Abstract
Precision medicine requires highly sensitive and specific diagnostic strategies with high spatiotemporal resolution. Accurate detection and monitoring of endogenously generated biomarkers at the very early disease stage is of extensive importance for precise diagnosis and treatment. Aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) have emerged as a new type of excellent optical agents, which show great promise for numerous biomedical applications. In this review, we highlight the recent advances of AIE-based probes for detecting reactive species (including reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), reactive sulfur species (RSS), and reactive carbonyl species (RCS)) and related biomedical applications. The molecular design strategies for increasing the sensitivity, tuning the response wavelength, and realizing afterglow imaging are summarized, and theranostic applications in reactive species-related major diseases such as cancer, inflammation, and vascular diseases are reviewed. The challenges and outlooks for the reactive species-activatable AIE systems for disease diagnostics and therapeutics are also discussed. This review aims to offer guidance for designing AIE-based specifically activatable optical agents for biomedical applications, as well as providing a comprehensive understanding about the structure–property application relationships. We hope it will inspire more interesting researches about reactive species-activatable probes and advance clinical translations.
1. Introduction
Precision medicine requires highly sensitive and specific diagnostic methods with high accuracy at the very early disease stage [1,2,3]. Some traditional imaging modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been widely used in clinic [4,5,6]. However, most of them suffer from low sensitivity, and it is usually difficult to recognize tiny pathological changes when the lesion is small [7,8]. Optical imaging techniques such as fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging have significant advantages such as high sensitivity, real-time monitoring, noninvasive imaging, and portable instruments, which are very promising for disease diagnosis and therapy [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Fluorescence has been used for in vitro examination of diseased samples and in vivo image-guided tumor surgery clinically. However, due to interference from the strong light–tissue interaction (e.g., absorption, scattering, and reflection) and autofluorescence, the sensitivity of fluorescence is significantly reduced [15,16]. Therefore, the development of new imaging agents that could improve the therapeutic performance (e.g., recognition of disease-related markers) is highly desirable.
Numerous materials have been used for optical imaging, for example, carbon nanomaterials, metal nanostructures, rare earth-doped nanoparticles (NPs), and organic materials [17,18,19,20,21]. Among them, organic compounds possess unique intrinsic merits including excellent reproducibility, specific chemical structures, and good biocompatibility [22,23,24,25,26]. Currently, small-molecule dyes, i.e., indocyanine green (ICG) and methylene blue (MB) have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical use, highlighting the great clinical translation potential of organic optical materials [27,28,29]. Nevertheless, most conventional organic dyes are planar structures, which face the obstacle of aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) effect in aggregate state due to strong intermolecular interactions (e.g., π-π stacking) [30,31]. The ACQ problem seriously hinders the applications of these hydrophobic molecules in a hydrophilic living environment. In 2001, Tang’s group first coined the the concept of aggregation-induced emission (AIE), representing a new type of optical materials that were weak or non-luminescent in dilute solution, but became highly emissive in aggregate form [32,33,34,35,36,37]. For AIE luminogens (AIEgens), the excited-state energy is consumed by the intensive intramolecular motion through non-radiative decay in solution, while the molecular motion is restricted in aggregate form, thus, the non-radiative pathway is closed and the radiative process is open (Figure 1) [38,39,40,41,42]. As a result, restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM) is considered to be the working principle of the AIE phenomenon, and a library of AIEgens with various properties have been developed [43,44,45,46]. AIEgens have been used in many areas such as optoelectronic devices, chemo/biosensing, and biological imaging [47,48,49,50]. In the biomedical field, AIEgens have shown excellent performance in organelle imaging, in vivo high-resolution imaging, disease theranostics, and activatable detection [51,52,53,54,55].
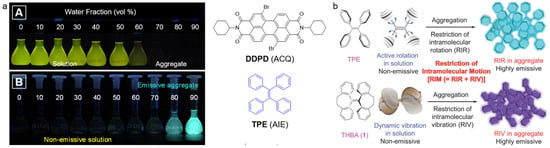
Figure 1.
(a) Photographs of ACQ and AIE molecules in the mixture of water/THF with different water fractions under 365 nm of UV light irradiation (reproduced with the permission from Ref. [40]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society); (b) schematic illustration of RIM mechanism, including restriction of intramolecular rotation and restriction of intramolecular vibration. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [39]. Copyright 2014, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim).
Excessive expression of various reactive species can lead to oxidative stress, which is known to cause DNA, protein, cell, and tissue damage, and affect signaling pathways [56,57,58]. These processes are closely associated with many diseases including inflammation, cancers, diabetes, and neurodegeneration diseases [59,60,61,62]. Thus, accurate detection and monitoring of these endogenously generated biomarkers is extensively important for precise disease diagnostics and therapeutics at an early stage [63,64,65]. According to their nature, reactive species can be divided into reactive oxygen species (ROS) including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hypochlorite/hypochlorous acid (HOCl/ClO−), hydroxyl radical (•OH), superoxide anion radical (O2•−), singlet oxygen (1O2), and peroxy radical (ROO•); reactive nitrogen species (RNS) including nitric oxide (NO), peroxynitrite (ONOO−), S-nitrosothiol (RSNO), and S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO); reactive sulfur species (RSS) including hydrogen sulfide (H2S), thiyl radical (RS), thiol (RSH), S-nitrosothiol, sulfenic acid, and sulfite; reactive carbonyl species (RCS) including carbon monoxide (CO), formaldehyde (FA), glyoxal (GO), acrolein, and glucosone [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. Reactive species have gained great interest from both fundamental biological scientists and clinical doctors, and more and more new phenomena about their functions have been discovered [76,77,78]. Numerous molecular probes for detecting ROS, RNS, RSS, and RCS have been exploited, focusing on understanding the physiological/pathological effects and disease theranostics [79,80,81,82,83,84]. Recently, the development of reactive species-responsive AIEgens has attracted considerable attention, which are advantageous for applications in the biomedical field [85,86,87,88].
Thanks to the salient merits of good stability, large Stokes shift, facile structure modification, and excellent sensitivity, AIEgens have emerged as a new type of potent probes for detecting various reactive species. Although there are many review papers that have focused on AIEgens [89,90,91,92,93,94], to the best of our knowledge, comprehensive summaries of reactive species-responsive AIEgens are very rare. In this review, we highlight the recent advances of AIEgen-based reactive species-activatable systems. The recent development of AIEgens for sensing reactive species such as ROS, RNS, RSS, and RCS are discussed. The molecular design strategies for increasing sensitivity, tuning the response wavelength, increasing the afterglow imaging efficiency, as well as different biomedical applications are reviewed. The challenges and outlooks for the reactive species-activatable AIE systems for biomedical applications are also discussed. This review aims to provide guidance for the development of activatable optical imaging agents with maximum disease biomarker recognition capability to improve the diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes of related biomedical applications. It provides a comprehensive understanding about the activatable molecular probe from molecular design, to probe property and biomedical applications, and thus, build the structure–property application relationships.
2. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Nitrogen Species
When designing a specific chemical/biological probe, a usually requisite is to synthesize molecules with specific recognition groups or moieties. The typical chemical structures of some reactive oxygen nitrogen species (RONS)-responsive AIEgens are listed in Figure 2. The boronate subunit is a popularly used building block for H2O2 sensors, as the boronate cage is nonfluorescent and the conversion of arylboronates to phenols results in turn-on emission [95,96,97]. The deprotonated H2O2 is a potent nucleophile, which can attack the boron center to generate a labile borate species that hydrolyses to the corresponding phenol [98]. For O2•− detection, the diphenyl phosphinyl group can be introduced into an organic compound, in which the fluorescence is strongly quenched at first, and obvious turn-on fluorescent signal is realized in the presence of O2•− [99,100]. The oxidative properties of ClO− can be utilized to destroy C=C or C=N bonds rapidly, therefor, the conjugation of fluorescence quencher through C=C or C=N bonds has turned out to be an efficient strategy to construct ClO− probes [101,102]. Some arylboronate groups, diphenylphosphinate groups, and nitrophenyloxoacetamide moieties have been employed as the response substitutes for ONOO− detection [103,104,105]. The tunability of molecular structure will alter the photophysical properties and biomedical applications as well.
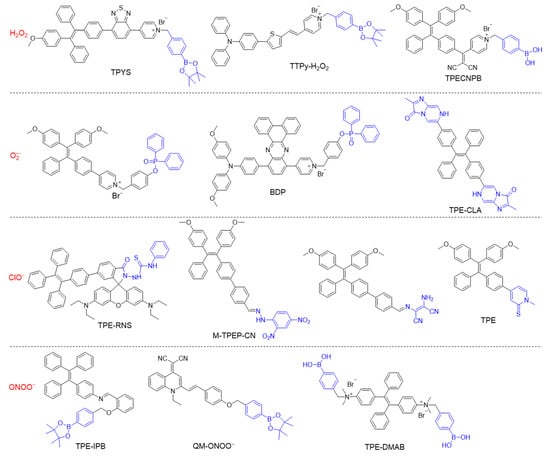
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of different types of RONS-responsive molecules.
H2O2 is an overexpressed molecule in many serious diseases, and thus, it is regarded as a pivotal biomarker for some biological processes and disease diagnoses [106,107,108]. A variety of H2O2-activatable probes have been exploited based on AIEgens, which exhibit excellent performance for both in vitro and in vivo applications [109,110,111,112]. Xia and Lou et al. developed a H2O2-responsive AIEgen for peroxidase-mediated selective imaging and inhibition of inflammatory cells [113]. As shown in Figure 3, the probe consisted of a TPE core and two tyrosine (Tyr) moieties, which could undergo enzyme-catalyzed dityrosine formation in the presence of peroxidase and H2O2. By conjugating two hydrophilic Tyr groups, the hydrophobic TPE molecule became hydrophilic TT, which showed weak fluorescence in aqueous solution due to the excited-state energy consumption via intense molecular motion. As a result, the H2O2-responsive and myeloperoxidase (MPO)-mediated TT self-assembly enabled turn-on fluorescence, which could be used for selectively imaging and inhibiting inflammatory cells containing overexpressed H2O2 and MPO. The AIE process could be activated through dityrosine linkage-induced hydrophobic aggregates formation, which helped to distinguish between inflammatory and normal cells. Additionally, the in situ formation of TT aggregates could inhibit RAW264.7 cell growth through inducing mitochondria damage and cell apoptosis.
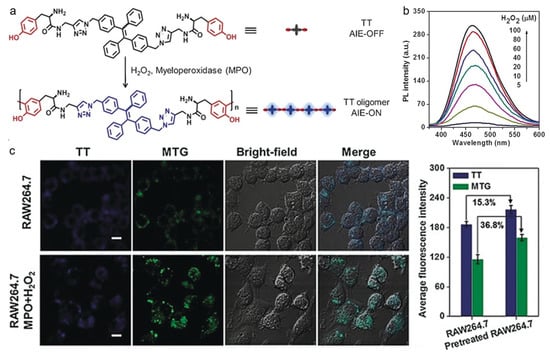
Figure 3.
(a) Peroxidase-catalyzed polymerization in the presence of H2O2; (b) PL spectra of TT with the treatment of different concentrations of H2O2; (c) CLSM images and corresponding fluorescence intensity of RAW264.7 cells pretreated without and with MPO and H2O2 incubating with TT. Scale bars: 20 µm. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [113]. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim).
Wang and Li et al. reported a ROS-responsive theranostic nanoplatform for accurate diagnosis and therapy of inflammation diseases [114]. As depicted in Figure 4, a two-photon AIEgen (TP) was conjugated with the widely used anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid, prednisolone (Pred) with the ROS-sensitive linkage to afford the compound TPP. Then, the TPP was encapsulated with an amphiphilic block copolymer PMPC−PMEMA (PMM) to give polymeric micelles (TPP@PMM). Noteworthy, the PMEMA part served as the hydrophobic block in the NPs formation, which could be oxidized in response to ROS to yield the hydrophilic sulphone product. The ROS-triggered hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic conversion was able to realize ROS-mediated drug delivery at an inflammatory site. This shell-core dual ROS-responsive nanoplatform was used in three different inflammatory murine models including acute lung injury, atherosclerosis, and arthritis. The deep-penetration two-photon fluorescence diagnosis and efficient serial ROS sensitive anti-inflammation could be used for both acute and chronic inflammation theranostics. Two-photon imaging with the AIEgen helped to provide unambiguous delineation of inflammatory tissue with minimum autofluorescence interference. Moreover, TPP@PMM also possessed excellent anti-inflammatory effect that reduced the inflammatory response and decreased inflammatory cytokines expression.
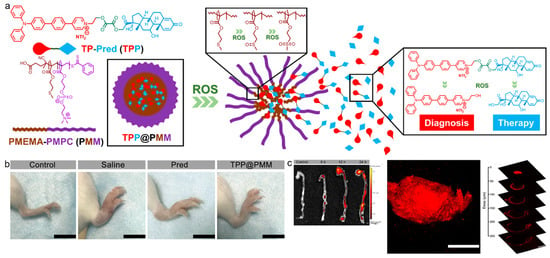
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic of the theranostic nanoplatform with serial ROS response; (b) photographs of the hind limbs from arthritic mice with different treatments; (c) two-photon fluorescence imaging of aortas, atherosclerotic plaques, and plaques. Scale bars: 200 μm. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [114]. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society).
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is an emerging biomedical imaging modality that originates from the thermoelastic expansions of light-absorption chromophores generating ultrasound signal [115,116,117]. PA imaging possesses the merits of good penetration depth and excellent spatial resolution, which has complementary advantages with fluorescence technique, thus, integration of PA imaging and fluorescence could greatly improve the diagnostic outcome [118,119]. Qu, Feng, and coworkers reported an activatable system for dual-modal imaging-guided PDT and self-reporting therapeutic process [120]. As displayed in Figure 5, the nanoplatform was composed of an AIEgen with ROS-recognition phenylboronate moiety and a photosensitizer ZnPc. Due to the ACQ effect, ZnPc in NPs was non-emissive with low PDT efficiency and strong PA signals, which could monitor the tumors’ locations with reduced phototoxicity. When ZnPc was gradually released from the NPs, its fluorescence and ROS generation property could be recovered, which was capable of reporting the release process. Upon light irradiation, the ROS generated by ZnPc could induce cell apoptosis and activate the AIE-based ROS probe, serving as an indicator of ROS production. Moreover, as the side product of AIEgens, quinone methide (QM) could deplete GSH in cancer cells, which enhanced the PDT effect. In vitro and in vivo experiments both revealed that this intelligent platform enabled highly efficient and accurate PDT of tumors. The activatable theranostic nanoprobe could eliminate the phototoxicity of conventional photosensitizer and provide clinicians with guidance about detailed disease information, as well as therapeutic process and outcome, rendering great promise for individual therapy and precision medicine.
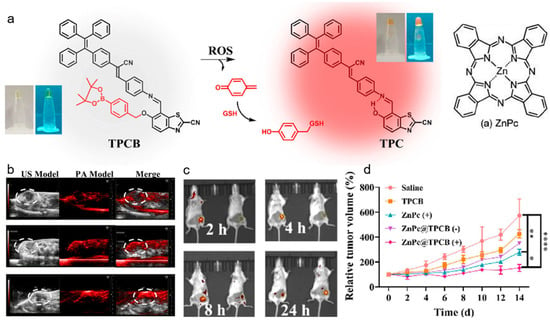
Figure 5.
(a) Chemical structure and the ROS-activatable process of TPCB probe; (b) in vivo ultrasound and PA and (c) fluorescence imaging of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice after injecting the nanoprobe; (d) tumor growth curves of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice with different treatments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [120]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society).
Wu, Tian, and Zeng et al. reported a ROS-activatable multifunctional nanosystem for liver and kidney inflammation diagnosis and therapy through modulating inflammatory pathways [121]. As presented in Figure 6, an AIEgen was linked with a Nrf2 activator fisetin through boronate bond, in which the fluorescence would be quenched and the boronate bond could be cleaved by ROS. This probe was co-encapsulated with a NF-kB inhibitor thalidomide, and macrophage cell membrane was employed as the coating to ensure effective target and accumulation in the inflammatory sites. In the lipopolysaccharides (LPS)/D-galactosamine (D-GalN)-induced acute liver injury/inflammation mouse model, the nanoprobe could actively target the inflammatory site and the boronate bonds could be cleaved by the overexpressed ROS, therefore, activating the near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence and PA signal for precisely imaging liver/kidney inflammatory diseases and the released drugs were able to treat acute liver inflammation through activation of the Nrf2 pathway and suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway with moderate suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome formation. The fluorescence and PA imaging were capable of monitoring the therapeutic process as well.
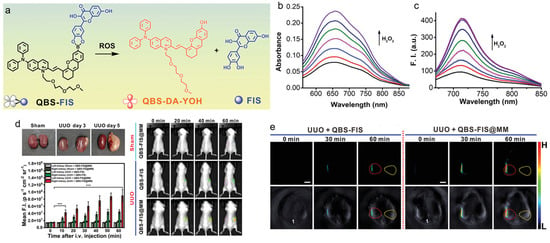
Figure 6.
(a) Chemical structure and ROS response of the theranostic probe; (b) absorption and (c) PL spectra of QBS-FIS with the treatment of different concentrations of H2O2; (d) fluorescence and (e) PA imaging of the sham-surgery and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) mice with different treatments. *** p ≤ 0.001. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [121]. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH).
Although a conventional NIR region (NIR-I, 700–900 nm) is considered to be a transparent biological window, it is still very difficult to realize high-resolution in vivo imaging. The recently emerging second NIR (NIR-II, 1000–1700 nm) window exhibits great promise for bioapplications as it possesses significantly reduced light–tissue interaction and enables large-depth and high-resolution imaging in a living body [122,123,124,125,126]. Zhao and Wu et al. reported on a H2O2-activatable AIE nanoprobe for sensitive disease diagnosis via NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging [127]. As displayed in Figure 7, the low-bandgap D-A compound consisted of two TPE groups that would result in AIE feature and increased conjugation, and two nitrophenyloxoacetamide moieties that could be cleaved in the presence of H2O2. The probe was nonfluorescent because the strong electron-withdrawing nitrophenyl group quenched the emission, but significant NIR-II fluorescence could be observed after the H2O2-inducing nitrobenzene cleavage. In the presence of H2O2, the maximal absorption of AIE nanoprobe shifted from 615 nm to 680 nm, and pronounced NIR-II fluorescence with a peak at 938 nm and a shoulder peak at 1028 nm was also obtained, which enabled NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging of H2O2-overexpressed diseases. After intravesically injecting into the interstitial cystitis mice, the AIE probe realized H2O2-activatable NIR-II fluorescence in the bladder, with 3D PA imaging to locate the bladder inflammation. In vivo experiments in trazodone-induced liver injury mice and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury mice also showed excellent diagnostic performance, indicating that the nanoprobe was a robust tool for detecting and imaging H2O2-related diseases with NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging.
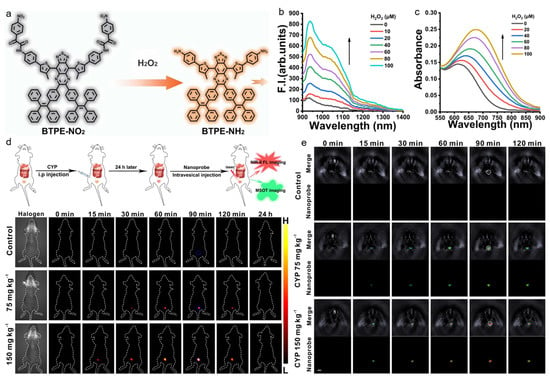
Figure 7.
(a) The AIE probe for H2O2 detection; (b) PL and (c) absorption spectra of BTPE-NO2 with the treatment of different concentrations of H2O2; (d) NIR-II fluorescence and (e) PA imaging of interstitial cystitis mice with different treatments at designed time points after administration. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [127]. Copyright 2021, The Authors).
Chemiluminescence (CL) is a revolutionized imaging technique for in vivo monitoring of biospecies in which the signal contrast and sensitivity can be significantly increased since the light emission is initiated by a chemical reaction with minimal autofluorescence interference [128,129,130,131]. However, most traditional CL emitters are dependent on the generation of unstable and short-lived emitting species, making the photons release uncontrollable, and dynamic biological imaging difficult [132,133]. Guo and coworkers reported on a sequential dual-lock photoactivatable chemiluminescent AIE probe for bright optical imaging [134]. As shown in Figure 8, for the first lock, the caging group was triggered and removed by the analyte, generating pre-chemiluminophores with twisting intramolecular charge transfer (TICT) property; for the second lock, the electron-rich double bond was activated by light for in situ generation of 1,2-dioxetane, accompanied with enhanced CL signal. As compared with traditional dioxetane-based one-lock CL probe, this type of dual-lock probe containing dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran (DCM) fluorophore displayed nearly 10-fold higher signal. The authors further constructed a probe based on AIEgen of quinoline-malononitrile (QM) unit, which displayed remarkably bright CL signal. After intratumorally injecting into xenograft 4T1 tumor-bearing mice, the nanoprobe showed gradually increased tumor microenvironment H2O2-activatable CL signal and realized an ultra-high S/N ratio 74 times higher than the background, in which the CL intensity was around 66-fold higher than that of typically used luminol emitter.
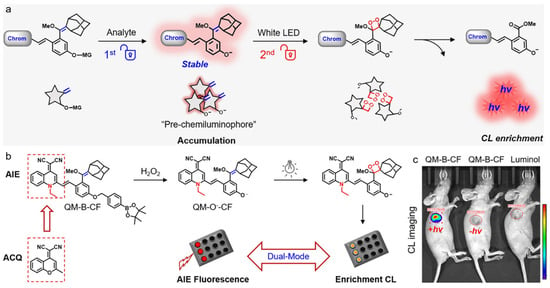
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic of the dual-lock probe triggered sequentially by analyte and light for CL imaging; (b) the reaction processes of AIE-based dual-lock probe QM-B-CF; (c) in vivo imaging of 4T1 xenograft tumor-bearing mice after intratumor injection of QM-B-CF or luminol. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [134]. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim).
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a clinically used method for treating some cancers, which is based on a light-triggered photosensitizer to generate ROS, especially the highly toxic 1O2 [135,136,137]. To monitor the in situ generation of 1O2 during PDT in real time is of comparative significance for tumor therapy and reduced side effects. Liu and coworkers reported on a self-reporting AIE probe for real-time monitoring of 1O2 generation and targeted PDT [138]. As depicted in Figure 9, the probe was constructed by conjugating a red emissive AIEgen and a rhodol dye with green fluorescence through 1O2-cleavable aminoacrylate (AA) linker. The probe TPETP-AA-Rho-cRGD emitted red fluorescence at first, whereas strong green fluorescence from rhodol could be observed upon image-guided light irradiation as the AA linker was cleaved by the photogenerated 1O2, which could be used for real-time and in situ monitoring of 1O2 production during PDT. After incubating with MDA-MB-231 cells followed by light irradiation for different periods of time, the green fluorescence from the probe intensified with time as more 1O2 was produced, and there was nearly no fluorescence in the cells treated with 1O2 scavenger ascorbic acid (Asc). These results indicated that the probe was capable of efficiently reporting the generated 1O2 concentration. The green fluorescence from the probe matched well with the red fluorescence from propidium iodide (PI), which demonstrated that the probe could be used to report 1O2 generation and predict the therapeutic effect in real time.
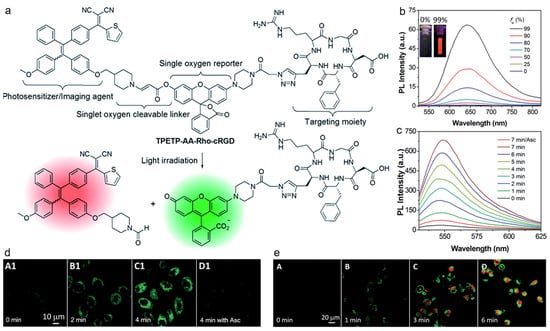
Figure 9.
(a) Schematic illustration of TPETP-AA-RhocRGD for self-reporting 1O2 detection; (b) photoluminescence of TPETP in DMSO/water mixture with different water fractions; (c) photoluminescence spectra of the probe under light irradiation at different time points; (d,e) CLSM images of MDA-MB-231 cells incubated with the probe under light irradiation at different time points as indicated. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [138]. Copyright 2016, The Royal Society of Chemistry).
O2•− is regarded as the primary ROS in the living body, the overproduction of which causes oxidative stress and disruption of the redox balance [139,140]. Thereby, precise detection of entogenous O2•− is of critical significance for understanding related diseases. Hua and coworkers reported on a NIR emission AIE probe for O2•− detection (Figure 10a,b) [141]. They synthesized a D-A-type compound with methoxy-substituted triphenylamine and dibenz[a,c]-phenazine as the D and A moieties, respectively, which showed maximal emission in the NIR region of longer than 700 nm and a large Stokes shift, and the diphenyl-phosphinyl group was linked as it could be cleaved by O2•−. The BDP probe exhibited weak emission, whereas the fluorescence was intensified in the presence of O2•−, which enabled good sensitivity and selectivity. The probe was first incubated with HepG2 cells, which were then treated with exogenous O2•− producer such as LPS, L-buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), generating very strong NIR fluorescence. Tang’s group developed an AIE probe for endogenous O2•− detection with turn-on fluorescence/CL imaging [142]. As shown in Figure 10c, the probe was synthesized by conjugating TPE with imidazopyrazinone (CLA), which was a well-established recognition group to O2•−. In the presence of O2•−, the CLA unit was oxidized to form a dioxetanone that decomposed to generate a singlet-excited amide, which then decayed to the ground state with concomitant CL emission and fluorescence as well. TPE-CLA was a highly sensitive probe to O2•− with low detection limits of 0.21 nM for fluorescence and 0.38 nM for CL. In the Raw264.7 cells pretreated with PBS (control), Tiron (a scavenger of O2•−), and PMA (a stimulator of O2•−), two-photon imaging of TPE-CLA with 800 nm excitation showed weak fluorescence in the control group, negative fluorescence in the Tiron group, and very bright fluorescence in the PMA group, which suggested that the probe was capable of detecting the endogenously stimulated O2•− and also capable of imaging native O2•− in living cells. In the LPS-induced acute inflammation model, TPE-CLA displayed rather strong CL signal, while the luminescence was quenched by mixing with Tiron, which demonstrated that the probe could be used as a specific O2•− biosensor in vivo.
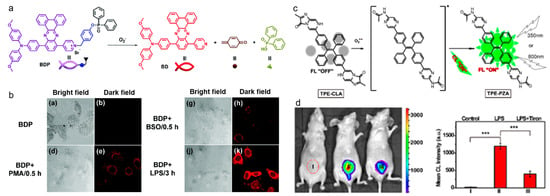
Figure 10.
(a) Chemical structure of BDP and the O2•−-activatable process; (b) CLSM imaging of HepG2 cells with different treatments (reproduced with the permission from Ref. [141]. Copyright 2018, The Royal Society of Chemistry); (c) chemical structure and the O2•−-response mechanism; (d) in vivo CL images and corresponding imaging intensity of LPS-induced inflammation in mice. *** p < 0.001. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [142]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society).
The excessive expression of ONOO− is an important feature of many major diseases such as cancer, diabetes, cardiopathy, Alzheimer’s disease, and acute and chronic inflammation [143,144,145]. Consequently, the specific detection of ONOO− is momentous for diagnosing these diseases and monitoring the therapeutic process. Tang and Ding et al. reported on an AIE-based probe for ONOO− detection and related inflammation imaging in living mice [146]. As shown in Figure 11, the phenylboronic ester in TPE-IPB was cleaved when treating with ONOO−, and the hydrogen bond formed in the product TPE-IPH led to bright fluorescence with a peak at 538 nm. The probe exhibited good selectivity toward ONOO− over other species such as H2O2, O2•−, •OH, ROO•, ClO−, and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP). After intravenous injection into living mice, the AIE nanoprobe showed selective turn-on fluorescence in the inflammatory region with elevated ONOO− production. In addition, the probe could also help to precisely and noninvasively monitor the in vivo therapeutic efficacy of antiinflammatory agents. After subcutaneously inoculating MRSA and Escherichia coli (E. coli) at different sides of nude mice, the inflammation-bearing mouse model with different infections was built. The AIE probe could clearly distinguish the inflammation-bearing mice with vancomycin for treating MRSA-caused infections or penicillin for treating E. coli-caused infections.
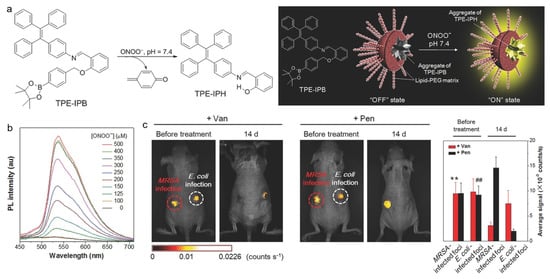
Figure 11.
(a) TPE-IPB probe for ONOO− detection with turn-on fluorescence; (b) PL spectra of TPE-IPB with the treatment of different concentrations of ONOO−; (c) in vivo fluorescence images and the corresponding fluorescence intensity of the mice infected with MRSA at left and E. coli at right before and after vancomycin and penicillin treatment. ** p < 0.01, in comparison between MRSA-infected foci before and after vancomycin treatment for 14 d; ## p < 0.01, in comparison between E. coli-infected foci before and after penicillin treatment for 14 d. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [146]. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim).
Recently, Ding’s group reported on an AIEgen with ONOO− and pH dual-responsive afterglow luminescence for neutrophil-involved diseases applications [147]. As depicted in Figure 12, an AIEgen and a Schaap’s dioxetane-based agent was mixed into one system to realize NIR afterglow luminescence, which could be triggered by both ONOO− and surrounding pH value. The working principle of this nanosystem was as follows: The AIEgen could produce 1O2 under light exposure, which oxidized the enol ether structure to four-membered 1,2-dioxetane with no phenylborate protection; the disease site-overexpressed ONOO− could cleave the phenylborate group to afford unstable dioxetane intermediate, and then emit persistent green luminescence; the energy transfer between the excited-state four-membered 1,2-dioxetane compound and AIEgen led to bright NIR afterglow luminescence for specific afterglow imaging of disease sites. The activatable nanoprobe possessed 553-fold enhancement in emission intensity upon the treatment of ONOO−, while it showed little response to other species such as H2O2, O2•−, •OH, ROO•, ClO−, and TBHP. Noteworthy, th—ONOO−-activated afterglow signal possessed a pH-dependent manner, as the intensity was very high at pH 7.0−7.4 and intensely decreased in low pH. As both ONOO− generation and acid environment were closely related to the inflammation processes, the ONOO− and pH dual-response characteristics allowed for precise inflammation imaging. The NIR afterglow luminescence of the nanoplatform could last for 14 days and achieve a high SBR of 29 with coverage of 10 mm chicken breast issues. In the LPS-induced acute skin inflammation of BALB/c mice, the nanoprobe dissolved in 5× PBS (pH 7.4) exhibite—ONOO−-activated afterglow luminescence and the intensity reached a maximum with a SBR of 461.3 at about 2 h. In the mouse model with ovalbumin-induced allergic skin disease in the left ear and LPS-induced acute inflammation in the right ear, very strong activated afterglow luminescence from the preirradiated probe was observed in the LPS-treated ear skin, but the afterglow signal was still in the “off” state in the allergic ear, which was due to the significant difference in infiltration of neutrophils and accumulation of ONOO− between the two disease models. Immunogenic cell death (ICD) represents a promising cell demise mode with a signature of immunostimulatory damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) emission and transformation from an environmental cold tumor to a hot tumor, during which neutrophils as the first innate immune responders are recruited into the tumor bed and promote the proliferation of CD8+ T cells in antitumor immunity. This probe was able to report the levels of infiltrating neutrophils and ONOO− generation in vivo, being beneficial for screening the ICD drugs in a fast and real-time manner.
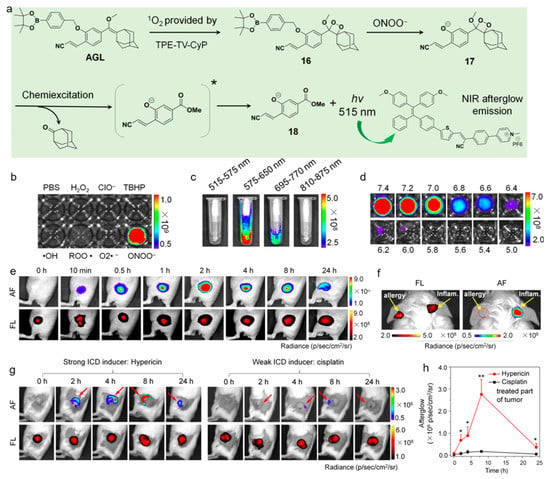
Figure 12.
(a) Chemical structures and working mechanism of the ONOO− and pH dual-response afterglow luminescence; (b) selectivity of the nanoprobe with various ROS treatments; afterglow intensity of the nanoprobe (c) in different spectral regions and (d) different pH environments; (e) fluorescence and afterglow images of the acute inflammation after injecting the preirradiated nanoprobe at different time points; (f) fluorescence and afterglow images of the mouse with allergic left ear and inflammatory right ear; (g) fluorescence and afterglow images of the 4T1 tumor-bearing mice at different time points after receiving PDT with hypericin or cisplatin treatment and (h) corresponding afterglow intensity. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [147]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society).
3. Detection of Gasotransmitters
Small gaseous molecules including NO, CO, and H2S, function as important signal transmitters in living systems as they are associated with many biological functions and major diseases [148,149,150,151]. NO is a neutral diatomic free radical that is produced from L-arginine by NO synthase (NOSs) isoforms such as neuronal NOS (nNOS), inducible NOS (iNOS), and endothelial NOS (eNOS) [152,153]. CO is the second gasotransmitter that is generated as a byproduct of haem cleavage by two distinct haem oxygenases [154]. H2S is predominantly formed from Cys or its derivatives by the enzymes cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase [155]. All these gasotransmitters play vital roles in vasorelaxation and inflammatory responses, thus, numerous molecular probes have been developed for precise monitoring of related diseases [156,157,158]. For example, the o-diamino aromatic moiety is a recognition group for NO, and the cyclization reaction of o-diamine with NO produces a triazole moiety, which alters the electronic property and conjugation nature [159,160,161]. For H2S detection, the popularly used approaches include reduction of azides into amines and nucleophilic addition of H2S to the electrophilic group [162,163]. Some representative AIEgens for sensing gasotransmitters are listed Figure 13, which show great potential for applications in biological imaging and disease diagnosis.
Figure 13.
Chemical structures of different types of gasotransmitter-responsive molecular probes.
Wu’s group developed a NO-activatable AIEgen for precisely diagnosing herbal medicine-induced liver injury with NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging [164]. As presented in Figure 14, they designed and synthesized a D-π-A-type probe (QY-N) consisting of an electron-rich bismethoxyphenyl-amine-containing dihydroxanthene group and an electron-deficient quinolinium moiety. The linking of electron-donating butylamine to the quinolinium group weakened the electron-accepting capability, and thus, quenched the fluorescence, and butylamine also served as a NO-responsive group based on the N-nitrosation reaction of aromatic secondary amine. In the presence of NO, the electron-donating butylamine was transformed into an electron-withdrawing butyl-N-nitroso group, which resulted in a bathochromic shift of absorption in the range of 700–850 nm for PA imaging, and boosted NIR-II fluorescence at 910–1110 nm. The AIE probe was able to detect and assess the severity of herbal medicine-induced liver injury in vivo in a high-contrast manner for significantly enhanced NIR-II fluorescence and PA signals via reacting with the overexpressed NO at a disease site. In addition, the probe was also capable of monitoring the rehabilitation of liver injury during the treatment process.
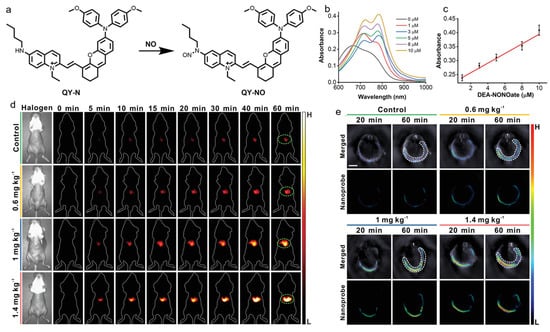
Figure 14.
(a) The response of QY-N towards NO; (b) absorption spectra and (c) intensity at 780 nm of QY-N with the treatment of different concentrations of DEA·NONOate; (d) NIR-II fluorescence and (e) PA imaging of liver injury mice intravenously injected with the nanoprobe QY-N at different time points. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [164]. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH).
Recently, Wu and Zeng et al. developed an activatable nanoprobe with AIE feature for detecting NO with NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging [165]. As displayed in Figure 15, the o-phenylenediamino group was incorporated as the core because it could react with NO, and two phenylnaphthalenamine moieties were conjugated to function as the electron donors and endow AIE characteristic. Then, the FDA-approved 2-hydroxypropyl-b-cyclodextrin (HβCD) was incorporated through the formation of a host–guest supramolecular complex to ensure good water dispersibility and biocompatibility without sacrificing NO responsivity. The resultant BNDA–HβCD complex was able to self-assemble into nanoaggregates in aqueous media, which displayed very weak absorption and fluorescence in the NIR spectral region. While, in the presence of NO, the o-phenylenediamino moiety reacted with NO to yield a triazole group, which greatly enhanced the electron-withdrawing capability and afforded strong absorption at 650–850 nm for PA imaging and fluorescence at 900–1100 nm for NIR-II imaging. By reacting with the disease-overexpressed NO, the nanoprobe was successfully applied for detecting and imaging liver injuries and monitoring the therapeutic outcome through activatable NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging. Moreover, the nanoprobe was also capable of detecting and tracking endogenous NO in soybean sprouts.
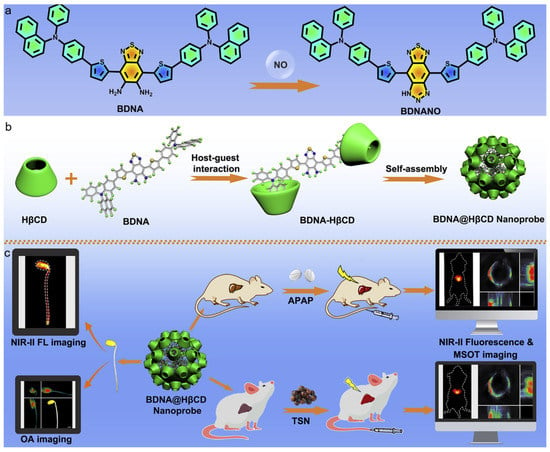
Figure 15.
(a) The mechanism of BDNA for NO detection; (b) the formation of host–guest supramolecular complex BNDA–HβCD and the nanoprobe; (c) the BNDA@HβCD nanoprobe for in vivo NIR-II fluorescence and PA imaging of liver injury and detecting NO in soybean sprouts. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [165]. Copyright 2021, The Authors).
High concentrations of CO (>35 ppm) cause high toxicity to living bodies, while this type of gas with low concentration is recognized as a biological regulator [166,167]. For example, CO can modulate inflammatory responses, promote neovascular growth, and prevent vascular dysfunction and tissue ischemia [168]. Therefore, the sensitive detection of CO is critically important for monitoring the related biological processes. Wang and coworkers developed an AIEgen-based probe (BTCV-CO) for CO detection and visualization [169]. As displayed in Figure 16, the allyl group in the BTCV-CO probe could be removed via CO treatment ([Ru(CO)3Cl2]2 (CORM-2) was used as the CO donator) to generate the phenolate intermediate, which underwent rapid cyclization and afforded the benzithiazolyl iminocoumarin (BTIC) product with bright fluorescence. During this process, a new fluorescence peak appeared at 546 nm, and the emission at long wavelength declined. As a result, the ratiometric response of I546/I710 displayed 39-fold enhancement, and the detection limit of CO was calculated to be as low as 30.8 nM. BTCV-CO also exhibited good selectivity as it showed no response toward other interfering species such as ClO−, GSH, H2S, H2O2, HNO, and Br−. The BTCV-CO probe could image CO sensitively in both CORM-2-treated cells and living mice.
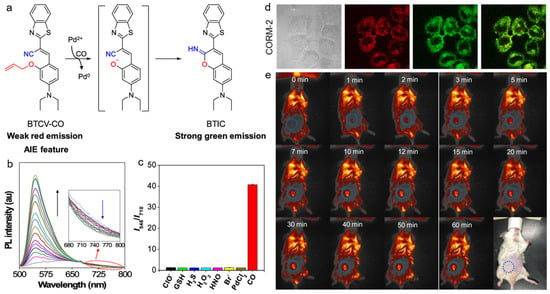
Figure 16.
(a) The mechanism of AIE-based probe for CO detection; (b) PL spectra of BTCV-CO probe incubated with different concentrations of CORM-2; (c) PL intensity ratios (I546/I710) of BTCV-CO with the treatment of various biomolecules; (d) CL images of MCF-7 cells incubated with the probe; (e) in vivo fluorescence imaging of CO with the probe. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [169]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society).
Tang and coworkers reported an AIEgen probe for detecting H2S [170]. As described in Figure 17a, the D-A compound was synthesized using tetraphenylpyrazine (TPP) as D, and malonitrile group as A. In the presence of H2S, the malonitrile was oxidized to a thiol intermediate, which underwent self-coupling to produce a dimer. During this process, the D–A interaction was destroyed, which resulted in a blue shift in the emission wavelength. The probe could be used for specific and sensitive H2S detection. Wu and Zeng et al. developed a fluorescent probe with both AIE and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) characteristics for H2S detection (Figure 17b–f) [171]. Due to the strong electron-withdrawing property of the nitrobenzene group, the fluorescence of the probe was remarkably quenched. While in the presence of H2S, the nitrophenyl moiety was cleaved, and ESIPT feature occurred, thereby, the fluorescence intensified. The probe was formulated into water-dispersible NPs, which showed fast response and excellent selectivity toward H2S over many other reactive species. In vitro experiments in HeLa cells revealed that the nanoprobe was capable of detecting the exogenous and endogenous H2S. For zebrafish pretreated with the nanoprobe, there was no fluorescence in the untreated fish, while strong green fluorescence was observed in the fish incubated with NaHS-containing (NaHS was used as the H2S donor) media. Except for the detection of various ROS, RNS, RSS, and RCS, AIEgens have also been utilized for monitoring other disease-associated biomarkers such as pH, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), glutathione (GSH), β-galactosidase, hypoxia, etc. [172,173,174,175,176]. Due to limited space, we do not discuss these in this review.
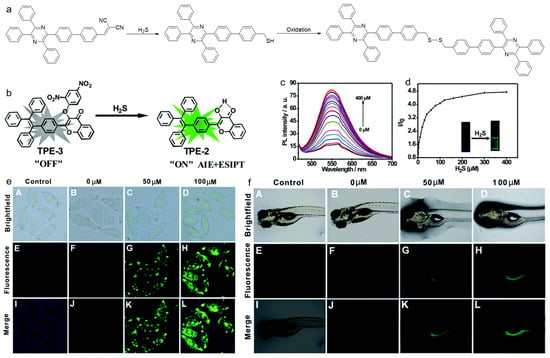
Figure 17.
(a) The proposed reaction process of TPP-PDCV for detecting H2S; (b) the AIE probe for H2S detection with turn-on fluorescence; (c) PL spectra and (d) the corresponding PL intensity ratio of the AIE probe treated with different concentrations of H2S; Fluorescence imaging of (e) HeLa cells and (f) zebrafish larvae treated with different concentrations of H2S. (Reproduced with the permission from Ref. [171]. Copyright 2016, The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Chinese Chemical Society).
4. Summary
In this review, we highlight the recent advances of AIE-based probes for detecting reactive species (including ROS, RNS, RSS, and RCS) and related biomedical applications. The molecular design approaches for constructing activatable AIEgens are summarized, and their applications in monitoring major diseases such as cancer, inflammation, and vascular diseases are also discussed. These types of probes turn out to be highly efficient for sensitive detection and precise disease theranostics. Future development can be focused on several aspects. First, the absorption and PL wavelengths of the reported AIE probes are relatively short, in which the unsatisfied penetration depth would limit in vivo applications. A bathochromic shift of the response region to a long-wavelength NIR-II region by tuning molecular structure would be beneficial for real applications. Second, the response of molecular probe in aggregate usually decreases as compared with the solution state, therefore, there is still some room to improve the response time and selectivity of AIE probes. For example, to design an AIE probe that is soluble in water at first and forms an aggregate after reacting with specific reactive species, would increase the sensitivity, and also realize turn-on fluorescence by making full use of AIE feature. Third, the afterglow-based detection imaging has a great advantage for bioimaging as it does not need external light excitation. Therefore, the activatable-afterglow AIE probe is favorable for high-contrast biosensing and diagnosis. Moreover, although reactive species play a key role in modulating many biological processes and diseases, and a number of probes have been developed, the real applications are still very rare. For future clinical transformation, biocompatibility as well as improved detection specificity and sensitivity should be carefully considered. Reactive species are important biomarkers for many diseases, yet they may not be the specific criterion for pathological changes and their abnormity may not be related to a specific disease as well. Thus, the combination of reactive species-based imaging and other diagnostic approaches would increase the disease theranostic precision. This review aims to offer guidance for designing AIE-based specifically activatable optical agents for biomedical applications, as well as provide a comprehensive understanding about the structure–property application relationships. We hope it will inspire more interesting research on reactive species-activatable probes and advance the clinical translations.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing, X.K., W.L. and J.Q.; literature collection, X.K., Y.L., S.Y. and J.Q.; editing, supervision, and funding acquisition, W.L. and J.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the NSFC (82172081, 82102200, and 52103168), the CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine (2021-I2M-1-043), and the Tianjin Applied Basic Research Multi-input Fund (21JCZDJC00970).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Park, S.M.; Aalipour, A.; Vermesh, O.; Yu, J.H.; Gambhir, S.S. Towards clinically translatable in vivo nanodiagnostics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letai, A. Functional precision cancer medicine–moving beyond pure genomics. Nat. Med. 2016, 23, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, E.A. Towards precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R. Scaling down imaging: Molecular mapping of cancer in mice. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, J.K.; Bruggen, N.V.; Dinkelborg, L.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Molecular imaging in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolson, F.; Kircher, M.F.; Stone, N.; Matousek, P. Spatially offset Raman spectroscopy for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumova, A.V.; Modo, M.; Moore, A.; Murry, C.E.; Frank, J.A. Clinical imaging in regenerative medicine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, D.A.; Al-Shimmari, H.A.T.; Radhi, M.M. Use of MgCl2 Nanoparticles as Alternative Contrast Media in Magnatic Resonance Imaging Molecular Imaging and Analyzed by Voltammetric Technique. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2020, 12, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V.; Yao, J. A practical guide to photoacoustic tomography in the life sciences. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, S.; Degtyaruk, O.; Mc Larney, B.; Rebling, J.; Hutter, M.A.; Deán-Ben, X.L.; Shoham, S.; Razansky, D. Rapid volumetric optoacoustic imaging of neural dynamics across the mouse brain. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yan, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Manipulating cell fate: Dynamic control of cell behaviors on functional platforms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8639–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.-S.; Min, T.; Li, Y.; Zha, M.; Zhang, P.; Ho, L.; Li, K. Planar AIEgens with enhanced solid-state luminescence and ROS generation for multidrug-resistant bacteria treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10179–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q. Advanced Fluorescence Imaging Technology in the Near-Infrared-II Window for Biomedical Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14789–14804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Peng, S.; Yu, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, W.; Ye, Z.; Qi, J.; Feng, Z.; Qian, J. Hot-Band-Absorption-Induced Anti-Stokes Fluorescence of Aggregation-Induced Emission Dots and the Influence on the Nonlinear Optical Effect. Biosensors 2021, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Xu, K.; Dai, Z. Current trends and key considerations in the clinical translation of targeted fluorescent probes for intraoperative navigation. Aggregate 2021, 2, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; del Rosal, B.; Jaque, D.; Uchiyama, S.; Jin, D. Advances and challenges for fluorescence nanothermometry. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Piper, J.A.; Zhang, F. Lifetime-engineered NIR-II nanoparticles unlock multiplexed in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, S. Emerging contrast agents for multispectral optoacoustic imaging and their biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7924–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, C.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Lei, Z.; Gao, W.; Blake, S.; De, D.; et al. Capturing functional two-dimensional nanosheets from sandwich-structure vermiculite for cancer theranostics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, N.; Li, M.; Sun, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-enhanced theranostics: AIE sparkles in biomedical field. Aggregate 2020, 1, 80–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Koo, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M.; Lu, S.; et al. Versatile types of inorganic/organic NIR-IIa/IIb fluorophores: From strategic design toward molecular imaging and theranostics. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 209–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Fang, Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Ding, D.; Tang, B.Z. Highly Stable Organic Small Molecular Nanoparticles as an Advanced and Biocompatible Phototheranostic Agent of Tumor in Living Mice. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7177–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Si, J.; Mou, X.; Dong, X. All-in-One Nanomedicine: Multifunctional Single-Component Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics. Small 2021, 17, 2103072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bhattarai, P.; Dai, Z.; Chen, X. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2053–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, J.; Pu, K.; James, T.D. Dual-locked spectroscopic probes for sensing and therapy. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, X.; Xu, F.; Kwok, R.T.K.; et al. Facilitation of molecular motion to develop turn-on photoacoustic bioprobe for detecting nitric oxide in encephalitis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antaris, A.L.; Chen, H.; Cheng, K.; Sun, Y.; Hong, G.; Qu, C.; Diao, S.; Deng, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. A small-molecule dye for NIR-II imaging. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Dai, W.; Chen, D.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Peng, Q.; Xie, H.; Cai, Z.; et al. Rational design of pyrrole derivatives with aggregation-induced phosphorescence characteristics for time-resolved and two-photon luminescence imaging. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P. Organic small molecule-based photothermal agents for cancer therapy: Design strategies from single-molecule optimization to synergistic enhancement. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2022, 464, 214564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Cheng, W.; Yuan, Q.; Müllen, K.; Yin, M. From Dyestuff Chemistry to Cancer Theranostics: The Rise of Rylenecarboximides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fang, M.; Li, Z. Organic luminescent materials: The concentration on aggregates from aggregation-induced emission. Aggregate 2020, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1, 2, 3, 4, 5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Fundamental understanding and future developments. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Tang, B.Z. AIE-based cancer theranostics. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2020, 402, 213076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Li, K. Recent Advances in AIEgen-Based Photodynamic Therapy and Immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, T.; Xie, Y.; Su, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, Q.; Jing, J.; Zhang, R.; Niu, G.; Zhang, X. In Vitro Light-Up Visualization of a Subunit-Specific Enzyme by an AIE Probe via Restriction of Single Molecular Motion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10003–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: New vistas at the aggregate level. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9888–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Tang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: The Whole Is More Brilliant than the Parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Liu, B. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Dots: Emerging Theranostic Nanolights. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, R.; Xu, Y.; Dang, D.; Shen, Q.; Meng, L.; Tang, B.Z. Seeing the unseen: AIE luminogens for super-resolution imaging. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ni, J.-S.; Li, Y.; Zha, M.; Tu, Y.; Li, K. Acceptor Engineering for Optimized ROS Generation Facilitates Reprogramming Macrophages to M1 Phenotype in Photodynamic Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Sun, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Zebibula, A.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Xi, W.; Zhu, L.; Cai, F.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen with Near-Infrared-II Excitation and Near-Infrared-I Emission for Ultradeep Intravital Two-Photon Microscopy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7936–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Min, T.; Gong, J.; Du, L.; Phillips, D.L.; Liu, J.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Williams, I.D.; et al. Time-Dependent Photodynamic Therapy for Multiple Targets: A Highly Efficient AIE-Active Photosensitizer for Selective Bacterial Elimination and Cancer Cell Ablation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9470–9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Meng, F.; Luo, L. Mitochondrion-Anchored Photosensitizer with Near Infrared-I Aggregation-Induced Emission for Near Infrared-II Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.; Chen, T.; Ghahfarokhi, A.J.; Tang, Y. AIEgen-enhanced protein imaging: Probe design and sensing mechanisms. Aggregate 2021, 2, e41. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Nie, H.; Zeng, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Gan, S.; Cai, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, S.-J.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Highly Efficient Nondoped OLEDs with Negligible Efficiency Roll-Off Fabricated from Aggregation-Induced Delayed Fluorescence Luminogens. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12971–12976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ji, W.; Dang, D.; Meng, L.; Tang, B.Z. Recent advances in luminescent materials for super-resolution imaging via stimulated emission depletion nanoscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Yue, Q.; Chen, S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Luo, L.; Tang, B.Z. Near-Infrared AIE Dots with Chemiluminescence for Deep-Tissue Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Fan, K.; Hong, Y.; Raston, C.L.; Tang, Y. In situ monitored vortex fluidic-mediated protein refolding/unfolding using an aggregation-induced emission bioprobe. Molecules 2021, 26, 4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Liu, B. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Recent Advances in Materials and Biomedical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9868–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Ou, H.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D. Gathering brings strength: How organic aggregates boost disease phototheranostics. Aggregate 2021, 2, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, R.; Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yin, P.; Situ, B.; Zhan, C.; et al. An AIE-Active Conjugated Polymer with High ROS-Generation Ability and Biocompatibility for Efficient Photodynamic Therapy of Bacterial Infections. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9952–9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; He, S.; Zheng, J.; Yang, B.; Qin, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Semiconducting Polymer Dots with Dual-Enhanced NIR-IIa Fluorescence for Through-Skull Mouse-Brain Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3691–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Cui, T.; Yao, S.; Jin, S.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, R.; et al. Golgi apparatus-targeted aggregation-induced emission luminogens for effective cancer photodynamic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Deep, G.; Singh, R.K.; Palle, K.; Yadav, U.C.S. Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, E.; Liu, Z.; Cao, F.; Chen, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Biomimetic nanoflowers by self-assembly of nanozymes to induce intracellular oxidative damage against hypoxic tumors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wijaya, A.; Liu, B.; Maruf, A.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Liao, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, G. ROS-responsive biomimetic nanoparticles for potential application in targeted anti-atherosclerosis. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wei, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Chang, J. Mitochondria-targeted nanoparticles in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanghathaipornsuk, S.; Farrell, E.J.; Alba-Rubio, A.C.; Zelenay, P.; Kim, D.-S. Detection Technologies for Reactive Oxygen Species: Fluorescence and Electrochemical Methods and Their Applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Zhao, Y. Engineered Hybrid Nanoparticles for On-Demand Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 3016–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ding, S.; Wang, S.; Shi, Z.; Pandey, N.K.; Chudal, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. Endogenous tumor microenvironment-responsive multifunctional nanoplatforms for precision cancer theranostics. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2021, 426, 213529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Sargaz, S.; Pandey, S.; Kang, M. Recent Advances in Nanotechnology-Based Diagnosis and Treatments of Human Osteosarcoma. Biosensors 2021, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S signalling through protein sulfhydration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2012, 13, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Pu, K. Molecular Probes for Autofluorescence-Free Optical Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13086–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y. Recent advances in multifunctional fluorescent probes for viscosity and analytes. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, B. Small-Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Imaging and Detection of Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species in Biological Systems. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Li, Q.; Lv, Y. Small molecule-based bioluminescence and chemiluminescence probes for sensing and imaging of reactive species. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Jiang, F.; Hong, Z.; Su, X.; Li, S.; Han, S. Activatable Dual ROS-Producing Probe for Dual Organelle-Engaged Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 4618–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-J.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, L.; Duan, C.; Yuan, Q.; Long, Z.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. Recent advances in stimuli-responsive theranostic systems with aggregation-induced emission characteristics. Aggregate 2021, 2, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Nanozyme for tumor therapy: Surface modification matters. Exploration 2021, 1, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.H.M.M.; Zhu, X.; Qin, J.; Tang, Y. Microalgae-Derived Health Supplements to Therapeutic Shifts: Redox-Based Study Opportunities with AIE-Based Technologies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, J.I.; Uranga, J.; Matxain, J.M. Computational Study on the Attack of •OH Radicals on Aromatic Amino Acids. Chem.-Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6862–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Gutierrez, C.; Bonora, N.; Bobo-Jimenez, V.; Jimenez-Blasco, D.; Lopez-Fabuel, I.; Fernandez, E.; Josephine, C.; Bonvento, G.; Enriquez, J.A.; Almeida, A.; et al. Astrocytic mitochondrial ROS modulate brain metabolism and mouse behaviour. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, A.; Dor, Y.K.; Nambara, K.; Pollina, E.A.; Lin, C.; Greenberg, M.E.; Rogulj, D. Sleep Loss Can Cause Death through Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Gut. Cell 2020, 181, 1307–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardeni, T.; Tanes, C.E.; Bittinger, K.; Mattei, L.M.; Schaefer, P.M.; Singh, L.N.; Wu, G.D.; Murdock, D.G.; Wallace, D.C. Host mitochondria influence gut microbiome diversity: A role for ROS. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaw3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Xu, W.; Gong, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Design Strategy of Fluorescent Probes for Live Drug-Induced Acute Liver Injury Imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, W.; Lu, M.; Qu, A.; Hao, C.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; et al. Ultrasmall Magneto-chiral Cobalt Hydroxide Nanoparticles Enable Dynamic Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species in Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; He, H.; Wang, S.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, F. ROS/RNS and Base Dual Activatable Merocyanine-Based NIR-II Fluorescent Molecular Probe for in vivo Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26337–26341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Rao, J.; Pu, K. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Dong, M.; Yao, S.Q.; Tang, B. Fluorescent probes for visualizing ROS-associated proteins in disease. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11620–11646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.Y.; Zhang, C.; Dong, X.; Yao, S.Q. Recent advances in polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 17797–17809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission luminogens for activity-based sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Zhang, R.; Shi, X.; Park, H.; Xie, S.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. AIE luminogens as fluorescent bioprobes. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kim, H.; Han, J.; Nguyen, V.-N.; Peng, X.; Yoon, J. Activity-based smart AIEgens for detection, bioimaging, and therapeutics: Recent progress and outlook. Aggregate 2021, 2, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Biomarker-activatable probes based on smart AIEgens for fluorescence and optoacoustic imaging. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2022, 458, 214438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Bioprobes based on AIE fluorogens. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Tang, B.Z. AIE luminogens for bioimaging and theranostics: From organelles to animals. Chem 2017, 3, 56–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, D.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens: Union Is Strength, Gathering Illuminates Healthcare. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Turley, A.T.; Wang, L.; McGonigal, P.R.; Tu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; et al. Aggregate science: From structures to properties. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Supramolecular materials based on AIE luminogens (AIEgens): Construction and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1144–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.; Dodani, S.C.; Chang, C.J. Reaction-based small-molecule fluorescent probes for chemoselective bioimaging. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-N.; Ha, J.; Cho, M.; Li, H.; Swamy, K.M.K.; Yoon, J. Recent developments of BODIPY-based colorimetric and fluorescent probes for the detection of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and cancer diagnosis. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2021, 439, 213936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Gu, X.; Zhang, P.; Lai, Q.; Wang, J. Lipid droplet-targetable fluorescence guided photodynamic therapy of cancer cells with an activatable AIE-active fluorescent probe for hydrogen peroxide. Adv. Optical Mater. 2020, 8, 2001119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.W.; Tulyathan, O.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Chang, C.J. Molecular imaging of hydrogen peroxide produced for cell signaling. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Feng, G.; Manghnani, P.N.; Hu, F.; Jiang, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.Z.; Tang, B.Z. A two-channel responsive fluorescent probe with AIE characteristics and its application for selective imaging of superoxide anions in living cells. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, B. Versatile Fluorescent Probes for Imaging the Superoxide Anion in Living Cells and In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4216–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Sun, H. An ultra-sensitive ratiometric fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid detection by the synergistic effect of AIE and TBET and its application of detecting exogenous/endogenous HOCl in living cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5125–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z. Designing Squaraine Dyes with Bright Deep-Red Aggregation-Induced Emission for Specific and Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of Hypochlorite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mao, D.; Cai, X.; Duan, Y.; Hu, F.; Kong, D.; Liu, B. ONOO− and ClO− Responsive Organic Nanoparticles for Specific in Vivo Image-Guided Photodynamic Bacterial Ablation. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3867–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, C.; Lai, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Tang, B.Z. An easily available ratiometric AIE probe for peroxynitrite in vitro and in vivo imaging. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 329, 129223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, W.; Zhang, D.; Ye, Y. A novel activatable AIEgen fluorescent probe for peroxynitrite detection and its application in EC1 cells. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 321, 128510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liew, S.S.; Wei, X.; Pu, K. Hemicyanine-Based Near-Infrared Activatable Probes for Imaging and Diagnosis of Diseases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 26454–26475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassalle, C.; Maltinti, M.; Sabatino, L. Targeting oxidative stress for disease prevention and therapy: Where do we stand, and where do we go from here. Molecules 2020, 25, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xu, H.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. ROS Responsive Nanoplatform with Two-Photon AIE Imaging for Atherosclerosis Diagnosis and “Two-Pronged” Therapy. Small 2020, 16, 2003253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Huang, F.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. Rapid-Response Fluorescent Probe for Hydrogen Peroxide in Living Cells Based on Increased Polarity of C−B Bonds. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9825–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Cao, D. An interface-targeting and H2O2-activatable probe liberating AIEgen: Enabling on-site imaging and dynamic movement tracking of lipid droplets. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 4491–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wu, W.; Ji, S.; Chen, C.; Hu, F.; Kong, D.; Ding, D.; Liu, B. Chemiluminescence-Guided Cancer Therapy Using a Chemiexcited Photosensitizer. Chem 2017, 3, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, L.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Nanoprobe for Detecting Hydrogen Peroxide in Inflammation and Ischemic Kidney Injury. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Dai, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, R.; Zhai, T.; Lou, X.; Xia, F. An Intracellular H2O2-Responsive AIEgen for the Peroxidase-Mediated Selective Imaging and Inhibition of Inflammatory Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3123–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Xu, H.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Reactive Oxygen Species Responsive Theranostic Nanoplatform for Two-Photon Aggregation-Induced Emission Imaging and Therapy of Acute and Chronic Inflammation. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5862–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: In vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Jokerst, J.V.; Mei, J.; Gambhir, S.S.; Bao, Z.; Rao, J. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as photoacoustic molecular imaging probes in living mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Beard, P.C.; Bohndiek, S.E. Contrast agents for molecular photoacoustic imaging. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Ji, S.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Ding, D.; Tang, B.Z. Light-driven transformable optical agent with adaptive functions for boosting cancer surgery outcomes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Liu, D.; Ding, D.; Tang, B.Z. Boosting fluorescence-photoacoustic-Raman properties in one fluorophore for precise cancer surgery. Chem 2019, 5, 2657–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Luo, R.; Zhu, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, F.; Feng, F.; Qu, W. An Activatable Theranostic Nanoprobe for Dual-Modal Imaging-Guided Photodynamic Therapy with Self-Reporting of Sensitizer Activation and Therapeutic Effect. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5366–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, F.; Tian, M.; Wu, S. A Targeted Nanosystem for Detection of Inflammatory Diseases via Fluorescent/Optoacoustic Imaging and Therapy via Modulating Nrf2/NF-κB Pathways. Small 2021, 17, 2102598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Diao, S.; Chang, J.; Antaris, A.L.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Atochin, D.N.; Huang, P.L.; Andreasson, K.I.; et al. Through-skull fluorescence imaging of the brain in a new near-infrared window. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Antaris, A.L.; Dai, H. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, O.T.; Bischof, T.S.; Harris, D.K.; Franke, D.; Shi, Y.; Riedemann, L.; Bartelt, A.; Jaworski, F.B.; Carr, J.A.; Rowlands, C.J.; et al. Next-generation in vivo optical imaging with short-wave infrared quantum dots. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Sun, C.; Zebibula, A.; Zhang, H.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Zhao, X.; Xi, W.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qian, J.; Tang, B.Z. Real-Time and High-Resolution Bioimaging with Bright Aggregation-Induced Emission Dots in Short-Wave Infrared Region. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Qi, J.; Tang, B.Z.; Qian, J.; Lin, H. Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Nanoparticles-Assisted NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Diagnosis and Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Y. A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, M.; Fdez. Galván, I.; Ding, B.-W.; Schramm, S.; Berraud-Pache, R.; Naumov, P.; Ferré, N.; Liu, Y.-J.; Navizet, I.; Roca-Sanjuán, D.; et al. Chemi- and Bioluminescence of Cyclic Peroxides. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6927–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, H.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Ren, X.; Wang, S. Luminescent, Oxygen-Supplying, Hemoglobin-Linked Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles for Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10660–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, C.; Miao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Pu, K. A generic approach towards afterglow luminescent nanoparticles for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Zheng, H.-L.; Xue, X.-S.; Ding, D. Near-Infrared Afterglow Luminescent Aggregation-Induced Emission Dots with Ultrahigh Tumor-to-Liver Signal Ratio for Promoted Image-Guided Cancer Surgery. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, B.; Pu, K.; Xu, F.-J. Chemiluminescence: From mechanism to applications in biological imaging and therapy. Aggregate 2021, 2, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Ji, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ou, H.; Gao, Z.; Feng, G.; Ding, D. Activatable Persistent Luminescence from Porphyrin Derivatives and Supramolecular Probes with Imaging-Modality Transformable Characteristics for Improved Biological Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, W.-H. A sequential dual-lock strategy for photoactivatable chemiluminescent probes enabling bright duplex optical imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9059–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, J.F.; Liu, T.W.B.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Activatable Photosensitizers for Imaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2839–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, G.-Q.; Ding, D. Design of superior phototheranostic agents guided by Jablonski diagrams. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8179–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Jia, S.; Kang, X.; Wu, X.; Hong, Y.; Shan, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D. Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles with Surface-Mimicking Protein Secondary Structure as Lysosome-Targeting Chimaeras for Self-Synergistic Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Xu, S.; Liu, B. A self-reporting AIE probe with a built-in singlet oxygen sensor for targeted photodynamic ablation of cancer cells. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Chuang, C.-C.; Wu, S.; Zuo, L. Reactive oxygen species in redox cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Su, D.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Tang, B. Oxidative Damage of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-2 Mediated by Peroxisomal Superoxide Anion Radical in Brains of Mouse with Depression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20735–20743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Tan, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Qu, X.; Hua, J. A turn-on near-infrared fluorescence probe with aggregation-induced emission based on dibenzo [a,c]phenazine for detection of superoxide anions and its application in cell imaging. Analyst 2018, 143, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, X.; Jiao, X.; Sun, C.; Tang, B. Simultaneous Fluorescence and Chemiluminescence Turned on by Aggregation-Induced Emission for Real-Time Monitoring of Endogenous Superoxide Anion in Live Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7210–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, K.; Shuhendler, A.J.; Rao, J. Semiconducting Polymer Nanoprobe for In Vivo Imaging of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10325–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Pu, K. Activatable Molecular Probes for Second Near-Infrared Fluorescence, Chemiluminescence, and Photoacoustic Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11717–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, L.; Gong, J.; Xiong, J.; Zi, S.; Xie, H.; Zhang, F.; Mao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Kim, J.S. An Activity-Based Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Fluctuations of Peroxynitrite (ONOO−) in the Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206894. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Mao, D.; Sung, S.H.P.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kong, D.; Ding, D.; Tang, B.Z. Activatable Fluorescent Nanoprobe with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Selective In Vivo Imaging of Elevated Peroxynitrite Generation. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7249–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gao, H.; Ou, H.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Ding, D. Amplification of Activated Near-Infrared Afterglow Luminescence by Introducing Twisted Molecular Geometry for Understanding Neutrophil-Involved Diseases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3429–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatalin, K.; Shatalina, E.; Mironov, A.; Nudler, E. H2S: A Universal Defense Against Antibiotics in Bacteria. Science 2011, 334, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, C. Gasotransmitters in cancer: From pathophysiology to experimental therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Bhalla, V.; Kumar, M. Recent developments of fluorescent probes for the detection of gasotransmitters (NO, CO and H2S). Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2335–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku-Damoah, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ta, H.T.; Xu, Z.P. Therapeutic gas-releasing nanomedicines with controlled release: Advances and perspectives. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Gladwin, M.T.; Weitzberg, E. Strategies to increase nitric oxide signalling in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Shang, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, N. Cu∥-loaded polydopamine coatings with in situ nitric oxide generation function for improved hemocompatibility. Regen. Biomater. 2020, 7, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Matson, J.B. Gasotransmitter delivery via self-assembling peptides: Treating diseases with natural signaling gases. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2017, 110–111, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Polhemus, D.J.; Lefer, D.J. Evolution of hydrogen sulfide therapeutics to treat cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Qing, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Yang, R. Ratiometric Visualization of NO/H2S Cross-Talk in Living Cells and Tissues Using a Nitroxyl-Responsive Two-Photon Fluorescence Probe. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Fan, J.; Du, J.; Peng, X. Small-molecule fluorescent probes for imaging gaseous signaling molecules: Current progress and future implications. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 5127–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Ren, N.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, R.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; et al. Probing the Intracellular Dynamics of Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide Using an Activatable NIR II Fluorescence Reporter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8450–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, B.; Tian, W. Silica nanoparticles based on an AIE-active molecule for ratiometric detection of RNS in vitro. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 9197–9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xie, M.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Y.; Yao, S.; He, T.; Ye, C.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Huang, W.; et al. Nitric oxide activatable photosensitizer accompanying extremely elevated two-photon absorption for efficient fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, M.Y.; East, A.K.; Reinhardt, C.J.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Su, S.; Lee, M.C.; Chan, J. Development of NIR-II photoacoustic probes tailored for deep-tissue sensing of nitric oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7196–7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, V.S.; Chen, W.; Xian, M.; Chang, C.J. Chemical probes for molecular imaging and detection of hydrogen sulfide and reactive sulfur species in biological systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4596–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Mazur, F.; Fan, Q.; Chandrawati, R. Synthetic nanoprobes for biological hydrogen sulfide detection and imaging. View 2022, 3, 20210008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ouyang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. An Activatable Probe with Aggregation-Induced Emission for Detecting and Imaging Herbal Medicine Induced Liver Injury with Optoacoustic Imaging and NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. Refashioning benzothiadiazole dye as an activatable nanoprobe for biomarker detection with NIR-II fluorescence/optoacoustic imaging. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, R. Carbon monoxide: Endogenous production, physiological functions, and pharmacological applications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 585–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lee, S.; Xu, Z.; Yoon, J. Recent Progress on the Development of Chemosensors for Gases. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7944–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulak, J.; Deshane, J.; Jozkowicz, A.; Agarwal, A. Heme Oxygenase-1 and Carbon Monoxide in Vascular Pathobiology. Circulation 2008, 117, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X.; Shi, M.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, G.; Tang, B.Z. An Easily Available Ratiometric Reaction-Based AIE Probe for Carbon Monoxide Light-up Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9388–9392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Qin, A.; et al. Malonitrile-Functionalized Tetraphenylpyrazine: Aggregation-Induced Emission, Ratiometric Detection of Hydrogen Sulfide, and Mechanochromism. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Nie, X.; Gao, M.; Zeng, F.; Qin, A.; Wu, S.; Tang, B.Z. A highly selective fluorescent nanoprobe based on AIE and ESIPT for imaging hydrogen sulfide in live cells and zebrafish. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, T.; Yan, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.-X.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Visualization of Biogenic Amines and In Vivo Ratiometric Mapping of Intestinal pH by AIE-Active Polyheterocycles Synthesized by Metal-Free Multicomponent Polymerizations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Huang, J.; Zeng, F.; Wu, S. A Fluorescent Probe with Aggregation-Induced Emission for Detecting Alkaline Phosphatase and Cell Imaging. Chem.-Asian J. 2019, 14, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Du, T.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; et al. Highly selective discrimination of cysteine from glutathione and homo-cysteine with a novel AIE-ESIPT fluorescent probe. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 325, 128786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zeng, G.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Tang, B.Z. A selective and light-up fluorescent probe for β-galactosidase activity detection and imaging in living cells based on an AIE tetraphenylethylene derivative. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4505–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zou, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Williams, I.D.; Tang, B.Z. A New Strategy toward “Simple” Water-Soluble AIE Probes for Hypoxia Detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).