Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
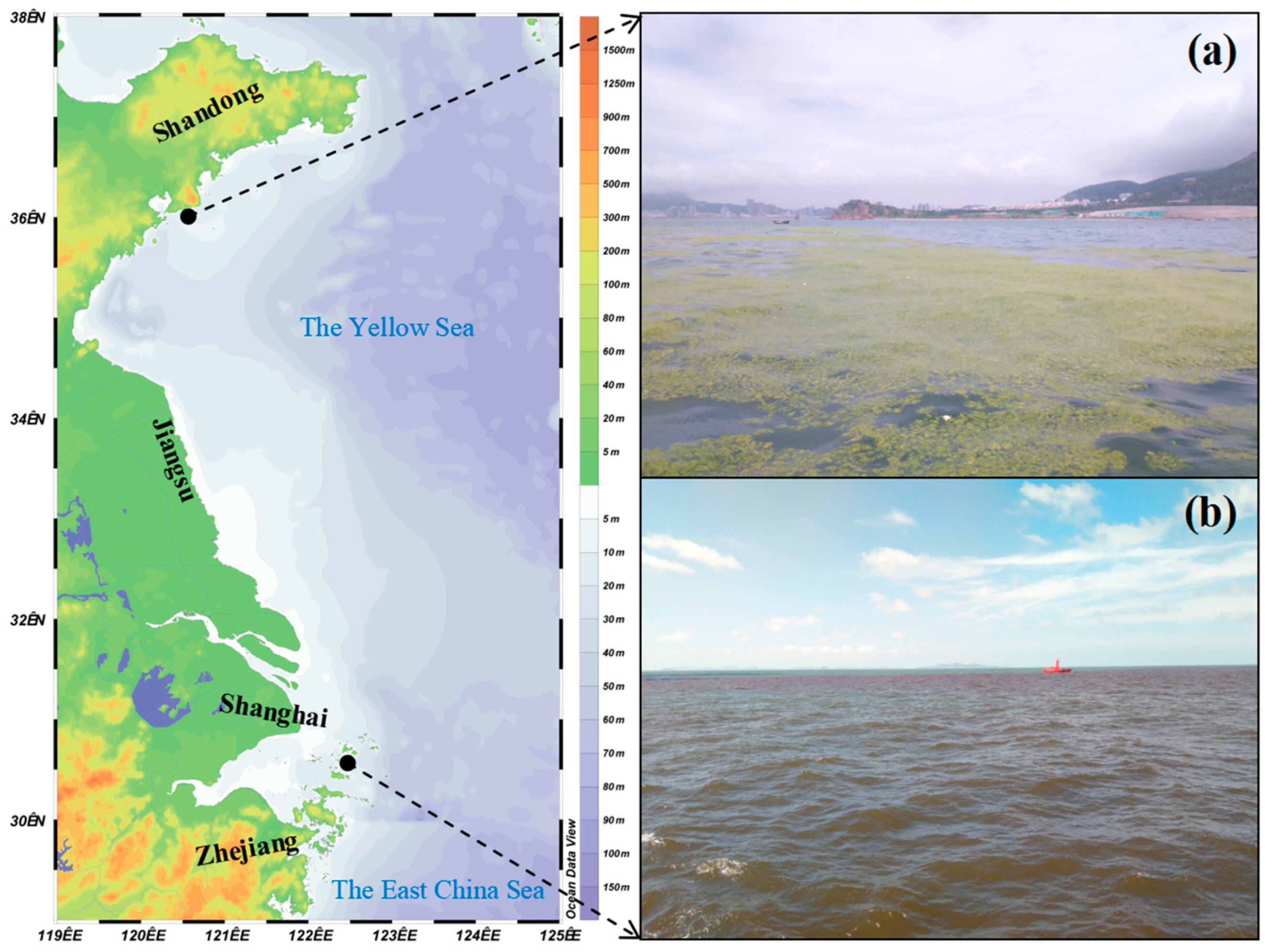
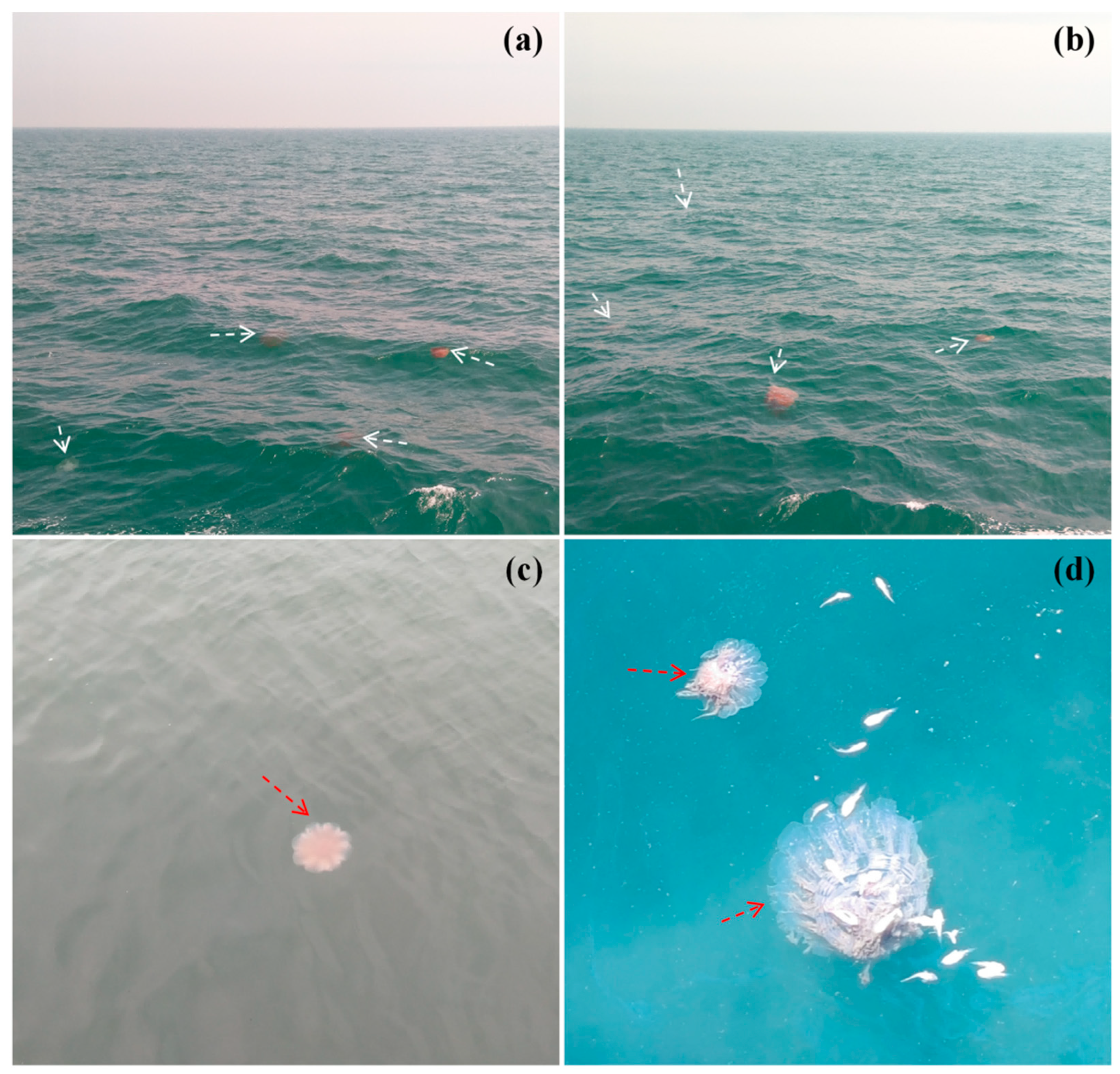
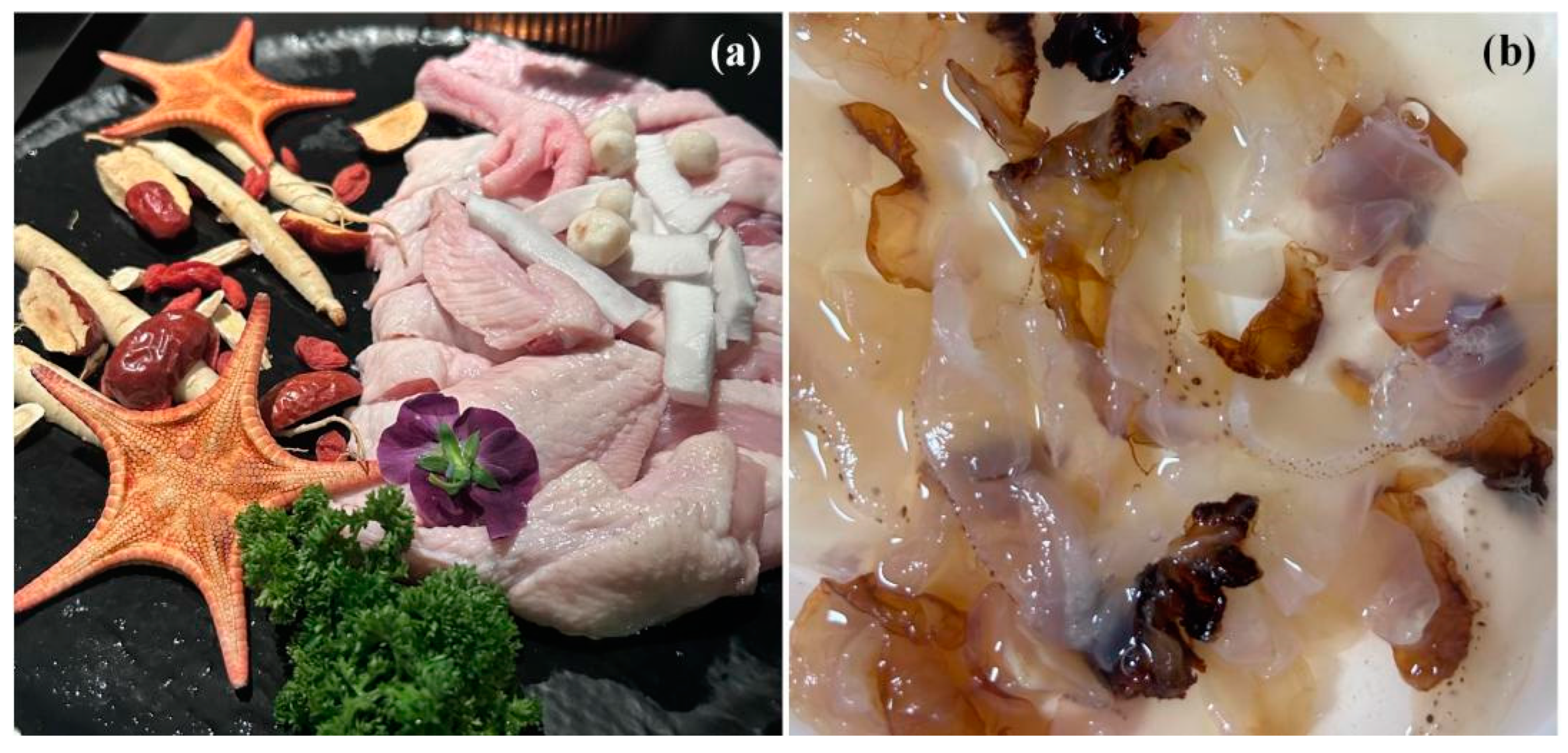
2. Cnidaria—The Biological Background of Jellyfish and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China
3. Annelida—The Biological Background of Urechis unicinctus Drasche, 1880 and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China
4. Mollusca—The Biological Background of Philine kinglipini S. Tchang, 1934, and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China

5. Arthropoda—The Biological Background of Acetes chinensis Hansen, 1919, and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China
6. Echinodermata
6.1. The Biological Background of Asteroidea and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China
6.2. The Biological Background of Ophiuroidea and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China
6.3. The Biological Background of Acaudina molpadioides Semper, 1867, and the Marine Ecological Disasters It Causes in China

7. Discussion
7.1. Short-Term Outbreaks of Marine Biological Disasters in China Are Anticipated to Persist
7.2. The Selected and Implemented Control Measures Should Aim to Minimize Disruption to Marine Ecosystems
7.3. Effective Resource Utilization of Outbreak Species Is a Long-Term Solution
7.4. Enhancing and Releasing Activities Require Careful Selection of Species to Be Released
7.5. Further Enhance Fundamental Research to Ensure the Sustainable Development of Offshore Ecosystems
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Jia, J. Spatial-temporal distribution of tropical cyclone activity on the eastern sea area of China since the late 1940s. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 277, 108067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, A.B.; Titov, V.V.; Moore, C.W.; Eblé, M.C. The 2004 Sumatra tsunami in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean: New Global Insight from Observations and Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 7992–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcene, E.; Ioannou, I.; Suppasri, A.; Pakoksung, K.; Paulik, R.; Syamsidik, S.; Bouchette, F.; Imamura, F. Characteristics of building fragility curves for seismic and non-seismic tsunamis: Case studies of the 2018 Sunda Strait, 2018 Sulawesi-Palu, and 2004 Indian Ocean tsunamis. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 2313–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, A.; Nakamura, H.; Asano, N.; Iizuka, S.; Miyama, T.; Moteki, Q.; Yoshioka, M.K.; Nishii, K.; Miyasaka, T. Impacts of a warming marginal sea on torrential rainfall organized under the Asian summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunden, J. State of the climate in 2021. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, S1–S465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, S.; He, P. Golden seaweed tides accumulated in Pyropia aquaculture areas are becoming a normal phenomenon in the Yellow Sea of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wu, L.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; He, P. Review of the development of the green tide and the process of control in the southern Yellow Sea in 2022. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 302, 108772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, W.; Liang, H.; Jiang, M.; Dai, Z. Response of storm surge and M2 tide to typhoon speeds along coastal Zhejiang Province. Ocean Eng. 2023, 270, 113646. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, N.; Takahashi, T.; Yasuda, T.; Yanagisawa, H. Survey of 2011 Tohoku earthquake tsunami inundation and run-up. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L00G14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dade, M.; Downing, A.; Benessaiah, K.; Falardeau, M.; Lin, M.; Rieb, J.; Rocha, J. Inequalities in the adaptive cycle: Reorganizing after disasters in an unequal world. Ecol. Soc. 2022, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Bao, F.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhong, S.; Yin, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Marine environmental monitoring with unmanned vehicle platforms: Present applications and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, W.; Tao, A.; Fan, J.; Xing, J.; Wang, G. Synergy between coastal ecology and disaster mitigation in China: Policies, practices, and prospects. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Natural Resources. China China Maritime Disaster Bulletin 2023; Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese)
- Sun, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, J.; Tong, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Fu, M.; Zhuang, M.; He, P.; et al. Prevention strategies for green tides at source in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y. Mitigation of harmful algal blooms using modified clays: Theory, mechanisms, and applications. Harmful Algae 2017, 69, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Cui, Q.; Bi, F.; Zhang, J.; He, P. Attached Ulva meridionalis on nearshore dikes may pose a new ecological risk in the Yellow Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 332, 121969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Shen, Z.L.; Yu, R.C. Responses of a coastal phytoplankton community to increased nutrient input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, K.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Y.; Xia, L.; Qin, Y.; et al. Controlling the source of green tides in the Yellow Sea: NaClO treatment of Ulva attached on Pyropia aquaculture rafts. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hao, P.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Yu, C. Dynamic causes contribute to the increasing trend of red tides in the east China sea during 2020–2022. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, H.; Yu, K.; Wang, L. A new strategy based on a cascade amplification strategy biosensor for on-site eDNA detection and outbreak warning of crown-of-thorns starfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Sun, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, F. Controls of Aurelia coerulea and Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) blooms in the coastal sea of China: Strategies and measures. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 946830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.N.; Wang, L.; Ou, D.Y.; Jia, C.; Li, W.W.; Ding, Y.; You, C.M.; Liao, J.J.; Huang, H. The ecological mechanisms of Acetes blooms as a threat to the security of cooling systems in coastal nuclear power plants. J. Coast. Conserv. 2021, 25, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.L.; Yu, Y.N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, N.S. Morphological and molecular analyses of a Philine kinglipini outbreak in summer of 2022 in Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.W.; He, P.M.; Ye, S.F.; Chen, B.; Huang, L.F.; Wang, H.L.; Yang, J.L.; He, W.H.; Sun, S.; Yang, H.S.; et al. Coastal Marine Ecology in China: Research and Management; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.P. The Diet and Trophic Relationship of Three Disaster Causing Jellyfish in Chinese Coastal Waters; Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: Qingdao, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S. New perception of jellyfish bloom in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 406–410. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Sun, X.X.; Jenkinson, I.R. Preface: Giant jellyfish blooms in Chinese waters. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C. Molecular Identification and Collagen Activity of Twojellyfish in the Northern South China Sea; Yantai University: Yantai, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, P.P.; Shi, Y.H.; Xu, J.B.; Liu, Y.S.; Jiang, F. Influence factors and harmfulness of water jellyfish outbreak for larval rearing ponds in Hangzhou Bay. Fish. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2018, 45, 280–284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.S. Study on Biological Control of Larval Stage of Giant Jellyfish; Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: Qingdao, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qu, C.F.; Song, J.M.; Li, N. The effects of jellyfish decomposition on marine ecological environments. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6224–6232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chiarelli, P.G.; Pegg, R.B.; Kumar, G.D.; Solval, K.M. Exploring the feasibility of developing novel gelatin powders from salted, dried cannonball jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris). Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, A.; Baba, T.; Dohmae, N.; Yamamura, M.; Wada, H.; Ushida, K. Mucin (Qniumucin), a glycoprotein from jellyfish, and determination of its main chain structure. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, T.; Ueno, M.; Goto, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Doi, M.; Akiyama, K.; Yamauchi, S. Immunostimulation Effect of the Jellyfish Collagen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.B.N.; Nishi, K.; Shiraishi, R.; Doi, M.; Sugahara, T. Jellyfish collagen stimulates maturation of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K. Jellyfish blooms in China: Dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Jin, Q.Q.; Yang, L.; Jia, C.; Guan, C.J.; Wang, H.N.; Guo, H. Aggregation process of two disaster-causing jellyfish species, Nemopilema nomurai and Aurelia coerulea, at the intake area of a nuclear power cooling-water system in Eastern Liaodong Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1098232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, S.W.; Zhang, G.T.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F. Selective suppression of in situ proliferation of scyphozoan polyps by biofouling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, M.G.; Barausse, A.; Luisetti, T.; Turner, K. Jellyfish blooms in the Northern Adriatic Sea: Fishermen’s perceptions and economic impacts on fisheries. Fish. Res. 2014, 155, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, V.L.; Angel, D.L.; Bayha, K.M.; Atienza, D.; Edelist, D.; Bordehore, C.; Gili, J.M.; Purcell, J.E. Blooms of the invasive ctenophore, span the Mediterranean Sea in 2009. Hydrobiologia 2010, 645, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rivera, E.; Abu El-Regal, M. A bloom of an edible scyphozoan jellyfish in the Red Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Gershwin, L.A.; Trew, T.; Strzelecki, J.; Bearham, D.; Liu, D.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zeidler, W.; Onton, K.; Slawinski, D. Role of winds and tides in timing of beach strandings, occurrence, and significance of swarms of the jellyfish Crambione mastigophora Mass 1903 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae: Catostylidae) in north-western Australia. Hydrobiologia 2016, 768, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cheng, H.Q.; Xu, H.G.; Francisco, A.S.; Manuel, J.Z.R.; Pablo, D.M.L.; William, J.F.L.Q. Trophic controls of jellyfish blooms and links with fisheries in the East China Sea. Ecol. Model. 2008, 212, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.B.; Liu, Z.L.; Xue, L.Y.; Chen, X.; An, Y. Review on the occurrence regularity and current situation of jellyfish disaster in Qinhuangdao coastal area. Hebei Fish. 2021, 6, 12–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Review on the current situation and perspective of Chinese jellyfish disasters’ research. J. Fish. Res. 2018, 40, 156–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.W.; Guan, C.J.; Xu, P.; Liu, G.Z.; Xu, Q.M.; Ye, J.Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.Q. Analysis on risk organisms for the cold source water of nuclear power plantin the eastern waters of Liaodong bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 41–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; He, J.; Sun, T.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.H.; Dong, Z.J. Molecular identification on the causative species jellyfish blooms in the northern South China Sea in 2019. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 142–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.M.; Rao, Q.H. Analysis of the causes of jellyfish outbreaks in the nearshore waters of Qinhuangdao and countermeasures against them. Hebei Fish. 2016, 1, 55–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.Z.; Ma, S.L.; Jin, B.W. Causes and effects of jellyfish outbreaks in the ocean. Hebei Fish. 2016, 7, 71–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, L.C.; Chou, C.; Chen, Q.C.; Hwang, J.S. Jellyfish assemblages are related to interplay waters in the southern east China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 103, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Purcell, J.E.; Li, Y.L.; Duan, Y.; Wang, A.Y.; Wang, B. Testing the influence of previous-year temperature and food supply on development of Nemopilema nomurai blooms. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.J.; Peng, S.J.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, C.; Yeasmin, M.; Zhao, J.M.; Dong, Z.J. Biodiversity and distribution patterns of blooming jellyfish in the Bohai Sea revealed by eDNA metabarcoding. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Sun, M.; Purcell, J.E.; Chai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, A.Y. Effect of salinity and light intensity on somatic growth and podocyst production in polyps of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Ishizaka, J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Siswanto, E.; Wang, S.Q. Relationships of interannual variability in SST and phytoplankton blooms with giant jellyfish (Nemopilema nomurai) outbreaks in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Kong, J.; Laws, E.A.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, M.R.; Yao, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhen, Y.; et al. The Link between Marine Thermal Discharges and Nemopilema Nomurai Blooms Around Nuclear Power Plants. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2023, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Sun, S. Benthic ecosystem determines jellyfish blooms by controlling the polyp colony development. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.H.; Li, S.F.; Ding, F.Y.; Yan, L.P. Primary analysis on the jellyfish blooms and its cause in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Fish. Inf. Strategy 2004, 5, 10–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.G. Phylogenetic Analyses of Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Urechis unicinctus (Echiura) Support That Eehiurans Are Derived Annelids; Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: Qingdao, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.C.; Li, B.J.; Jiao, X.D. Research progress in molecular biology of Urechis unicinctus. Bull. Biol. 2020, 55, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.S.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Shang, H.X.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.T.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Analysis of the relationship between geography and body color with the genetic diversity in the Echiura worm Urechis unicinctus based on the mitochondrial COI and D-loop sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2021, 6, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.B.; Zhang, S.S.; Sun, Y.; Tian, B.; Song, L.J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, T. Effects of substrate on the physiological characteristics and intestinal microbiota of Echiura worm (Urechis unicinctus) juveniles. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Sato-Okoshi, W.; Tanaka, M.; Okoshi, K.; Teramoto, W.; Kondoh, T.; Nishitani, G.; Endo, Y. Swimming behavior of the spoon worm Urechis unicinctus (Annelida, Echiura). Zoology 2014, 117, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xin, Y.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, X.Q.; Liang, D.; Wei, S.Y.; Sun, M.C.; Xu, M.; Yu, R.C. Characteristics of Urechis unicinctus and breeding Techniques. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 20, 178–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.H.; Liu, X.; Sun, N.; Zuo, B.N.; Li, H.Y. Ecological Artificial Breeding Techniques for Urechis unicinctus. Sci. Fish Farming 2021, 1, 66–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Du, M.R.; Li, W.H.; Jiang, W.W.; Lin, F.; Yao, L.; Wu, Y.P.; Jiang, Z.J. Effect of bioturbation of Urechis unicinctus on the diffusion flux of nitrogen and phosphorus at the sediment-water interface. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 102–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y. Effects of Bioturbation by Urechis Unicinctus on Key Process of Sediment Nitrogen Cycle in Coastal Aquaculture Area; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Effect of Digestion Process of Filter Feeders on Silicon Cycle in the Ocean; Qingdao University of Science and Technology: Qingdao, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.Y.; Hou, M.Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, R.Y.; Chen, W.B. Experiment on the purification effect of the Urechis unicinctus on Aquaculture Tail Water. China Fish. 2024, 2, 97–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Song, S.L.; Tang, Y.Z.; Meng, R.P.; Wang, B.G. Analysis of Amino Acid Composition and Content in the Body Wall of the Urechis unicinctus. Shandong Fish. 2000, 5, 26–27+49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.Y.; Sun, C.H.; Wang, C.W.; Du, F.; Li, B.F. Technology research of preparation of seafood flavor condiment base from Urechis unicinctus. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 168–171+176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.R.; Xiao, H.; Gu, M.H.; Ji, A.G.; Song, S.L. Study on the bioactive components of Urechis Unicinctus and the development of condiments. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 45, 253–258. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.N.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.E. Preparation of flavor seasoning by maillard reaction of enzymatic hydrolysate of Urechis unicinctus. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 48, 243–250. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Zhao, R.P.; Deng, J.H.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zuo, J.C.; Huang, L.; Jing, M.D. Genetic diversity and population structure of penis fish (Urechis unicinctus) based on mitochondrial and nuclear gene markers. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.M.; Peng, G.; Che, C.Y.; Gong, H.S.; Zhang, Z.M. Research advance on the nutrient component and bioactive substance in Urechis unicinctus. J. Ludong Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 27, 342–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Q.Q.; Han, B.Q.; Feng, Y.L.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.S. Antithrombotic effects of a newly purified fibrinolytic protease from Urechis unicinctus. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, E135–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Lu, J.J.; Asakiya, C.; Huang, K.L.; Zhou, X.Z.; Liu, Q.L.; He, X.Y. Extraction and Identification of Three New Urechis unicinctus Visceral Peptides and Their Antioxidant Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Kim, M.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, S.K. Statistical optimization of high temperature/pressure and ultra-wave assisted lysis of Urechis unicinctus for the isolation of active peptide which enhance the erectile function in vitro. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.Y.; Liu, P.; Han, X.; Cui, Q.M. Hypoglycemic Effects of Glycosaminoglycan from Urechis unicinctus in Diabetic Mice. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F. The Oxidative Detoxification and Metabolic Adaptation of Urechis Unicinctus to Sulfide; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xv, X.H.; Liu, T.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Ding, Z.Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.L.; Xu, G.C. Acute Toxicity of Pb, Cd, Cr, and Zn heavy metal salts to echiuran worm Urechis unicinctus. Fish. Sci. 2022, 41, 1029–1035. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Gan, H.T.; Meng, X.; Yao, H.Y.; Xu, G.C.; Xu, J.T.; Liu, T.H.; Cao, L.X.; Xu, X.H. Effects of Cadmium on Non-specific Immunity and Bioaccumulation of Urechis unicinctus. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2019, 14, 106–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.Z.; Rao, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Lin, J.X.; Fu, S.J.; Zhou, X.P. Two risk indices for benthic macrofauna entrapment evaluation on the water intake systems in coastal nuclear power plants. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 655–662. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Sun, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.B.; Zheng, B.Q.; Lu, C.; Li, J.; Mu, J.L. Ecological environment and the potential hazard-causing organisms in the sea area near the nuclear power plant. Mar. Sci. 2022, 46, 32–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.Y. Studies of Artificial Breeding and Early Cultivation of Urechis Unicinctus; Dalian Ocean University: Dalian, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.X.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.P.; Zhang, H.Z.; Ji, Y.L.; Pu, S.C. A Fishing Device for Philine kinglipini. Patent for Invention CN202310311601.3, 6 June 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.S.; Ni, D.P.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, Z.N. Structure of benthic food web and trophic relationships of the macrofauna in the Yellow Sea. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 50, 20–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Chen, J.; Ji, Y.L.; Chen, L.L.; Li, H.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Li, B.Q.; Xing, R.L. Benthic food web structure of Xiaoqing River Estuary adjacent sea area near revealed by carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis. Haiyang Xuebao 2022, 44, 89–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.Y. Trophic Structure of Major Species in Jiaozhou Bay Considered through Stable-Isotope Analysis; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, P.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.S.; Wang, J.H.; Song, H.; Song, A.H.; Shi, Y. Identification and Classification of Philine Species in Jiaozhou Bay and Analysis of the Causes of Population Outbreaks; China Fisheries: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Li, B.Q.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, H.F. The species diversity of microbenthic fauna in Jiaozhou Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 2, 416–422. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.L.; Liu, W.X.; Sui, J.X.; Qu, F.Y.; Zhao, F.Q.; Zhong, H.X.; Zhang, M.S.; Yu, Z.S. The community structure of macrobenthos in the southern coastal waters nearby the Shandong peninsula in summer. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 27–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, F.Y.; Sui, J.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; Ji, X.X.; Zhao, N.; Yu, Z.S. Community structure and diversity of macrobenthos in the western waters of Liaodong Bay during summer. Mar. Sci. 2016, 40, 40–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, A.G.; Dong, Y.T.; Wang, H.Z.; Wang, Y.H. Preliminary study on the distribution of mollusca ecology in sublittoral of Nanji Islands. J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 2, 50–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C. Long-Term Changes of the Macrobenthic Community Structure in the Cold Water Mass of the Southern Yellow Sea; Shanxi Normal University: Taiyuan, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.B. Assessing the Restoration Effect of Artificial Reefs by Macrobenthos in Shuangdao Bay; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. China Ecological Environment Status Bulletin 2022; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese)
- Zhang, Y.Q. Community Structure, Feeding Ecology, and Movement Behavior of Demersal Fish around Qiansan Islets; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology): Qingdao, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.J.; Yang, F.; Zhong, X.M.; Song, D.D.; Li, G.D.; Kang, Z.J.; Xiong, Y. Review of the life history of Acetes chinensis. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2022, 31, 1032–1040. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.G.; Park, J.K.; Min, G.S. Complete mitochondrial genome of the northern mauxia shrimp Acetes chinensis (Decapoda, Dendrobranchiata, Sergestoidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2012, 23, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.M.; Shi, Y.C.; Tang, F.H.; Chen, J.L.; Xiong, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, L. YOLOv7-DCN-SORT: An algorithm for detecting and counting targets on Acetes fishing vessel operation. Fish. Res. 2024, 274, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.D.; Li, D.J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, X.M.; Tang, J.H.; Song, D.D.; Shi, J.J.; Yang, F.; Kang, Z.J.; Yan, X.; et al. Changes in the resource distribution of Acetes chinensis and patterns of species replacement in Haizhou Bay in summer based on BeiDou VMS data. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.R.; Song, D.D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, X.M.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Kang, Z.J.; Li, G.D.; Li, D.J.; Shi, J.J.; et al. Population biological characteristics and exploitation status of Acetes chinensis in Haizhou Bay. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2023, 54, 573–582. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zan, H. Feasibility Study on Development of Acetes Chinensis Seafood Sauce; Zhejiang Ocean University: Zhoushan, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.H.; Zhang, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Hong, P.Z. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutrients of Acetes Chinensis. J. Fish. Res. 2001, 1, 8–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.F. Key Technology in Preparation of Acetes Chinensis Peptide Chelating Calcium and Development of the Paste Enriched with Peptide Chelating Calcium; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Hui, T.T.; Zhu, B.H.; Xu, C.C.; Li, Y.; Li, X.H. Effects of Peptides from Acetes chinensis on Immunoregulation in Immunocompromised Mice. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 380–386. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.T. The Study of Active Peptide from Acetes Chinensis with Inhibitory Activity on Neuraminidase of Influenza Virus; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.H.; Zhang, C.H.; Hong, P.Z.; Ji, H.W.; Hao, J.M. Purification and identification of an ACE inhibitory peptide from the peptic hydrolysate of Acetes chinensis and its antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Sun, C.Y.; Mang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. Analysis of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease-hydrolyzed marine shrimp Acetes chinensis. J. Pept. Sci. 2006, 12, 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.H.; He, X.Q.; Zhang, C.H.; Hao, J.M.; Zhao, Z.K. Inhibition type of two angiontensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Acetes chinensis. Food Mach. 2013, 29, 4–7+34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.P.; Yu, X.B.; Meng, B.F.; Wu, C.C. Classification and characteristics of the risk organisms in cold source water intake area of coastal nuclear power plants. Mar. Sci. 2023, 47, 131–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Hu, Z.C. Construction and Research of Cooling-water Interception System for Coastal Nuclear Power Plants. Electr. Saf. Technol. 2019, 21, 45–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.S. Real-Time Detection System for Underwater Disaster-Causing Organisms in Coastal Nuclear Power Plant; Xiamen University: Xiamen, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, G.B.; Wang, T.; Yang, B.Z.; Yu, J.; Liao, X.L.; Huang, H.H. Acoustic detection and analysis of Acetes chinensis in the adjacent waters of the Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant. J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 1029–1039. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sha, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Bai, W. Investigation and analysis for marine biological monitoring technologies of nuclear power plants’ water intake. Water Wastewater Eng. 2020, 56, 13–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, Y.F.; Zhang, R.Y. Analysis on the origin of Acetes chinensis outbreak in the water intake area of nuclear power plant. Reg. Gov. 2022, 25, 141–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- An, L.N.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Ou, D.Y.; Li, W.W. Population dynamics of Acetes chinensis and its response to environmental factors in western Daya Bay. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2021, 40, 403–412. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.F.; Zhang, Z.L.; Tang, J.M.; Guo, T.X.; Wang, S.; Tao, Z. Study on the lssue about Water Intake Blockage by Marine Organism in Nuclear Power Plant. Nucl. Saf. 2021, 20, 103–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.C.; Ding, X.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Zhao, B.B. Species, Distribution, and Comprehensive Utilization of Starfish Resources in China. Spec. Econ. Anim. Plants 2013, 16, 9–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y. The Breliminary Studies on Behavior and Control Strategies of Asterias amurensis; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Preliminary Study of Foraging Behavior and Reproductive Biology of the Sea Star Asterias amurensis; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.M.; Miao, Z.; Xie, C.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, X.W. Chemical Constituents and Bioactivities of Starfishes: An Update. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, A.S.; Jagt, J.W.M. The fossil record of the family Benthopectinidae (Echinodermata, Asteroidea), a reappraisal. Eur. J. Taxon. 2021, 755, 149–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Liao, Y.L.; Liu, R.Y.; Liu, J.Y. Records of the genus Henricia Gray, 1840 (Echinodermata: Asteroidea: Echinasteridae) from Chinese waters. Zootaxa 2011, 3115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Liao, Y.L. Three new records of deep-water goniasterids (Echinodermata: Asteroidea: Goniasteridae) from China seas. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.B.; Guo, H.; Cao, L.Q.; Jin, Y. Advances and Perspectives on the Research of Starfish Outbreak in Northern China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1146–1152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Z.L. Characterization of Lipid Profiles in Different Body Parts of Asterias amurensis. J. Dalian Polytech. Univ. 2018, 37, 313–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, F.; Lan, W.J. Chemical Constituents and Its Biological Analyses of the Fatty Acids from Whole Body of Starfish Acanthaster planci. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2009, 48, 55–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, T.J.; Yuan, W.P.; Zhang, Z.; Cong, R.S. Purification and Anti-tumor Activity Examination of Water-Soluble asterosaponin from Asterias rollestoni bell. J. Shandong Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 48, 30–35+42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, M.D.E.; Thomson, D.P.; Babcock, R.C.; Pillans, R.D.; Keesing, J.K.; Miller, M.; Rochester, W.A.; Donovan, A.; Evans, R.D.; Shedrawi, G.; et al. Crown-of-thorns starfish impede the recovery potential of coral reefs following bleaching. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Bradbury, R.H.; Devantier, L.M.; Riddle, M.J.; Death, G. Geological evidence for recurring outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns starfish: A reassessment from an ecological perspective. Coral Reefs 1992, 11, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthicke, S.; Schaffelke, B.; Byrne, M. A boom-bust phylum? Ecological and evolutionary consequences of density variations in echinoderms. Ecol. Monogr. 2009, 79, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, R.C.; Milton, D.A.; Pratchett, M.S. Relationships between size and reproductive output in the crown-of-thorns starfish. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.C.; Yu, K.F.; Liao, Z.H.; Chen, B.; Yu, X.P.; Wei, F.; Hu, B.Q. A Review of Crown-of-Thorns Starfish and Their Ecological Effects on Coral Reefs. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7517–7528. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Ni, G.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, M.Y. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the northern Pacific seastar Asterias amurensis. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.J. Heavy Metal Content and Bioaccumulation Characteristics of Acanthaster Planci in Coral Reef of South China Sea; Guangxi University: Nanning, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.H.; Fang, J.G. Prey Selection and Feeding Rate of Sea Star Asterias amurensis and Asterina pectinifera on Three Bivalves. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 4878–4884. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Duan, Z.L.; He, Z.Y.; Chen, N.S. Molecular Analysis of the Asterias amurensis from Starfish Outbreak in Jiaozhou Bay in Summer 2022. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2023, 54, 1656–1671. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, J.D.; Kise, H.; Wee, H.B.; Lee, C.L.; Soong, K. Crown-of-thorns starfish outbreak at oceanic Dongsha Atoll in the northern South China Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2495–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Wu, Z.J.; Liang, J.L.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhao, J.M. Analysis on the Outbreak Period and Cause of Acanthaster planci in Xisha Islands in Recent 15 Years. Chin. Sci. Bull. -Chin. 2019, 64, 3478–3484. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.T.; Li, J.; Guan, C.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.W. Feeding Selectivity Feeding on Five Species Bivalve and Feeding Rhythm of Asterias amurensis. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2015, 36, 97–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Z.B.; Xie, S.J.; Liu, S.G.; Miao, X.; Wang, W.; Xiao, J.G.; Wang, R.; Lin, L.S. Discussion on Species Validity of Crown-of-thorns Starfish in the South China Sea. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2024, 43, 201–207. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Xia, W.T.; Xie, S.G.; Song, Y.Q. Preliminary Study on the Reproductive Biology of Crown-of-Thorns Starfish (Acanthaster solaris) in the Xisha Islands. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2024, 1–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heng, W.K.; Ho, M.J.; Kuo, C.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Jeng, M.S.; Chen, C.A. Crown-of-thorns starfish outbreak at Taiping Island (Itu Aba), Spratlys, South China Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2022, 98, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.T.; Chen, H.Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.F. Effects of Four Microalgae on the Survival and Growth of Acanthaster spp. Larvae. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 633–642. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.H.; Ren, G.B.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhang, F.F.; Ma, Y.; Li, M.J.; Wang, R.F. High Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring and Analysis of Coral Reef Degradation Caused by Outbreaks of Biological Natural Enemies: A Case Study of the Taiping Island in the South China Sea. Trop. Geogr. 2023, 43, 1856–1873. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.C.; Xing, J.J.; Cai, W.Q.; Zhang, K.D.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, Y.C.; Tang, J.; Zhou, Z. Study on the population distribution of Acanthaster planci in the reef area of the Xisha Islands based on environmental DNA technology. Haiyang Xuebao 2023, 45, 76–83. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.L.; Ning, Z.M.; Yu, K.F.; Fang, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Wei, F. Study on the impacts of crown-of-thorns starfish on nutrient dynamics in the coral reef sediments. Haiyang Xuebao 2022, 44, 23–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.A.; Mellin, C.; Pratchett, M.S. Larval connectivity and water quality explain spatial distribution of crown-of-thorns starfish outbreaks across the Great Barrier Reef. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2020, 87, 223–258. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, A.R.; Gumanao, G.S.; Mueller, B.; Saceda-Cardoza, M.M.E. Management of crown-of-thorns sea star (Acanthaster planci L.) outbreaks: Removal success depends on reef topography and timing within the reproduction cycle. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 71, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.S.; Hay, M.E. Size matters: Predator outbreaks threaten foundation species in small Marine Protected Areas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichsteller, A.; Taylor, J.; Stöhr, S.; Brix, S.; Martìnez Arbizu, P. DNA Barcoding of Cold-Water Coral-Associated Ophiuroid Fauna from the North Atlantic. Diversity 2022, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; McNamara, K. End-Permian extinction and subsequent recovery of the Ophiuroidea (Echinodermata). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 236, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.Y.; Lu, Y.L.; Pan, Y.J.; Guo, C.H.; Qu, J.Y. Progress on the Biological Research of Ophiuroidea. J. Hainan Trop. Ocean Univ. 2016, 23, 92–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N. Study on the Mechanism of Quantity Variations of Brittle Stars in the Zhangzi Island Area; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Qingdao, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thuy, B. Temporary expansion to shelf depths rather than an onshore-offshore trend: The shallow-water rise and demise of the modern deep-sea brittle star family Ophiacanthidae (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea). Eur. J. Taxon. 2013, 48, 1–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.L.; Xiao, N. Species composition and faunal characteristics of echinoderms in China seas. Biodivers. Sci. 2011, 19, 729–736. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X. Population Structure and Genetic Divergence of Ophiura Sarsii Vadicola from Yellow Sea; First Institute of Oceanography: Qingdao, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y. On the discovery of a scythic ophiuroid from Kueichou, China. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 1960, 2, 97–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.L. New discovery of fossil ophiuroids from Guizhou and Southern Sichuan, China. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 1985, 3, 337–343+374–376. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.T.; Wang, X.J. Ophiuroid fossils from the Middle Permian Tongzi Formation, Longyan, Fujian Province. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 2002, 3, 396–398. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Y.; Zhang, D.S.; Wang, C.S. Two new records of genus Ophiurothamnus (Ophiuroidea, Ophiacanthidae) from a deep-sea seamount of the South China Sea. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 649–655. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.H.; Li, Y.X.; Na, J.Y.; Han, X.Q.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, D.S.; Qiu, J.W. Description of a new species of Histampica (Ophiuroidea: Ophiothamnidae) from cold seeps in the South China Sea and analysis of its mitochondrial genome. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2021, 178, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethupul, H.; Stöhr, S.; Zhang, H.B. Order Euryalida (Echinodermata, Ophiuroidea), new species and new records from the South China Sea and the Northwest Pacific seamounts. ZooKeys 2022, 1090, 161–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethupul, H.; Stöhr, S.; Zhang, H.B. New species, redescriptions and new records of deep-sea brittle stars (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea) from the South China Sea, an integrated morphological and molecular approach. Eur. J. Taxon. 2022, 810, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethupul, H.; Stöhr, S.; Zhang, H.B. Review of Ophioplinthaca Verrill, 1899 (Echinodermata, Ophiuroidea, Ophiacanthidae), description of new species in Ophioplinthaca and Ophiophthalmus, and new records from the Northwest Pacific and the South China Sea. ZooKeys 2022, 1099, 155–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, T. Present Status and Prospect of the Study of Echinoderms. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2016, 51, 125–131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Jiang, Z.J.; Mao, Y.Z.; Zang, Y.Q.; Fang, J.G. The Analysis of Nutrient Components of Three Brittle Star Species in the North Yellow Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2015, 36, 17–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cong, J.S.; Zhen, J.R.; Qu, J.Y.; Guo, C.H. Analysis of Nutrient Constituents in Stegophiura sladeni. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2016, 38, 308–310. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G.T.; Zhang, F. Reproductive cycle of Ophiopholis mirabilis (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea) in Zhangzi Island area, northern Yellow Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sui, J.X.; Li, X.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, B.L.; Shuai, L.M. Variations of Macrofaunal Community Classification in the South Yellow Sea. Guangxi Sci. 2016, 23, 339–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.Z.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, B.L.; Shuai, L.M.; An, J.M. Comparison in macrobenthic community composition inside and outside the Cold Water Mass in the Southern Yellow Sea in summer. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2017, 48, 312–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, G.T.; Zhang, F.; Sun, X.X. An enhanced underwater camera apparatus for seabed observation of megabenthic epifauna in the northern Yellow Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.C.; Cai, L.Z.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lin, J.X.; Zhou, X.P. Potential risk assessment of macrozoobenthos blocking nuclear power cold source system in three subtidal zone of Fujian, Guangdong and Hainan coasts. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 286–293. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Z.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, H.H. Community Structure of Macrobenthos and Seasonal Variations in the Zhangzi Island Waters of the Northern Yellow Sea. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2016, 51, 245–257. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.Q.; Ji, X.; Xia, Y.J.; Lin, J.; Huang, W.; Cheng, H.; Liu, S.H.; Qin, Y.T.; Liu, W. Morphological Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Sea Cucumber Acaudina molpadioides in the Fujian Coastal Waters. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2022, 41, 427–435. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Lu, C.; Guo, Y.C.; Dong, B. The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenetic analysis of Acaudina molpdioides. Mitochondrial DNA Part B-Resour. 2019, 4, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.W.; Su, X.R.; Qin, Y.M.; Wang, M.Q.; He, J.J.; Hu, G.Z.; Huang, S.F.; Zhou, J. The Phylogenetic Relation of Sea Cucumber Acaudina molpadioides. Fish. Sci. 2009, 28, 733–736. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.F. Study on Typical Disaster-causing Organisms of Coastal Nuclear Power Operation Safety: Taking Ningde Nuclear Power as an Example; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Li, B.F.; Ma, J.J.; Dong, S.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zeng, M.Y. Purification and Synthesis of ACE Inhibitory Peptide from Acaudina molpadioidea Protein Hydrolysate. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2012, 33, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.W.; Chang, Y.G.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, C.H.; Shi, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.M. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Acaudina molpadioides improves hyperglycemia via activation of PKB/GLUT4 signaling in skeletal muscle of insulin resistant mice. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Rao, Y.Y.; Liao, X.L.; Dai, M.; Huang, H.H. Spatial Distribution and Habitat Condition of Acaudina molpadioides in Western Daya Bay. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 286–293. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.L.; Liu, S.H.; Yuan, Y.M.; Jiang, K.J.; Wang, T.; Qin, Y.T.; Ren, Y.H. The Potential Suitability Habitat Prediction of Acaudina molpadioides Based on Maxent Model. J. Oceanogr. 2021, 43, 65–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H. Research on the Causes, Prevention and Control Measures of Bio-Blogging on Nuclear Power Cold Source by Acaudina molpadioides; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yi, X.T.; Wang, N.L.; Pei, D.; Wei, J.T.; Di, D.L.; Wang, L.T. Evaluation of In Vitro Hypoglycemic Activity in Vitro for Polypeptides from Acaudina molpadioides. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 245–248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y. Isolation, Purification, Identification, and Activity Evaluation of Hypoglycemic Peptides from Acaudina molpadioides; Lanzhou University of Technology: Lanzhou, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.W.; Wang, J.F.; Li, S.J.; Jiang, W.; Song, W.D. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides in the Liver of Insulin Resistant Mice. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2016, 38, 24–29+35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Wang, P.Y. Study on the Distribution of Heavy Metals and Nutrients in Acaudina molpadioides. Chin. Prev. Med. 2016, 17, 55–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.L.; Yu, P.L.; Zhao, L.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Q.Q.; Fan, K.Q.; Tian, K.; Pei, D. Determination of Active Substances and Evaluation of Hypoglycemic Activity in Acaudina molpadioides from Different Producing Areas. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2019, 38, 11–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.L.; Wei, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.F.; Pei, D.; Di, D.L. In Vitro Evaluation of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Acaudina molpadioides. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 224–226+232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Feng, T.Y.; Zhang, B.; Sugawara, T.; Xue, C.H. Isolation and Anti-Fatty Liver Activity of a Novel Cerebroside from the Sea Cucumber Acaudina molpadioides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.X.; Xu, H.P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.W.; Xie, H. Preparation and Evaluation of Peptides with Potential Antioxidant Activity by Microwave Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Collagen from Sea Cucumber Acaudina Molpadioides Obtained from Zhejiang Province in China. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Jin, H.X. Collagen peptides from Acaudina molpadioides prevent CCl4-induced liver injury via Keap1/Nrf2-ARE, PI3K/AKT, and MAPKs pathways. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Guo, Y.C.; Liu, W.; Zheng, B.Q.; Huang, Q.Z.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Huan, F. Risk Analysis Aggregation Behavior of Acaudina molpadioides on Nuclear Power Plant Cooling Sources. Nucl. Saf. 2024, 23, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.X.; Wang, X.B. Macrobenthic Biomass and Secondary Production in the Northern East China Sea and the Relative Importance of Environmental Variables. Pac. Sci. 2019, 73, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.Q.; Lu, C.; Liu, W.; Guo, Y.C.; Huang, W.; Cheng, H.; Lin, J. Gonadal development of the sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides in north coast of Fujian. Haiyang Xuebao 2021, 43, 133–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wu, X.P.; Qu, R. The impact of climate change on species distribution patterns. 7th Int. Forum Biodivers. Conserv. China 2010, 7, 269–280. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Jiang, S.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, Y.; He, J.S. Complex relationships and feedback mechanisms between climate change and biodiversity. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 293–311. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollasch, S. The importance of ship hull fouling as a vector of species introductions into the North Sea. Biofouling 2002, 18, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, P.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, R.T.; Qiu, J.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, Q.G.; Jiang, Z.J.; Wang, H.; He, W.H.; et al. How to control pollution from tailwater in large scale aquaculture in China: A review. Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanta, M.A.; Al Hasibi, R.A.; Tambunan, H.B.; Ruly; Syamsuddin, A.; Aditya, I.A.; Susanto, B. Towards a Net Zero-Emission Electricity Generation System by Optimizing Renewable Energy Sources and Nuclear Power Plant. Energies 2024, 17, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.M.; Guo, H.; Dai, L.H.; Liu, M.L.; Xiao, Y.; Cong, T.L.; Gu, H.Y. The role of nuclear energy in the carbon neutrality goal. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2023, 162, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Yu, Z.Y. China’s nuclear exports: Understanding the dynamics between domestic governance reforms and international market competition. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 103, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Xia, J.; Tong, Y.C.; Li, C.X.; Zhao, S.; Zhuang, M.M.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhang, J.H.; He, P.M. Research development on resource utilization of green tide algae from the Southern Yellow Sea. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.R.G.; Amador-Castro, L.F.; Ramírez-Partida, A.E.; García-Cayuela, T.; Carrillo-Nieves, D.; Alper, H.S. Valorization of Caribbean Sargassum biomass as a source of alginate and sugars for de novo biodiesel production. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.N.; Zhang, N.Y.; Sun, S.; Yuan, J.G.; Chen, J.; Li, M.M.; Lin, N.; You, Y.; Wang, W.J.; Ding, S.X. Application of microsatellite markers for evaluating the effect of restocking enhancement in Larimichthys crocea. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 1100–1108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.X.; Zhou, L.; Wei, Q.W. Stock status and conservation dilemma of species of Acipenseriformes in the Yangtze River and relevant suggestions. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 62–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.H.; Wu, Z.; Feng, B.B.; Deng, S.S.; Zhen, W.Q.; Liao, Y.Y.; Jie, X.Y.; Kwan, K.Y. Global conservation of Tachypleus tridentatus: Present status and recommendations. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 621–629. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful algal blooms in China: History, recent expansion, current status, and future prospects. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| The Administrative Region Where the Nuclear Power Plant Is Located | The Name of Nuclear Power Plant | The Sea Area Where the Nuclear Power Plant Is Located | The Number of Generating Units in the Nuclear Power Plant | Whether a Biological Outbreak Disaster Exists |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fujian Province | Ningde Nuclear Power Plant | The East China Sea | 4 | √ |
| Fujian Province | Fuqing Nuclear Power Plant | The East China Sea | 6 | - |
| Guangdong Province | Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 2 | √ |
| Guangdong Province | Ling’ao Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 4 | √ |
| Guangdong Province | Yangjiang Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 6 | √ |
| Guangdong Province | Taishan Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 2 | - |
| Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region | Fangchenggang Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 4 | - |
| Hainan Province | Changjiang Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 2 | - |
| Jiangsu Province | Tianwan Nuclear Power Plant | The Yellow Sea | 6 | - |
| Liaoning Province | Hongyanhe Nuclear Power Plant | The Bohai Sea | 6 | √ |
| Shandong Province | Haiyang Nuclear Power Plant | The Yellow Sea | 2 | - |
| Shandong Province | Shidao Bay Nuclear Power Plant | The Yellow Sea | 1 | - |
| Taiwan Province | The Third Nuclear Power Plant | The South China Sea | 2 | - |
| Zhejiang Province | Fangjiashan Nuclear Power Station | The East China Sea | 2 | - |
| Zhejiang Province | Sanmen Nuclear Power Plant | The East China Sea | 2 | - |
| Zhejiang Province | Qinshan Nuclear Power Plant | The East China Sea | 1 | - |
| Zhejiang Province | Qinshan Nuclear Power Plant Phase II | The East China Sea | 4 | - |
| Zhejiang Province | Qinshan Nuclear Power Plant Phase III | The East China Sea | 2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, L.; He, P.; Xia, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights. Biology 2024, 13, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090678
Yao L, He P, Xia Z, Li J, Liu J. Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights. Biology. 2024; 13(9):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090678
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Lulu, Peimin He, Zhangyi Xia, Jiye Li, and Jinlin Liu. 2024. "Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights" Biology 13, no. 9: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090678
APA StyleYao, L., He, P., Xia, Z., Li, J., & Liu, J. (2024). Typical Marine Ecological Disasters in China Attributed to Marine Organisms and Their Significant Insights. Biology, 13(9), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090678







