Development of New Anti-Wrinkle Peptide Using Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptidomimetic Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ex Vivo Human Skin Explant Model Study
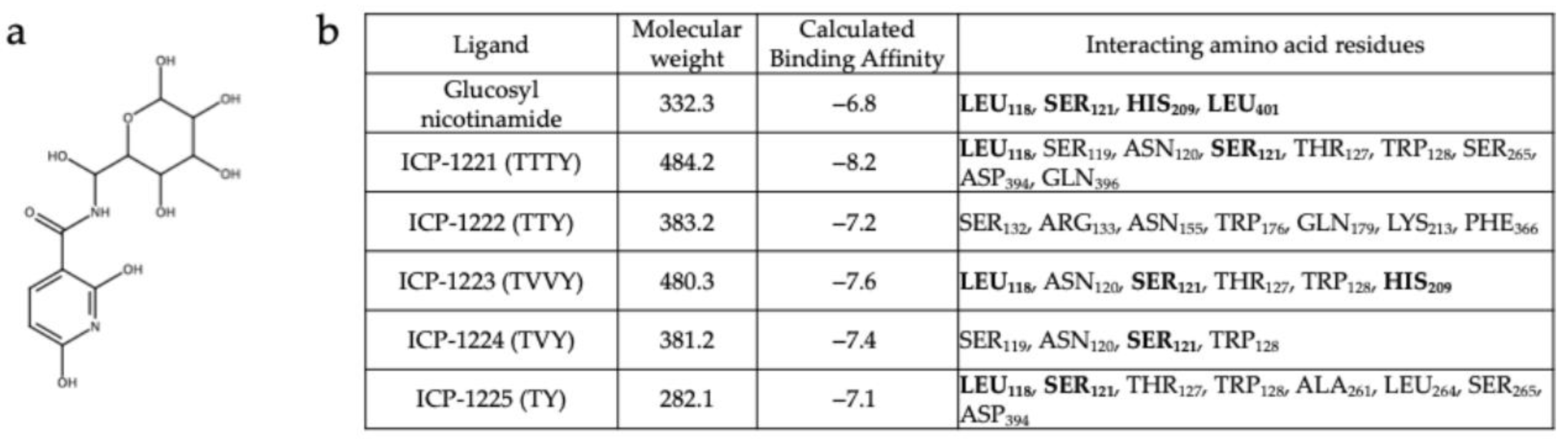
2.3. Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptides Screening and Molecular Docking
2.4. In Vitro Efficacy Assessment
2.4.1. Cell Viability Assay
2.4.2. Western Blot
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
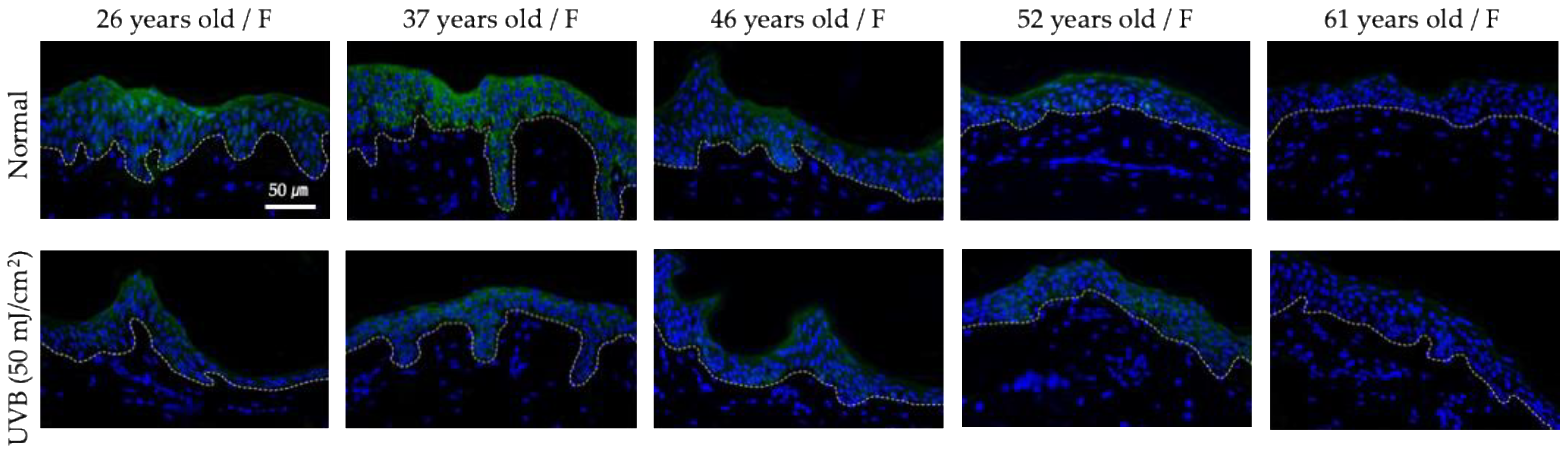
3.1. Clinical Assessment of Hsp47 as a Potential Anti-Wrinkle Target
3.2. In Silico Design of Hsp47 Binding Peptide
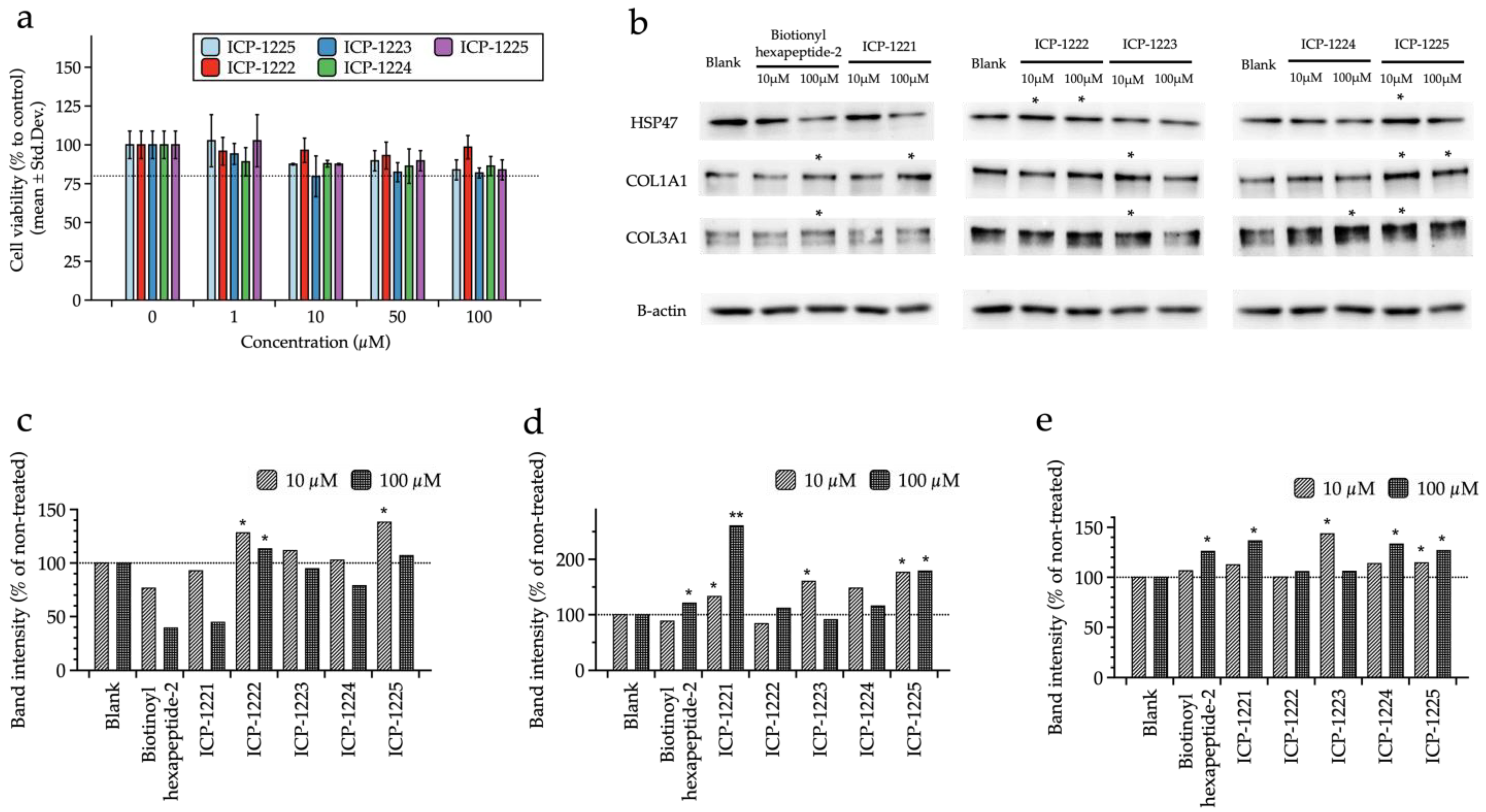
3.3. In Vitro Efficacy Assessment
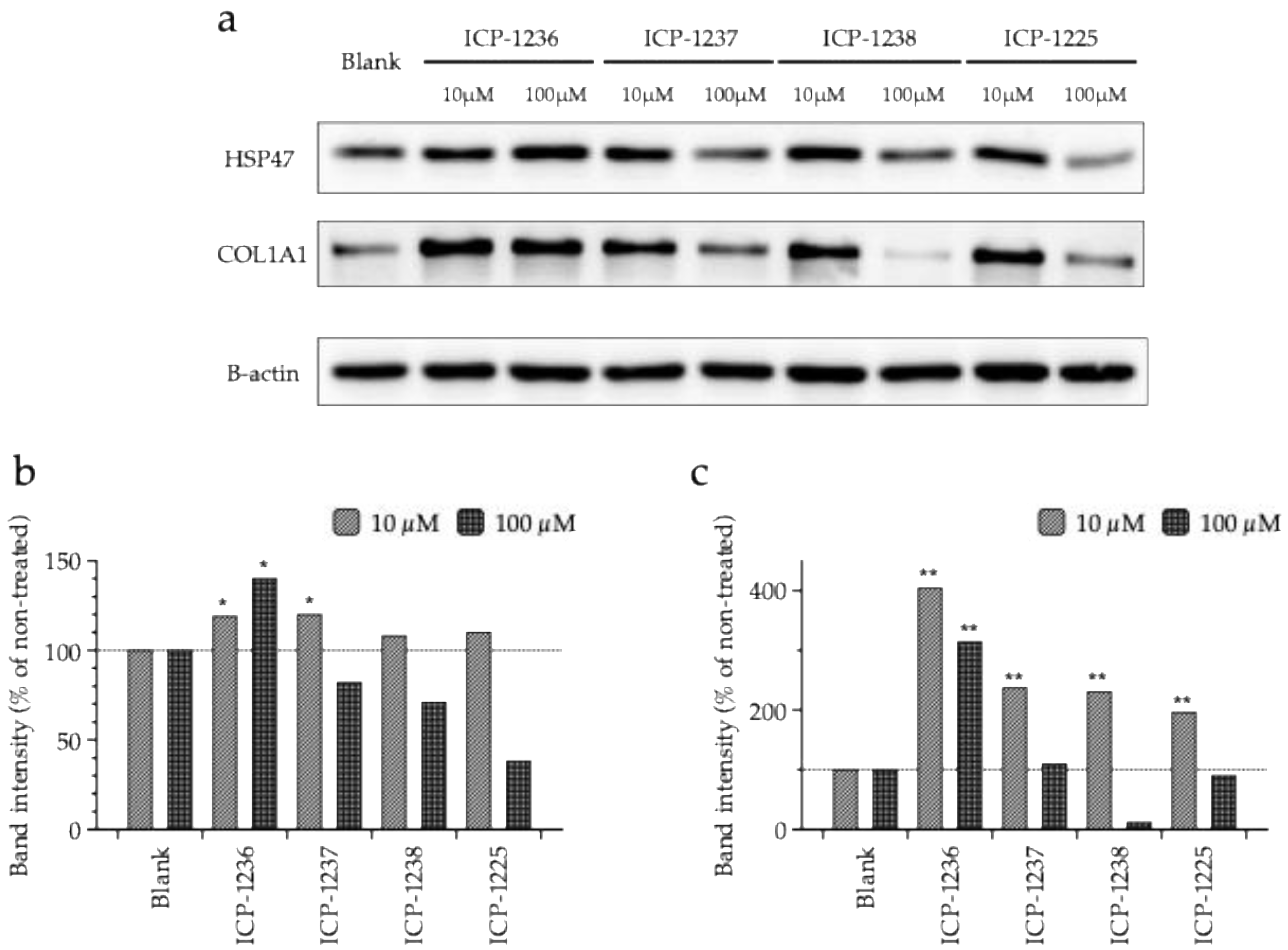
3.4. Synthesis and Efficacy Evaluation of Peptide Derivatives
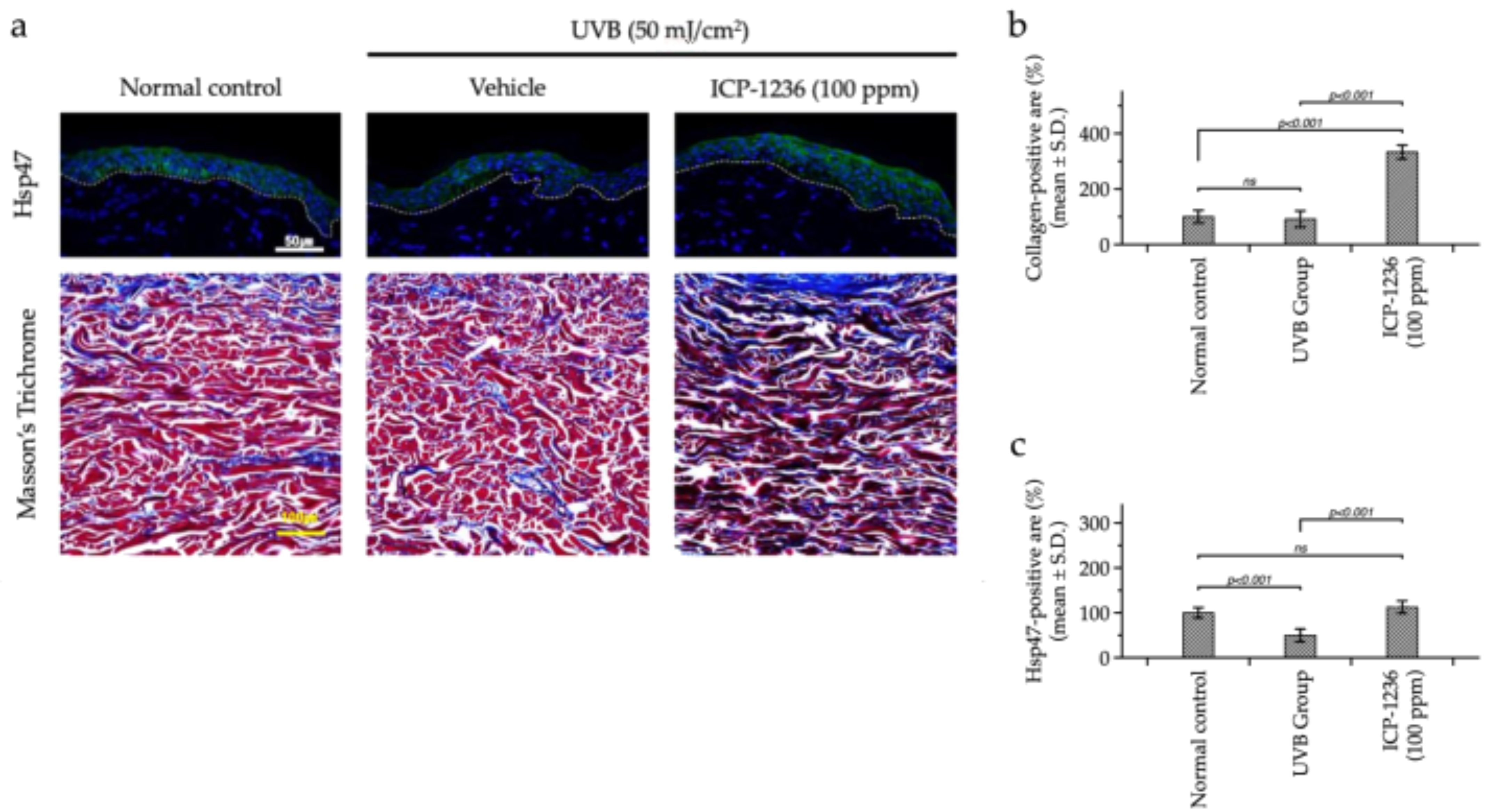
3.5. Ex Vivo Efficacy Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pintea, A.; Manea, A.; Pintea, C.; Vlad, R.-A.; Bîrsan, M.; Antonoaea, P.; Rédai, E.M.; Ciurba, A. Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence—A Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Nie, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Peptides in Cosmetics: From Pharmaceutical Breakthroughs to Skincare Innovations. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Mao, J.; Zheng, W.; Hu, Y.; Shi, J. Advance in Peptide-Based Drug Development: Delivery Platforms, Therapeutics and Vaccines. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, A.; Karaś, M.; Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk, K.; Zielińska, E.; Zieliński, D. Current Trends of Bioactive Peptides—New Sources and Therapeutic Effect. Foods 2020, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apone, F.; Barbulova, A.; Colucci, M.G. Plant and Microalgae Derived Peptides Are Advantageously Employed as Bioactive Compounds in Cosmetics. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Kamau, P.M.; Lai, R. Bioactive Peptides and Proteins from Wasp Venoms. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepek, I.A.; Bode, J.W. Synthetic Fermentation of Bioactive Molecules. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 46, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, R.; White, P.; Offer, J. Advances in Fmoc Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, H.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Y.-B. A Comprehensive Dataset of Therapeutic Peptides on Multi-Function Property and Structure Information. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goles, M.; Daza, A.; Cabas-Mora, G.; Sarmiento-Varón, L.; Sepúlveda-Yañez, J.; Anvari-Kazemabad, H.; Davari, M.D.; Uribe-Paredes, R.; Olivera-Nappa, Á.; Navarrete, M.A.; et al. Peptide-Based Drug Discovery through Artificial Intelligence: Towards an Autonomous Design of Therapeutic Peptides. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, P.; Barnard, J.M.; Downs, G.M. Chemical Similarity Searching. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1998, 38, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RDKit. Available online: https://www.rdkit.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Hu, C.; Yang, J.; Qi, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, B.; Zou, F.; Mei, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q. Heat Shock Proteins: Biological Functions, Pathological Roles, and Therapeutic Opportunities. MedComm 2022, 3, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.Y.; Pyo, M.J.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H.; Lee, S.-T. HSP47 Increases the Expression of Type I Collagen in Fibroblasts through IRE1α Activation, XBP1 Splicing, and Nuclear Translocation of β-Catenin. Cells 2024, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H. Clinical Efficacy of Adiponectin-Stimulating Peptide on UV-Induced Skin Damage. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, J.; Kor, M.; Shin, K.; Lim, C.; Han, H.S.; Lee, H.; Park, K.-Y.; et al. Anti-Wrinkle Benefits of Peptides Complex Stimulating Skin Basement Membrane Proteins Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajusz, D.; Rácz, A.; Héberger, K. Why Is Tanimoto Index an Appropriate Choice for Fingerprint-Based Similarity Calculations? J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, N.; Chalensouk-Khaosaat, J.; Gonzalez, S. Stimulation of the Fibrillar Collagen and Heat Shock Proteins by Nicotinamide or Its Derivatives in Non-Irradiated or UVA Radiated Fibroblasts, and Direct Antioxidant Activity of Nicotinamide Derivatives. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitson, R.R.A.; Kitsonová, D.; Siegel, D.; Ross, D.; Moody, C.J. Geldanamycin, a Naturally Occurring Inhibitor of Hsp90 and a Lead Compound for Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 17946–17963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, S. High Glucose Induces HSP47 Expression and Promotes the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors through the IRE1α/XBP1/HIF-1α Pathway in Retinal Müller Cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Hong, J.; Ryu, H.G.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kim, K.; Won, J.; Lee, J.; Chun, S.I. Monopolar Radiofrequency for Dermal Temperature Regulation and Remodeling: A Porcine Model Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3955–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scieglinska, D.; Krawczyk, Z.; Sojka, D.R.; Gogler-Pigłowska, A. Heat Shock Proteins in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of Epidermal Keratinocytes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2019, 24, 1027–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; O’Brien, K.; Guo, J.; Lincoln, V.; Kajiwara, C.; Chen, M.; Woodley, D.T.; Udono, H.; Li, W. Extracellular and Non-Chaperone Function of Heat Shock Protein-90α Is Required for Skin Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Nagata, K. Biology of Hsp47 (Serpin H1), a Collagen-Specific Molecular Chaperone. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams, S.D.; De Liefde-van Beest, M.; Nuijs, A.M.; Oomens, C.W.J.; Baaijens, F.P.T. Heat Shocks Enhance Procollagen Type I and III Expression in Fibroblasts in Ex Vivo Human Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2011, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, F.; Fujii, N.; Katsuyama, M.; Okumoto, S.; Matsusaki, M. Effects of Radiofrequency and Ultrasound on the Turnover Rate of Skin Aging Components (Skin Extracellular Matrix and Epidermis) via HSP47-Induced Stimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, K.-A.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, S.; Batsukh, S.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Radiofrequency Treatment Attenuates Age-Related Changes in Dermal–Epidermal Junctions of Animal Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-K.; Zheng, J.-S.; Liu, L. Mirror-Image Protein and Peptide Drug Discovery through Mirror-Image Phage Display. Chem 2024, 10, 2390–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.; Jeong, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Chung, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Hong, I.K.; Nam, G. Development of New Anti-Wrinkle Peptide Using Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptidomimetic Design. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060260
Baek S, Jeong S, Yoon S, Kim Y, Kim S, Chung H-J, Kim H-J, Hong IK, Nam G. Development of New Anti-Wrinkle Peptide Using Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptidomimetic Design. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(6):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060260
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Soyoon, Sekyoo Jeong, Seokjeong Yoon, Yeonjae Kim, Sungwoo Kim, Hwa-Jee Chung, Hyun-Jung Kim, In Ki Hong, and Gaewon Nam. 2025. "Development of New Anti-Wrinkle Peptide Using Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptidomimetic Design" Cosmetics 12, no. 6: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060260
APA StyleBaek, S., Jeong, S., Yoon, S., Kim, Y., Kim, S., Chung, H.-J., Kim, H.-J., Hong, I. K., & Nam, G. (2025). Development of New Anti-Wrinkle Peptide Using Cheminformatics-Assisted Peptidomimetic Design. Cosmetics, 12(6), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060260






