Sound Insulation Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Floor Systems Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper proposes a data-driven methodology that enables accurate prediction of automotive floor system sound insulation performance, creating a direct mapping from structural and material parameters to system-level acoustic characteristics. It breaks through the limitations of traditional simulation analysis that relies on a large number of calculations and experimental verifications. It significantly enhances modeling efficiency without compromising prediction accuracy, thereby offering a promising alternative for NVH development in the early vehicle design phase.
- The SE-ResNet model is constructed by combining the channel attention mechanism with the ResNet, which effectively enhances the performance of key acoustic features and improves the generalization performance of the model. This approach effectively captures the intricate interactions within complex acoustic structures, a challenge for traditional deep learning models, while maintaining interpretability. It thereby delivers more actionable insights to guide acoustic package design and optimization decisions.
2. The Proposed Method
2.1. ResNet
2.2. SE-ResNet
3. Experiment
4. Model Development
4.1. Development of SE-Resnet Model
4.2. Prediction of SE-Resnet Model
5. Result and Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Prediction Model
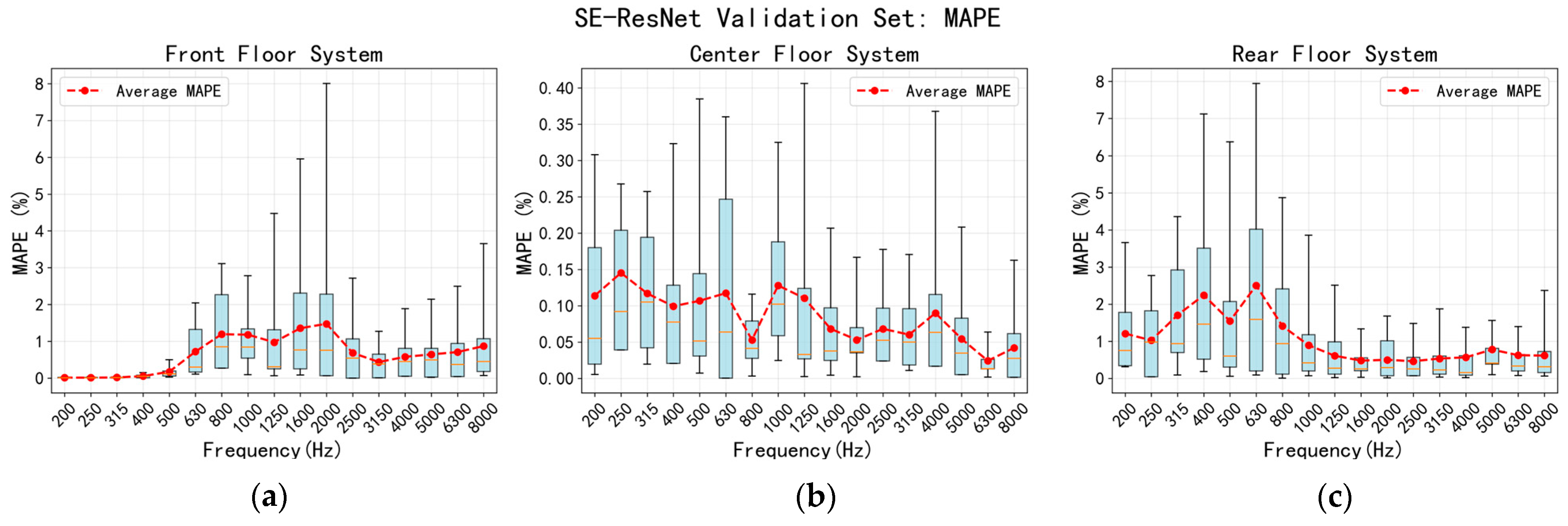
5.2. Validation of the Prediction Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, X.; Pang, J. Vehicle vibro-acoustical comfort optimization using a multi-objective interval analysis method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soresini, F.; Barri, D.; Ballo, F.; Manzoni, S.; Gobbi, M.; Mastinu, G. Vibration, and Harshness Countermeasures of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Viscoelastic Layer Material. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2025, 9, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilevicius, A.; Karpenko, M.; Krivanek, V. Research on the Noise Pollution from Different Vehicle Categories in the Urban Area. Transport 2023, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, M.; Prentkovskis, O.; Skackauskas, P. Analysing the impact of electric kick-scooters on drivers: Vibration and frequency transmission during the ride on different types of urban pavements. Eksploat. I Niezawodn.-Maint. Reliab. 2025, 27, 199893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Liu, X.; Peng, C.; Cai, K.; Yan, J.; Huang, H. Prediction of vehicle front wall sound insulation performance using Wasserstein generative adversarial network and Res-InceptionNet. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D—J. Automob. Eng. 2025, 09544070251359709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Cheng, S.; Sun, M.; Ren, C.; Song, J.; Huang, H. Prediction of Sound Transmission Loss of Vehicle Floor System Based on 1D-Convolutional Neural Networks. Sound Vib. 2024, 58, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dai, P.; Yin, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H. Predicting and optimizing pure electric vehicle road noise via a locality-sensitive hashing transformer and interval analysis. ISA Trans. 2025, 157, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Zhang, C. Research on the Influence of Door and Window Sealing on Interior Wind Noise Based on Statistical Energy Analysis. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2025, 9, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, F.; Gu, C.; Hao, Y. Highly Efficient Robust Optimization Design Method for Improving Automotive Acoustic Package Performance. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2020, 4, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, C.T.; Manning, J.E.; Peng, G.C. Predicting Vehicle Interior Sound with Statistical Energy Analysis. Sound Vib. 2012, 46, 8–14. Available online: http://www.sandv.com/downloads/1212muss.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Wu, W.; Ding, P.; Zi, X.; Liu, B. An Acoustic Target Setting and Cascading Method for Vehicle Trim Part Design; SAE Technical Paper 2019-01-1581; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Fard, M.; Davy, J.L. Prediction of the acoustic effect of an interior trim porous material inside a rigid-walled car air cavity model. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 165, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeon, J.H.; Kang, Y.J. Application of global sensitivity analysis to statistical energy analysis: Vehicle model development and transmission path contribution. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 146, 368–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmani, H.; Khalkhali, A.; Mohsenifar, A. A practical procedure for vehicle sound package design using statistical energy analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D–J. Automob. Eng. 2023, 237, 3054–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, C.; Zhong, C.; Wang, L.; Han, H.; Deng, L. Optimization of pickup truck engine noise based on SEA and ENR methods. J. Vib. Shock. 2025, 44, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, W.; Cao, S.; Luo, X. Design and optimization of acoustic packages using RSM coupled with range analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D–J. Automob. Eng. 2025, 239, 4345–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, W.; Yang, M. Multi-Objective Prediction and Optimization of Vehicle Acoustic Package Based on ResNet Neural Network. Sound Vib. 2023, 57, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Luo, T.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. A multi-dimensional driving condition recognition method for data-driven vehicle noise and vibration platform based on speed separation strategy and deep learning model. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 236, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Ding, W.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J. Optimization of electric vehicle sound package based on LSTM with an adaptive learning rate forest and multiple-level multiple-object method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 187, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Ding, W. Exploratory study on sound quality evaluation and prediction for engineering machinery cabins. Measurement 2025, 253, 117684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yin, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Ding, W.; Huang, H. Evaluation and prediction of vibration comfort in engineering machinery cabs using random forest with genetic algorithm. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2024, 8, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, N.; Bergen, B.; Keppens, T.; Desmet, W. A Design Space Exploration Framework for Automotive Sound Packages in the Mid-Frequency Range. In Proceedings of the SAE 2017 Noise and Vibration Conference and Exhibition, NVC 2017, Grand Rapids, MI, USA, 13–15 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Hu, F.; Zeng, F.; Wei, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J. Research of transfer path analysis based on contribution factor of sound quality. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yan, J.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Pan, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, P. The Prediction of Sound Insulation for the Front Wall of Pure Electric Vehicles Based on AFWL-CNN. Machines 2025, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Mao, T.; Jia, W.; Jia, X.; Dai, P.; Huang, H. Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Interior Road Noise Based on Mechanism and Data Series Modeling. Sound Vib. 2024, 58, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, M.; Ding, W. Sound quality prediction and improving of vehicle interior noise based on deep convolutional neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 160, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Hong, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, K.; Song, Y. Correlation Analysis of Noise, Vibration, and Harshness in a Vehicle Using Driving Data Based on Big Data Analysis Technique. Sensors 2022, 22, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xiong, X.; Shen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Small-sample and imbalanced milling chatter detection: Improved GAN with attention and hybrid deep learning. Sound Vib. 2025, 59, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, M.A.; Behrmann, M.; Egan, R.; Minshew, N.J.; Carrasco, M.; Heeger, D.J. Endogenous Spatial Attention: Evidence for Intact Functioning in Adults With Autism. Autism Res. 2025, 6, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, W. Hybrid attention based vehicle trajectory prediction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D—J. Automob. Eng. 2024, 238, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bender, G.; Le, Q.V.; Ngiam, J. CondConv: Conditionally Parameterized Convolutions for Efficient Inference. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 1296–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.B.; Li, R.X.; Yang, M.L.; Lim, T.C.; Ding, W.P. Evaluation of vehicle interior sound quality using a continuous restricted Boltzmann machine-based DBN. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 84, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y. A Multiscale Model Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation Network for Classifying Obstacles in Front of Vehicles in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 14219–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, P.; Yonghui, L. A High Resolution Convolutional Neural Network with Squeeze and Excitation Module for Automatic Modulation Classification. China Commun. 2024, 21, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shan, P.; Miao, L.; Sun, P.; Peng, S. PSigmoid: Improving squeeze-and-excitation block with parametric sigmoid. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 7427–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Hancock, E.R.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W. Pooling Attention-based Encoder-Decoder Network for semantic segmentation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Fan, D.; Pang, J. Uncertainty optimization of pure electric vehicle interior tire/road noise comfort based on data-driven. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 165, 108300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Research on Vehicle Road Noise Prediction Based on AFW-LSTM. Machines 2025, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lim, T.C.; Wu, J.; Ding, W.; Pang, J. Multitarget prediction and optimization of pure electric vehicle tire/road airborne noise sound quality based on a knowledge- and data-driven method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, J. Engineering vibration recognition using CWT-ResNet. Sound Vib. 2025, 59, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafapourtehrany, M.; Rezaie, F.; Jun, C.; Heggy, E.; Bateni, S.M.; Panahi, M.; Özener, H.; Shabani, F.; Moeini, H. Mapping Post-Earthquake Landslide Susceptibility Using U-Net, VGG-16, VGG-19, and Metaheuristic Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. Analysis on the Relationship between Convolutional Network Depth and Model Performance in Tree Species Classification. Forests 2022, 13, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-Seol, K. Vehicle Detection Algorithm Using Super Resolution Based on Deep Residual Dense Block for Remote Sensing Images. J. Broadcast Eng. 2023, 28, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M. SE-ResNet based disturbance identification algorithm for microthrust measurement system. AIP Adv. 2025, 15, 065111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Dai, P.; Yang, M.; Jia, W.; Jia, X.; Huang, H. Research on maglev vibration isolation technology for vehicle road noise control. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2022, 6, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, R.; Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Ying, Q.; Huang, H. Physics-informed GRU model for vehicle road noise prediction: Integrating transfer path analysis and hybrid data. Sound Vib. 2025, 59, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J1400-2023; Laboratory Measurement of the Airborne Sound Barrier Performance of Flat Materials and Assemblies. SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2023.
- Huang, Y.; Boerboom, M.; Wolff, K.; Bengt, J. Find Optimal Suspension Kinematics Targets for Vehicle Dynamics Using Reinforcement Learning. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2025, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, R.; Strano, S.; Terzo, M.; Tordela, C. Enhancing Roll Reduction in Road Vehicles on Uneven Surfaces through the Fusion of Proportional Control and Reinforcement Learning. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2025, 9, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ding, W.; Pang, J. Prediction and optimization of pure electric vehicle tire/road structure-borne noise based on knowledge graph and multi-task ResNet. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.R.; Saharkhiz, A.; Milani, S.; Fu, C.; Jazar, R.; Marzbani, H. Analysis for Comfortable Handling and Motion Sickness Minimization in Autonomous Vehicles Using Ergonomic Path Planning with Cost Function Evaluation. SAE Int. J. Connect. Autom. Veh. 2022, 5, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Lim, T.C.; Yang, M.; Ding, W. Pure electric vehicle nonstationary interior sound quality prediction based on deep CNNs with an adaptable learning rate tree. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 148, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Components | Area (m2) | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carpet | 2.74 | 98 |
| Trunk Carpet | 1.10 | 78 |
| Rear Floor Carpet | 0.3 | 21 |
| Front Floor Metal | 2.80 | / |
| Center Floor Metal | 0.64 | / |
| Rear Floor Metal | 1.41 | / |
| Thickness (mm) | Carpet | Trunk Carpet | Rear Floor Carpet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The proportion of each thickness area of the acoustic package | 0 | T ≤ 2.5 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 2.5 < T ≤ 7.5 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 10 | 7.5 < T ≤ 12.5 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 1.00 | |
| 15 | 12.5 < T ≤ 17.5 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | |
| 20 | 17.5 < T ≤ 22.5 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 25 | 22.5 < T ≤ 27.5 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 30 | 27.5 < T ≤ 32.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 35 | 32.5 < T ≤ 37.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 40 | 37.5 < T ≤ 42.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Equivalent Thickness | 18.95 | 4.00 | 10.00 | ||
| Thickness (mm) | Front Floor Metal | Center Floor Metal | Rear Floor Metal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (m2) | 2.80 | 0.64 | 1.41 | |
| The proportion of each thickness area of sheet metal | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.7 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 0.8 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| 0.9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.2 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.5 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.7 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1.9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 2.1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 2.2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Equivalent Thickness | 0.91 | 1.06 | 0.80 | |
| Components | Equivalent Thickness (mm) | Area (m2) | Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carpet | 18.95 | 2.74 | 98 |
| Trunk Carpet | 4.00 | 1.10 | 78 |
| Rear Floor Carpet | 10.00 | 0.3 | 21 |
| Front Floor Metal | 0.91 | 2.80 | 0 |
| Center Floor Metal | 1.06 | 0.64 | 0 |
| Rear Floor Metal | 0.80 | 1.41 | 0 |
| Network Layer | Parameter | Parameter Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Input layer | / | / |
| SE-Res Block 1 | Convolution Kernel | 16 × 6 × 2 |
| SE-Res Block 2 | Convolution Kernel | 32 × 16 × 2 |
| SE-Res Block 3 | Convolution Kernel | 64 × 32 × 1 |
| Global Pooling | / | / |
| Fully connected layer 1 | Weight Matrix | 64 × 32 |
| Fully connected layer 2 | Weight Matrix | 32 × 13 |
| Output layer | / | 13 |
| Set | RMSE (dB) | CORR |
|---|---|---|
| Train Set | 0.3243 | 0.9997 |
| Test Set | 0.4048 | 0.9996 |
| Prediction Model | RMSE (dB) | CORR |
|---|---|---|
| SE-ResNet | 0.4048 | 0.9996 |
| SE-CNN | 0.9207 | 0.9979 |
| SE-LSTM | 0.4591 | 0.9995 |
| ResNet | 0.6493 | 0.9990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Ding, W. Sound Insulation Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Floor Systems Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Method. Electronics 2026, 15, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010184
Ma Y, Wang J, Pan D, Zhao W, Yang X, Liu X, Yan J, Ding W. Sound Insulation Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Floor Systems Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Method. Electronics. 2026; 15(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yan, Jingjing Wang, Dianlong Pan, Wei Zhao, Xiaotao Yang, Xiaona Liu, Jie Yan, and Weiping Ding. 2026. "Sound Insulation Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Floor Systems Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Method" Electronics 15, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010184
APA StyleMa, Y., Wang, J., Pan, D., Zhao, W., Yang, X., Liu, X., Yan, J., & Ding, W. (2026). Sound Insulation Prediction and Analysis of Vehicle Floor Systems Based on Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Method. Electronics, 15(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010184







