Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptors Stimulate MAPK-Mediated Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Transactivating HER4 in a Neuregulin-1, MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner Requiring Activation of the ROS-System
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Cells Culture
2.2.2. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.2.3. Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation
2.2.4. Transfection with siRNA
2.2.5. NRG1-β1 ELISA
2.2.6. Proliferation Assays
2.2.7. Statistics
3. Results
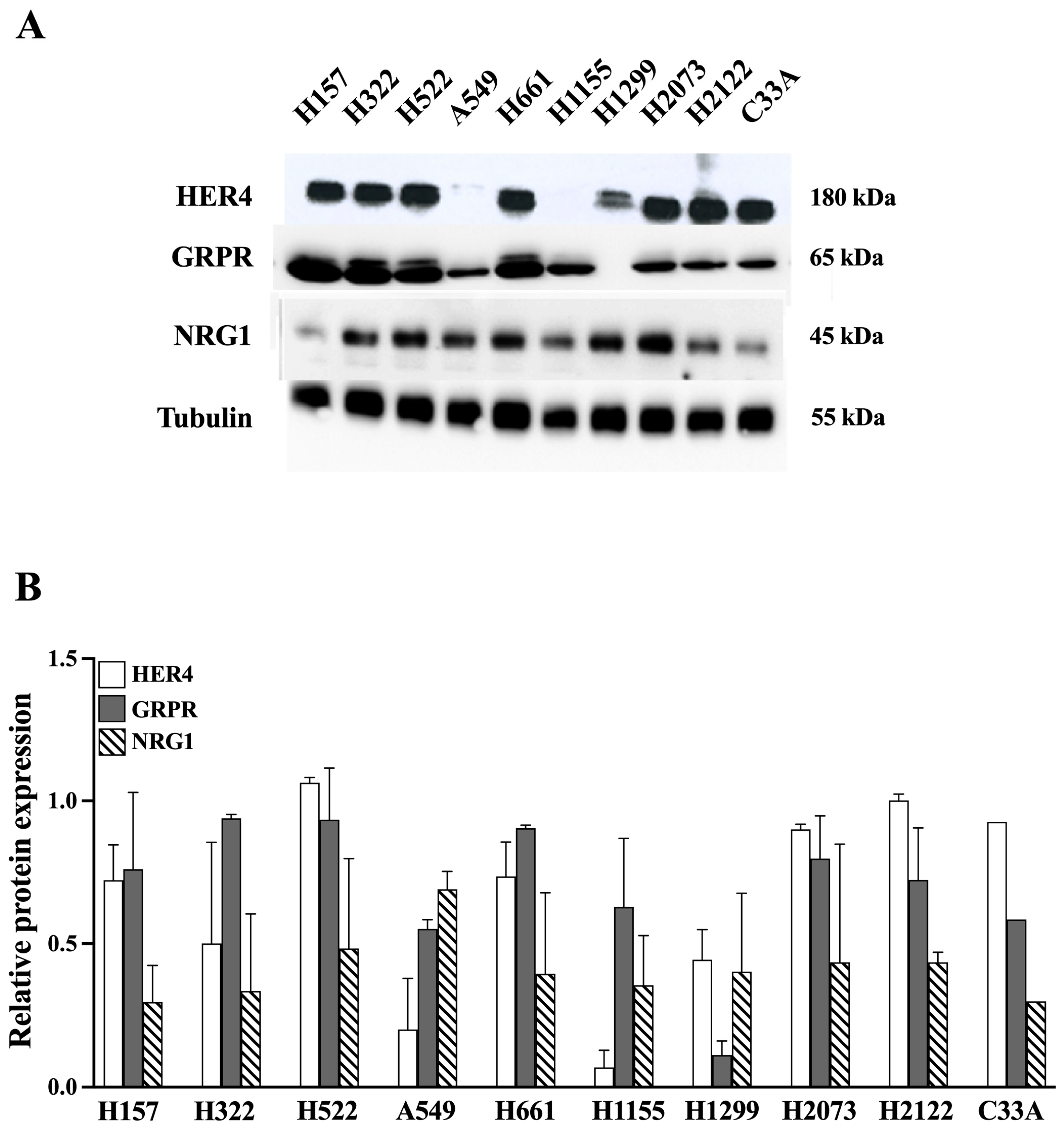
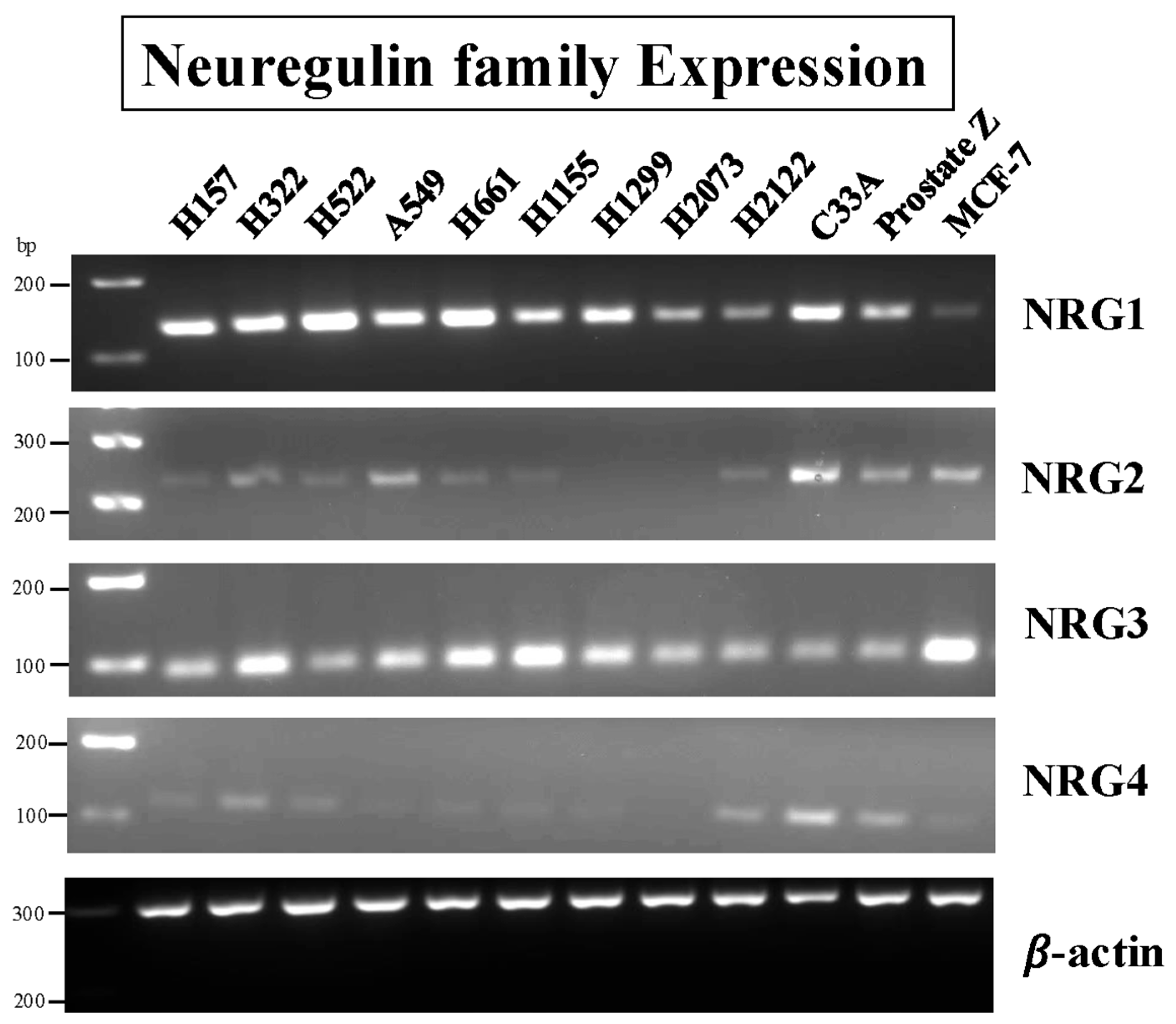
3.1. RT-PCR of Cell Line Extracts
3.2. Western Blot of Cell Line Extracts
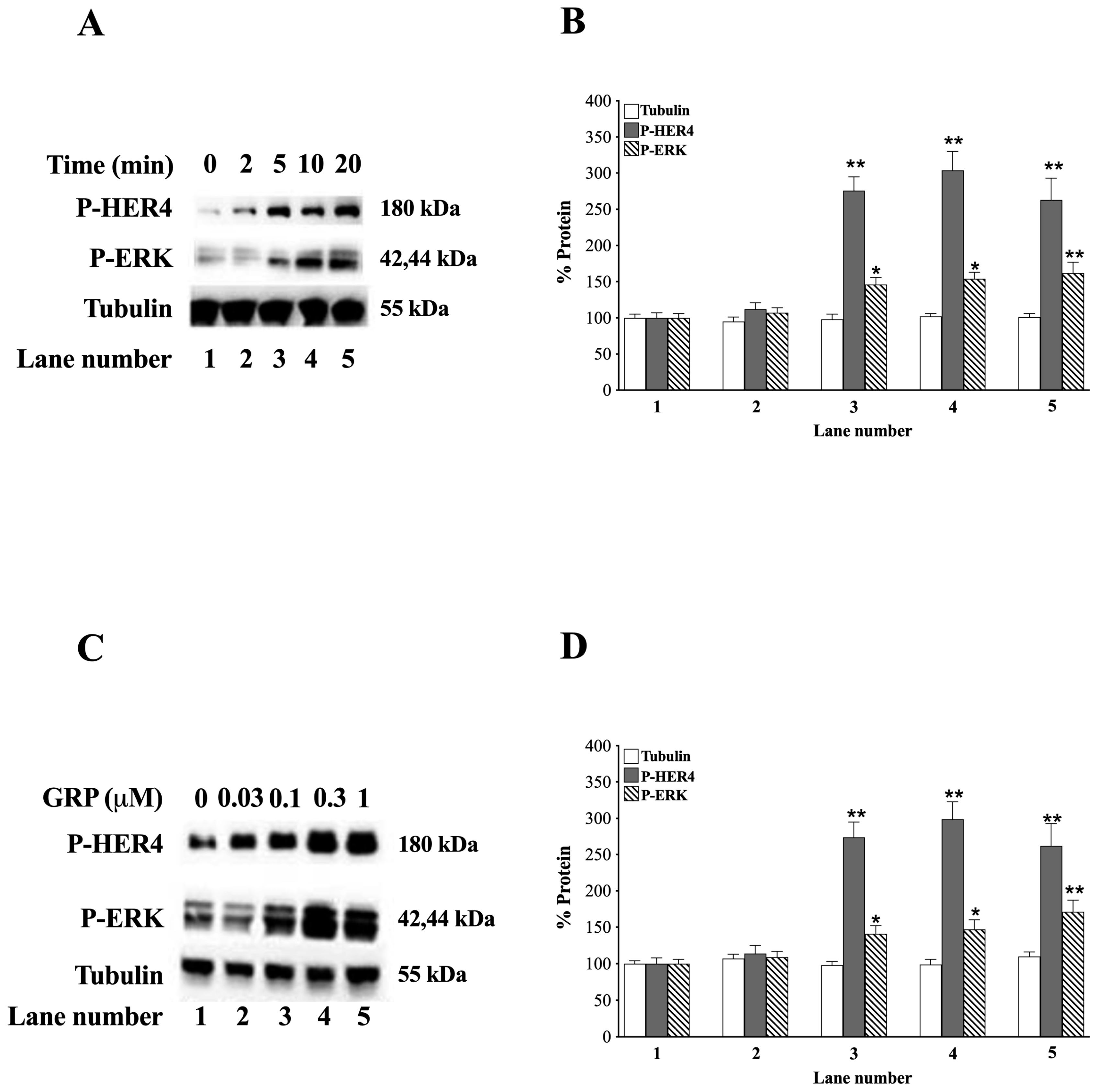
3.3. GRP and HER4 Phosphorylation
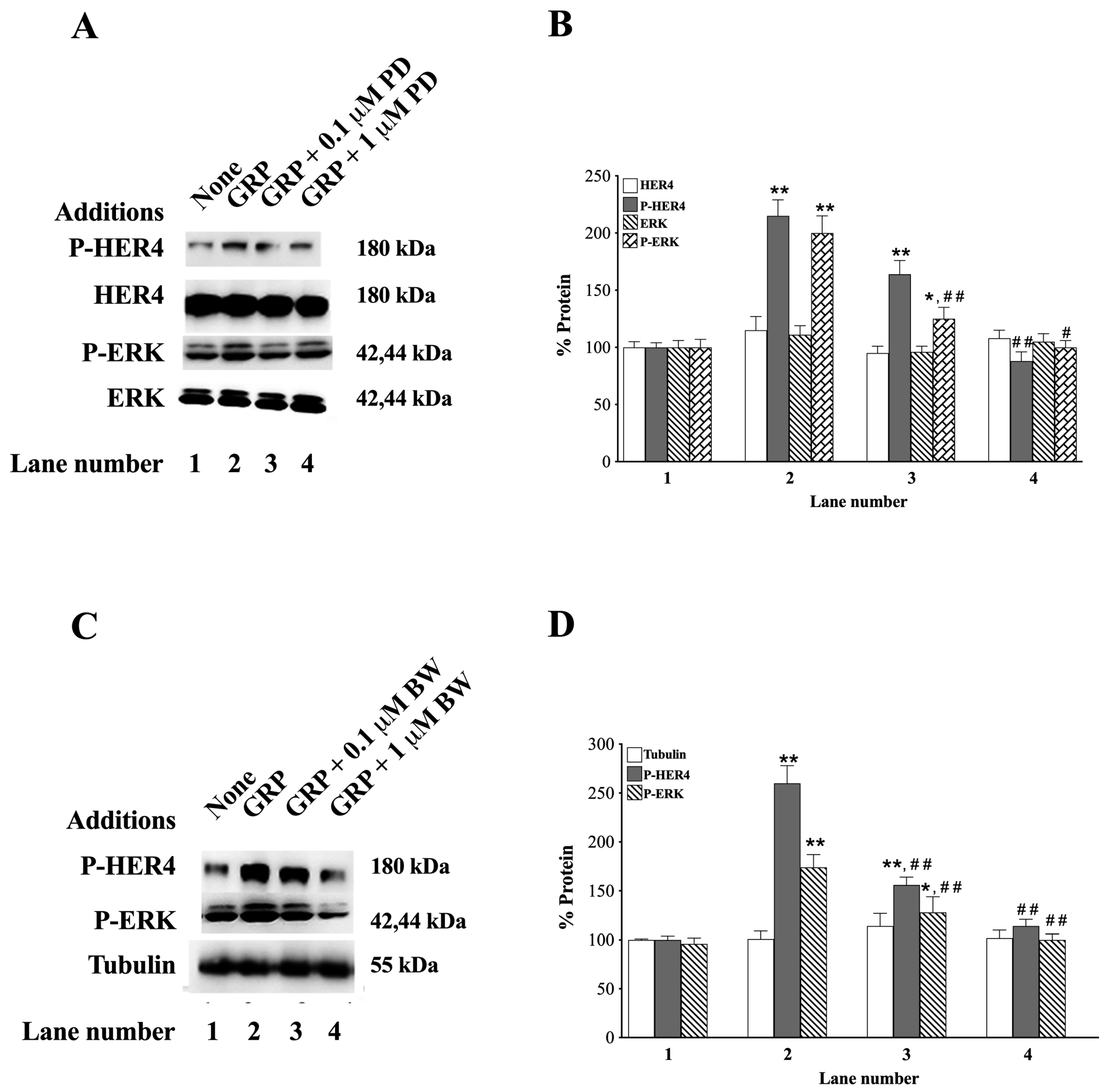
3.4. GRP Receptor Antagonists
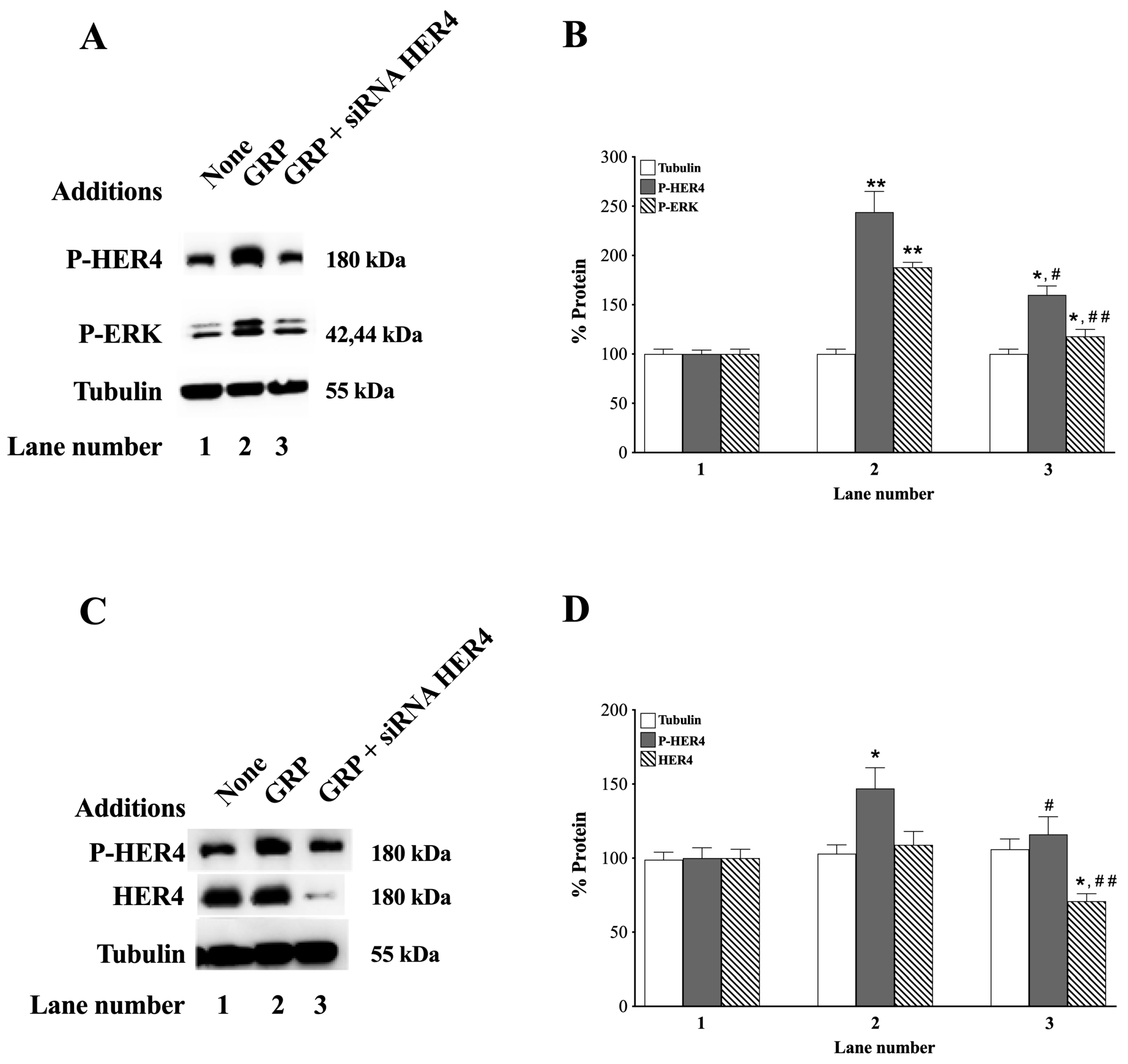
3.5. siRNA HER4
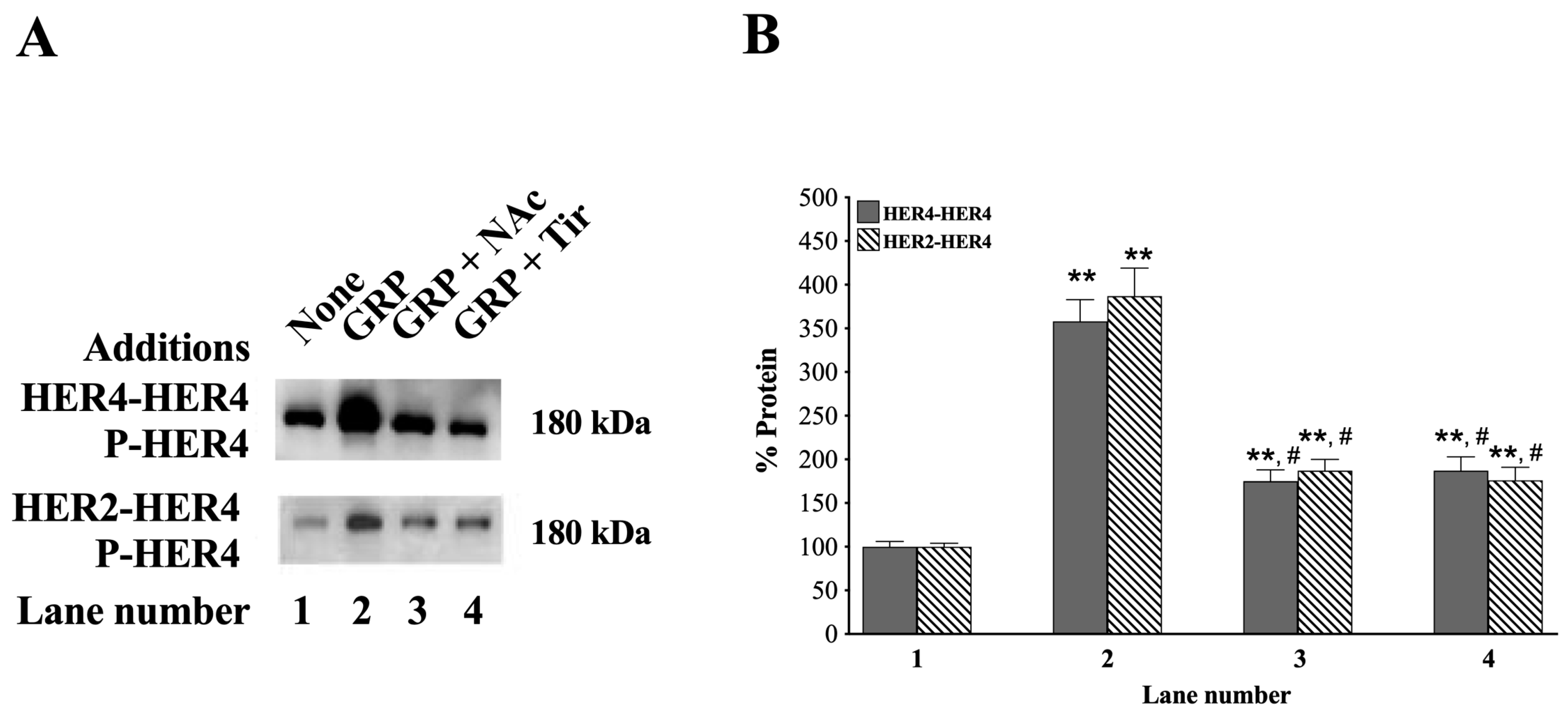
3.6. HER4 Dimerization and the Effect of ROS Inhibitors
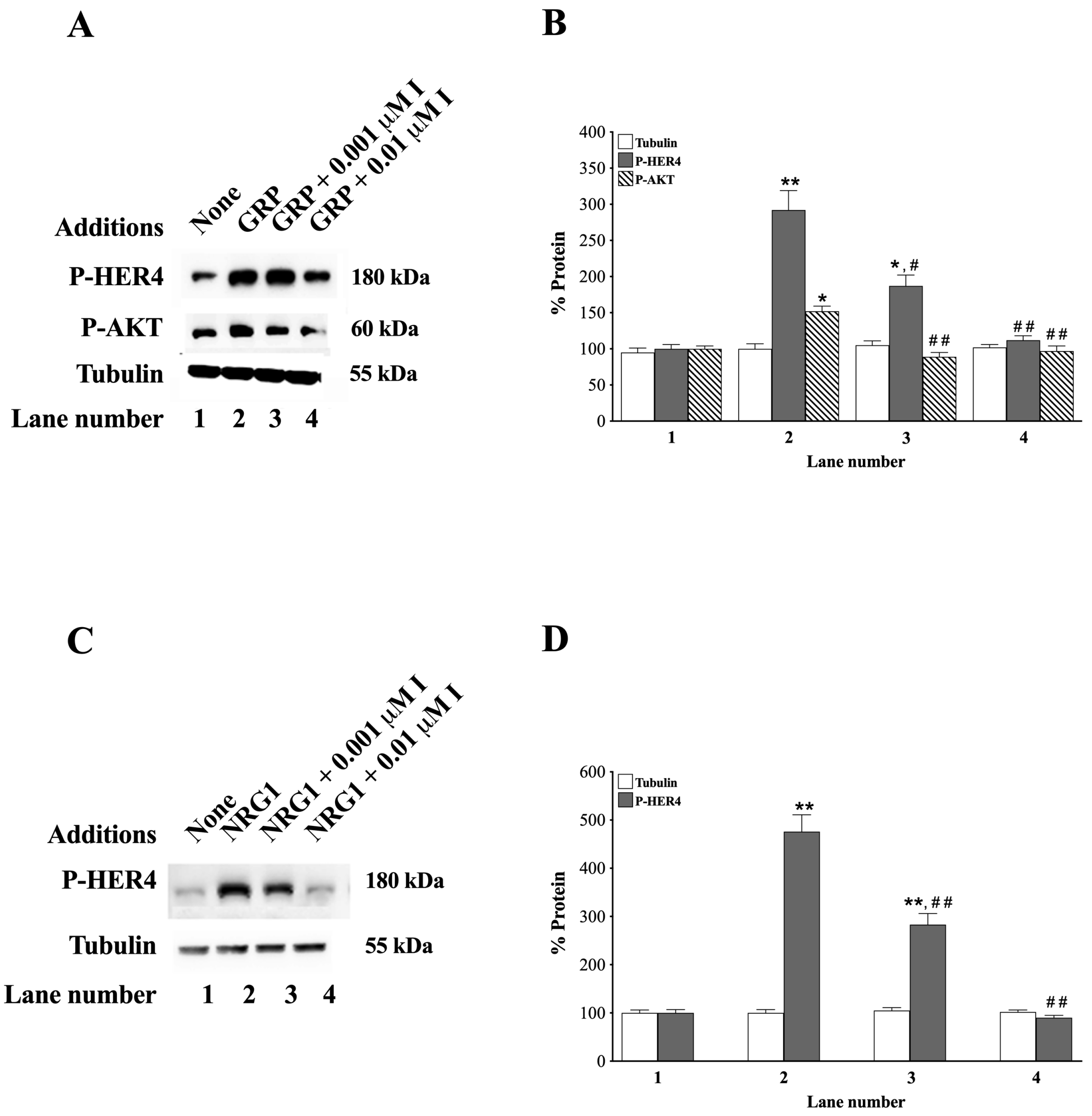
3.7. Effects of Ibrutinib
3.8. Effects of NRG1
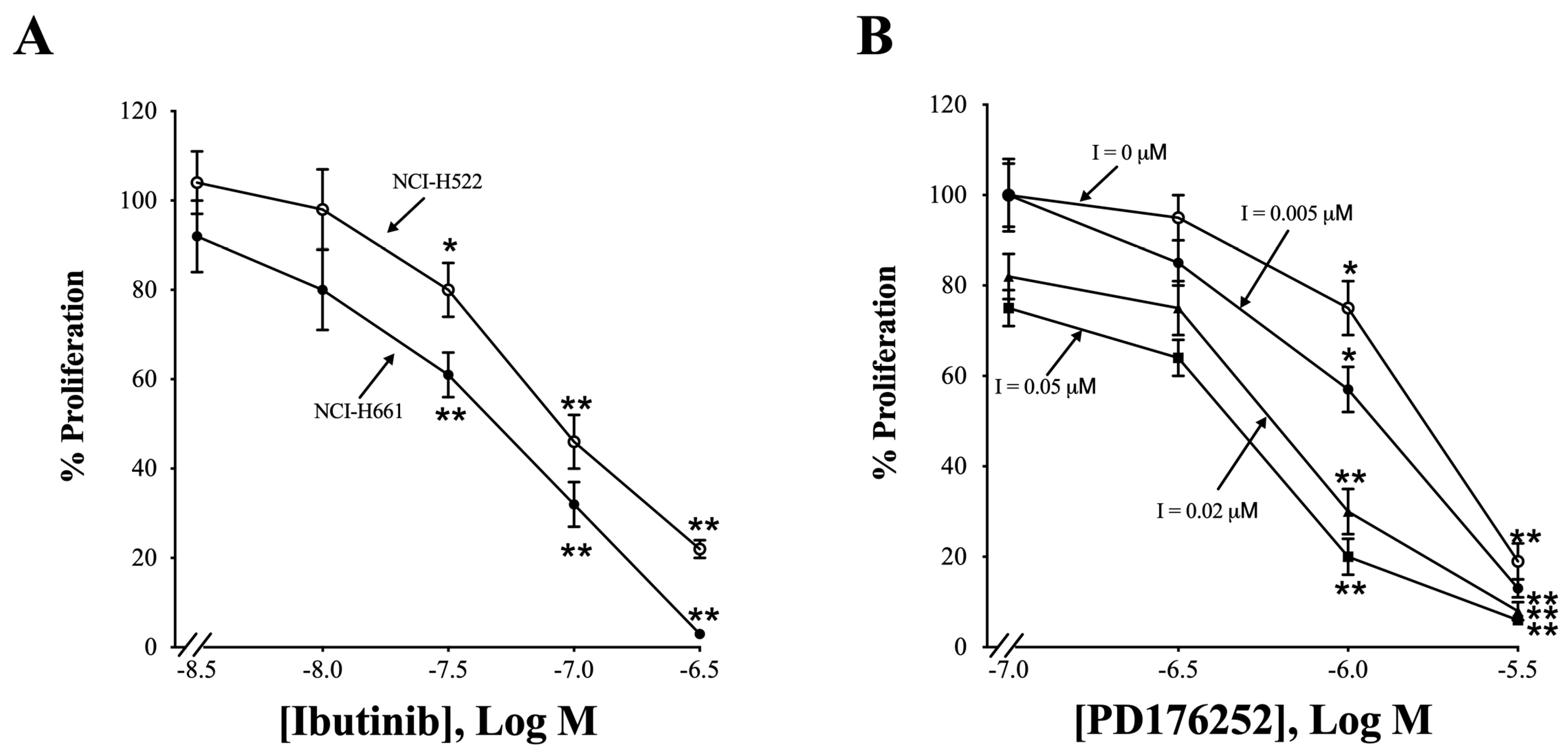
3.9. Proliferation
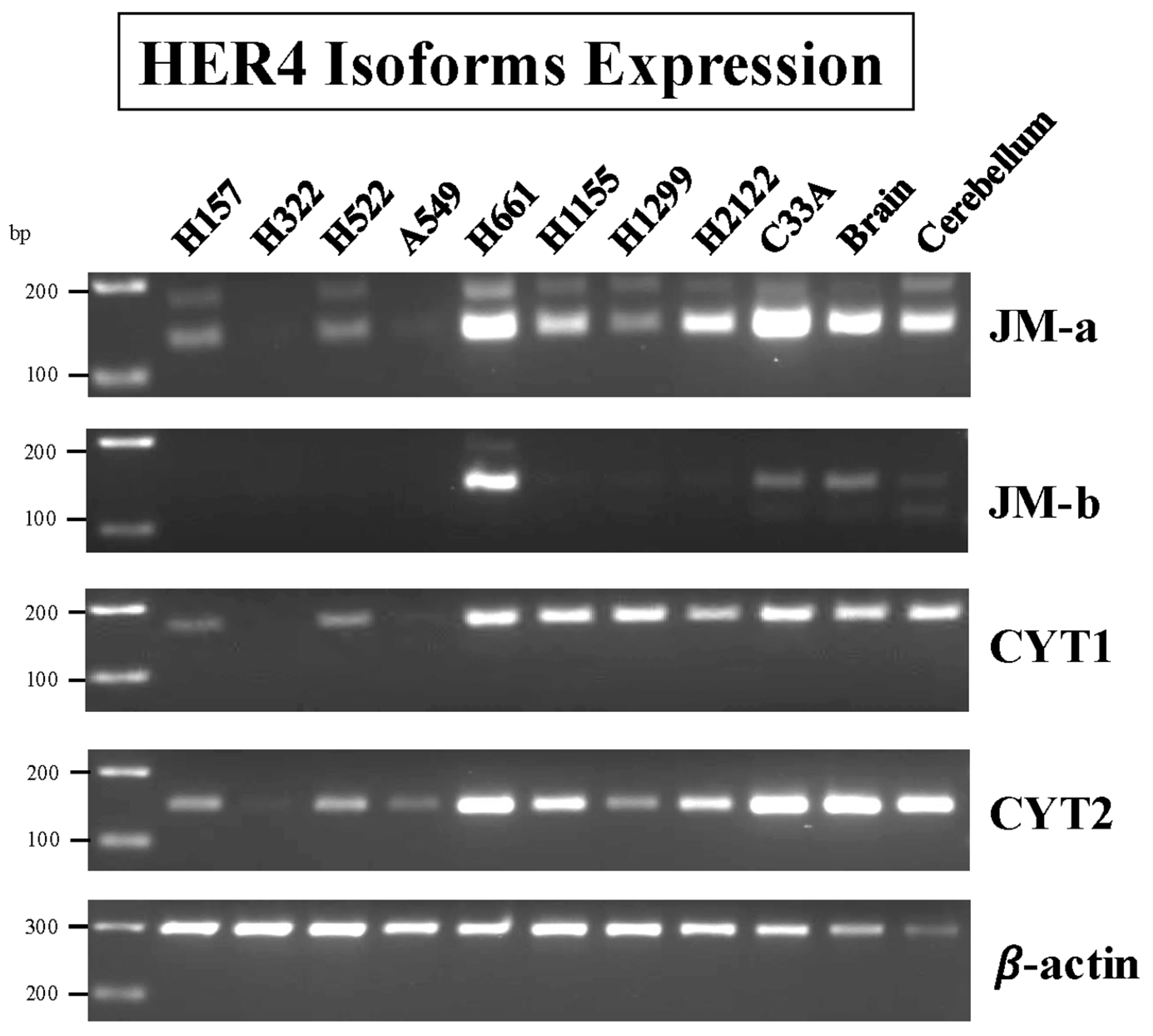
3.10. HER4 Splice Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boch, T.; Kohler, J.; Janning, M.; Loges, S. Targeting the EGF receptor family in non-small cell lung cancer-increased complexity and future perspectives. Cancer Biol. Med. 2022, 19, 1543–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, V.F.M.; Dugaucquier, L.; Feyen, E.; Shakeri, H.; De Keulenaer, G.W. The role of ErbB4 in cancer. Cell Oncol. 2020, 43, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.M.; Dwivedi, V.; Senfeld, J.I.; Cullum, R.L.; Mill, C.P.; Piazza, J.T.; Bryant, I.N.; Cook, L.J.; Miller, S.T.; Lott, J.H.; et al. The Yin and Yang of ERBB4: Tumor Suppressor and Oncoprotein. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 18–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. ErbB Receptors and Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1652, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Gamal, M.I.; Mewafi, N.H.; Abdelmotteleb, N.E.; Emara, M.A.; Tarazi, H.; Sbenati, R.M.; Madkour, M.M.; Zaraei, S.O.; Shahin, A.I.; Anbar, H.S. A Review of HER4 (ErbB4) Kinase, Its Impact on Cancer, and Its Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollmen, M.; Elenius, K. Potential of ErbB4 antibodies for cancer therapy. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veikkolainen, V.; Vaparanta, K.; Halkilahti, K.; Iljin, K.; Sundvall, M.; Elenius, K. Function of ERBB4 is determined by alternative splicing. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, C.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Peschon, J.J.; Corfas, G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme is required for cleavage of erbB4/HER4. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10379–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jung, K.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Bennett, L.B.; Lee, J.S.; Mei, L.; Kim, T.W. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, C.I.; Zhou, H.; Kozlowska, E.; Guttridge, K.; Kawata, E.; Caskey, L.; Harrelson, J.; Hynes, N.; Ethier, S.; Calvo, B.; et al. Her4 mediates ligand-dependent antiproliferative and differentiation responses in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 4265–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gong, L.; Qian, Z.; Song, G.; Liu, J. ERBB4 promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2892–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.J.; Perry, R.H.; Kelly, P.J.; Pearson, A.D.; Lunec, J. Prognostic significance of HER2 and HER4 coexpression in childhood medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson, R.J.; Bentley, L.; Hernan, R.; Junttila, T.T.; Frank, A.J.; Haapasalo, H.; Connelly, M.; Wetmore, C.; Curran, T.; Elenius, K.; et al. ERBB receptor signaling promotes ependymoma cell proliferation and represents a potential novel therapeutic target for this disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3054–3064. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.R.; Li, Q.X.; Wei, H.F.; Ma, Y. miR-326 inhibits the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting MAPK1 and ERBB4. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Inoue, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Kurozumi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nakamoto, Y.; Akiyoshi, H.; Kamishina, H. The NRG3/ERBB4 signaling cascade as a novel therapeutic target for canine glioma. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 400, 112504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, T.T.; Sundvall, M.; Lundin, M.; Lundin, J.; Tanner, M.; Harkonen, P.; Joensuu, H.; Isola, J.; Elenius, K. Cleavable ErbB4 isoform in estrogen receptor-regulated growth of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, A.A.; Sorensen, B.S.; Meldgaard, P.; Fokdal, L.; Thykjaer, T.; Nexo, E. The relation between survival and expression of HER1 and HER2 depends on the expression of HER3 and HER4: A study in bladder cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhoff, G. “Shedding” light on HER4 signaling in normal and malignant breast tissues. Cell Signal 2022, 97, 110401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.V.; de la Cruz, C.C.; Chiu, C.; Alag, N.; Schaefer, G.; Crocker, L.; Ross, S.; Goldenberg, D.; Merchant, M.; Tien, J.; et al. Blocking NRG1 and other ligand-mediated Her4 signaling enhances the magnitude and duration of the chemotherapeutic response of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 171ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurppa, K.J.; Denessiouk, K.; Johnson, M.S.; Elenius, K. Activating ERBB4 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepp-Lorenzino, L.; Eberhard, I.; Ma, Z.; Cho, C.; Serve, H.; Liu, F.; Rosen, N.; Lupu, R. Signal transduction pathways induced by heregulin in MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. Oncogene 1996, 12, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Lee, L.; Mantey, S.A.; Jensen, R.T. Development and Characterization of a Novel, High-Affinity, Specific, Radiolabeled Ligand for BRS-3 Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 369, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kim, S.; Smith, A.W. HER4 is a high-affinity dimerization partner for all EGFR/HER/ErbB family proteins. Protein Sci. 2024, 33, e5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falls, D.L. Neuregulins: Functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.V. NRG1 fusions: Biology to therapy. Lung Cancer 2021, 158, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellmon, N.; Li, C.; Yang, Z. Allosterically targeting EGFR drug-resistance gatekeeper mutations. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 1756–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, H.; Weiss, F.U.; Wallasch, C.; Ullrich, A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 1996, 379, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, T.W.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Jensen, R.T. Peptide G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and ErbB Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Cancer. Biology 2023, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bhola, N.E.; Lui, V.W.; Siwak, D.R.; Thomas, S.M.; Gubish, C.T.; Siegfried, J.M.; Mills, G.B.; Shin, D.; Grandis, J.R. Antitumor mechanisms of combined gastrin-releasing peptide receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in head and neck cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Thomas, S.M.; Lui, V.W.; Xi, S.; Siegfried, J.M.; Fan, H.; Smithgall, T.E.; Mills, G.B.; Grandis, J.R. Phosphorylation of TNF-alpha converting enzyme by gastrin-releasing peptide induces amphiregulin release and EGF receptor activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6901–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 389–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.T.; Battey, J.F.; Spindel, E.R.; Benya, R.V. International Union of Pharmacology. LVIII. Mammalian Bombesin Receptors: Nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, signaling and functions in normal and disease states. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, A.; Koenig, M.; Balboni, G.; Damge, C. Expression and characterization of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor in normal and cancerous pancreas. Pancreas 1996, 12, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Leyton, J.; Garcia-Marin, L.; Jensen, R.T. Nonpeptide gastrin releasing peptide receptor antagonists inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 474, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.M.; Grandis, J.R.; Wentzel, A.L.; Gooding, W.E.; Lui, V.W.; Siegfried, J.M. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor mediates activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in lung cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2005, 7, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.T.; Moody, T.W. Bombesin-related peptides and neurotensin: Effects on cancer growth/proliferation and cellular signaling in cancer. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 1st ed.; Kastin, A.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, P.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moody, T.W.; Jensen, R.T. Bombesin related peptides/receptors and their promising therapeutic roles in cancer imaging, targeting and treatment. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets. 2016, 20, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Lee, L.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Iordanskaia, T.; Mantey, S.A.; Jensen, R.T. Bombesin Receptor Family Activation and CNS/Neural Tumors: Review of Evidence Supporting Possible Role for Novel Targeted Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 728088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Qu, X. Recent advances in the biology of bombesin-like peptides and their receptors. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moody, T.W.; Mantey, S.A.; Jensen, R.T. Neuropeptide bombesin receptor activation stimulates growth of lung cancer cells through HER3 with a MAPK-dependent mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowman, G.D.; Culouscou, J.M.; Whitney, G.S.; Green, J.M.; Carlton, G.W.; Foy, L.; Neubauer, M.G.; Shoyab, M. Ligand-specific activation of HER4/p180erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, S.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Attur, S.; Dhaunsi, G.S.; Yousif, M.H.; Benter, I.F. Transactivation of ErbB Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Is Inhibited by Angiotensin-(1-7) via Its Mas Receptor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141657. [Google Scholar]
- Omoto, Y.; Higa-Nakamine, S.; Higa, A.; Yamamoto, H. ErbB4 cleavage by gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor stimulation in cultured gonadotroph cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 799, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Armant, D.R. Lysophosphatidic acid regulates murine blastocyst development by transactivation of receptors for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 296, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, T.W.; Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Nakamura, T.; Jensen, R.T. EGFR Transactivation by Peptide G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Yu, W.; Hu, G.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, D.; Tan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, W. [A study on the expression of erbB4/HER4 in non-small cell lung cancer]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2002, 5, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, G.; Del Sordo, R.; Colella, R.; Ludovini, V.; Ragusa, M.; Bianconi, F.; Ferri, I.; Borri, F.; Chiari, R.; Puma, F.; et al. Co-expression of receptors of the HER family correlates with clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 663–671. [Google Scholar]
- Merimsky, O.; Staroselsky, A.; Inbar, M.; Schwartz, Y.; Wigler, N.; Mann, A.; Marmor, S.; Greif, J. Correlation between c-erbB-4 receptor expression and response to gemcitabine-cisplatin chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Ishida, M.; Tezuka, N.; Fujino, S.; Asai, T.; Okabe, H. HER1-4 expression status correlates with the efficacy of gefitinib treatment and tumor cell proliferative activity in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timotheadou, E.; Skarlos, D.V.; Samantas, E.; Papadopoulos, S.; Murray, S.; Skrickova, J.; Christodoulou, C.; Papakostantinou, C.; Pectasides, D.; Papakostas, P.; et al. Evaluation of the prognostic role of a panel of biomarkers in stage IB-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer patients. Anticancer. Res. 2007, 27, 4481–4489. [Google Scholar]
- al Moustafa, A.E.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.; Paterson, J.; O’Connor-McCourt, M. Expression of P185erbB-2, P160erbB-3, P180erbB-4, and heregulin alpha in human normal bronchial epithelial and lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer. Res. 1999, 19, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Gollamudi, M.; Nethery, D.; Liu, J.; Kern, J.A. Autocrine activation of ErbB2/ErbB3 receptor complex by NRG-1 in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Lung Cancer 2004, 43, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.; Chen, F.F.; Wu, M.H.; Chow, N.H.; Su, W.C.; Ma, M.C.; Su, P.F.; Chen, H.; Lin, M.Y.; Tseng, Y.L. Immunohistochemical analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor family members in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 1868–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Hirata, A.; Kometani, T.; Miyagawa, M.; Ueda, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Fujii, T.; Kuwano, M. Sensitivity to gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines correlates with dependence on the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and EGF receptor/Akt pathway for proliferation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liao, J.; Geng, X.; Dan, H.; Chen, L. Concurrent inhibition of ErbB family and MEK/ERK kinases to suppress non-small cell lung cancer proliferation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 847–856. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Soh, J.; Shigematsu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yamamoto, H.; Peyton, M.; Girard, L.; Lockwood, W.W.; et al. Alterations in genes of the EGFR signaling pathway and their relationship to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor sensitivity in lung cancer cell lines. PLoS. ONE 2009, 4, e4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanotte, R.; Garambois, V.; Gaborit, N.; Larbouret, C.; Musnier, A.; Martineau, P.; Pelegrin, A.; Chardes, T. Biasing human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4) tyrosine kinase signaling with antibodies: Induction of cell death by antibody-dependent HER4 intracellular domain trafficking. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2508–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, V.; Bruss, C.; Tumen, D.; Piendl, G.; Weber, F.; Dahl, E.; Seitz, S.; Ortmann, O.; Wege, A.K.; Brockhoff, G. HER4 Affects Sensitivity to Tamoxifen and Abemaciclib in Luminal Breast Cancer Cells and Restricts Tumor Growth in MCF-7-Based Humanized Tumor Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, V.; Brownhill, V.; Higginbottom, M.; Horwell, D.C.; Hughes, J.; Lewthwaite, R.A.; McKnight, A.T.; Pinnock, R.D.; Pritchard, M.C.; Suman-Chauhan, N.; et al. PD 176252—The first high affinity non-peptide gastrin-releasing peptide (BB2) receptor antagonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998, 8, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, N.; Mantey, S.A.; Pradhan, T.K.; Sancho, V.; Moody, T.W.; Coy, D.H.; Jensen, R.T. Characterization of putative GRP- and NMB-receptor antagonist’s interaction with human receptors. Peptides 2009, 30, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A. Ligand-induced ErbB receptor dimerization. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezerina, D.; Takano, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Urano, Y.; Dick, T.P. N-Acetyl Cysteine Functions as a Fast-Acting Antioxidant by Triggering Intracellular H(2)S and Sulfane Sulfur Production. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, F.A. Mechanism of tiron as scavenger of superoxide ions and freee electrons. J. Spectrosc. 2008, 22, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, F.; Festa, F.; Park, J.G.; Magee, M.; Eaton, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Betanzos, C.M.; Gonzalez-Malerva, L.; LaBaer, J. Ibrutinib inhibition of ERBB4 reduces cell growth in a WNT5A-dependent manner. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2237–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estupinan, H.Y.; Berglof, A.; Zain, R.; Smith, C.I.E. Comparative Analysis of BTK Inhibitors and Mechanisms Underlying Adverse Effects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Washer, A.; Robak, T. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies: Current status and future directions. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Yue, C.; Liu, L.; Du, L.; Xu, K.; Zhou, Y. Overexpression of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2023, 2023, 3377316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainulainen, V.; Sundvall, M.; Maatta, J.A.; Santiestevan, E.; Klagsbrun, M.; Elenius, K. A natural ErbB4 isoform that does not activate phosphoinositide 3-kinase mediates proliferation but not survival or chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8641–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hu, C.H.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhou, J.S.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, M.D.; Qiu, Z.H.; Deng, C.; Ma, F.; Xia, C.F.; et al. Association between pretreatment emotional distress and immune checkpoint inhibitor response in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Re, M.; Cucchiara, F.; Petrini, I.; Fogli, S.; Passaro, A.; Crucitta, S.; Attili, I.; De Marinis, F.; Chella, A.; Danesi, R.; et al. erbB in NSCLC as a molecular target: Current evidences and future directions. ESMO. Open 2020, 5, e000724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Gong, K.; Wohlfeld, B.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Zhao, D.; Habib, A.A. Ligand-Independent EGFR Signaling. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.; Mantey, S.A.; Lee, S.H.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moody, T.W.; Jensen, R.T. A possible new target in lung-cancer cells: The orphan receptor, bombesin receptor subtype-3. Peptides 2018, 101, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Wenger, S.; Schumuckli-Maurer, J.; Schaer, J.C.; Gugger, M. Bombesin receptor subtypes in human cancers: Detection with the universal radoligand (125)I-[D-TYR(6), beta-ALA(11),PHE(13), NLE(14)] bombesin(6-14). Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Canfield, K.; Li, J.; Wilkins, O.M.; Morrison, M.M.; Ung, M.; Wells, W.; Williams, C.R.; Liby, K.T.; Vullhorst, D.; Buonanno, A.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase ERBB4 mediates acquired resistance to ERBB2 inhibitors in breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMichele, M.A.; Davis, A.L.; Hunt, J.D.; Landreneau, R.J.; Siegfried, J.M. Expression of mRNA for three bombesin receptor subtypes in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1994, 11, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ren, L.; Chen, A.; Chen, Z.F.; Zhang, H. Structures of human gastrin-releasing peptide receptors bound to antagonist and agonist for cancer and itch therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2216230120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Julia, G.; Rubio-Martinez, J.; Perez, J.J. Assessment of the bound conformation of bombesin to the BB1 and BB2 receptors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 255, 127843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrieri, A.; Lacivita, E.; Belviso, B.D.; Caliandro, R.; Mastrorilli, P.; Gallo, V.; Niso, M.; Leopoldo, M. Structural Determinants in the Binding of BB2 Receptor Ligands: In Silico, X-Ray and NMR Studies in PD176252 Analogues. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Thomas, S.M.; Smithgall, T.E.; Siegfried, J.M.; Kamens, J.; Gooding, W.E.; Grandis, J.R. SRC family kinases mediate epidermal growth factor receptor ligand cleavage, proliferation, and invasion of head and neck cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, T.W.; Lee, L.; Iordanskaia, T.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moreno, P.; Boudreau, H.E.; Leto, T.L.; Jensen, R.T. PAC1 regulates receptor tyrosine kinase transactivation in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. Peptides 2019, 120, 170017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Schwappacher, R.; Roth, M.; Boergermann, J.H.; Hassel, S.; Knaus, P. PP2A regulates BMP signalling by interacting with BMP receptor complexes and by dephosphorylating both the C-terminus and the linker region of Smad1. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroshow, J.H.; Juhasz, A.; Ge, Y.; Holbeck, S.; Lu, J.; Antony, S.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Roy, K. Antiproliferative mechanisms of action of the flavin dehydrogenase inhibitors diphenylene iodonium and di-2-thienyliodonium based on molecular profiling of the NCI-60 human tumor cell panel. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isacke, C.M.; Meisenhelder, J.; Brown, K.D.; Gould, K.L.; Gould, S.J.; Hunter, T. Early phosphorylation events following the treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells with bombesin and the mammalian bombesin-related peptide, gastrin-releasing peptide. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, M.; Bae, Y.K.; Han, C.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, S.S.; Han, J.Y. Oncogenic KRAS promotes growth of lung cancer cells expressing SLC3A2-NRG1 fusion via ADAM17-mediated shedding of NRG1. Oncogene 2022, 41, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Kang, B.; Zhao, P.; Ran, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Luo, H.; Tao, L. Targeting Neuregulin 1 (NRG1): A Novel Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2021, 40, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, H.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.P.; He, J.; Poteete, A.; Jiang, H.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Shibata, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. HER4 and EGFR Activate Cell Signaling in NRG1 Fusion-Driven Cancers: Implications for HER2-HER3-specific Versus Pan-HER Targeting Strategies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, L.; Cao, H.; Wang, T.; Yang, S.; Tong, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q. Analysis on the pathogenesis and treatment progress of NRG1 fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1405380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Yang, Q.; Ding, F.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Tian, X. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4) is a favorable prognostic marker of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76693–76703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yun, S.; Kwak, Y.; Nam, S.K.; Seo, A.N.; Oh, H.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, S.B.; Lee, H.S. Ligand-Independent Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Overexpression Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munk, M.; Memon, A.; Poulsen, S.S.; Borre, M.; Nexo, E.; Sorensen, B.S. The HER4 isoform JM-a/CYT2 relates to improved survival in bladder cancer patients but only if the estrogen receptor α is not expressed. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2013, 73, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutras, A.; Kalogeras, K.T.; Wirtz, R.M.; Alexopoulou, Z.; Bobos, M.; Zagouri, F.; Veltrup, E.; Timotheadou, E.; Gogas, H.; Pentheroudakis, G.; et al. Evaluation of the prognostic significance of HER family mRNA expression in high-risk early breast cancer: A Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) validation study. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, A.; Greif, J.; Vexler, A.; Ashkenazy-Voghera, M.; Gladesh, V.; Rubin, C.; Kerber, G.; Marmor, S.; Lev-Ari, S.; Inbar, M.; et al. ErbB4 increases the proliferation potential of human lung cancer cells and its blockage can be used as a target for anti-cancer therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Okuda, K.; Kawano, O.; Endo, K.; Yukiue, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. ErbB4 expression and mutation in Japanese patients with lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2007, 8, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Tidow, C.; Diederichs, S.; Bulk, E.; Pohle, T.; Steffen, B.; Schwable, J.; Plewka, S.; Thomas, M.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; et al. Identification of metastasis-associated receptor tyrosine kinases in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, K.; Suda, K.; Onozato, R.; Kuwano, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Analysis of ERBB4 mutations and expression in japanese patients with lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1859–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; MacDonald, G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Shen, K.; Huang, R.; Wang, Z. The Biological Roles and Clinical Applications of the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Targeted Therapy Resistance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Yu, F.; Lin, J. HER4 promotes the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys Sin. 2020, 52, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenius, K.; Paul, S.; Allison, G.; Sun, J.; Klagsbrun, M. Activation of HER4 by heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor stimulates chemotaxis but not proliferation. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, K.; Hommyo, A.; Yonemitsu, R.; Abe, S. ErbB4 signals Neuregulin1-stimulated cell proliferation and c-fos gene expression through phosphorylation of serum response factor by mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010, 339, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.; Minturn, J.E.; Hishiki, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Cnaan, A.; Maris, J.; Evans, A.E.; Brodeur, G.M. Proliferation of human neuroblastomas mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9868–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsara, B.R.; Pei, J.; Mitsuuchi, Y.; Page, R.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Wang, H.; Unger, M.; Testa, J.R. Frequent activation of AKT in non-small cell lung carcinomas and preneoplastic bronchial lesions. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2053–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, L.; Cao, Z.; Wu, X.; Ingalla, E.R.; Baron, C.; Young, L.J.; Gregg, J.P.; Cardiff, R.D.; Borowsky, A.D.; Sweeney, C.; et al. Loss of Nrdp1 enhances ErbB2/ErbB3-dependent breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11279–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirouac, D.C.; Du, J.; Lahdenranta, J.; Onsum, M.D.; Nielsen, U.B.; Schoeberl, B.; McDonagh, C.F. HER2+ Cancer Cell Dependence on PI3K vs. MAPK Signaling Axes Is Determined by Expression of EGFR, ERBB3 and CDKN1B. PLoS. Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, J.; Xu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Li, X. HER2/PI3K/AKT pathway in HER2-positive breast cancer: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e38508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, J.T.; Olivares, M.G.; Rinehart, C.; Granja-Ingram, N.D.; Sanchez, V.; Chakrabarty, A.; Dave, B.; Cook, R.S.; Pao, W.; McKinely, E.; et al. Transcriptional and posttranslational up-regulation of HER3 (ErbB3) compensates for inhibition of the HER2 tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5021–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergina, N.V.; Rausch, M.; Wang, D.; Blair, J.; Hann, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Moasser, M.M. Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the kinase-inactive HER3. Nature 2007, 445, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, D.; Ligon, G.F.; Lillquist, J.S.; Seibel, S.B.; Wallweber, G.; Neumeister, V.M.; Rimm, D.L.; McMahon, G.; LaVallee, T.M. ErbB activation signatures as potential biomarkers for anti-ErbB3 treatment in HNSCC. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Castanaro, C.; Luan, B.; Yang, K.; Fan, L.; Fairhurst, J.L.; Rafique, A.; Potocky, T.B.; Shan, J.; Delfino, F.J.; et al. ERBB3/HER2 signaling promotes resistance to EGFR blockade in head and neck and colorectal cancer models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddes, R.J.; Janes, P.W.; Sivertsen, S.P.; Sutherland, R.L.; Musgrove, E.A.; Daly, R.J. Inhibition of the MAP kinase cascade blocks heregulin-induced cell cycle progression in T-47D human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Han, J.; Shin, I.; Kil, W.H.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J. A functional comparison between the HER2(high)/HER3 and the HER2(low)/HER3 dimers on heregulin-beta1-induced MMP-1 and MMP-9 expression in breast cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, S.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Larsen, M.S.; Sorensen, B.S.; Yde, C.W. Estrogen receptor alpha is the major driving factor for growth in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and supported by HER/ERK signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Grijalva, R.; Zhang, L.; Nguyen, N.T.; Pisters, P.W.; Pollock, R.E.; Yu, D. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer cells by the heregulin-beta1-activated p38 signaling pathway enhances endothelial cell migration. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zheng, C.; Li, C.; Hou, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Che, X.; Qu, X. 4-Phenybutyric acid promotes gastric cancer cell migration via histone deacetylase inhibition-mediated HER3/HER4 up-regulation. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, M.S.; Blakely, C.M.; Riess, J.W. Targeting MEK in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2024, 49, 101065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; Xu, S. Endogenous thrombopoietin promotes non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by regulating EGFR signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6644–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Carlisle, D.L.; Swick, M.C.; Gaither-Davis, A.; Grandis, J.R.; Siegfried, J.M. Gastrin-releasing peptide activates Akt through the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway and abrogates the effect of gefitinib. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Shang, C.; Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Shi, W. Activation of M3 muscarinic receptor by acetylcholine promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion via EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Ito, S.; Itoh, K. EGF-stimulated AKT activation is mediated by EGFR recycling via an early endocytic pathway in a gefitinib-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gen | Primer | Sequence | Product Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Forward | 5′-TCTTCGGGGAGCAGCGAT-3′ | 119 |
| Reverse | 5′-TCGTCGCCTTGGCAAACTTTC-3′ | ||
| HER2 | Forward | 5′-AGCCGCAGTGAGCACCATGG-3′ | 102 |
| Reverse | 5′-GTGCCGGTGCACACTTGGGT-3′ | ||
| HER3 | Forward | 5′-CCTATGCAGGGCTACGATTGG-3′ | 131 |
| Reverse | 5-GTTGGGCTCAGCAGGTAACT-3′ | ||
| HER4 | Forward | 5′CATTTGACCATGACCATGTAAACGTC-3′ | 135 |
| Reverse | 5′-GGAACTGATGACCTTTGGAGGAA-3′ | ||
| NRG1 | Forward | 5′-TCGGTGTGAAACCAGTTCTGA-3′ | 130 |
| Reverse | 5′-GCGAAGTTCTGACTTCCCTG-3′ | ||
| NRG2 | Forward | 5′-GCTGGTACCCCACTGATGATGAC-3′ | 232 |
| Reverse | 5′-CACATCACCCCAGAGTGGAG-3′ | ||
| NRG3 | Forward | 5′-AGTCAAGTTTTGTCGGCCCC-3′ | 93 |
| Reverse | 5′-AAGAGGATAGACTCCTGTGGTG-3′ | ||
| NRG4 | Forward | 5′-ATCAGTCCATCGGCAACTGCTA-3′ | 116 |
| Reverse | 5′-ACATTTGCCTCTGGTTGCTTC-3′ | ||
| JM-a | Forward | 5′-GAAATGTCCAGATGGCCTACAGGG-3′ | 175 |
| Reverse | 5′-AATGCAGTCATGACTAGTGGGACC-3′ | ||
| JM-b | Forward | 5′-CCACCCATCCCATCCAAA-3′ | 180 |
| Reverse | 5′-CCAATTACTCCAGCTGCAATC-3′ | ||
| CYT1 | Forward | 5′-GGATGAAGAGGATTTGGAAG-3′ | 145 |
| Reverse | 5′-TCCTGACATGGGGGTGTA-3′ | ||
| CYT2 | Forward | 5′-GAATAGGAACCAGTTTGTATACCG-3′ | 205 |
| Reverse | 5′-ACAGCAGGAGTCATCAAAAATC-3′ | ||
| β-actin | Forward | 5′-CCTCGCCTTTGCCGATCC-3′ | 205 |
| Reverse | 5′-GGAATCCTTCTGACCCATGC-3′ |
| NCI-H522 Cells | NCI-H661 Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | NRG1β (pg/mL) | p-Value | NRG1β (pg/mL) | p-Value |
| None | 140 ± 16 | 152 ± 21 | ||
| GRP, 0.1 μM | 235 ± 29 | p = 0.02 vs. None | 322 ± 41 | p = 0.004 vs. None |
| GRP + PD176252, 1 μM | 162 ± 22 | p = 0.05 vs. GRP, 0.1 μM | 217 ± 27 | p = 0.03 vs. GRP, 0.1 μM |
| Colony Number | +0.1 μM GRP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value |
| None | 27 ± 3 | 54 ± 6 | p = 0.006 vs. None | |
| PD176252, 10 μM | 16 ± 3 | p = 0.02 vs. None | 33 ± 5 | p = 0.009 vs. + 0.1 μM GRP |
| Ibrutinib, 10 μM | 21 ± 4 | p = 0.06 vs. None | 41 ± 7 | p = 0.07 vs. + 0.1 μM GRP |
| PD + Ibrutinib | 12 ± 5 | p = 0.02 vs. None | 26 ± 4 | p = 0.005 vs. + 0.1 μM GRP |
| siRNA HER4 | 9 ± 3 | p = 0.001 vs. None | 19 ± 5 | p = 0.001 vs. + 0.1 μM GRP |
| NRG1, 10 ng/mL | 60 ± 7 | p = 0.004 vs. None | n.d. | |
| NRG1 + Ibrutinib | 39 ± 6 | p = 0.05 vs. None p = 0.02 vs. NRG1 | n.d. | |
| P-HER4 | P-ERK | P-AKT | Proliferation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value | Mean ± S.D. | p-Value |
| None | 100 ± 6 | 100 ± 7 | 100 ± 8 | 100 ± 5 | ||||
| GRP, 0.1 μM | 284 ± 15 | *, p = 0.001 | 216 ± 13 | *, p = 0.001 | 148 ± 12 | *, p = 0.02 | n.d. | |
| PD, 10 μM | 95 ± 6 | #, p = 0.001 | 92 ± 7 | #, p = 0.001 | 103 ± 9 | #, p = 0.05 | 72 ± 6 | *, p = 0.013 |
| LY, 10 μM | 103 ± 9 | #, p = 0.007 | 105 ± 6 | #, p = 0.003 | 92 ± 8 | #, p = 0.02 | 104 ± 7 | |
| GRP + PD | 246 ± 13 | *, p = 0.001 #, p = 0.07 | 113 ± 6 | #, p = 0.007 | 152 ± 14 | *, p = 0.01 #, p = 0.76 | n.d. | |
| GRP + LY | 293 ± 16 | *, p = 0.001 | 224 ± 18 | *, p = 0.002 | 104 ± 5 | #, p = 0.04 | n.d. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moody, T.W.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Iordanskaia, T.; Mantey, S.A.; Jensen, R.T. Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptors Stimulate MAPK-Mediated Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Transactivating HER4 in a Neuregulin-1, MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner Requiring Activation of the ROS-System. Biology 2025, 14, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091225
Moody TW, Ramos-Alvarez I, Iordanskaia T, Mantey SA, Jensen RT. Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptors Stimulate MAPK-Mediated Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Transactivating HER4 in a Neuregulin-1, MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner Requiring Activation of the ROS-System. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091225
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoody, Terry W., Irene Ramos-Alvarez, Tatiana Iordanskaia, Samuel A. Mantey, and Robert T. Jensen. 2025. "Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptors Stimulate MAPK-Mediated Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Transactivating HER4 in a Neuregulin-1, MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner Requiring Activation of the ROS-System" Biology 14, no. 9: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091225
APA StyleMoody, T. W., Ramos-Alvarez, I., Iordanskaia, T., Mantey, S. A., & Jensen, R. T. (2025). Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptors Stimulate MAPK-Mediated Growth of Lung Cancer Cells by Transactivating HER4 in a Neuregulin-1, MAP Kinase-Dependent Manner Requiring Activation of the ROS-System. Biology, 14(9), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091225







