Simulated Discharge of Ballast Water Reveals Potential Contribution to Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Geographically Isolated Receiving Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
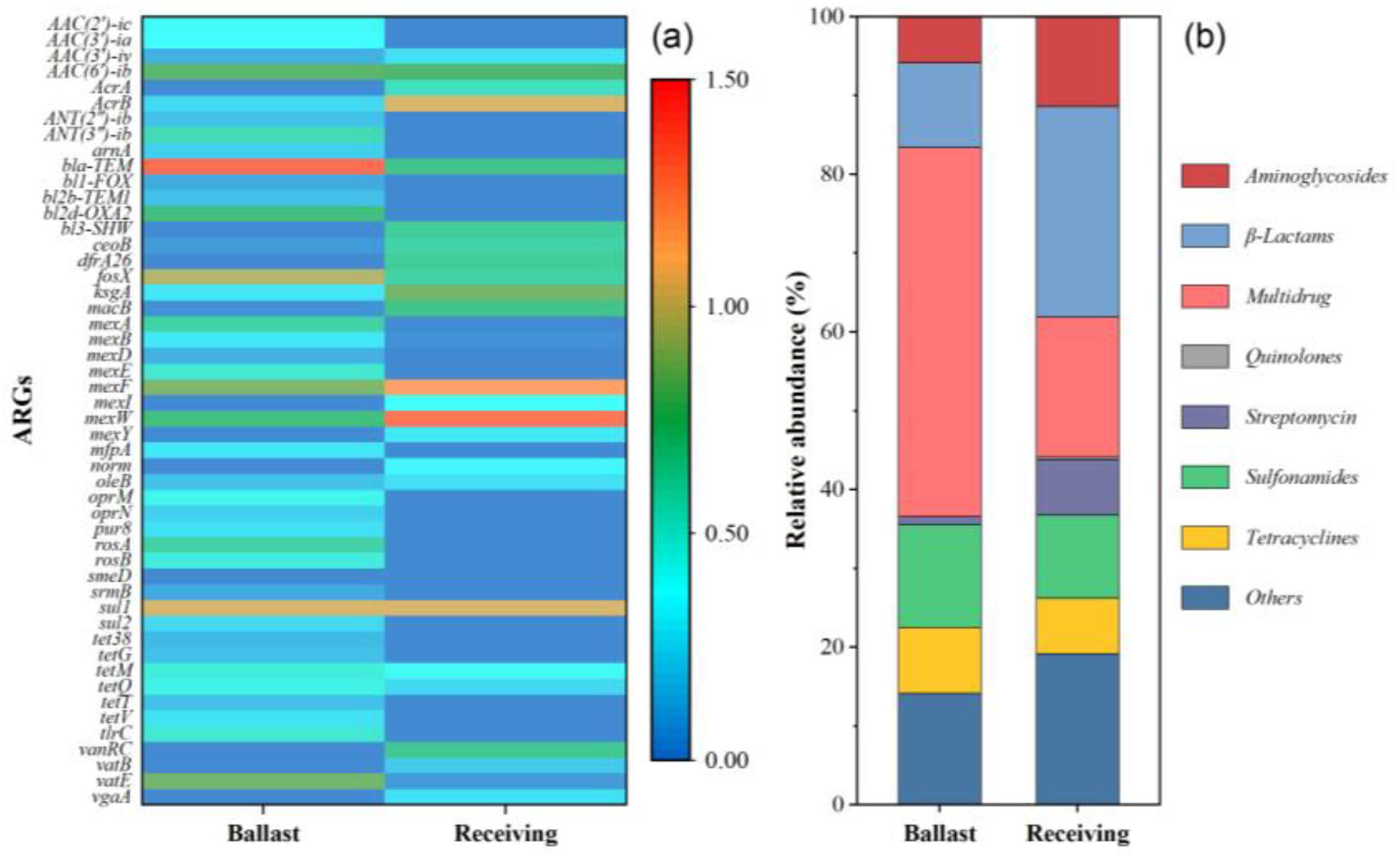
2.1. ARG Profiles in Initial Samples
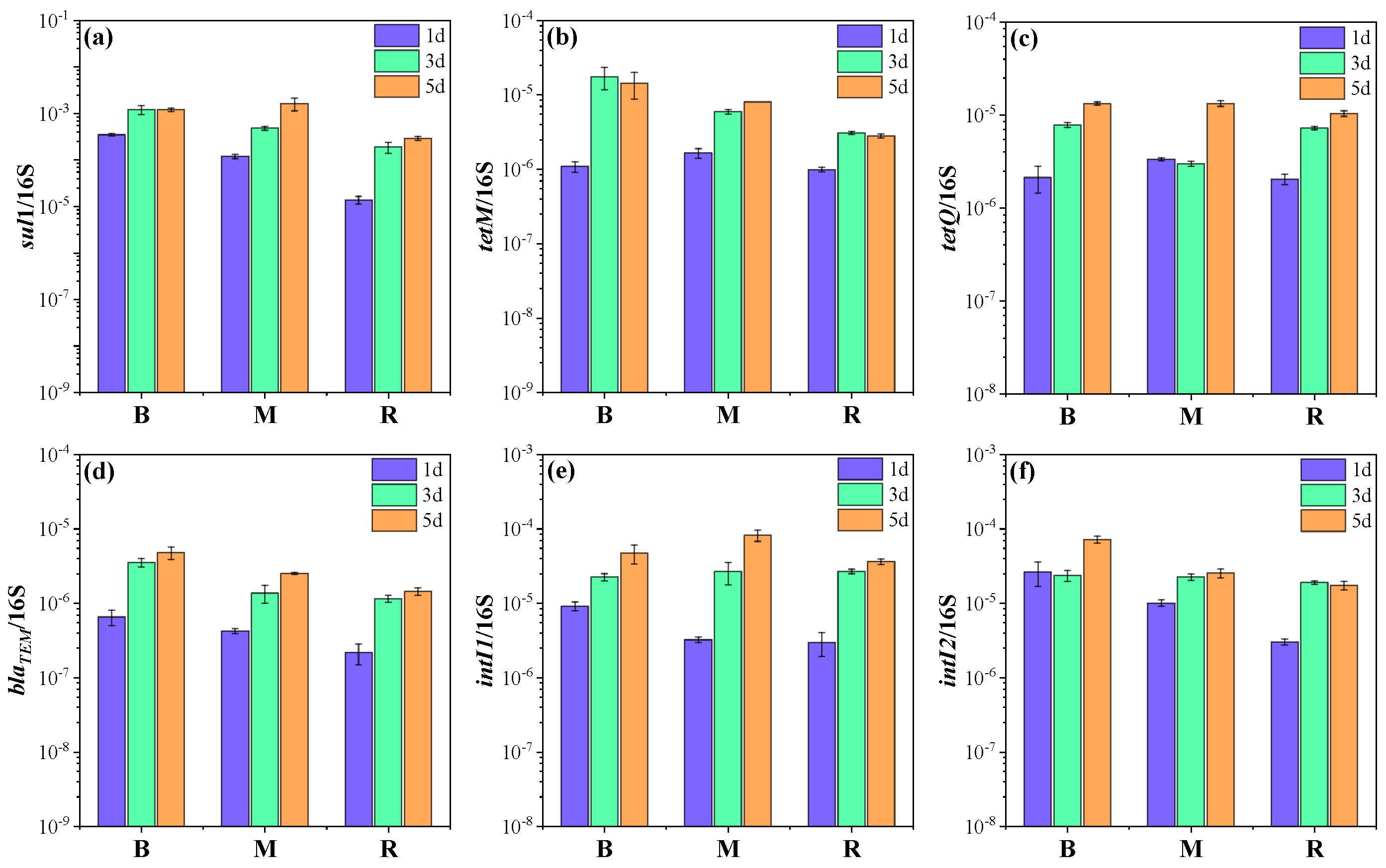
2.2. Changes in ARGs and MGEs in Microcosms
2.3. Transformation of Bacterial Communities in Microcosms
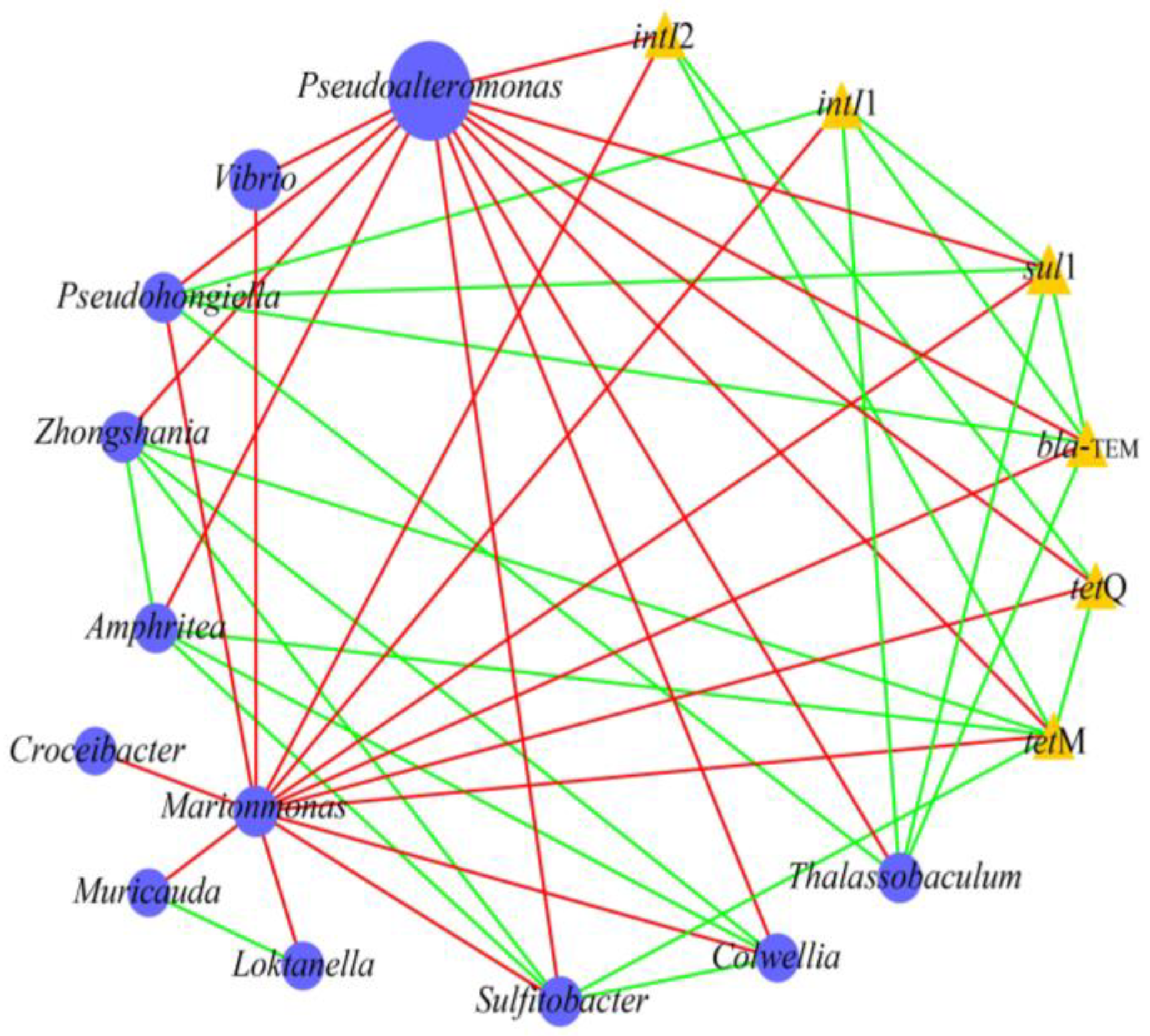
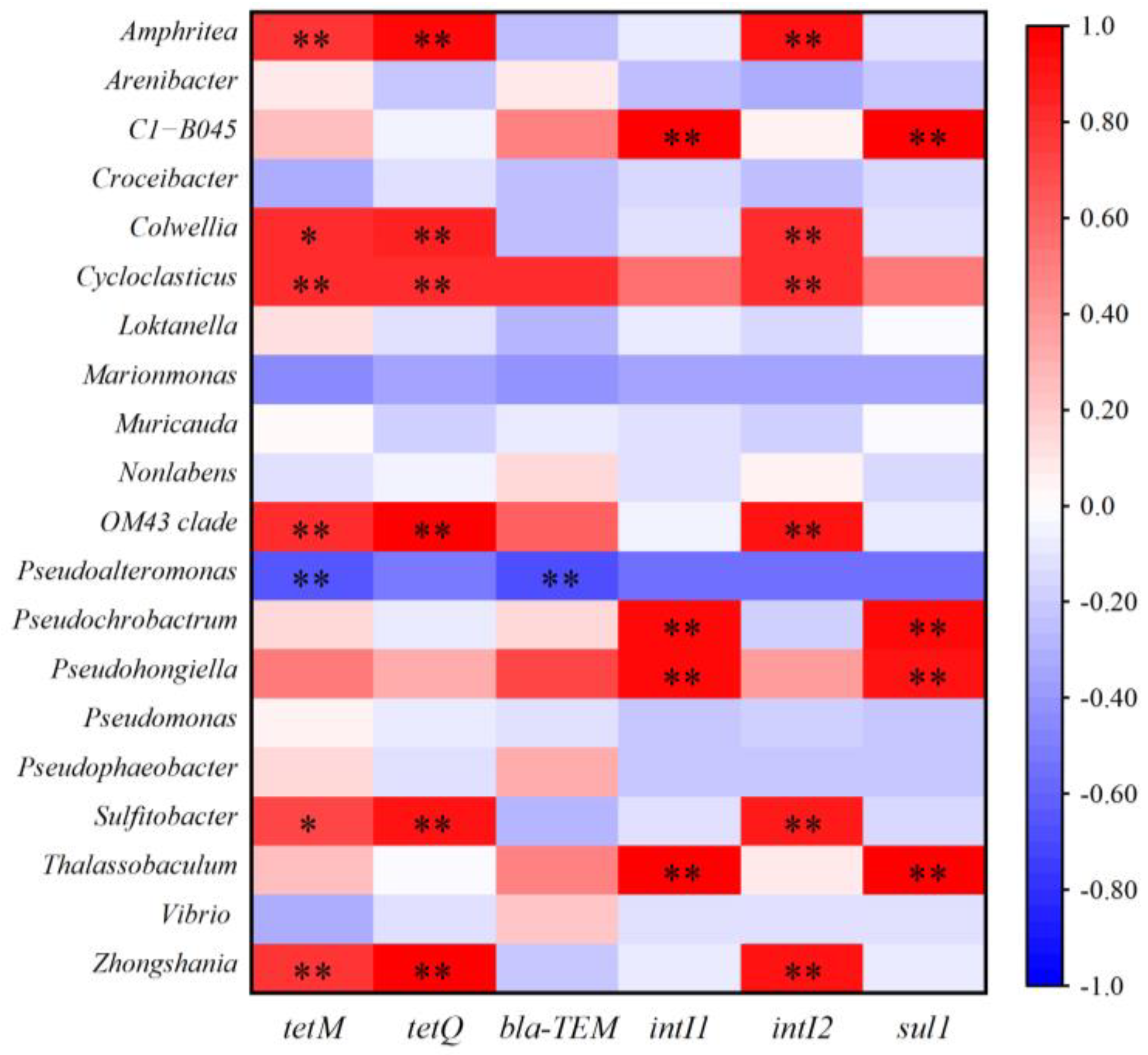
2.4. Relationship Between Bacterial Communities, MGEs, and ARGs in Microcosms
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Processing
3.2. Metagenomic Analysis of ARGs in the Initial Samples
3.3. Microcosm Setup and DNA Extraction
3.4. Quantification of ARGs
3.5. Bacterial Community
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lin, Y.C.; Luo, Y.M. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological-health risks of selected antibiotics in coastal waters along the coastline of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, J. Continental-scale spatio-temporal distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in coastal waters along coastline of China. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.H.; Luo, Y.M. Potential risks of microplastics combined with superbugs: Enrichment of antibiotic resistant bacteria on the surface of microplastics in mariculture system. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, A.; Pei, R.; Storteboom, H.; Carlson, K.H. Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Studies in Northern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7445–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.W.; Olivares-Rieumont, S.; Knapp, C.W.; Lima, L.; Werner, D.; Bowen, E. Antibiotic resistance gene abundances associated with waste discharges to the Almendares River near Havana, Cuba. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Cheng, W.X.; Xu, L.K.; Jiao, Y.N.; Baig, S.A.; Chen, H. Occurrence and removal of antibiotics and the corresponding resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants: Effluents’ influence to downstream water environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6826–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Rawlings, T.K.; Dobbs, F.C.; Drake, L.A.; Mullady, T.; Huq, A.; Colwell, R.R. Global spread of microorganisms by ships. Nature 2000, 408, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.W.; Minton, M.S.; Ruiz, G.M. Geographic limitations and regional differences in ships’ ballast water management to reduce marine invasions in the contiguous United States. BioScience 2011, 61, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altug, G.; Gurun, S.; Cardak, M.; Ciftci, P.S.; Kalkan, S. The occurrence of pathogenic bacteria in some ships’ ballast water incoming from various marine regions to the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmeyer, R. Diversity of bacteria in ships ballast water as revealed by next generation DNA sequencing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Aw, T.G.; Teal, T.K.; Rose, J.B. Metagenomic investigation of viral communities in ballast water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8396–8407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Lin, J.D.; Xue, J.Z. The biological content of ballast water in China: A review. Aquac. Fish. 2017, 2, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, B.Y.; Cui, Y.X.; Tian, W.; Li, J.; Xie, B.; Yin, F. Abundances and profiles of antibiotic resistance genes as well as co-occurrences with human bacterial pathogens in ship ballast tank sediments from a shipyard in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, B.; Jiang, C.; Han, Y.; Wu, D.; Jin, L. Diverse bacterial hosts and potential risk of antibiotic resistomes in ship ballast water revealed by metagenomic binning. Environ. Res. 2024, 253, 119056. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, P.; Gong, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, W.; Fu, B.; Huang, X. Metagenomic profiles of the resistome in subtropical estuaries: Co-occurrence patterns, indicative genes, and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Hou, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, H. Metagenomics highlights the impact of climate and human activities on antibiotic resistance genes in China’s estuaries. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, W.A.; Gunsch, C.K. Higher normalized concentrations of tetracycline resistance found in ballast and harbor water compared to ocean water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 151, 110796. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, J.A.; Martinson, J.; Gong, Y.G.; Okum, S.; Pilgrim, E.; Lohan, K.M.P.; Carney, K.J.; Ruiz, G.M. Ballast water exchange and invasion risk posed by intracoastal vessel traffic: An evaluation using high throughput sequencing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9926–9936. [Google Scholar]
- Hess-Erga, O.; Moreno-Andrés, J.; Enger, Ø.; Vadstein, O. Microorganisms in ballast water: Disinfection, community dynamics, and implications for management. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 704–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zaiko, A.; Martinez, J.L.; Ardura, A.; Clusa, L.; Borrell, Y.J.; Samuiloviene, A.; Roca, A.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Detecting nuisance species using NGST: Methodology shortcomings and possible application in ballast water monitoring. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.P.; Ju, F.; Guo, F.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic and network analysis reveal wide distribution and co-occurrence of environmental antibiotic resistance genes. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2490–2502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nogales, B.; Lanfranconi, M.P.; Piña-Villalonga, J.M.; Bosch, R. Anthropogenic perturbations in marine microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ying, C.W.; Chang, M.J.; Hu, C.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chao, W.L.; Yeh, S.L.; Chang, S.J.; Hsu, J.T. The effects of marine farm-scale sequentially integrated multi-trophic aquaculture systems on microbial community composition, prevalence of sulfonamide-resistant bacteria and sulfonamide resistance gene sul1. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 643, 681–691. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, J.M.; Sun, W.C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.W. Effect of temperature on sulfonamide antibiotics degradation, and on antibiotic resistance determinants and hosts in animal manures. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the coastal area of the Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, R.; Zhang, Y.P.; Niu, Z.G. Variation pattern of terrestrial antibiotic resistances and bacterial communities in seawater/freshwater mixed microcosms. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Dönhöfer, A.; Franckenberg, S.; Wickles, S.; Berninghausen, O.; Beckmann, R.; Wilson, D.N. Structural basis for tetM-mediated tetracycline resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16900–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Xue, J.; Wu, H. Comparison of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in ballast tank sediments based on two applicable reference standards. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 196, 115543. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Chen, X.; Tian, W.; Qian, Q.; Shen, H.; Liao, D.; Lv, B. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in ballast tank sediment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.G.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, T. Co-occurrence of antibiotic and metal resistance genes revealed in complete genome collectio. ISME J. 2017, 11, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, X.X.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, T. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes and their associations with bacterial community in livestock breeding wastewater and its receiving river water. Water Res. 2017, 124, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashif, J.; Buriro, R.; Memon, J.; Yaqoob, M.; Soomro, J.; Dongxue, D.; Jinhu, H.; Liping, W. Detection of class 1 and 2 integrons, β-lactamase genes and molecular characterization of sulfonamide resistance in escherichia coli isolates recovered from poultry in China. Pak. Vet. J. 2013, 33, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, S.J.; Farrugia, D.N.; Paulsen, I.T.; Hall, R.M. A novel family of genomic resistance islands, abgri2, contributing to aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates belonging to global clone 2. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, L.; von Schiller, D.; Sanchez-Melsio, A.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Balcazar, J.L. Occurrence and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in river biofilms after wastewater inputs in small rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.R.; Qu, Z.T.; Yuan, Z.T.; Yu, H.C. Influence of reclaimed water discharge on the dissemination and relationships of sulfonamide, sulfonamide resistance genes along the Chaobai River, Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso-da-Rocha, C.; Manaia, C.M. The influence of the autochthonous wastewater microbiota and gene host on the fate of invasive antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.C.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.J.; Xu, X.R.; Xu, W.J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Wen, G.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Cao, Y.C. Occurrence and temporal variation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in shrimp aquaculture: ARGs dissemination from farming source to reared organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J. Alteration of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.H.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Philip, L.B.; Yuan, Z.G. Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements. Water Res. 2017, 123, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mao, D.Q.; Rysz, M.; Zhou, Q.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Xu, L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Trends in antibiotic resistance genes occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gheldre, Y.; Avesani, V.; Berhin, C.; Delmée, M.; Glupczynski, Y. Evaluation of Oxoid combination discs for detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Huang, Z.T.; Yang, K.; Graham, D.; Xie, B. Relationships between antibiotics and antibiotic resistance gene levels in municipal solid waste leachates in Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4122–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; de Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| sul1 | tetM | tetQ | blaTEM | intI1 | intI2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sul1 | 1 | / | / | / | / | / |
| tetM | 0.174 | 1 | / | / | / | / |
| tetQ | 0.280 | 0.972 ** | 1 | / | / | / |
| blaTEM | 0.610 * | 0.782 ** | 0.806 ** | 1 | / | / |
| intI1 | 0.999 ** | 0.173 | 0.277 | 0.613 * | 1 | / |
| intI2 | 0.247 | 0.956 ** | 0.956 ** | 0.845 ** | 0.264 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Ji, C.; Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Lv, B. Simulated Discharge of Ballast Water Reveals Potential Contribution to Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Geographically Isolated Receiving Waters. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040340
Shi J, Ji C, Wang R, Sun C, Lv B. Simulated Discharge of Ballast Water Reveals Potential Contribution to Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Geographically Isolated Receiving Waters. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jianhong, Chengyuan Ji, Rui Wang, Chaoli Sun, and Baoyi Lv. 2025. "Simulated Discharge of Ballast Water Reveals Potential Contribution to Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Geographically Isolated Receiving Waters" Antibiotics 14, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040340
APA StyleShi, J., Ji, C., Wang, R., Sun, C., & Lv, B. (2025). Simulated Discharge of Ballast Water Reveals Potential Contribution to Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Geographically Isolated Receiving Waters. Antibiotics, 14(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14040340





