Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Phages Infecting Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae from Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Phages KpTDp1 and KpTDp2
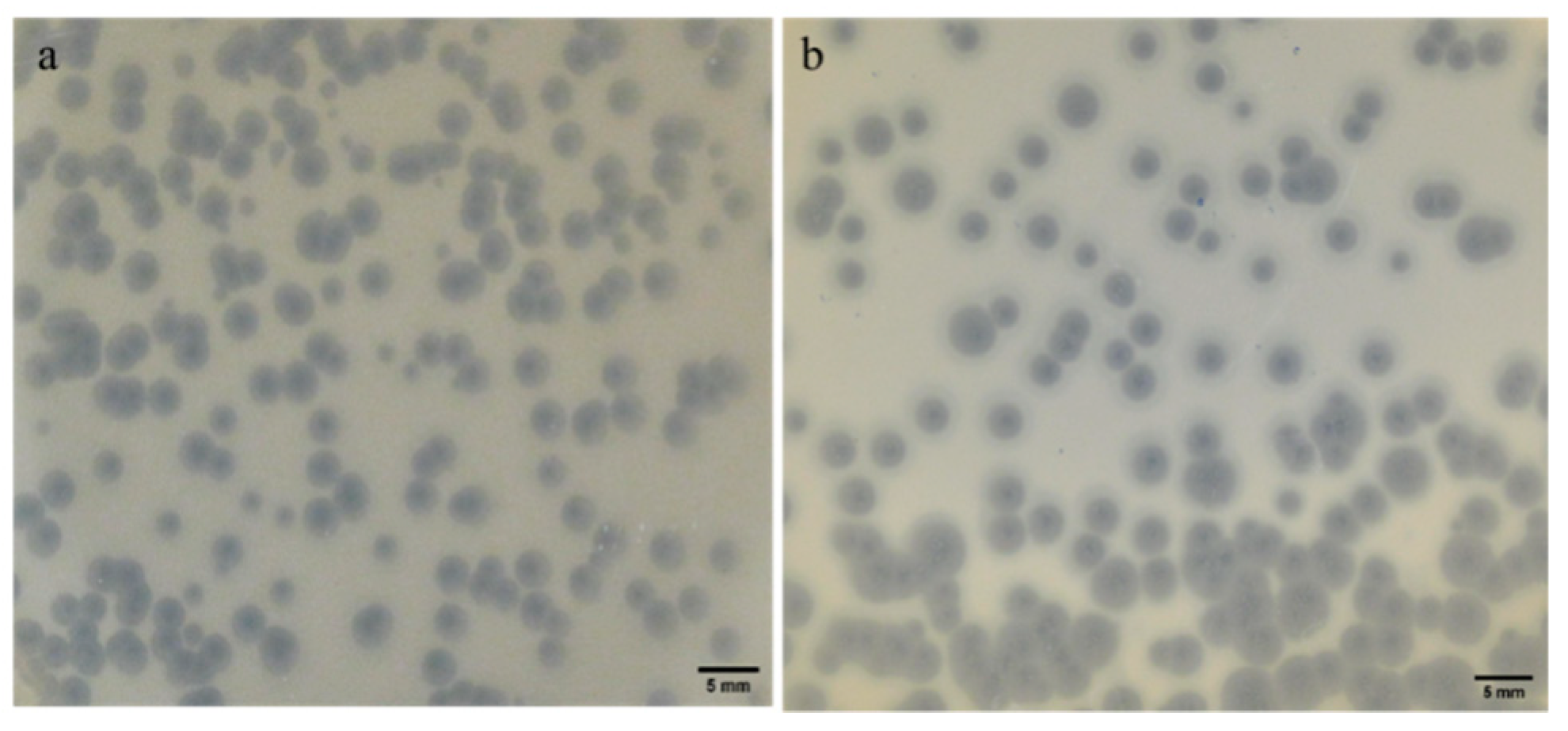
2.2. Plaque Morphology: Similar Morphology, Different Size
2.3. Phages Exhibit a Narrow Host Range
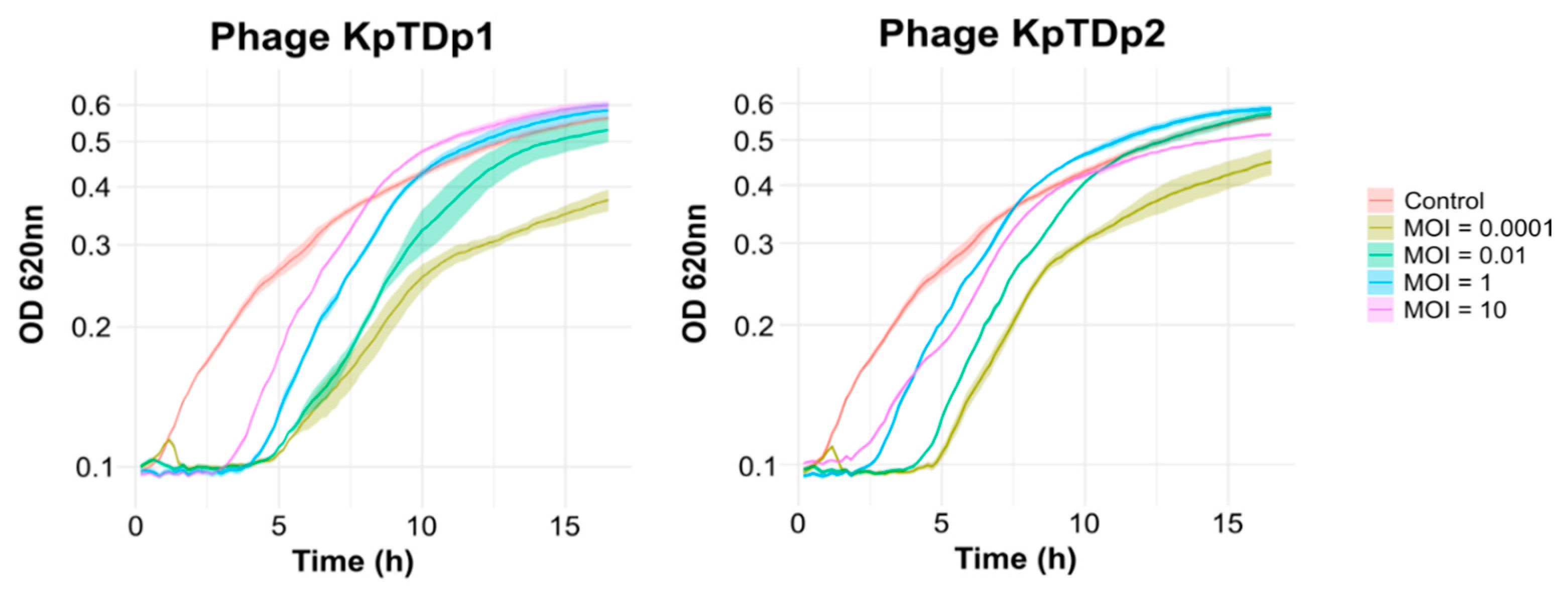
2.4. Lower MOI Enhances Phage Replication
2.5. Lower MOI Prolongs Phage Control of Bacterial Growth
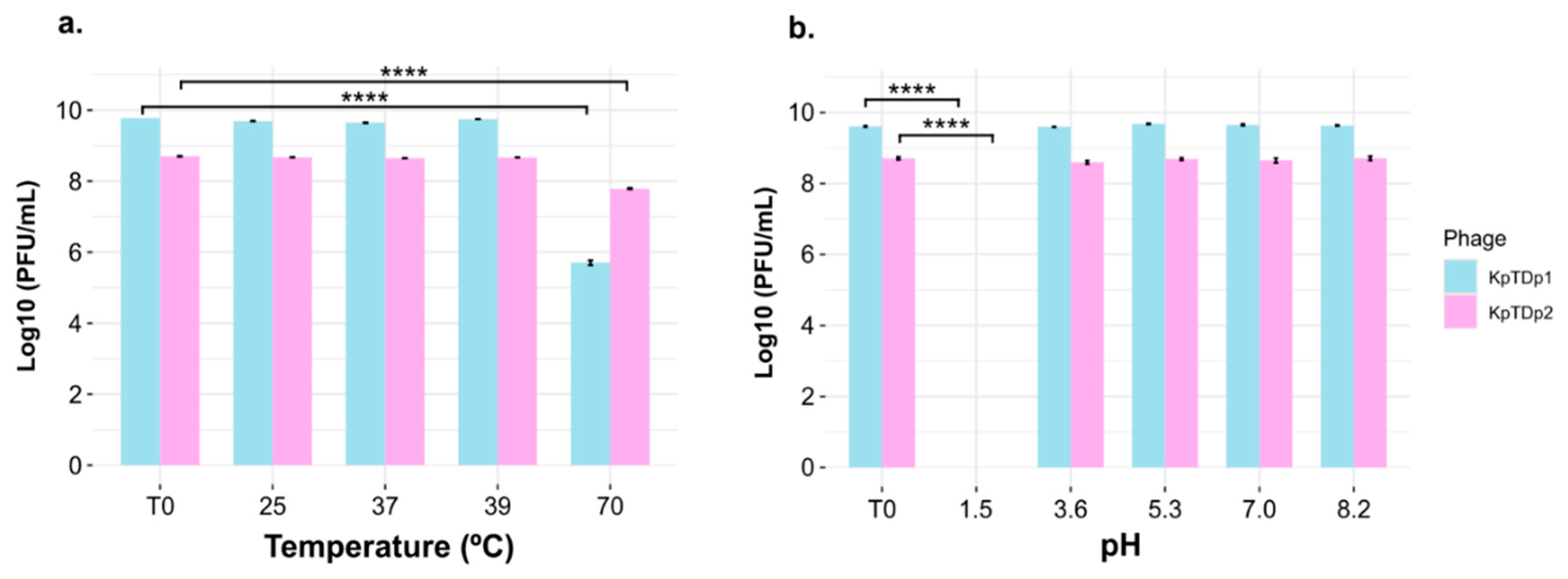
2.6. Temperature and pH Tolerance of Phages
2.7. Genomic Features and Lifestyle Prediction of KpTDp1 and KpTDp2
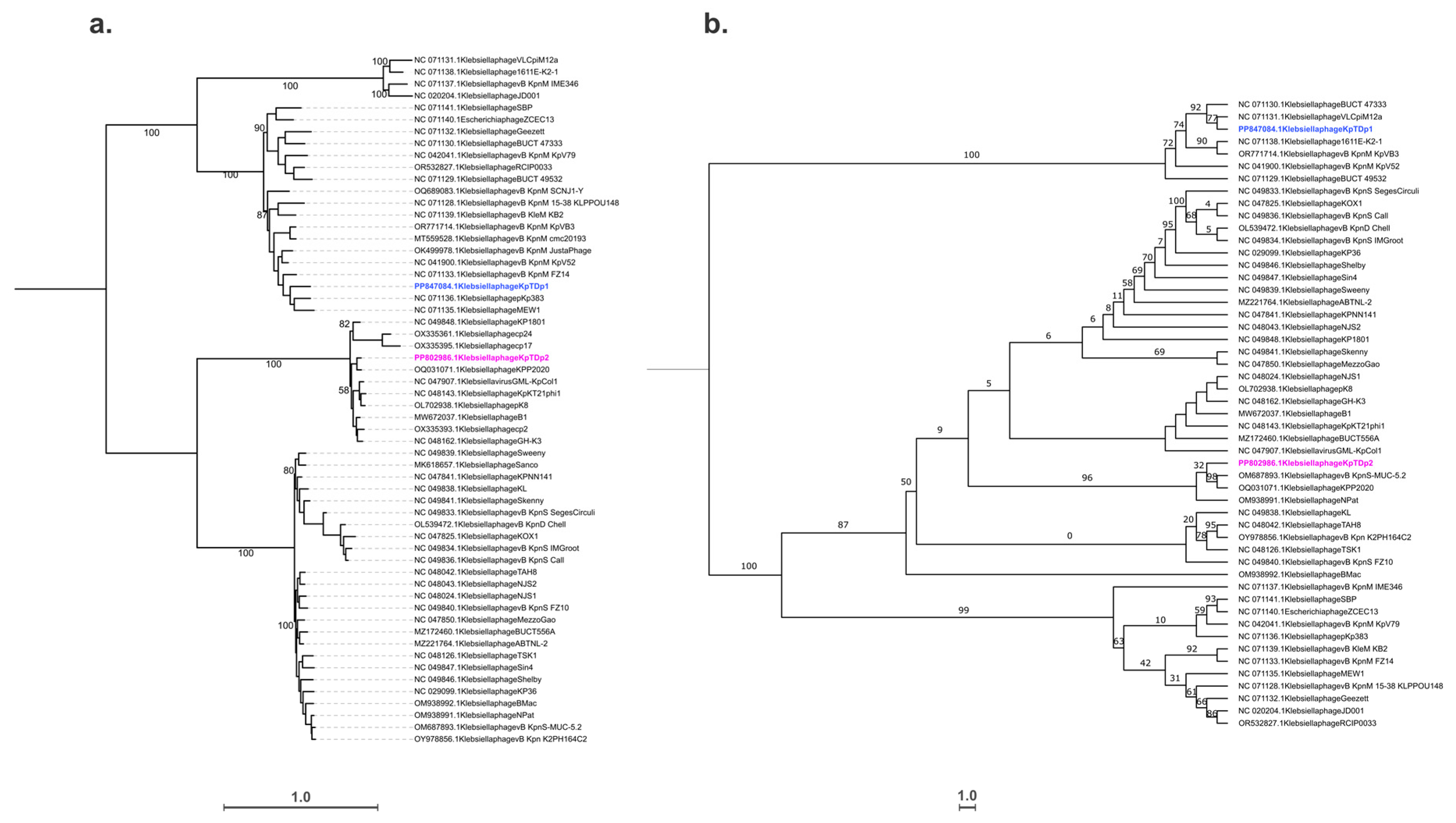
2.8. Taxonomic and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.9. Functional Annotation
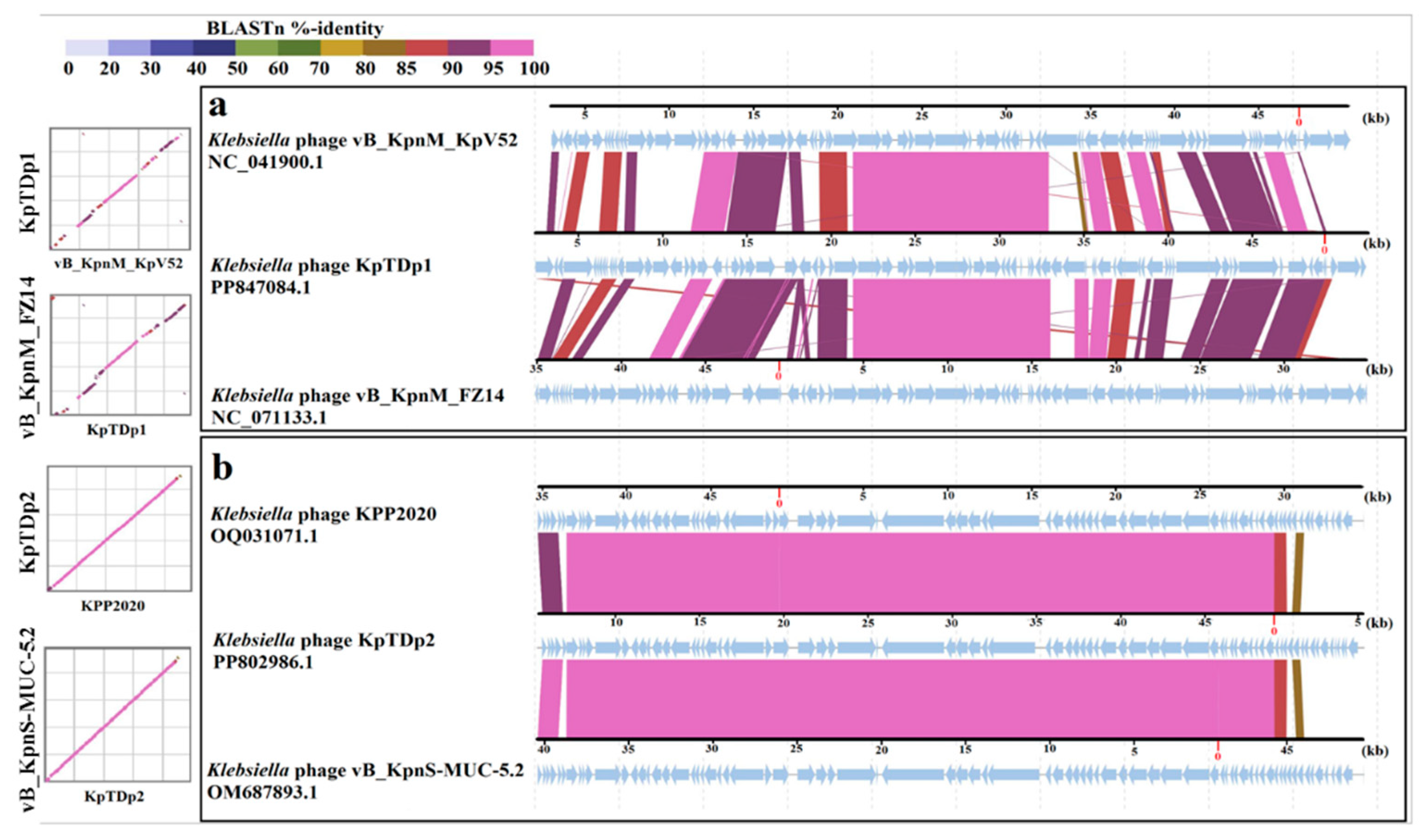
2.10. Comparison of KpTDp1 and KpTDp2 Genomes with Closely Related Phages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain
4.2. Determination of the Capsular Type
4.3. Phage Isolation
4.4. Phage Amplification and Titration
4.5. The Multiplicity of Infection (MOI)
4.6. Host Range Determination
4.7. Effect of Phages on Bacterial Growth
4.8. Phage Temperature and pH Stability
4.9. Adsorption and One Step Growth Curve
4.10. DNA Isolation and Sequencing
4.11. Genome Assembly, Annotation, and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.12. Data Availability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence Factors, Molecular Epidemiology and Latest Updates in Treatment Options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Klebsiella species: Taxonomy, hypervirulence and multidrug resistance. eBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.-S.; Garin, B.; Le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H.; et al. Genomic definition of hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.R.; Irum, S.; Mahnoor, I.; Ismatullah, H.; Mumtaz, M.; Andleeb, S.; Rahman, A.; Jamal, M. Exploring the resistome, virulome, and mobilome of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: Deciphering the molecular basis of carbapenem resistance. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wei, J.; Zhou, W.; Yan, X.; Cao, X.; Zuo, L.; Chen, S.; Yao, K.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; et al. Risk factors and mortality for patients with Bloodstream infections of Klebsiella pneumoniae during 2014–2018: Clinical impact of carbapenem resistance in a large tertiary hospital of China. J. Infect. Public Health. 2020, 13, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Hu, D. The making of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matovina, M.; Abram, M.; Repac-Antić, D.; Knežević, S.; Bubonja-Šonje, M. An outbreak of ertapenem-resistant, carbapenemase-negative and porin-deficient ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae complex. Germs 2021, 11, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopotsa, K.; Mbelle, N.M.; Osei Sekyere, J. Epigenomics, genomics, resistome, mobilome, virulome and evolutionary phylogenomics of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical strains. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Gong, Y.; Dunstan, R.A.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, D.; Tang, M.; Lithgow, T.; Zhou, T. A Klebsiella-phage cocktail to broaden the host range and delay bacteriophage resistance both in vitro and in vivo. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Du, F.; Long, M.; Li, P. Limitations of phage therapy and corresponding optimization strategies: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.T.; Amirmozafari, N.; Shariati, A.; Hallajzadeh, M.; Mirkalantari, S.; Khoshbayan, A.; Jazi, F.M. How Phages Overcome the Challenges of Drug Resistant Bacteria in Clinical Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, A.; Mansour, W.; Jaidane, N.; Chaouch, C.; Boujaâfar, N.; Bouallègue, O. Epidemiology of resistance and phenotypic characterization of carbapenem resistance mechanisms in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates at Sahloul University Hospital-Sousse, Tunisia. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouaoui, E.; Mercuri, P.S.; Radaoui, A.; Ben Salah, N.; Galleni, M.; Ben-Mahrez, K.; Réjiba, S. Highprevalence of blaNDM among carbapenam non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Tunisian hospital. First report of blaNDM-9, blaKPC-20 and blaKPC-26 genes. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, S.; Stender, J.; Mzoughi, S.; Vogele, K.; Kühn, J.; Friese, D.; Bugert, C.; Handrick, S.; Ferjani, M.; Wölfel, R.; et al. Isolation and characterization of lytic phage TUN1 specific for Klebsiella pneumoniae K64 clinical isolates from Tunisia. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Pei, G.; Tong, Y.; Bai, C. Characterization and genomic analysis of bacteriophage vB_KpnM_IME346 targeting clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae strain of the K63 capsular type. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongari, R.; Rajaure, M.; Cahill, J.; Rasche, E.; Mijalis, E.; Berry, J.; Young, R. Phage spanins: Diversity, topological dynamics and gene convergence. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.; Young, R. Phage lysis: Multiple genes for multiple barriers. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 103, 33–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakasis, A.; Panitsa, G. Bacteriophage therapy as an alternative treatment for human infections. A comprehensive review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Padmesh, S.; Dwivedi, M.; Kostova, I. How good are bacteriophages as an alternative therapy to mitigate biofilms of nosocomial infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 503–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, B. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: An update on epidemiology, detection and antibiotic resistance. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriol-González, C.; Concha-Eloko, R.; Bernabéu-Gimeno, M.; Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Cañada-García, J.E.; García-Cobos, S.; Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Targeted phage hunting to specific Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates is an efficient antibiotic resistance and infection control strategy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0025424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chegini, Z.; Khoshbayan, A.; Vesal, S.; Moradabadi, A.; Hashemi, A.; Shariati, A. Bacteriophage therapy for inhibition of multi drug-resistant uropathogenic bacteria: A narrative review. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsieh, P.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. Klebsiella phage ΦK64-1 encodes multiple depolymerases for multiple host capsular types. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02457-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha-Eloko, R.; Barberán-Martínez, P.; Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Broad-range capsule-dependent lytic Sugarlandvirus against Kleb Sp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0429822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, S.; Rousseau, G.M.; Labrie, S.J.; Tremblay, D.M.; Kourda, R.S.; Slama, K.B.; Moineau, S. Characterization of two polyvalent phages infecting Enterobacteriaceae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.; Máximo, C.; Costa, P.; Oliveira, V.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Romalde, J.L.; Pereira, C.; Almeida, A. Potential of an isolated bacteriophage to inactivate Klebsiella pneumoniae: Preliminary studies to control urinary tract infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamud, B.; García-González, N.; Gómez-Ortega, M.; González-Candelas, F.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Sanjuan, R. Genetic determinants of host tropism in Klebsiella phages. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letarov, A.V. Bacterial virus forcing of bacterial O-antigen shields: Lessons from coliphages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Calap, P.; Beamud, B.; Mora-Quilis, L.; González-Candelas, F.; Sanjuán, R. Isolation and characterization of two Klebsiella pneumoniae phages encoding divergent depolymerases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha-Eloko, R.; Stock, M.; De Baets, B.; Briers, Y.; Sanjuán, R.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Boeckaerts, D. DepoScope: Accurate phage depolymerase annotation and domain delineation using large language models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1011831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veira, M.; Duarte, J.; Domingues, R.; Oliveira, H.; Dias, O. Phage DPO: Phage Depolymerase Finder. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, D.J.; Skvortsov, T.A. DePolymerase Predictor (DePP): A machine learning tool for the targeted identification of phage depolymerases. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Nong, L.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, D. Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophages, KP1 and KP12, with deep learning-based structure prediction. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 990910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqer, A.A.; Fang, K.; Mohd-Assaad, N.; Adnan, S.N.A.; MdNor, N.S. In vitro activity, stability and molecular characterization of eight potent bacteriophages infecting carbapenem-resistant Kleb pneumoniae. Viruses 2022, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhao, W.; Han, B.; Barkema, H.W.; Niu, Y.D.; Liu, Y.; Kastelic, J.P.; Gao, J. Biological and genomic characteristics of two bacteriophages isolated from sewage, using one multidrug-resistant and one non-multidrug-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 943279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, T.; Virmani, N.; Kumar, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Pavulraj, S.; Bera, B.C.; Vaid, R.K.; Ahlawat, U.; Tripathi, B. Phage therapy for treatment of virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a mouse model. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tao, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X. Isolation and characterization of novel bacteriophage vB_KpP_HS106 for Klebsiella pneumonia K2 and applications in foods. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1227147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Qi, C.; Shi, N.; Gao, X.; Feng, Q.; Qing, H.; Li, F.; Tong, Y. Characterization and genomic analysis of a novel drexlervirial bacteriophage IME268 with lytic activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.J.; Kwon, J.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.J. The Biotechnological application of bacteriophages: What to do and where to go in the middle of the post-antibiotic era. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Guo, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, J. Phage therapy for bone and joint infections: A comprehensive exploration of challenges, dynamics, and therapeutic prospects. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 39, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber-Dąbrowska, B.; Jończyk-Matysiak, E.; Żaczek, M.; Łobocka, M.; Łusiak-Szelachowska, M.; Górski, A. Bacteriophage procurement for therapeutic purposes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S.; Pryer, K.M.; Miao, V.P.; Palmer, J.D. Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Haugaard, A.B.; Babosan, A.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Struve, C.; Decré, D. wzi gene sequencing, a rapid method for determination of capsular type for Klebsiella strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Mazzocco, A.; Waddell, T.E.; Lingohr, E.; Johnson, R.P. Enumeration of bacteriophages by double agar overlay plaque assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 501, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisakhtpour, B.; Mirzaei, A.; Karbasizadeh, V.; Hosseini, N.; Shabani, M.; Moghim, S. The characteristic and potential therapeutic effect of isolated multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii lytic phage. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, F.; Montaseri, M.; Yousefi, M.H.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Berizi, E.; Wagemans, J.; Vallino, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S. Isolation and characterization of two Staphylococcus aureus lytic bacteriophages “Huma” and “Simurgh”. Virology 2024, 595, 110090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Le, S.; Gu, J.; Bao, J.; Qin, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, T. Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 isolates and their interactions with lytic phages. Viruses 2019, 11, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Saffari, M.; Siadat, S.D.; Hejazi, S.H.; Shayestehpour, M.; Motallebi, M.; Eidi, M. Isolation, characterization, therapeutic potency, and genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage vB_KshKPC-M against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains (CRKP) isolated from ventilator-associated pneumoniae (VAP) infection of COVID-19 patients. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; You, X.; Guo, M.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, R.; Li, Y. Characterization and genomic analysis of a broad-spectrum lytic phage HZ2201 and its antibiofilm efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Virus Res. 2023, 335, 199184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senhaji-Kacha, A.; Bernabéu-Gimeno, M.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Seoane-Blanco, M.; Otaegi-Ugartemendia, S.; van Raaij, M.J.; Esteban, J.; García-Quintanilla, M. Isolation and characterization of two novel bacteriophages against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1421724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tynecki, P.; Guziński, A.; Kazimierczak, J.; Jadczuk, M.; Dastych, J.; Onisko, A. PhageAI-bacteriophage life cycle recognition with machine learning and natural language processing. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y. PhaTYP: Predicting the lifestyle for bacteriophages using BERT. Brief Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbac487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. MBE 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, C.; Varsani, A.; Kropinski, A.M. VIRIDIC- A novel tool to calculate the intergenomic similarities of prokaryote-infecting viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yamada, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Ogata, H. DiGAlign: Versatile and interactive visualization of sequence alignment for comparative genomics. Microbes Environ. 2024, 39, ME23061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bacteria | KpTDp1 | KpTDp2 |
|---|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae 704 (clinical strain) | + | + |
| K. pneumoniae 156 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| K. pneumoniae 443 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| K. pneumoniae 636 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| K. pneumoniae 754 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| K. pneumoniae 956 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| K. pneumoniae K2 (reference strain B5055) | + | + |
| K. oxytoca (clinical strain) | + | − |
| P. aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) | − | − |
| P. aeruginosa (clinical strain) | − | − |
| P. putida (clinical strain) | − | − |
| P. aureus (ATCC 29213) | − | − |
| S. aureus (clinical strain) | − | − |
| S. xylosus (clinical strain) | − | − |
| E. coli (ATCC 25922) | − | − |
| E. coli (clinical strain) | − | − |
| S. bongori (clinical strain) | − | + |
| A. baumannii 15277 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| A. baumannii 10783 (clinical strain) | − | − |
| C. freundii (clinical strain) | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mourali, D.; Kazdaghli, R.; Gara-Ali, M.; Ben-Miled, H.; Mora-Quilis, L.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Ben-Mahrez, K. Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Phages Infecting Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae from Tunisia. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121154
Mourali D, Kazdaghli R, Gara-Ali M, Ben-Miled H, Mora-Quilis L, Domingo-Calap P, Ben-Mahrez K. Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Phages Infecting Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae from Tunisia. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(12):1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121154
Chicago/Turabian StyleMourali, Donia, Rahma Kazdaghli, Marwa Gara-Ali, Houda Ben-Miled, Lucas Mora-Quilis, Pilar Domingo-Calap, and Kamel Ben-Mahrez. 2024. "Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Phages Infecting Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae from Tunisia" Antibiotics 13, no. 12: 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121154
APA StyleMourali, D., Kazdaghli, R., Gara-Ali, M., Ben-Miled, H., Mora-Quilis, L., Domingo-Calap, P., & Ben-Mahrez, K. (2024). Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Phages Infecting Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae from Tunisia. Antibiotics, 13(12), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13121154






