Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Hormonal Physiology of the Skin
3.1. Structure and Function of the Skin in Relation to Hormonal Receptors
3.2. Main Hormones Involved in Skin Health and Appearance
3.2.1. Estrogens
3.2.2. Progesterone
3.2.3. Androgens
3.2.4. Cortisol and Adrenal Hormones
3.2.5. Thyroid Hormones
3.3. Hormonal Changes Across Life Stages
4. Mechanisms of Action of Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology
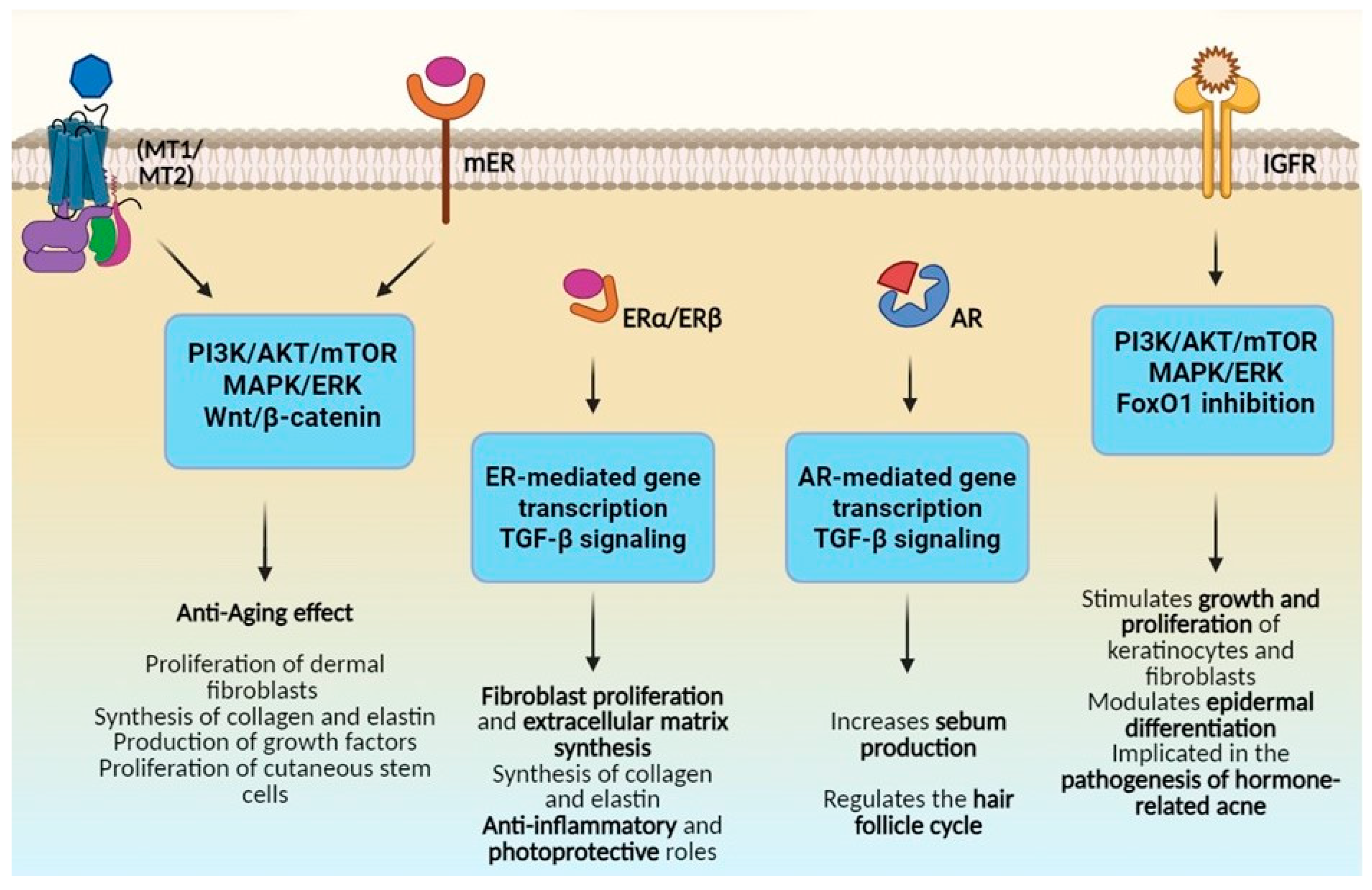
4.1. Modulation of Cutaneous Hormonal Receptors
4.2. Influence on Collagen and Elastin Synthesis
4.3. Regulation of Sebum Production
4.4. Effects on Pigmentation and Melanogenesis
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory and Regenerative Actions
5. Clinical Applications
Anti-Aging and Skin Rejuvenation
6. Modes of Administration
6.1. Systemic Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
6.2. Topical Hormone-Based Therapies
6.3. Peptides and Non-Steroidal Hormonal Modulators
6.4. Combined Device-Based and Hormonal Approaches
7. Safety and Ethical Considerations
7.1. Risks and Contraindications
7.2. Clinical Monitoring and Follow-Up
7.3. Off-Label Use and Regulatory Issues
8. Future Perspectives
8.1. Emerging Molecules and Technologies
8.2. Personalized Therapies Based on Hormonal Profiling
8.3. Integrated Approaches with Regenerative Medicine
8.4. Practical Limitations and Evidence Gaps
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Böhm, M.; Stegemann, A.; Paus, R.; Kleszczyåski, K.; Maity, P.; Wlaschek, M.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Endocrine Controls of Skin Aging. Endocr. Rev. 2025, 46, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, W.C.; Thornton, M.J.; Qin, K.; Rosenfield, R. Sexual hormones in human skin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Manna, P.R.; Tuckey, R.C. On the role of skin in the regulation of local and systemic steroidogenic activities. Steroids 2015, 103, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Miro, C.; Di Cicco, E.; Dentice, M. Thyroid hormone action in epidermal development and homeostasis and its implications in the pathophysiology of the skin. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2021, 44, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.; Del Vecchio, C.; Zupin, L.; Crovella, S. Unraveling the Role of Sex Hormones on Keratinocyte Functions in Human Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kosmadaki, M.; Roó, E.; Vexiau-Robert, D.; Kerob, D.; Goldstein, S.R. Skin, hair and beyond: The impact of menopause. Climacteric 2022, 25, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenfield, D.Z.; Sprague, J.; Eichenfield, L.F. Management of Acne Vulgaris: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, S.; Pathak, B.D.; Lamichhane, R.; Ghimire, B.; Devkota, S.; Ghimire, S.; Shrestha, P.; Acharya, S.; Baniya, S.; Bogati, K.; et al. Risk factors and severity of melasma in patients attending dermatology outpatient department of a tertiary care hospital: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2024, 103, e39674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reus, T.L.; Brohem, C.A.; Schuck, D.C.; Lorencini, M. Revisiting the effects of menopause on the skin: Functional changes, clinical studies, in vitro models and therapeutic alternatives. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 185, 111193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, R.M.; Chander, R.; Jetten, A.M.; Slominski, A.T. Neuro–immuno–endocrinology of the skin: How environment regulates body homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treviño, L.S.; Gorelick, D.A. The interface of nuclear and membrane steroid signaling. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker Frost, D.A.; Savchenko, A.; Ogunleye, A.; Armstrong, M.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. Elucidating the cellular mechanism for E2-induced dermal fibrosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, G.; Ren, L. Localization of sex steroid receptors in human skin. Histol. Histopathol. 2004, 19, 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, B.; Byemerwa, J.; Krebs, T.; Lim, F.; Chang, C.Y.; McDonnell, D.P. Estrogen Receptor Signaling in the Immune System. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.Y.; Maibach, H.I. Estrogen and skin: Therapeutic options. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 12, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darawsha, A.; Trachtenberg, A.; Levy, J.; Sharoni, Y. The protective effect of carotenoids, polyphenols, and estradiol on dermal fibroblasts under oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeza, M.; Bautista, L.; Bravo, M.G.; Heuze, Y. Molecular Interactions of Different Steroids Contributing to Sebum Production. Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Sawada, A.; Mori, T.; Sakuyama, S.; Tokudome, Y. Effect of estrogen/progesterone ratio on the differentiation and the barrier function of epidermal keratinocyte and three-dimensional cultured human epidermis. Life Sci. 2022, 293, 120356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Wei, Z.; Ju, Q.; Chen, W.C. Sex hormones and acne: State of the art. JDDG J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2021, 19, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altendorf, S.; Bertolini, M.; Le Riche, A.; Tosti, A.; Paus, R. Frontiers in the physiology of male pattern androgenetic alopecia: Beyond the androgen horizon. Physiol. Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ottaviani, M. Acne as an altered dermato-endocrine response problem. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimba, A.; Ikuta, K. Control of immunity by glucocorticoids in health and disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.K.; Man, M.Q.; Santiago, J.L.; Scharschmidt, T.C.; Hupe, M.; Martin-Ezquerra, G.; Youm, J.K.; Zhai, Y.; Trullas, C.; Feingold, K.R.; et al. Paradoxical benefits of psychological stress in inflammatory dermatoses models are glucocorticoid mediated. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2890–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paus, R.; Ramot, Y.; Kirsner, R.S.; Tomic-Canic, M. Topical L-thyroxine: The Cinderella among hormones waiting to dance on the floor of dermatological therapy? Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Cadesky, A.; Jaggi, S. Dermatologic manifestations of thyroid disease: A literature review. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1167890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrhoff, S.; Pomeranz, M.K. Specific dermatoses of pregnancy and their treatment. Dermatol. Ther. 2013, 26, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. A role for estrogen in skin ageing and dermal biomechanics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 197, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, M.J. Oestrogen functions in skin and skin appendages. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier-Sevrain, S.; Yaar, M.; Cantatore, J.; Traish, A.; Gilchrest, B.A. Estradiol induces proliferation of keratinocytes via receptor- mediated mechanisms. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1252–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittié, L.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Induction of Collagen by Estradiol: Difference Between Sun-Protected and Photodamaged Human Skin In Vivo. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C. Therapie der akne mit antiandrogenen—Eine evidenzbasierte übersicht. JDDG J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2003, 1, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, T.W.; Watson, R.E.B.; Langton, A.K. Skin ageing and topical rejuvenation strategies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189 (Suppl. 1), I17–I23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnesecchi, J.; Malbouyres, M.; De Mets, R.; Balland, M.; Beauchef, G.; Vié, K.; Chamot, C.; Lionnet, C.; Ruggiero, F.; Vanacker, J.-M. Estrogens induce rapid cytoskeleton re-organization in human dermal fibroblasts via the non-classical receptor GPR30. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidian, M.; Kolli, H.; Moy, R.L. Management of skin thinning and aging: Review of therapies for neocollagenesis; hormones and energy devices. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birzniece, V.; Ho, K.K.Y. Paracrine and endocrine control of the growth hormone axis by estrogen. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, R269–R278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Q.; Tao, T.; Hu, T.; Karadağ, A.S.; Al-Khuzaei, S.; Chen, W.C. Sex hormones and acne. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 35, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, A.; Thiboutot, D.; Stein Gold, L.; Cartwright, M.; Gerloni, M.; Fragasso, E.; Mazzetti, A. Efficacy and Safety of Topical Clascoterone Cream, 1%, for Treatment in Patients with Facial Acne: Two Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.M.; Randolph, M.; Rajabi-Estarabadi, A.; Keri, J.; Tosti, A. Hormonal Contraceptives and Dermatology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logesh, R.; Prasad, S.R.; Chipurupalli, S.; Robinson, N.; Mohankumar, S.K. Natural tyrosinase enzyme inhibitors: A path from melanin to melanoma and its reported pharmacological activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Simon, S.R. Asoprisnil, a selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM), inhibits melanosome export in B16F10 cells and HEMn-DP melanocytes. Molecules 2020, 25, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, R.; Tan, J.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, X.; Jin, S.; Ouyang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, X.; et al. Hormonal interventions in skin wounds—A mini review. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, J.P.; Zimmermann, M.; Faas, M.; Stifel, U.; Chambers, D.; Krishnacoumar, B.; Taudte, R.V.; Grund, C.; Erdmann, G.; Scholtysek, C.; et al. Metabolic rewiring promotes anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Nature 2024, 629, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, H.D.; Cooke, P.S. Targeting estrogen signaling and biosynthesis for aged skin repair. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1281071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Chantre, C.O.; Ardoña, H.A.M.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Campbell, P.H.; Parker, K.K. Biomimetic and estrogenic fibers promote tissue repair in mice and human skin via estrogen receptor β. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.V.S.; Andrade, S.S. Decoding the impact of ageing and environment stressors on skin cell communication. Biogerontology 2025, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, N.; Yan, Y.L.; Xiong, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, K.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Q.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.D. Recent advances in the anti-aging effects of phytoestrogens on collagen, water content, and oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja-Agius, J.; Brincat, M.; Borg, M. Skin connective tissue and ageing. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Obs. Gynaecol. 2013, 27, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. Phytoestrogens (Resveratrol and equol) for estrogen-deficient skin—Controversies/misinformation versus anti-aging in vitro and clinical evidence via nutraceutical-cosmetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, K.; Bansal, P.; Sharma, L.K.; Garga, U.C.; Vats, G. A study comparing the clinical and hormonal profile of late onset and persistent acne in adult females. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzyszkowska, D.; Niedzielska, M.; Kozłowski, M.; Brodowska, A.; Przepiera, A.; Malczyk-Matysiak, K.; Cymbaluk-Płoska, A.; Sowińska-Przepiera, E. Evaluation of Hormonal Factors in Acne Vulgaris and the Course of Acne Vulgaris Treatment with Contraceptive-Based Therapies in Young Adult Women. Cells 2022, 11, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.V.; Yeung, H.; Cheng, C.E.; Cook-Bolden, F.; Desai, S.R.; Druby, K.M.; Freeman, E.E.; Keri, J.E.; Gold, L.F.; Tan, J.K.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 1006.e1–1006.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabalik-Hoganson, J.; Frey, K.M.; Ozdener-Poyraz, A.E.; Slugocki, M. Clascoterone: A Novel Topical Androgen Receptor Inhibitor for the Treatment of Acne. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, P.; George, M. Clascoterone: A new topical anti-androgen for acne management. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, L.; Reyes-Hadsall, S.; Barbieri, J.S.; Mostaghimi, A. New Developments in Topical Acne Therapy. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, S.T.; Khan, Z.; Abbas, S.; Imran, L.; Munir, S.; Tahir, M.J.; Kheljee, A.Z.; Eljack, M.M.; Ahmed, A. Role of topical spironolactone in the treatment of acne: A systematic review of clinical trials—Does this therapy open a path towards favorable outcomes? J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piętowska, Z.; Nowicka, D.; Szepietowski, J.C. Understanding Melasma-How Can Pharmacology and Cosmetology Procedures and Prevention Help to Achieve Optimal Treatment Results? A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.; Wang, R.F.; Ozog, D.; Lim, H.W.; Mohammad, T.F. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. Part II. Review of management and treatment options for hyperpigmentation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Rodrigues, M. An Update on New and Existing Treatments for the Management of Melasma. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2024, 25, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Alas-Carbajal, R.; Bonifaz-Araujo, J.F.; Marín-Castro, H.; Valenzuela-Ahumada, F.; Véliz-Barandiarán, J.L.; Vila Echague, A.; Zepeda-Reyes, D.E.; Miot, H.A. Latin American consensus on the treatment of melasma. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 64, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, A.C.P.; Rigon, R.B.; Bagatin, E.; Leonardi, G.R. Perspectives of topical formulations for melasma. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKesey, J.; Tovar-Garza, A.; Pandya, A.G. Melasma Treatment: An Evidence-Based Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 173–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, M.; Berneburg, M.; Arellano, I.; Picardo, M. Treatment of melasma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 5 (Suppl. 2), S272–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saceda-Corralo, D.; Domínguez-Santas, M.; Vañó-Galván, S.; Grimalt, R. What’s new in therapy for male androgenetic alopecia? Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 15–24. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36169916/ (accessed on 6 August 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devjani, S.; Ezemma, O.; Kelley, K.J.; Stratton, E.; Senna, M. Androgenetic Alopecia: Therapy Update. Drugs 2023, 83, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Talukder, M. Efficacy and safety of dutasteride in the treatment of alopecia: A comprehensive review. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2025, 26, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, M.M.; Avram, M.; McMichael, A.; Tosti, A.; Lipner, S.R. Antiandrogen therapy for the treatment of female pattern hair loss: A clinical review of current and emerging therapies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2025, 93, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarchi, S.; Bienenfeld, A.; Lo Sicco, K.; Marchbein, S.; Shapiro, J.; Nagler, A.R. Androgens in women: Hormone-modulating therapies for skin disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraccini, B.M.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Scarci, F.; Jansat, J.M.; Falqués, M.; Otero, R.; Tamarit, M.L.; Galván, J.; Tebbs, V.; Massana, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of topical finasteride spray solution for male androgenetic alopecia: A phase III, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.H.; Prasad, S.; De Souza, B.; Burns, L.J.; Senna, M.M. Topical Antiandrogen Therapies for Androgenetic Alopecia and Acne Vulgaris. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jimenez, J.J. Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia Using PRP to Target Dysregulated Mechanisms and Pathways. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 843127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, P.; Dionisi, L.; Pizzicannella, J.; De Angelis, B.; De Fazio, D.; Garcovich, S. A Randomized Blinded Retrospective Study: The combined use of Micro-needling Technique, Low-Level Laser Therapy and Autologous Non-Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma improves Hair Re-Growth in patients with Androgenic Alopecia. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, N.; Arruda, S.; Swearingen, A.; Forouzan, E.; Sadick, N.S. Evaluating the Efficacy of Platelet Rich Plasma and 1550 nm Fractional Laser in Combination and Alone for Management of Androgenetic Alopecia. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Mays, R.R.; Dotzert, M.S.; Versteeg, S.G.; Shear, N.H.; Piguet, V. Efficacy of non-surgical treatments for androgenetic alopecia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.; Phillips, T.J. Estrogen and skin: The effects of estrogen, menopause, and hormone replacement therapy on the skin. J Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine-Fenning, N.J.; Brincat, M.P.; Muscat-Baron, Y. Skin aging and menopause: Implications for treatment. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 371–378. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12762829/ (accessed on 6 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.F. Postmenopausal skin and estrogen. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2012, 28 (Suppl. 2), 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yokozeki, H.; Katagiri, K. Physiological and functional changes in the stratum corneum restored by oestrogen in an ovariectomized mice model of climacterium. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.C.; Pilkington, S.M.; Wray, J.R.; Newton, V.L.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Bell, M.; Watson, R.E.; Nicolaou, A. Menopause induces changes to the stratum corneum ceramide profile, which are prevented by hormone replacement therapy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Muguet, V.; Christen-Zaech, S. Restoring Skin Hydration and Barrier Function: Mechanistic Insights Into Basic Emollients for Xerosis Cutis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 64 (Suppl. 1), 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, C.J.; Mehta, J.M.; Manson, J.E. Management of Menopausal Symptoms: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, J.V. Hormone Therapy for Postmenopausal Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Files, J.; Kling, J.M. Transdermal delivery of bioidentical estrogen in menopausal hormone therapy: A clinical review. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 543–549. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31795776/ (accessed on 6 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Genazzani, A.R.; Monteleone, P.; Giannini, A.; Simoncini, T. Hormone therapy in the postmenopausal years: Considering benefits and risks in clinical practice. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 27, 1115–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, C.M.; Barry, M.J.; Nicholson, W.K.; Cabana, M.; Caughey, A.B.; Chelmow, D.; Coker, T.R.; Davis, E.M.; Donahue, K.E.; Jaén, C.R.; et al. Hormone Therapy for the Primary Prevention of Chronic Conditions in Postmenopausal Persons: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2022, 328, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.B.; Binder, M.; Demschik, G.; Bieglmayer, C.; Reiner, A. Treatment of skin aging with topical estrogens. Int. J. Dermatol. 1996, 35, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Ip, K.; Biundo, B.; Carvalho, M.; Day, A.J.; Bassani, A.S.; Song, H.; Valdez, B.C.; Banov, D. In Vitro Percutaneous Absorption of Permeation-Enhancing Estrogen Formulations. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DailyMed—ESTROGEL—Estradiol Gel, Metered. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=762ac371-bb8b-47e7-b48f-e80d452c9dd4 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Gasser, S.; Heidemeyer, K.; von Wolff, M.; Stute, P. Impact of progesterone on skin and hair in menopause–a comprehensive review. Climacteric 2021, 24, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier-Sévrain, S. Effect of estrogens on skin aging and the potential role of selective estrogen receptor modulators. Climacteric 2007, 10, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, S.; Thornton, J. Effect of estrogens on skin aging and the potential role of SERMs. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, M.J.; Emmerson, E.; Campbell, L.; Ashcroft, G.S. Selective estrogen receptor modulators accelerate cutaneous wound healing in ovariectomized female mice. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gao, X.; Guo, Y.; Xie, W. Research Progress on Bioactive Factors against Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintea, A.; Manea, A.; Pintea, C.; Vlad, R.A.; Bîrsan, M.; Antonoaea, P.; Rédai, E.M.; Ciurba, A. Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence: A Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Domyati, M.; El-Ammawi, T.S.; Medhat, W.; Moawad, O.; Mahoney, M.G.; Uitto, J. Expression of transforming growth factor-β after different non-invasive facial rejuvenation modalities. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natari, S.; Kim, K.E.; Ryu, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Device-Induced Neocollagenesis: Profibrotic Response or True Neocollagenesis? Lasers Surg. Med. 2020, 52, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.Y.; Hwang, S.; Chun SIl Kim, S.M.; Almurayshid, A.; Oh, S.H. A Prospective, Split-Face, Comparative Study of Combined Treatment with Fractional Microneedle Radiofrequency and Nonablative 1927-nm Fractional Thulium Fiber Laser for Wrinkle Treatment. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, E101–E105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.D.; Salame, N.; Eber, A.; Labadie, J.G.; Kandula, P.; Dover, J.S. Combination Use of 1440-nm and 1927-nm Nonablative Fractional Laser with Monopolar Radiofrequency for the Treatment of Facial Skin Laxity, Skin Texture, and Pigmentation. Dermatol. Surg. 2025, 51, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Baek, E.J.; Kim, H.R.C.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Comparison of the effects of fractional microneedle radiofrequency and microneedling on modulating the senescent fibroblast milieu in aged skin. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartlehner, G.; Patel, S.V.; Reddy, S.; Rains, C.; Schwimmer, M.; Kahwati, L. Hormone Therapy for the Primary Prevention of Chronic Conditions in Postmenopausal Persons: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2022, 328, 1747–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, E.; Kling, J.M.; Lobo, A.S.; Faubion, S.S. Menopausal hormone therapy in women with medical conditions. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergendal, A.; Kieler, H.; Sundström, A.; Hirschberg, A.L.; Kocoska-Maras, L. Risk of venous thromboembolism associated with local and systemic use of hormone therapy in peri- and postmenopausal women and in relation to type and route of administration. Menopause 2016, 23, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, J.A.E.; Crandall, C.J.; Rossouw, J.E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Anderson, G.L.; Stefanick, M.L.; Aragaki, A.K.; Cauley, J.A.; Wells, G.L.; LaCroix, A.Z.; et al. The Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Trials and Clinical Practice: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DailyMed—ELESTRIN—Estradiol Gel, Metered. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=eff2dea1-f117-11e3-ac10-0800200c9a66 (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Bushnell, C.; McCullough, L.D.; Awad, I.A.; Chireau, M.V.; Fedder, W.N.; Furie, K.L.; Howard, V.J.; Lichtman, J.H.; Lisabeth, L.D.; Piña, I.L.; et al. Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Women A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2014, 45, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, Y.; Coupland, C.; Hippisley-Cox, J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: Nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ 2019, 364, k4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, A.; Robson, D.; Tellis, B.; Smith, S.; Dunkley, S.; Baber, R. Safety of menopause hormone therapy in postmenopausal women at higher risk of venous thromboembolism: A systematic review. Climacteric 2025, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjoribanks, J.; Farquhar, C.; Roberts, H.; Lethaby, A.; Lee, J. Long-term hormone therapy for perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, CD004143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goodman, N.; Cobin, R.; Ginzburg, S.; Katz, I.; Woode, D. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Menopause: Executive summary of recommendations. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, N.; Papadopoulou, M.A.; Samaras, D.; Ongaro, F. Off-label use of hormones as an antiaging strategy: A review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, K.; Kurtti, A.; Jagdeo, J. The Role of Hormone Therapy in Female Aesthetic Rejuvenation. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternicka, J.; Nowicki, R.J.; Bieniaszewski, L.; Purzycka-Bohdan, D. Off-Label Treatment in Inflammatory Skin Diseases-European Point of View. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gallez, A.; Palazzo, C.; Blacher, S.; Tskitishvili, E.; Noël, A.; Foidart, J.M.; Evrard, B.; Pequeux, C.; Piel, G. Liposomes and drug-in-cyclodextrin-in-liposomes formulations encapsulating 17β-estradiol: An innovative drug delivery system that prevents the activation of the membrane-initiated steroid signaling (MISS) of estrogen receptor α. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, R.P.; MacLaughlin, E.J.; Courtney, L.A.; Vineyard, D.D. An ethical assessment of compounded bioidentical hormone therapy. Climacteric 2024, 27, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Compounded Bioidentical Menopausal Hormone Therapy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 142, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, J.V. Concerns about Compounded Bioidentical Menopausal Hormone Therapy. Cancer J. 2022, 28, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.E. The role of personalized medicine in identifying appropriate candidates for menopausal estrogen therapy. Metabolism 2013, 62 (Suppl. 1), S15–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šitum, M.; Franceschi, D.; Franceschi, N. Challenges and strategies in dermatologic therapy—Personalized medicine, patient safety, and pharmacoeconomics. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Miller, V.M. Improving clinical outcomes through attention to sex and hormones in research. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godic, A. The role of stem cells in anti-aging medicine. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 37, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almadori, A.; Butler, P.E.M. Scarring and Skin Fibrosis Reversal with Regenerative Surgery and Stem Cell Therapy. Cells 2024, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.; Podesta, L.; Lana, J.F.; Shapiro, G.; Domingues, R.B.; van Zundert, A.; Alexander, R.W. The Regenerative Marriage Between High-Density Platelet-Rich Plasma and Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdek, M.T.; Wyles, C.C.; Stalboerger, P.G.; Terzic, A.; Behfar, A.; Moran, S.L. Collagen and Fractionated Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold for Dermal Regeneration. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Naughton, G.K.; Makino, E.T.; Kadoya, K.; Maitra, P. Regenerative Skincare Technologies Derived from Human Fibroblasts: Growth Factors and Exosomes for Transformative Outcomes. Dermatol. Surg. 2024, 50, S139–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, L.; Guo, P.; Hui, W.; Xia, F.; Yi, C. Recent advances in dermal fibroblast senescence and skin aging: Unraveling mechanisms and pioneering therapeutic strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1592596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yue, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, P. Uncovering key mechanisms and intervention therapies in aging skin. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2024, 79, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.; Sousa-Victor, P.; Jasper, H. Rejuvenating Strategies for Stem Cell-Based Therapies in Aging. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Jo, J.; Hyun, H.; Lee, G.; Ma, S.; Sohn, J.; Sung, D.K.; Han, C.Y.; Kim, M.; Hwang, D.; et al. Extracellular vesicle as therapeutic agents in anti-aging: Mechanistic insights and future potential. J. Control. Release 2025, 383, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Yoo, D.; Lee, S.; Go, D.; Bui, V.D.; Jung, W.K.; You, D.G.; Park, J.H.; Um, W. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Skin Antiaging Treatments. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 22504–22527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanczyk, F.Z. Treatment of postmenopausal women with topical progesterone creams and gels: Are they effective? Climacteric 2014, 17, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, O.G.; Williams, S.; Goldie, K. The therapeutic and commercial landscape of stem cell vesicles in regenerative dermatology. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hormone | Key Pathways | Cutaneous Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogens | PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK, Wnt/β-catenin | Increases collagen and elastin synthesis, improves hydration, reduces wrinkles |
| Androgens | AR-mediated transcription, TGF-β | Stimulates sebum production, regulates hair cycle, contributes to acne and alopecia |
| Insulin/IGF-1 | PI3K/AKT/mTOR, MAPK/ERK, FoxO1 | Enhances proliferation of keratinocytes and fibroblasts; implicated in acne |
| Melatonin | PI3K/AKT, MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, stimulates skin regeneration, UV protective |
| DHEA | SIRT1, Nrf2/ARE, NF-κB, ERβ, AR | Anti-aging, antioxidant via SIRT1 and Nrf2, reduces inflammation via NF-κB |
| Indication | Hormonal Strategies | Mechanisms/Clinical Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Skin aging and rejuvenation | Systemic HRT, topical estrogens, phytoestrogens, combination with energy-based devices | Stimulates fibroblast activity; increases collagen and ECM synthesis; improves hydration; reduces wrinkles |
| Hormonal acne | Systemic antiandrogens (spironolactone, cyproterone acetate), combined oral contraceptives, topical clascoterone | Reduces sebum production and inflammation via androgen receptor blockade; controls acne flares |
| Melasma and pigmentary disorders | Hormonal modulation (adjustment of contraceptives), topical depigmenting agents, procedural interventions (peels, lasers), tranexamic acid | Reduces melanocyte stimulation; enhances efficacy of depigmenting agents; improves hormonal stability |
| Androgenetic alopecia | 5α-reductase inhibitors (finasteride, dutasteride), topical antiandrogens, COCs, PRP, LLLT | Reduces DHT levels; slows follicular miniaturization; promotes hair regrowth; enhances follicular response |
| Postmenopausal atrophy and skin dryness | Systemic HRT, topical estrogens, phytoestrogens, supportive skincare (ceramide emollients, gentle cleansers) | Restores barrier function; improves hydration; increases epidermal thickness; reduces irritation and xerosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosset, F.; Marino, M.; Mastorino, L.; Pala, V.; Santaniello, U.; Sciamarrelli, N.; Giunipero di Corteranzo, I.; Aquino, C.; Ribero, S.; Quaglino, P. Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050207
Rosset F, Marino M, Mastorino L, Pala V, Santaniello U, Sciamarrelli N, Giunipero di Corteranzo I, Aquino C, Ribero S, Quaglino P. Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(5):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050207
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosset, Francois, Marta Marino, Luca Mastorino, Valentina Pala, Umberto Santaniello, Nadia Sciamarrelli, Isotta Giunipero di Corteranzo, Carola Aquino, Simone Ribero, and Pietro Quaglino. 2025. "Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives" Cosmetics 12, no. 5: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050207
APA StyleRosset, F., Marino, M., Mastorino, L., Pala, V., Santaniello, U., Sciamarrelli, N., Giunipero di Corteranzo, I., Aquino, C., Ribero, S., & Quaglino, P. (2025). Hormonal Therapies in Cosmetic Dermatology: Mechanisms, Clinical Applications, and Future Perspectives. Cosmetics, 12(5), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12050207







