Research on the Mechanical Strengths and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Inner Steel Bars of RPC with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Fly Ash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Raw Materials
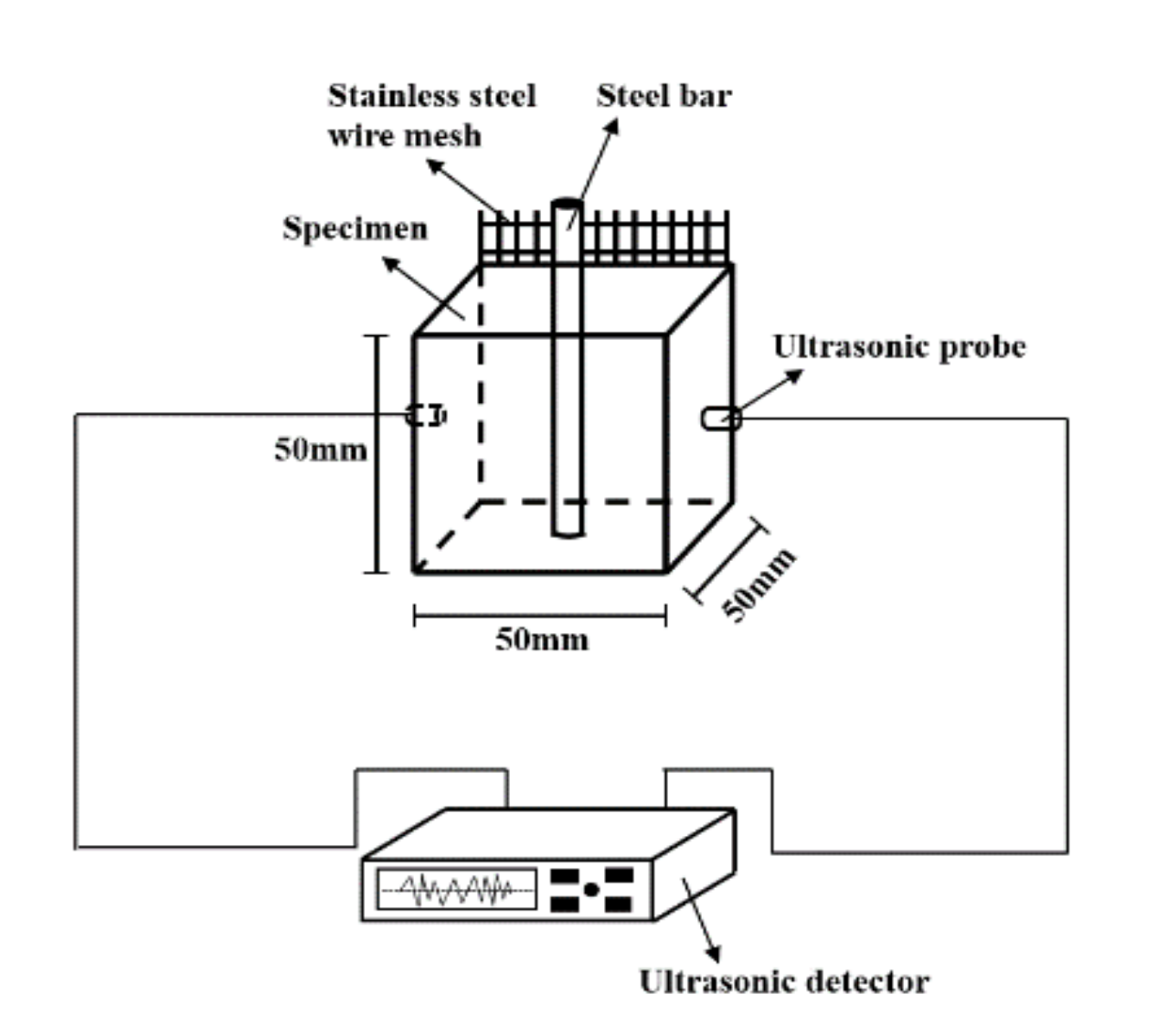
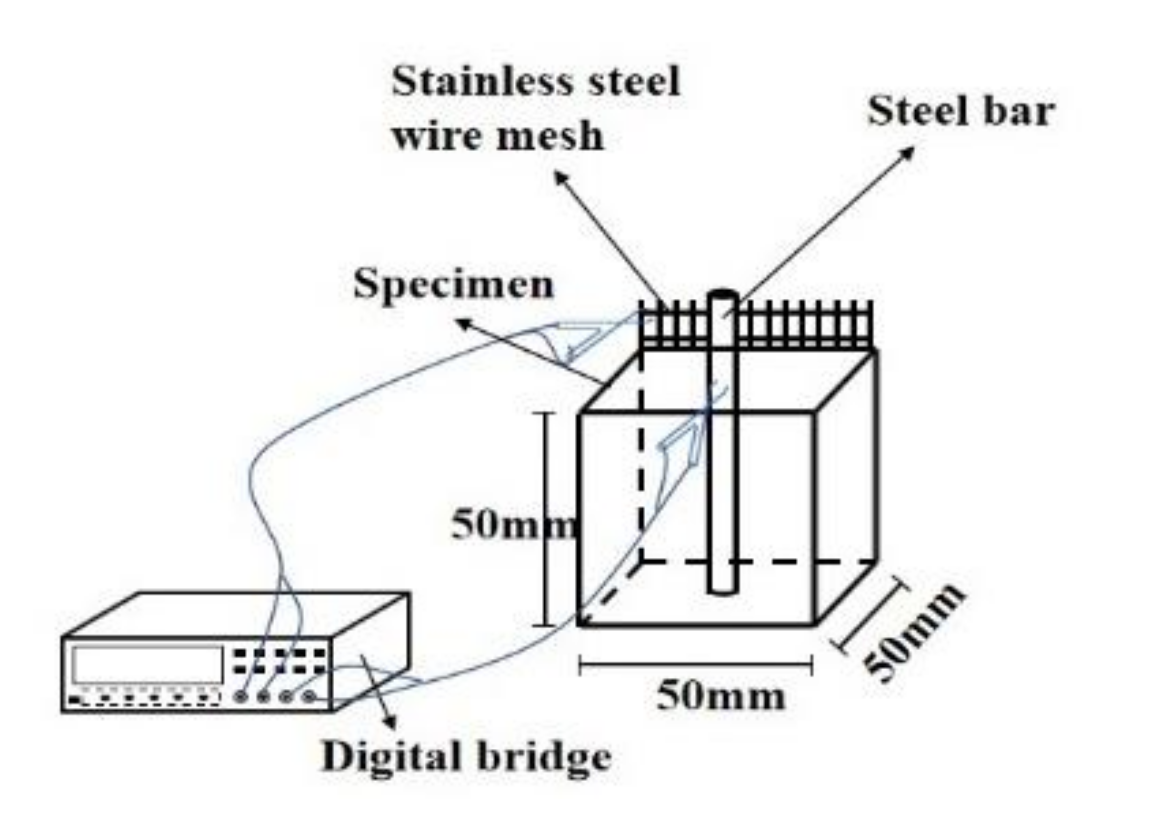
2.2. Specimen Preparation and Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Slump Flow of Fresh RPC Paste
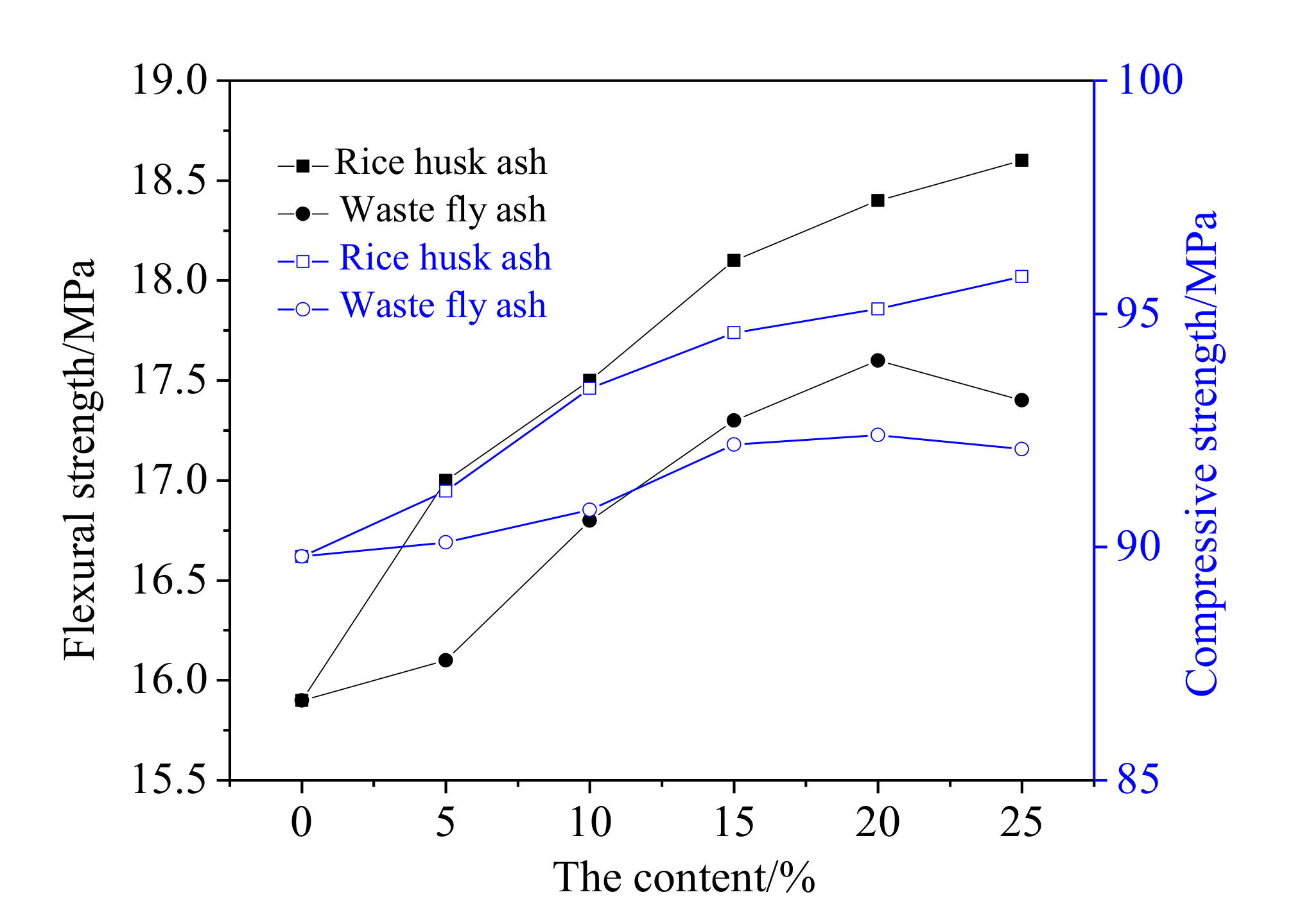
3.2. The Mechanical Strengths
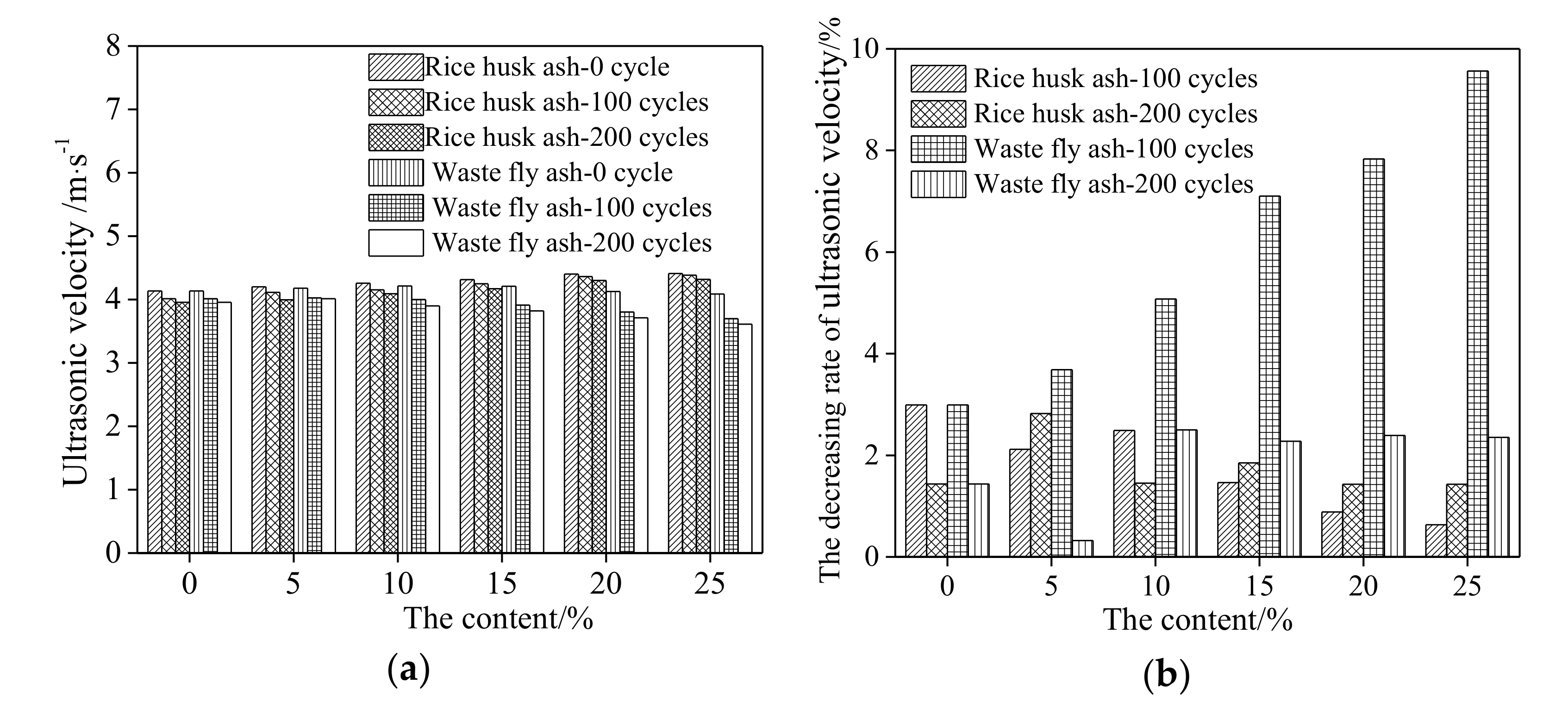
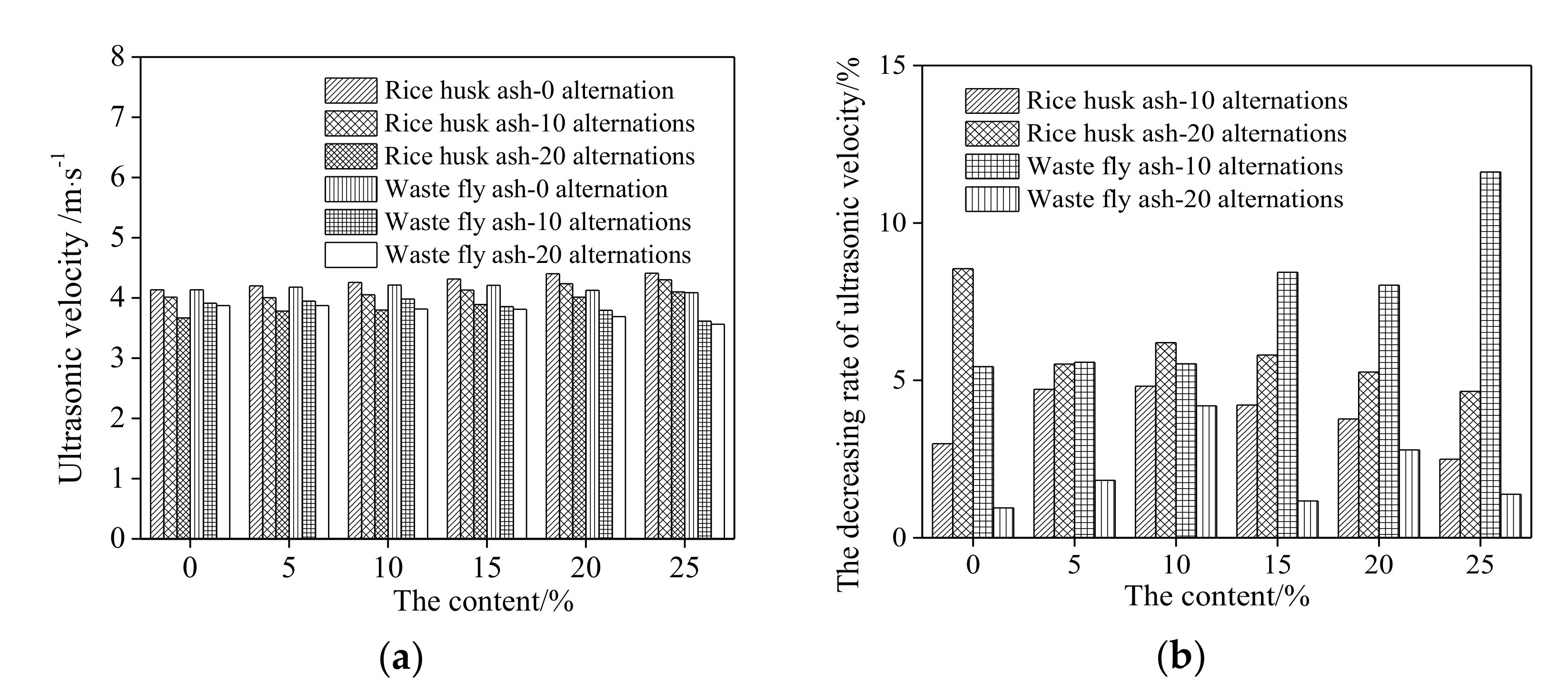
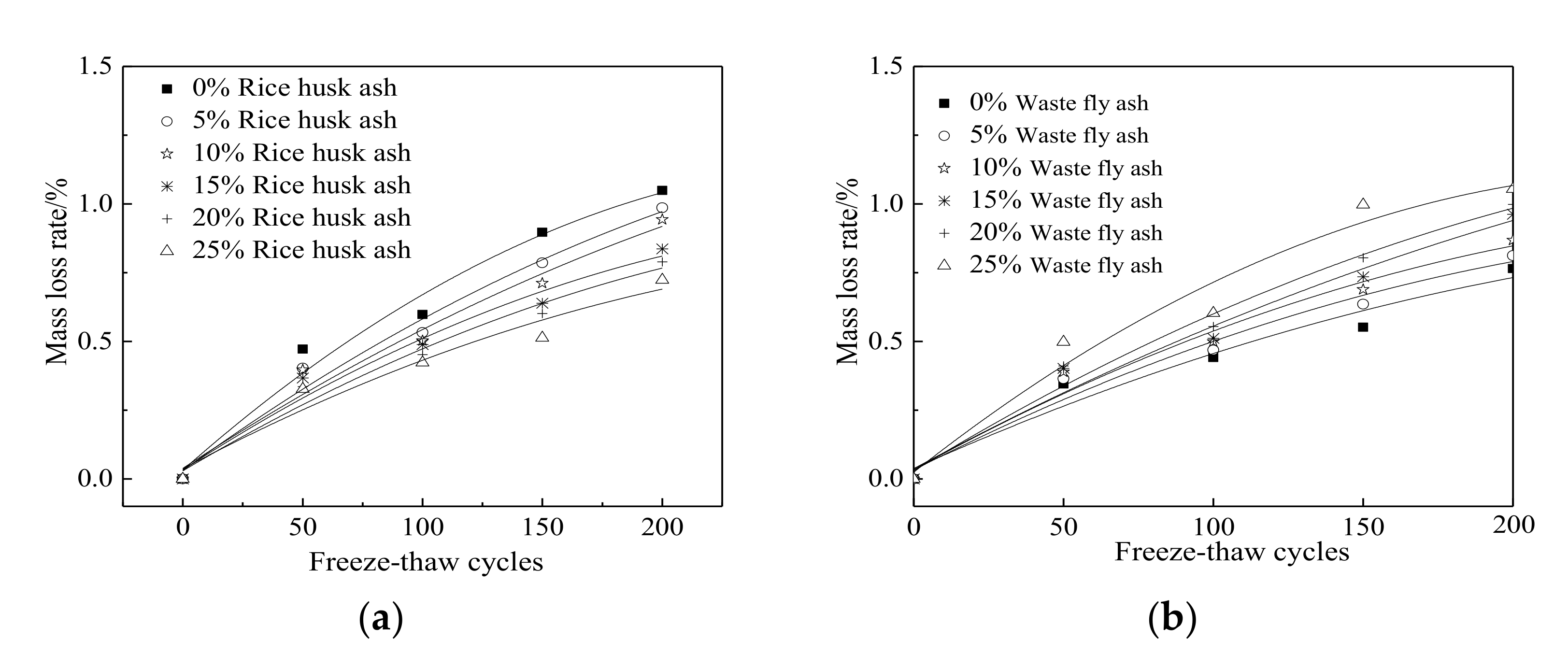
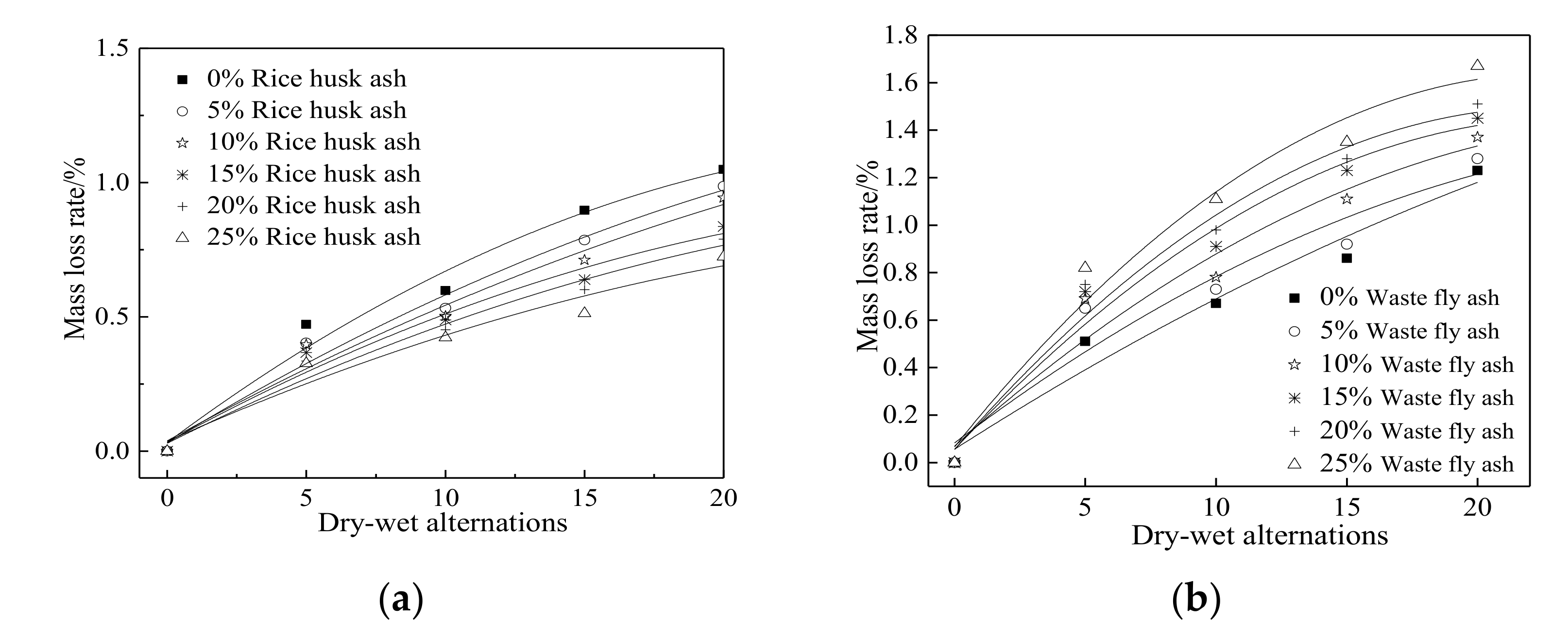
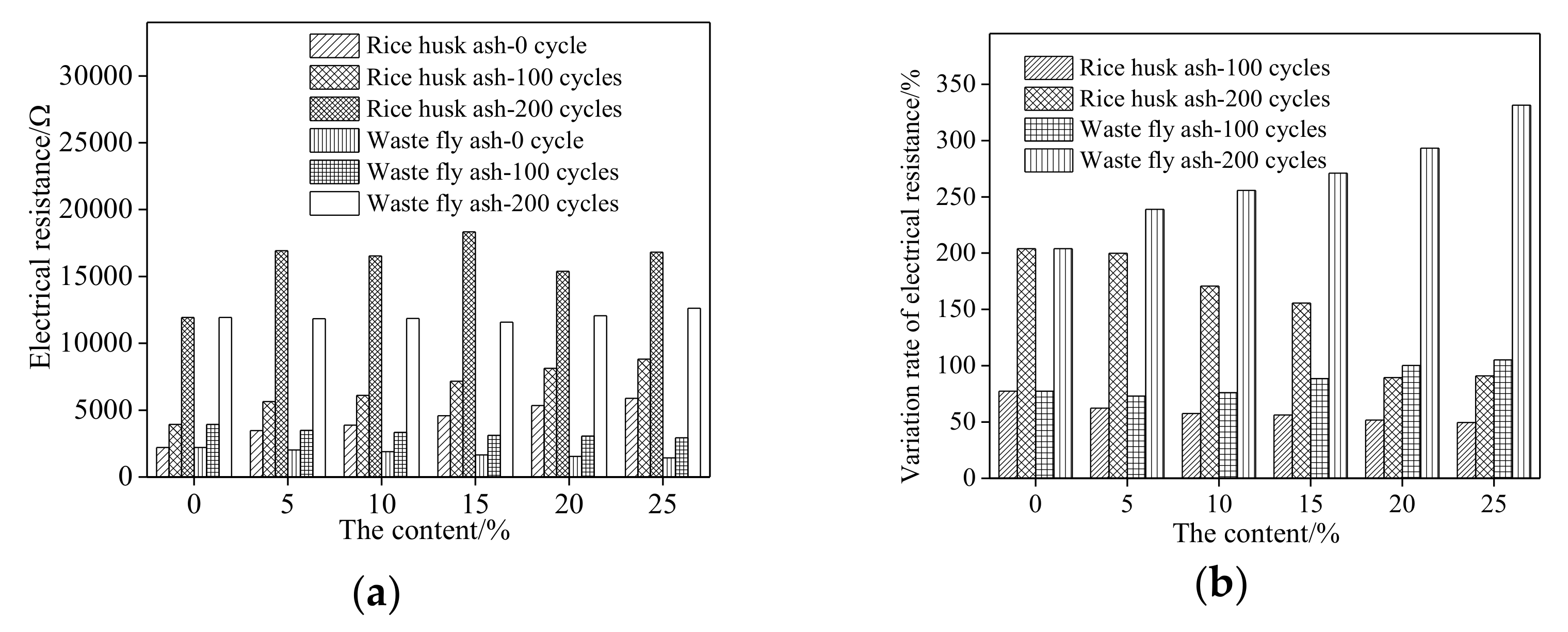
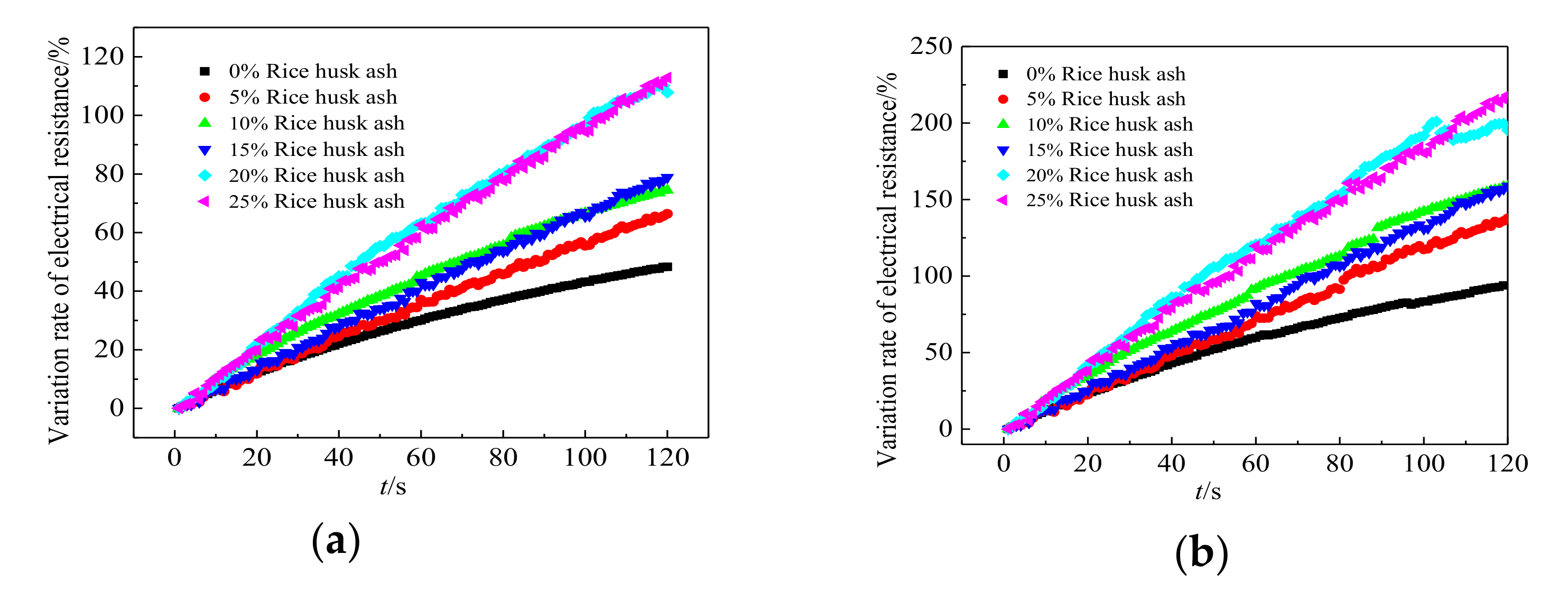
3.3. The Corrosion Resistance of Steel Bars in RPC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avila-López, U.; Almanza-Robles, J.M.; Escalante-García, J. Investigation of novel waste glass and limestone binders using statistical methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 82, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, V.; Christiane, R.; Danh-Daiet, B.; Ludwig, H.-M. Rice husk ash as both pozzolanic admixture and internal curing agent in ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.V.; Guang, Y.; Van Breugel, K.; Copuroglu, O. Hydration and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete incorporating rice husk ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, L.; Hu, Q.; Dai, J.-G.; Tsang, D.C.W. Stabilisation/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by phosphate-enhanced calcium aluminate cement. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 408, 124404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, H. Influence of rice husk ash on strength and permeability of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensale, G.; Ribeiro, A.; Gonçalves, A. Effects of RHA on autogenous shrinkage of Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.; Hu, J.; Stroeven, P. Particle size effect on the strength of rice husk ash blended gap-graded Portland cement concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Loya, E.; Allouche, E.; Eklund, E.; Joshi, A.R.; Kupwade-Patil, K. Toxicity mitigation and solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash using alkaline activated coal ash. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Cao, P.; Luo, B.; Tang, J.; Shi, F.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Jin, K. The Application of Electrical Parameters to Reflect the Hydration Process of Cement Paste with Rice Husk Ash. Materials 2019, 12, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrvoje, M.; Jaromír, K.; Vujanović, M.; Urbaniec, K.; Duić, N. Reducing greenhouse gasses emissions by fostering the deployment of alternative raw materials and energy sources in the cleaner cement manufacturing process. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 136, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Gao, X.-J.; Shi, F.-T.; Lin, X.-J.; Feng, L.-Y. Hydration process of rice husk ash cement paste and the following corrosion resistance of embedded steel bar. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 11, 3464–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, R. Influence of rice husk ash and rice tiller ash along with chromate reducing agents on strength and hydration properties of Ordinary Portland Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, J. Use of municipal solid waste incineration ash in 3D printable concrete. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 142, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Li, J.; Fang, J.; Liu, J. Comparison of long-term stability under natural ageing between cement solidified and chelator-stabilised MSWI fly ash. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderete, N.; Joseph, A.; Van den Heede, P.; Matthys, S.; De Belie, N. Effective and sustainable use of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash in concrete regarding strength and durability. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Saand, A.; Bangwar, D.; Buller, A.; Ahmed, Z. Mechanical and Durability Properties of Aerated Concrete Incorporating Rice Husk Ash (RHA) as Partial Replacement of Cement. Crystals 2021, 11, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.; Fraaij, A.; Klaassen, A.; Kentgens, A. A structural investigation relating to the pozzolanic activity of rice husk ashes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShareedah, O.; Nassiri, S. Pervious concrete mixture optimization, physical, and mechanical properties and pavement design: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 228, 125095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.; Siddique, R.; Goyal, S. Strength, permeation and micro-structural characteristics of concrete incorporating waste marble. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binici, H.; Aksogan, O. Durability of concrete made with natural granular granite, silica sand and powders of waste marble and basalt as fine aggregate. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 19, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshaghani, A.; Moeini, M. Evaluating the effects of sugarcane-bagasse ash and rice-husk ash on the mechanical and durability properties of mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 0401814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sensale, G. Effect of rice-husk ash on durability of cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fapohunda, C.; Akinbile, B.; Shittu, A. Structure and properties of mortar and concrete with rice husk ash as partial replacement of ordinary Portland cement-A review. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Hu, L.; Dong, Z.; Tang, L.; Xing, F.; Liu, J. Effect of silica fume on the mechanical property and hydration characteristic of alkali-activated municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubeyli, G.; Artir, R. Properties of Hardened Concrete Produced by Waste Marble Powder, World Conference on Technology. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ting, M.; Wong, K.; Rahman, M.; Joo, M.S. Mechanical and durability performance of marine sand and seawater concrete incorporating silicomanganese slag as coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Iqbal, M.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Rauf, M. Prediction of chloride diffusivity in concrete using artificial neural network: Modelling and performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Test Method for Fluidity of Cement Mortar; National Cement Standardization Technical Committee: Beijing, China, 1994; GB/T2419-1994.
- Method of Testing Cements-Determination of Strength; The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 1999; GB/T17671-1999.
- Standard for Test Method of Long-Term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete; Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009; GB/T50082-2009.
- Wang, H.; Shi, F.; Shen, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Jin, K.; Feng, L.; Tang, Z. Research on the self-sensing and mechanical properties of aligned stainless steel fiber reinforced reactive powder concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 119, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleib, J.; Aouad, G.; Abriak, N.; Benzerzour, M. Production of Portland cement clinker from French Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Matlina Mohtar, A.; Zainudin, N.; Bhatia, S.; Mohamed, A.R. Optimum conditions for preparation of flue gas desulfurization absorbent from rice husk ash. Fuel 2005, 84, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchariyakun, K.; Asavapisit, S.; Sombatsompop, K. Properties of autoclaved aerated concrete incorporating rice husk ash as partial replacement for fine aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yuan, L.; Ji, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z. Cooperative action and compatibility between Portland cement and MSWI bottom ash alkali-activated double gel system materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lastra, R.; Malhotra, V. Rice-husk ash paste and concrete: Some aspects of hydration and the microstructure of the interfacial zone between the aggregate and paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Pramada, P.; Raghavan, P.; Satyanarayana, K.; Gupta, T. Microsilica from rice hush ash as a possible substitute for condensed silica fume for high performance concrete. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, J. Effects of salt freeze-thaw cycles and cyclic loading on the piezoresistive properties of carbon nano-fibers mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, J. Coupling effect of salt freeze-thaw cycles and cyclic loading on performance degradation of carbon nanofiber mortar. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-eswed, B.I. Chemical evaluation of immobilization of wastes containing Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in alkali-activated materials: A critical review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.; Farina, I.; Race, M.; Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R.; Fabbricino, M. Pre-treatments of MSWI fly-ashes: A comprehensive review to determine optimalconditions for their reuse and/or environmentally sustainable disposal. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Tyrer, M.; Quanyuan, C. Stabilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash using silica fume. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2494–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, L.; Tang, L.; Ren, J. Utilisation of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash with metakaolin for preparation of alkali-activated cementitious material. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 402, 123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, F. Influence of NaCl freeze thaw cycles and cyclic loading on the mechanical performance and permeability of sulphoaluminate cement reactive powder concrete. Coatings 2020, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jin, K.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, F.; Feng, L. External erosion of sodium chloride on the degradation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of aligned stainless steel fiber reinforced reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 287, 06629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, J. Research on the Influence of Carbonation on the Content and State of Chloride Ions and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Steel Bars in Cement Paste. Coatings 2020, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Shu, H. Study on the influence of compound rust inhibitor on corrosion of steel bars in chloride concrete by electrical parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Oui, P.; Rakdee, C.; Thanmathorn, P. Use of rice husk ash as filler in natural rubber vulcanizates: In comparison with other commercial fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuad, M.; Ismail, Z.; Ishak, Z.; Omar, A. Application of rice husk ash as fillers in polypropylene: Effect of titanate, zirconate and silane coupling agents. Eur. Polym. J. 1995, 31, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, E.H. Early age hydration of blended cement with different size fractions of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Influence of Rust Inhibitor on the Corrosion Resistance of Reinforcement in Cement Paste with Chloride. Coatings 2021, 11, 11050606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Types | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | SO3 | Ti2O | CdO | Cr2O3 | PbO | CuO | ZnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WFA | 22.47 | 4.46 | 0.94 | / | 20.31 | 9.25 | 10.24 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.52 |
| RHA | 91.56 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 1.07 | 0.47 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| OPC | 20.86 | 5.47 | 3.94 | 1.73 | 62.23 | 2.66 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| GGBS | 34.06 | 14.74 | 0.23 | 9.73 | 35.93 | 0.23 | 3.51 | / | / | / | / | / |
| SF | 90 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0 | 7.4 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Types | Particle Size/μm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | 0.6 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 64 | 360 | |
| WFA | 0.13 | 0.46 | 2.15 | 17.21 | 31.34 | 97.52 | 100 |
| RHA | 0 | 0.58 | 6.84 | 18.32 | 32.14 | 96.32 | 100 |
| OPC | 0 | 0.33 | 2.66 | 15.01 | 28.77 | 93.59 | 100 |
| GGBS | 0.025 | 0.1 | 3.51 | 19.63 | 35.01 | 97.9 | 100 |
| SF | 31.2 | 58.3 | 82.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Water | OPC | WFA | RHA | SF | GGBS | Quartz Sand | Water-Reducer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 244.4 | 740.7 | 0 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 679.6 | 61.1 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 618.5 | 122.2 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 557.4 | 183.3 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 496.3 | 244.4 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 435.2 | 305.5 | 0 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 740.7 | 0 | 61.1 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 679.6 | 0 | 122.2 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 618.5 | 0 | 183.3 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 557.4 | 0 | 244.4 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| 244.4 | 496.3 | 0 | 305.5 | 370.3 | 111.1 | 977.9 | 16.3 |
| Types | Content/% | a | b | c | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPC with RHA after NaCl freeze−thaw cycles | 0 | −1.33 × 10−5 | 0.0077 | 0.032 | 0.96 |
| 5 | −8.03 × 10−6 | 0.0063 | 0.030 | 0.97 | |
| 10 | −6.46 × 10−6 | 0.0057 | 0.038 | 0.95 | |
| 15 | −8.86 × 10−6 | 0.0057 | 0.033 | 0.95 | |
| 20 | −7.49 × 10−6 | 0.0052 | 0.029 | 0.96 | |
| 25 | −6.80 × 10−6 | 0.0046 | 0.037 | 0.91 | |
| RPC with WFA after NaCl freeze−thaw cycles | 0 | −7.09 × 10−6 | 0.0049 | 0.038 | 0.92 |
| 5 | −8.89 × 10−6 | 0.0056 | 0.032 | 0.95 | |
| 10 | −9.71 × 10−6 | 0.0060 | 0.033 | 0.95 | |
| 15 | −6.71 × 10−6 | 0.0059 | 0.037 | 0.95 | |
| 20 | −9.34 × 10−6 | 0.0067 | 0.029 | 0.97 | |
| 25 | −1.69 × 10−5 | 0.0086 | 0.024 | 0.93 | |
| RPC with RHA after NaCl dry−wet alternations | 0 | −1.33 × 10−3 | 0.077 | 0.032 | 0.96 |
| 5 | −8.03 × 10−4 | 0.063 | 0.030 | 0.97 | |
| 10 | −6.46 × 10−4 | 0.057 | 0.038 | 0.95 | |
| 15 | −8.86 × 10−4 | 0.057 | 0.033 | 0.95 | |
| 20 | −7.49 × 10−4 | 0.052 | 0.029 | 0.96 | |
| 25 | −6.80 × 10−4 | 0.046 | 0.037 | 0.91 | |
| RPC with WFA after NaCl dry−wet alternations | 0 | −7.14 × 10−4 | 0.070 | 0.056 | 0.93 |
| 5 | −1.34 × 10−3 | 0.083 | 0.083 | 0.86 | |
| 10 | −1.77 × 10−3 | 0.099 | 0.069 | 0.91 | |
| 15 | −2.49 × 10−3 | 0.12 | 0.056 | 0.95 | |
| 20 | −2.77 × 10−3 | 0.13 | 0.056 | 0.96 | |
| 25 | −3.0 × 10−3 | 0.14 | 0.066 | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Wang, H. Research on the Mechanical Strengths and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Inner Steel Bars of RPC with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Fly Ash. Coatings 2021, 11, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121480
Cui L, Wang H. Research on the Mechanical Strengths and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Inner Steel Bars of RPC with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Fly Ash. Coatings. 2021; 11(12):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121480
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Lili, and Hui Wang. 2021. "Research on the Mechanical Strengths and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Inner Steel Bars of RPC with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Fly Ash" Coatings 11, no. 12: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121480
APA StyleCui, L., & Wang, H. (2021). Research on the Mechanical Strengths and the Following Corrosion Resistance of Inner Steel Bars of RPC with Rice Husk Ash and Waste Fly Ash. Coatings, 11(12), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121480






