Recreational Exercise and Inflammatory Patterns in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from a Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wrońska, K.; Hałasa, M.; Szczuko, M. The Role of the Immune System in the Course of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: The Current State of Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Ye, X.-P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, C.-F.; Li, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, R.-J.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Lymphocyte Infiltration and Thyrocyte Destruction Are Driven by Stromal and Immune Cell Components in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewegen, K.L.; Mooij, C.F.; van Trotsenburg, A.S.P. Persisting Symptoms in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease despite Normal Thyroid Hormone Levels: Does Thyroid Autoimmunity Play a Role? A Systematic Review. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razvi, S.; Mrabeti, S.; Luster, M. Managing Symptoms in Hypothyroid Patients on Adequate Levothyroxine: A Narrative Review. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R241–R250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.M.; Podell, D.N. Bone and Joint Manifestations of Hypothyroidism. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 24, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lin, C.-L.; Yeh, J.-H.; Kao, C.-H. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, and L-Thyroxine Treatment: A Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundus, H.; Khan, S.A.; Zaidi, S.; Chhabra, C.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, H. Effect of Long-Term Exercise-Based Interventions on Thyroid Function in Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2025, 92, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasson, C.L.; Sadhir, S.; Pontzer, H. Daily Physical Activity Is Negatively Associated with Thyroid Hormone Levels, Inflammation, and Immune System Markers among Men and Women in the NHANES Dataset. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsios, G.S.; Moe, R.H.; Kitas, G.D. Exercise and Inflammation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyh, C.; Krüger, K.; Strasser, B. Physical Activity and Diet Shape the Immune System during Aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, K.; Watad, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Lichtbroun, M.; Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y. Physical Activity and Autoimmune Diseases: Get Moving and Manage the Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Xiang, D.; Ji, X.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Y.; Nieman, D.C.; Chen, P. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Exercise on Autoimmune Diseases: A 20-Year Systematic Review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2024, 13, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brčić, L.; Barić, A.; Gračan, S.; Brekalo, M.; Kaličanin, D.; Gunjača, I.; Torlak Lovrić, V.; Tokić, S.; Radman, M.; Škrabić, V.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Suggests Novel Loci for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Kaličanin, D.; Barić, A.; Vuletić, M.; Gunjača, I.; Torlak Lovrić, V.; Škrabić, V.; Punda, A.; Boraska Perica, V. Vitamin D and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from CROHT Biobank. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.H.S.; Brabant, G.; Duntas, L.H.; Monzani, F.; Peeters, R.P.; Razvi, S.; Wemeau, J.-L. 2013 ETA Guideline: Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusić, Z.; Novosel, S.A.; Dabelić, N.; Punda, M.; Rončević, S.; Labar, Ž.; Lukinac, L.J.; Nöthig-Hus, D.; Staničić, A.; Kaić-Rak, A.; et al. Croatia Has Reached Iodine Sufficiency. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2003, 26, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Punda, A.; Brekalo, M.; Plosnić, M.; Barić, A.; Kaličanin, D.; Brčić, L.; Vuletić, M.; Gunjača, I.; Torlak Lovrić, V.; et al. Presence or Severity of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Does Not Influence Basal Calcitonin Levels: Observations from CROHT Biobank. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, L.; Nordberg, N.; Broberg, J.; Björkesten, J.; Assarsson, E.; Henriksson, S.; Grundberg, I.; Pettersson, E.; Westerberg, C.; Liljeroth, E.; et al. Proximity Extension Assay in Combination with Next-Generation Sequencing for High-Throughput Proteome-Wide Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.; Israeli, D.; Shoenfeld, Y. Exercise, Autoimmune Diseases and T-Regulatory Cells. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 149, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunner, B.E.M.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Eckstein, M.L.; Scherl, L.; Schierbauer, J.R.; Haupt, S.; Stumpf, C.; Reusch, L.; Moser, O. Myokines and Resistance Training: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutuli, D.; Decandia, D.; Giacovazzo, G.; Coccurello, R. Physical Exercise as Disease-Modifying Alternative against Alzheimer’s Disease: A Gut-Muscle-Brain Partnership. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Mei, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; He, Z.; Geffen, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Wan, R.; et al. Voluntary Exercise Sensitizes Cancer Immunotherapy via the Collagen Inhibition-Orchestrated Inflammatory Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modarresi Chahardehi, A.; Masoumi, S.A.; Bigdeloo, M.; Arsad, H.; Lim, V. The Effect of Exercise on Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis on the Modulation of Inflammation. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, S.L.; Van Phan, H.; Ye, C.J.; Lanata, C.; González, S.C.; Park, J.; Criswell, L.A.; Barbour, K.E.; Yazdany, J.; Dall’Era, M.; et al. Physical Inactivity Exacerbates Pathologic Inflammatory Signalling at the Single Cell Level in Patients with Systemic Lupus. eBioMedicine 2024, 110, 105432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minasian, V.; Nazari, M. The Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise/Physical Activity and Prolongation of the Honeymoon Phase in Patients. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Chronic Inflammation as an Immunological Abnormality and Effectiveness of Exercise. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chong, W. Interleukin-24 Immunobiology and Its Roles in Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, J.; Floege, J.; Ostendorf, T.; Ludwig, A. Key Metalloproteinase-Mediated Pathways in the Kidney. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoude, J.; Koh, Y. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Exercise and Obesity. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purroy, A.; Roncal, C.; Orbe, J.; Meilhac, O.; Belzunce, M.; Zalba, G.; Villa-Bellosta, R.; Andrés, V.; Parks, W.C.; Páramo, J.A.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-10 Deficiency Delays Atherosclerosis Progression and Plaque Calcification. Atherosclerosis 2018, 278, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilla, L.; Roncal, C.; Ibarrola, J.; Arrieta, V.; García-Peña, A.; Fernández-Celis, A.; Navarro, A.; Álvarez, V.; Gainza, A.; Orbe, J.; et al. A Role for MMP-10 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-10) in Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cui, C.; Lainscak, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, S. Type-Specific Dysregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in End-Stage Heart Failure Patients: Relationship between MMP-10 and LV Remodelling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clase, K.L.; Mitchell, P.J.; Ward, P.J.; Dorman, C.M.; Johnson, S.E.; Hannon, K. FGF5 Stimulates Expansion of Connective Tissue Fibroblasts and Inhibits Skeletal Muscle Development in the Limb. Dev. Dyn. 2000, 219, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Qi, S.; Si, D.; Man, Z.; Deng, S.; Liu, G.; et al. Metabolic Differences in MSTN and FGF5 Dual-Gene Edited Sheep Muscle Cells during Myogenesis. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, K.; Xu, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-S.; Zhang, J.-L.; Wu, S.-J.; Liu, Z.-M.; Yuan, Y.-M.; Guo, X.-F.; et al. A MSTNDel73C Mutation with FGF5 Knockout Sheep by CRISPR/Cas9 Promotes Skeletal Muscle Myofiber Hyperplasia. eLife 2024, 12, RP86827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Zong, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S. The Effects of Exercise on FGF21 in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.; Richardson, K.A.; Funderburk, L. Effect of Exercise on Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Healthy Males and Females. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0321738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Almeda-Valdés, P.; Meza-Arana, C.E.; Brito-Córdova, G.; Gómez-Pérez, F.J.; Mehta, R.; Oseguera-Moguel, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A. Exercise Increases Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallini, F.; Rimondi, E.; Secchiero, P. TRAIL and Osteoprotegerin: A Role in Endothelial Physiopathology? Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakareko, K.; Rydzewska-Rosołowska, A.; Zbroch, E.; Hryszko, T. TRAIL and Cardiovascular Disease—A Risk Factor or Risk Marker: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolo, G.; Secchiero, P.; De Giorgi, S.; Tisato, V.; Zauli, G. The Energy Balance Positively Regulates the Levels of Circulating TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand in Humans. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, C.; Kenny, H.; Ashley, D.T.; O’Sullivan, E.P.; Smith, D.; O’Gorman, D.J. The Effect of Exercise on Osteoprotegerin and TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Obese Patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşgüven, P.; Gündüz, Y.; Kılıç, M. Effects of Thyroid Autoimmunity on Early Atherosclerosis in Euthyroid Girls with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2016, 8, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.; Rabin, R.L.; Yannelli, J.R.; Koniaris, L.G.; Vanguri, P.; Farber, J.M. Human Mig Chemokine: Biochemical and Functional Characterization. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hosoyama, T.; Shigemizu, D.; Yasuoka, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Maeda, K.; Takemura, M.; Matsui, Y.; Arai, H.; Satake, S. Association between Circulating Levels of CXCL9 and CXCL10 and Physical Frailty in Older Adults. Gerontology 2024, 70, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.H.; Corr, M.; Patel, S.; Lui, L.-Y.; Cauley, J.A.; Evans, D.; Mau, T.; Lane, N.E. Chemokine CXCL9, a Marker of Inflammaging, Is Associated with Changes of Muscle Strength and Mortality in Older Men. Osteoporos. Int. 2024, 35, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Zhang, K.; Paul, K.C.; Zhou, J.; Bronstein, J.M.; Kusters, C.D.J.; Ritz, B.R. Physical Activity Affects DNA Methylation-Derived Inflammation Markers in a Community-Based Parkinson’s Disease Study. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2025, 46, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X. The Role of Chemokines in Obesity and Exercise-Induced Weight Loss. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Kumaki, S.; Ahdieh, M.; Bertles, J.; Tometsko, M.; Loomis, A.; Giri, J.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; et al. Functional Characterization of the Human Interleukin-15 Receptor αChain and Close Linkage of IL15RA and IL2RA Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29862–29869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.-H.; Shin, E.-C. IL-15 in T-Cell Responses and Immunopathogenesis. Immune Netw. 2024, 24, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duitman, E.H.; Orinska, Z.; Bulanova, E.; Paus, R.; Bulfone-Paus, S. How a Cytokine Is Chaperoned through the Secretory Pathway by Complexing with Its Own Receptor: Lessons from Interleukin-15 (IL-15)/IL-15 Receptor α. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 4851–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, S.; Figueras, M.; Almendro, V.; López-Soriano, F.J.; Argilés, J.M. Interleukin-15 Increases Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle. An Antidiabetogenic Effect of the Cytokine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ma, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, D. IL-15/SIL-15Rα Gene Transfer Induces Weight Loss and Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Obese Mice. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, M.; Maleki, A.H.; Symonds, M.E.; Sakhaei, M.H.; Rosenkranz, S.K.; Ehsanifar, M.; Korivi, M.; Liu, Y. Interleukin-15 Responses to Acute and Chronic Exercise in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1288537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emdad, L.; Bhoopathi, P.; Talukdar, S.; Pradhan, A.K.; Sarkar, D.; Wang, X.-Y.; Das, S.K.; Fisher, P.B. Recent Insights into Apoptosis and Toxic Autophagy: The Roles of MDA-7/IL-24, a Multidimensional Anti-Cancer Therapeutic. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 66, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, S.R.; Winkles, J.A. TWEAK, a Member of the TNF Superfamily, Is a Multifunctional Cytokine That Binds the TweakR/Fn14 Receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.N.; Wang, Y.C.; Lund, J.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Leal, J.A.; Wiley, S.R. TWEAK Induces Angiogenesis and Proliferation of Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8455–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, P.J.; Richards, C.M.; Brown, S.A.N.; Hanscom, H.N.; Buschman, J.; Thangada, S.; Hla, T.; Williams, M.S.; Winkles, J.A. TWEAK Is an Endothelial Cell Growth and Chemotactic Factor That Also Potentiates FGF-2 and VEGF-A Mitogenic Activity. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbauer, R.; Lichtenauer, M.; Paar, V.; Emich, M.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; Schukro, C.; Strametz-Juranek, J.; Sponder, M. Regular Training Increases STWEAK and Its Decoy Receptor SCD163-Does Training Trigger the STWEAK/SCD163-Axis to Induce an Anti-Inflammatory Effect? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Ogura, Y.; Mishra, V.; Shin, J.; Bhatnagar, S.; Hill, B.G.; Kumar, A. TWEAK Promotes Exercise Intolerance by Decreasing Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Phosphorylation Capacity. Skelet. Muscle 2013, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Ogura, Y.; Kumar, A. TWEAK/Fn14 Signaling Axis Mediates Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Metabolic Dysfunction. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sasaki, F.; Nakashima, T. RANKL Biology: Bone Metabolism, the Immune System, and Beyond. Inflamm. Regen. 2020, 40, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenuik, P.J. Osteoprotegerin and RANKL Regulate Bone Resorption, Density, Geometry and Strength. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, S.; Drury, J.; Fordham, J.N.; Datta, H.K.; Francis, R.M.; Tuck, S.P. Osteoprotegerin, RANKL and Bone Turnover in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 64, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y. The Association of Osteoprotegerin and RANKL with Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobeiha, M.; Moghadasian, M.H.; Amin, N.; Jafarnejad, S. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6910312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, E.A.; Wanderley, F.; Machado, L.; Sousa, F.; Viana, J.L.; Moreira-Gonçalves, D.; Moreira, P.; Mota, J.; Carvalho, J. Effects of Resistance and Aerobic Exercise on Physical Function, Bone Mineral Density, OPG and RANKL in Older Women. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.S.; Eri, R.; Lyons, A.B.; Grimm, M.C.; Korner, H. CC Chemokine Ligand 20 and Its Cognate Receptor CCR6 in Mucosal T Cell Immunology and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Odd Couple or Axis of Evil? Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-R.; Mabuchi, T.; Riutta, S.J.; Wu, X.; Peterson, F.C.; Volkman, B.F.; Hwang, S.T. The Chemokine, CCL20, and Its Receptor, CCR6, in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2023, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, N.; Meitei, H.T.; Sonar, S.A.; Sharma, P.K.; Mujeeb, V.R.; Srivastava, S.; Boppana, R.; Lal, G. CCR6 Signaling Inhibits Suppressor Function of Induced-Treg during Gut Inflammation. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 88, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.K.; Jensen, S.M.; Schjerling, P.; Mackey, A.L.; Andersen, J.L.; Kjaer, M. The Effect of Resistance Exercise upon Age-Related Systemic and Local Skeletal Muscle Inflammation. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 121, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.J.; So, W.Y. Effects of Resistance Exercise Intensity on Cytokine and Chemokine Gene Expression in Atopic Dermatitis Mouse Model. J. Mens. Health 2018, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Aenlle, K.K.; Curtis, K.M.; Roos, B.A.; Howard, G.A. Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Together Stimulate Human Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells toward the Osteogenic Phenotype by HGF-Induced up-Regulation of VDR. Bone 2012, 51, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Ma, G.; Yang, B. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Improves Bone Regeneration via the Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2-mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6045–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Bai, J.; Shi, C.; Shi, X.; Shan, H.; Zhou, X. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Overexpression Promotes Osteoclastogenesis and Exacerbates Bone Loss in CIA Mice. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 27, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.; Goto, Y.; Takaki, H.; Asaumi, Y.; Baba, T.; Miyazaki, S.; Nonogi, H. Exercise-Induced Hepatocyte Growth Factor Production in Patients after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Its Relationship to Exercise Capacity and Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, P.; Jansen, F.; Achtzehn, S.; Schmitz, T.; Bloch, W.; Mester, J.; Werner, N. Effects of High Intensity Training and High Volume Training on Endothelial Microparticles and Angiogenic Growth Factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Less Than an Hour | Between 1–2 h | Over 2 h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 2–3 times a week | 8 | 16 | 16 |
| Once a week | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| Occasionally | 0 | 0 | 0 |
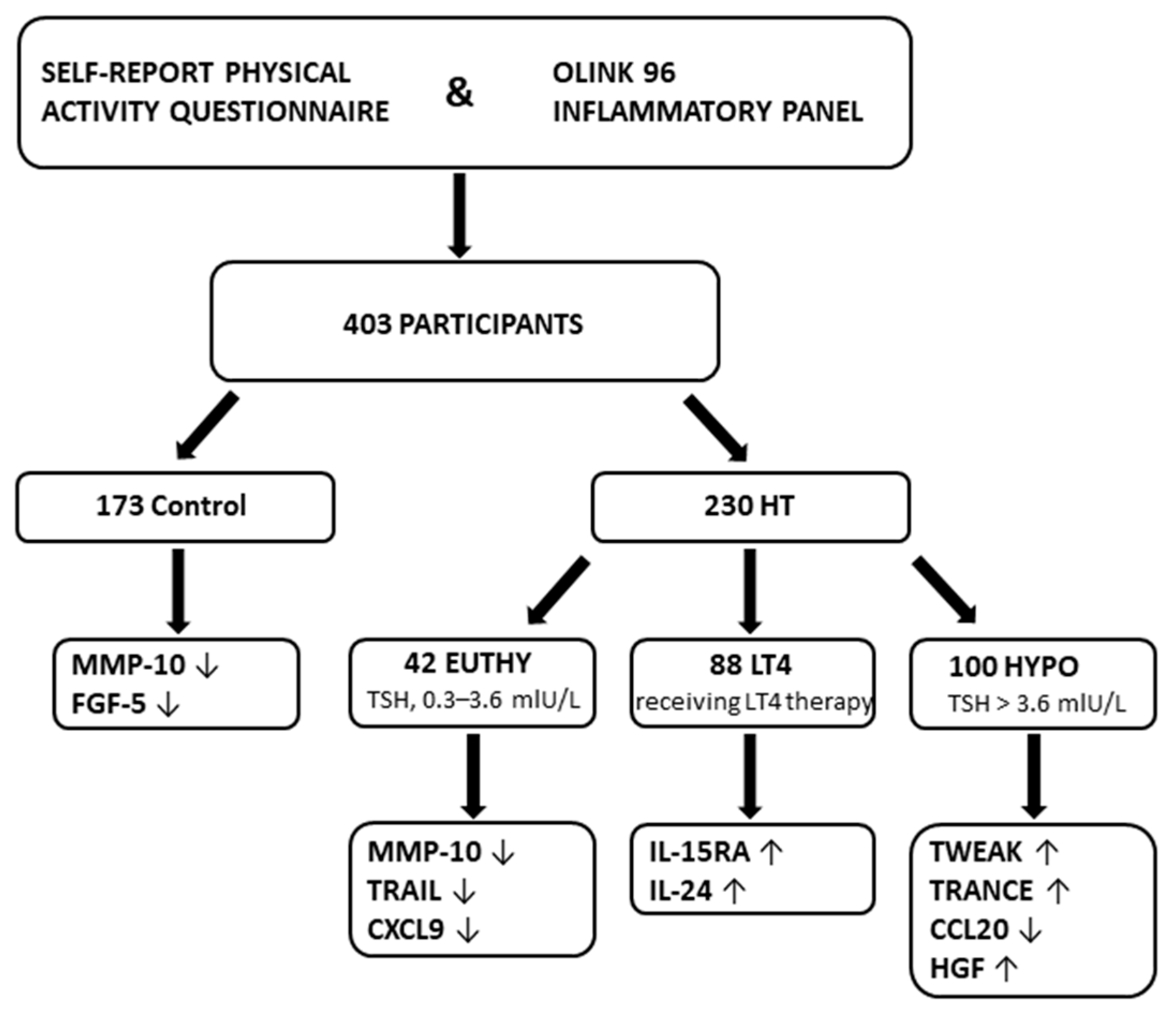
| Phenotype | Control | EUTHY | LT4 | HYPO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 173 | n = 42 | n = 88 | n = 100 | |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |
| Age, years | 39.24 (11.88) | 34.39 (12.67) | 40.48 (13.87) | 39.05 (13.22) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.58 (3.92) | 23.80 (3.80) | 24.21 (4.25) | 24.19 (4.22) |
| T3, nmol/L | 1.55 (0.22) | 1.62 (0.42) | 1.64 (0.32) | 1.51 (0.39) |
| T4, nmol/L | 102.92 (20.30) | 98.52 (22.92) | 114.47 (26.78) | 94.18 (27.05) |
| fT4, pmol/L | 12.89 (1.62) | 12.64 (1.53) | 13.09 (2.40) | 10.50 (2.50) |
| TSH, mIU/L | 1.61 (0.67) | 2.11 (0.96) | 4.89 (8.78) | 15.89 (24.93) |
| TgAb, IU/mL | 17.36 (17.46) | 730.52 (1177.64) | 575.48 (1126.23) | 618.80 (1048.81) |
| TPOAb, IU/mL | 5.73 (5.88) | 522.37 (483.10) | 546.01 (575.37) | 620.51 (692.42) |
| RE, hours/month | 5.80 (5.68) | 4.57 (6.34) | 5.45 (6.79) | 4.00 (6.15) |
| Assay | Estimate * | p-value | adjusted p-value |
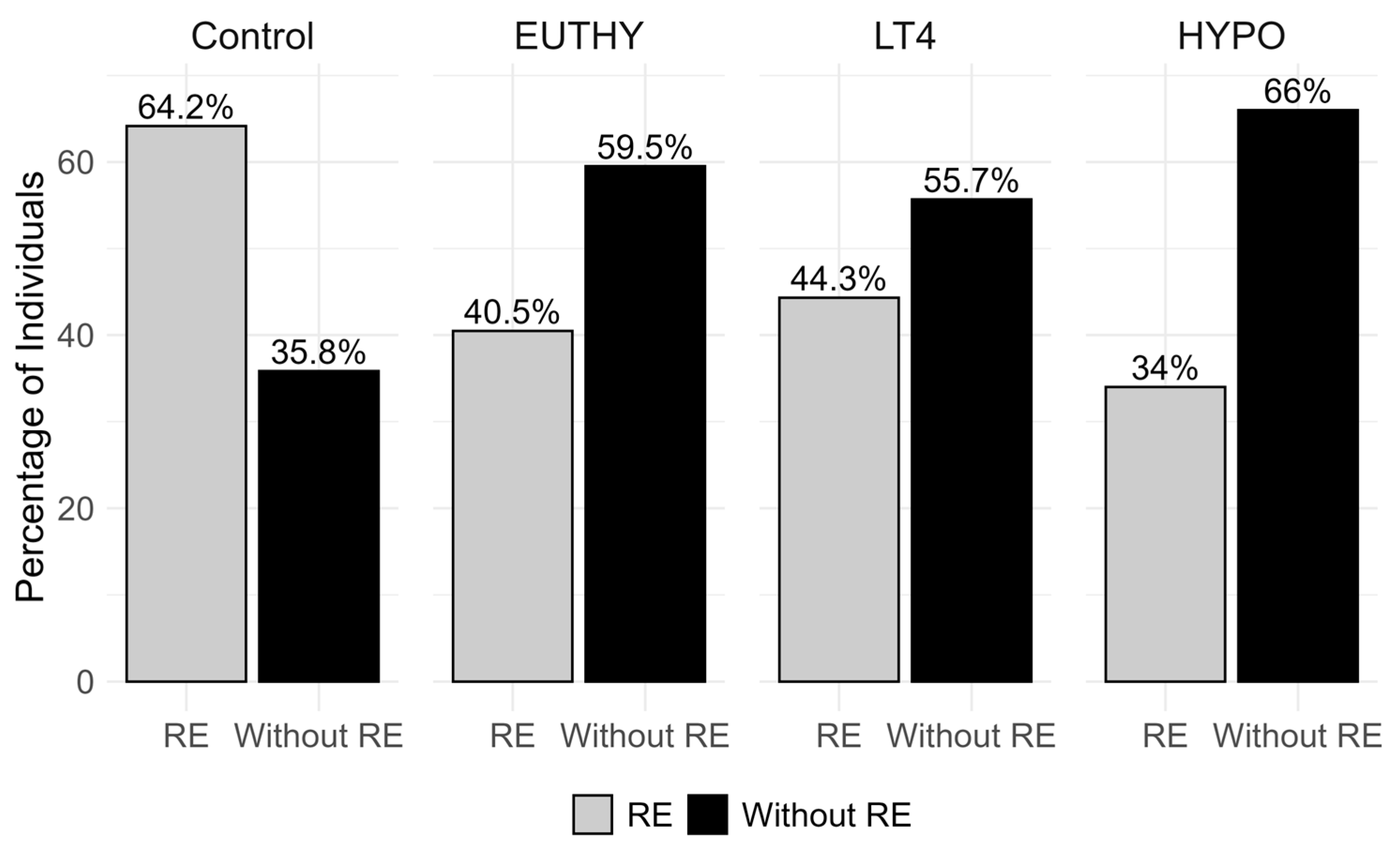
| Control (RE = 111, Without RE = 62) | |||
| MMP-10 | −0.4133 | 0.0026 | 0.0065 |
| FGF-5 | −0.0957 | 0.0058 | 0.0292 |
| EUTHY (RE = 17, Without RE = 25) | |||
| MMP-10 | −0.5335 | 0.0070 | 0.0175 |
| TRAIL | −0.2298 | 0.0150 | 0.0375 |
| CXCL9 | −0.4858 | 0.0165 | 0.0412 |
| LT4 (RE = 39, Without RE = 49) | |||
| IL-15RA | 0.1958 | 0.0042 | 0.0126 |
| IL-24 | 0.4020 | 0.0098 | 0.0163 |
| HYPO (RE = 34, Without RE = 66) | |||
| TWEAK | 0.2526 | 0.0019 | 0.0047 |
| TRANCE | 0.3096 | 0.0272 | 0.0340 |
| CCL20 | −0.4781 | 0.0218 | 0.0364 |
| HGF | 0.1936 | 0.0275 | 0.0459 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuletić, M.; Žnidar, V.; Barić Žižić, A.; Sladić, S.; Kaličanin, D.; Torlak Lovrić, V.; Cvek, M.; Punda, A.; Boraska Perica, V. Recreational Exercise and Inflammatory Patterns in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from a Cross-Sectional Study. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111510
Vuletić M, Žnidar V, Barić Žižić A, Sladić S, Kaličanin D, Torlak Lovrić V, Cvek M, Punda A, Boraska Perica V. Recreational Exercise and Inflammatory Patterns in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from a Cross-Sectional Study. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111510
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuletić, Marko, Vanna Žnidar, Ana Barić Žižić, Sanda Sladić, Dean Kaličanin, Vesela Torlak Lovrić, Maja Cvek, Ante Punda, and Vesna Boraska Perica. 2025. "Recreational Exercise and Inflammatory Patterns in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from a Cross-Sectional Study" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111510
APA StyleVuletić, M., Žnidar, V., Barić Žižić, A., Sladić, S., Kaličanin, D., Torlak Lovrić, V., Cvek, M., Punda, A., & Boraska Perica, V. (2025). Recreational Exercise and Inflammatory Patterns in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Observations from a Cross-Sectional Study. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111510






