Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
- pH of the formulation mixture before cross-linking,
- PT concentration (10%, 15%, 20%, and 30% w/w) in the formulation,
- type of cross-linking method (UV-irradiation, microwaving, and oven-assisted crosslinking),
- exposure time of the film to the cross-linking method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Chemicals, and Reagents
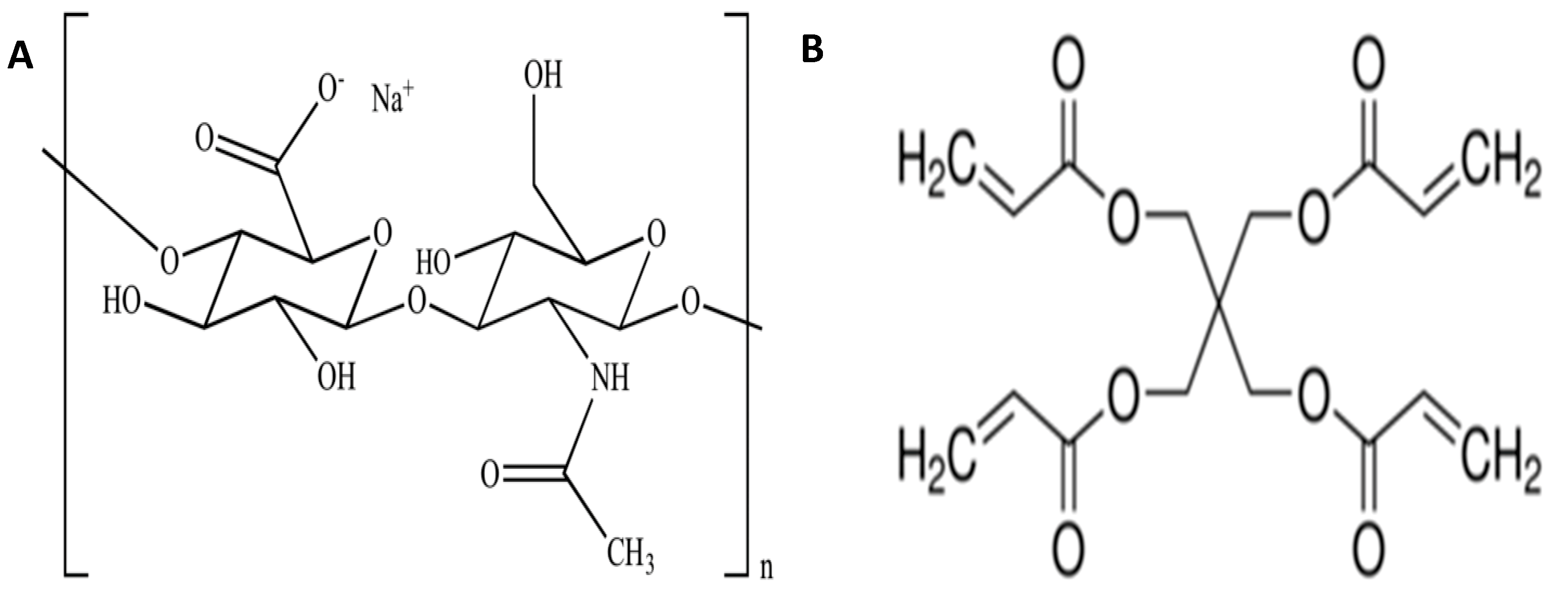
2.2. Preparation of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels
2.3. Cross-Linking Experiment
2.3.1. UV-Light Irradiation
2.3.2. Microwave Irradiation
2.3.3. Thermal Cross-Linking
2.4. Hydrogel Swelling Studies
2.5. Comparisons of Average MW between Crosslinks, Crosslinking Density, and Mesh Size
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
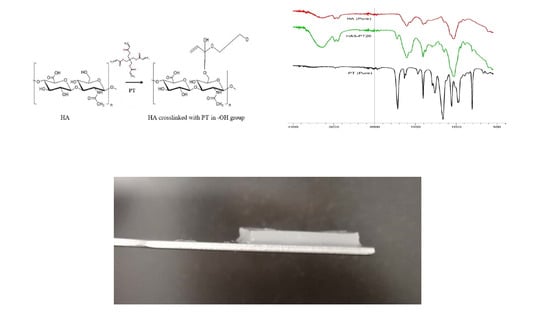
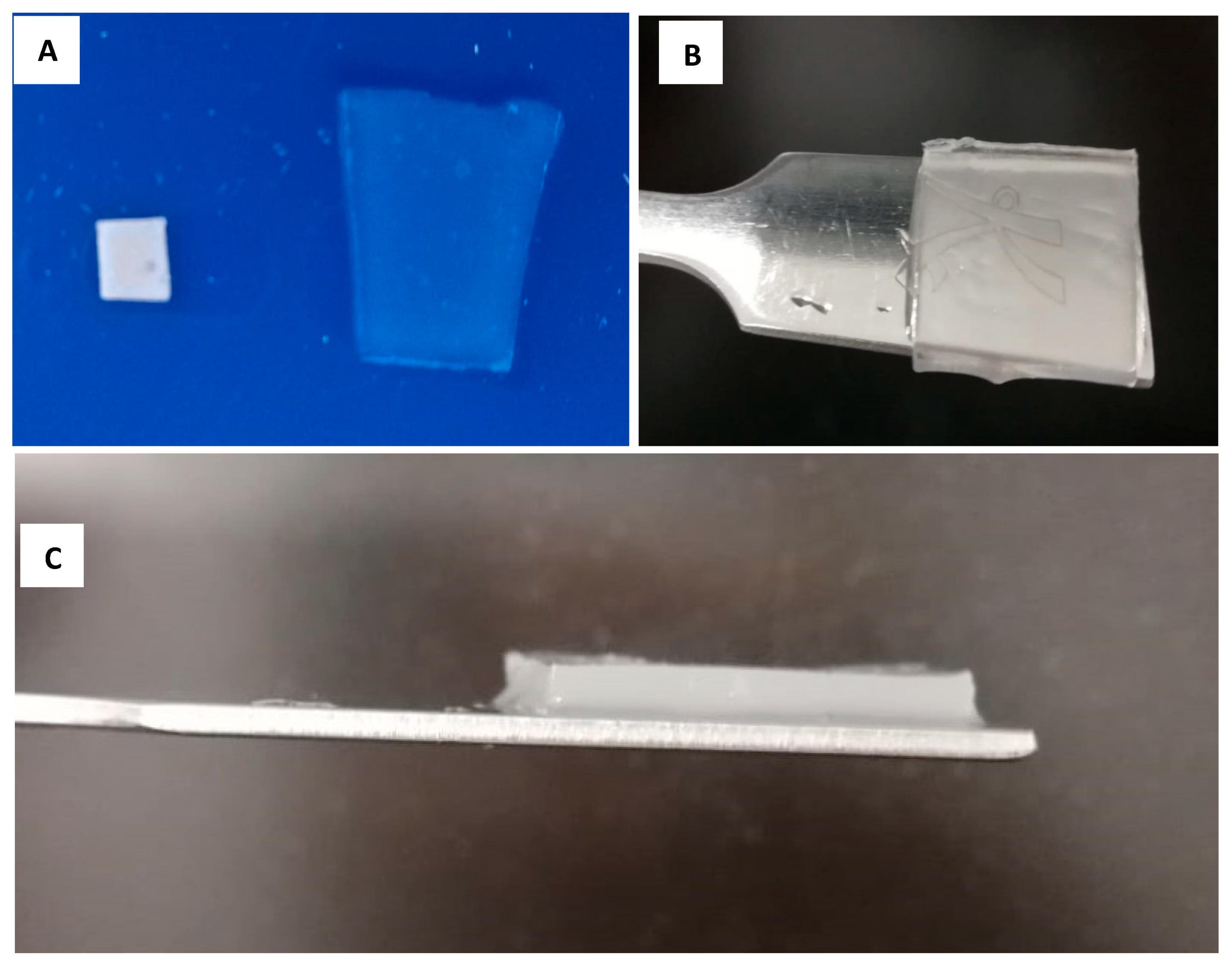
3.1. Hydrogel Characterization
3.2. Effect of pH on Hydrogel Film Formation
3.3. Cross-Linking Method
3.3.1. Effect of UV-Irradiation Time
3.3.2. Microwave Method
3.3.3. Oven Method
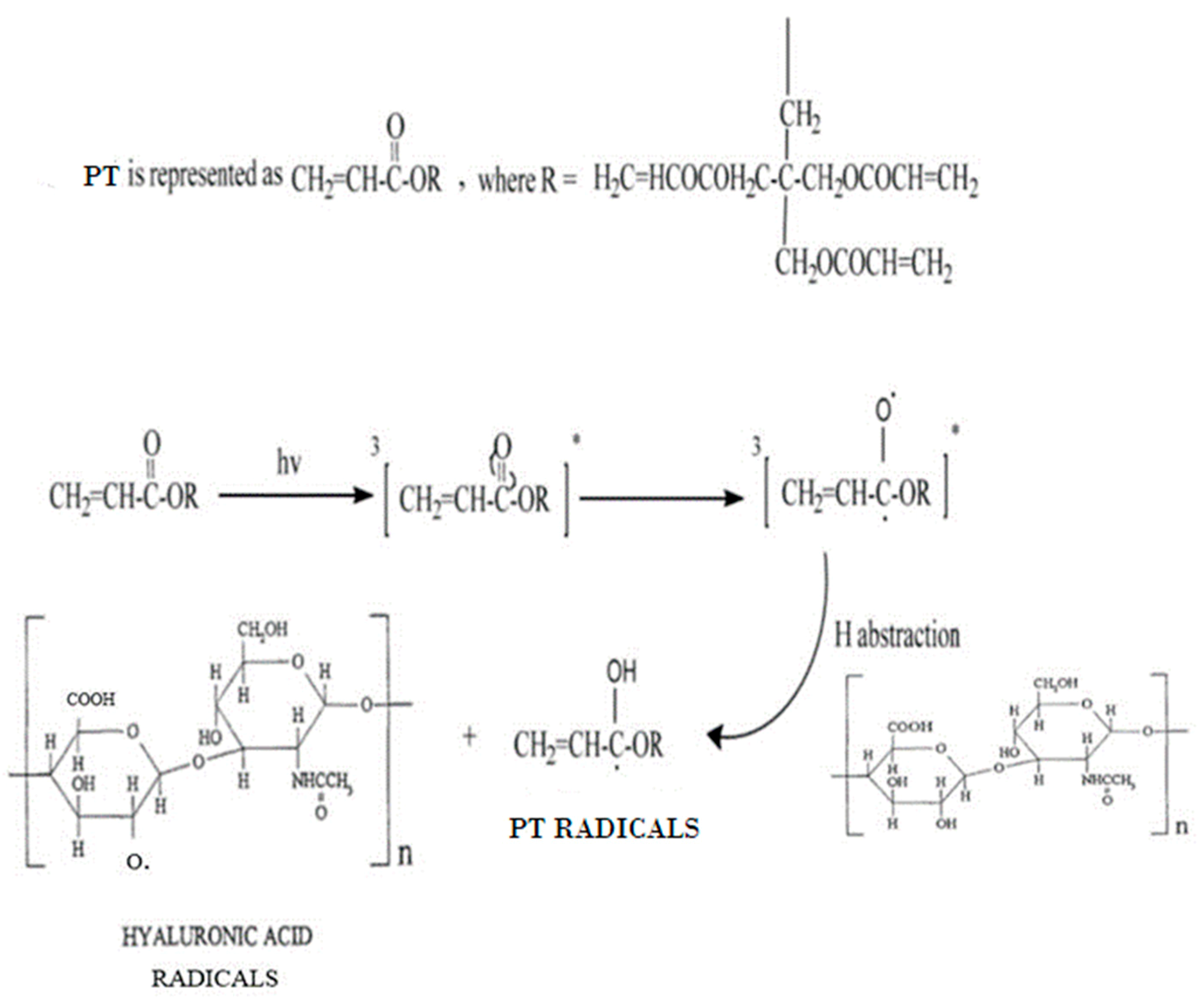
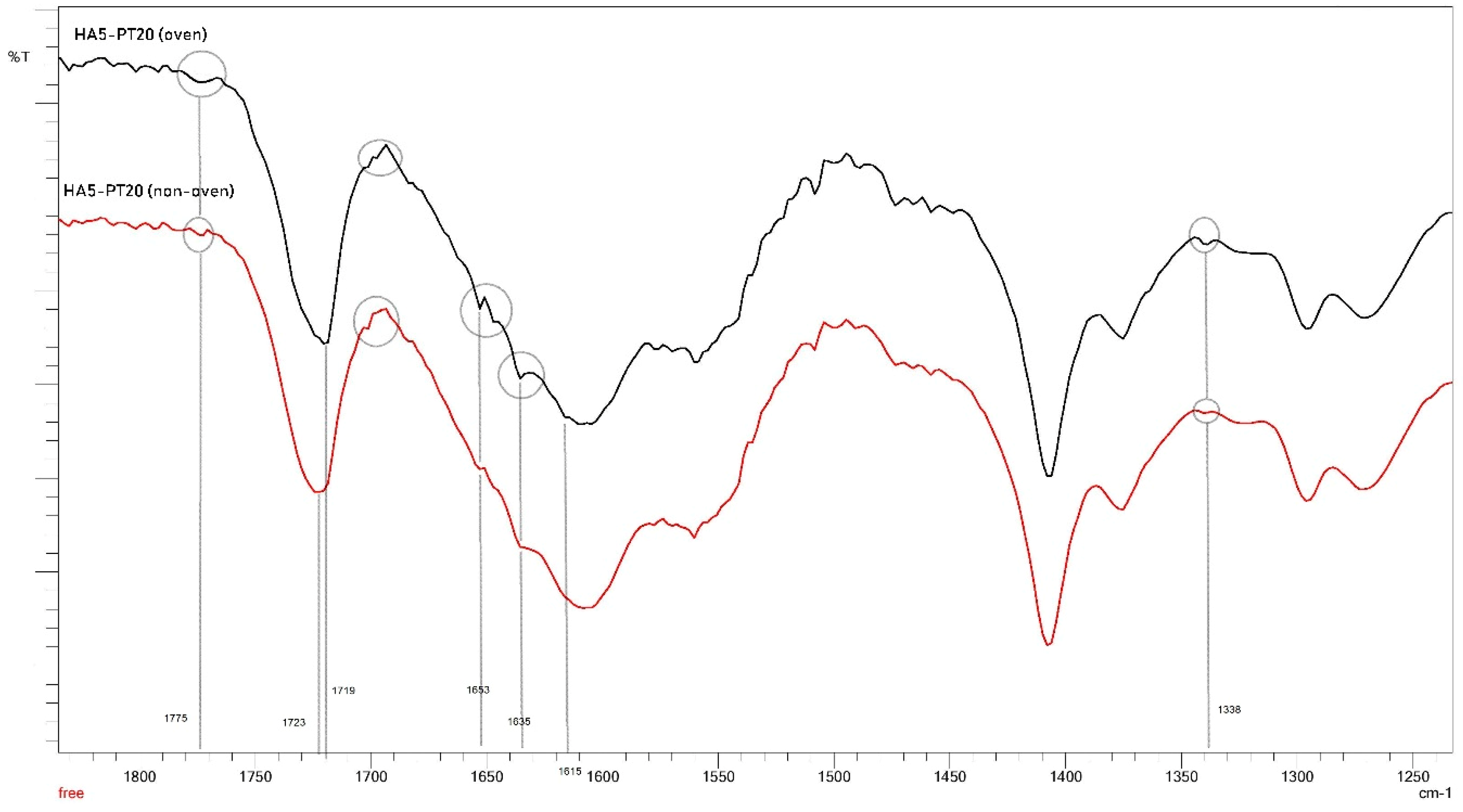
3.4. Cross-Linking Mechanism
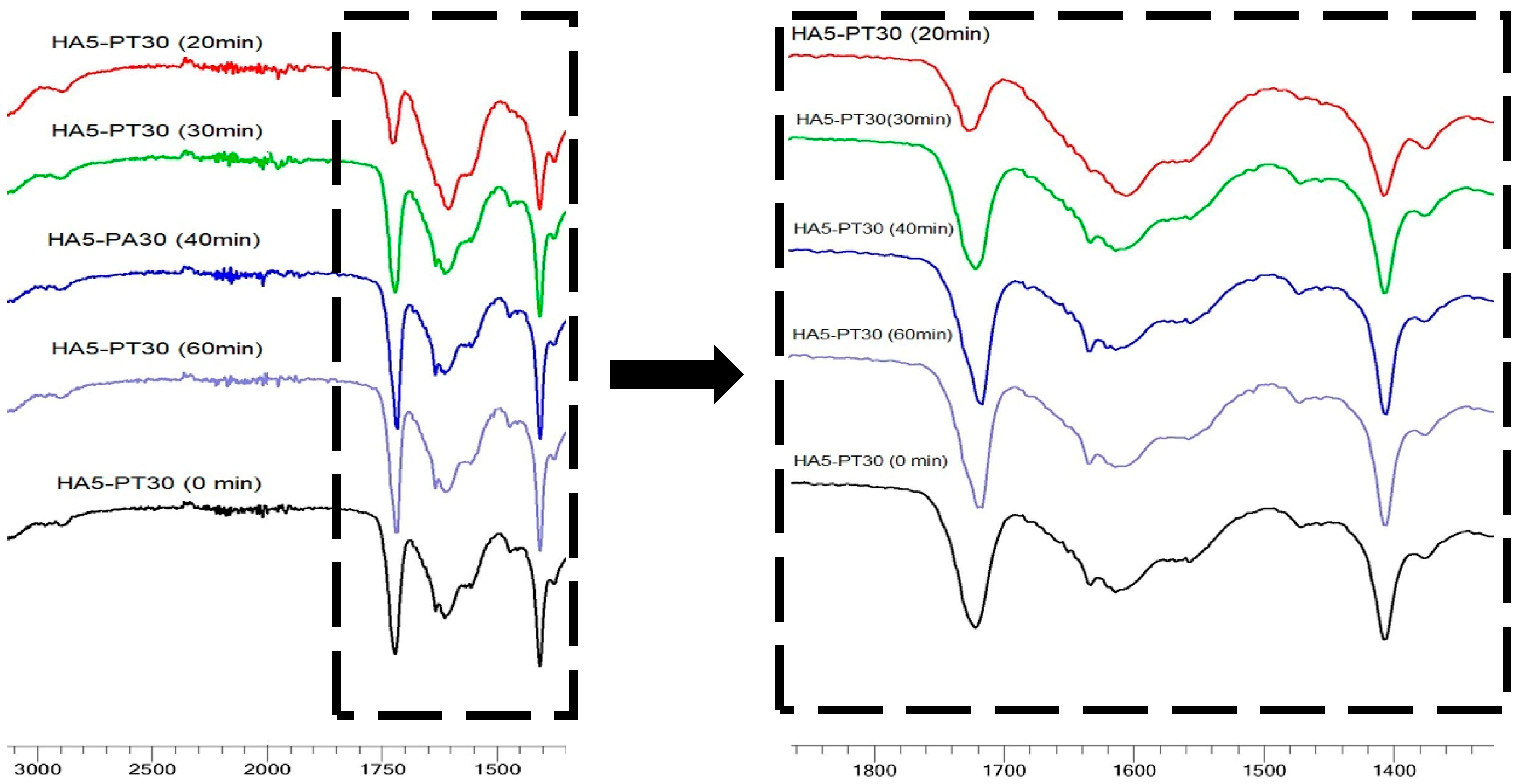
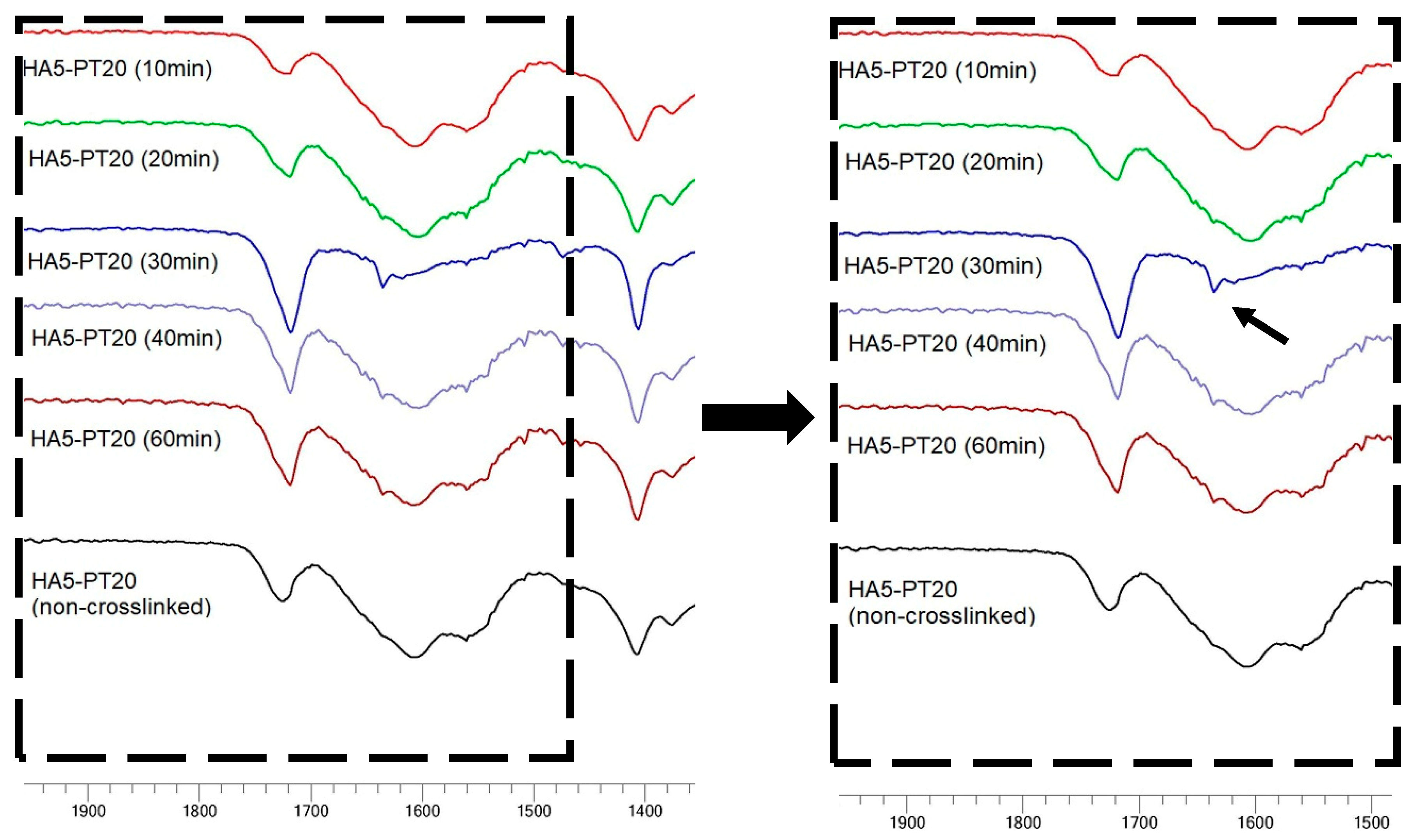
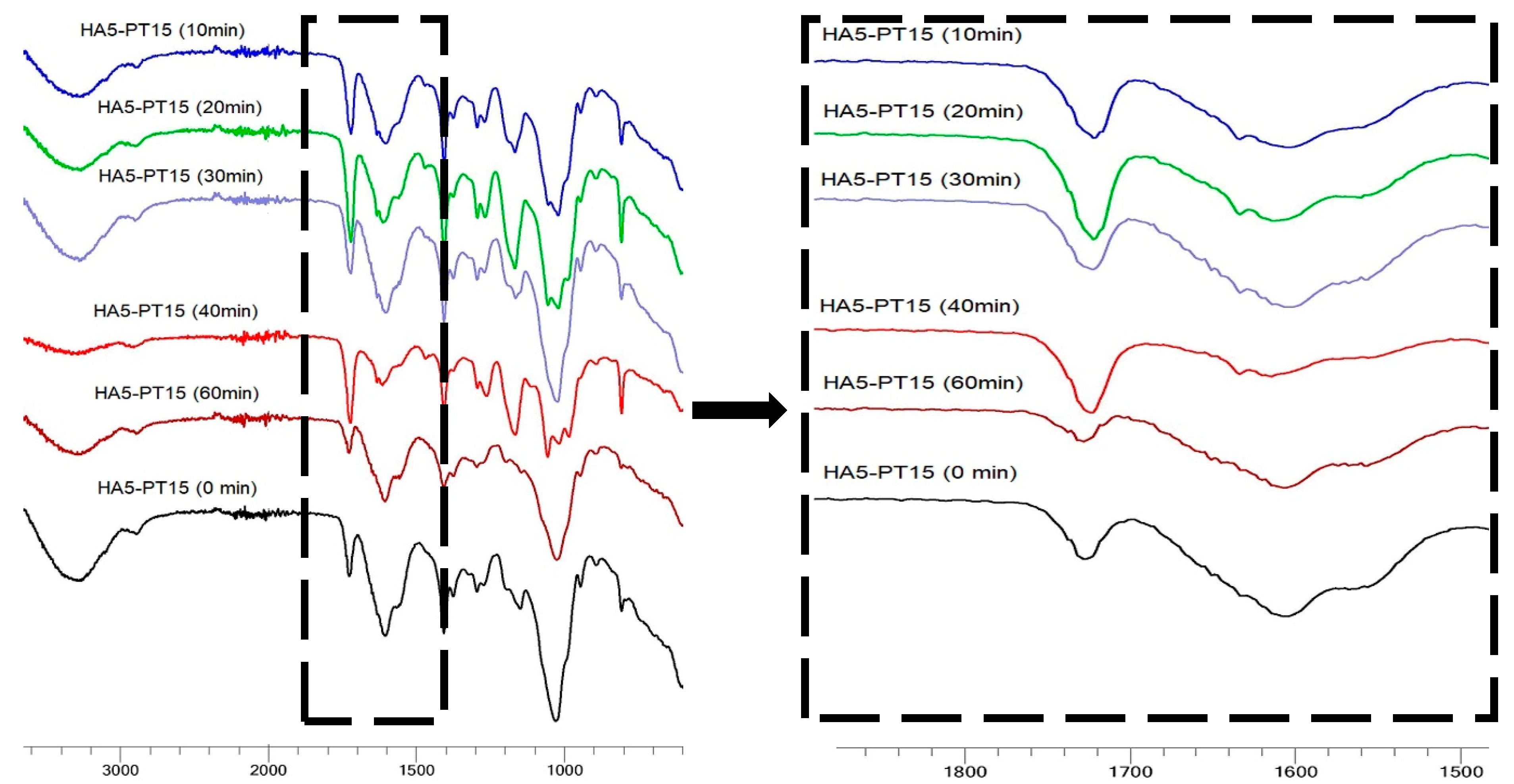
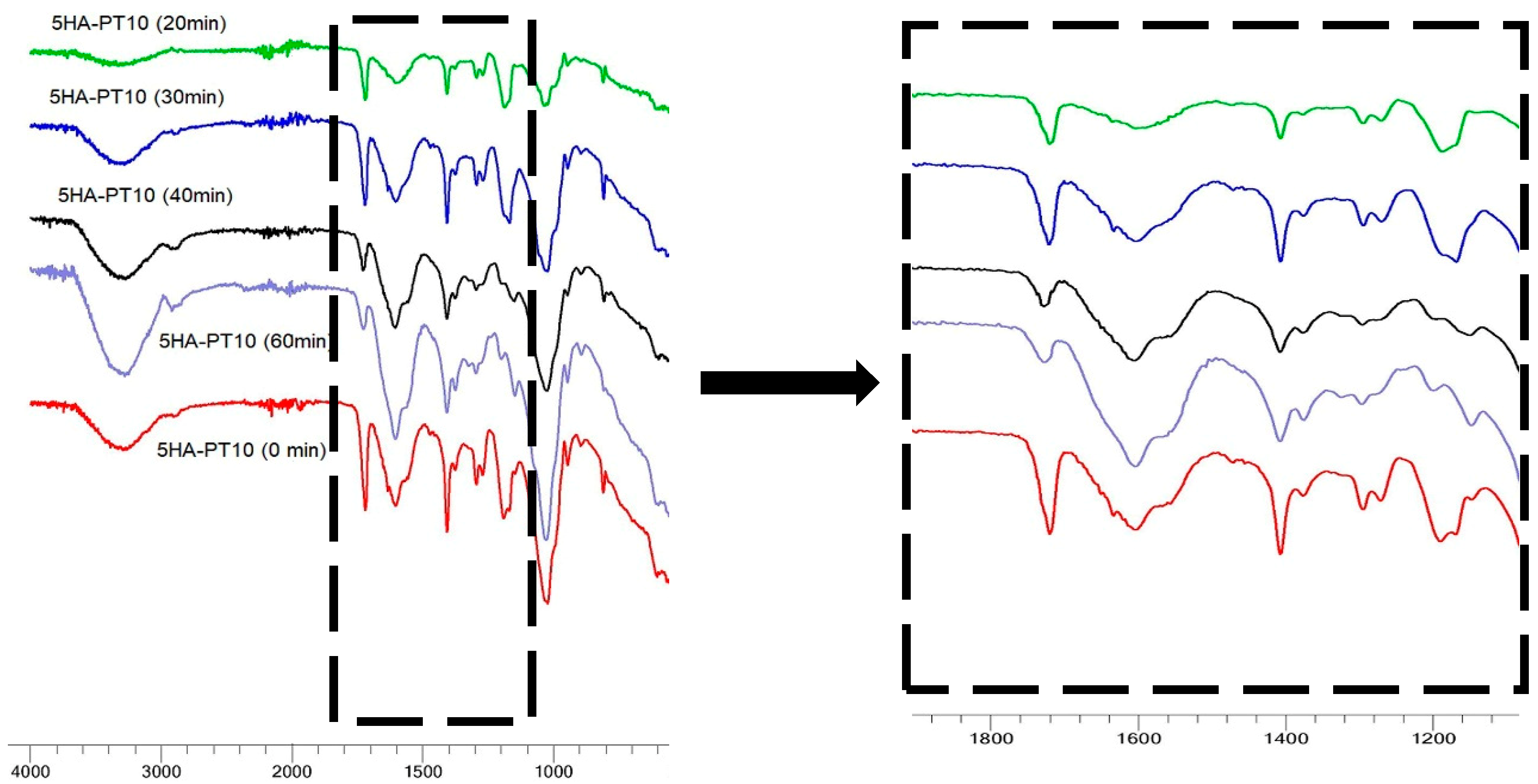
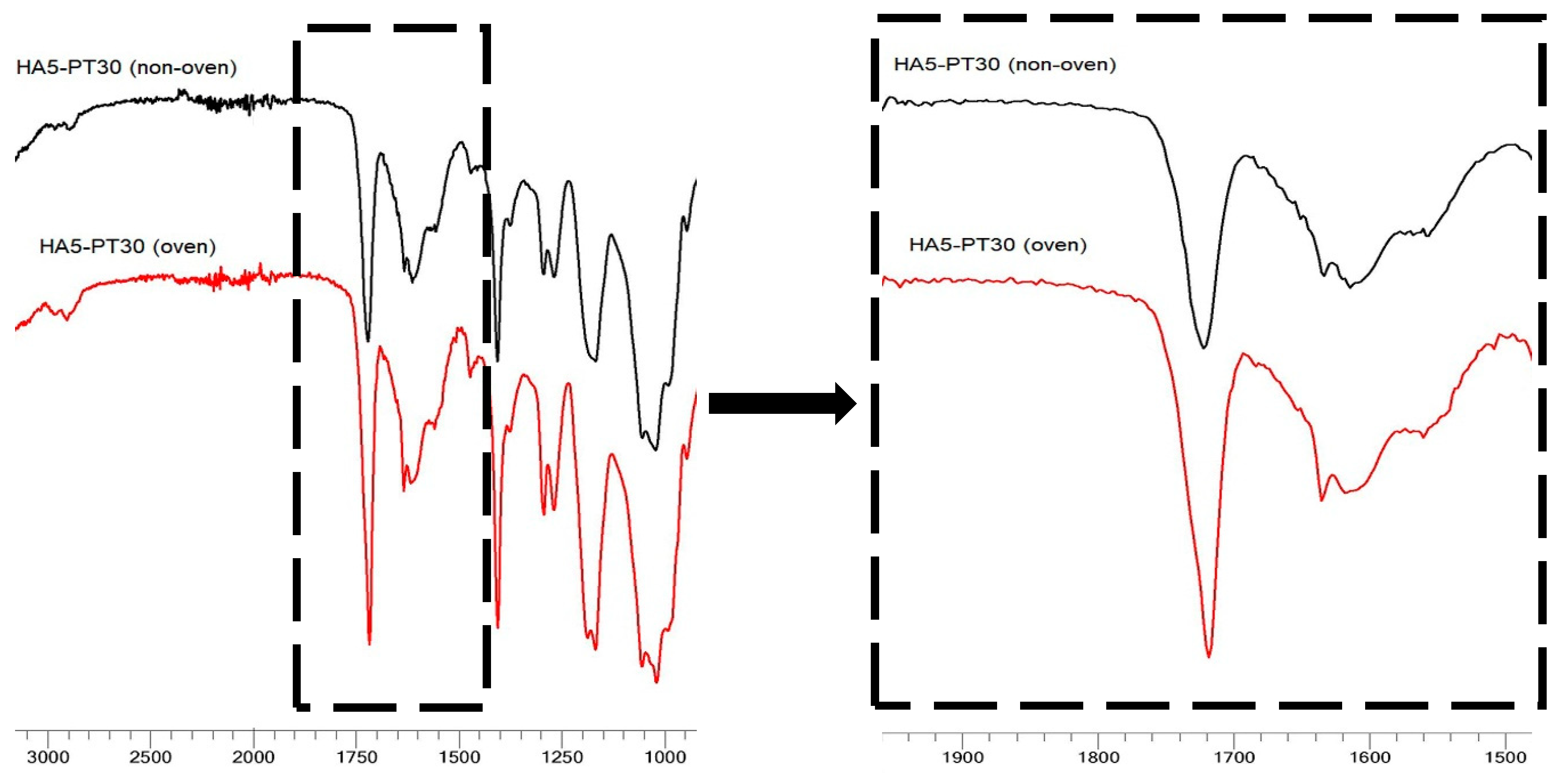
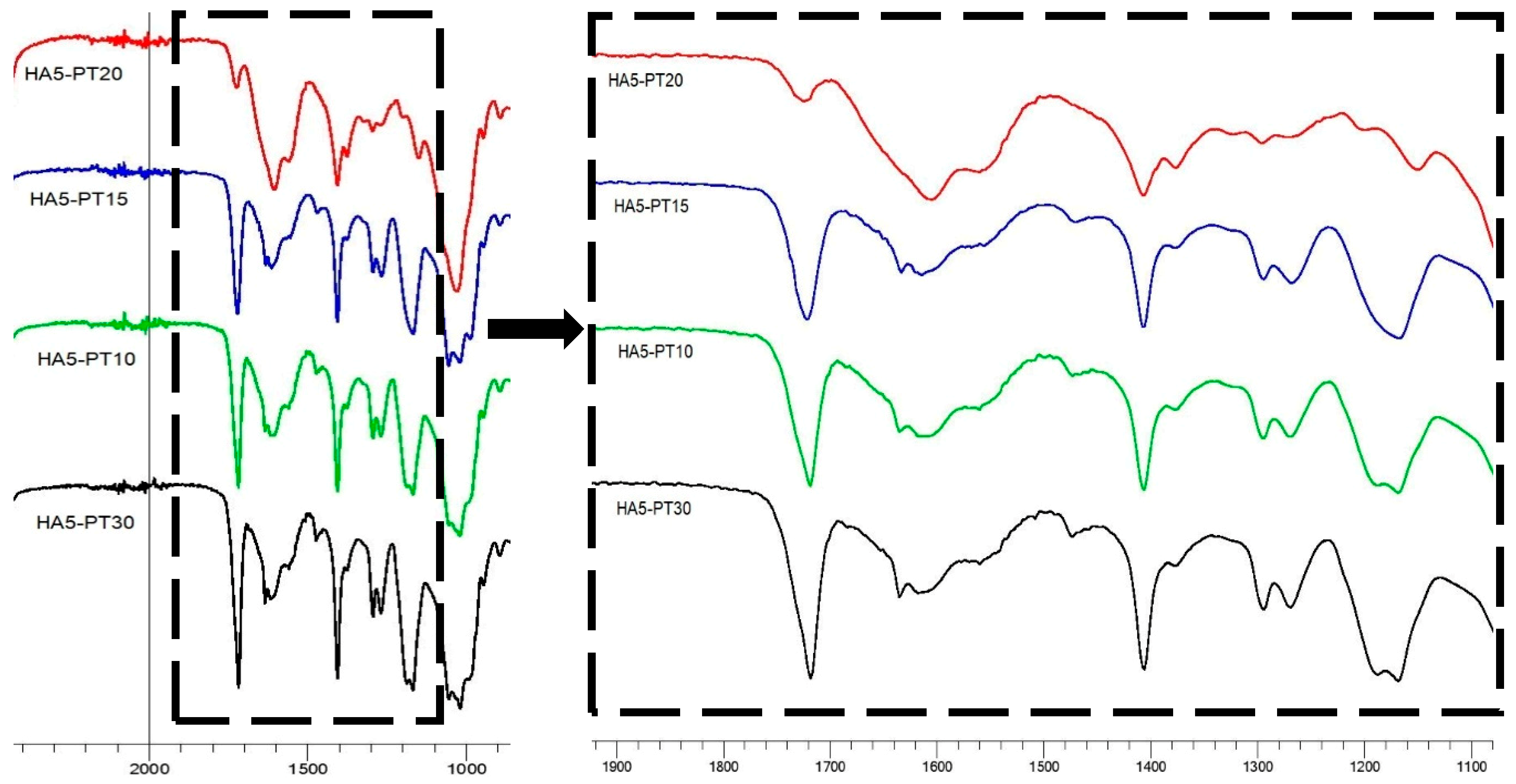
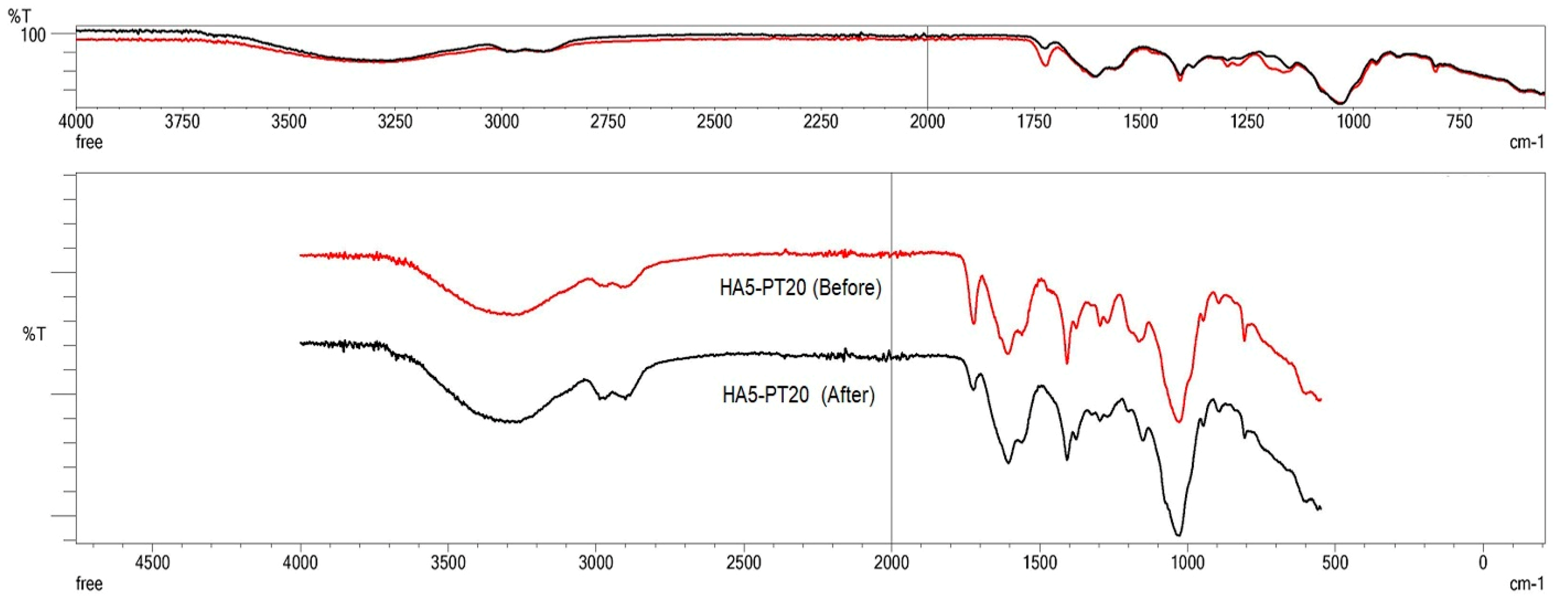
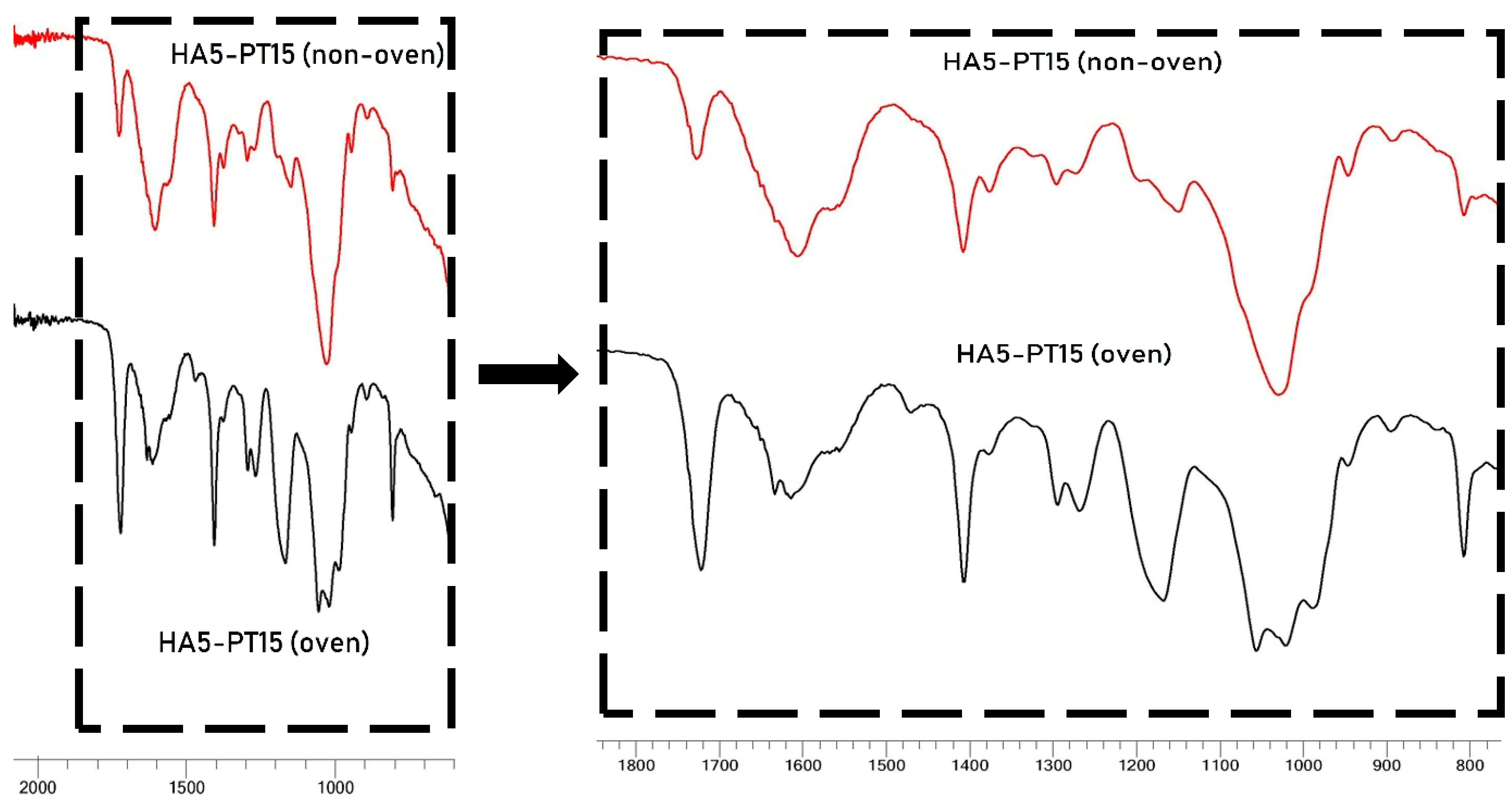
3.5. FTIR Spectral Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulrez, S.K.H.; Al-Assaf, S.; Glyn, O. Hydrogels: Methods of Preparation, Characterisation and Applications. In Progress in Molecular and Environmental Bioengineering-From Analysis and Modeling to Technology Applications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Larraneta, E.; Henry, M.; Irwin, N.J.; Trotter, J.; Perminova, A.A.; Donnelly, R.F. Synthesis and characterization of hyaluronic acid hydrogels crosslinked using a solvent-free process for potential biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyles, D.A.; Castro, L.D.; Silva, J.O.C.; Ribeiro-Costa, R.M. A review of the designs and prominent biomedical advances of natural and synthetic hydrogel formulations. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Jones, S.A.; Forbes, B.; Martin, G.P.; Brown, M.B. Hyaluronan: Pharmaceutical characterization and drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sibani, M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Rhh, N. Characterization of Linear and Chemically Cross-linked Hyaluronic acid using Various Analytical Techniques Including FTIR, ESI-MS, H1 NMR, and SEM. J. Biochem. Anal. Stud. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ström, A.; Larsson, A.; Okay, O. Preparation and physical properties of hyaluronic acid-based cryogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, E.L.; Roberts, J.L.; Moseley, R.; Griffiths, P.C.; Thomas, D.W. Evaluation of the physical and biological properties of hyaluronan and hyaluronan fragments. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Chen, H. Preparation of aroma microcapsules with sodium alginate and tetradecylallyldimethylammonium bromide (TADAB) and its potential applications in cosmetics. Flavour Fragr. J. 2018, 33, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.P.; Goodall, G.W.; Khutoryanskaya, O.V.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Microwave-Assisted Hydrogel Synthesis: A New Method for Crosslinking Polymers in Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.N.; Birkinshaw, C. Investigation of the swelling behavior of crosslinked hyaluronic acid films and hydrogels produced using homogeneous reactions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier Leach, J.; Bivens, K.A.; Patrick, C.W., Jr.; Schmidt, C.E. Photocrosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels: Natural, biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 82, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.Y.; Yuan, G.; Qi, Y.P.; Li, L.L. Synthesis and Properties of Polyacrylate Emulsion Modified by Pentaerythritol Tetraacrylate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 781–784, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caló, E.; Barros, J.M.S.D.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, M.; San Román, J.; Ballamy, L.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Antimicrobial hydrogels based on autoclaved poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic anhydride) mixtures for wound care applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55211–55219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Dodou, K. Effect of Drug Loading Method and Drug Physicochemical Properties on the Material and Drug Release Properties of Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Hydrogels for Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2017, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Analysis of residual crosslinking agent content in UV cross-linked poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogels for dermatological application, by gas chromatography. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, A.D. Trimethylolpropane Triacrylate. In Executive Summary of Safety and Toxicity Information; 1991; pp. 20–21. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/tmtpa_508.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2019).
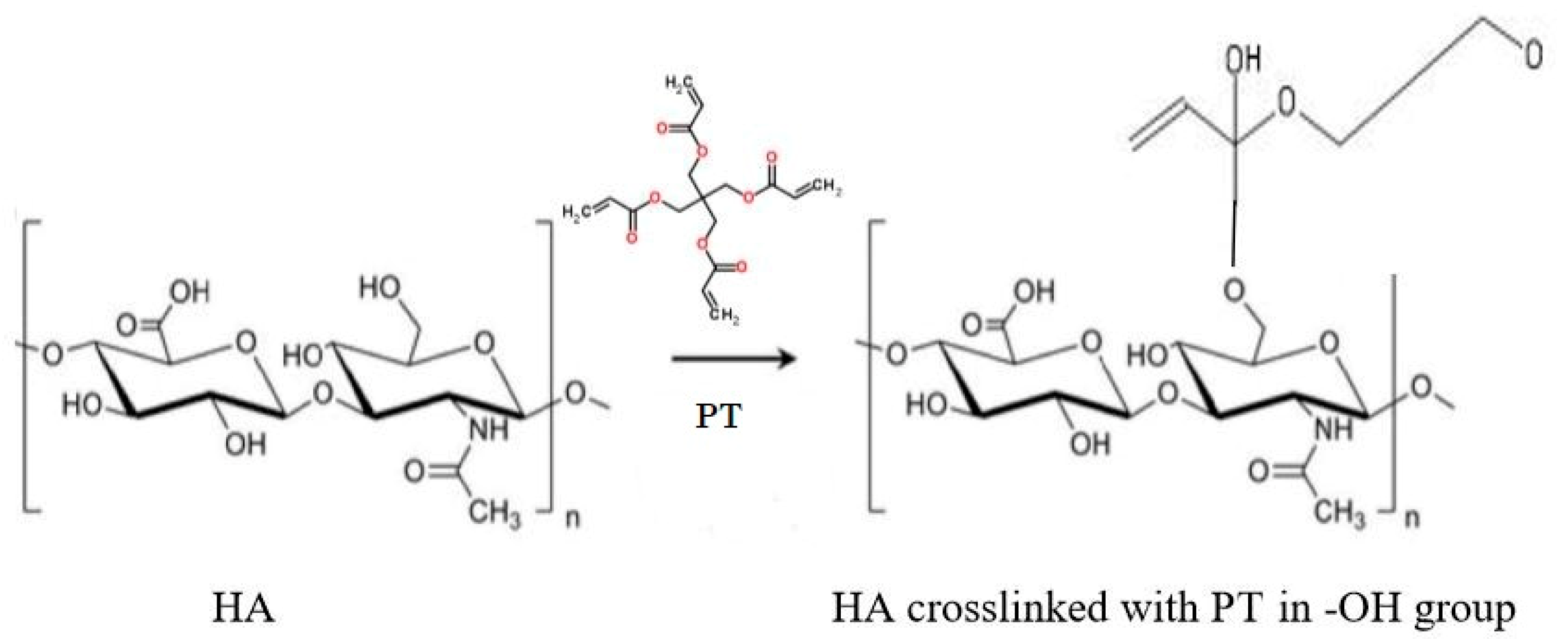
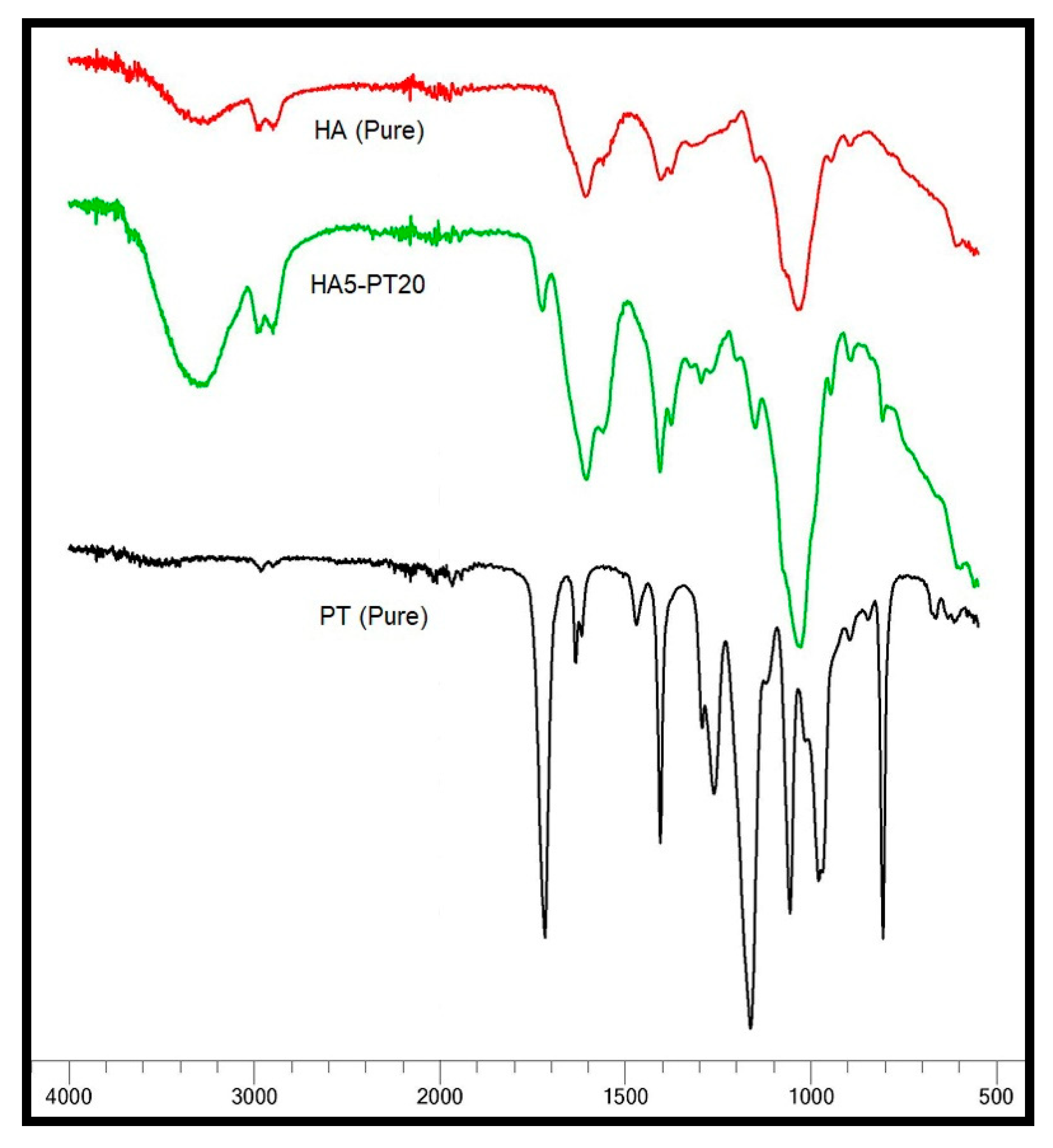
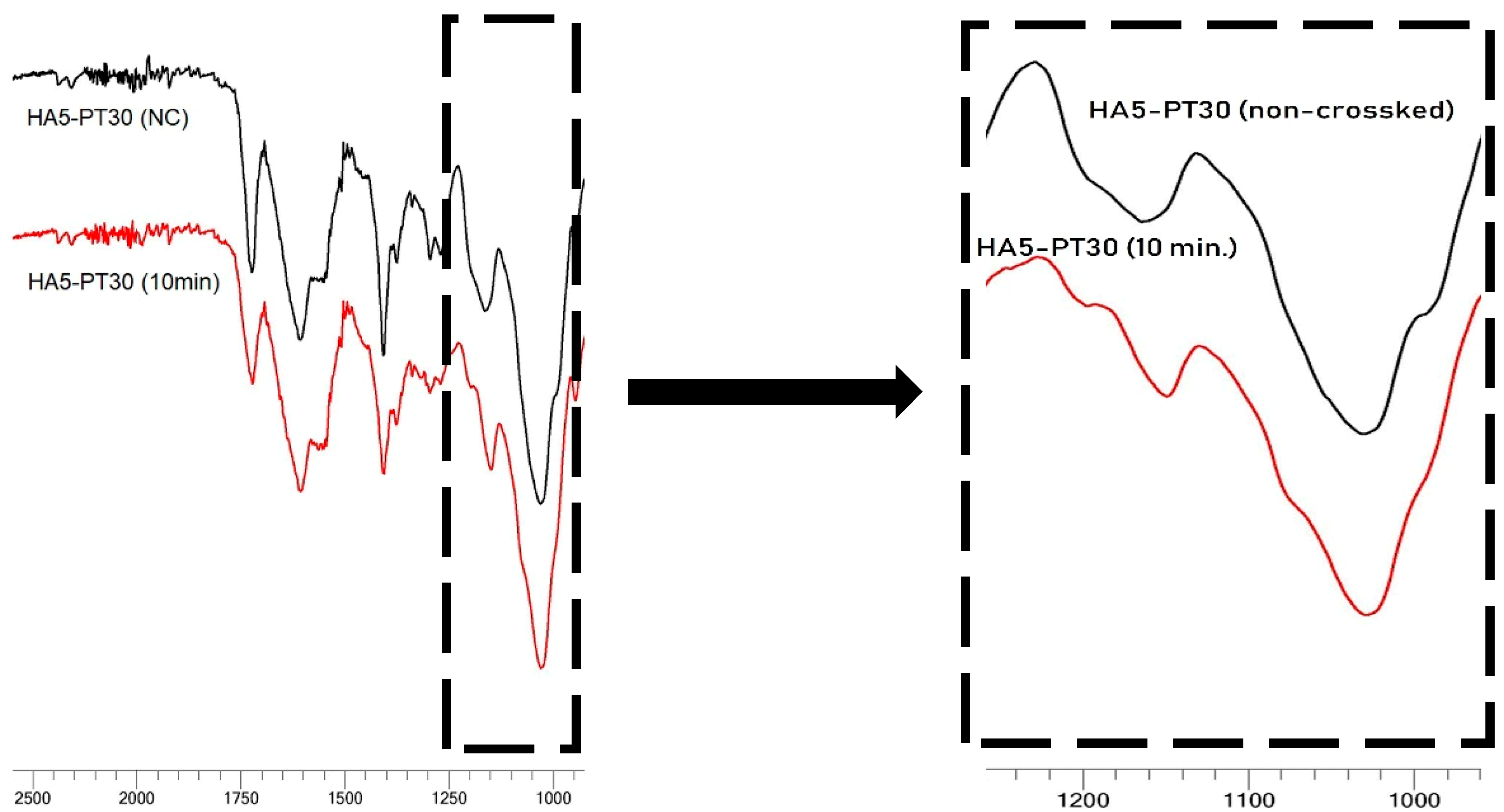
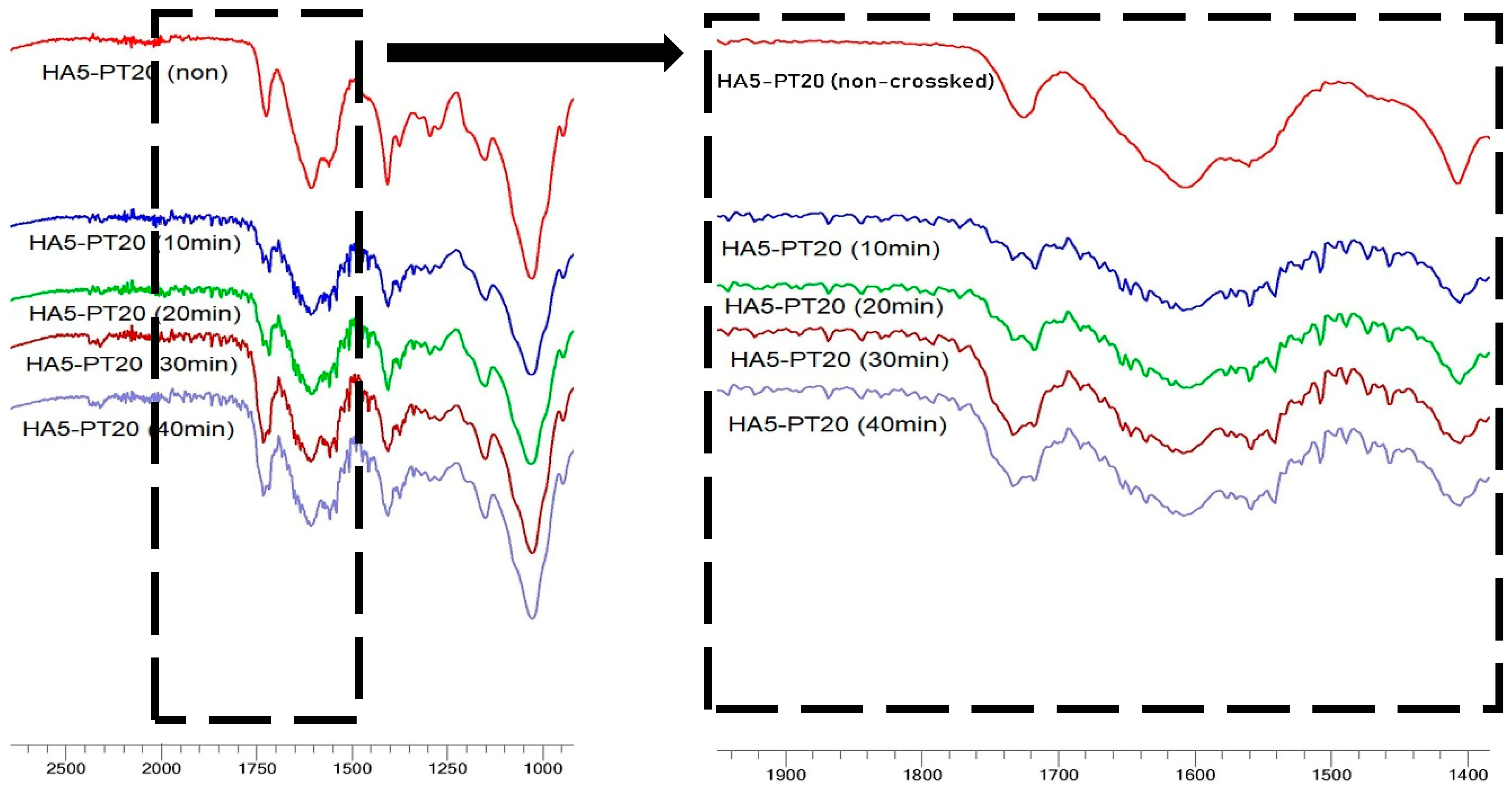

| Hydrogel Name | % w/v of HA in Aq Solution | % w/w of PT in HA | pH Condition | PT: HA Ratio in the Xerogel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA2 * | 2 | ----- | 7 | ---- |
| HA2-PT5 * | 2 | 5 | 7 | 1:20 |
| HA5-PT5 * | 5 | 5 | 7 | 1:20 |
| HA2-PT10 * | 2 | 10 | 7 | 1:10 |
| HA5-PT15 * | 5 | 15 | 7 | 1:6.7 |
| HA5-PT20 * | 5 | 20 | 7 | 1:5 |
| HA2 * | 2 | ----- | 2 | ---- |
| HA2-PT5 * | 2 | 5 | 2 | 1:20 |
| HA5-PT5 * | 5 | 5 | 2 | 1:20 |
| HA2-PT10 * | 2 | 10 | 2 | 1:10 |
| HA5-PT15 * | 5 | 15 | 2 | 1:6.7 |
| HA5-PT20 * | 5 | 20 | 2 | 1:5 |
| Hydrogel Name | % w/v of HA in Sq Solution | % w/w of PT in HA | PT: HA Ratio in the Xerogel |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA2 * | 2 | --- | --- |
| HA2-PT5 * | 2 | 5 | 1:20 |
| HA5-PT5 * | 5 | 5 | 1:20 |
| HA5-PT10 | 5 | 10 | 1:10 |
| HA5-PT15 | 5 | 15 | 1:6.7 |
| HA5-PT20 | 5 | 20 | 1:5 |
| HA5-PT30 | 5 | 30 | 1:3.3 |
| UV Time (min) | Swelling (%) | Equilibrium Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh Size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5692 (±493) | 98.26 (±0.14) | 71.39 (±4.77) | 126 (±10.69) | 3.74 × 106 | 1699 (±172) | 3.31 × 10−7 |
| 20 | 5979 (±647) | 98.28 (±0.17) | 79.45 (±2.85) | 128 (±13.65) | 3.86 × 106 | 1733 (±215) | 3.24 × 10−7 |
| 30 | 8670 (±1984) | 98.48 (±0.25) | 78.96 (±4.08) | 192 (±44.41) | 4.38 × 106 | 2779 (±751) | 1.75 × 10−7 |
| 40 | 11,894 (±745) | 99.16 (±0.05) | 69.22 (±6.50) | 264 (±16.65) | 1.27 × 107 | 4014 (±292) | 6.41 × 10−7 |
| Microwave Time (min) | Swelling (%) | Equilibrium Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh Size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | -- | -- | --- | ||||
| 20 | 8593 (±266) | 98.84 (±0.03) | 63.04 (±1.57) | 191 (±5.56) | 7.43 × 106 | 2746 (±99.41) | 1.65 × 10−7 |
| 30 | 7737 (±328) | 98.69 (±0.05) | 79.13 (±3.75) | 168 (±7.09) | 6.01 × 106 | 2369 (±119.9) | 3.06 × 10−7 |
| 40 | 6370 (±305) | 98.44 (±0.07) | 80.38 (±2.75) | 141 (±6.80) | 4.51 × 106 | 1937 (±108.4) | 2.72 × 10−7 |
| 60 | 5700 (±599) | 98.25 (±1.88) | 83.55 (±3.67) | 126 (±13.2) | 3.76 × 106 | 2283 (±207.8) | 3.32 × 10−7 |
| Microwave Time (min) | Swelling (%) | Eq. Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh Size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 7968 (±791) | 98.74 (±0.11) | 70.15 (±1.13) | 177 (±17.43) | 6.57 × 106 | 2516 (±292) | 1.89 × 10−7 |
| 20 | 4094 (±532) | 97.32 (±0.75) | 82.43 (±1.36) | 85 (±21.37) | 1.97 × 106 | 1073 (±313) | 3.78 × 10−6 |
| 30 | 3755 (±536) | 97.49 (±0.54) | 89.22 (±3.20) | 83 (±12.28) | 1.88 × 106 | 1046 (±174) | 6.75 × 10−7 |
| 40 | 4037 (±958) | 97.25 (±0.99) | 94.87 (±2.82) | 89 (±21.07) | 2.15 × 106 | 1142 (±312) | 6.40 × 10−7 |
| 60 | 4612 (±571) | 97.85 (±0.28) | 92.90 (±1.77) | 102 (±12.42) | 2.64 × 106 | 1330 (±190) | 4.77 × 10−7 |
| Microwave Time (min) | Swelling (%) | Eq. Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 7763 (±211) | 98.72 (±0.03) | 86.57 (±1.85) | 172 (±5.13) | 6.27 × 106 | 2440 (±77.9) | 2.62 × 10−7 |
| 20 | 2341 (±342) | 95.84 (±0.62) | 95.35 (±1.46) | 51 (±7.76) | 5.48 × 105 | 603 (±102.6) | 1.49 × 10−6 |
| 30 | 1171 (±31) | 92.12 (±2.34) | 95.82 (±0.17) | 19 (±5.50) | 1.73 × 105 | 195 (±64.6) | 4.96 × 10−6 |
| 40 | 1216 (±180) | 92.29 (±1.28) | 97.95 (±1.73) | 26 (±4.16) | 2.88 × 105 | 281 (±48.2) | 4.45 × 10−6 |
| 60 | 1267 (±196) | 92.57 (±1.46) | 90.93 (±0.92) | 25 (±5.85) | 2.70 × 105 | 267 (±67.7) | 4.90 × 10−6 |
| Microwave Time (min) | Swelling (%) | Eq. Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh Size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 9158 (±595) | 98.91 (±0.07) | 77.45 (±3.11) | 203 (±13.5) | 8.27 × 107 | 2959 (±224) | 1.49 × 10−7 |
| 30 | 8806 (±591) | 98.87 (±0.07) | 79.24 (±3.54) | 195 (±13.3) | 7.75 × 107 | 2827 (±221) | 1.59 × 10−7 |
| 40 | 7198 (±397) | 98.62 (±0.06) | 75 (±3.57) | 160 (±8.88) | 5.53 × 107 | 2234 (±144) | 2.22 × 10−7 |
| 60 | 8121 (±584) | 98.77 (±0.08) | 79.44 (±4.19) | 180 (±12.8) | 6.77 × 107 | 2572 (±216) | 1.82 × 10−7 |
| Hydrogel Name | Swelling (%) | Eq. Swelling (%) | Gel Fraction (%) | Qv | Mc g/mol | Mesh Size (ξ) nm | Crosslinking Density (Ve) mol/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA5-PT30 | 7683 (±1053) | 98.69 (±0.15) | 81.98 (±2.65) | 171 (±23.3) | 6.20 × 107 | 7239 (±388) | 2.03 × 10−7 |
| HA5-PT20 | 1806 (±456) | 94.54 (±1.33) | 101.23 (±0.47) | 40 (±10) | 5.65 × 105 | 446 (±130.5) | 2.45 × 10−6 |
| HA5-PT15 | 5848 (±785) | 98.29 (±0.21) | 102.63 (±2.73) | 129 (±17.21) | 3.93 × 106 | 1755 (±276) | 3.21 × 10−7 |
| HA5-PT10 | 8101 (±174) | 98.77 (±0.02) | 87.30 (±1.58) | 180 (±4.00) | 6.73 × 106 | 2564 (±64.04) | 1.82 × 10−7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, F.; Albayati, M.; Dodou, K. Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6040059
Rashid F, Albayati M, Dodou K. Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid. Cosmetics. 2019; 6(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Fatimah, Mustafa Albayati, and Kalliopi Dodou. 2019. "Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid" Cosmetics 6, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6040059
APA StyleRashid, F., Albayati, M., & Dodou, K. (2019). Studies on Novel Methods for Formulating Novel Cross-Linked Hydrogel Films of Hyaluronic Acid. Cosmetics, 6(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6040059