Effects of Burdock Addition and Different Starters on the Quality and Flavor Improvement of Duck Sausages
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Preparation of Fermented Burdock Sausage Samples
2.4. Sensory Evaluation
2.5. Color Difference Analysis
2.6. Texture Analysis
2.7. Extraction
2.8. Detection of the Total Phenolics and Total Flavonoids
2.9. Antioxidant Capacity of Fermented Burdock Sausage Samples
2.10. Determination of Volatile Flavor Substances by HS-SPME-GC-MS
2.11. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Candidate Strains for Combination Starter Cultures
3.2. Sensory Evaluation for Selection of Optimal Starter Combination
3.3. Color and pH Evaluation for Selection of Optimal Starter Combination
3.4. Texture Evaluation for Selection of Optimal Starter Combination
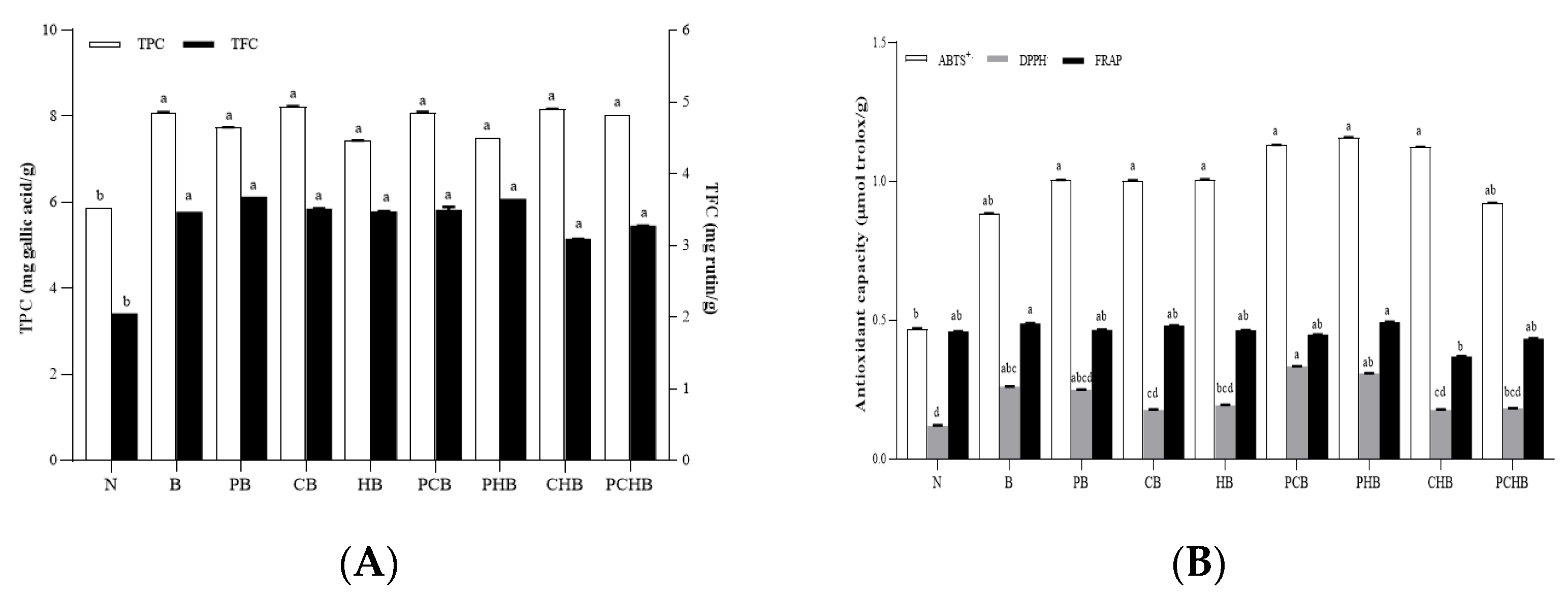
3.5. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content Evaluation for Selection of Optimal Starter Combination
3.6. Antioxidant Capacity Evaluation for Selection of Optimal Starter Combination
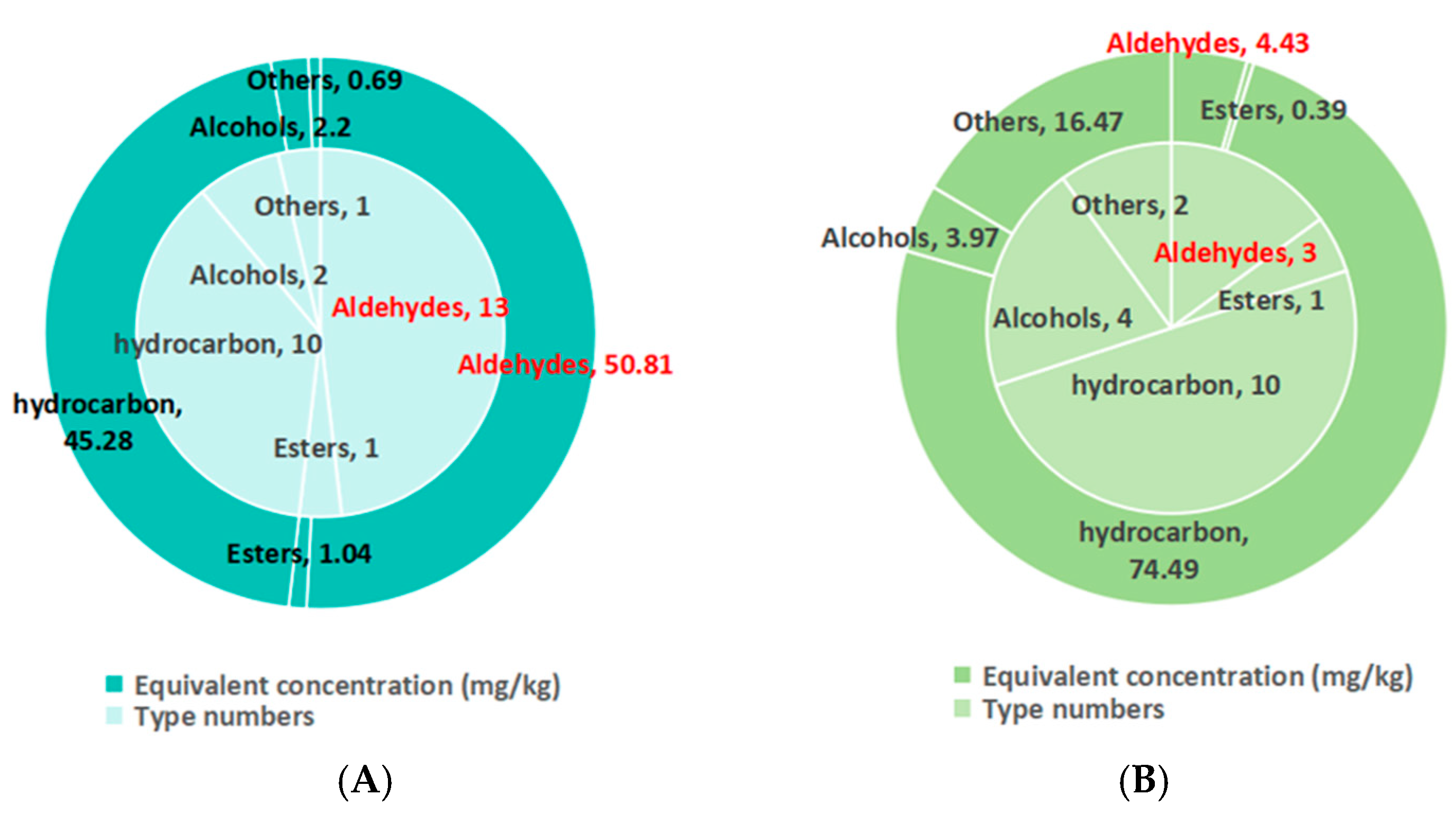
3.7. Volatile Substance Difference Between Spontaneously Fermented (N) and Combination-Starter-Fermented (PHB) Burdock Duck Sausages
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Duck production for food security. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 372, 01207. [Google Scholar]
- Moirangthem, S.; Laskar, S.K.; Das, A.; Upadhyay, S.; Hazarika, R.A.; Mahanta, J.D.; Sangtam, H.M. Effect of incorporation of soy protein isolate and inulin on quality characteristics and shelf-life of low-fat duck meat sausages. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Patra, G.; Das, A.K.; Das, S.K. Technological investigation into duck meat and its products—A potential alternative to chicken. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 75, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, L.H.; Huang, J.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.Q. Contribution of microbial community to flavor formation in tilapia sausage during fermentation with Pediococcus pentosaceus. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Cao, Z.X.; Yu, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.C.; Zhao, K.L. Effect of inoculating mixed starter cultures of Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus on bacterial communities and volatile flavor in fermented sausages. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2023, 12, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Herrera-Balandrano, D.D.; Huang, W.; Chai, Z.; Beta, T.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Comparison of nutritional and nutraceutical properties of burdock roots cultivated in Fengxian and Peixian of China. Foods 2021, 10, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, W.C.; Song, H.Z.; Huang, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, J. Effects of extraction methods on the physicochemical properties and functionalities of pectic polysaccharides from burdock (Arctium lappa L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Beta, T.; Huang, W.Y. Immune regulation and inflammation inhibition of Arctium lappa L. polysaccharides by TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Balandrano, D.D.; Beta, T.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.Y. Effect of in vitro gastro-intestinal digestion on the phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of burdock roots at different harvest time. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ting, F.W.; Liu, X.M. Screening and identification of two strains of lactic acid bacteria with excellent antioxidant capacity in vitro. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2013, 34, 149–153+157. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.C.; Feng, M.Q.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Optimization of probiotic starter inoculation process for fermented sausage by response surface methodology. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Gomezulu, A.D.; Mongi, R.J. Protein content and anti-nutritional factors in pigeon pea and effect of its protein isolate on physical properties and consumer preference of beef sausages. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.L.; Guo, X.L. Effects of Tartary buckwheat powder on antioxidant capacity and quality of Chinese sausage. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 45, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Liu, D.; Rui, H.L. Sodium borohydride/chloranil-based assay for quantifying total flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9337–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xiang, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y. Identification and quantification of free, esterified, and insoluble-bound phenolics in grains of hulless barley varieties and their antioxidant activities. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 1096–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.G.; Xu, D.L.; Xu, L.; Yang, S.T.; Deng, J.H. Analysis on the quality and antioxidant activity of dry red and rose wine simultaneously produced by juice pouring method. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, N.A.A.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Siajam, S.I.; Hean, C.G.; Harun, M.R. Optimization studies and compositional analysis of subcritical water extraction of essential oil from Citrus hystrix DC. leaves. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 178, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyn-Krajewska, D. Effects of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LOCK900 on development of volatile compounds and sensory quality of dry fermented sausages. Molecules 2021, 26, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. Effects of inoculation of commercial starter cultures on the quality and histamine accumulation in fermented sausages. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, F.O.; Fabio, C.H.; Felipe, V.; Daniela, B.O.; Alexandre, C.S.J.; Eder, D.R.; Meire, L.L.M. Effect of the fruit aqueous extract of Brazilian pepper tree (Schinus terebinthifolius, Raddi) on selected quality parameters of frozen fresh pork sausage. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100055. [Google Scholar]
- Laguna, L.; Primo-Martín, C.; Varela, P.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. HPMC and inulin as fat replacers in biscuits: Sensory and instrumental evaluation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Puolanne, E.; Ertbjerg, P. Mimicking myofibrillar protein denaturation in frozen-thawed meat: Effect of pH at high ionic strength. Food Chem. 2020, 338, 128017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surasani, V.K.R.; Varadaraju, R.C.; Singh, A. Biochemical, microbial, and textural quality changes in rohu protein isolates supplemented pangas mince sausages packed in LDPE and cellulose casing during frozen storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, 15767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.; Chrisfield, B.J.; Hopfer, H.; Elias, R.J. Impact of copper-based fungicides on the antioxidant quality of ethanolic hop extracts. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Textural, sensory and volatile compounds analyses in formulations of sausages analogue elaborated with edible mushrooms and soy protein isolate as meat substitute. Foods 2021, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; Bai, Y.; di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Gänzle, M.G. Metabolism of phenolic compounds by Lactobacillus spp. during fermentation of cherry juice and broccoli puree. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Guan, X. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus and tussah immune reactive substances on disease resistance of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus against Vibrio splendidus. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4601–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.I.; Feng, Y.Z.; Yang, N.N.; Jiang, T.; Xu, H.D.; Lei, H.J. Fermentation of kiwifruit juice from two cultivars by probiotic bacteria: Bioactive phenolics, antioxidant activities and flavor volatiles. Food Chem. 2021, 373, 31455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, A.; Nejati, F. Development of antioxidant activity during milk fermentation by wild isolates of Lactobacillus helveticus. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, X.; Agar, O.T.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. Phenolic compounds profiling and their antioxidant capacity in the peel, pulp, and seed of Australian grown avocado. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multari, S.; Marsol-Vall, A.; Yang, B.; Suomela, J.P. Effects of aromatic herb flavouring on carotenoids and volatile compounds in edible oil from blue sweet lupin, Lupinus angustifolius. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1800227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, Y. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria and their effects on the off-odor of burdocks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7485–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Dong, S.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Q. Response of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar flavor to environmental salinity while culturing between freshwater and seawater. Aquaculture 2020, 530, 735953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.C.; Xu, L.G.; Gu, T.T.; Sun, Y.Y.; Xia, Q.; He, J.; Lu, L.Z. Investigation into the characteristic volatile flavor of old duck. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Fu, X.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, M. Comparison of aroma-active compounds in broiler broth and native chicken broth by aroma extract dilution analysis, AEDA, odor activity value, OAV and omission experiment. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Kong, X.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, C.; Shen, Q.W. Fatty acid content, flavor compounds, and sensory quality of pork loin as affected by dietary supplementation with l-arginine and glutamic acid. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Lou, A.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Shen, Q.W. Duck breast muscle proteins, free fatty acids and volatile compounds as affected by curing methods. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lv, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Characterization of selected Harbin red sausages on the basis of their flavour profiles using HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, C.; Sado Kamdem, S.L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Vannini, L.; Guerzoni, M.E. Oxylipins generation in Lactobacillus helveticus in relation to unsaturated fatty acid supplementation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorino, G.M.; Tlais, A.Z.A.; Losito, I.; Filannino, P.; Gobbetti, M.; di Cagno, R. Triacylglycerols hydrolysis and hydroxyand epoxy-fatty acids release during lactic fermentation of plant matrices: An extensive study showing inter- and intra-species capabilities of lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liao, L.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y. Characteristic fingerprints and volatile flavor compound variations in Liuyang Douchi during fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Willige, R.W.; Linssen, J.P.; Voragen, A.G. Influence of food matrix on absorption of flavour compounds by linear low-density polyethylene: Proteins and carbohydrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zope, D.D.; Patnekar, S.G.; Kanetkar, V.R. Novel synthesis of flavour quality γ-lactones. Flavour Fragr. J. 2006, 21, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time (Day) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | SUM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||||||
| Steamed burdock duck sausages | Control | 6.12 ± 0.66 aB | 7.10 ± 0.66 aA | 6.98 ± 0.26 aA | 7.14 ± 0.55 aA | 27.34 ± 1.40 a |
| Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | 6.14 ± 0.37 aB | 7.20 ± 0.40 abA | 7.06 ± 0.20 aA | 6.76 ± 0.48 aA | 27.16 ± 0.80 a | |
| Lactobacillushelveticus | 5.66 ± 0.55 aB | 7.00 ± 0.45 abA | 6.44 ± 0.21 aA | 6.62 ± 0.47 aA | 25.72 ± 0.64 a | |
| Lacticaseibacillus casei | 6.34 ± 0.76 aA | 6.70 ± 0.75 bcA | 6.88 ± 0.21 aA | 6.70 ± 0.43 abA | 26.62 ± 1.77 a | |
| Latilactobacillus sake | 6.24 ± 0.41 aA | 6.24 ± 0.39 bcA | 6.44 ± 0.33 aA | 6.54 ± 0.23 aA | 25.46 ± 0.64 a | |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | 6.32 ± 0.59 aA | 6.70 ± 0.75 bcA | 6.72 ± 0.42 aA | 6.24 ± 0.22 abA | 25.98 ± 0.80 a | |
| Lactobacillusacidophilus | 6.10 ± 0.42 aAB | 6.02 ± 0.63 bcB | 6.80 ± 0.40 aA | 6.60 ± 0.26 abAB | 25.52 ± 0.90 a | |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus | 5.70 ± 0.60 aA | 6.44 ± 0.39 cA | 2.20 ± 0.75 bB | 2.00 ± 0.89 bcB | 16.34± 1.66 b | |
| Debaryomyces hansenii | 6.30 ± 1.33 aA | 6.60 ± 0.58 bcA | 5.76 ± 0.69 bA | 6.88 ± 0.19 cA | 25.54 ± 1.31 a | |
| Baked burdock duck sausages | Control | 7.72 ± 0.70 aA | 6.20 ± 0.24 cdfB | 7.62 ± 0.35 aA | 6.72 ± 0.38 aB | 28.26 ± 0.73 ab |
| Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | 7.54 ± 0.70 aAB | 7.80 ± 0.81 aA | 7.42 ± 0.43 abAB | 6.64 ± 0.55 aB | 29.40 ± 1.66 a | |
| Lactobacillushelveticus | 7.20 ± 1.03 abA | 6.60 ± 0.58 bcdA | 6.48 ± 0.55 abcA | 6.08 ± 0.55 aA | 26.36 ± 1.29 bc | |
| Lacticaseibacillus casei | 6.64 ± 0.42 abAB | 7.46 ± 0.82 abA | 5.98 ± 0.84 cB | 6.76 ± 0.64 aAB | 26.84 ± 1.30 bc | |
| Latilactobacillus sake | 6.80 ± 0.51 abA | 5.50 ± 0.89 fAB | 4.70 ± 1.99 dB | 6.48 ± 0.93 aAB | 23.48 ± 2.67 d | |
| Lactiplantibacillus plantarum | 7.16 ± 0.90 abA | 6.20 ± 0.81 cdfA | 6.24 ± 0.67 bcA | 6.46 ± 0.83 aA | 26.06 ± 1.28 bc | |
| Lactobacillusacidophilus | 6.52 ± 0.79 abA | 5.90 ± 0.92 dfA | 6.10 ± 0.60 bcA | 6.74 ± 0.44 aA | 25.26 ± 1.06 cd | |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus | 6.62 ± 1.04 abA | 7.20 ± 0.40 abcA | 6.34 ± 0.31 abcA | 6.68 ± 0.72 aA | 26.84 ± 0.52 bc | |
| Debaryomyces hansenii | 6.02 ± 0.82 bB | 7.16 ± 0.21 abcA | 6.48 ± 0.45 abcAB | 5.92 ± 0.48 aB | 25.58 ± 1.81 cd |
| Group | Sensory Evaluation Scores | Color Analysis | Texture Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightness | Redness | Yellowness | Hardness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Chewiness | ||
| N | 6.92 ± 0.78 ab | 9.25 ± 0.98 a | 0.39 ± 0.23 b | 1.79 ± 0.36 c | 0.22 ± 0.15 c | 0.05 ± 0.01 f | 0.08 ± 0.04 c | 0.02 ± 0.01 d |
| B | 6.99 ± 0.45 ab | 12.59 ± 1.44 a | 0.65 ± 0.41 b | 2.35 ± 0.28 bc | 0.40 ± 0.27 bc | 0.70 ± 0.32 cde | 0.22 ± 0.14 abc | 0.20 ± 0.17 abcd |
| PB | 6.67 ± 0.73 b | 10.03 ± 1.41 a | 3.42 ± 0.44 a | 4.79 ± 0.06 ab | 1.09 ± 0.31 abc | 1.05 ± 0.06 bc | 0.48 ± 0.15 abc | 0.49 ± 0.13 abc |
| CB | 6.93 ± 1.03 ab | 9.31 ± 1.78 a | 3.22 ± 0.08 a | 4.48 ± 0.55 abc | 0.20 ± 0.01 c | 0.29 ± 0.04 ef | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 d |
| HB | 6.83 ± 0.80 ab | 9.44 ± 2.37 a | 2.95 ± 0.74 a | 3.81 ± 1.39 abc | 0.50 ± 0.03 bc | 0.64 ± 0.01 cde | 0.26 ± 0.02 abc | 0.19 ± 0.01 bcd |
| PCB | 7.06 ± 0.54 ab | 12.71 ± 3.00 a | 2.25 ± 0.10 a | 4.72 ± 0.65 ab | 0.84 ± 0.62 abc | 0.81 ± 0.20 bcd | 0.36 ± 0.25 abc | 0.35 ± 0.28 abcd |
| PHB | 7.19 ± 0.60 a | 11.28 ± 0.81 a | 3.34 ± 0.45 a | 5.96 ± 0.80 a | 1.72 ± 0.86 a | 1.78 ± 0.24 a | 0.59 ± 0.28 a | 0.59 ± 0.14 ab |
| CHB | 7.02 ± 0.66 ab | 9.45 ± 2.76 a | 2.53 ± 0.04 a | 4.10 ± 0.99 abc | 1.21 ± 0.24 ab | 1.21 ± 0.07 b | 0.51 ± 0.10 ab | 0.62 ± 0.15 a |
| PCHB | 7.16 ± 0.49 a | 9.52 ± 3.62 a | 2.43 ± 0.16 a | 5.00 ± 1.12 ab | 0.17 ± 0.02 c | 0.43 ± 0.01 def | 0.11 ± 0.01 bc | 0.05 ± 0.003 cd |
| Compound | CAS | LRI | Aroma Threshold (μg/L) | Equivalent Concentration (mg/kg) | ROAV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | PHB | N | PHB | ||||
| Aldehydes | |||||||
| Hexanal | 66-25-1 | 802 | 0.32 | 13.95 | - | 100 | - |
| 2-Heptenal, (E)- | 18829-55-5 | 960 | 34 | 3.20 | - | 0.22 | - |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | 971 | 24 | 4.44 | - | 0.42 | - |
| Octanal | 124-13-0 | 1006 | 7 | 2.75 | - | 0.9 | - |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | 122-78-1 | 1053 | 4 | 6.67 | - | 3.82 | - |
| Nonanal | 124-19-6 | 1102 | 2.8 | 11.52 | 3.60 | 9.43 | 100 |
| 2-Nonenal, (E)- | 18829-56-6 | 1166 | 0.15 | 1.24 | - | 18.98 | - |
| 2-Octenal, (E)- | 2548-87-0 | 1063 | 3 | 2.17 | - | 1.66 | - |
| 2,4-Nonadienal, (E,E)- | 5910-87-2 | 1210 | 0.1 | 0.24 | - | 5.47 | - |
| 2-Decenal, (E)- | 3913-81-3 | 1262 | 0.3 | 0.92 | - | 7.00 | - |
| Decanal | 112-31-2 | 1175 | 1.97 | 0.81 | 0.39 | 0.95 | 15.49 |
| 2,4-Decadienal, (E,E)- | 25152-84-5 | 1317 | 0.2 | 0.81 | - | 9.34 | - |
| 14-Octadecenal | 56554-89-3 | 1863 | - | 2.09 | - | - | - |
| Hexadecanal | 629-80-1 | 1830 | - | - | 0.44 | - | - |
| Esters | |||||||
| Octadecanoic acid, phenylmethyl ester | 5531-65-7 | 2794 | - | 1.04 | 0.39 | - | - |
| Hydrocarbon | |||||||
| Toluene | 108-88-3 | 774 | 1000 | 11.31 | 20.77 | 0.00 | 1.62 |
| p-Xylene | 106-42-3 | 865 | 530 | 2.62 | 3.77 | 0.01 | 0.55 |
| Styrene | 100-42-5 | 893 | 50 | 16.47 | 18.19 | 0.76 | 1.94 |
| Decane | 124-18-5 | 1000 | - | 9.74 | - | 0.08 | |
| Undecane | 1120-21-4 | 1100 | 10,000 | 3.07 | 17.05 | 0.00 | 0.13 |
| Undecane, 3-methyl- | 1002-43-3 | 1170 | - | 0.51 | 1.08 | - | - |
| Tetradecane | 629-59-4 | 1400 | 1000 | 2.18 | 2.43 | 0.00 | 0.19 |
| Tetradecane, 2,6,10-trimethyl- | 14905-56-7 | 1539 | - | - | 0.30 | - | - |
| Nonadecane | 629-92-5 | 1900 | - | 0.71 | 0.79 | - | - |
| Octane, 2,7-dimethyl- | 1072-16-8 | 928 | - | 7.14 | - | - | - |
| Cyclohexene, 3-(2-methylpropyl)- | 4104-56-7 | 1001 | - | 0.72 | - | - | - |
| Octadecane, 6-methyl- | 10544-96-4 | 1842 | - | 0.55 | 0.37 | - | - |
| Alcohols | |||||||
| 1,2-Propanediol, 3-methoxy- | 623-39-2 | 977 | - | - | 3.47 | - | - |
| 2-Propanol, 1-chloro-3-methoxy- | 4151-97-7 | 904 | - | 1.51 | - | - | - |
| 2-Hexadecanol | 14852-31-4 | 1702 | - | - | 0.05 | - | - |
| 1-Hexadecanol, 2-methyl- | 2490-48-4 | 1870 | - | - | 0.19 | - | - |
| Cedrol | 77-53-2 | 1598 | - | 0.69 | 0.26 | - | - |
| Others | |||||||
| Pyrazine, tetramethyl- | 1124-11-4 | 1089 | 1000 | - | 15.99 | - | 1.24 |
| Formamide, N,N-dibutyl- | 761-65-9 | 1310 | - | 0.69 | 0.48 | - | - |
| Compound | Odor Descriptor | ROAV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | PHB | Change | ||
| Aldehydes | ||||
| Hexanal | Fresh green, leafy fruity, sweaty | 100 | - | ↓ |
| 2-Octenal, (E)- | Fruity, aldehyde-like, fatty, | 1.66 | - | ↓ |
| Nonanal | Waxy, fresh orris, orange peel | 9.43 | 100 | ↑ |
| 2-Nonenal, (E)- | Fatty, green | 18.98 | - | ↓ |
| 2,4-Decadienal, (E,E)- | Orange, coriander, geranium, fatty | 9.34 | - | ↓ |
| Decanal | Soap, orange peel, tallow | <1 | 15.49 | ↑ |
| 2,4-Nonadienal, (E,E)- | Fatty, grassy | 5.47 | - | ↓ |
| 2-Decenal, (E)- | Tallow, orange | 7.00 | - | ↓ |
| Hydrocarbon | ||||
| Styrene | Balsamic, gasoline | <1 | 1.94 | ↑ |
| Toluene | Paint | <1 | 1.62 | ↑ |
| Heterocyclic compounds | ||||
| Pyrazine, tetramethyl- | Roast, earth | - | 1.24 | ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Zhao, X.; Song, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, T.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y. Effects of Burdock Addition and Different Starters on the Quality and Flavor Improvement of Duck Sausages. Biology 2025, 14, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080996
Cui L, Zhao X, Song X, Zhou W, Wang T, Huang W, Guo Y. Effects of Burdock Addition and Different Starters on the Quality and Flavor Improvement of Duck Sausages. Biology. 2025; 14(8):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080996
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Li, Xuan Zhao, Xingye Song, Wenjing Zhou, Tao Wang, Wuyang Huang, and Yuxing Guo. 2025. "Effects of Burdock Addition and Different Starters on the Quality and Flavor Improvement of Duck Sausages" Biology 14, no. 8: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080996
APA StyleCui, L., Zhao, X., Song, X., Zhou, W., Wang, T., Huang, W., & Guo, Y. (2025). Effects of Burdock Addition and Different Starters on the Quality and Flavor Improvement of Duck Sausages. Biology, 14(8), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080996








