
Chicago/Turabian StyleCascio, Paolo. 2025. "Not Just PA28γ: What We Know About the Role of PA28αβ in Carcinogenesis" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060880
APA StyleCascio, P. (2025). Not Just PA28γ: What We Know About the Role of PA28αβ in Carcinogenesis. Biomolecules, 15(6), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060880






