Evaluation of HLA Region-Specific High-Throughput Sequencing FASTQ Reads Combined with Ensemble HLA-Typing Tools for Rapid and High-Confidence HLA Typing
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Data
2.2. Computational Environment
2.3. HLA Database
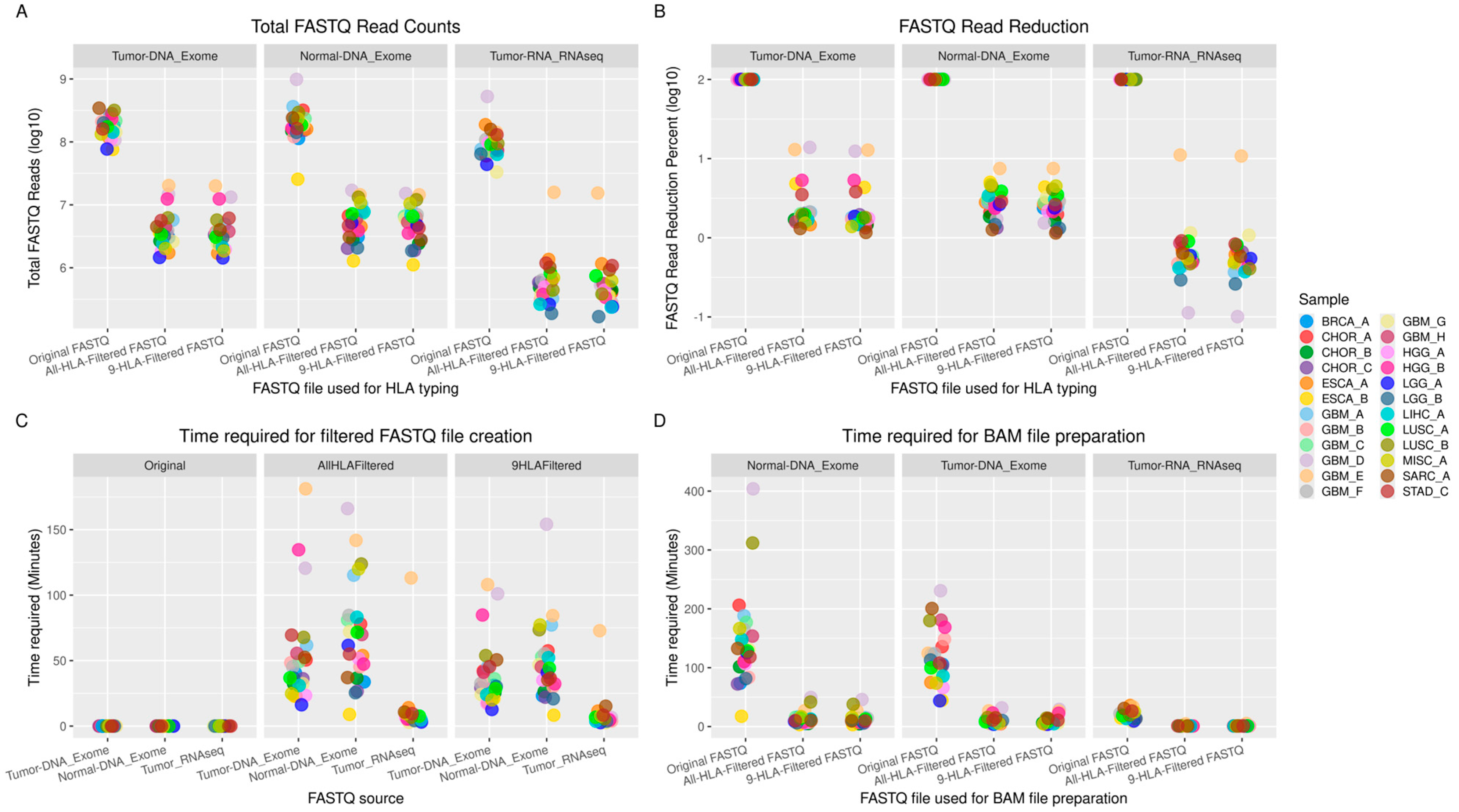
2.4. FASTQ Read Filtering
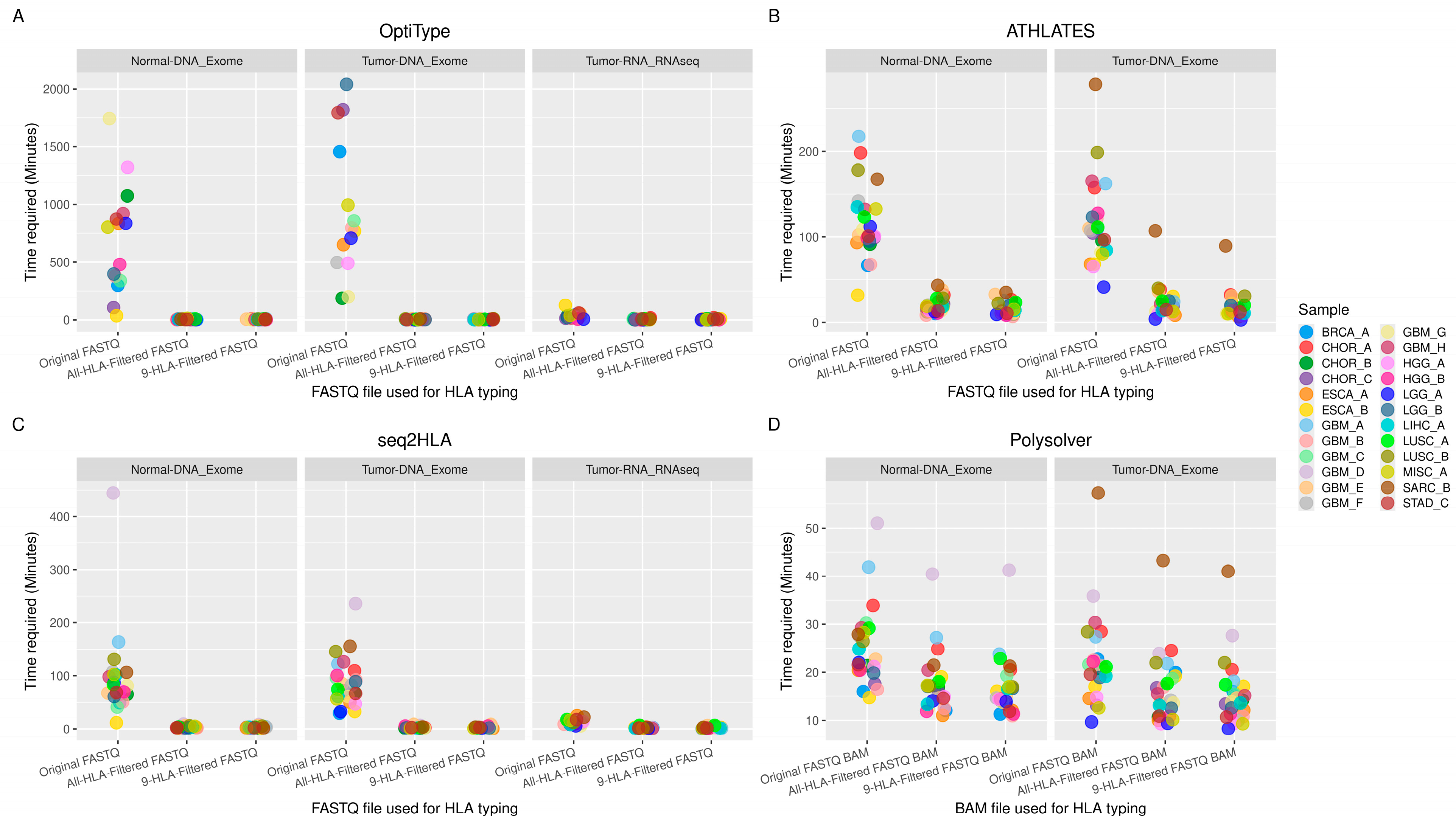
2.5. HLA Typing
2.6. BAM Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Time Required for FASTQ Read Filtering
3.2. Time Required for HLA Typing
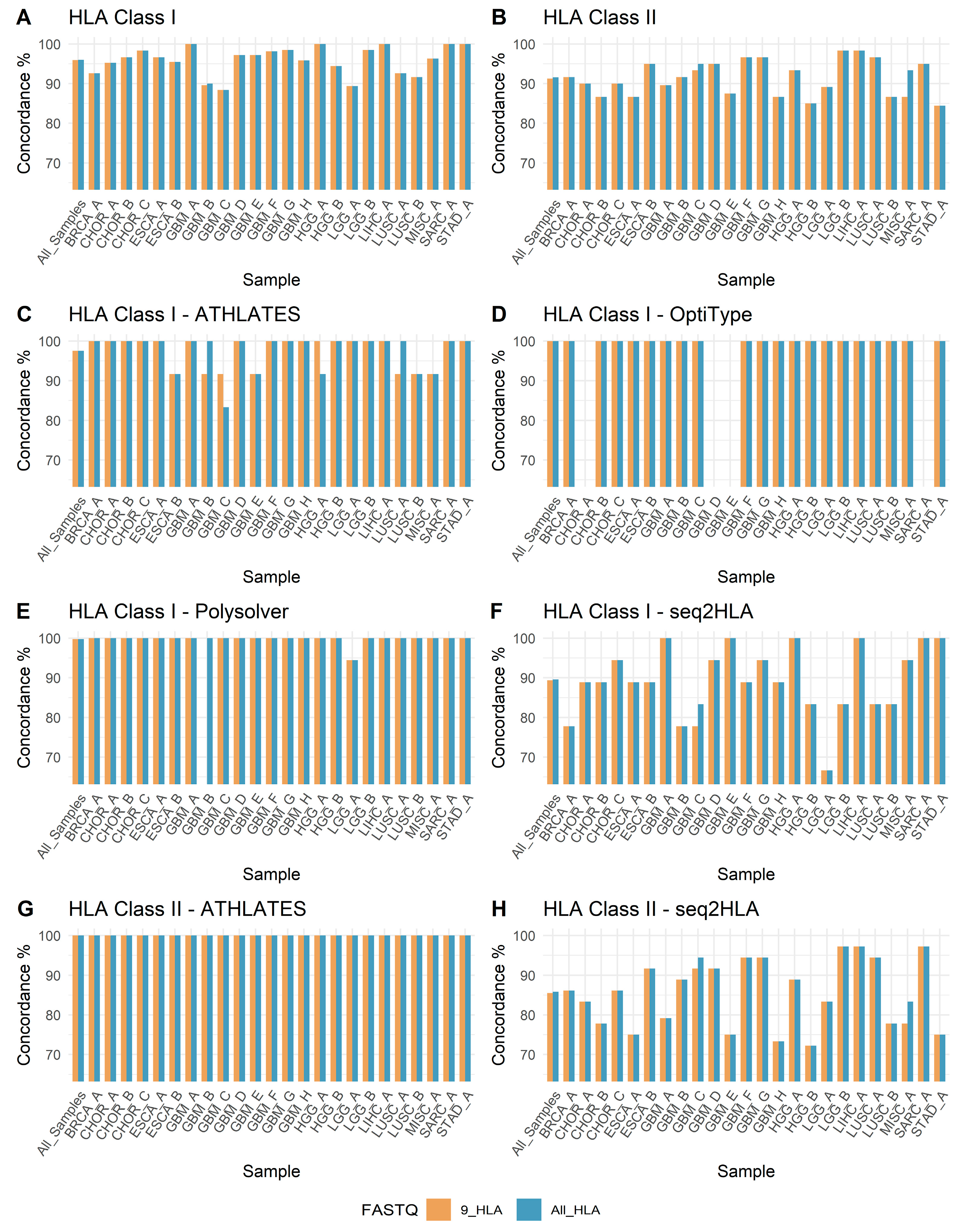
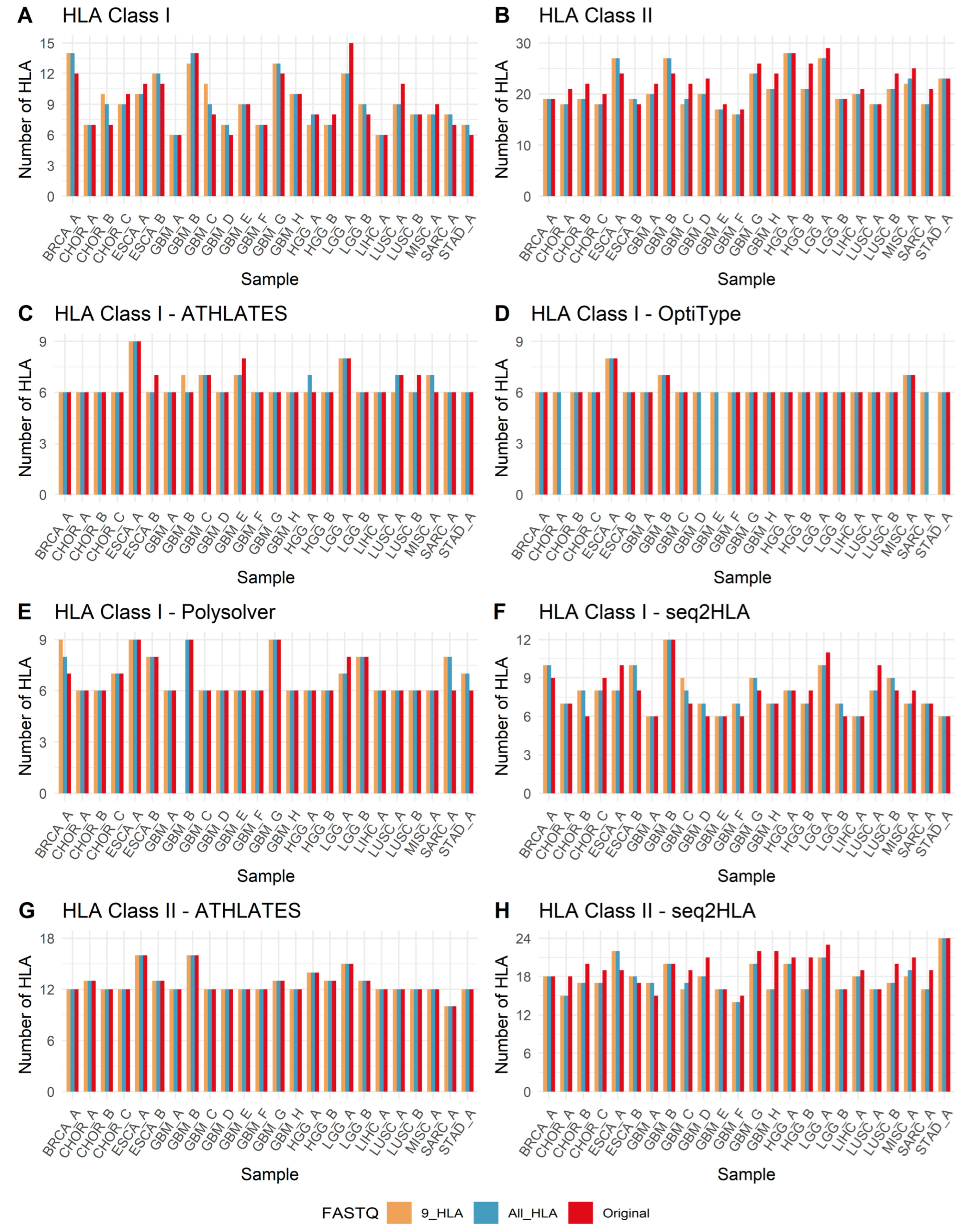
3.3. HLA Genotyping and Concordance
3.4. Software-Wise Concordance of HLA Genotypes
3.5. Unanimous and Non-Unanimous HLA Calls
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Tapias, P.; Castiblanco, J.; Anaya, J.-M. Major Histocompatibility Complex: Antigen Processing and Presentation. In Autoimmunity: From Bench to Bedside [Internet]; El Rosario University Press: Bogotá, Colombia, 2013; pp. 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.M.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a Systems Understanding of MHC Class I and MHC Class II Antigen Presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Boehmer, H.; Kisielow, P. Self-Nonself Discrimination by T Cells. Science 1990, 248, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Wilming, L.; Rand, V.; Lovering, R.C.; Bruford, E.A.; Khodiyar, V.K.; Lush, M.J.; Povey, S.; Talbot, C.C.; Wright, M.W.; et al. Gene Map of the Extended humanMHC. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MHC sequencing consortium. Complete Sequence and Gene Map of a Human Major Histocompatibility Complex. Nature 1999, 401, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Maccari, G.; Georgiou, X.; Cooper, M.A.; Flicek, P.; Robinson, J.; Marsh, S.G.E. The IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1053–D1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipps, C.; McMillan, M.; Flood, P.M.; Murphy, D.B.; Forman, J.; Lancki, D.; Womack, J.E.; Goodenow, R.S.; Schreiber, H. Identification of a Unique Tumor-Specific Antigen as a Novel Class I Major Histocompatibility Molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5140–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in Cancer Immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaad, Y.M. Clinical Role of Human Leukocyte Antigen in Health and Disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 82, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacohen, N.; Fritsch, E.F.; Carter, T.A.; Lander, E.S.; Wu, C.J. Getting Personal with Neoantigen-Based Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennerz, V.; Fatho, M.; Gentilini, C.; Frye, R.A.; Lifke, A.; Ferel, D.; Wölfel, C.; Huber, C.; Wölfel, T. The Response of Autologous T Cells to a Human Melanoma Is Dominated by Mutated Neoantigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16013–16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, G.; Miller, M.L.; Aksoy, B.A.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Schultz, N.; Sander, C. Emerging Landscape of Oncogenic Signatures across Human Cancers. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richters, M.M.; Xia, H.; Campbell, K.M.; Gillanders, W.E.; Griffith, O.L.; Griffith, M. Best Practices for Bioinformatic Characterization of Neoantigens for Clinical Utility. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Mardis, E.R. Applications of Immunogenomics to Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Lundegaard, C.; Blicher, T.; Lamberth, K.; Harndahl, M.; Justesen, S.; Røder, G.; Peters, B.; Sette, A.; Lund, O.; et al. NetMHCpan, a Method for Quantitative Predictions of Peptide Binding to Any HLA-A and -B Locus Protein of Known Sequence. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolek, A.; Schubert, B.; Mohr, C.; Sturm, M.; Feldhahn, M.; Kohlbacher, O. OptiType: Precision HLA Typing from next-Generation Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3310–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Chen, K.; Huang, B.; Liu, Q.; Ye, H. Benchmarking HLA Genotyping and Clarifying HLA Impact on Survival in Tumor Immunotherapy. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunce, M.; Passey, B. HLA Typing by Sequence-Specific Primers. In Transplantation Immunology; Zachary, A.A., Leffell, M.S., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 1034, pp. 147–159. ISBN 978-1-62703-492-0. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, W.M.; Carter, V.; Clark, B. The HLA System: Immunobiology, HLA Typing, Antibody Screening and Crossmatching Techniques. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Fürst, D.; Faé, I.; Wenda, S.; Zollikofer, C.; Mytilineos, J.; Fischer, G.F. HLA Typing by Next-Generation Sequencing—Getting Closer to Reality: HLA Typing by NGS. Tissue Antigens 2014, 83, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, D.; Dinauer, D.; Duke, J.; Erlich, H.A.; Holcomb, C.L.; Lind, C.; Mackiewicz, K.; Monos, D.; Moudgil, A.; Norman, P.; et al. 16th IHIW: Review of HLA Typing by NGS. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2013, 40, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubin, M.M.; Artyomov, M.N.; Mardis, E.R.; Schreiber, R.D. Tumor Neoantigens: Building a Framework for Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, J.C.; Kreiter, S.; Diekmann, J.; Löwer, M.; Van De Roemer, N.; De Graaf, J.; Selmi, A.; Diken, M.; Boegel, S.; Paret, C.; et al. Exploiting the Mutanome for Tumor Vaccination. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, N.; Van Buuren, M.M.; Philips, D.; Velds, A.; Toebes, M.; Heemskerk, B.; Van Dijk, L.J.A.; Behjati, S.; Hilkmann, H.; El Atmioui, D.; et al. Tumor Exome Analysis Reveals Neoantigen-Specific T-Cell Reactivity in an Ipilimumab-Responsive Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e439–e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.F.; Lu, Y.-C.; El-Gamil, M.; Li, Y.F.; Gross, C.; Gartner, J.; Lin, J.C.; Teer, J.K.; Cliften, P.; Tycksen, E.; et al. Mining Exomic Sequencing Data to Identify Mutated Antigens Recognized by Adoptively Transferred Tumor-Reactive T Cells. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, A.; Merseburger, P.; Staut, J.; Marchal, K.; Van Den Eynden, J. Benchmark of Tools for in Silico Prediction of MHC Class I and Class II Genotypes from NGS Data. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuesen, N.H.; Klausen, M.S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Trolle, T.; Renaud, G. Benchmarking Freely Available HLA Typing Algorithms across Varying Genes, Coverages and Typing Resolutions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Pan Genome Consortium; Matey-Hernandez, M.L.; Brunak, S.; Izarzugaza, J.M.G. Benchmarking the HLA Typing Performance of Polysolver and Optitype in 50 Danish Parental Trios. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, M.; Gong, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Dong, H.; Meng, R.; et al. Benchmarking the Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing Performance of Three Assays and Seven Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Algorithms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 652258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.A.; Rooney, M.S.; Rajasagi, M.; Tiao, G.; Dixon, P.M.; Lawrence, M.S.; Stevens, J.; Lane, W.J.; Dellagatta, J.L.; Steelman, S.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Cancer-Associated Somatic Mutations in Class I HLA Genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padul, V.G.; Biswas, N.; Gill, M.; Perez, J.A.; Lopez, J.J.; Kesari, S.; Ashili, S. Assessment of Functional Status of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Genes in Cancer Tissues in the Context of Personalized Neoantigen Peptide Vaccine Immunotherapy. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2025, 9, e2400174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Duffy, B.; Mohanakumar, T.; Mitra, R.D.; Zody, M.C.; Pfeifer, J.D. ATHLATES: Accurate Typing of Human Leukocyte Antigen through Exome Sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boegel, S.; Löwer, M.; Schäfer, M.; Bukur, T.; de Graaf, J.; Boisguérin, V.; Türeci, Ö.; Diken, M.; Castle, J.C.; Sahin, U. HLA Typing from RNA-Seq Sequence Reads. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.C.; Zadoorian, A.; Wilson, L.O.W.; Melbourne Genomics Health Alliance; Thorne, N.P. Evaluation of Computational Programs to Predict HLA Genotypes from Genomic Sequencing Data. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 19, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, S.G.E.; Albert, E.D.; Bodmer, W.F.; Bontrop, R.E.; Dupont, B.; Erlich, H.A.; Fernández-Viña, M.; Geraghty, D.E.; Holdsworth, R.; Hurley, C.K.; et al. Nomenclature for Factors of the HLA System, 2010. Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 291–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Yeo, Z.X.; Wong, M.; Piper, J.; Long, T.; Kirkness, E.F.; Biggs, W.H.; Bloom, K.; Spellman, S.; Vierra-Green, C.; et al. Fast and Accurate HLA Typing from Short-Read next-Generation Sequence Data with xHLA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8059–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundal, J.; Kiwala, S.; McMichael, J.; Miller, C.A.; Xia, H.; Wollam, A.T.; Liu, C.J.; Zhao, S.; Feng, Y.-Y.; Graubert, A.P.; et al. pVACtools: A Computational Toolkit to Identify and Visualize Cancer Neoantigens. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning Sequence Reads, Clone Sequences and Assembly Contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, D.; Holtgrewe, M.; Reinert, K. RazerS 3: Faster, Fully Sensitive Read Mapping. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2592–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Seo, J.-H.; Song, S.; Song, I.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-A.; Gong, G.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, H.J. A New Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing Algorithm Combined with Currently Available Genotyping Tools Based on Next-Generation Sequencing Data and Guidelines to Select the Most Likely Human Leukocyte Antigen Genotype. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Su, X. Investigations of Sequencing Data and Sample Type on HLA Class Ia Typing with Different Computational Tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Krishnakumar, S.; Wilhelmy, J.; Babrzadeh, F.; Stepanyan, L.; Su, L.F.; Levinson, D.; Fernandez-Viña, M.A.; Davis, R.W.; Davis, M.M.; et al. High-Throughput, High-Fidelity HLA Genotyping with Deep Sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8676–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padul, V.G.; Gill, M.; Perez, J.A.; Lopez, J.J.; Kesari, S.; Ashili, S. Evaluation of HLA Region-Specific High-Throughput Sequencing FASTQ Reads Combined with Ensemble HLA-Typing Tools for Rapid and High-Confidence HLA Typing. Biology 2025, 14, 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121717
Padul VG, Gill M, Perez JA, Lopez JJ, Kesari S, Ashili S. Evaluation of HLA Region-Specific High-Throughput Sequencing FASTQ Reads Combined with Ensemble HLA-Typing Tools for Rapid and High-Confidence HLA Typing. Biology. 2025; 14(12):1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121717
Chicago/Turabian StylePadul, Vijay G., Mini Gill, Jesus A. Perez, Javier J. Lopez, Santosh Kesari, and Shashaanka Ashili. 2025. "Evaluation of HLA Region-Specific High-Throughput Sequencing FASTQ Reads Combined with Ensemble HLA-Typing Tools for Rapid and High-Confidence HLA Typing" Biology 14, no. 12: 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121717
APA StylePadul, V. G., Gill, M., Perez, J. A., Lopez, J. J., Kesari, S., & Ashili, S. (2025). Evaluation of HLA Region-Specific High-Throughput Sequencing FASTQ Reads Combined with Ensemble HLA-Typing Tools for Rapid and High-Confidence HLA Typing. Biology, 14(12), 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121717





