Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure and Preliminary Structural Analysis
2.1. Preparation of H-Free a-Si Thin-Film Samples by RFMS
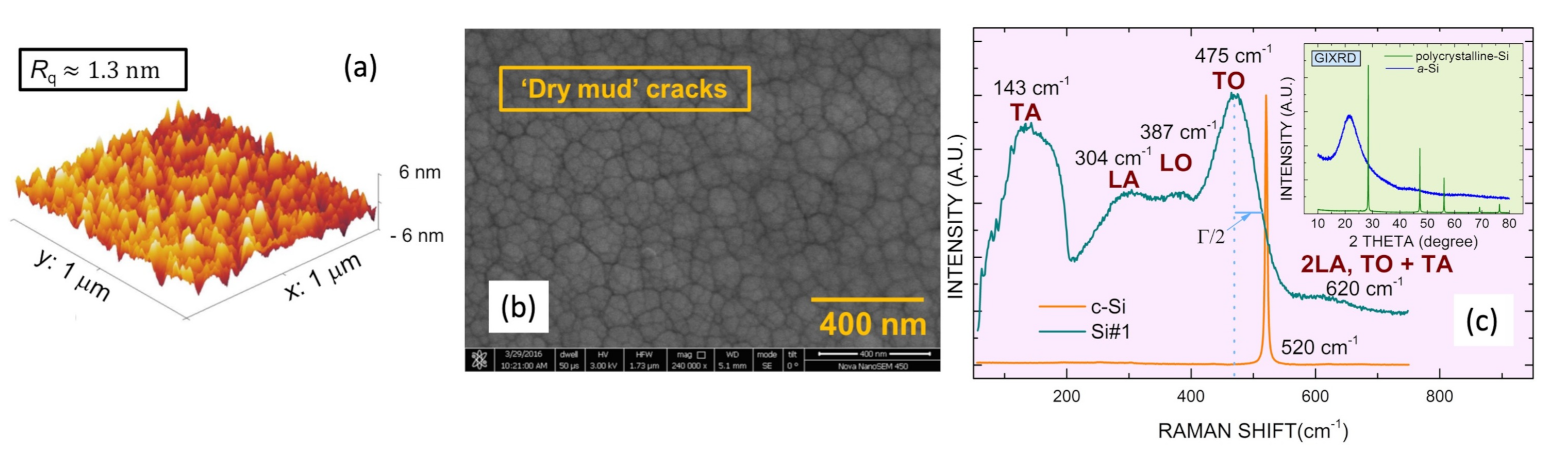
2.2. Surface, Structural and Optical Characterizations of the a-Si Films
3. Thin-Film Optics Theory and Model Dielectric Function
3.1. Some Basic Theoretical Considerations
3.2. Spectral Transmittance for a Nonuniform Semiconductor Film onto a Transparent Glass Substrate
3.3. Optical Phase Change: Correcting Integer Numbers and
3.4. Determination of the Optical Constants by Applying the TLUC Dispersion Model
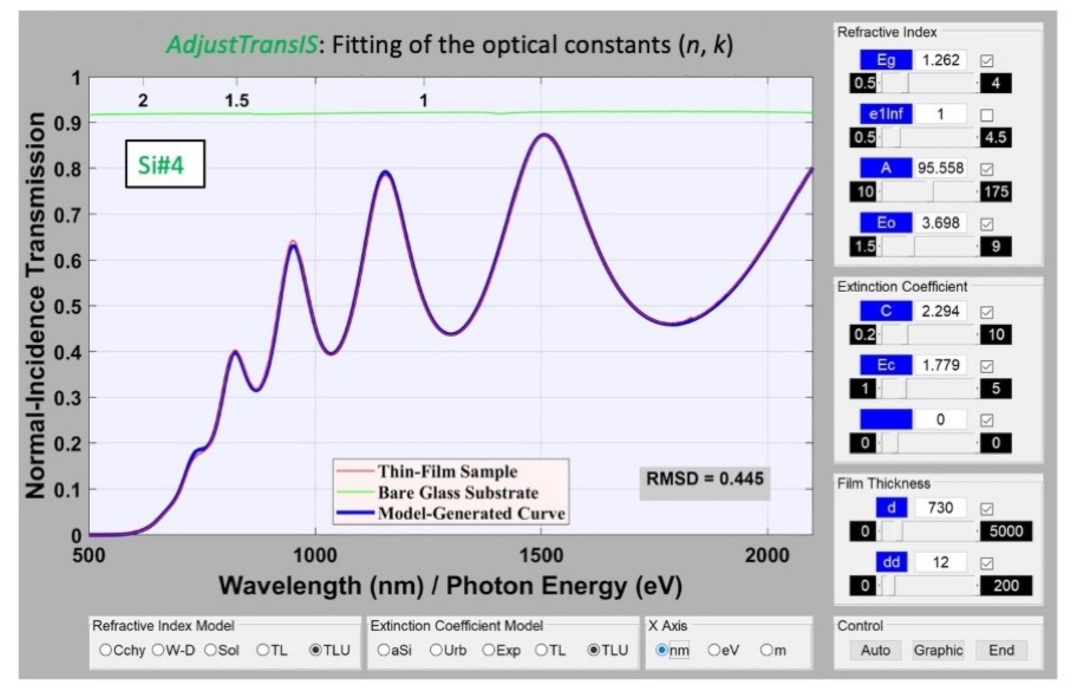
3.5. ‘AdjustTransIS’: Matlab Computational Program for Optical Characterization of Amorphous Semiconductor Films
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Computation of the Optical Properties by ‘AdjustTransIS’
4.2. Comparison with the Transmission Data Analysis by the Swanepoel Envelope Method
4.3. Wemple–DiDomenico Framework: Insight into Material Porosity
4.4. Bruggeman Effective Medium Approximation: Alternate Void-Volume-Fraction Determination
4.5. Absorption Edge and Dielectric Function of RFMS-a-Si
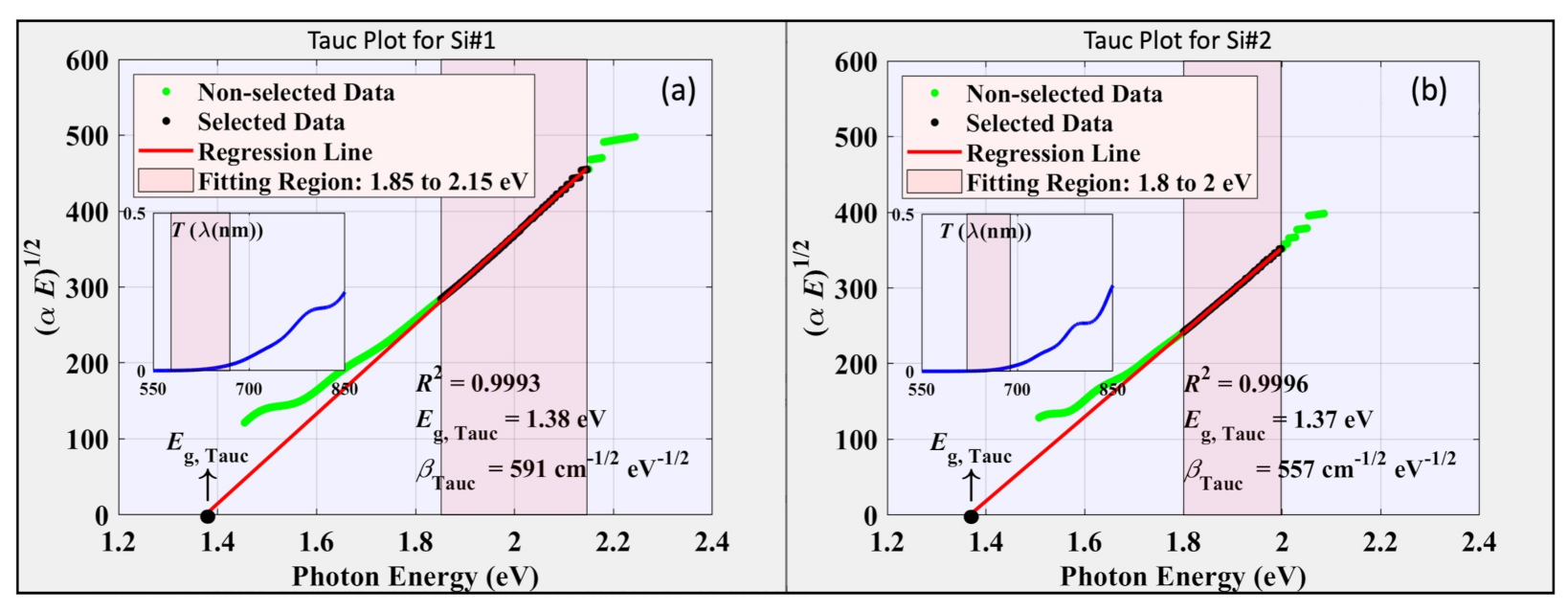
4.6. Determination of the Band-Gap Energy by Tauc’s Extrapolation Method
5. Summary and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Street, R.A. Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Street, R.A. Technology and Applications of Amorphous Silicon; Springer: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Morigaki, K.; Kugler, S.; Shimakawa, K. Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic Properties; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, M.J. The physics of amorphous-silicon thin-film transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1989, 36, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bye, G.; Ceccaroli, B. Solar grade silicon: Technology status and industrial trends. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 130, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschke, J.; Amkreutz, D.; Korte, L.; Ruske, F.; Rech, B. Towards wafer quality crystalline silicon thin-film solar cells on glass. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 128, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschke, J.; Amkreutz, D.; Rech, B. Liquid phase crystallized silicon on glass: Technology, material quality and back contacted heterojunction solar cells. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 04EA04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.; Lesh, G.; Huggins, R. All-solid lithium electrodes with mixed-conductor matrix. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1981, 128, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabacak, T.; Demirkan, M.T. Density Modulated Thin Film Electrodes, Methods of Making Same, and Applications of Same. U.S. Patent 10,333,148, 25 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Poelman, D.; Smet, P.F. Methods for the determination of the optical constants of thin films from single transmission measurements: A critical review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, P.; Willoughby, A.; Kasap, S. Optical Properties of Materials and Their Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, M. Optical Properties of Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel, O. The Physics of Thin Film Optical Spectra; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heavens, O.S. Optical Properties of Thin Solid Films; Dover books on physics; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-de Marcos, L.V.; Larruquert, J.I. Analytic optical-constant model derived from Tauc-Lorentz and Urbach tail. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 28561–28572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smit, C.; Van Swaaij, R.; Donker, H.; Petit, A.; Kessels, W.; Van de Sanden, M. Determining the material structure of microcrystalline silicon from Raman spectra. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Leary, S.; Fogal, B.; Lockwood, D.; Baribeau, J.M.; Noël, M.; Zwinkels, J. Optical dispersion relationships in amorphous silicon grown by molecular beam epitaxy. J.-Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 290, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogal, B.; O’Leary, S.; Lockwood, D.; Baribeau, J.M.; Noël, M.; Zwinkels, J. Disorder and the optical properties of amorphous silicon grown by molecular beam epitaxy. Solid State Commun. 2001, 120, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orapunt, F.; Tay, L.L.; Lockwood, D.J.; Baribeau, J.M.; Noël, M.; Zwinkels, J.C.; O’Leary, S.K. An amorphous-to-crystalline phase transition within thin silicon films grown by ultra-high-vacuum evaporation and its impact on the optical response. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 065702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roura, P.; Farjas, J.; Roca i Cabarrocas, P. Quantification of the bond-angle dispersion by Raman spectroscopy and the strain energy of amorphous silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 073521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beeman, D.; Tsu, R.; Thorpe, M. Structural information from the Raman spectrum of amorphous silicon. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D. Thin-Film Deposition: Principles and Practice; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanepoel, R. Determination of the thickness and optical constants of amorphous silicon. J. Phys. E Sci. Instruments 1983, 16, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.J.R. Nuevos metodos de caracterizacion optica de semiconductores basados en medidas espectroscopicas de reflexion. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cadiz, Cadiz, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolski, J.; Ho, F.; Waldorf, A. Determination of optical constants of thin film coating materials based on inverse synthesis. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, R. Determination of surface roughness and optical constants of inhomogeneous amorphous silicon films. J. Phys. E Sci. Instruments 1984, 17, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldyna, M.; Postava, K.; Bouchala, J.; Pistora, J.; Yamaguchi, T. Model dielectric functional of amorphous materials including Urbach tail. In Microwave and Optical Technology 2003; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5445, pp. 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Jellison, G., Jr.; Modine, F. Parameterization of the optical functions of amorphous materials in the interband region. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 371–373, Erratum in 1996, 69, 2137–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Domínguez, M.; González-Leal, J.; Márquez, E.; Outón, J.; Ramírez-del Solar, M. Insights into the annealing process of sol-gel TiO2 films leading to anatase development: The interrelationship between microstructure and optical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Pérez, J.J.; Navarro, E.M. Optical Transmittance for Strongly-Wedge-Shaped Semiconductor Films: Appearance of Envelope-Crossover Points in Amorphous As-Based Chalcogenide Materials. Coatings 2020, 10, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S. Optical Constants of Crystalline and Amorphous Semiconductors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ferlauto, A.; Ferreira, G.; Pearce, J.M.; Wronski, C.; Collins, R.; Deng, X.; Ganguly, G. Analytical model for the optical functions of amorphous semiconductors from the near-infrared to ultraviolet: Applications in thin film photovoltaics. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Márquez, E.; Blanco, E.; García-Vázquez, C.; Díaz, J.; Saugar, E. Spectroscopic ellipsometry study of non-hydrogenated fully amorphous silicon films deposited by room-temperature radio-frequency magnetron sputtering on glass: Influence of the argon pressure. J.-Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 547, 120305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palik, E.D. Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Minkov, D.; Gavrilov, G.; Moreno, J.; Vázquez, C.; Márquez, E. Optimization of the graphical method of Swanepoel for characterization of thin film on substrate specimens from their transmittance spectrum. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, D.; Gavrilov, G.; Angelov, G.; Moreno, J.; Vázquez, C.; Ruano, S.; Márquez, E. Optimisation of the envelope method for characterisation of optical thin film on substrate specimens from their normal incidence transmittance spectrum. Thin Solid Films 2018, 645, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, E.; Ramírez-Malo, J.; Villares, P.; Jiménez-Garay, R.; Ewen, P.; Owen, A. Calculation of the thickness and optical constants of amorphous arsenic sulphide films from their transmission spectra. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1992, 25, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Malo, J.; Márquez, E.; Villares, P.; Jiménez-Garay, R. Determination of the Refractive Index and Optical Absorption Coefficient of Vapor-Deposited Amorphous As–S Films from Transmittance Measurements. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 1992, 133, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, E.; Ramírez-Malo, J.; Villares, P.; Jiménez-Garay, R.; Swanepoel, R. Optical characterization of wedge-shaped thin films of amorphous arsenic trisulphide based only on their shrunk transmission spectra. Thin Solid Films 1995, 254, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, E.; Díaz, J.; García-Vázquez, C.; Blanco, E.; Ruíz-Pérez, J.; Minkov, D.; Angelov, G.; Gavrilov, G. Optical characterization of amine-solution-processed amorphous AsS2 chalcogenide thin films by the use of transmission spectroscopy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 721, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, E.; Saugar, E.; Díaz, J.; García-Vázquez, C.; Fernández-Ruano, S.; Blanco, E.; Ruíz-Pérez, J.; Minkov, D. The influence of Ar pressure on the structure and optical properties of non-hydrogenated a-Si thin films grown by rf magnetron sputtering onto room-temperature glass substrates. J.-Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 517, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Pérez, J.; González-Leal, J.; Minkov, D.; Márquez, E. Method for determining the optical constants of thin dielectric films with variable thickness using only their shrunk reflection spectra. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemple, S.; DiDomenico, M., Jr. Behavior of the electronic dielectric constant in covalent and ionic materials. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 3, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemple, S. Refractive-index behavior of amorphous semiconductors and glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shen, W. Perspectives in the characteristics and applications of Tauc-Lorentz dielectric function model. Eur. Phys. J. B-Condens. Matter Complex Syst. 2005, 43, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Mori, H. Optical properties of fully amorphous silicon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, B.; Aspnes, D.; Celler, G.; Adams, A. Optical characterization of chemically vapor deposited and laser-annealed polysilicon. MRS Online Proc. Libr. (OPL) 1981, 4, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.E. Optical properties of thin films. Thin Solid Films 1982, 89, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, V.D. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. I. Dielektrizitätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 416, 636–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, G. Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon; Pankove, J.I., Ed.; Part B; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, I. Band-structure determination by subgap spectroscopy in thin films of semiconductors. Philos. Mag. B 1997, 76, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkan, M.; Trahey, L.; Karabacak, T. Low-density silicon thin films for lithium-ion battery anodes. Thin Solid Films 2016, 600, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| a-Si Material | RFMS-a-Si (Si#1) | RFMS-a-Si (Si#2) | RFMS-a-Si (Si#3) | RFMS-a-Si (Si#4) | e-a-Si Jellison-Modine | i-a-Si Adichi-Mori |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data reference | Present work | Present work | Present work | Present work | [29] | [32] |
| Wavelength/Energy range (nm/eV) | 400–2500 | 400–2500 | 400–2500 | 400–2500 | 0.8–5.9 | 1.5–5.2 |
| Figure-of-merit | 0.421 | 0.565 | 0.445 | 0.446 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 1.19 | 1.19 | 1.26 | 1.27 | 1.20 | 1.11 |
| Offset, | 1.00 (fixed) | 1.00 (fixed) | 1.00 (fixed) | 1.00 (fixed) | 1.15 | 0.17 |
| ) | 102 | 95 | 96 | 104 | 122 | 150 |
| ) | 3.72 | 3.73 | 3.70 | 3.65 | 3.45 | 3.40 |
| ) | 2.54 | 2.26 | 2.29 | 2.35 | 2.54 | 2.55 |
| ) | 1.76 | 1.73 | 1.78 | 1.79 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 253 | 240 | 245 | 245 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 2.19 | 1.28 | 1.2 | 1.3 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 770 | 1123 | 730 | 795 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 777 | 1112 | 735 | 789 | N/A | N/A |
| ) | 25 | 0 | 12 | 13 | N/A | N/A |
| 3.2 | 0 | 1.6 | 1.6 | N/A | N/A | |
| ) | 1.38 | 1.37 | 1.43 | 1.43 | N/A | N/A |
| (cm | 591 | 557 | 574 | 604 | N/A | N/A |
| Dispersion model | TLUC | TLUC | TLUC | TLUC | TL | TL |
| Sample ID | Approach | () | () | () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si#1 | Inverse Synthesis | 18.6 | 3.71 | 3.24 | 29.2 | 3.158 | 20.6 | 20.8 |
| Si#1 | Envelope Method | N/A | N/A | 3.26 | 28.0 | 3.099 | 21.2 | 21.4 |
| Si#2 | Inverse Synthesis | 19.5 | 3.72 | 3.27 | 28.2 | 3.102 | 22.5 | 22.5 |
| Si#2 | Envelope Method | N/A | N/A | 3.33 | 29.1 | 3.199 | 18.4 | 20.8 |
| e-a-Si Palik [35] | Reflectance | 20.8 | 3.50 | 3.01 | 30.9 | 3.359 | 15.1 | 13.2 |
| i-a-Si Adachi-Mori [32] | VASE | 26.6 | 3.45 | 2.87 | 36.4 | 3.697 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Márquez, E.; Ruíz-Pérez, J.J.; Ballester, M.; Márquez, A.P.; Blanco, E.; Minkov, D.; Ruano, S.M.F.; Saugar, E. Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization. Coatings 2021, 11, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111324
Márquez E, Ruíz-Pérez JJ, Ballester M, Márquez AP, Blanco E, Minkov D, Ruano SMF, Saugar E. Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization. Coatings. 2021; 11(11):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111324
Chicago/Turabian StyleMárquez, Emilio, Juan J. Ruíz-Pérez, Manuel Ballester, Almudena P. Márquez, Eduardo Blanco, Dorian Minkov, Susana M. Fernández Ruano, and Elias Saugar. 2021. "Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization" Coatings 11, no. 11: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111324
APA StyleMárquez, E., Ruíz-Pérez, J. J., Ballester, M., Márquez, A. P., Blanco, E., Minkov, D., Ruano, S. M. F., & Saugar, E. (2021). Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization. Coatings, 11(11), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111324









