Mediating Effects of Serum Lipids and Physical Activity on Hypertension Management of Urban Elderly Residents in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
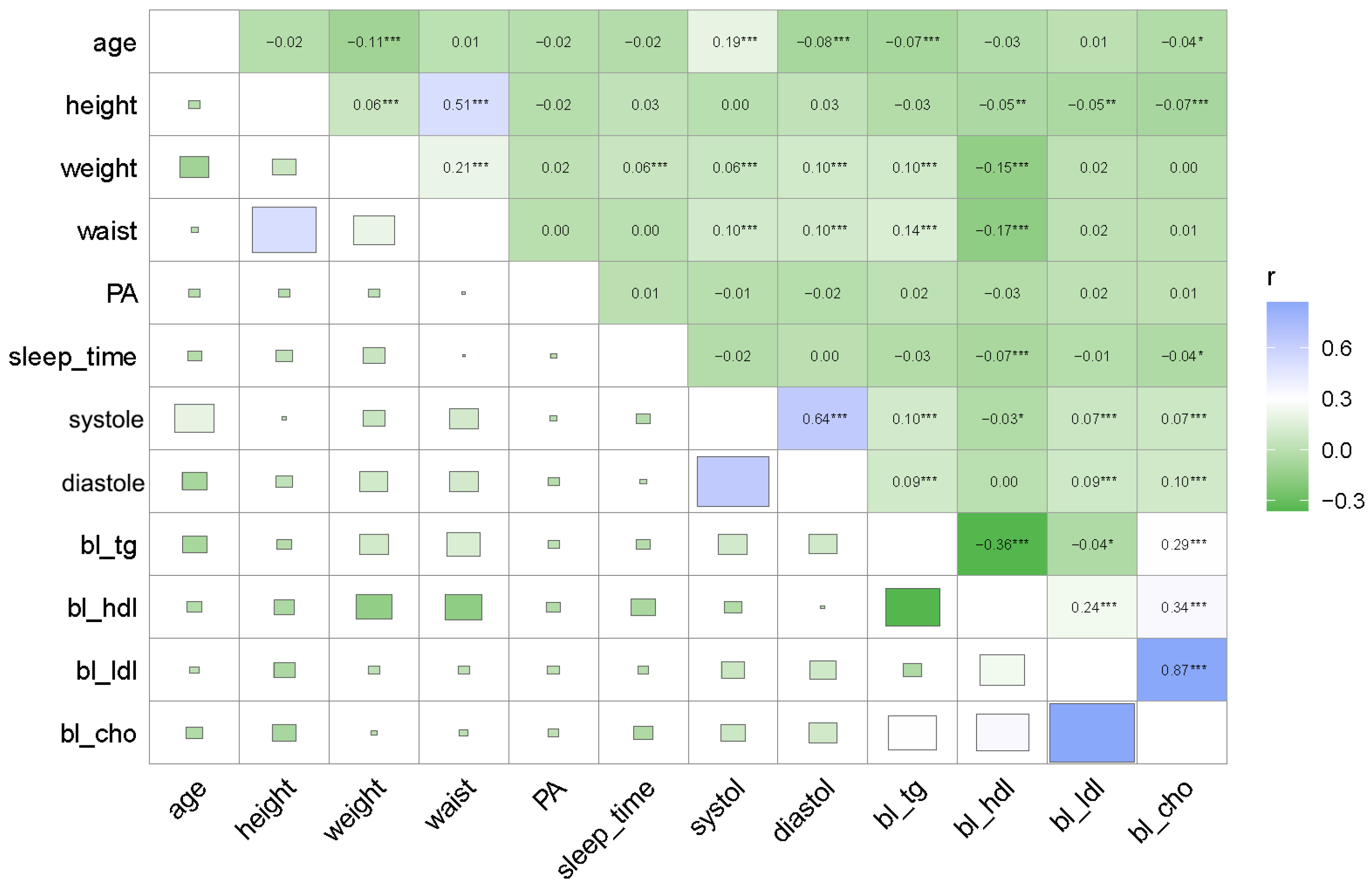
3.2. Pearson Correlation Analysis
3.3. Logistic Regression Analysis
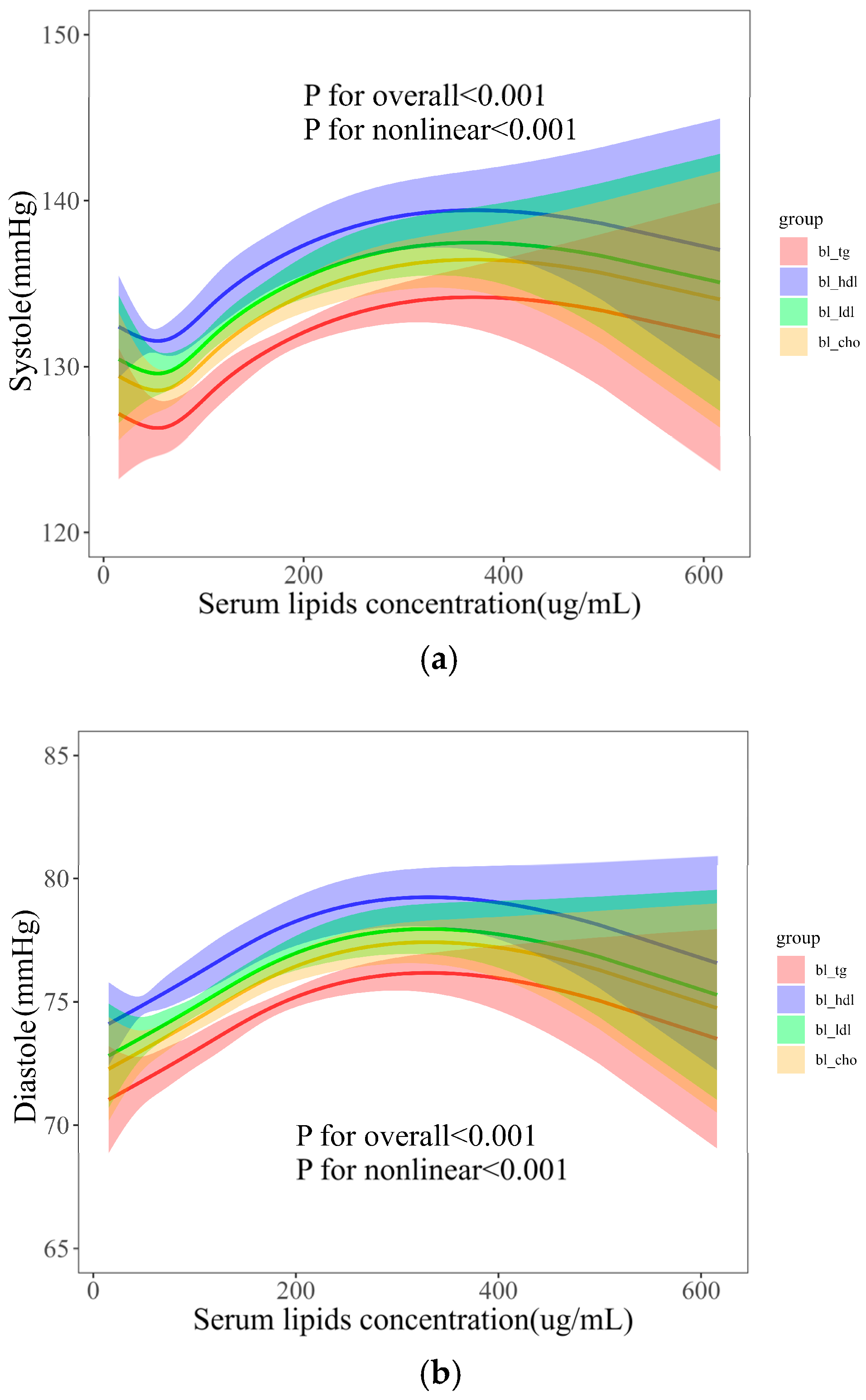
3.4. Dose–Effects of Serum Lipids with BP
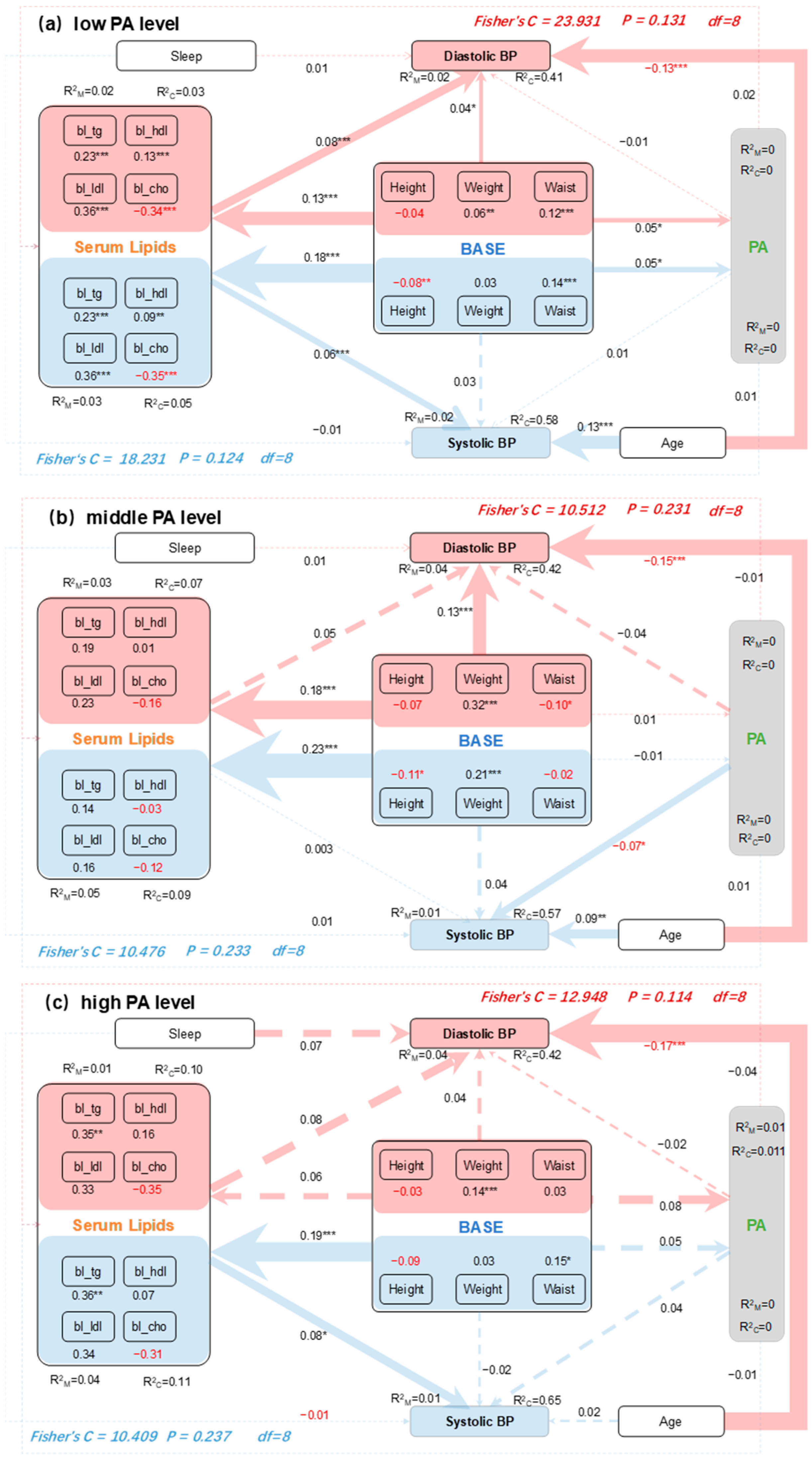
3.5. Mediating Effects of PA and Serum Lipids on BP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Serum lipids have significant nonlinear relationships with BP, and PA levels have varying effects on BP. Meanwhile, the BP health of urban residents is influenced by factors such as age, weight, and waist measurements.
- (2)
- There are significant mediating effects of serum lipids and weak mediating effects of PA on the relationship between individual body variables and SBP/DBP. These effects differ among PA levels, highlighting the importance of low PA levels in elderly hypertension management.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boersma, P.; Black, L.I.; Ward, B.W. Prevalence of Multiple Chronic Conditions Among US Adults, 2018. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2020, 17, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.D.; Whelton, P.K. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 2020, 75, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, L.; Tian, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, C. Status of hypertension in China: Results from the China hypertension survey, 2012–2015. Circulation 2018, 137, 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-G.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Hypertension in China: Epidemiology and treatment initiatives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Jing, L.; Tian, Y.; Lin, M.; Du, Z.; Yan, H.; Ren, G.; Dong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S. Urban–Rural disparities in status of hypertension in northeast China: A population-based study, 2017–2019. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 coun-tries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Khemka, S.; Reddy, A.; Garcia, R.I.; Jacobs, M.; Reddy, R.P.; Roghani, A.K.; Pattoor, V.; Basu, T.; Sehar, U.; Reddy, P.H. Role of diet and exercise in aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and other chronic diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalifu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hamulati, X.; Wang, Y.-S.; Deng, L.; Adili, N.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.-N.; Li, X.-M. Joint association of physical activity and diet quality with dyslipidemia: A cross-sectional study in Western China. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayatnia, M.; Asadi, Z.; Zare-Feyzabadi, R.; Yaghooti-Khorasani, M.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Ghaffarian-Zirak, R.; Nosrati-Tirkani, A.; Mohammadi-Bajgiran, M.; Rohban, M.; Sadabadi, F.; et al. Dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease risk among the MASHAD study population. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, E.; Narkiewicz, K. Hypertension and dyslipidemia: The two partners in endothelium-related crime. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, F.W.; Gordon, S.E.; Carlson, C.J.; Hamilton, M.T. Waging war on modern chronic diseases: Primary prevention through exercise biology. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 88, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börjesson, M.; Onerup, A.; Lundqvist, S.; Dahlöf, B. Physical activity and exercise lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension: Narrative review of 27 RCTs. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.M.; Galliano, L.M.; Del Vecchio, F.B. Effectiveness of high-intensity interval training versus moderate-intensity continuous training in hypertensive patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isath, A.; Koziol, K.J.; Martinez, M.W.; Garber, C.E.; Martinez, M.N.; Emery, M.S.; Baggish, A.L.; Naidu, S.S.; Lavie, C.J.; Arena, R. Exercise and cardiovascular health: A state-of-the-art review. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 79, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, K.M.; Booth, J.N., III; Seals, S.R.; Abdalla, M.; Dubbert, P.M.; Sims, M.; Ladapo, J.A.; Redmond, N.; Muntner, P.; Shimbo, D. Physical activity and incident hypertension in African Americans: The Jackson Heart Study. Hypertension 2017, 69, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byambasukh, O.; Snieder, H.; Corpeleijn, E. Relation between leisure time, commuting, and occupational physical activity with blood pressure in 125 402 adults: The lifelines cohort. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, K.; Bovbjerg, M.; Schuna, J., Jr.; Branscum, A.; Varma, R.P.; Ismail, R.; Barbarash, O.; Dominguez, J.; Altuntas, Y.; Anjana, R.M. Urbanization and physical activity in the global Prospective Urban and Rural Epidemiology study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Liu, H.L.; Qu, Q.; Cheng, C.; Kong, X.Q.; Huang, W.J.; Sun, W. High waist circumference is a risk factor of new-onset hypertension: Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced body shape change coupled with PA is the key to hypertension management for urban residents. Public Health Nurs. 2024, 41, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Smith, J.P.; Strauss, J.; Yang, G. Cohort profile: The China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sember, V.; Meh, K.; Sorić, M.; Starc, G.; Rocha, P.; Jurak, G. Validity and reliability of international physical activity questionnaires for adults across EU countries: Systematic review and meta analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Paul, D.R. The relationships between depressive symptoms, functional health status, physical activity, and the availability of recreational facilities: A rural-urban comparison in middle-aged and older Chinese adults. Int. J. Behav. Sci. 2018, 25, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Xin, C.; Duan, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Niu, Z. Associations of long-term exposure to air pollution, physical activity with blood pressure and prevalence of hypertension: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1137118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1·9 million participants. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H.; Gao, Y. Physical activity during pregnancy and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, W.; Lewandowski, A.J.; Huckstep, O.J.; Lapidaire, W.; Ooms, A.; Tan, C.; Mohamed, A.; Alsharqi, M.; Bertagnolli, M.; Woodward, W. Effect of moderate to high intensity aerobic exercise on blood pressure in young adults: The TEPHRA open, two-arm, parallel superiority randomized clinical trial. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 48, 101445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Fan, F.; Jia, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Lipid profiles and the risk of new-onset hypertension in a Chinese community-based cohort. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovas. Dis. 2021, 31, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvari, Z.; Tarantini, S.; Kiss, T.; Wren, J.D.; Giles, C.B.; Griffin, C.T.; Murfee, W.L.; Pacher, P.; Csiszar, A. Endothelial dysfunction and angiogenesis impairment in the ageing vasculature. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.M.; Yano, S.; Tabassum, S.; Nagai, A. The Role of the Vascular System in Degenerative Diseases: Mechanisms and Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Lu, C.; Chen, K.; Song, B.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. Associations between various anthropometric indices and hypertension and hyperlipidaemia: A cross-sectional study in China. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.S. Association between physical activity levels and mortality across adiposity: A longitudinal study of age-specific Asian populations. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, W.; Cao, S.; Xu, H.; Tian, Q.; Gan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yan, S.; Yan, F.; Yue, W. Association of adiposity indicators with hypertension among Chinese adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovas. 2021, 31, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Li, T. Signaling pathways in obesity: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Su, C.; Du, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Luo, S.; Tan, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X. The mediation and moderation effect association among physical activity, body-fat percentage, blood pressure, and serum lipids among Chinese adults: Findings from the China Health and Nutrition Surveys in 2015. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, E.; Kamalumpundi, V.; Peterson, J.; Gismondi, R.A.; Oigman, W.; de Gusmão Correia, M.L. Highlights of mechanisms and treatment of obesity-related hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2022, 36, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic [n/N(%)|Mean (SD)] 1 | Unit | Hypertension? | p-Value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| not, N = 1724 | yes, N = 1649 | |||
| Gender | 0.606 | |||
| Male | — | 369/1724 (21%) | 341/1649 (21%) | |
| Female | — | 1355/1724 (79%) | 1308/1649 (79%) | |
| PA_level | 0.015 | |||
| Low | — | 1248/1724 (72%) | 1157/1649 (70%) | |
| Moderate | — | 274/1724 (16%) | 322/1649 (20%) | |
| High | — | 202/1724 (12%) | 170/1649 (10%) | |
| Smoke | 0.764 | |||
| Yes | — | 126/1724 (7.3%) | 125/1649 (7.6%) | |
| Not | — | 1598/1724 (93%) | 1524/1649 (92%) | |
| Drink | — | 0.206 | ||
| Yes | — | 382/1724 (22%) | 336/1649 (20%) | |
| Not | — | 1342/1724 (78%) | 1313/1649 (80%) | |
| Urban | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | — | 648/1724 (38%) | 724/1649 (44%) | |
| Not | — | 1076/1724 (62%) | 925/1649 (56%) | |
| Age | years | 66.74 (5.93) | 68.42 (6.40) | <0.001 |
| Height | cm | 154.00 (22.27) | 153.81 (22.93) | 0.465 |
| Weight | kg | 55.24 (25.01) | 59.43 (12.22) | <0.001 |
| Waist | cm | 83.30 (25.85) | 88.54 (13.51) | <0.001 |
| PA | MET·h/w | 15.62 (29.92) | 16.20 (28.95) | 0.223 |
| Sleep_time | h | 6.19 (2.09) | 6.08 (2.14) | 0.116 |
| Systole | mmHg | 119.35 (11.92) | 146.42 (18.85) | <0.001 |
| Diastole | mmHg | 69.27 (8.09) | 80.29 (11.21) | <0.001 |
| bl_tg | μg/mL | 131.88 (80.28) | 155.38 (90.09) | <0.001 |
| bl_hdl | μg/mL | 53.11 (11.37) | 51.17 (11.10) | <0.001 |
| bl_ldl | μg/mL | 105.63 (27.86) | 107.78 (29.44) | 0.023 |
| bl_cho | μg/mL | 188.72 (36.11) | 192.14 (36.38) | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. Mediating Effects of Serum Lipids and Physical Activity on Hypertension Management of Urban Elderly Residents in China. Metabolites 2024, 14, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120707
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Wang F. Mediating Effects of Serum Lipids and Physical Activity on Hypertension Management of Urban Elderly Residents in China. Metabolites. 2024; 14(12):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120707
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yang, Yike Zhang, and Fei Wang. 2024. "Mediating Effects of Serum Lipids and Physical Activity on Hypertension Management of Urban Elderly Residents in China" Metabolites 14, no. 12: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120707
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wang, F. (2024). Mediating Effects of Serum Lipids and Physical Activity on Hypertension Management of Urban Elderly Residents in China. Metabolites, 14(12), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120707







