Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Zeaxanthin Epoxidase Gene in Ulva prolifera
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alga Material and Treatment
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) Analysis
2.3. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
2.4. Full-Length of the UpZEP Gene Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. C. reinhardtii Transformation and Screening of Positive Clones
2.6. Functional Characterization via Heterologous Expressions of the UpZEP Gene in Yeasts
2.7. Measurement of Chlorophyll Contents in C. reinhardtii
Chl. b = 24.96 × OD649 − 7.32 × OD665
Total chlorophyll = Chl. a + Chl. b
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
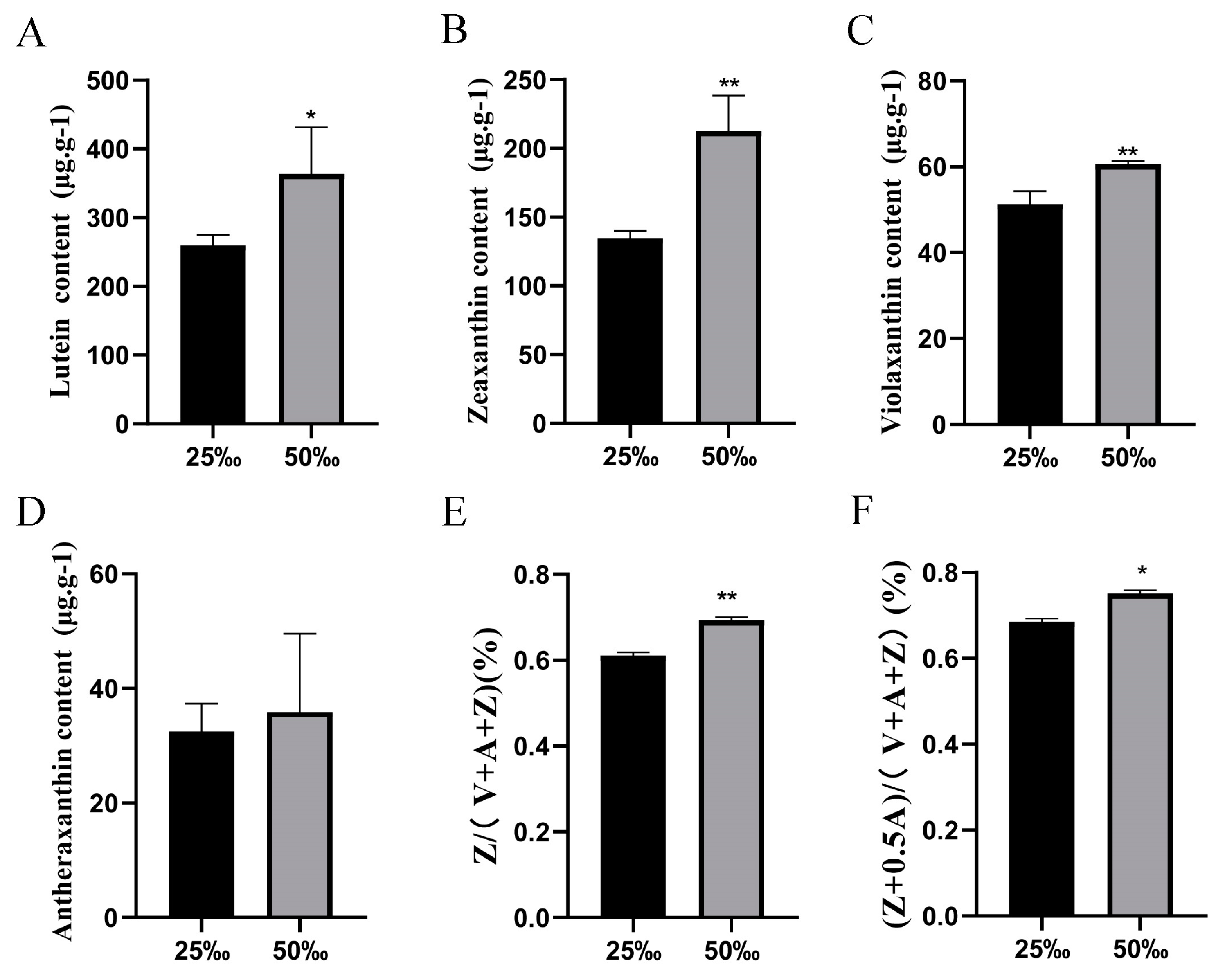
3.1. Determination of Relative Content of Xanthophylls in U. prolifera
3.2. Full-Length Cloning and Characterization of the UpZEP Gene
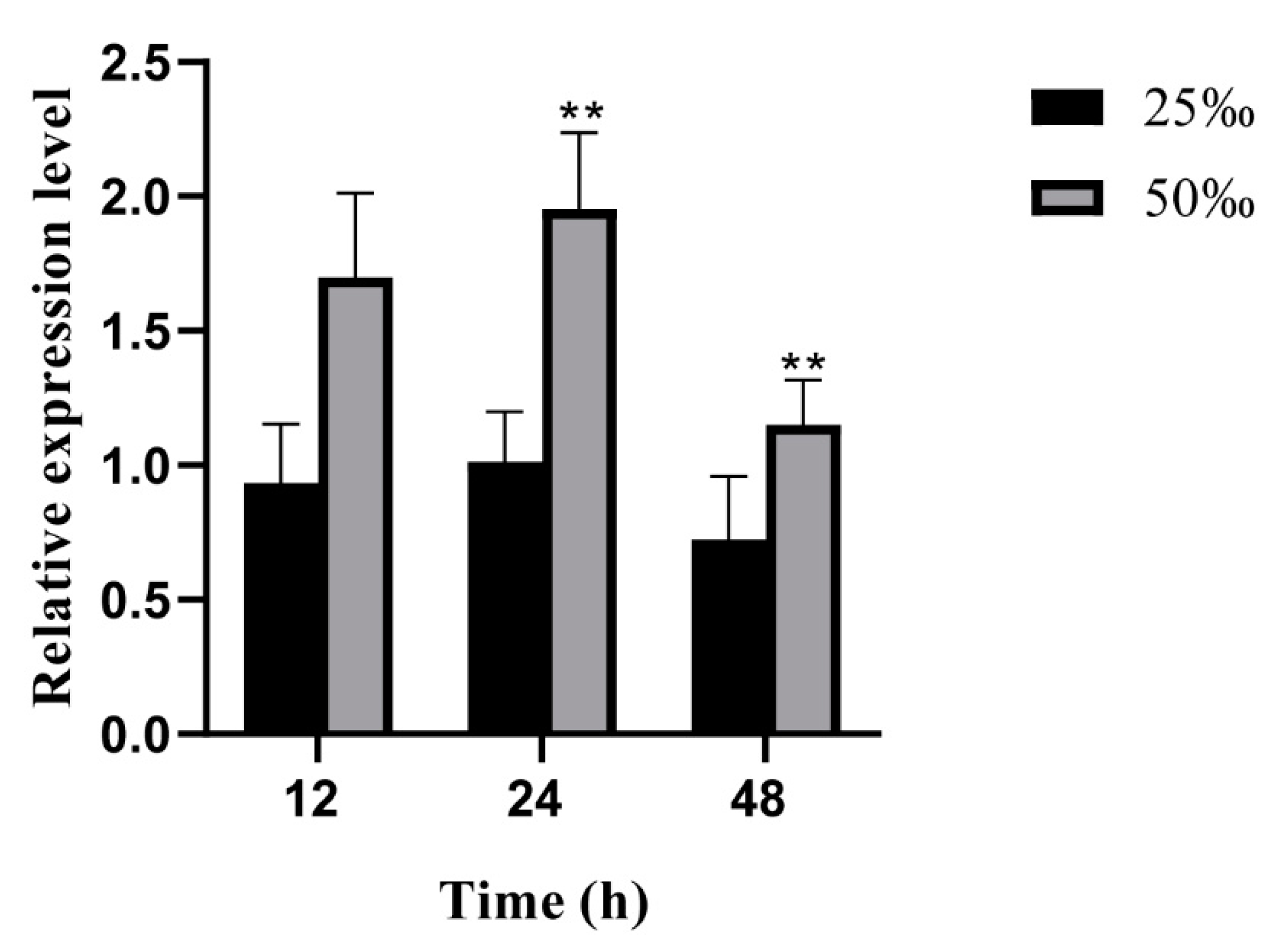
3.3. Expression Levels of the UpZEP Gene under High-Salt Stress
3.4. Functional Characterization via Heterologous Expressions of the UpZEP Gene in Yeast
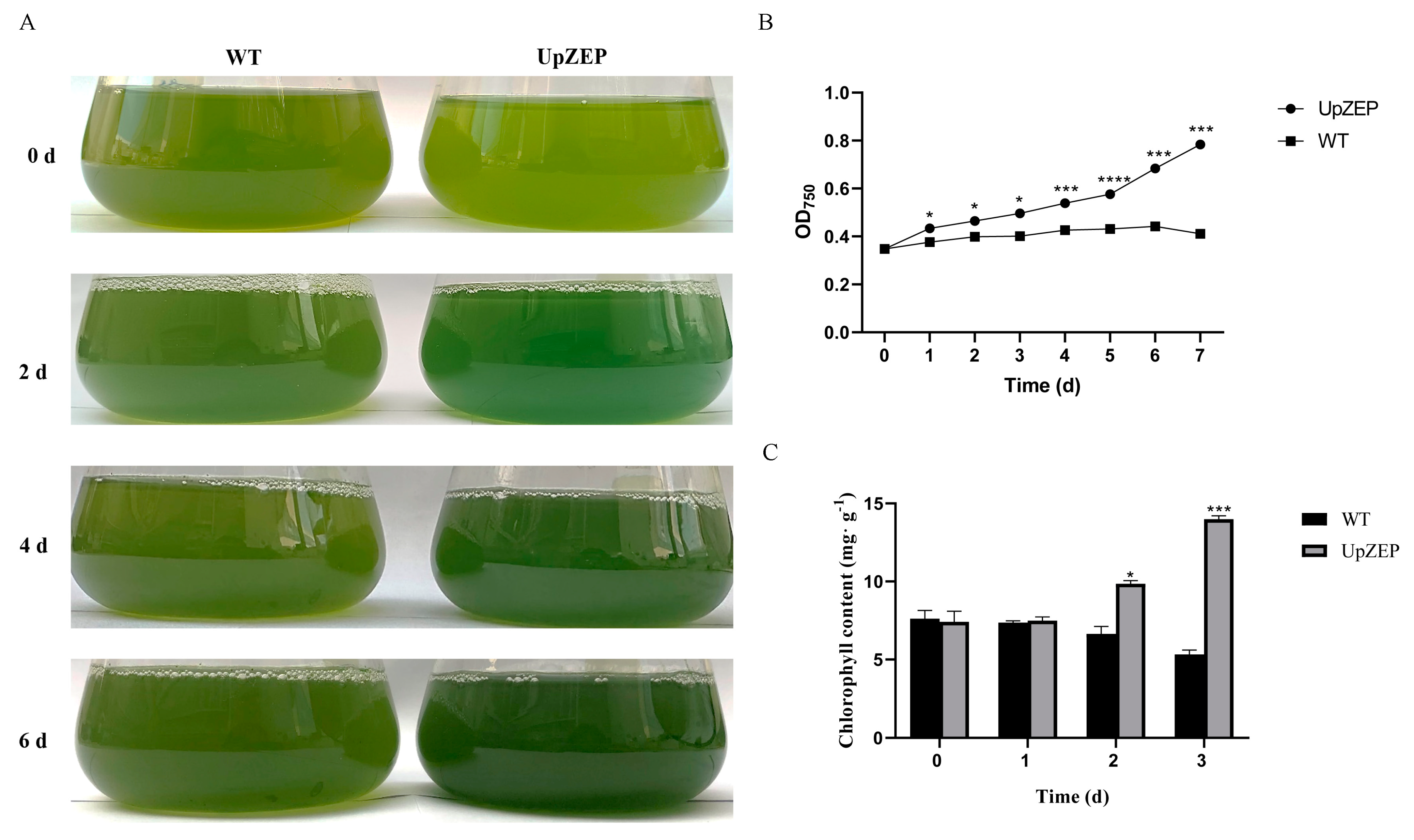
3.5. Validation of C. reinhardtii Transformation and UpZEP Gene Expression Levels under High-Salt Stress
3.6. Analysis of High-Salt Stress Tolerance in Transgenic C. reinhardtii
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Yu, K.; He, P. Adaptability of free-floating green tide algae in the Yellow Sea to variable temperature and light intensity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Liang, C.-W.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.-M.; Wang, Q.-Y. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Shi, X.; Su, R.; et al. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Yu, K.; Chen, Q.; He, Q.; Han, W.; Chen, L.; Cao, J.; Shi, D.; He, P. Growth characteristics and reproductive capability of green tide algae in Rudong coast, China. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, Z.; Wei, W.; Lin, H.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Qin, S. The yellow sea green tides were dominated by one species, Ulva (Enteromorpha) prolifera, from 2007 to 2011. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 58, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Jiang, M.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X. Effect of temperature, salinity and irradiance on growth and photosynthesis of Ulva prolifera. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Cooperation between photosynthetic and antioxidant systems: An important factor in the adaptation of Ulva prolifera to abiotic factors on the sea surface. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, G.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Physiological acclimation of the green tidal alga Ulva prolifera to a fast-changing environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Lin, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhong, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, N. Salinity mediates the effects of nitrogen enrichment on the growth, photosynthesis, and biochemical composition of Ulva prolifera. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19982–19990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Shi, M.; Huan, L.; Wang, G. Transcriptomic analysis of Ulva prolifera in response to salt stress. Water 2022, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, G.; Cock, M. High salt stress in the upper part of floating mats of Ulva prolifera, a species that causes green tides, enhances non-photochemical quenching. J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, F. Salinity-Induced oxidative stress and regulation of antioxidant defense system in the marine macroalga Ulva prolifera. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 409, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J. Changes in morphological plasticity of Ulva prolifera under different environmental conditions: A laboratory experiment. Harmful Algae 2016, 59, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Adams, W. Xanthophyll cycle and light stress in nature: Uniform response to excess direct sunlight among higher plant species. Planta 1996, 198, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Marín, B.; Roach, T.; Verhoeven, A.; García-Plazaola, J.I. Shedding light on the dark side of xanthophyll cycles. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig-Adams, B.; Adams, W. The role of xanthophyll cycle carotenoids in the protection of photosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, P.; Holzwarth, A.R. The role of the xanthophyll cycle and of lutein in photoprotection of photosystem II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2012, 1817, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, R.; Cinque, G.; Holzwarth, A.; Bassi, R. The Soret absorption properties of carotenoids and chlorophylls in antenna complexes of higher plants. Photosynth. Res. 2000, 64, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welc, R.; Luchowski, R.; Kluczyk, D.; Zubik-Duda, M.; Grudzinski, W.; Maksim, M.; Reszczynska, E.; Sowinski, K.; Mazur, R.; Nosalewicz, A.; et al. Mechanisms shaping the synergism of zeaxanthin and PsbS in photoprotective energy dissipation in the photosynthetic apparatus of plants. Plant J. 2021, 107, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieber, A.; Bugos, R.; Yamamoto, H. Plant lipocalins: Violaxanthin de-epoxidase and zeaxanthin epoxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1482, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.-P.; Mi, J.; Ali, S.; Ohyanagi, H.; Moreno, J.C.; Ablazov, A.; Balakrishna, A.; Berqdar, L.; Fiore, A.; Diretto, G.; et al. An alternative, zeaxanthin epoxidase-independent abscisic acid biosynthetic pathway in plants. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audran, C.; Liotenberg, S.; Gonneau, M.; North, H.; Frey, A.; Tap-Waksman, K.; Vartanian, N.; Marion-Poll, A. Localisation and expression of zeaxanthin epoxidase mRNA in Arabdopsis in response to drought stress and during seed development. Funct. Plant Biol. 2001, 28, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.; Armbruster, U.; Iven, T.; Brückle, L.; Melzer, M.; Feussner, I.; Jahns, P. Tissue specific accumulation and regulation of zeaxanthin epoxidase in Arabidopsis reflect the multiple functions of the enzyme in plastids. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Jackson, A.; Parker, R.; Morpeth, D.R.; Burbidge, A.; Taylor, I.B. Abscisic acid biosynthesis in tomato: Regulation of zeaxanthin epoxidase and 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase mRNAs by light/dark cycles, water stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 42, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Fang, W.; Han, H.; Sui, N.; Li, B.; Meng, Q.W. Overexpression of zeaxanthin epoxidase gene enhances the sensitivity of tomato PSII photoinhibition to high light and chilling stress. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhang, T.; An, J.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sha, X.; Hu, T.; et al. MsZEP, a novel zeaxanthin epoxidase gene from alfalfa (Medicago sativa), confers drought and salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 35, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, P.; Latowski, D.; Strzalka, K. Mechanism and regulation of the violaxanthin cycle: The role of antenna proteins and membrane lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Yang, X.; Fu, C.; Zhang, D.; Dong, J.; Zeb, A.; Qu, J.; Shen, S. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen of Ulva prolifera is involved in the response to temperature stress. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ma, Y.; Du, Y.; Shen, S. Differential gene expression for carotenoid biosynthesis in a green alga Ulva prolifera based on transcriptome analysis. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Bairoch, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Duvaud, S.; Appel, R.D. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kang, J.; Kang, Y.; Kang, B.S.; Jin, E. Loss of function in zeaxanthin epoxidase of Dunaliella tertiolecta caused by a single amino acid mutation within the substrate-binding site. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchi, V.; Barera, S.; Bassi, R.; Dall’Osto, L. Potential and challenges of improving photosynthesis in algae. Plants 2020, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaichi, S. Carotenoids in algae: Distributions, biosyntheses and functions. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1101–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shen, S. Effects of light and salinity on carotenoid biosynthesis in Ulva prolifera. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.-E.; Laporte, D.; González, A.; Mendez, K.N.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Meneses, C.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P.; Moenne, A. Copper-Induced increased expression of genes involved in photosynthesis, carotenoid synthesis and C assimilation in the marine alga Ulva compressa. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, A.; Berera, R.; Ilioaia, C.; van Stokkum, I.H.M.; Kennis, J.T.M.; Pascal, A.A.; van Amerongen, H.; Robert, B.; Horton, P.; van Grondelle, R. Identification of a mechanism of photoprotective energy dissipation in higher plants. Nature 2007, 450, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Pérez-Bueno, M.; Zia, A.; Horton, P.; Ruban, A. The zeaxanthin-independent and zeaxanthin-dependent qE components of nonphotochemical quenching involve common conformational changes within the photosystem II antenna in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.; Xie, X.; Gao, S.; Gu, W.; Pan, G.; Wang, G. Desiccation induces accumulations of antheraxanthin and zeaxanthin in intertidal macro-alga Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Cock, M. Slow zeaxanthin accumulation and the enhancement of CP26 collectively contribute to an atypical non-photochemical quenching in macroalga Ulva prolifera under high light. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautermann, O.; Lohr, M. A functional zeaxanthin epoxidase from red algae shedding light on the evolution of light-harvesting carotenoids and the xanthophyll cycle in photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plant J. 2017, 92, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, U.; Dietzel, L.; Breitenbach, J.; Büchel, C.; Sandmann, G. Identification of genes coding for functional zeaxanthin epoxidases in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 192, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Ding, W.; Pan, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, J. Zeaxanthin epoxidase is involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis and light-dependent growth of the marine alga Nannochloropsis oceanica. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kang, Y.; Jin, E. Gene expression analysis of zeaxanthin epoxidase from the marine microalga Dunaliella tertiolecta in response to light/dark cycle and salinity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hoang, M.; Jeon, Y.; Wu, G.; Lee, C. Differential down-regulation of zeaxanthin epoxidation in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars with different chilling sensitivities. J. Plant Biol. 2017, 60, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, M.; Kim, H.; Zulfugarov, I.; Lee, C. Down-Regulation of zeaxanthin epoxidation in vascular plant leaves under normal and photooxidative stress conditions. J. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.; Seok, H.-Y.; Park, B.-K.; Kim, S.H.; Goh, C.H.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, Y.H. Overexpression of Arabidopsis ZEP enhances tolerance to osmotic stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, M.; Shimajiri, Y.; Oshima, A.; Hase, A.; Mikami, K.; Akama, K. Functional expression of an animal type-Na+-ATPase gene from a marine red seaweed Porphyra yezoensis increases salinity tolerance in rice plants. Plant Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, H.; Yang, X.; Zeb, A.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Yang, J.; Xiang, W.; Shen, S. Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Zeaxanthin Epoxidase Gene in Ulva prolifera. Biology 2024, 13, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090695
He H, Yang X, Zeb A, Liu J, Gu H, Yang J, Xiang W, Shen S. Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Zeaxanthin Epoxidase Gene in Ulva prolifera. Biology. 2024; 13(9):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090695
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Hongyan, Xiuwen Yang, Aurang Zeb, Jiasi Liu, Huiyue Gu, Jieru Yang, Wenyu Xiang, and Songdong Shen. 2024. "Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Zeaxanthin Epoxidase Gene in Ulva prolifera" Biology 13, no. 9: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090695
APA StyleHe, H., Yang, X., Zeb, A., Liu, J., Gu, H., Yang, J., Xiang, W., & Shen, S. (2024). Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Zeaxanthin Epoxidase Gene in Ulva prolifera. Biology, 13(9), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13090695





