cPLA2α Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. PBMC Isolation and Treatment
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay Detection of Eicosanoids
2.4. Culture of HaCaT Keratinocytes
2.4.1. Maintenance
2.4.2. Eicosanoid Release
2.5. [3H]-Arachidonic Acid Release Assay
2.6. Resazurin Assay
2.7. High Throughput Microscopy Assay for Population Analysis of Cell Cycle and Apoptosis
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.9. 3D Culture of HaCaT Keratinocytes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
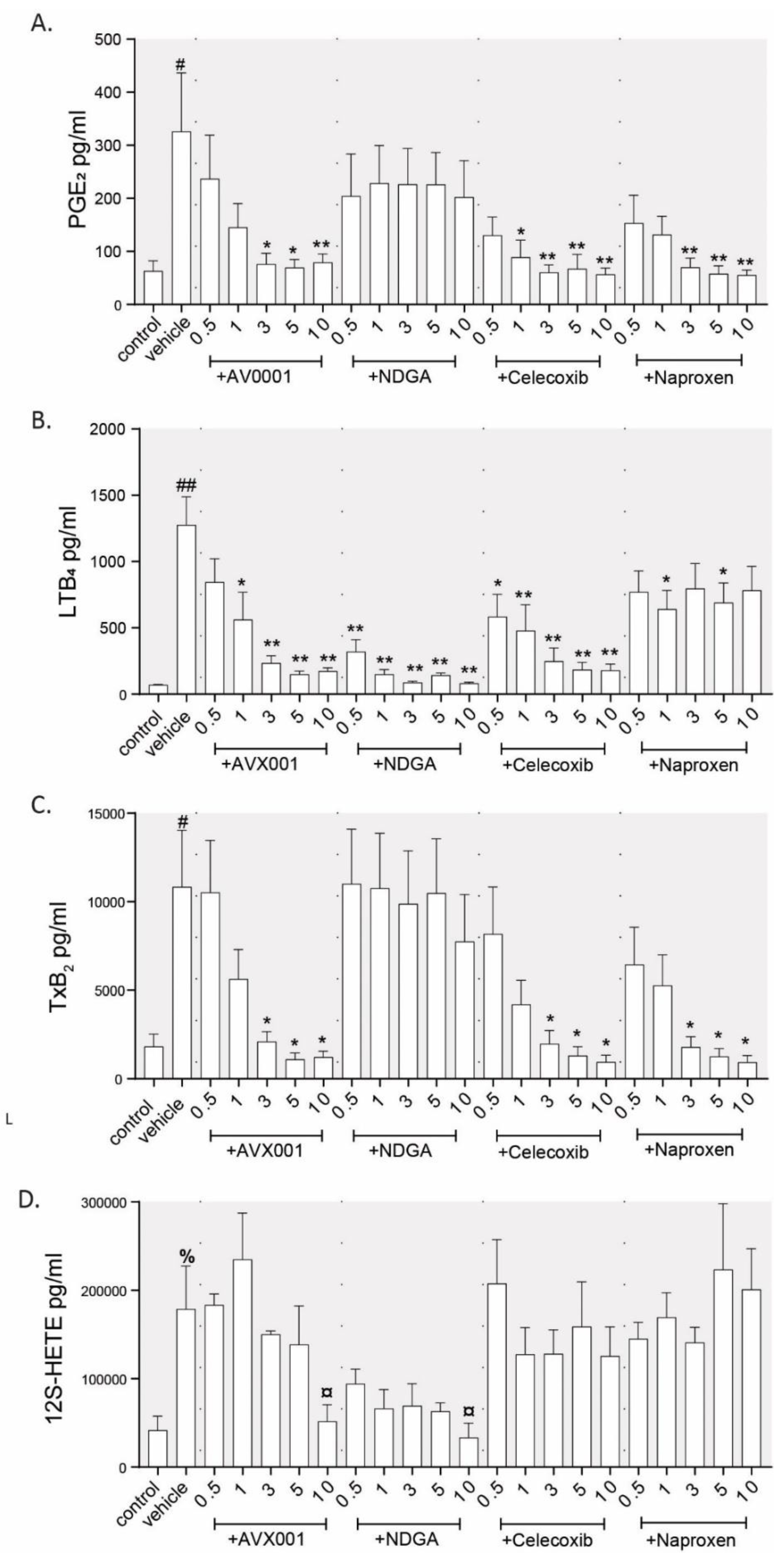
3.1. Inhibition of cPLA2α Using AVX001 Resulted in a Balanced Reduction of Eicosanoids
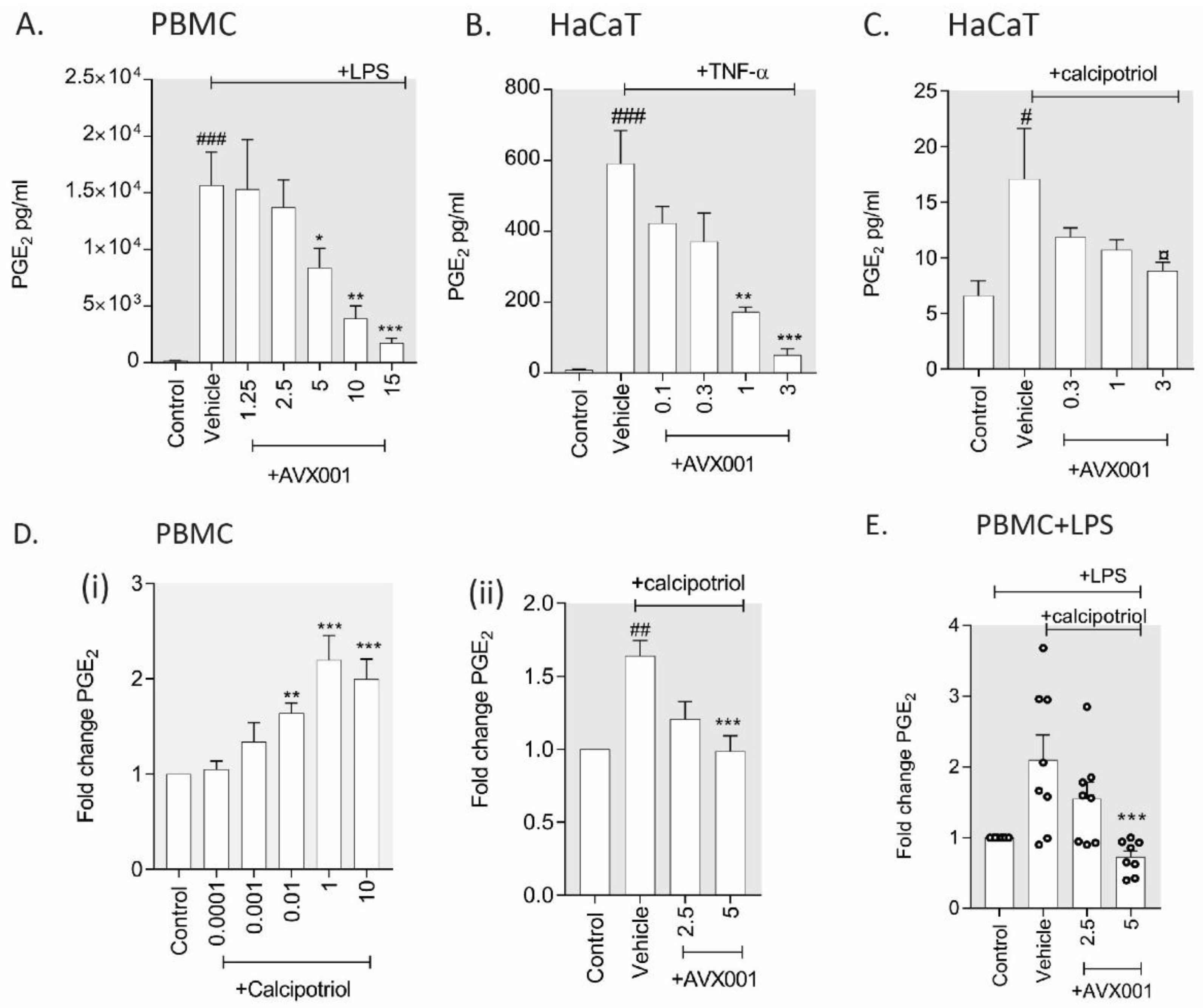
3.2. AVX001 Inhibited PGE2 Release in Response to Inflammatory Stimuli
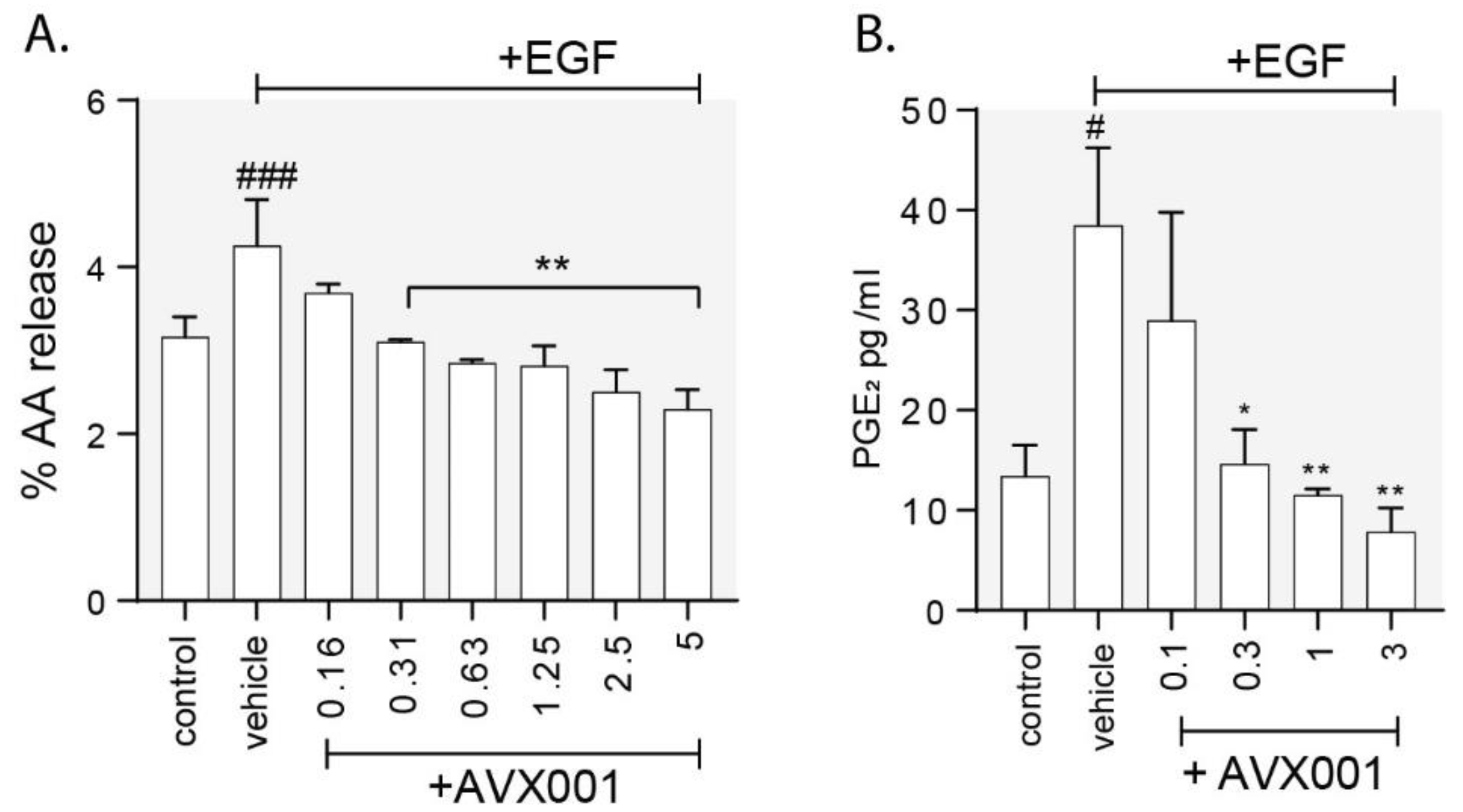
3.3. AVX001 Inhibited EGF-Stimulated Release of AA and PGE2.
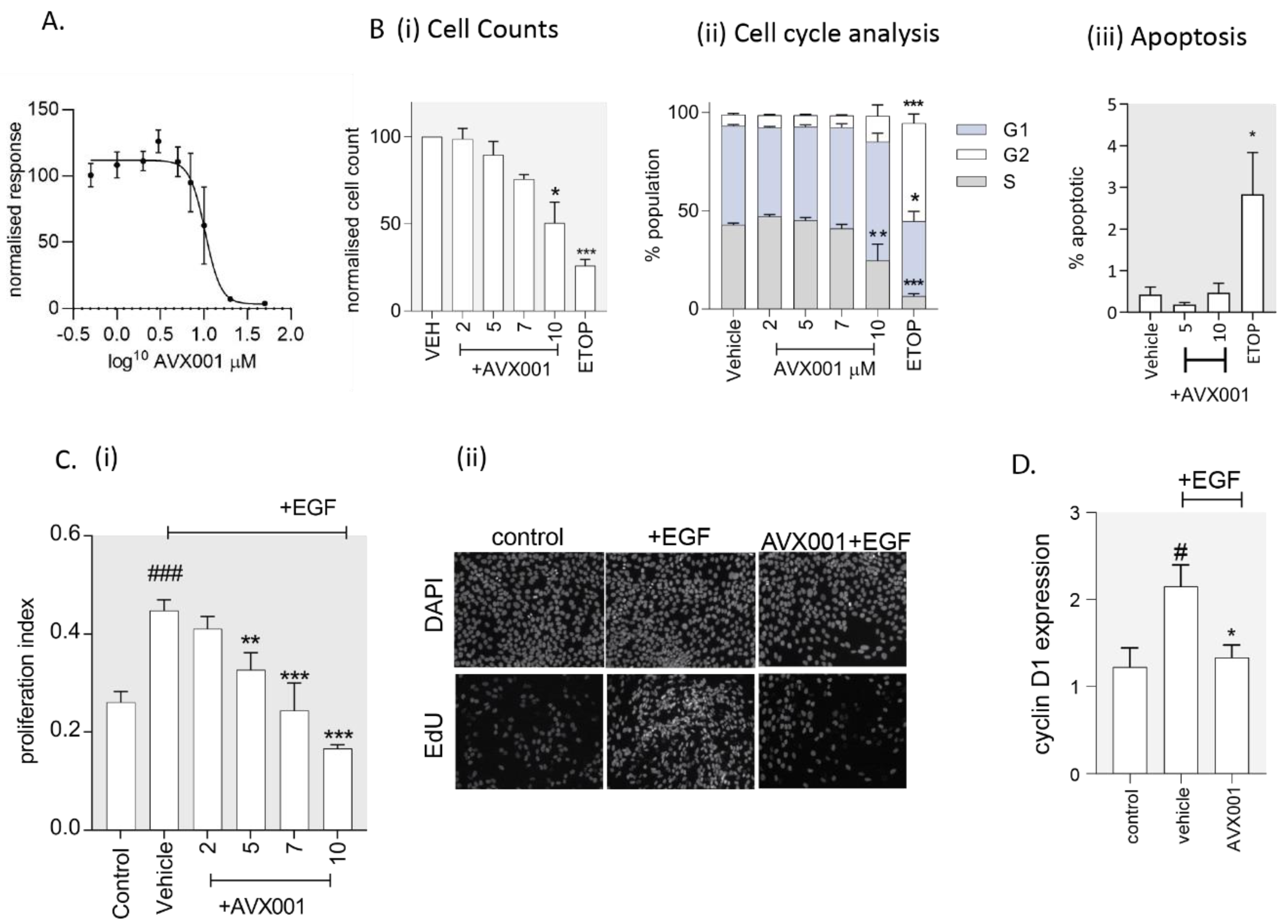
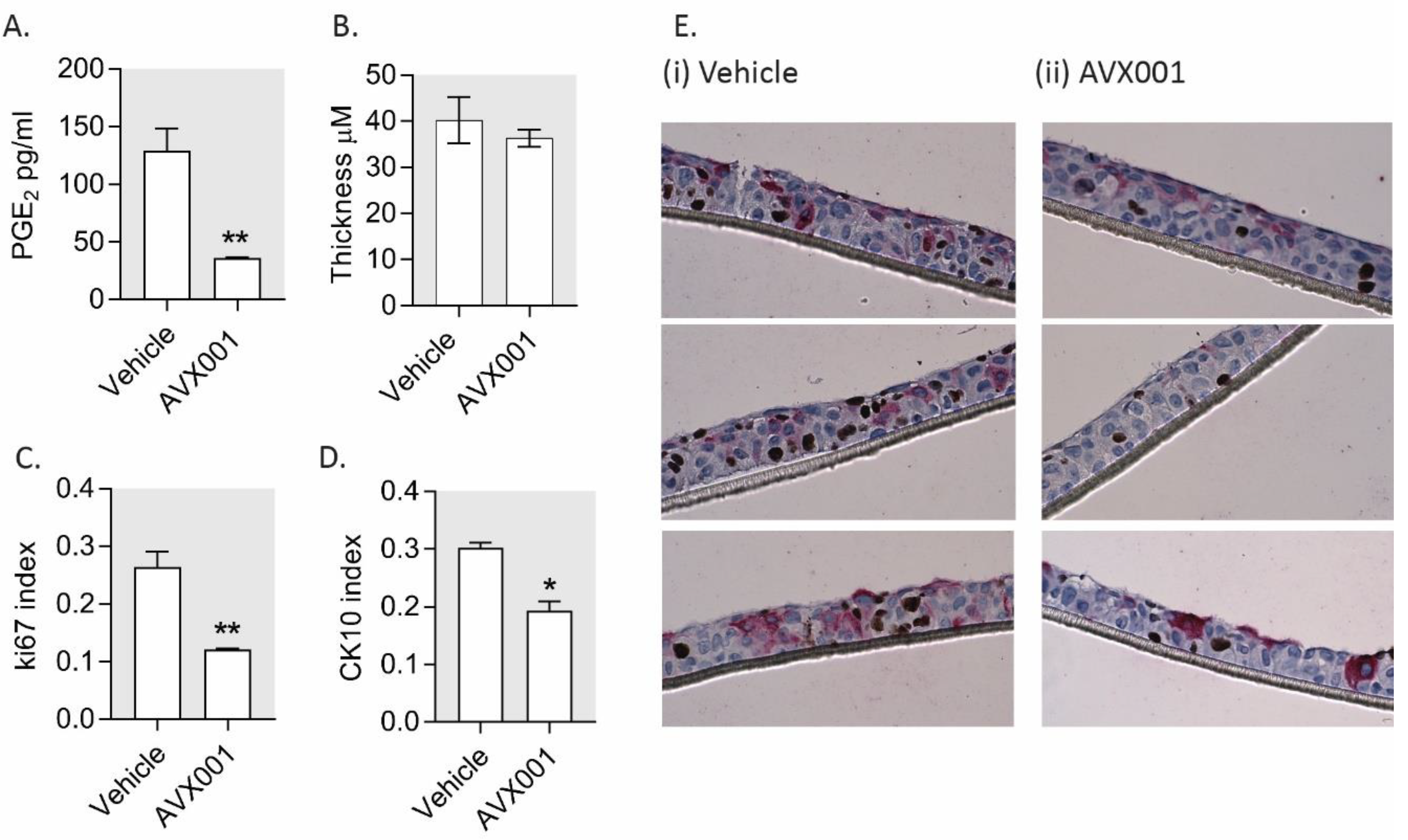
3.4. AVX001 Inhibited Keratinocyte Proliferation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Leslie, C.C. Cytosolic phospholipase A2: Physiological function and role in disease. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1386–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.D.; Lin, L.-L.; Kriz, R.W.; Ramesha, C.S.; Sultzman, L.A.; Lin, A.Y.; Milona, N.; Knopf, J.L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca2+-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell 1991, 65, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalkwijk, C.G.; Spaargaren, M.; Defize, L.H.; Verkleij, A.J.; van den Bosch, H.; Boonstra, J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces serine phosphorylation-dependent activation and calcium-dependent translocation of the cytosolic phospholipase A2. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievella, A.R.; Regier, M.K.; Smith, W.L.; Lin, L.L. Calcium-mediated translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 30749–30754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshak, A.; Sathe, G.A. Marshall, L. Suppression of monocyte 85-kDa phospholipase A2 by antisense and effects on endotoxin-induced prostaglandin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 25999–26005. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, B.L.; Fujishima, H.; Mejia, R.S.; Sapirstein, A.; Bonventre, J.V.; Austen, K.F.; Arm, J.P. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is essential for both the immediate and the delayed phases of eicosanoid generation in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 1999, 59, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raichel, L.; Berger, S.; Hadad, N.; Kachko, L.; Karter, M.; Szaingurten-Solodkin, I.; Williams, R.O.; Feldmann, M.; Levy, R. Reduction of cPLA2alpha overexpression: An efficient anti-inflammatory therapy for collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengarten, M.; Hadad, N.; Solomonov, Y.; Lamprecht, S.; Levy, R. Cytosolic phospholipase A2α has a crucial role in the pathogenesis of DSS-induced colitis in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 46, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uozumi, N.; Kume, K.; Nagase, T.; Nakatani, N.; Ishii, S.; Tashiro, F.; Komagata, Y.; Maki, K.; Ikuta, K.; Ouchi, Y.; et al. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in allergic response and parturition. Nature 1997, 390, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaviya, R.; Ansell, J.; Hall, L.; Fahmy, M.; Argentieri, R.L.; Olini, G.C.; Pereira, D.W.; Sur, R.; Cavender, D. Targeting cytosolic phospholipase A2 by arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone prevents chronic inflammation in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 539, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Huang, Z.; Taheri, M.R.; O’Leary, E.; Li, E.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Sapirstein, A. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nat. 1997, 390, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, A.; Kokotou, M.G.; Vasilakaki, S.; Kokotos, G. Small-molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics and as tools to understand the role of phospholipases A2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 941–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, C.A.; Patel, S.; Calzetta, L.; Campwala, H.; Havard, S.; Luscombe, E.; Clarke, P.A.; Peachell, P.T.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of an Inhibitor of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α for the Treatment of Asthma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 340, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, R.; Clark, S.; Bonventre, J.V.; Leong, J.M.; McCormick, B.A. Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α Promotes Pulmonary Inflammation and Systemic Disease during Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerherm, A.J.; Dennis, E.A.; Johansen, B. Cytosolic group IVA phospholipase A2 inhibitors, AVX001 and AVX002, ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. The Interplay Between Keratinocytes and Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Michibata, H.; Wakimoto, K.; Seishima, M.; Kawasaki, S.; Okubo, K.; Mitsui, H.; Torii, H.; Imai, Y. Cloning of a gene for a novel epithelium-specific cytosolic phospholipase A2, cPLA2delta, induced in psoriatic skin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12890–12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Sjursen, W.; Volden, G.; Johansen, B. Elevated expression of human nonpancreatic phospholipase A2 in psoriatic tissue. Inflammation 1994, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, M.; Knapp, B.; Garzorz, N.; Mattii, M.; Pullabhatla, V.; Pennino, D.; Andres, C.; Traidl-Hoffmann, P.-D.D.C.; Cavani, A.; Theis, F.J.; et al. Intraindividual genome expression analysis reveals a specific molecular signature of psoriasis and eczema. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 244ra90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstrom, S.; Hamberg, M.; Samuelsson, B.; Duell, E.A.; Stawiski, M.; Voorhees, J.J. Increased concentrations of nonesterified arachidonic acid, 12L-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid, prostaglandin E2, and prostaglandin F2alpha in epidermis of psoriasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 5130–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryborg, A.; Grøn, B.; Kragballe, K. Increased lysophosphatidylcholine content in lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 133, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.; Wong, E.; Mallet, A.; Olins, L.; Greaves, M. The analysis of arachidonic acid metabolites in normal, uninvolved and lesional psoriatic skin. Prostaglandins 1984, 28, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, T.; Simmet, T.; Peskar, B.A.; Ring, J. Skin levels of arachidonic acid-derived inflammatory mediators and histamine in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1986, 86, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, H.; Yanagida, K.; Kita, Y.; Abe, J.; Matsushima, K.; Nakamura, M.; Ishii, S.; Sato, S.; Shimizu, T. Interplay between CXCR2 and BLT1 Facilitates Neutrophil Infiltration and Resultant Keratinocyte Activation in a Murine Model of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueharaguchi, Y.; Honda, T.; Kusuba, N.; Hanakawa, S.; Adachi, A.; Sawada, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Kitoh, A.; Dainichi, T.; Egawa, G. Thromboxane A2 facilitates IL-17A production from Vgamma4(+) gammadelta T cells and promotes psoriatic dermatitis in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Honda, T.; Nakamizo, S.; Otsuka, A.; Ogawa, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kabashima, K. Resolvin E1 attenuates murine psoriatic dermatitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Aoki, T.; Thumkeo, D.; Siriwach, R.; Yao, C.; Narumiya, S. T cell-intrinsic prostaglandin E2-EP2/EP4 signaling is critical in pathogenic TH17 cell-driven inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 43, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaghan, P. A turbulent decade for NSAIDs: Update on current concepts of classification, epidemiology, comparative efficacy, and toxicity. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 32, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, L.; Baker, B.S. Triggering psoriasis: The role of infections and medications. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.K.; Del Rosso, J.Q. Drug-Provoked Psoriasis: Is It Drug Induced or Drug Aggravated? J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2010, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liaras, K.; Fesatidou, M.; Geronikaki, A. Thiazoles and Thiazolidinones as COX/LOX Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwiler, A.; Feuerherm, A.J.; Sakem, B.; Pastukhov, O.; Filipenko, I.; Nguyen, T.; Johansen, B. The omega3-polyunsaturated fatty acid derivatives AVX001 and AVX002 directly inhibit cytosolic phospholipase A(2) and suppress PGE(2) formation in mesangial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, S.; Habicht, A.; Damsbo, P.; Wilms, J.; Johansen, B.; Gniadecki, R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation first-in-man study (phase 0) to assess the safety and efficacy of topical cytosolic phospholipase A2 inhibitor, AVX001, in patients with mild to moderate plaque psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonsen, M.W.; Solhaug, A.; Johansen, B. Functional Coupling between Secretory and Cytosolic Phospholipase A2Modulates Tumor Necrosis Factor-α- and Interleukin-1β-induced NF-κB Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30527–30536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestvang, J.; Anthonsen, M.W.; Johansen, B. Role of secretory and cytosolic phospholipase A(2) enzymes in lysophosphatidylcholine-stimulated monocyte arachidonic acid release. FEBS Lett. 2003, 555, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjursen, W.; Brekke, O.-L.; Johansen, B. Secretory and cytosolic phospholipase A2regulate the long-term cytokine-induced eicosanoid production in human keratinocytes. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommesen, L.; Sjursen, W.; Gåsvik, K.; Hanssen, W.; Brekke, O.L.; Skattebøl, L.; Holmeide, A.K.; Espevik, T.; Johansen, B.; Laegreid, A. Selective inhibitors of cytosolic or secretory phospholipase A2 block TNF-induced activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B and expression of ICAM-1. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 3421–3430. [Google Scholar]
- Naini, S.M.; Choukroun, G.J.; Ryan, J.R.; Hentschel, D.M.; Shah, J.V.; Bonventre, J.V. Cytosolic phospholipase A 2 α regulates G 1 progression through modulating FOXO1 activity. FASEB J. 2015, 30, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.E.; Fusenig, N. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Kemeny, L.; Szell, M.; Dobozy, A.; Bata-Csorgo, Z. Ethanol and acetone stimulate the proliferation of HaCaT keratinocytes: The possible role of alcohol in exacerbating psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2003, 295, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B. HaCaT Cell Line as a Model System for Vitamin D3 Metabolism in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 108, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, E.; Rotem, C.; Miodovnik, M.; Ravid, A.; Koren, R. Two modes of ERK activation by TNF in keratinocytes: Different cellular outcomes and bi-directional modulation by vitamin D. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.E.; Anderson, R.J.; Cunningham, A.C.; Donaldson, M.; Groundwater, P.W. Evaluation of a Range of Anti-Proliferative Assays for the Preclinical Screening of Anti-Psoriatic Drugs: A Comparison of Colorimetric and Fluorimetric Assays with the Thymidine Incorporation Assay. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2010, 8, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yan, H.; Zhai, Z.; Hao, F.; Ye, Q.; Zhong, B. Pharmacology and therapeutics: Neutrophil elastase promotes proliferation of HaCaT cell line and transwell psoriasis organ culture model. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerherm, A.J.; Jørgensen, K.M.; Sommerfelt, R.M.; Eidem, L.E.; Lægreid, A.; Johansen, B. Platelet-activating factor induces proliferation in differentiated keratinocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 384, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, G.; Guidi, M.; Laudicina, F.; Marazzi, M.; Falcone, L.; Betti, R.; Crosti, C.; Muller, E.E.; DiMattia, G.E.; Locatelli, V.; et al. IGF-I stimulates proliferation of spontaneously immortalized human keratinocytes (HACAT) by autocrine/paracrine mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2004, 27, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.E.; Jones, T.R.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Clarke, C.; Kang, I.H.; Friman, O.; A. Guertin, D.; Chang, J.H.; Lindquist, R.A.; Moffat, J.; et al. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Domenichiello, A.F.; Dey, A.K.; Yuan, Z.-X.; Goyal, A.; Rose, S.M.; Playford, M.P.; Ramsden, C.E.; Mehta, N.N. Bioactive Lipid Mediator Profiles in Human Psoriasis Skin and Blood. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, K.; Hohjoh, H.; Inazumi, T.; Tsuchiya, S.; Sugimoto, Y. Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: Relevance of prostaglandin E receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundhaug, J.E.; Simper, M.S.; Surh, I.; Fischer, S.M. The role of the EP receptors for prostaglandin E2 in skin and skin cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Han, J.; Qureshi, A. Use of aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and acetaminophen (paracetamol), and risk of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A cohort study. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, T.J.; Tausch, L.; Hoernig, M.; Coste, O.; Schmidt, R.; Angioni, C.; Metzner, J.; Groesch, S.; Pergola, C.; Steinhilber, D. Celecoxib inhibits 5-lipoxygenase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, A. Eicosanoids in skin inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 88, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruner, C.R.; Feldman, S.; Ventrapragada, M.; Fleischer, A.B. A systematic review of adverse effects associated with topical treatments for psoriasis. Dermatol. Online J. 2003, 9, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ravid, A.; Shenker, O.; Buchner-Maman, E.; Rotem, C.; Koren, R. Vitamin D Induces Cyclooxygenase 2 Dependent Prostaglandin E2Synthesis in HaCaT Keratinocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 231, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Stepan, A.F.; O’Mahony, A.; Velichko, S.; Folias, A.E.; Houle, C.; Shaffer, C.L.; Marcek, J.; Whritenour, J.; Stanton, R.; et al. Mechanisms of Skin Toxicity Associated with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Negative Allosteric Modulators. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Werner, S.; Paus, R.; Wolf, E. Beyond wavy hairs: The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in skin biology and pathology. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.L.; Wartmann, M.; Lin, A.Y.; Knopf, J.L.; Seth, A.; Davis, R.J. cPLA2 is phosphorylated and activated by MAP kinase. Cell 1993, 72, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.R.; Hanks, A.N.; Allen, S.M.; Alexander, A.; Diedrich, M.J.; Grossman, D. Apoptosis Regulators and Responses in Human Melanocytic and Keratinocytic Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calay, D.; Vind-Kezunovic, D.; Frankart, A.; Lambert, S.; Poumay, Y.; Gniadecki, R. Inhibition of Akt Signaling by Exclusion from Lipid Rafts in Normal and Transformed Epidermal Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-R.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.T.; Cho, S.-G. Modulation of Apoptosis in HaCaT Keratinocytes via Differential Regulation of ERK Signaling Pathway by Flavonoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31498–31507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, C.; Doi, K. Etoposide induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in neural progenitor cells via DNA damage and an ATM/p53-related pathway. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeon, G.A.; Ryu, P.D.; Myeong, J.N. Membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase gene induces antitumor effect by G2/M arrest in etoposide phosphate-treated cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 252, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duronio, R.J.; Xiong, Y. Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinitt, C.; Benn, T.; Threadgold, S.; Wood, J.; Williams, C.; Hague, A. BAG-1L promotes keratinocyte differentiation in organotypic culture models and changes in relative BAG-1 isoform abundance may lead to defective stratification. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoop, V.M.; Fusenig, N.E.; Mirancea, N. Epidermal Organization and Differentiation of HaCaT Keratinocytes in Organotypic Coculture with Human Dermal Fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas-Szabowski, N.; Stärker, A.; Fusenig, N.E. Epidermal tissue regeneration and stromal interaction in HaCaT cells is initiated by TGF-alpha. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamand, N.; Picard, S.; Lemieux, L.; Pouliot, M.; Bourgoin, S.G.; Borgeat, P. Effects of pyrrophenone, an inhibitor of group IVA phospholipase A2, on eicosanoid and PAF biosynthesis in human neutrophils. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, K.A.; Legault, H.; Hang, C.; Hill, A.; Kasaian, M.; Donaldson, D.; Bensch, G.W.; Baker, J.; Reddy, P.S.; Wood, N.; et al. In vitro allergen challenge of peripheral blood induces differential gene expression in mononuclear cells of asthmatic patients: Inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A2α overcomes the asthma-associated response. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, M.G.; McCormack, A.L.; Olson, E.; Ghomashchi, F.; Gelb, M.H.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Leslie, C.C. Identification of phosphorylation sites of human 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 expressed in insect cells and present in human monocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6987–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Gilliet, M. Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Targeted Therapies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.-H.; Jeong, G.-S. Fisetin inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammatory action and hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells through PI3K/AKT/Nrf-2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrabeitia, M.T.; Riancho, J.A.; Amado, J.A.; Olmos, J.M.; Gonzalez-Macias, J. Effect of calcitriol on the secretion of prostaglandin E2, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor alpha by human monocytes. Bone 1992, 13, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudi, M.; Plaisance, M.C.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. Membrane actions of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 are mediated by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in bone and cartilage cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, K.A.; Guenther, L.; Boyden, B.; Larsen, F.G.; Harvima, R.J.; Guilhou, J.J.; Kaufmann, R.; Rogers, S.; Van De Kerkhof, P.; Hanssen, L.I.; et al. Early onset of action and efficacy of a combination of calcipotriene and betamethasone dipropionate in the treatment of psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.; Moshonov, S.; Chen, X.; Berchansky, A.; Furstenberger, G.; Zor, U. Crosstalk between elevation of [Ca2+]i, reactive oxygen species generation and phospholipase A2 stimulation in a human keratinocyte cell line. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1997, 433, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, R.; Zor, U.; Meller, R.; Moshonov, S.; Fürstenberger, G.; Seger, R. Activation of Map Kinases, cPLA2 and Reactive Oxygen Species Formation by EGF and Calcium Mobilizing Agonists in a Human Keratinocyte Cell Line. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1997, 407, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Huh, N.-H. S100A11, a dual growth regulator of epidermal keratinocytes. Amino Acids 2010, 41, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Murata, H.; Sonegawa, H.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Futami, J.-I.; Kitazoe, M.; Yamada, H.; Huh, N.-H. Truncation of Annexin A1 Is a Regulatory Lever for Linking Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling with Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in Normal and Malignant Squamous Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35679–35686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Rosenberg, D.W. Roles of cPLA2α and arachidonic acid in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Lee, S.; Do, H.; Youn, B. Targeting the enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism to improve radiotherapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, A.P.; Needleman, P. Modulation of keratinocyte proliferation in vitro by endogenous prostaglandin synthesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conconi, M.; Bruno, P.; Bonali, A.; De Angeli, S.; Parnigotto, P. Relationship between the proliferation of keratinocytes cultured in vitro and prostaglandin E2. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 1996, 178, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftin, C.D.; Eling, T.E. Prostaglandin Synthase 2 Expression in Epidermal Growth Factor-Dependent Proliferation of Mouse Keratinocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 330, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.M.; Sung, Y.M.; He, G.; Fischer, S.M. Prostaglandin receptor EP2 is responsible for cyclooxygenase-2 induction by prostaglandin E2 in mouse skin. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.M.; He, G.; Fischer, S.M. Lack of Expression of the EP2 but not EP3 Receptor for Prostaglandin E2 Results in Suppression of Skin Tumor Development. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9304–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.A.; Dy, L.C.; Southall, M.D.; Yi, Q.; Smietana, E.; Kapur, R.; Marques, M.; Travers, J.B.; Spandau, D.F. The platelet-activating factor receptor activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces proliferation of epidermal cells through an epidermal growth factor-receptor-dependent pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Kume, K.; Ito, C.; Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T. Accelerated proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes by the transgenic expression of the platelet-activating factor receptor. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1999, 291, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Huettner, B.; Koefeler, H.; Mayer, G.; Bambach, I.; Wallbrecht, K.; Schon, M.P.; Wolf, P. Platelet-activating factor blockade inhibits the T-helper type 17 cell pathway and suppresses psoriasis-like skin disease in K5.hTGF-beta1 transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inhibitor | PGE2 | 6-keto PGF1α | LTB4 | TxB2 | 12S-HETE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVX001 | 93 ± 9 5 µM * | 114 ± 16 5 µM | 95 ± 6 5 µM * | 106 ± 3 5 µM * | 90 ± 6 10 µM |
| Naproxen | 96 ± 6 5 µM ** | 102 ± 18 5 µM | 48 ± 7 5 µM | 106 ± 2 5 µM ** | −18 ± 24 10 µM |
| Celecoxib | 97 ± 5 5 µM * | 108 ± 20 5 µM | 91 ± 3 5 µM * | 107 ± 2 5 µM ** | 42 ± 35 10 µM |
| NDGA | 49 ± 7 10 µM | 34.3 ± 7 10 µM | 99 ± 1 10 µM * | 42 ± 12 10 µM | 105 ± 1 10 µM * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashcroft, F.J.; Mahammad, N.; Midtun Flatekvål, H.; J. Feuerherm, A.; Johansen, B. cPLA2α Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101402
Ashcroft FJ, Mahammad N, Midtun Flatekvål H, J. Feuerherm A, Johansen B. cPLA2α Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101402
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshcroft, Felicity J., Nur Mahammad, Helene Midtun Flatekvål, Astrid J. Feuerherm, and Berit Johansen. 2020. "cPLA2α Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101402
APA StyleAshcroft, F. J., Mahammad, N., Midtun Flatekvål, H., J. Feuerherm, A., & Johansen, B. (2020). cPLA2α Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101402




