Twelve New Taxa of Xylaria Associated with Termite Nests and Soil from Northeast Thailand
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. ITS, Alpha-Actin and Beta-Tubulin Sequence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.2. Taxonomy
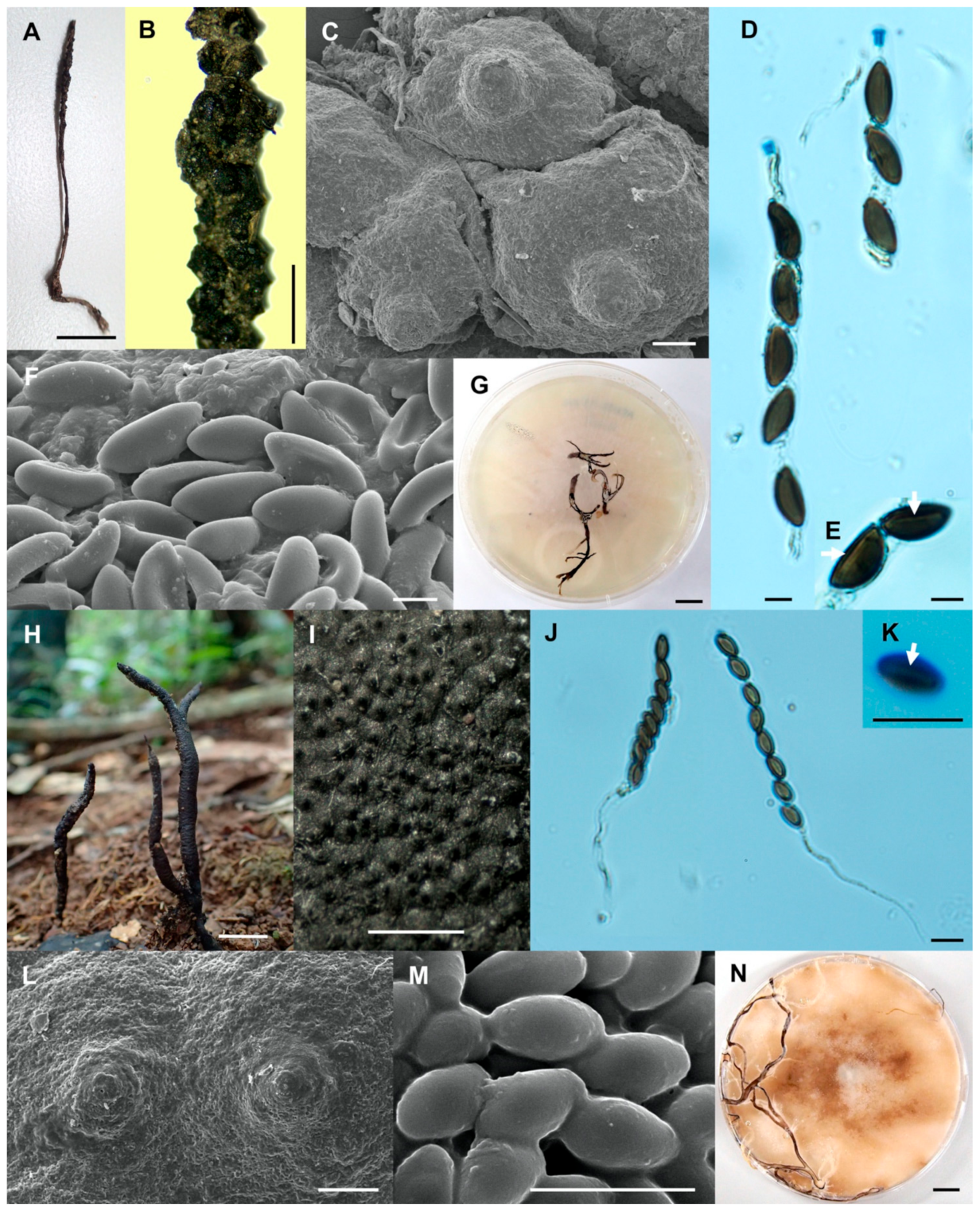
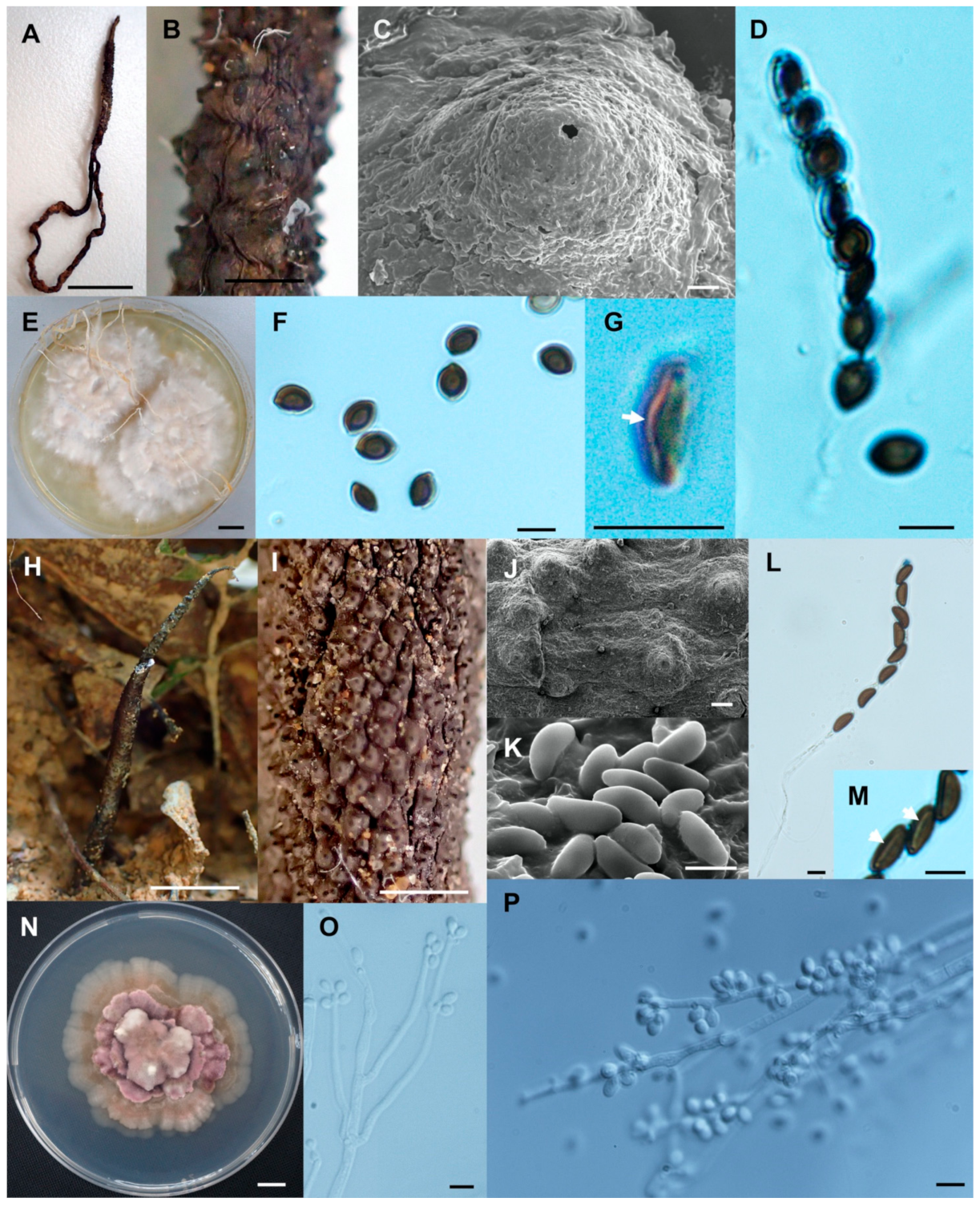
- Xylaria chaiyaphumensis Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 3A–H.
- 2.
- Xylaria conica Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 3I–Q.
- 3.
- 4.
- Xylaria fulvescens Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 4G–L.
- 5.
- Xylaria ischnostroma Wangsawat N, Ju, Y.-M., Phosri C., Whalley A.J.S. & Suwannasai N., sp. nov. Figure 5A–G.
- 6.
- Xylaria margaretae Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 5H–N.
- 7.
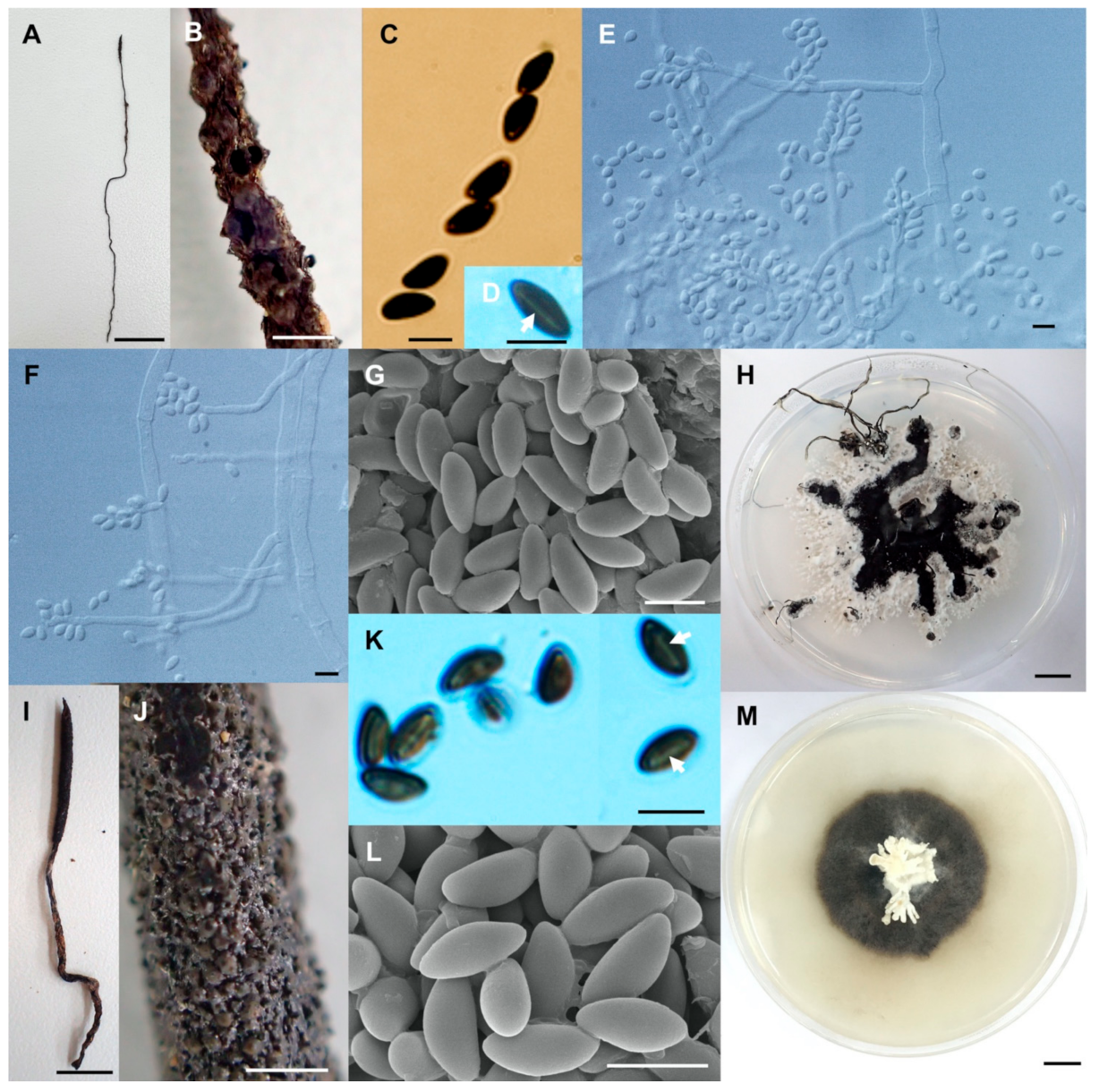
- Xylaria minima Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 6A–H.
- 8.
- 9.
- Xylaria reinkingii var. microspora Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, var. nov. Figure 7A–H.
- 10.
- Xylaria siamensis Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 7I–R.
- 11.
- Xylaria sihanonthii Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 8A–F.
- 12.
- Xylaria subintraflava Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 8G–O.
- 13.
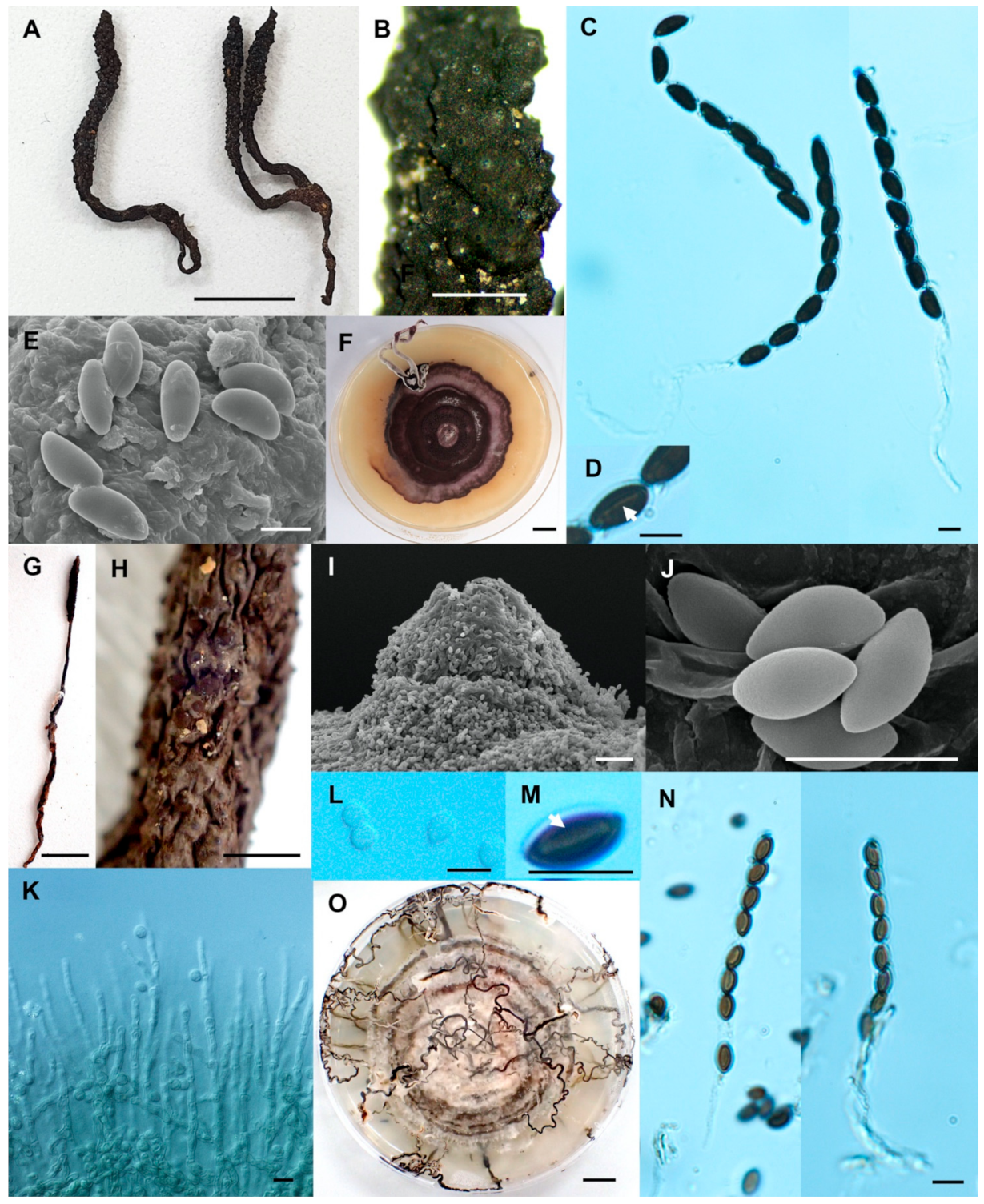
- Xylaria thienhirunae Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 9A–G.
- 14.
- Xylaria vinacea Wangsawat N, Y.-M. Ju, Phosri C, Whalley AJS & Suwannasai N, sp. nov. Figure 9H–P.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batra, L.R.; Batra, S.W.T. Termite-fungus mutualism. In Insect-Fungus Symbiosis-Nutrition, Mutualism and Commensalism; Batra, L.R., Montclair, N.J., Eds.; Allanheld, Osmun & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 117–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.-M.; Lin, C.-R.; Fang, M.-J.; Rogers, J.D.; Fournier, J.; Lechat, C.; Ju, Y.-M. Phylogenetic status of Xylaria subgenus Pseudoxylaria among taxa of the subfamily Xylarioideae (Xylariaceae) and phylogeny of the taxa involved in the subfamily. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petch, T. Termite fungi: A resume. Ann. Roy. Bot. Gard. 1913, 5, 303–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, R.W.G. Xylarioideae and Thamnomycetoideae of Congo. Bull. Jard. Bot. l’État Brux. 1961, 31, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.D.; Ju, Y.-M.; Lehmann, J. Some Xylaria species on termite nests. Mycologia 2005, 97, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.-M.; Hsieh, H.-M. Xylaria species associated with nests of Odontotermes formosanusin Taiwan. Mycologia 2007, 99, 936–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.D. The Xylariaceae: Systematic, Biological and Evolutionary Aspects. Mycologia 1979, 71, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-M.; Chou, J.-C.; Ju, Y.-M. Xylaria insolita and X. subescharoidea: Two newly described species collected from a termite nesting site in Hua-lien, Taiwan. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thienhirun, S. A preliminary account of the Xylariaceae of Thailand. Ph.D. Thesis, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Srihanant, N.; Petcharat, V. Some Xylaria species in oil palm and Pará rubber plantation in southern Thailand. Khon. Kaen. Agri. J. 2015, 43, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- McKnight, K.H.; Rayner, R.W. A Mycological Colour Chart. Mycologia 1972, 64, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Shinsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasai, N.; Martín, M.P.; Phosri, C.; Sihanonth, P.; Whalley, A.J.S.; Spouge, J.L. Fungi in Thailand: A Case Study of the Efficacy of an ITS Barcode for Automatically Identifying Species within the Annulohypoxylon and Hypoxylon Genera. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hoehna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.2, a Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees. 2014. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/0 (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Guedegbe, H.J.; Miambi, E.; Pando, A.; Houngnandan, P.; Rouland-Lefevre, C. Molecular diversity and host specificity of termite-associated Xylaria. Mycologia 2009, 101, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ju, Y.-M.; Hsieh, H.-M.; He, X.-S. Xylaria coprinicola, a new species that antagonizes cultivation of Coprinus comatus in China. Mycologia 2011, 103, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Jo, J.W.; Kwag, Y.-N.; Oh, S.-O.; Lee, S.-G.; Sung, G.-H.; Han, J.-G.; Oh, J.; Shrestha, B.; Kim, S.-Y.; et al. New Records of Xylaria Species in Korea: X. ripicola sp. nov. and X. tentaculata. Mycobiology 2016, 44, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.-N.; Hsieh, H.-M.; Ju, Y.-M. Xylaria terricola sp. nov., a terrestrial anamorphic Xylaria species found in Taiwan. Fungal Sci. 2017, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, A.A.; Ros, V.I.; De Beer, Z.W.; Debets, A.J.; Hartog, E.; Kuyper, T.W.; Læssoe, T.; Slippers, B.; Aanen, D.K. Levels of specificity of Xylaria species associated with fungus-growing termites: A phylogenetic approach. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, C.G. Mycological notes 51. Mycol. Writ. 1917, 5, 717–732. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.-M.; Ju, Y.-M.; Rogers, J.D. Molecular phylogeny of Hypoxylon and closely related genera. Mycologia 2005, 97, 844–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-B.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, Y.-C. Global Diversity and Taxonomy of Sidera (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota): Four New Species and Keys to Species of the Genus. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedijn, K.B. On a new family of the Sphaeriales. Persoonia 1959, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- U’Ren, J.M.; Miadlikowska, J.; Zimmerman, N.B.; Lutzoni, F.; Stajich, J.E.; Arnold, A.E. Contributions of North American endophytes to the phylogeny, ecology, and taxonomy of Xylariaceae (Sordariomycetes, Ascomycota). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 98, 210–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, L.; Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Heitkämper, S.; Lambert, C.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Luangsa-Ard, J.J.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Persoh, D.; et al. Resurrection and emendation of the Hypoxylaceae, recognised from a multigene phylogeny of the Xylariales. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konta, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Phookamsak, R.; Xu, J.C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Daranagama, D.A.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Boonmee, S.; Tibpromma, S.; Eungwanichayapant, P.D.; et al. Polyphyletic genera in Xylariaceae (Xylariales): Neoxylaria gen. nov. and Stilbohypoxylon. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 2629–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.; Grimaldi, D.A.; Krishna, V.; Engel, M.S. Treatise on the Isoptera of the world 4. Termitidae (Part one). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2013, 377, 977–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Sornnuwat, Y.; Vongkaluang, C.; Takematsu, Y. A systematic key to termites of Thailand. Kasetsart J. 2004, 38, 349–368. [Google Scholar]

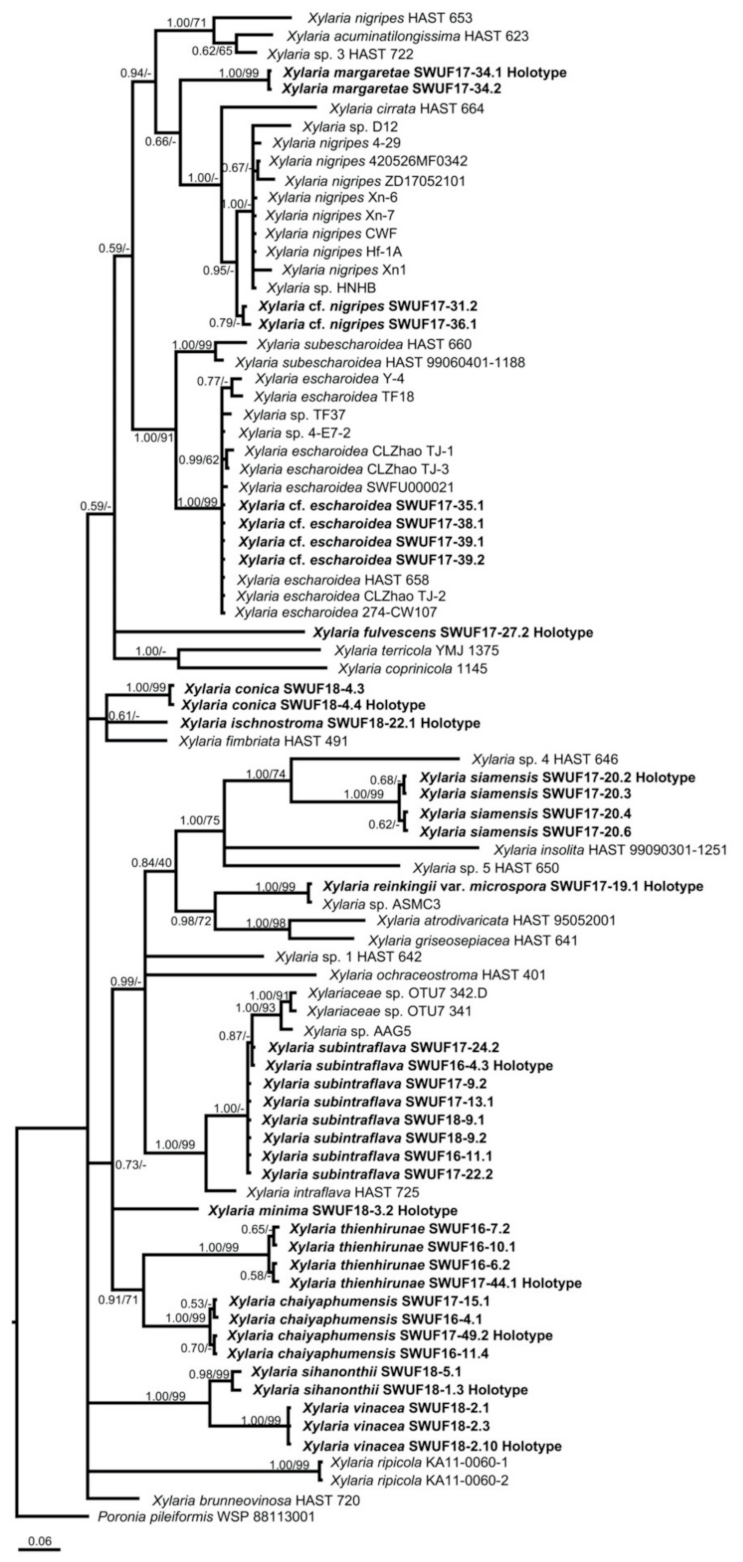



| Species | Collection Number | Country | GenBank Accession Number ITS | Reference | GenBank Accession Number Beta-Tubulin | Reference | GenBank Accession Number Alpha-Actin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astrocystis bambusae | HAST 89021904 | Taiwan | - | - | GQ495942 | [2] | GQ449239 | [2] |
| A. mirabilis | HAST 94070803 | Taiwan | - | - | GQ495941 | [2] | GQ449238 | [2] |
| A. sublimbata | HAST 89032207 | Taiwan | - | - | GQ495940 | [2] | GQ449236 | [2] |
| Kretzschmariaclavus | JDR 114 | French Guiana | - | - | EF025611 | [2] | EF025596 | [2] |
| K. guyanensis | HAST 89062903 | Taiwan | GU300079 | [2] | GQ478214 | [2] | GQ408901 | [2] |
| K. sandvicensis | JDR 113 | USA, Hawaiian Islands | - | - | GQ478211 | [2] | GQ398234 | [2] |
| Nemania bipapillata | HAST 90080610 | Taiwan | - | - | GQ470221 | [2] | GQ389693 | [2] |
| N. diffusa | HAST 91020401 | Taiwan | - | - | GQ470220 | [2] | GQ389692 | [2] |
| N. illita | JDR 236 | USA | - | - | EF025608 | [2] | EF025593 | [2] |
| Poronia pileiformis | WSP 88113001 | Taiwan | GU324760 | [2] | GQ502720 | [2] | GQ455449 | [2] |
| Rosellinia buxi | JDR 99 | France | - | - | GQ470228 | [2] | GQ398228 | [2] |
| R. necatrix | HAST 89062904 | Taiwan | - | - | EF025603 | [2] | EF025588 | [2] |
| Xylaria acuminatilongissima | HAST 623 | Taiwan | EU178738 | [6] | GQ502711 | [2] | GQ853046 | [2] |
| X. adscendens | JDR 865 | Thailand | GU322432 | [2] | GQ487709 | [2] | GQ438746 | [2] |
| X. apoda | HAST 90080804 | Taiwan | GU322437 | [2] | GQ495930 | [2] | GQ438751 | [2] |
| X. arbuscula var. plenofissura | HAST 93082814 | Taiwan | GU339495 | [2] | GQ478225 | [2] | GQ421285 | [2] |
| X. atrodivaricata | HAST 95052001 | Taiwan | EU178739 | [6] | GQ502713 | [2] | GQ853048 | [2] |
| X. atrosphaerica | HAST 91111214 | Taiwan | GU322459 | [2] | GQ495953 | [2] | GQ452363 | [2] |
| X. bambusicola | JDR 162 | Thailand | GU300088 | [2] | GQ478223 | [2] | GQ408910 | [2] |
| X. brunneovinosa | HAST 720 | Taiwan | EU179862 | [6] | GQ502706 | [2] | GQ853041 | [2] |
| X. chaiyaphumensis | SWUF16-04.1 | Thailand | MT622777 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. chaiyaphumensis | SWUF16-11.4 | Thailand | MT622776 | This study | MW459236 | This study | MW459213 | This study |
| X. chaiyaphumensis | SWUF17-15.1 | Thailand | MT622774 | This study | - | - | MW459214 | This study |
| X. chaiyaphumensis | SWUF17-49.2 | Thailand | MT622775 | This study | - | - | MW459215 | This study |
| X. cirrata | HAST 664 | Taiwan | EU179863 | [6] | GQ502707 | [2] | GQ853042 | [2] |
| X. coccophora | HAST 786 | French Guiana | GU300093 | [2] | GQ487701 | [2] | GQ421289 | [2] |
| X. conica | SWUF18-4.3 | Thailand | MT622786 | This study | - | - | MW459223 | This study |
| X. conica | SWUF18-4.4 | Thailand | MT622787 | This study | MW459243 | This study | MW459224 | This study |
| X. coprinicola | 1145 | China | HM585020 | [23] | HM585018 | [23] | HM585017 | [23] |
| X. crozonensis | HAST 398 | France | GU324748 | [2] | GQ502697 | [2] | GQ455441 | [2] |
| X. cubensis | GENT 159 | Papua New Guinea | - | - | GQ502702 | [2] | GQ455446 | [2] |
| X. cubensis | HAST 515 | French West Indies | GU373810 | [2] | GQ502701 | [2] | GQ455445 | [2] |
| X. culleniae | JDR 189 | Thailand | GU322442 | [2] | GQ495935 | [2] | GQ438756 | [2] |
| X. curta | HAST 92092022 | Taiwan | GU322443 | [2] | GQ495936 | [2] | GQ438757 | [2] |
| X. escharoidea | HAST 658 | Taiwan | EU179864 | [6] | GQ502709 | [2] | GQ853044 | [2] |
| X. escharoidea | CLZhao TJ-1 | China | MK343687 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | CLZhao TJ-2 | China | MK343688 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | CLZhao TJ-3 | China | MK343689 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | SWFU000021 | China | MK862248 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | 274-CW107 | China | KU194333 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | TF18 | China | MN509048 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. escharoidea | Y-4 | China | KC462194 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. cf. escharoidea | SWUF17-35.1 | Thailand | MT622792 | This study | MW459227 | This study | MW459200 | This study |
| X. cf. escharoidea | SWUF17-38.1 | Thailand | MT622793 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. cf. escharoidea | SWUF17-39.1 | Thailand | MT622794 | This study | MW459228 | This study | MW459201 | This study |
| X. cf. escharoidea | SWUF17-39.2 | Thailand | MT622795 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. fimbriata | HAST 491 | French West Indies | GU324753 | [2] | GQ502705 | [2] | GQ853040 | [2] |
| X. fulvescens | SWUF17-27.2 | Thailand | MT622780 | This study | MW459238 | This study | MW459218 | This study |
| X. griseosepiacea | HAST 641 | Taiwan | EU179865 | [6] | GQ502714 | [2] | GQ853049 | [2] |
| X. hypoxylon | HAST 95082001 | Taiwan | GU300095 | [2] | GQ487703 | [2] | GQ427195 | [2] |
| X. ianthinovelutina | HAST 553 | French West Indies | GU322441 | [2] | GQ495934 | [2] | GQ438755 | [2] |
| X. insolita | HAST 99090301-1251 | Taiwan | MN655979 | [8] | MN656983 | [8] | MN656985 | [8] |
| X. intracolorata | HAST 90080402 | Taiwan | GU324741 | [2] | GQ502690 | [2] | GQ452375 | [2] |
| X. intraflava | HAST 725 | Taiwan | EU179866 | [6] | GQ502718 | [2] | GQ853053 | [2] |
| X. ischnostroma | SWUF18-22.1 | Thailand | MT622788 | This study | MW459244 | This study | MW459225 | This study |
| X. juruensis | HAST 92042501 | Taiwan | GU322439 | [2] | GQ495932 | [2] | GQ438753 | [2] |
| X. laevis | HAST 95,072,910 | Taiwan | GU324747 | [2] | GQ502696 | [2] | GQ455440 | [2] |
| X. luteostromata var. macrospora | HAST 508 | French West Indies | GU324739 | [2] | GQ502688 | [2] | GQ452373 | [2] |
| X. margaretae | SWUF17-34.1 | Thailand | MT622778 | This study | - | - | MW459216 | This study |
| X. margaretae | SWUF17-34.2 | Thailand | MT622779 | This study | MW459237 | This study | MW459217 | This study |
| X. minima | SWUF18-3.2 | Thailand | MT622789 | This study | MW459245 | This study | MW459226 | This study |
| X. multiplex | HAST 580 | French West Indies | GU300098 | - | GQ487705 | [2] | GQ427198 | [2] |
| X. nigripes | HAST 653 | Taiwan | GU324755 | [2] | GQ502710 | [2] | GQ853045 | [2] |
| X. nigripes | Xn1 | China | MK748600 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | Xn-6 | China | JQ967448 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | Xn-7 | China | JQ979095 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | CWF | Taiwan | KJ627787 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | 420526MF0342 | China | MG712340 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | Hf-1A | Taiwan | JQ927570 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | 4-29 | China | HM050414 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. nigripes | ZD17052101 | China | MN523323 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| X. cf. nigripes | SWUF17-31.2 | Thailand | MT622790 | This study | MW459229 | This study | MW459202 | This study |
| X. cf. nigripes | SWUF17-36.1 | Thailand | MT622791 | This study | - | - | MW459203 | This study |
| X. ochraceostroma | HAST 401 | Taiwan | EU179869 | [6] | GQ502717 | [2] | GQ853052 | [2] |
| X. oligotoma | HAST 784 | French Guiana | GU300092 | [2] | GQ487700 | [2] | GQ421288 | [2] |
| X. ophiopoda | HAST 93082805 | Taiwan | GU322461 | [2] | GQ452365 | [2] | GQ495955 | [2] |
| X. plebeja | HAST 91122401 | Taiwan | GU324740 | [2] | GQ502689 | [2] | GQ452374 | [2] |
| X. polymorpha | JDR1012 | USA | GU322460 | [2] | GQ495954 | [2] | GQ452364 | [2] |
| X. reinkingii var. microspora | SWUF17-19.1 | Thailand | MT622769 | This study | MW459234 | This study | MW459209 | This study |
| X. ripicola | KA11-0060-1 | South Korea | NR153251 | [24] | - | - | - | - |
| X. ripicola | KA11-0060-2 | South Korea | KM817200 | [24] | - | - | - | - |
| X. siamensis | SWUF17-20.2 | Thailand | MT622765 | This study | MW459233 | This study | MW459208 | This study |
| X. siamensis | SWUF17-20.3 | Thailand | MT622766 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. siamensis | SWUF17-20.4 | Thailand | MT622767 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. siamensis | SWUF17-20.6 | Thailand | MT622768 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. sihanonthii | SWUF18-5.1 | Thailand | MT622784 | This study | MW459241 | This study | MW459221 | This study |
| X. sihanonthii | SWUF18-1.3 | Thailand | MT622785 | This study | MW459242 | This study | MW459222 | This study |
| X. striata | HAST 304 | Taiwan | GU300089 | [2] | GQ478224 | [2] | GQ421284 | [2] |
| X. subescharoidea | HAST 660 | Taiwan | GU324754 | [2] | GQ502708 | [8] | GQ853043 | [8] |
| X. subescharoidea | HAST 99060401-1188 | Taiwan | MN655980 | [8] | MN656984 | [8] | MN656986 | [8] |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF16-4.3 | Thailand | MT622762 | This study | MW459230 | This study | MW459204 | This study |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF16-11.1 | Thailand | MT622763 | This study | - | - | MW459205 | This study |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF17-9.2 | Thailand | MT622758 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF17-13.1 | Thailand | MT622759 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF17-22.2 | Thailand | MT622764 | This study | MW459231 | This study | MW459206 | This study |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF17-24.2 | Thailand | MT622757 | This study | MW459232 | This study | MW459207 | This study |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF18-9.1 | Thailand | MT622760 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. subintraflava | SWUF18-9.2 | Thailand | MT622761 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. terricola | YMJ 1375 | Taiwan | MF577042 | [25] | MF577044 | [25] | MF577045 | [25] |
| X. thienhirunae | SWUF16-6.2 | Thailand | MT622770 | This study | MW459235 | This study | MW459210 | This study |
| X. thienhirunae | SWUF16-7.2 | Thailand | MT622772 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. thienhirunae | SWUF16-10.1 | Thailand | MT622773 | This study | - | - | MW459211 | This study |
| X. thienhirunae | SWUF17-44.1 | Thailand | MT622771 | This study | - | - | MW459212 | This study |
| X. venustula | HAST 88113002 | Taiwan | GU300091 | [2] | GQ487699 | [2] | GQ421287 | [2] |
| X. vinacea | SWUF18-2.1 | Thailand | MT622781 | This study | MW459239 | This study | MW459219 | This study |
| X. vinacea | SWUF18-2.3 | Thailand | MT622782 | This study | - | - | - | - |
| X. vinacea | SWUF18-2.10 | Thailand | MT622783 | This study | MW459240 | This study | MW459220 | This study |
| X. sp. 1 | HAST 642 | Taiwan | GU324759 | [2] | GQ502719 | [2] | GQ853054 | [2] |
| X. sp. 3 | HAST 722 | Taiwan | GU324756 | [2] | GQ502712 | [2] | GQ853047 | [2] |
| X. sp. 4 | HAST 646 | Taiwan | GU324757 | [2] | GQ502715 | [2] | GQ853050 | [2] |
| X. sp. 5 | HAST 650 | Taiwan | GU324758 | [2] | GQ502716 | [2] | GQ853051 | [2] |
| Xylaria sp. | ASMC3 | Vietnam | EU164404 | [22] | - | - | - | - |
| Xylaria sp. | AAG5 | Africa | EU164400 | [22] | - | - | - | - |
| Xylaria sp. | HNHB | China | FN812862 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| Xylaria sp. | D12 | China | KC414236 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| Xylaria sp. | TF37 | China | MN526593 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| Xylaria sp. | 4-E7-2 | China | FN812842 | Unpublished | - | - | - | - |
| Xylariaceae sp. | 342.D | South Africa | FJ425676 | [26] | - | - | - | - |
| Xylariaceae sp. | 341 | South Africa | FJ425675 | [26] | - | - | - | - |
| 1. Ascospores with a median germ pore, (3.6–)3.9–4.7(–5) × (2.35–)2.5–3.2(–3.5) µm | X. escharoidea |
| 1. Ascospores with a germ slit | 2 |
| 2. Stromata usually repeatedly branched, with prominent perithecial mounds, ascospores shorter than 6 µm | 3 |
| 2. Stromata unbranched or sparingly branched, perithecia naked or presenting either inconspicuous or conspicuous perithecial mounds | 4 |
| 3. Stromatal surface white when immature, becoming blackish at maturity; ascospores ellipsoid-inequilateral, germ slit straight spore-length or nearly on flattened side, 5.0–6.0 × 2.5–3.5 µm | X. siamensis |
| 3. Stromatal surface dull coloured, becoming blackish at maturity; ascospores short fusoid-inequilateral, 3.5–5.0 × 2.0–3.0 µm | X. atrodivaricata * |
| 4. Ascospores > 10 µm, germ slit straight full spore-length | 5 |
| 4. Ascospores < 10 µm, germ slit straight 3/4 or full spore-length | 7 |
| 5. Stromal surface whitish to greyish with black ostioles; ascospores blackish-brown,(11–)14.0–19.4 × (6.5–)7.0–10.0 µm | X. tanganyikaensis * |
| 5. Stromatal surface blackish-brown to black with black ostioles; ascospores light brown, brown to dark brown, frequently < 14 µm | 6 |
| 6. Perithecia immersed, usually with prominent perithecial mounds; ascospores ellipsoid-inequilateral with narrowly rounded ends, (10–)10.8–12.3(–13.2) × 4.5–6(–6.4) µm; apical apparatus 4–4.5 × 2–3 µm | X. conica |
| 6. Perithecia naked or nearly so; ascospores ellipsoid-inequilateral with narrowly rounded ends, some pinched at the ends,10.3–11.6(–12) × 4.8–5.6 µm; apical apparatus 1.5–2 × 2–3 µm | X. ischnostroma |
| 7. Stromatal surface white at maturity; ascospores 5.4–6(–6.3) × 2.4–3.0 µm, straight germ slit nearly spore-length on convex side | X. reinkingii var. microspora |
| 7. Stromatal surface other than white, usually dull coloured at maturity | 8 |
| 8. Stromata usually more or less cylindrical, often exceeding 3 mm in diameter | 9 |
| 8. Stromata usually slender, fusiform to cylindrical, rarely exceeding 3 mm in diameter | 12 |
| 9. Stromatal surface blackish-brown to black or dark brick; ascospores mostly longer than 5 µm | 10 |
| 9. Stromatal surface ochraceous to fawn, luteous, greyish or dull black; ascospores mostly shorter than 5 µm | 11 |
| 10. Perithecia presenting very conspicuous mounds, blackish-brown; ostioles conic-papillate; ascospores 7.5–9.5 × (3.2–)3.5–4.5 µm | X. sihanonthii |
| 10. Perithecia immersed, brown; ostioles papillate; ascospores 6.7–8 × 2.8–3.7 µm | X. vinacea |
| 11. Stromata acuminate at the apex, unbranched, ochraceous to yellowish-brown on surface; ascospores inequilateral, 4–5 × 1.8–2.5 µm | X. acuminatilongissima * |
| 11. Stromata usually blunt or, infrequently, mucronate at the apex, greyish-brown on surface; ascospores slightly inequilateral to nearly equilateral, 3.5–5 × 2–3 µm | X. nigripes * |
| 12. Ascospores mostly > 5 µm | 13 |
| 12. Ascospores mostly < 5 µm | 14 |
| 13. Stromata very thin, 0.5–1 mm broad; perithecia naked or so on, hairy; ascospores 5.8–6.8 × 2.7–3.2 µm | X. minima |
| 13. Stromata slender, perithecia immersed, forming conspicuous mounds, without hair; ascospores (4.5–)5–6.2 × 2.2–3 µm | X. fulvescens |
| 14. Ascospores short, fusoid, pinched at the ends | 15 |
| 14. Ascospores ellipsoid-inequilateral to nearly equilateral with narrowly rounded ends | 16 |
| 15. Perithecia 0.3–0.7 mm diameter, 3–4 ostioles/mm; ostioles conic-papillate; ascospores fusoid with pinched ends, 4–5(–5.7) × (2.5–)3–3.8 µm; germ slit of half-full ascospore length | X. chaiyaphumensis |
| 15. Perithecia 0.5–0.8 mm diameter, 2–3 ostioles/mm; ostioles conic-papillate; ascospores fusoid with pinched ends, 4–5.2(–5.7) × 2.7–4 µm; germ slit full ascospore length | X. thienhirunae |
| 16. Stromatal surface longitudinally wrinkled with long stipes, unbranched with fertile parts; ascospores 3.5–5 × 1.8–2.5 µm | X. subintraflava |
| 16. Stromatal surface wrinkled with acuminate at apex, without fertile parts, unbranched or two-branched at apex; ascospores (3.2–)3.8–5 × (1.8–)2–2.5 µm | X. margaretae |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wangsawat, N.; Ju, Y.-M.; Phosri, C.; Whalley, A.J.S.; Suwannasai, N. Twelve New Taxa of Xylaria Associated with Termite Nests and Soil from Northeast Thailand. Biology 2021, 10, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070575
Wangsawat N, Ju Y-M, Phosri C, Whalley AJS, Suwannasai N. Twelve New Taxa of Xylaria Associated with Termite Nests and Soil from Northeast Thailand. Biology. 2021; 10(7):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070575
Chicago/Turabian StyleWangsawat, Niwana, Yu-Ming Ju, Cherdchai Phosri, Anthony J. S. Whalley, and Nuttika Suwannasai. 2021. "Twelve New Taxa of Xylaria Associated with Termite Nests and Soil from Northeast Thailand" Biology 10, no. 7: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070575
APA StyleWangsawat, N., Ju, Y.-M., Phosri, C., Whalley, A. J. S., & Suwannasai, N. (2021). Twelve New Taxa of Xylaria Associated with Termite Nests and Soil from Northeast Thailand. Biology, 10(7), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070575





