Vacuum Energy in Saez-Ballester Theory and Stabilization of Extra Dimensions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of Problem and Solutions
3. Discussion
4. Stabilization of Extra Dimensions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H. The energy conservation in our universe and the pressureless dark energy. J. Gravity 2015, 2015, 384673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M. The cosmological constant. Living Rev. Rel. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, S.M. Dark energy and the preposterous universe. arXiv 2001, arXiv:astro-ph/0107571. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, P.J.E.; Ratra, B. The cosmological constant and dark energy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 559–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Singh, K.P. A higher dimensional cosmological model for the search of dark energy source. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2021, 18, 2150026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Singh, K.P. f(R,T) Gravity model behaving as a dark energy source. New Astron. 2021, 84, 101542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pogosian, L.; Zhao, G.B.; Zucca, A. Evolution of dark energy reconstructed from the latest observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 869, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, D.E.S. More than dark energy—An overview. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 1270–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Dikshit, B. Quantum mechanical explanation for dark energy, cosmic coincidence, flatness, age, and size of the universe. Open Astron. 2019, 28, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, H.; Sheykhi, A.; Riazi, N.; Wang, B. Necessity of Dark energy from thermodynamic arguments. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2014, 2014, 718583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, G. Dark Energy, a Summary. Nucl. Part. Phys. Proc. 2015, 267–269, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J. The speed of dark energy. Nature 2013, 500, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.; Jaffe, M.; Haslinger, P.; Simmons, Q.; Muller, H.; Khoury, J. Atom-interferometry constraints on dark energy. Science 2015, 349, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josset, T.; Perez, A.; Sudarsky, D. Dark Energy from Violation of Energy Conservation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clery, D. Survey finds galaxy clumps stirred up by dark energy. Science 2017, 357, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.H. A Natural Solution to the Dark Energy Problem. Phys. Sci. Int. J. 2015, 5, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified gravity and cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Pradhan, A. Probing κ(R,T) cosmology via empirical approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.03798v1. [Google Scholar]
- Gorji, M.A. Late time cosmic acceleration from natural infrared cutoff. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 760, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Narain, G.; Li, T. Non-locality and late-time cosmic acceleration from an Ultraviolet Complete Theory. Universe 2018, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, L.; Khoury, J.; Wang, J. Universe without dark energy: Cosmic acceleration from dark matter-baryon interactions. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 123530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, P. Planck 2018 results: VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Sangwan, A.; Jassal, H. Dark energy equation of state parameter and its evolution at low redshift. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, I.; Wang, L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Quintessence, cosmic coincidence, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1753–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousso, R. The holographic principle. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 825–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Holographic dark energy. Phys. Rep. 2017, 696, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Dixit, A.; Bhardwaj, V.K. Barrow HDE model for statefinder diagnostic in FLRW universe. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2021, 36, 2150030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sharma, U.K.; Pradhan, A. New holographic dark energy in Bianchi-III universe with k-essence. New Astron. 2019, 68, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanthi, U.Y.D.; Aditya, Y. Anisotropic Renyi holographic dark energy models in general relativity. Results Phys. 2020, 17, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korunur, M. Tsallis holographic dark energy in Bianchi type-III spacetime with scalar fields. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 34, 1950310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.R.K.; Raju, P.; Sobhanbabu, K. Five dimensional spherically symmetric minimally interacting holographic dark energy model in Brans–Dicke theory. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.R.K.; Anitha, S.; Umadevi, S. Five dimensional minimally interacting holographic dark energy model in Brans–Dicke theory of gravitation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Singh, P.S. Dark energy on higher dimensional spherically symmetric Brans–Dicke universe. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 60, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, A.D.; Tsujikawa, S. f(R) Theories. Living Rev. Relativ. 2010, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.H.; Wang, B.; Abdalla, E. Deep connection between f(R) gravity and the interacting dark sector model. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 123526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumalacárregui, M.; Koivisto, T.S.; Mota, D.F. DBI Galileons in the Einstein frame: Local gravity and cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 083010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofinas, G.; Papantonopoulos, E.; Saridakis, E.N. Modified Brans–Dicke cosmology with matter-scalar field interaction. Class. Quan. Gravit. 2016, 33, 155004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, L.; Tocchini-Valentini, D. Stationary dark energy: The present universe as a global attractor. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 043509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, W.; Pavón, D.; Chimento, L.P. Interacting quintessence. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 521, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, W.; Pavón, D. Letter: Statefinder Parameters for Interacting Dark Energy. Gen. Relat. Gravit. 2004, 36, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.G.; Wang, A. Cosmology with interaction between phantom dark energy and dark matter and the coincidence problem. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 3, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.P.; Kumar, P. Holographic dark energy models with statefinder diagnostic in modified f(R,T) gravity. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.07314v2. [Google Scholar]
- Sadri, E.; Khurshudyan, M.; Chattopadhyay, S. An interacting new holographic dark energy in the framework of fractal cosmology. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2018, 363, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.C.; Sharma, U.K. Comparing the holographic principle inspired dark energy models. New Astron. 2021, 86, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.C. Dark energy from vacuum entanglement. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 08, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukohyama, S.; Seriu, M.; Kodama, H. Can the entanglement entropy be the origin of black-hole entropy? Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 7666–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Holographic dark energy with cosmological constant. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 08, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, Y.S. Instability of holographic dark energy models. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 652, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, T.K.; Suresh, J.; Divakaran, D. Modified holographic Ricci dark energy model and state finder diagnosis in flat universe. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1350056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, D.; Ballester, V. A simple coupling with cosmological implications. Phys. Lett. A 1986, 113, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, Y.; Raju, K.D.; Ravindranath, P.J.; Reddy, D.R.K. Dynamical aspects of anisotropic Bianchi type VI0 cosmological model with dark energy fluid and massive scalar field. Indian J. Phys. 2021, 95, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Brans-Dicke theory as a unified model for dark matter-dark energy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 364, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panotopoulos, G.; Rincón, N. Stability of cosmic structures in scalar–tensor theories of gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Sarkar, C.; Sanyal, A.K. Early universe with modified scalar-tensor theory of gravity. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 05, 078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, A.H. Inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A. A new inflationary universe scenario: A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy and primordial monopole problems. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 108, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Kumar Singh, A.; Chouhan, D.S. Accelerating Bianchi Type-V Cosmology with Perfect Fluid and Heat Flow in Sáez-Ballester Theory. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.K.; Zia, R.; Pradhan, A. Transit cosmological models with perfect fluid and heat flow in Sáez-Ballester theory of gravitation. J. Astrophys. Astr. 2019, 40, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, T. Zum Unitätsproblem der Physik (On the unification problem in physics). Sitzungsber. Preuss Akad. Wiss. Berlin Math. Phys. 1921, K1, 966. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, O. Quantentheorie und fünfdimensionale Relativitätstheorie (Quantum theory and five-dimensional relativity theory). Z. Phys. 1926, 37, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.K.; Bhuyan, K. Dynamics of higher-dimensional FRW cosmology in Rpexp(λR) gravity. Pramana J. Phys. 2017, 88, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.A. Tsallis holographic dark energy with Granda-Oliveros scale in (n + 1)-dimensional FRW universe. Adv. Astron. 2019, 2019, 8138067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajollahi, H.; Amiri, H. A 5D noncompact Kaluza-Klein cosmology in the presence of null perfect fluid. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2010, 19, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, P.S. The status of modern five-dimensional gravity (A short review: Why physics needs the fifth dimension). Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2015, 24, 1530001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciano, W.J. Time variation of the fundamental constants and Kaluza-Klein theories. Phy. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Debnath, U. Higher dimensional cosmology with normal scalar field and tachyonic field. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2010, 49, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Heal the world: Avoiding the cosmic doomsday in the holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 683, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astefanesei, D.; Herdeiro, C.; Oliveira, J.; Radu, E. Higher dimensional black hole scalarization. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarnejad, H.; Farsam, M.; Yaraie, E. Effects of quintessence dark energy on the action growth and butterfly velocity. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 9529356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, G.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Wesley, D.H. Dark energy, extra dimensions, and the Swampland. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 6, 091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Ghose, S. Interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy in higher dimensional cosmology. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2020, 365, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, U.K.; Pradhan, A. A comparative study of Kaluza–Klein model with magnetic field in Lyra manifold and general relativity. New Astron. 2019, 70, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Pradhan, A. Crossing the phantom divide line in universal extra dimensions. New Astron. 2020, 80, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, G.C.; Dhal, S.N. Higher dimensional cosmological models filled with perfect fluid in f(R,T) theory of gravity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. Holographic dark energy model with linearly varying deceleration parameter and generalised Chaplygin gas dark energy model in Bianchi type-I universe. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 349, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. Interacting holographic dark energy with variable deceleration parameter and accreting black holes in Bianchi type-V universe. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 352, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Sheykhi, A.; Dehghani, M. Statefinder diagnosis for holographic dark energy in the DGP braneworld. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.M.; Samanta, G.C. Dark energy in spherically symmetric universe coupled with Brans-Dicke scalar field. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2019, 2019, 5234014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.R.; Kamionkowski, M.; Weinberg, N.N. Phantom energy: Dark energy with ω < −1 causes a cosmic doomsday. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 071301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollah, M.R.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, P.S. Bianchi type-III cosmological model with quadratic EoS in Lyra geometry. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2018, 15, 1850194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, Y.; Reddy, D.R.K. Anisotropic new holographic dark energy model in Saez–Ballester theory of gravitation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2018, 363, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibba, R. Crunch, rip, freeze or decay—How will the Universe end? Nature 2020, 584, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, K. The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking); Scribner: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Camarena, D.; Marra, V. Local determination of the Hubble constant and the deceleration parameter. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 013028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Ruchika; Sen, A.A. Model-independent constraints on dark energy evolution from low-redshift observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 4484–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.P.; Bishi, B.K. Bulk viscous cosmological model in Brans-Dicke theory with new form of time varying deceleration parameter. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2017, 2017, 1390572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.; Debnath, U.; Ghosh, S.; Guha, B.K. Study of QCD generalized ghost dark energy in FRW universe. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Chand, A. Cosmological models in Sáez-Ballester theory with bilinear varying deceleration parameter. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2020, 365, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.F.R.; Elst, H.V. Cosmological models (Cargèse lectures 1998). NATO Adv. Study Inst. Ser. C Math. Phys. Sci. 1999, 541, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khodadi, M.; Heydarzade, Y.; Nozari, K.; Darabi, F. On the stability of Einstein static universe in doubly general relativity scenario. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.J.; Freese, K. Curvature and flatness in a Brans-Dicke universe. Nucl. Phys. B 1994, 421, 635–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, M. How Problematic is the Near-Euclidean spatial geometry of the large-scale Universe? Found. Phys. 2018, 8, 1617–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, E.D.; Melchiorri, A.; Silk, J. Planck evidence for a closed Universe and a possible crisis for cosmology. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Nawazish, I.; Shahid, F.; Irshad, N. Evolution of non-flat cosmos via GGPDE f(R) model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, G.G.L.; Hanafy, W. A built-in inflation in the f(T)-cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2014, 74, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.J.; Overduin, J.M. The nearly flat universe. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2005, 37, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kribs, G.D. TASI 2004 Lectures on the phenomenology of extra dimensions. arXiv 2006, arXiv:hep-ph/0605325v1. [Google Scholar]
- Ketov, S.V. Modified gravity in higher dimensions, flux compactification, and cosmological inflation. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, N.A.; Dimopoulos, S.; Dvali, G. Large extra dimensions: A new arena for particle physics. Phys. Today 2002, 55, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, W.D.; Wise, M.B. Modulus stabilization with bulk fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 4922–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Geddes, J.; Hoffman, M.B.; Wald, R.M. Classical stabilization of homogeneous extra dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 024036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.J.H.; Freese, K. Cosmological challenges in theories with extra dimensions and remarks on the horizon problem. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 61, 023511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arapoğlu, A.S.; Yalçınkaya, E.; Yükselci, A.E. Dynamical system analysis of a five-dimensional cosmological model. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2018, 363, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A.; Rubinn, S.G. Self-stabilization of extra dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrum, R. TASI 2004 lectures: To the fifth dimension and back. arXiv 2005, arXiv:hep-th/0508134v2. [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen, K.; Sunhede, D. Dark energy, scalar-tensor gravity, and large extra dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 083510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, A. Extra dimensions and inflation. Phys. Lett. B 1999, 469, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, F.; Rasanen, S. Lovelock inflation and the number of large dimensions. J. High Energy Phys. 2007, 11, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Pavluchenko, S.A. Some aspects of the cosmological dynamics in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 36, 2150092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.M.M.; Moniz, P.V. Modified Saez–Ballester scalar–tensor theory from 5D space-time. Class. Quantum Grav. 2018, 35, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.H.R.S.; Correa, R.A.C. The importance of scalar fields as extra dimensional metric components in Kaluza-Klein models. Adv. Astron. 2019, 2019, 5104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, C.D.E.; Longden, C. Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity with extra dimensions. Galaxies 2019, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, N.A.; Cohen, A.G.; Georgi, H. (De)Constructing dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4757–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosa, Y. Classical Kaluza-Klein cosmology for a torus space with a cosmological constant and matter. Phys. Rev. D 1984, 30, 2054, Erratum in Phys. Rev. D 1985, 31, 2697.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.O.; Volobuev, I.P. Stabilization of the extra dimension size in RS model by bulk Higgs field. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 798, 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, E.; Quiros, M. Five-dimensional massive vector fields and radion stabilization. Nucl. Phys. B 2005, 721, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kanti, P.; Olive, K.A.; Pospelov, M. On the stabilization of the size of extra dimensions. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 538, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ponton, E.; Poppitz, E. Casimir energy and radius stabilization in five and six dimensional orbifolds. J. High Energy Phys. 2001, 06, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mukherjee, H.; Paul, T.; SenGupta, S. Radion stabilization in higher curvature warped spacetime. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongjun, P. Casimir dark energy, stabilization of the extra dimensions and Gauss–Bonnet term. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, A.; Wu, Q. Cosmological constant and late transient acceleration of the universe in the Horava–Witten heterotic M-theory on S1/Z2. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 663, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Santos, N.O.; Vo, P.; Wang, A. Late transient acceleration of the universe in string theory on S1/Z2. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 09, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, A. Thick de Sitter 3-branes, dynamic black holes, and localization of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 024024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rador, T. Acceleration of the Universe via f(R) gravities and the stability of extra dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 064033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, B.R.; Levin, J. Dark energy and stabilization of extra dimensions. J. High Energy Phys. 2007, 11, 096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.D. Vacuum Energy. arXiv 2001, arXiv:hep-th/0012062v3. [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose, S. Casimir Energy of the Universe and the Dark Energy Problem. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 384, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupays, A.; Lamine, B.; Blanchard, A. Can dark energy emerge from quantum effects in a compact extra dimension? Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 554, A60. [Google Scholar]
- Shiromizu, T.; Maeda, K.I.; Sasaki, M. The Einstein equations on the 3-brane world. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R. Brane worlds. Class. Quant. Grav. 2001, 18, R1–R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, C.J. Classical gravitational-wave backgrounds from formation of the brane world. Class. Quant. Grav. 2001, 18, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiki, K.; Yahiro, M.; Kajino, T.; Orito, M.; Mathews, G.J. Observational constraints on dark radiation in brane cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 043521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, K.; Lewis, M. Cardassian expansion: A model in which the universe is flat, matter dominated, and accelerating. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 540, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Fujimoto, M. Cardassian expansion: Constraints from compact radio source angular size versus redshift data. Astrophys. J. 2002, 581, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Langlois, D. Cosmology in a brane-universe. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2003, 283, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Fujimoto, M. Constraints on Cardassian expansion from distant type Ia supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2003, 585, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Fujimoto, M. Constraints on the Cardassian scenario from the expansion turnaround redshift and the Sunyaev-Zeldovich/X-ray data. Astrophys. J. 2004, 602, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dvali, G.; Gabadadze, G.; Porrati, M. 4D gravity on a brane in 5D Minkowski space. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 485, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaniz, J.S. Dark energy and some alternatives: A brief overview. Braz. J. Phys. 2006, 36, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeshkumar, V.H.; Suresh, P.K. Understanding gravity: Some extra-dimensional perspectives. ISRN Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 2011, 131473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, V.H.S.; Suresh, P.K. Are We Living in a Higher Dimensional Universe? arXiv 2005, arXiv:gr-qc/0506125v2. [Google Scholar]
- Dvali, G.; Turner, M.S. Dark energy as a modification of the Friedmann equation. arXiv 2003, arXiv:astro-ph/0301510v1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A. Orbifold branes in string/M-Theory and their cosmological applications. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1003.4991v1. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Wang, A. Brane cosmology in the Horava-Witten heterotic M-theory on S1/Z2. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 6, 015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Santos, N.O. The cosmological constant in the brane world of string theory on S1/Z2. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 669, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Santos, N.O. The hierarchy problem, radion mass, localization of gravity and 4D effective newtonian potential in string theory on S1/Z2. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2010, 25, 1661–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devin, M.; Ali, T.; Cleaver, G.; Wang, A.; Wu, Q. Branes in the MD × Md+ × Md− compactification of type II string on S1/Z2 and their cosmological applications. J. High Energy Phys. 2009, 10, 095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Cai, R.-G.; Santos, N.O. Two 3-Branes in Randall-Sundrum setup and current acceleration of the universe. Nucl. Phys. B 2008, 797, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garriga, J.; Pomarol, A. A stable hierarchy from Casimir forces and the holographic interpretation. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 560, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garriga, J.; Pujolas, O.; Tanaka, T. Radion effective potential in the Brane-World. Nucl. Phys. B 2001, 605, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
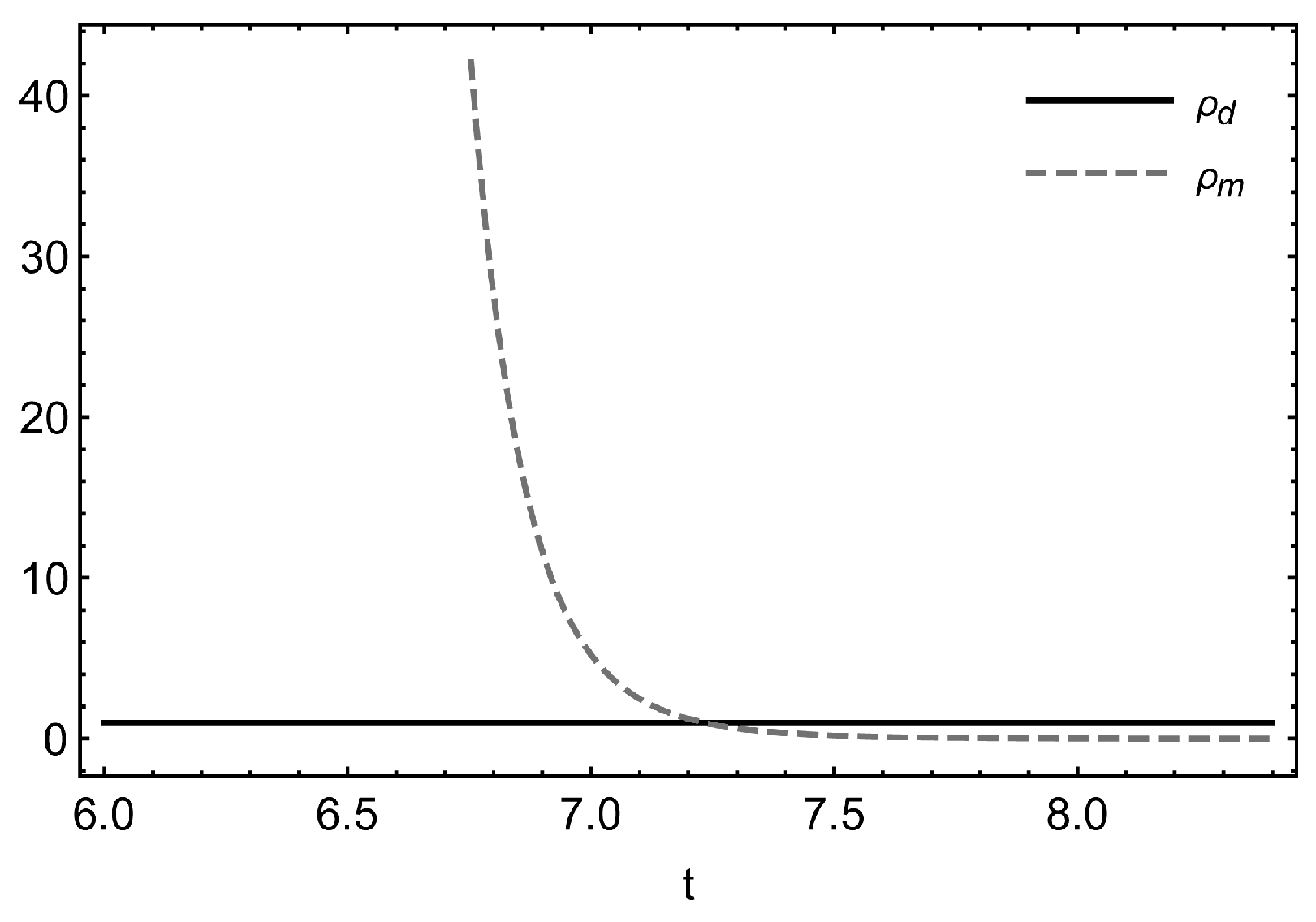
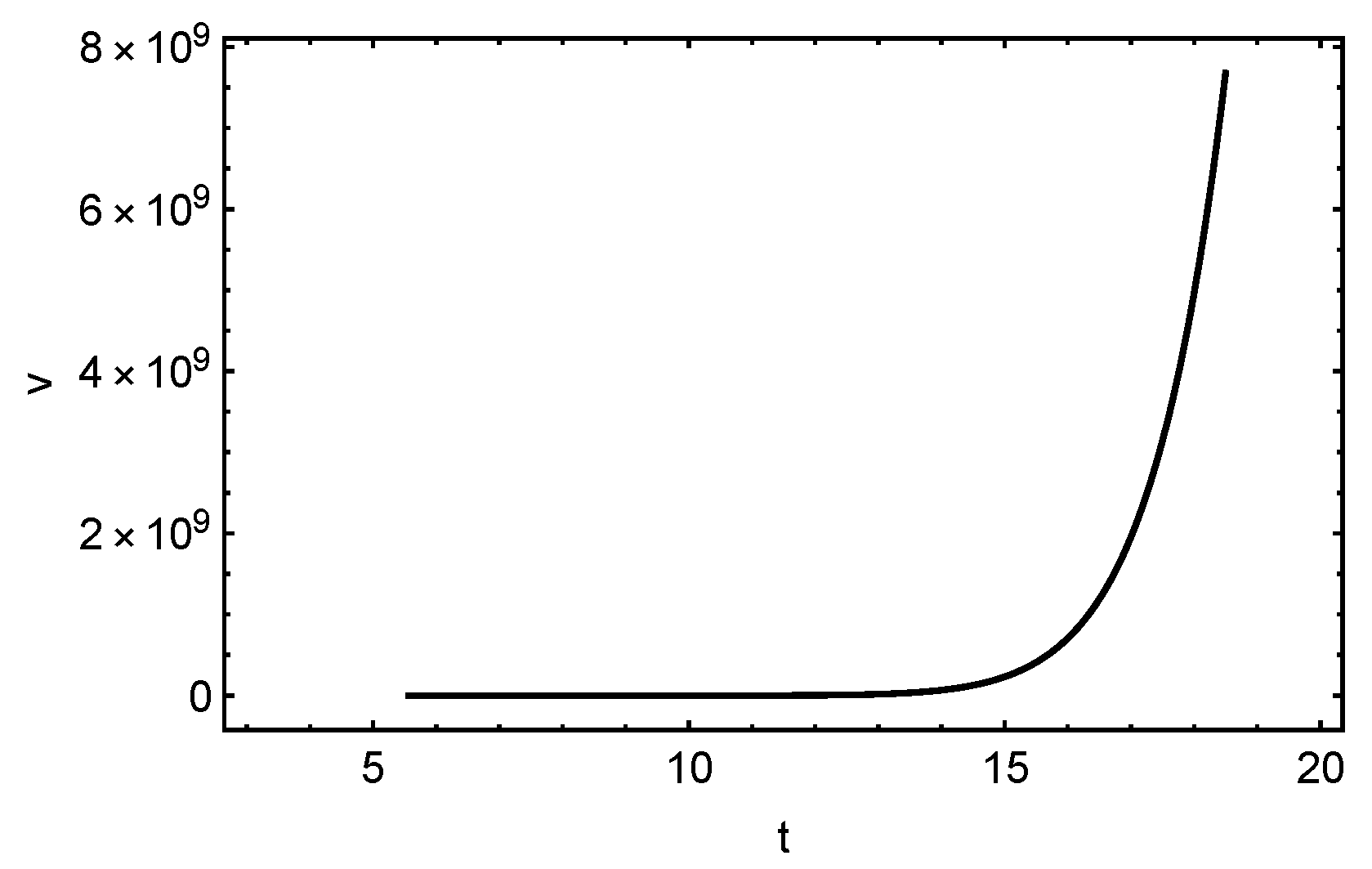
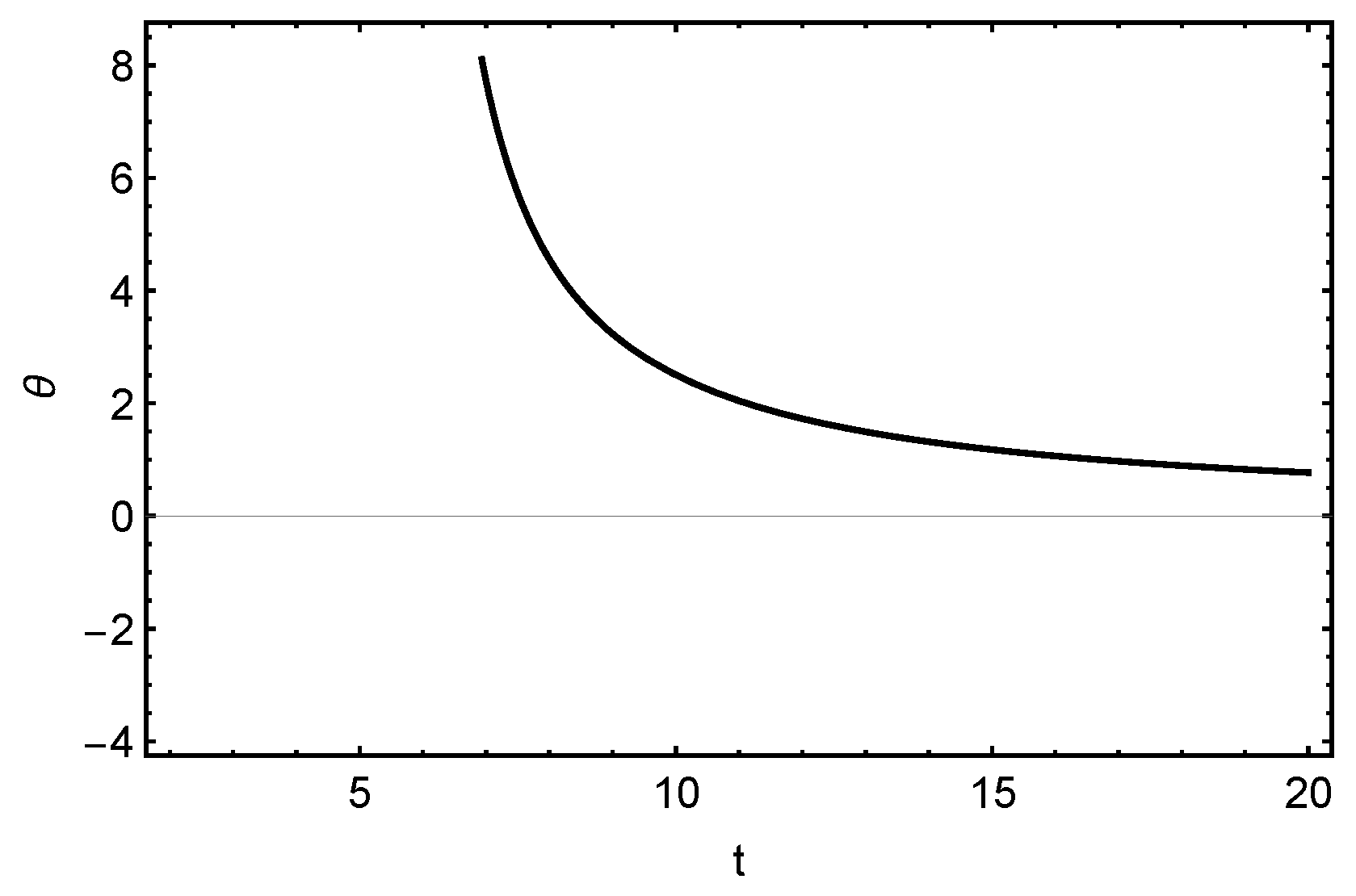



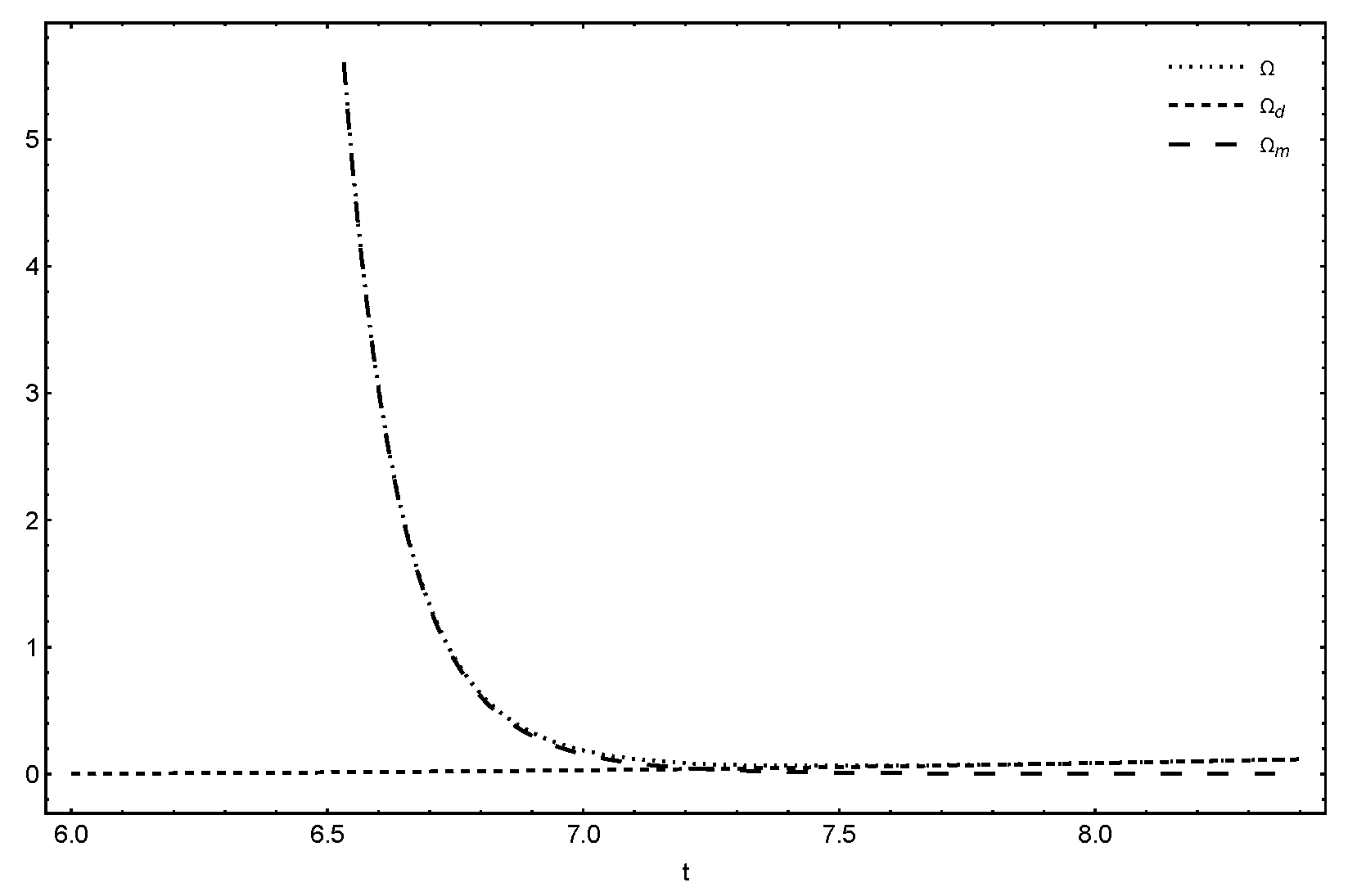
| u | v | k | q |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.78 | 1 | −0.64 | |
| 2.78 | 1 | −0.55 | |
| 2.25 | 1 | −0.55 | |
| 2.25 | 1.9 | −0.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.S.; Singh, K.P. Vacuum Energy in Saez-Ballester Theory and Stabilization of Extra Dimensions. Universe 2022, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8020060
Singh PS, Singh KP. Vacuum Energy in Saez-Ballester Theory and Stabilization of Extra Dimensions. Universe. 2022; 8(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Pheiroijam Suranjoy, and Kangujam Priyokumar Singh. 2022. "Vacuum Energy in Saez-Ballester Theory and Stabilization of Extra Dimensions" Universe 8, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8020060
APA StyleSingh, P. S., & Singh, K. P. (2022). Vacuum Energy in Saez-Ballester Theory and Stabilization of Extra Dimensions. Universe, 8(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8020060







