Microstructural and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analyses on Argon Ion Implantations in Tantalum Thin Films for Microelectronic Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
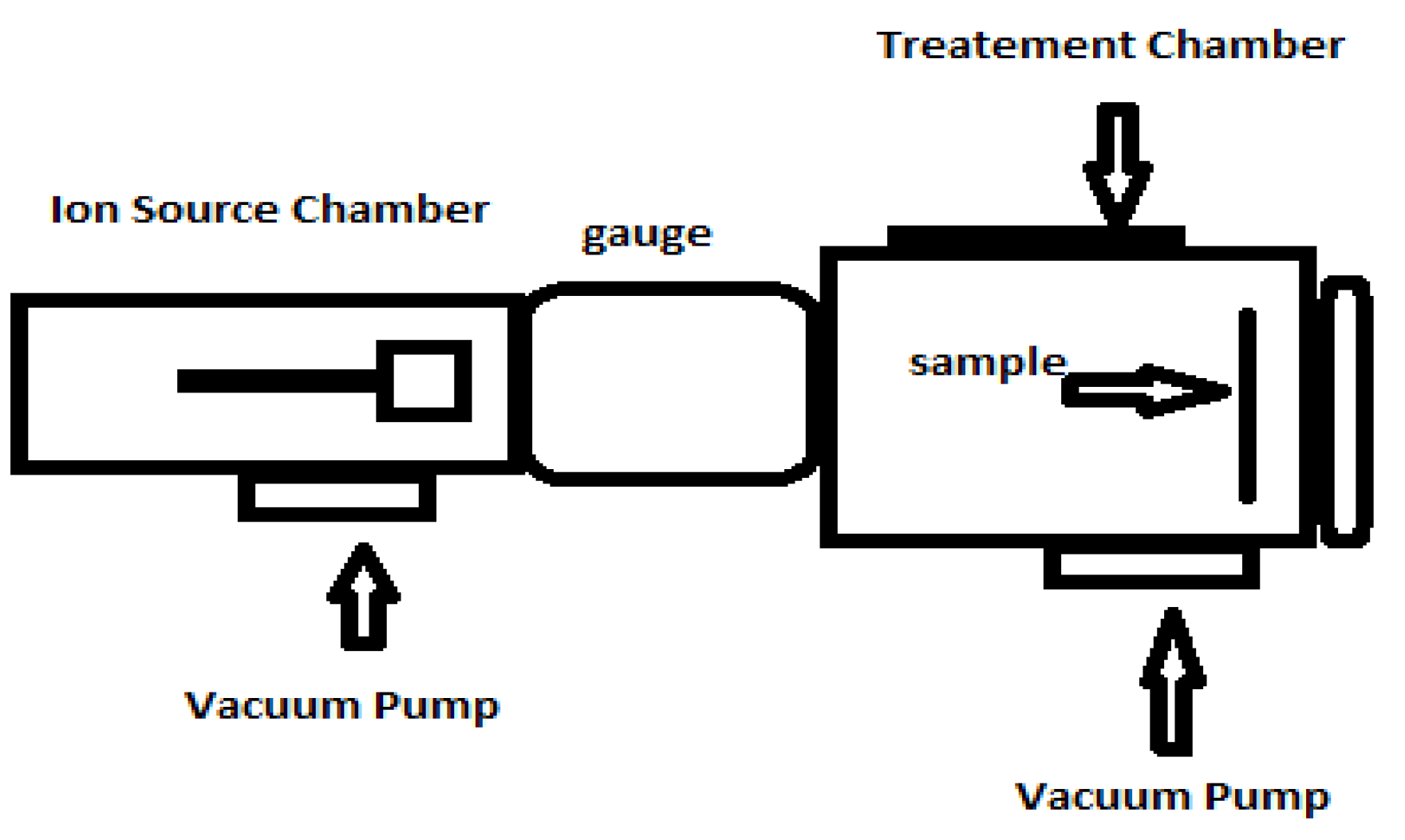
2. Materials and Methods
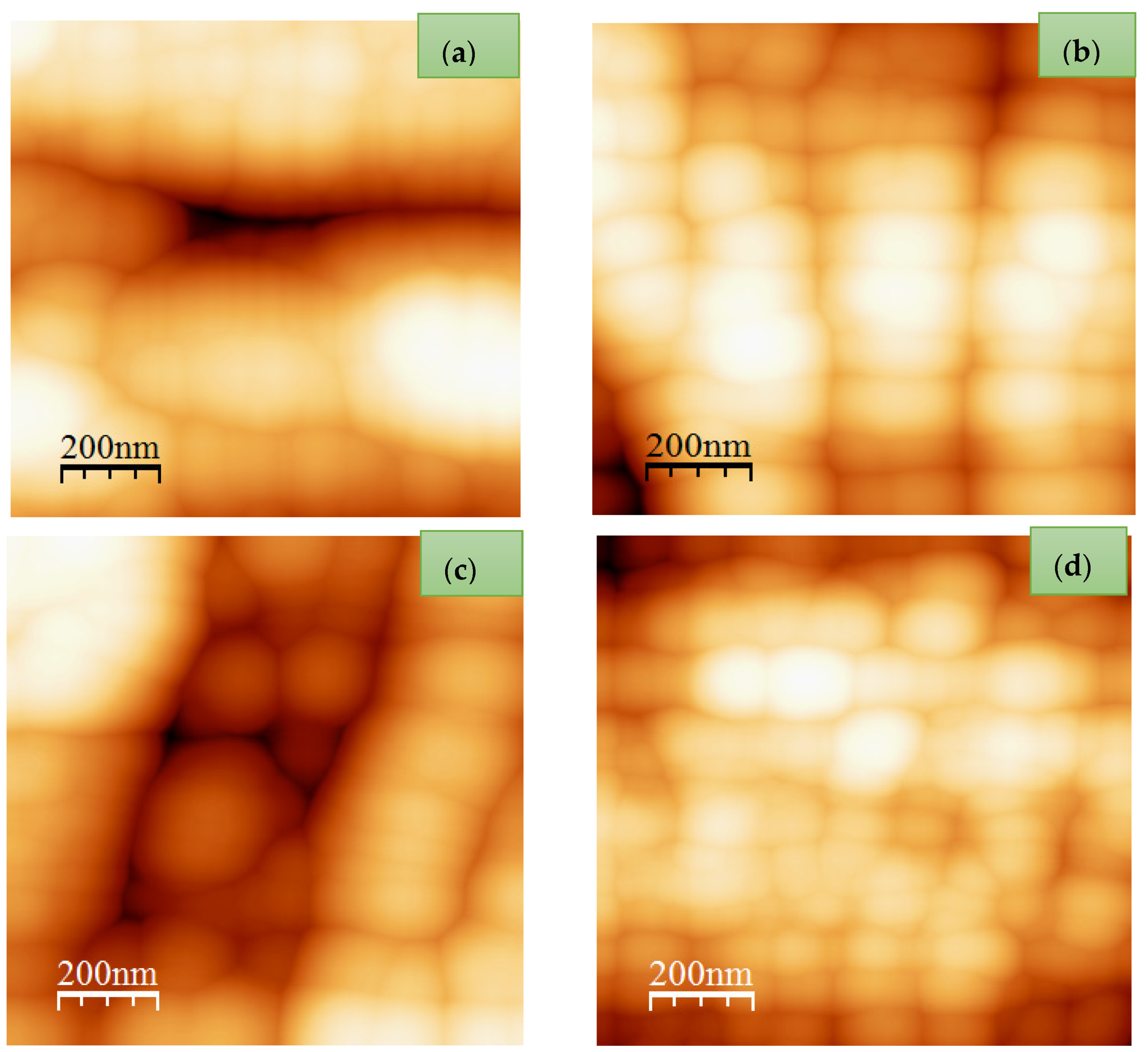
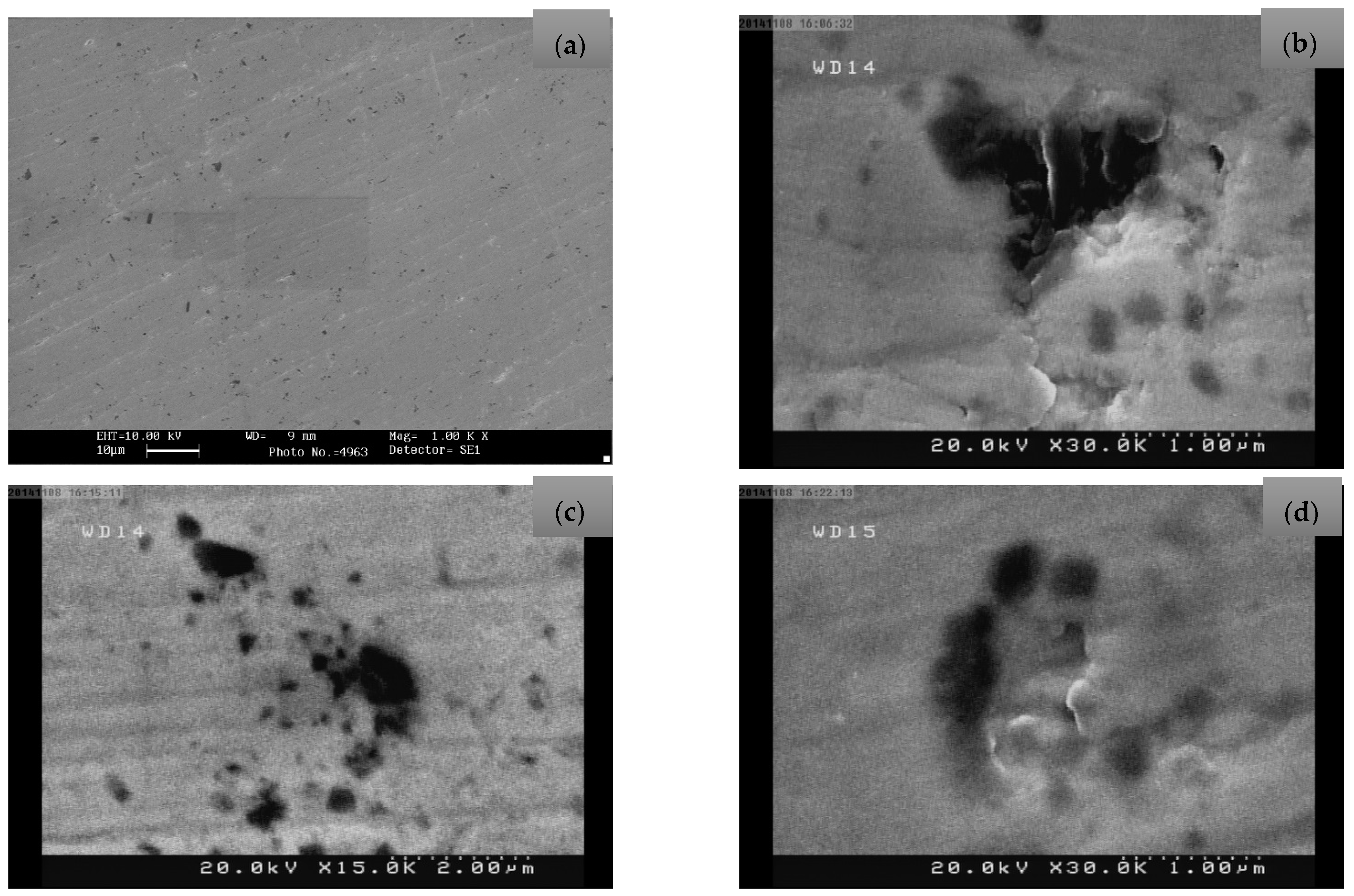
Preparation of Argon Ion-Implanted Tantalum Thin Film with SEM and AFM Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Monofractal Analysis of Roughness Based on Statistical Properties at Various Argon Ion Implanted Doses
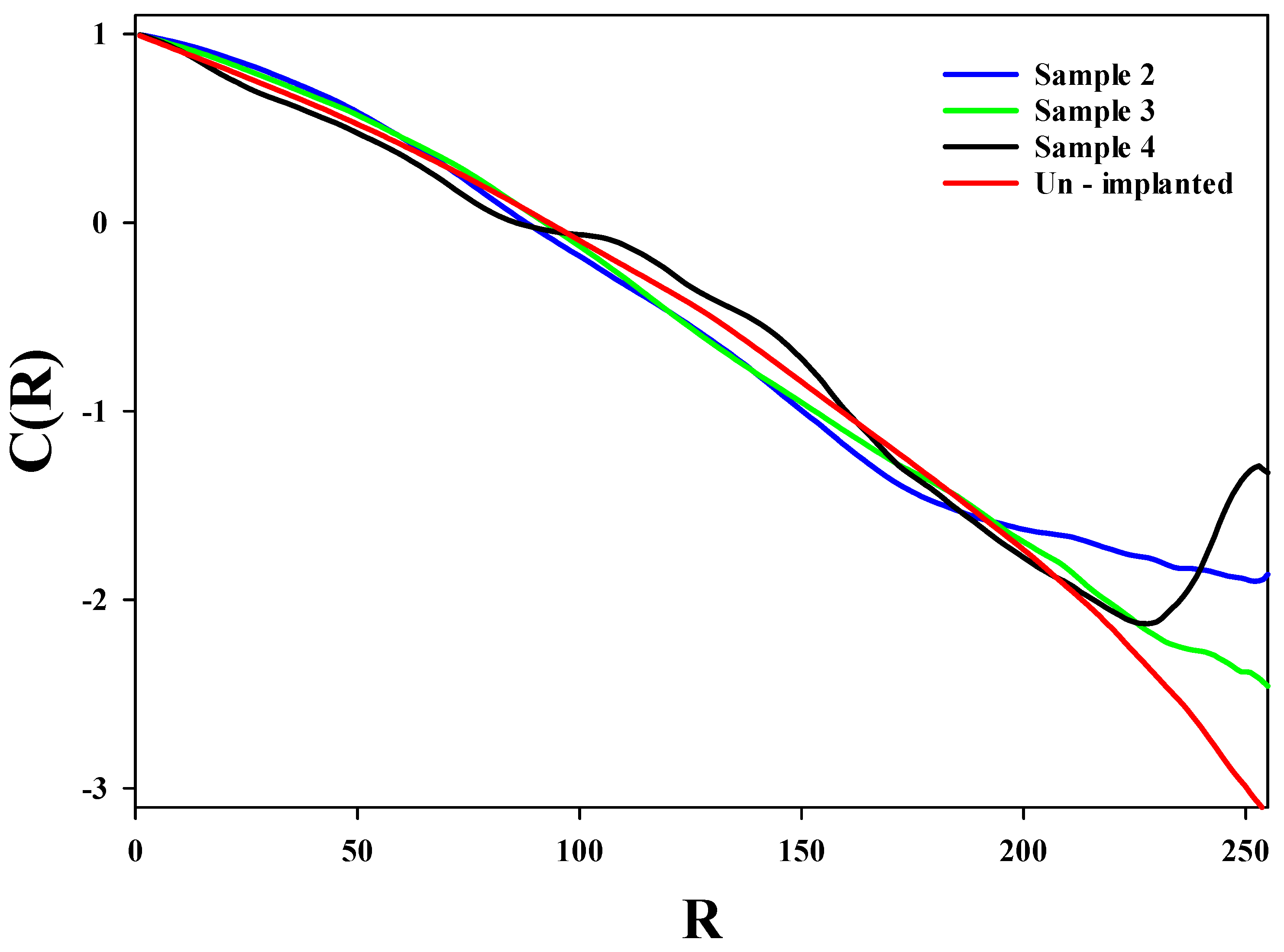
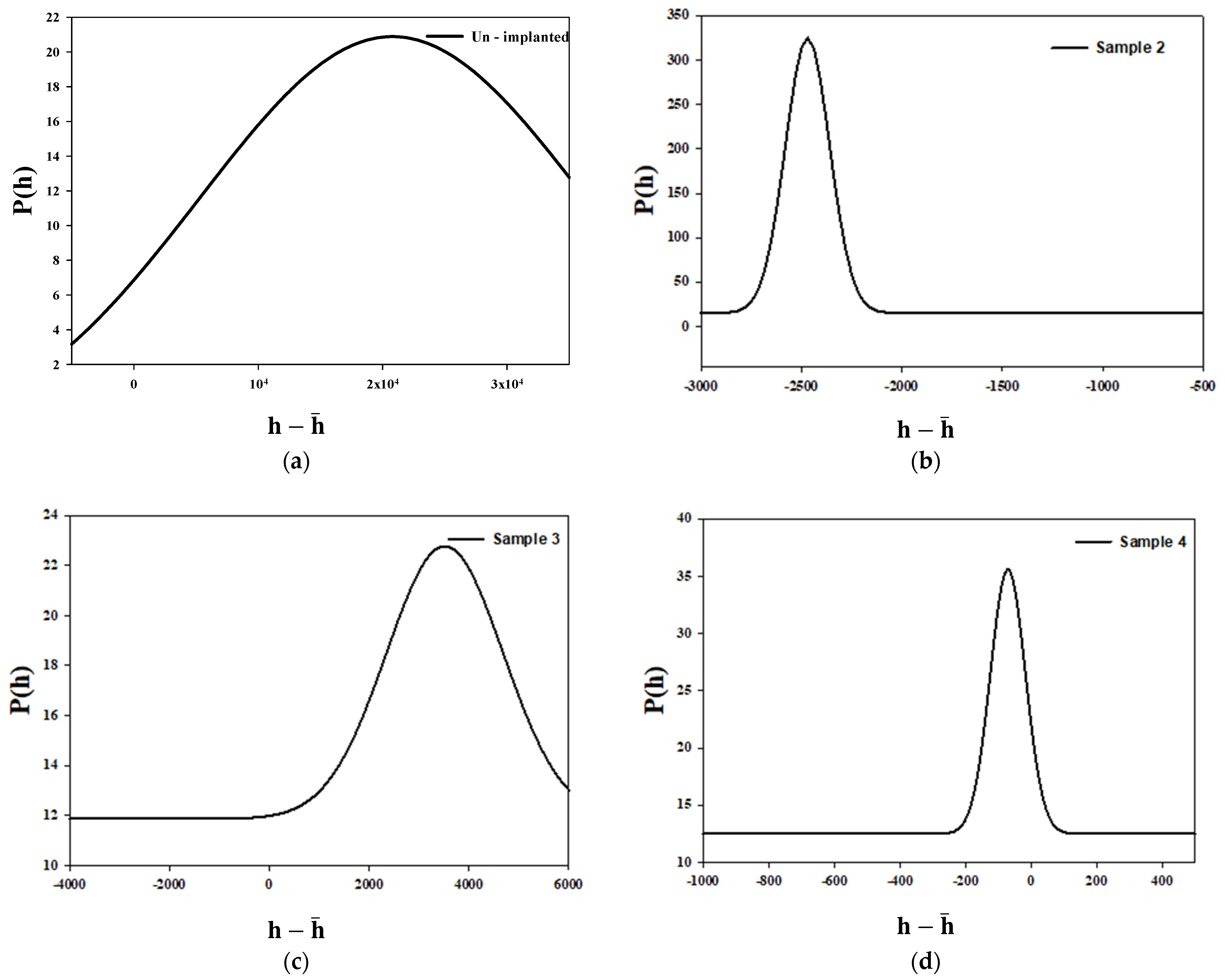
3.2. Monofractal Analysis of Height Distribution Based on Statistical Properties at Various Argon Ion Implanted Doses
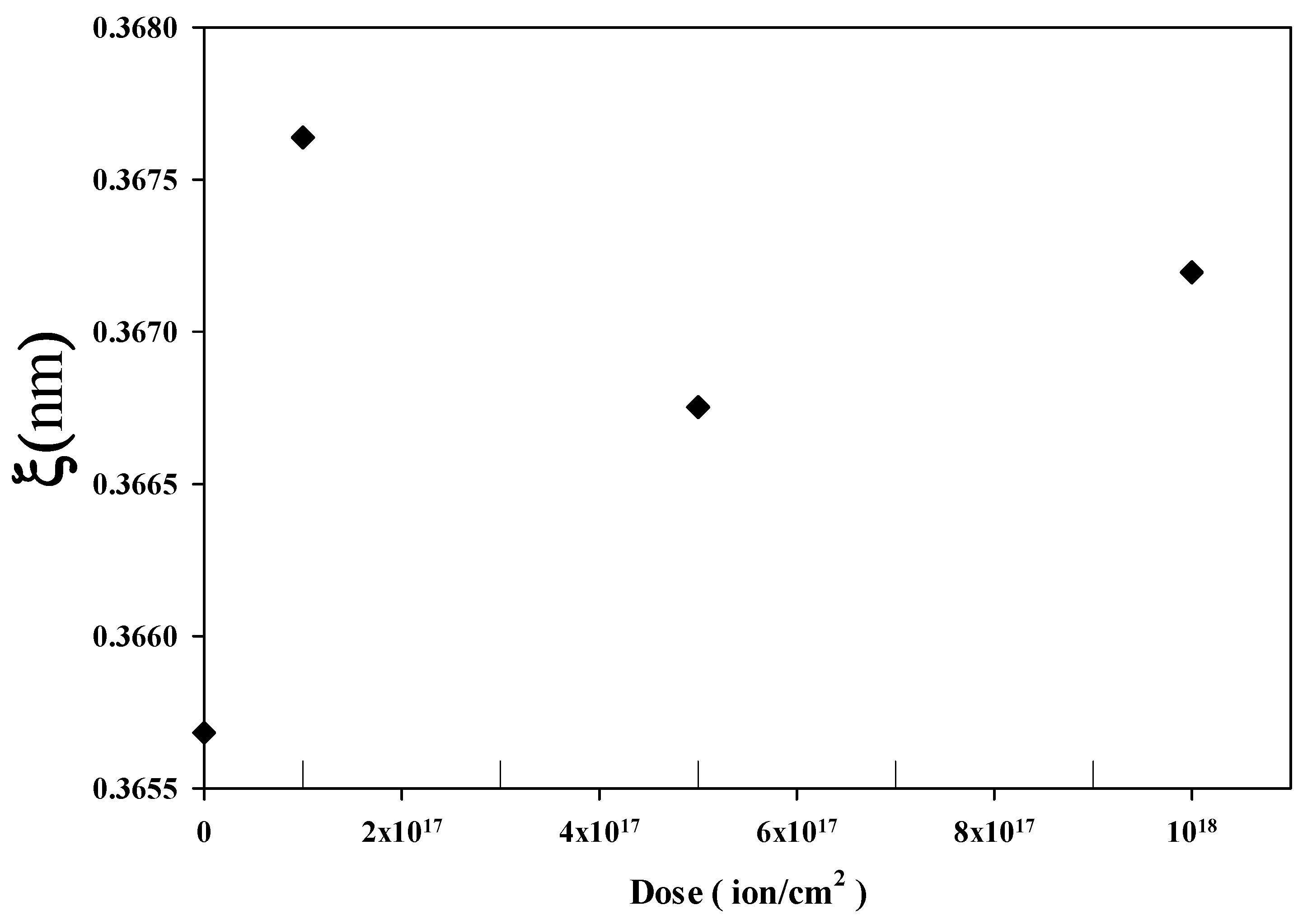
3.3. Hurst (Roughness) Exponent and Fractal Dimension
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyanasundaram, N.; Moore, M.C.; Freund, J.B.; Johnson, H.T. Stress evolution due to medium-energy ion bombardment of silicon. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, F.; Atmani, F.; Malki, B.; Sedjal, H.; Kerkar, M.; Dalard, F. Study of corrosion behaviour of Ti-coated AISI 316L stainless steel in a simulated body fluid solution. In Passivation of Metals and Semiconductors, and Properties of Thin Oxide Layers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 371–376. ISBN 9780444522245. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Zu, X.T.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Huang, X.Q. Phase formation in nitrogen ion implanted Ti-Al-Zr alloy and modification of corrosion property. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2005, 237, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Fernandes, R.P.; Patel, N.K.; Rayjada, P.A.; Raole, P.M.; Kothari, D.C. Corrosion resistance study of argon implanted and ion-beam-mixed 316 SS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 196, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; Murdock, D.C.; Mataya, M.C.; Comstock, R.J. Deformation-induced phase transformation and strain hardening in type 304 austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.S.; Chen, S.T. Diffusion barrier properties of single- and multilayered quasi-amorphous tantalum nitride thin films against copper penetration. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 8473–8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.C.; Chen, M.C. Properties of thin Ta-N films reactively sputtered on Cu/SiO2/Si substrates. Thin Solid Films 1998, 322, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrev, M.; Fischer, D.; Wenzel, C.; Drescher, K.; Mattern, N. Crystallographic and morphological characterization of reactively sputtered Ta, Ta-N and Ta-N-O thin films. Thin Solid Films 1997, 307, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.H.; Sari, A.H.; Shokouhy, A. The effects of argon ion bombardment on the corrosion resistance of tantalum. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, G. Corrosion behavior and surface characterization of tantalum implanted TiNi alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3017–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Pandey, R.K. Assessment of fractal and multifractal features of sol-gel spin coated ZnO thin film surface. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 086454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifano, T.G.; Johnson, H.T.; Bierden, P.; Mali, R.K. Elimination of stress-induced curvature in thin-film structures. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Stanley, H.E. Fractal Concepts in Surface Growth; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, K.; Pandey, R.K. Fractal assessment of ZnO thin films using Higuchi’s algorithm. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics Inc.: College Park, MD, USA, 2019; Volume 2115, p. 030280. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvy, J.A.; Foster, J.R. Rough surfaces: Gaussian or exponential statistics? J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 1989, 22, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelmawla, E.S.; Koura, M.M.; Maksoud, T.M.A.; Elewa, I.M.; Soliman, H.H. Roughness parameters. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 123, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasantzas, G.; Barnaś, J. Surface-roughness fractality effects in electrical conductivity of single metallic and semiconducting films. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1997, 56, 7726–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovski, L. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:37104664 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M. Characterization of Amorphous and Crystalline Rough Surface—Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahiminejad, Z.; Masoudi, S.F.; Jafari, G.R.; Dariani, R.S. Effects of self-affine roughness characteristics on electron transmission through tunneling structures. Thin Solid Films 2012, 522, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgerini, F.L.; Figueiredo, W. Random deposition of particles of different sizes. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2009, 79, 041602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarão Reis, F.D.A. Roughness fluctuations, roughness exponents and the universality class of ballistic deposition. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 364, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silveira, F.A.; Aarão Reis, F.D.A. Surface and bulk properties of deposits grown with a bidisperse ballistic deposition model. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2007, 75, 061608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, D.; Hosseinpanahi, F. The effect of film thickness on surface morphology of ITO thin films. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.H.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Ebrahiminejad, Z. Statistical and fractal analysis of nitrogen ion implanted tantalum thin films. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.H.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Ebrahiminejad, Z. Structural and mechanical properties of tantalum thin films ected by nitrogen ion implantation. Mod. Phys. Lett. Bvol. 2020, 34, 2050163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample No. | Dose of Extracted Ions (ion/cm2) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Un-implanted | ------------ |
| 2 | 1 × 1017 | 360 |
| 3 | 3 × 1017 | 1050 |
| 4 | 7 × 1017 | 2560 |
| Sample | Dose (ion/cm2) | Corrosion Current * (10−6) | Corrosion Potential * (10−4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | Unimplanted | 0.107 | −1.78 |
| Sample 2 | 1 × 1017 | 0.0116 | −0.681 |
| Sample 3 | 3 × 1017 | 0.0259 | −5.037 |
| Sample 4 | 7 × 1017 | 0.0347 | −0.680 |
| Sample | Dose (ion/cm2) | RMS Roughness (Å) | Average Roughness (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ----- | 22.3 | 15.7 |
| 2 | 1 × 1017 | 30.52 | 5.64 |
| 3 | 3 × 1017 | 41.1 | 32.8 |
| 4 | 7 × 1017 | 50.3 | 41.3 |
| Sample | Kurtosis | Skewness |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.57 | −1.53 |
| 2 | 1.87 | −1.33 |
| 3 | 1.56 | 1.22 |
| 4 | 1.51 | −1.04 |
| Dose (Ion/cm2) | 1 × 1017 | 3 × 1017 | 7 × 1017 |
| Hurst Exponent | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.87 |
| Dose (Ion/cm2) | 1 × 1017 | 3 × 1017 | 7 × 1017 |
| Df | 1.1 | 1.09 | 1.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramezani, A.H.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Ebrahiminejad, Z.; Sangashekan, M.; Memon, S. Microstructural and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analyses on Argon Ion Implantations in Tantalum Thin Films for Microelectronic Substrates. Electronics 2021, 10, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232941
Ramezani AH, Hoseinzadeh S, Ebrahiminejad Z, Sangashekan M, Memon S. Microstructural and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analyses on Argon Ion Implantations in Tantalum Thin Films for Microelectronic Substrates. Electronics. 2021; 10(23):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232941
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamezani, Amir Hoshang, Siamak Hoseinzadeh, Zhaleh Ebrahiminejad, Milad Sangashekan, and Saim Memon. 2021. "Microstructural and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analyses on Argon Ion Implantations in Tantalum Thin Films for Microelectronic Substrates" Electronics 10, no. 23: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232941
APA StyleRamezani, A. H., Hoseinzadeh, S., Ebrahiminejad, Z., Sangashekan, M., & Memon, S. (2021). Microstructural and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analyses on Argon Ion Implantations in Tantalum Thin Films for Microelectronic Substrates. Electronics, 10(23), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10232941







