New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction: A Historical Perspective to Tissue Metabolomics
2. An Overview of Tissue Metabolomic Workflows
3. Tissue Collection and Sample Preparation
4. Instrumental Methods for Tissue Metabolomics
5. Pre-Analytical Considerations to Reduce False Discoveries in Tissue Metabolomics
6. Data Preprocessing and Statistical Analysis
7. Unknown Compound Identification via High Resolution MS/MS
8. Applications of Tissue Metabolomics in Clinical Research: Recent Advances
9. Current Challenges in Tissue Metabolomics: Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bichat, X. Recherches Physiologiques Sur La Vie et La Mort, 13th ed.; Brosson: Paris, France, 1805. [Google Scholar]
- Haigh, E. Xavier Bichat and the Medical Theory of the Eighteenth Century. Med. Hist. Suppl. 1984, 4, 1–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kün, M. A New Instrument for the Diagnosis of Tumours. Month J. Med. Sci. 1847, 853–854. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, A.J. Early Microscopy: History of Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) with Particular Reference to Goitres. Cytopathology 2001, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M. Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: A Historical Overview. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2008, 36, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.E.; Ellis, E.B. Biopsy by Needle Puncture and Aspiration. Ann. Surg. 1930, 92, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeffner, F.; Wilson, K.; Martin, N.T.; Black, J.C.; Luengo Hendriks, C.L.; Bolon, B.; Rudmann, D.G.; Gianani, R.; Koegler, S.R.; Krueger, J.; et al. The Gold Standard Paradox in Digital Image Analysis: Manual Versus Automated Scoring as Ground Truth. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelotti, G.; Machado, M.; Diehl, A. NAFLD, NASH and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoi, M.; Sasaki, K.; Sagawa, H.; Abe, K.; Kogiso, T.; Tokushige, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Ohashi, Y.; Britz-McKibbin, P. High Throughput Screening of Serum γ-Glutamyl Dipeptides for Risk Assessment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis with Impaired Glutathione Salvage Pathway. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorkas, P.A.; Abellona, U.M.R.; Li, J.V. Tissue Multiplatform-Based Metabolomics/ Metabonomics for Enhanced Metabolome Coverage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1738, 239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The Apogee of the Omics Trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond Biomarkers and Towards Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuehnbaum, N.L.; Kormendi, A.; DiBattista, A.; Lam, K.P.; Gillen, J.B.; Gibala, M.J.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Multiplexed Separations for Biomarker Discovery in Metabolomics: Elucidating Adaptive Responses to Exercise Training. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellington, N.; Shanmuganathan, M.; de Souza, R.J.; Zulyniak, M.A.; Azab, S.M.; Bloomfield, J.; Mell, A.; Ly, R.; Desai, D.; Anand, S.S.; et al. Metabolic Trajectories Following Contrasting Prudent and Western Diets from Food Provisions: Identifying Robust Biomarkers of Short-Term Changes in Habitual Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zukunft, S.; Prehn, C.; Rohring, C.; Moller, G.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Adamski, J.; Tokarz, J. High-Throughput Extraction and Quantification Method for Targeted Metabolomics in Murine Tissues. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Riano, C.; Garcia, A.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics Studies in Brain Tissue: A Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 25, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, T.D.; Zhou, M. Tissue Proteomics and Metabolomics: An Excellent Start and a Promising Future. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.M.; Reifsnyder, P.R.; Pan, H.; German, J.B.; Leiter, E.H. Lipid Metabolome-Wide Effects of the PPARgamma Agonist Rosiglitazone. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala-Korpela, M.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P. Quantitative High-throughput Metabolomics: A New Era in Epidemiology and Genetics. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Davidson, R.L.; Viant, M.R. Characterising and Correcting Batch Variation in an Automated Direct Infusion Mass Spectrometry (DIMS) Metabolomics Workflow. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, P.C.; Nagornov, K.O.; Kozhinov, A.N.; Kilgour, D.P.A.; Tsybin, Y.O.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Ellis, S.R. Increased Throughput and Ultra-high Mass Resolution in DESI FT-ICR MS Imaging Through New-generation External Data Acquisition System and Advanced Data Processing Approaches. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riquelme, G.; Zabalegui, N.; Marchi, P.; Jones, C.M.; Monge, M.E. A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC-MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows. Metabolites 2020, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Quinn, R.A. Illuminating the Dark Matter in Metabolomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12549–12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrer, T.; Zamboni, N. High-throughput Discovery Metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Erban, A.; Weber, R.J.M.; Creek, D.J.; Brown, M.; Breitling, R.; Hankemeier, T.; Goodacre, R.; Neumann, S.; Kopka, J.; et al. Mass Appeal: Metabolite Identification in Mass Spectrometry-Focused Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2012, 9, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and Considerations for the Use of System Suitability and Quality Control Samples in Mass Spectrometry Assays Applied in Untargeted Clinical Metabolomic Studies. Metabolomics 2008, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global Metabolic Profiling of Animal and Human Tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.A.; Sheth, S.G.; Chopra, S. Liver Biopsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A. Core Needle Biopsy versus Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy in Breast—A Historical Perspective and Opportunities in the Modern Era. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruening, W.; Fontananrosa, J.; Tipton, K.; Treadwell, J.R.; Launders, J.; Schoelles, K. Systematic Review: Comparative Effectiveness of Core-Needle and Open Surgical Biopsy to Diagnose Breast Lesions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Pearce, E.; Smith, K.; Lach, B. Suction-Modified Bergström Muscle Biopsy Technique: Experience with 13,500 Procedures. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padia, S.A.; Baker, M.E.; Schaeffer, C.J.; Remer, E.M.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Winans, C.; Herts, B.R. Safety and Efficacy of Sonographic-Guided Random Real-Time Core Needle Biopsy of the Liver. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2009, 37, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.E.; Smith, D.N.; Lester, S.C.; Kaelin, C.; DiPiro, P.J.; Denison, C.M.; Christian, R.L.; Harvey, S.C.; Selland, D.L.; Durfee, S.M. Large-Core Needle Biopsy of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions. JAMA 1999, 281, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Yehuda, D.; Polliack, A.; Okon, E.; Sherman, Y.; Fields, S.; Lebenshart, P.; Lotan, H.; Libson, E. Image-Guided Core-Needle Biopsy in Malignant Lymphoma: Experience with 100 Patients that Suggests the Technique Is Reliable. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 2431–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasiewica, E.; Ziemiecka, A.; Jakubowski, W.; Vojinovic, J.; Bogucevska, M.; Dobruch-Sobczak, K. Fine-Needle versus Core-Needle Biopsy—Which One to Choose in Preoperative Assessment of Focal Lesions in the Breasts? Literature Review. J. Ultrason. 2017, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, A.; Ono, J.C.; Hughes, K.S.; Pitman, M.B.; Balassanian, R. Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Palpable Breast Masses: Patterns of Clinical Use and Patient Experience. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2016, 14, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, H.; Goellner, J.R.; Johnson, D.A. Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid. A 12-Year Experience with 11,000 Biopsies. Clin. Lab. Med. 1993, 13, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gress, F.; Gottlieb, K.; Sherman, S.; Lehman, G. Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Suspected Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoi, M.; Percival, M.; Nemr, C.; Li, A.; Gibala, M.J.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Characterization of the Human Skeletal Muscle Metabolome for Elucidating the Mechanisms of Bicarbonate Ingestion on Strenuous Exercise. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, P.; Alves, A.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Nicholson, J.K.; Want, E.J. Optimization and Evaluation of Metabolite Extraction Protocols for Untargeted Metabolic Profiling of Liver Samples by UPLC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7779–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, P.; Spagou, K.; Nicholson, J.K.; Want, E.J. Technical and Biological Variation in UPLC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolic Profiling of Liver Extracts: Application in an Experimental Toxicity Study on Galactosamine. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, F.M.; Want, E.J.; Leroi, A.M.; Bundy, J.G. Cross-Platform Comparison of Caenorhabditis Elegans Tissue Extraction Strategies for Comprehensive Metabolome Coverage. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3730–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romisch-Margl, W.; Prehn, C.; Rohring, C.; Suhre, K.; Adamski, J. Procedure for Tissue Sample Preparation and Metabolite Extraction for High-Throughput Targeted Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2011, 8, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wu, H.; Tjeerdema, R.S.; Viant, M.R. Evaluation of Metabolite Extraction Strategies from Tissue Samples Using NMR Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, J.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kroezen, Z.; Shanmuganathan, M.; Ly, R.; Hart, L.; Pai, N.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Lyophilized Fecal Short-chain Fatty Acid and Electrolyte Determination by Capillary Electrophoresis with Indirect UV Detection for Assessment of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Southam, A.D.; Hines, A.; Viant, M.R. High-throughput Tissue Extraction Protocol for NMR- and MS-based Metabolomics. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 372, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.W.; Adams, K.J.; Adamski, J.; Asad, Y.; Borts, D.; Bowden, J.A.; Byram, G.; Dang, V.; Dunn, W.B.; Fernandez, F.; et al. International Ring Trial of a High Resolution Targeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics Platform for Serum and Plasma Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14407–14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Hirayama, A.; Ikeda, K.; Kita, Y.; Horie, K.; Saigusa, D.; Saito, K.; Sawada, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; et al. Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration. Metabolites 2019, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beltran, A.; Suarez, M.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Vinaixa, M.; Samino, S.; Arola, L.; Correig, X.; Yanes, O. Assessment of Compatibility between Extraction Methods for NMR- and LC/MS-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5838–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Ellis, D.I. Metabolomics: Current Analytical Platforms and Methodologies. TrAC 2005, 24, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehnbaum, N.L.; Britz-McKibbin, P. New Advances in Separation Science for Metabolomics: Resolving Chemical Diversity in a Post-genomic Era. Chem. Rev. 2013, 13, 2437–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bothwell, J.H.F.; Griffin, J.L. An Introduction to Biological Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Biol. Rev. 2011, 86, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Julia, A. Analytical Methods in Untargeted Metabolomics: State of the Art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging Applications of Metabolomics in Drug Discovery and Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snytnikova, O.A.; Khlichkina, A.A.; Sagdeev, R.Z.; Tsentalovich, Y.P. Evaluation of Sample Preparation Protocols for Quantitative NMR-based Metabolomics. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, S.; Liu, P.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Mandal, R.; Grant, J.R.; Wilson, M.; Eisner, R.; Sinelnikov, I.; Hu, X.; Luchinat, C.; et al. Accurate, Fully-automated NMR Spectral Profiling for Metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.L.; Lean, C.L.; Bogdanova, A.; Wright, S.C., Jr.; Ackerman, J.L.; Brady, T.J.; Garrido, L. Enhanced Resolution of Proton NMR Spectra of Malignant Lymph Nodes Using Magic-Angle Spinning. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.A.; He, W.; Wu, C.-L.; Cheng, L.L. Quantitative Pathology in Tissue MR Spectroscopy Based Human Prostate Metabolomics. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 3, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsang, T.M.; Griffin, J.L.; Haselden, J.; Fish, C.; Holmes, E. Metabolic Characterization of Distinct Neuroanatomical Regions in Rats by Magic Angle Spinning 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinges, S.S.; Vandergrift, L.A.; Wu, S.; Berker, Y.; Habbel, P.; Taupitz, M.; Wu, C.-L.; Cheng, L.L. Metabolomic Prostate Cancer Fields in HRMAS MRS-Profiled Histologically Benign Tissue Vary with Cancer Status and Distance from Cancer. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, F.; Bai, C. Staging Research of Human Lung Cancer Tissues by High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H NMR) and Multivariate Data Analysis. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, e232–e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukaas, T.H.; Euceda, L.R.; Giskeodegard, G.F.; Lamichhane, S.; Krohn, M.; Jernstrom, S.; Aure, M.R.; Lingjaerde, O.C.; Schlichting, E.; Garred, O.; et al. Metabolic Clusters of Breast Cancer in Relation to Gene- and Protein Expression Subtypes. Cancer Metab. 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vandergrift, L.A.; Decelle, E.A.; Kurth, J.; Wu, S.; Fuss, T.L.; DeFeo, E.M.; Halpern, E.F.; Taupitz, M.; McDougal, W.S.; Olumi, A.F.; et al. Metabolomic Prediction of Human Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness: Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Histologically Benign Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’Auria, J.; Ewald, J.C.; Ewald, J.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics: A Guide for Annotation, Quantification and Best Reporting Practices. Nat. Met. 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Gross, R.W. Shotgun Lipidomics: Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometric Analysis and Quantitation of Cellular Lipidomes Directly from Crude Extracts of Biological Samples. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 367–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; Reid, G.E. Chemical Derivatization and Ultrahigh Resolution and Accurate Mass Spectrometry Strategies for "Shotgun" Lipidome Analysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Weber, R.J.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Viant, M.R. Direct Infusion Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Dataset: A Benchmark for Data Processing and Quality Control. Sci. Data. 2014, 1, 140012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clendinen, C.S.; Monge, M.E.; Fernandez, F.M. Ambient Mass Spectrometry in Metabolomics. Analyst 2017, 142, 3101–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takats, Z.; Wiseman, J.M.; Gologan, B.; Cooks, R.G. Mass Spectrometry Sampling under Ambient Conditions with Desorption Electrospray Ionization. Science 2004, 306, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberlin, L.S.; Norton, I.; Orringer, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Liu, X.; Ide, J.L.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Ligon, K.L.; Jolesz, F.A.; Golby, A.J.; et al. Ambient Mass Spectrometry for the Intraoperative Molecular Diagnosis of Human Brain Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pirro, V.; Alfaro, C.M.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Hattab, E.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Cooks, R.G. Intraoperative Assessment of Tumor Margins During Glioma Resection by Desorption Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6700–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiraoka, K.; Nishidate, K.; Mori, K.; Asakawa, D.; Suzuki, S. Development of Probe Electrospray Using a Solid Needle. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3138–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, P.; Vertes, A. Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization for Atmospheric Pressure, in Vivo, and Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8098–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, J.; Sasi-Szabo, L.; Kinross, J.; Lewis, M.R.; Muirhead, L.J.; Veselkov, K.; Mirnezami, R.; Dezso, B.; Damjanovich, L.; Darzi, A.; et al. Intraoperative Tissue Identification Using Rapid Evaporative Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 194ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieblein-Boff, J.C.; Johnson, E.J.; Kennedy, A.D.; Lai, C.-S.; Kuchan, M.J. Exploratory Metabolomic Analyses Reveal Compounds Correlated with Lutein Concentration in Frontal Cortex, Hippocampus, and Occipital Cortex of Human Infant Brain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136904. [Google Scholar]
- Meller, S.; Meyer, H.-A.; Bethan, B.; Dietrich, D.; Gonzalez Maldonado, S.; Lein, M.; Montani, M.; Reszuka, R.; Schatz, P.; Peter, E.; et al. Integration of Tissue Metabolomics, Transcriptomics and Immunohistochemistry Reveals ERG- and Gleason Score-Specific Metabolomic Alterations in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1421–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garvey, S.M.; Dugle, J.E.; Kennedy, A.D.; McDunn, J.E.; Kline, W.; Guo, L.; Guttridge, D.C.; Pereira, S.L.; Edens, N.K. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Severe Skeletal Muscle Group-Specific Perturbations of Metabolism in Aged FBN Rats. Biogerontology 2014, 15, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Riano, C.; Tapia-Gonzalez, S.; Garcia, A.; Munoz, A.; DeFelipe, J.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics and Neuroanatomical Evaluation of Post-Mortem Changes in the Hippocampus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2831–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatazawa, Y.; Senoo, N.; Tadaishi, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Ezaki, O.; Kamei, Y.; Miura, S. Metabolomic Analysis of the Skeletal Muscle Mice Overexpressing PGC-1α. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Yachida, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Oshima, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Akamoto, S.; Tabata, S.; Saitoh, K.; Kato, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Global Metabolic Reprogramming of Colorectal Cancer Occurs at Adenoma Stage and Is Induced by MYC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7697–E7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Zeng, J.; Geng, P.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Yin, P.; Hu, C.; et al. Global Metabolic Profiling Identifies a Pivotal Role of Proline and Hydroxyproline Metabolism in Supporting Hypoxic Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saoi, M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Gohir, W.; Sloboda, D.M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. Placental Metabolomics for Assessment of Sex-specific Differences in Fetal Development During Normal Gestation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, A.; Pontis, S.; Piomelli, D.; Armirotti, A. Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry Enhances Low-abundance Species Detection in Untargeted Lipidomics. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, S.; Miurhead, L.J.; Speller, A.V.M.; Golf, O.; Strittmatter, N.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Goldin, R.D.; Jones, E.; Veselkov, K.; Nicholson, J.; et al. Spatially Resolved Metabolic Phenotyping of Breast Cancer by Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paine, M.R.L.; Kim, J.; Bennett, R.V.; Parry, R.M.; Gaul, D.A.; Wang, M.D.; Matzuk, M.M.; Fernandez, F.M. Whole Reproductive System Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Mass Spectrometry Imaging of an Early-Stage Ovarian Cancer Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, P.; Yong, T.; Wang, H.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cai, Z. MALDI-MS Imaging Reveals Asymmetric Spatial Distribution of Lipid Metabolites from Bisphenol S-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3196–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.I.; Kell, D.B. Statistical Strategies for Avoiding False Discoveries in Metabolomics and Related Experiments. Metabolomics 2006, 2, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A. Why Most Published Research Findings Are False: Author’s Reply to Goodman and Greenland. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Atherton, H.J.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Systems Level Studies of Mammalian Metabolomes: The Roles of Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 387–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, D.; Caragacianu, D.; Liu, X.; Norton, I.; Thompson, C.J.; Richardson, A.L.; Golshan, M.; Easterling, M.L.; Santagata, S.; Dillon, D.A.; et al. Application of Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging in Breast Cancer Margin Analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15184–15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudzik, D.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; Garcia, A.; Barbas, C. Quality Assurance Procedures for Mass Spectrometry Untargeted Metabolomics. A Review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.B.; Bandukwala, A.; Bethan, B.; Broadhurst, D.; Clish, C.B.; Dasari, S.; Derr, L.; Evans, A.; Fischer, S.; et al. Towards Quality Assurance and Quality Control in Untargeted Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; O’Donovan, C.; Playdon, M.; Beecher, C.; Beger, R.D.; Bowden, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.; Clish, C.B.; Dasari, S.; Dunn, W.B.; et al. Metabolomics Quality Assurance, Quality Control Consortium (mQACC). Dissemination and Analysis of the Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Practices of LC-MS based Untargeted Metabolomics Practitioners. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.A.; Heckert, A.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Jones, C.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Abdullah, L.; Ahonen, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Armando, A.M.; Asara, J.M.; et al. Harmonizing Lipidomics: NIST Interlaboratory Comparison Exercise for Lipidomics Using SRM 1950-Metabolites in Frozen Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendriks, M.M.W.B.; van Eeuwijk, F.A.; Jellema, R.H.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Reijmers, T.H.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smilde, A.K. Data-Processing Strategies for Metabolomics Studies. TrAC 2011, 30, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M. Centering, Scaling, and Transformations: Improving the Biological Information Content of Metabolomics Data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castillo, S.; Gopalacharyulu, P.; Yetukuri, L.; Oresic, M. Algorithms and Tools for the Preprocessing of LC-MS Metabolomics Data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2011, 108, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, N.G.; Patti, G.J. Systems-Level Annotation of a Metabolomics Data Set Reduces 25,000 Features to Fewer than 1000 Unique Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10397–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganathan, M.; Kroezen, Z.; Gill, B.; Azab, S.; de Souza, R.J.; Teo, K.K.; Atkinson, S.; Subbarao, P.; Desai, D.; Anand, S.S.; et al. The Maternal Serum Metabolome by Multisegment Injection-Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry: A Standardized Data Workflow for Large-scale Epidemiological Studies. Nat. Prot. 2021, 16, 1966–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, K.H. Multivariate Methods in Metabolomics—From Pre-Processing to Dimension Reduction and Statistical Analysis. TrAC 2011, 30, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, E.G.; Godzien, J.; Alonso-Herranz, V.; López-Gonzálvez, Á.; Barbas, C. Missing Value Imputation Strategies for Metabolomics Data. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B. New Software tools, Databases, and Resources in Metabolomics: Updates from 2020. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinaixa, M.; Samino, S.; Saez, I.; Duran, J.; Guinovart, J.J.; Yanes, O.A. Guideline to Univariate Statistical Analysis for LC/MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics-Derived Data. Metabolites 2012, 2, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Anfora, A.T.; Liu, J.; Schultz, P.G.; Lesley, S.A.; Peters, E.C.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Large Effects of Gut Microflora on Mammalian Blood Metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lommen, A. Ultrafast PubChem Searching Combined with Improved Filtering Rules for Elemental Composition Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5463–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, J.M.; Viant, M. Confidence in Metabolite Identification Dictates the Applicability of Metabolomics to Regulatory Toxicology. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 16, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züllig, T.; Köfeler, H.C. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry in Lipidomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 40, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Djoumbou Feunang, Y.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN: A Metabolite Mass Spectral Database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Fahy, E.; Aoki, J.; Dennis, E.A.; Durand, T.; Ejsing, C.S.; Fedorova, M.; Feussner, I.; Griffiths, W.J.; Köfeler, H.; et al. Update On LIPID MAPS Classification, Nomenclature, and Shorthand Notation for MS-derived Lipid Structures. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stancliffe, E.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Sindelar, M.; Patti, G.J. DecoID Improves Identification Rates in Metabolomics Through Database-assisted MS/MS Deconvolution. Nat. Meth. 2021, 18, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.P.; Heo, D.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, J.G.; Lee, A.; Kim, D.H. Metabolomics-guided Global Pathway Analysis Reveals Better Insights into the Metabolic Alterations of Breast Cancer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 202, 114134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumsiek, J.; Suhre, K.; Evans, A.M.; Mitchell, M.W.; Mohney, R.P.; Milburn, M.V.; Wägele, B.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Illig, T.; Adamski, J.; et al. Mining the Unknown: A Systems Approach to Metabolite Identification Combining Genetic and Metabolic Information. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Torbašinović, H.; Obrenović, S.; Mehta, S.S.; Tsugawa, H.; Wermuth, T.; Schauer, N.; Jahn, M.; Biedendieck, R.; et al. Comprehensive Comparison of In Silico MS/MS Fragmentation Tools of The CASMI Contest: Database Boosting Is Needed to Achieve 93% Accuracy. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Kondić, T.; Neumann, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Bolton, E.E. Empowering Large Chemical Knowledge Bases for Exposomics: PubChemLite Meets MetFrag. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Ikeda, S.; Niigata, K.; Tomita, M.; Sato, H.; Soga, T. MMMDB: Mouse Multiple Tissue Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D809–D814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, A.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Mandal, R.; Piri-Moghadam, H.; Zheng, J.; Guo, A.; Li, C.; Guan, L.L.; Wishart, D.S. The Bovine Metabolome. Metabolites 2020, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganathan, M.; Sarfaraz, M.O.; Kroezen, Z.; Philbrick, H.; Poon, R.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Puglia, M.; Wishart, D.; Britz-McKibbin, P. A Cross-platform Metabolomics Comparison Identifies Serum Metabolite Signatures of Liver Fibrosis Progression from Chronic Hepatitis C Patients. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 676349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles Delineate Potential Role for Sarcosine in Prostate Cancer Progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jentzmik, F.; Stephan, C.; Miller, K.; Schrader, M.; Erbersdobler, A.; Kristiansen, G.; Lein, M.; Jung, K. Sarcosine in Urine after Digital Rectal Examination Fails as a Marker in Prostate Cancer Detection and Identification of Aggressive Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankerst, D.P.; Liss, M.; Zapata, D.; Hoefler, J.; Thompson, I.M.; Leach, R.J. A Case Control Study of Sarcosine as an Early Prostate Cancer Detection Biomarker Urological Oncology. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vogel, S.; Ulvik, A.; Meyer, K.; Ueland, P.M.; Nygard, O.; Vollset, S.E.; Tell, G.S.; Gregory, J.F.; Tretli, S.; Bjorge, T. Sarcosine and Other Metabolites along the Choline Oxidation Pathway in Relation to Prostate Cancer—A Large Nested Case-Control Study within the JANUS Cohort in Norway. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schalken, J.A. Is Urinary Sarcosine Useful to Identify Patients with Significant Prostate Cancer? The Trials and Tribulations of Biomarker Development. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.M.; Niehaus, K.; Neumann, N.; Knobloch, H.C.; Bremmer, F.; Krafft, U.; Kellner, U.; Nyirady, P. Szarvas, T. A New Technological Approach in Diagnostic Pathology: Mass Spectrometry Imaging-based Metabolomics for Biomarker Detection in Urachal Cancer. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglik, A.; Koyuncu, I.; Gonel, A.; Yalcin, H.; Adibelli, F.M.; Toptan, M. Metabolomics Analysis in Pterygium Tissue. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuthold, P.; Schaeffeler, E.; Winter, S.; Buttner, F.; Hofmann, U.; Murdter, T.E.; Rausch, S.; Sonntag, D.; Wahrheit, J.; Fend, F.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling of Human Kidney Tissue: A Platform Comparison. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Takasaki, S.; Saigusa, D.; Ota, H.; Shimada, S.; Yamashita, S.; Mitsuzuka, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Value of Global Metabolomics in Association with Diagnosis and Clinicopathological Factors of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaffy, T.; Duncan, R.; Riemer, D.D.; Tietje, O.; Elgart, G.; Milikowski, C.; Defazio, A. Differential Volatile Signatures from Skin, Naevi and Melanoma: A Novel Approach to Detect a Pathological Process. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashrafi, M.; Xu, Y.; Muhamadali, H.; White, I.; Wilkinson, M.; Hollywood, K.; Goodacre, R.; Bayat, A. A Microbiome and Metabolomic Signature of Phases of Cutaneous Healing Identified by Profiling Sequential Acute Wounds of Human Skin: An Exploratory Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.D.; Reeves, R.; Resar, L.S.; Hill, H.H., Jr. Metabolomics of Colorectal Cancer: Past and Current Analytical Platforms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5013–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, B.A.; Parker, K.D.; Nosler, M.J.; Rao, S.; Craig, R.; Seiler, C.; Ryan, E.P. Metabolite Profile Comparisons between Ascending and Descending Colon Tissue in Healthy Adults. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, M.F.; Chua, E.G.; Gan, H.M.; Thulasi, K.; Wanyiri, J.W.; Thevambiga, I.; Lee Goh, K.; Wong, W.F.; Vadivelu, J. Metabolomics and 16S rRNA Sequencing of Human Colorectal Cancers and Adjacent Mucosa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Dejea, C.M.; Edler, D.; Hoang, L.T.; Santidrian, A.F.; Felding, B.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Cho, K.; Wick, E.C.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; et al. Metabolism Links Bacterial Biofilms and Colon Carcinogenesis. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walejko, J.M.; Chelliah, A.; Keller-Wood, M.; Gregg, A.; Edison, A.S. Global Metabolomics of the Placenta Reveals Distinct Metabolic Profiles Between Maternal and Fetal Placental Tissues Following Delivery in Non-Labored Women. Metabolites 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fattuoni, C.; Mandò, C.; Palmas, F.; Anelli, G.M.; Novielli, C.; Parejo Laudicina, E.; Savasi, V.M.; Barberini, L.; Dessì, A.; Pintus, R.; et al. Preliminary Metabolomics Analysis of Placenta in Maternal Obesity. Placenta 2018, 61, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmugl, B.; Desoye, G.; Catalano, P.; Klymiuk, I.; Scharnagl, H.; Payr, S.; Kitzinger, E.; Schliefsteiner, C.; Lang, U.; Wadsack, C.; et al. Maternal Obesity Modulates Intracellular Lipid Turnover in the Human Term Placenta. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neeland, I.J.; Boone, S.C.; Mook-Kanamori, D.O.; Ayers, C.; Smit, R.A.J.; Tzoulaki, I.; Karaman, I.; Boulange, C.; Vaidya, D.; Punjabi, N.; et al. Metabolomics Profiling of Visceral Adipose Tissue: Results from MESA and the NEO Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorkas, P.A.; Issac, G.; Anwar, M.A.; Davies, A.H.; Want, E.J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E. Untargeted UPLC-MS Profiling Pipeline to Expand Tissue Metabolome Coverage: Application to Cardiovascular Disease. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Han, W.; Chan, W.; Li, L. Metabolomic Coverage of Chemical-Group-Submetabolome Analysis: Group Classification and Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12108–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, T.; Troyer, D.A.; Li, L. Metabolite Analysis and Histology on the Exact Same Tissue: Comprehensive Metabolomic Profiling and Metabolic Classification of Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, T. Spatial Metabolomics and Imaging Mass Spectrometry in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2020, 3, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; He, J.; Mao, X.; Bu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Guo, C.; Tang, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; et al. In Situ Biomarker Discovery and Label-Free Molecular Histopathological Diagnosis of Lung Cancer by Ambient Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilvo, M.; de Santiago, I.; Gopalacharyulu, P.; Schmitt, W.D.; Budczies, J.; Kuhberg, M.; Dietel, M.; Aittokallio, T.; Markowetz, F.; Denkert, C.; et al. Accumulated Metabolites of Hydroxybutyric Acid Serve as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Ovarian High-Grade Serous Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, K.; Zeng, S.; Mao, W. Tissue-Based Metabolomics Reveals Metabolic Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 197, 113937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletcher, M.J.; Pignone, M. Evaluating the Clinical Utility of a Biomarker: A Review of Methods for Estimating Health Impact. Circulation 2011, 123, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
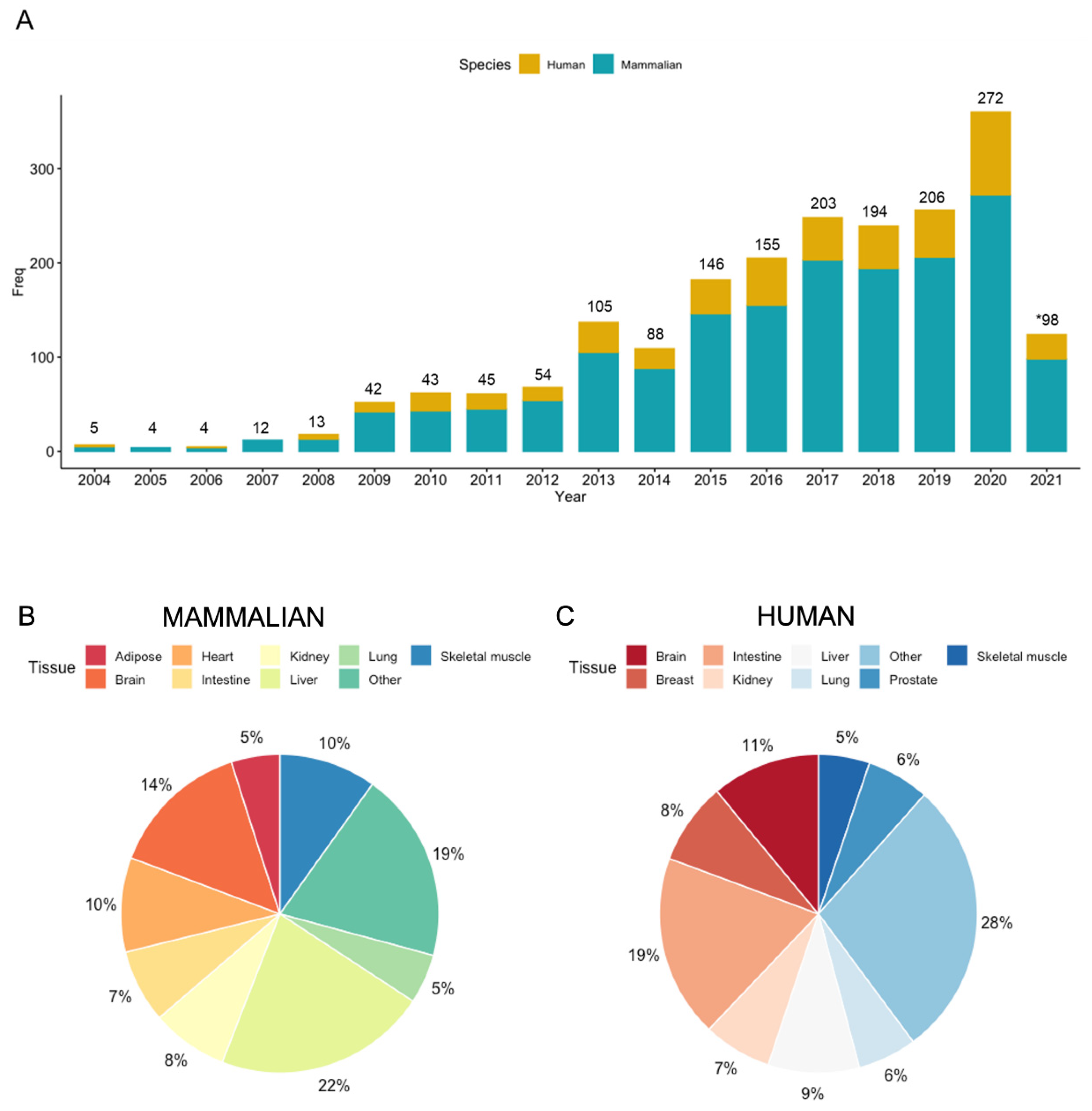





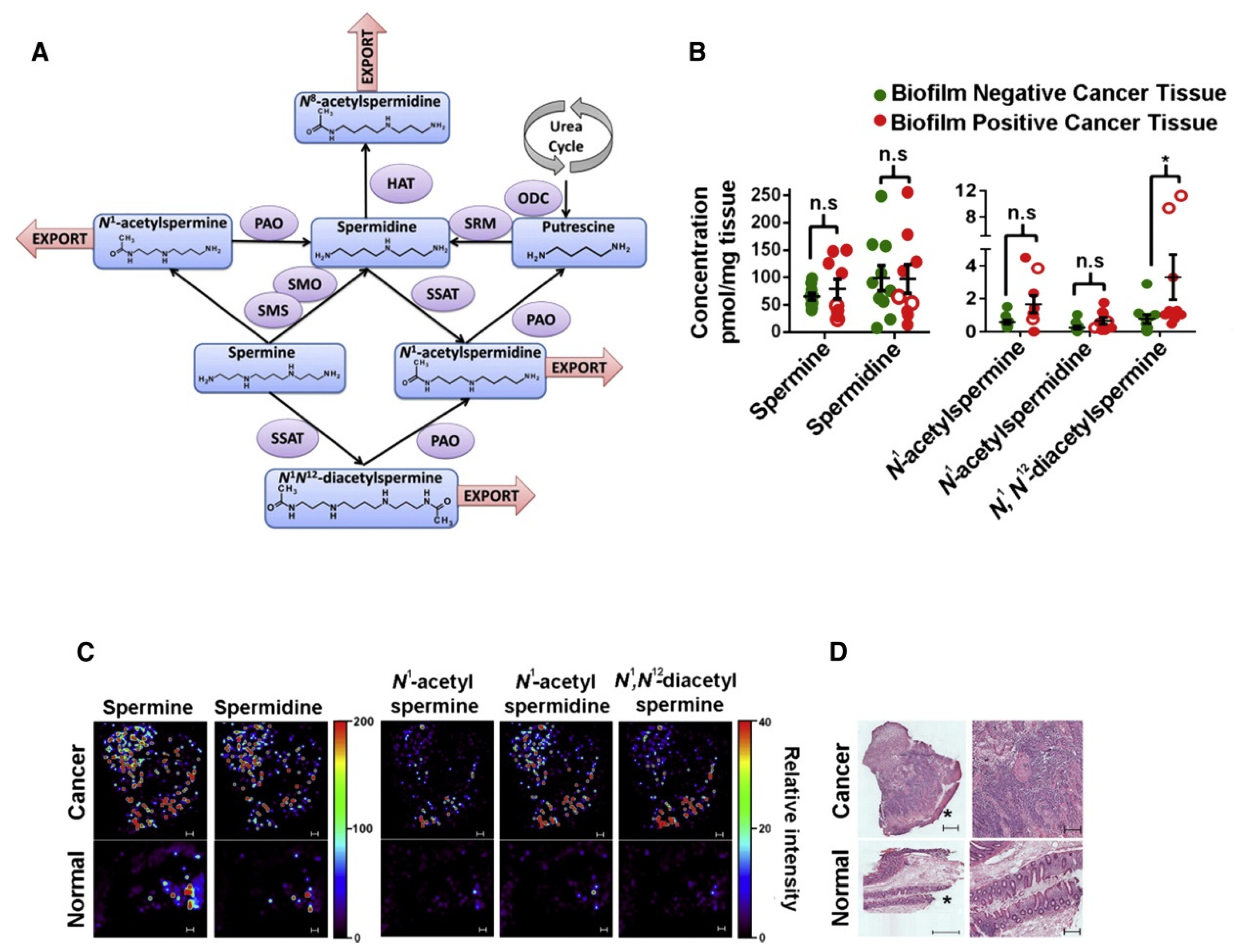
| Analytical Platform | Tissue Type | Sample Size | Unique Features | Key Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-MS | Kidney | n = 5 | Global analysis of metabolites and lipids by RP/HILIC | >1000 features reliably measured in kidney tissue with differentiation of malignant from non-cancerous tissue | Leuthold et al., 2017 |
| LC-MS | Colon | n = 24 | Analysis of ascending versus descending colon tissue | Colon lipids and metabolites elevated in obese/overweight as compared to normal weight with distinct regional differences in colon profiles | Baxter et al., 2020 |
| LC-MS | Esophagus | n = 211 | Validation of biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Diagnostic/predictive metabolites with good accuracy that also provide insights into esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue calcification | Chen et al., 2021 |
| GC-MS | Skin wound | n = 11 | Novel tissue specimen and sampling method | Dynamic microbiome and metabolome analysis of >346 features during normal wound healing using patch sampling | Ashrafi et al., 2020 |
| GCxGC-MS | Ovaries | n = 224 | Predictive biomarkers of ovarian tumor burden and patient survival | Accumulation of hydroxybutyric acids with strong predictive ability of patient survival prior to surgery as confirmed by gene expression data | Hilvo et al., 2016 |
| NMR | Placenta | n = 13 | Novel tissue specimen from non-labored pregnancies | Differentiation of maternal and fetal placental tissue reflecting flux from mother to fetus following delivery | Walejko et al., 2018 |
| NMR | Adipose | n = 3640 | Visceral adipose tissue extract analysis in two large cohorts | Validation of a metabolite/lipid signature of visceral adiposity that persisted after adjustment for BMI | Neeland et al., 2019 |
| HRMAS-NMR | Prostate | n = 365 | Direct analysis of tumor grade and stage of prostate cancer | Differential analysis revealed metabolites were upregulated in tumor tissues with elevated myo-inositol | Vandergrift et al., 2018 |
| DESI-MS | Brain smears | n = 73 | Spatial imaging of tumor margins for resection | High tumor cell percentage at surgical margins with 93% sensitivity and 83% specificity for safe tumour resection | Pirro et al., 2017 |
| DI-MS | Cardiac | n = 20 | Best practice data workflows and rigorous quality assurance | 8 batches of cardiac tissue extracts acquired over 7 days with inter-batch adjustment with QC spectra | Kirwan et al., 2014 |
| MSI-CE-MS | Skeletal muscle | n = 14 | Repeat muscle tissue biopsies in cross-over study using a multiplexed CE-MS platform | Modest treatment effect from bicarbonate intake prior to exercise with intramuscular changes in potassium, uric acid, oxidized mixed glutathione and anserine | Saoi et al., 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saoi, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review. Metabolites 2021, 11, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11100672
Saoi M, Britz-McKibbin P. New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review. Metabolites. 2021; 11(10):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11100672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaoi, Michelle, and Philip Britz-McKibbin. 2021. "New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review" Metabolites 11, no. 10: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11100672
APA StyleSaoi, M., & Britz-McKibbin, P. (2021). New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review. Metabolites, 11(10), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11100672







