Effect of Elevated Temperature on Physical Activity and Falls in Low-Income Older Adults Using Zero-Inflated Poisson and Graphical Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Observation and Hypothesis
1.4. Contributions
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Zero-Inflated Poisson (ZIP) Regression
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode for Zero-Inflated Poisson (ZIP) Regression |
| Input: Data matrix , response vector Output: Parameter estimates and |
2.3.2. Mixed Undirected Graphical Model (MUGM)
- Continuous variables: Daily outdoor temperature, MVPA, SB, age, and fall incidents.
- Categorical variables: Gender, race/ethnicity, education level, living condition, financial difficulty, and self-rated health.
| Algorithm 2 Pseudocode for Mixed Undirected Graphical Model (MUGM) |
| Input: A dataset features X, including both continuous and categorical variables Output: Estimated undirected graph
|
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Results
4.2. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EBIC | Extended Bayesian Information Criterion |
| LOAs | Low-income older adults |
| LPA | Light-intensity physical activity |
| MVPA | Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity |
| MUGM | Mixed undirected graphical model |
| PA | Physical activity |
| RR | Relative risk |
| SB | Sedentary behavior |
| ZIP | Zero-inflated Poisson |
References
- Gamble, J.L.; Balbus, J.; Berger, M.; Bouye, K.; Campbell, V.; Chief, K.; Conlon, K.; Crimmins, A.; Flanagan, B.; Gonzalez-Maddux, C.; et al. Ch 9: Populations of Concern. In The Impacts of Climate Change on Human Health in the United States: A Scientific Assessment; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, P.D.; Marlon, J.R.; Wang, X.; Leiserowitz, A. Public perceptions of the health risks of extreme heat across US states, counties, and neighborhoods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6743–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Capon, A.; Berry, P.; Broderick, C.; de Dear, R.; Havenith, G.; Honda, Y.; Kovats, R.S.; Ma, W.; Malik, A.; et al. Hot weather and heat extremes: Health risks. Lancet 2021, 398, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S. The Convergence of Population Ageing with Climate Change. Popul. Ageing 2019, 12, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, A.G.; Gonzalez, D.J.X.; Cushing, L.J. Racial Disparities in Climate Change-Related Health Effects in the United States. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronlund, C.J. Racial and socioeconomic disparities in heat-related health effects and their mechanisms: A review. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2014, 1, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prina, M.; Khan, N.; Khan, S.A.; Caicedo, J.C.; Peycheva, A.; Seo, V.; Sadana, R. Climate change and healthy ageing: An assessment of the impact of climate hazards on older people. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, R.D.; Akerman, A.P.; Notley, S.R.; McGinn, R.; Poirier, P.; Gosselin, P.; Kenny, G.P. Physiological factors characterizing heat-vulnerable older adults: A narrative review. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worfolk, J.B. Heat waves: Their impact on the health of elders. Geriatr. Nurs. 2000, 21, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, L.; Rasiah, R.L.; Laing, R.; Thompson, S.C. Considerations in Planning Physical Activity for Older Adults in Hot Climates: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Gillespie, W.J.; Sherrington, C.; Gates, S.; Clemson, L.M.; Lamb, S.E. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD007146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.; Kwok, W.; Wallbank, G.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Howard, K.; Clemson, L.; Hopewell, S.; Lamb, S.E. Evidence on physical activity and falls prevention for people aged 65+ years: Systematic review to inform the WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Vasconez, A.S.; Linke, S.; Muñoz, M.; Pekmezi, D.; Ainsworth, C.; Cano, M.; Williams, V.; Marcus, B.H.; Larsen, B.A. Promoting Physical Activity Among Underserved Populations. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2016, 15, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papalia, G.F.; Papalia, R.; Diaz Balzani, L.A.; Torre, G.; Zampogna, B.; Vasta, S.; Fossati, C.; Alifano, A.M.; Denaro, V. The Effects of Physical Exercise on Balance and Prevention of Falls in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaud, M.; Bloch, F.; Tournoux-Facon, C.; Brèque, C.; Rigaud, A.S.; Dugué, B.; Kemoun, G. Impact of physical activity and sedentary behaviour on fall risks in older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.M.; Gaynanova, I. Sensing the impact of extreme heat on physical activity and sleep. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241241509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, A.; O’Neill, M.S.; Gronlund, C.J.; Schwartz, J.D. Susceptibility to Mortality in Weather Extremes: Effect Modification by Personal and Small-Area Characteristics. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y.; Lee, H.; Chang, V.W. Cumulative exposure to extreme heat and trajectories of cognitive decline among older adults in the USA. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2023, 77, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somta, S.; Völker, M.; Widyastari, D.A.; Mysook, S.; Wongsingha, N.; Potharin, D.; Katewongsa, P. Willingness-to-pay in physical activity: How much older adults value the community-wide initiatives programs? Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1282877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastl, C.; Arnberger, A.; Gallistl, V.; Stein, V.K.; Dorner, T.E. Heat vulnerability: Health impacts of heat on older people in urban and rural areas in Europe. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2024, 136, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalopoulou, C.; Stubbs, B.; Kralj, C.; Koukounari, A.; Prince, M.; Prina, A.M. Physical activity and healthy ageing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 38, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Lam, H.Y.C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Goggins, W.B.; Mo, P.K.H.; Chan, E.Y.Y. Factors affecting outdoor physical activity in extreme temperatures in a sub-tropical Chinese urban population: An exploratory telephone survey. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, J.H.; Willard, A.; Edwards, J.R.; Harhay, M.N.; Schinasi, L.H.; Matthews, J.; May, N. Time Series Analysis: Associations Between Temperature and Primary Care Utilization in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 67, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.Y.; Goggins, W.B.; Mo, P.K.H.; Chan, E.Y.Y. The effect of temperature on physical activity: An aggregated time-series analysis of smartphone users in five major Chinese cities. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X. Zero-inflated Smoothing Spline (ZISS) Models for Individual-level Single-cell Temporal Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.15309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, L.; Shi, K.; Wu, Y.; Lin, S.; Fang, Y. Interpretable Machine Learning for Fall Prediction Among Older Adults in China. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 65, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Cooray, U.; Hariyama, M.; Aida, J.; Kondo, K.; Murakami, M.; Osaka, K. An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach to Predict Fall Risk Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Three-Year Longitudinal Study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Garikipati, A.; Shokouhi, S.; Hurtado, M.; Barnes, G.; Hoffman, J.; Calvert, J.; Katzmann, L.; Mao, Q.; Das, R. Predicting Falls in Long-term Care Facilities: Machine Learning Study. JMIR Aging 2022, 5, e35373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, M.; Moulton, B.D.; Su, S.W.; Celler, B.G.; Nguyen, H.T. Unsupervised machine-learning method for improving the performance of ambulatory fall-detection systems. BioMed. Eng. Online 2012, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Arif, W.; Hung Nguyen, Q.; Trung Le, T.; Van Pham, H. Picture Fuzzy Directed Hypergraphs With Applications Toward Decision-Making and Managing Hazardous Chemicals. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 87816–87827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Liang, W.; Zou, F. A novel approach for estimating multi-attribute Gaussian copula graphical models. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2025, 222, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiamwong, L.; Kim, D.; Xie, R.; Emrich, C.; Zhong, Y.; Crook, J.; Hawthorne, T. Climate-creative Communities to Promote Physical Activity and Health Equity in Low-Income Settings. Innov. Aging 2024, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.L.; Preisser, J.S.; Herring, A.H.; Golin, C.E. A Marginalized Zero-Inflated Poisson Regression Model with Overall Exposure Effects. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 5151–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilder, C.R.; Loughin, T.M. Analysis of Categorical Data with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.L.; Ory, M.G. Multi-directional nature of falls among older adults: A rationale for prevention and management. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Shan, H.H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.J.; Liu, S.G.; Lin, F. Graph modeling of relational structures among functioning variables with low back pain: An exploratory analysis based on International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 60, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqui, S.H.A.; Alaeddini, A.; Chang, M.C.; Shirinkam, S.; Jaramillo, C.; NajafiRad, P.; Wang, J.; Pugh, M.J. Summarizing Complex Graphical Models of Multiple Chronic Conditions Using the Second Eigenvalue of Graph Laplacian: Algorithm Development and Validation. JMIR Med. Inform. 2020, 8, e16372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Thiamwong, L.; Lou, Q.; Xie, R. Unveiling Fall Triggers in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Graphical Model Analysis. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2019 Poverty Guidelines. 2019. Available online: https://aspe.hhs.gov/topics/poverty-economic-mobility/poverty-guidelines/prior-hhs-poverty-guidelines-federal-register-references/2019-poverty-guidelines (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Thiamwong, L.; Stout, J.R.; Park, J.H.; Yan, X. Technology-Based Fall Risk Assessments for Older Adults in Low-Income Settings: Protocol for a Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e27381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migueles, J.H.; Rowlands, A.V.; Huber, F.; Sabia, S.; van Hees, V.T. GGIR: A Research Community-Driven Open Source R Package for Generating Physical Activity and Sleep Outcomes From Multi-Day Raw Accelerometer Data. J. Meas. Phys. Behav. 2019, 2, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menai, M.; van Hees, V.T.; Elbaz, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Sabia, S. Accelerometer assessed moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and successful ageing: Results from the Whitehall II study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiamwong, L.; Xie, R.; Park, J.H.; Choudhury, R.; Malatyali, A.; Li, W.; Eckstrom, E.; Stout, J.R. Levels of Accelerometer-Based Physical Activity in Older Adults With a Mismatch Between Physiological Fall Risk and Fear of Falling. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2023, 49, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visual Crossing Corporation. Visual Crossing: Weather Data & Weather API. 2025. Available online: https://www.visualcrossing.com/ (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Kalman, R. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems Trans. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression Analysis of Count Data; Number 53; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D. Zero-Inflated Poisson Regression, with an Application to Defects in Manufacturing. Technometrics 1992, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Kleiber, C.; Jackman, S. Regression Models for Count Data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Undirected Graphical Models. In The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Hastie, T.J. Learning the Structure of Mixed Graphical Models. J. Comput. Graph Stat. 2015, 24, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgewick, A.J.; Shi, I.; Donovan, R.M.; Benos, P.V. Learning mixed graphical models with separate sparsity parameters and stability-based model selection. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17 (Suppl. 5), 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Extended Bayesian information criteria for model selection with large model spaces. Biometrika 2008, 95, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Roeder, K.; Wasserman, L. Stability Approach to Regularization Selection (StARS) for High Dimensional Graphical Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2010, 24, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haslbeck, J.M.B.; Waldorp, L.J. mgm: Estimating Time-Varying Mixed Graphical Models in High-Dimensional Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2020, 93, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epskamp, S.; Cramer, A.O.J.; Waldorp, L.J.; Schmittmann, V.D.; Borsboom, D. qgraph: Network Visualizations of Relationships in Psychometric Data. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.B.; Oliveira, J.S.; Baldwin, J.N.; Hassett, L.; Costa, N.; Gilchrist, H.; Wang, B.; Kwok, W.; Bull, F.C.; Tiedemann, A.; et al. Impact of physical activity programs and services for older adults: A rapid review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.J.; Yan, T.; Keusch, F.; Gallagher, N.A. The Impact of Weather on Mobility and Participation in Older U.S. Adults. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenman, D.P.; Wilhalme, H.; Tseng, C.-H.; Chester, M.; English, P.; Pincetl, S.; Dhaliwal, S.K. Heat Death Associations with the Built Environment, Social Vulnerability, and Their Interactions with Rising Temperature. Health Place 2016, 41, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajacova, A.; Lawrence, E.M. The Relationship Between Education and Health: Reducing Disparities Through a Contextual Approach. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, R.; Bartle-Haring, S. Variations in the association between education and self-reported health by race/ethnicity and structural racism. SSM-Popul. Health 2022, 19, 101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemson, L.; Stark, S.; Pighills, A.C.; Torgerson, D.J.; Sherrington, C.; Lamb, S.E. Environmental Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD013258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Hegazy, F. Enhancing Footwear Safety for Fall Prevention in Older Adults: A Comprehensive Review of Design Features. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2024, 28, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

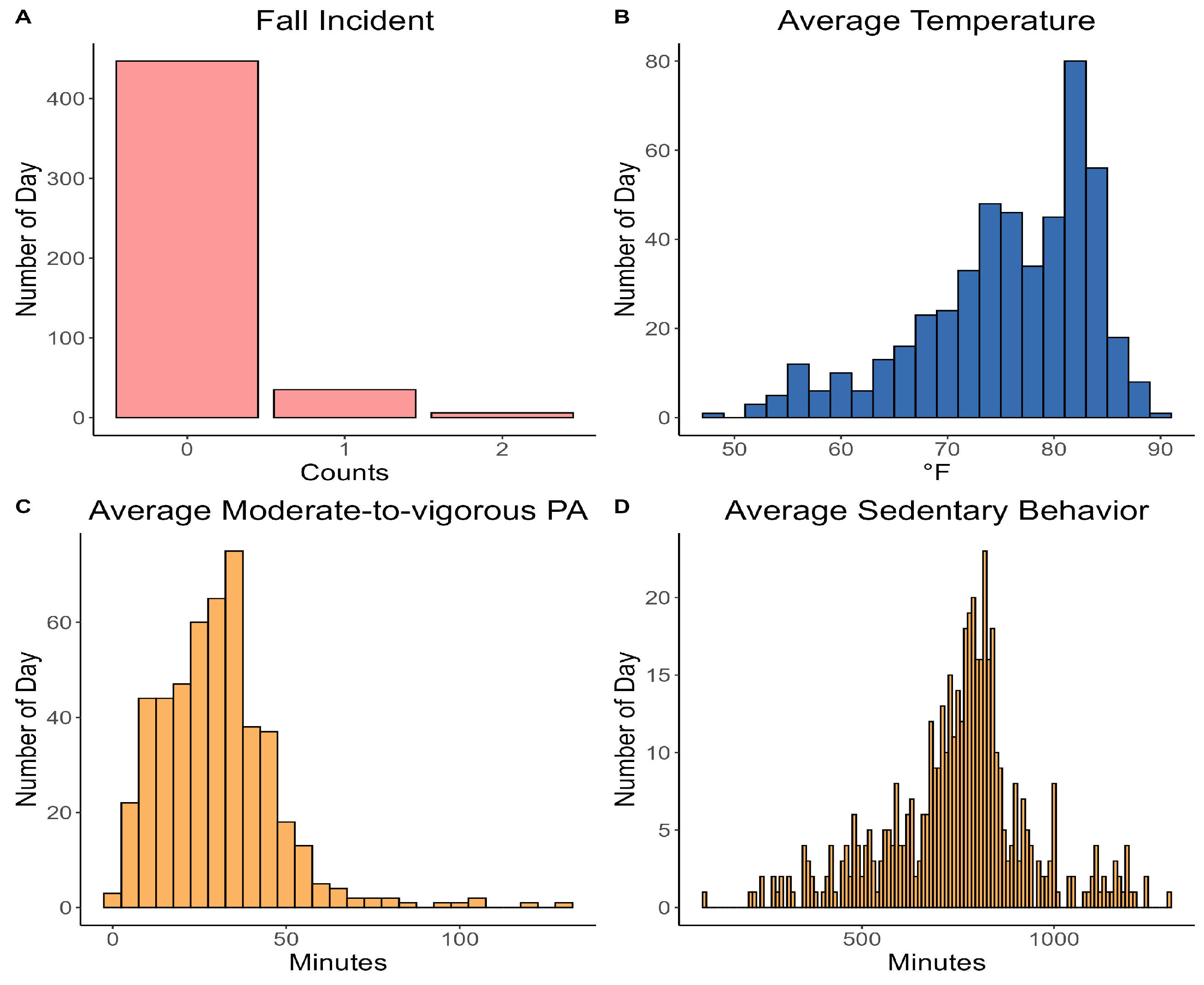
| Study Variables | Participants, N = 304 |
|---|---|
| Sociodemographic | |
| Age (Years), mean (SD) | 74.71 (7.23) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 262 (86.2%) |
| Male | 42 (13.8%) |
| Race/ethnicity | |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 22 (7.2%) |
| Non-Hispanic African American | 117 (38.5%) |
| Hispanic | 90 (29.6%) |
| Non-Hispanic White | 69 (22.7%) |
| Education level | |
| High school or below | 163 (53.6%) |
| College or higher | 138 (45.8%) |
| Financial difficulty | |
| Adequate or less | 64 (21.1%) |
| More than adequate | 235 (77.3%) |
| Living condition | |
| Alone | 168 (55.3%) |
| With others | 133 (43.8%) |
| Self-rated health | |
| Excellent or very good | 107 (35.2%) |
| Good or below | 194 (63.8%) |
| Physical activity: Accelerometer measurement | |
| SB 1 (mins/day), mean (SD) | 729.84 (112.88) |
| LPA 2 (mins/day), mean (SD) | 204.70 (65.85) |
| MVPA 3 (mins/day), mean (SD) | 31.35 (27.05) |
| Fall events | |
| None | 264 (86.8%) |
| 1 | 33 (10.9%) |
| 2 | 6 (2.0%) |
| More than 2 | 1 (0.3%) |
| Temperature | SB | MVPA | Age | Fall events | |
| Temperature | 1.000 | ||||
| SB | 0.020 | 1.000 | |||
| MVPA | −0.008 | −0.098 *** | 1.000 | ||
| Age | 0.018 | 0.089 *** | −0.304 *** | 1.000 | |
| Fall events | 0.131 *** | −0.003 | −0.036 ** | 0.015 | 1.000 |
| Dependent Variable = Fall Incidents | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | Estimate () | Standard Error | p-Value |
| Intercept | −1.927 | 0.463 | <0.0001 |
| MVPA | −0.105 | 0.050 | 0.037 |
| Temperature | 0.550 | 0.047 | <0.0001 |
| SB | 0.023 | 0.048 | 0.636 |
| Age | −0.006 | 0.006 | 0.312 |
| Race/ethnicity | |||
| Non-Hispanic African American | 0.197 | 0.152 | 0.194 |
| Hispanic | 0.177 | 0.153 | 0.247 |
| Non-Hispanic White | 0.839 | 0.152 | <0.0001 |
| Financial difficulty | |||
| More than adequate | 0.149 | 0.095 | 0.116 |
| MVPA × Temperature | −0.066 | 0.051 | 0.191 |
| Temperature × SB | −0.206 | 0.049 | <0.0001 |
| MVPA × SB | −0.169 | 0.048 | 0.0004 |
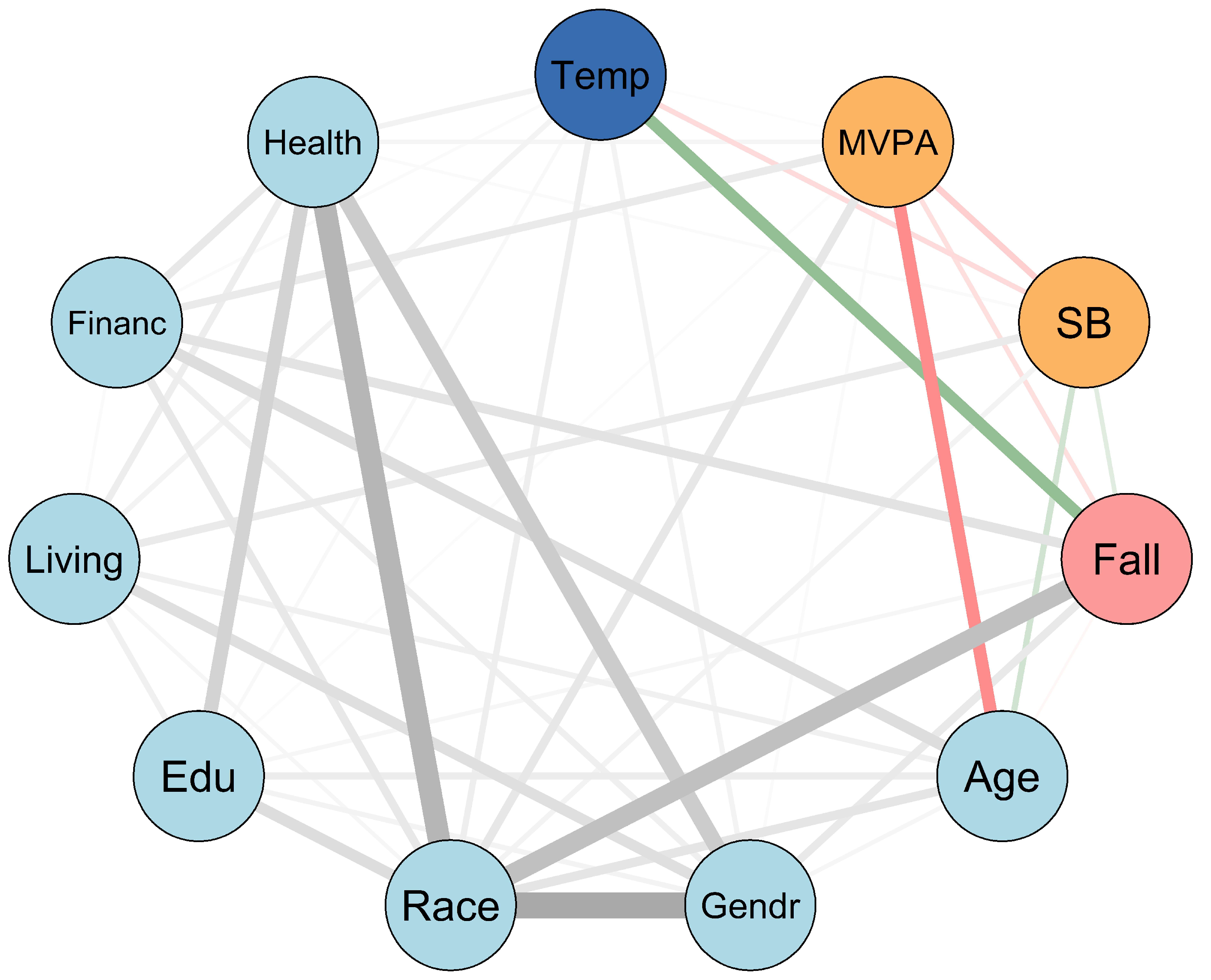
| Temp | MVPA | SB | Fall | Age | Gendr | Race | Edu | Living | Financ | |
| Temp | ||||||||||
| MVPA | 0.011 | |||||||||
| SB | 0.087 | 0.118 | ||||||||
| Fall | 0.263 | 0.081 | 0.073 | |||||||
| Age | 0.286 | 0.117 | 0.031 | |||||||
| Gendr | 0.091 | 0.037 | 0.163 | 0.093 | ||||||
| Race | 0.121 | 0.174 | 0.084 | 0.460 | 0.220 | 0.596 | ||||
| Edu | 0.051 | 0.033 | 0.066 | 0.148 | 0.093 | 0.229 | ||||
| Living | 0.090 | 0.148 | 0.121 | 0.234 | 0.052 | 0.114 | ||||
| Financ | 0.034 | 0.150 | 0.205 | 0.266 | 0.116 | 0.142 | 0.041 | |||
| Health | 0.095 | 0.069 | 0.031 | 0.363 | 0.433 | 0.315 | 0.126 | 0.158 |
| Variables (Nodes) | EBIC Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 748.5300 |
| MVPA | 788.4328 |
| SB | 826.1322 |
| Fall events | 716.3211 |
| Age | 784.1348 |
| Gender | 244.4354 |
| Race/ethnicity | 1197.0724 |
| Education level | 502.6574 |
| Living condition | 415.4221 |
| Financial difficulty | 945.5156 |
| Self-rated health | 402.2602 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.; Kim, D.; Li, Y.; Emrich, C.T.; Crook, J.; Thiamwong, L.; Xie, R. Effect of Elevated Temperature on Physical Activity and Falls in Low-Income Older Adults Using Zero-Inflated Poisson and Graphical Models. Information 2025, 16, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060442
Nguyen T, Kim D, Li Y, Emrich CT, Crook J, Thiamwong L, Xie R. Effect of Elevated Temperature on Physical Activity and Falls in Low-Income Older Adults Using Zero-Inflated Poisson and Graphical Models. Information. 2025; 16(6):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060442
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Tho, Dahee Kim, Yingru Li, Christopher T. Emrich, Jennifer Crook, Ladda Thiamwong, and Rui Xie. 2025. "Effect of Elevated Temperature on Physical Activity and Falls in Low-Income Older Adults Using Zero-Inflated Poisson and Graphical Models" Information 16, no. 6: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060442
APA StyleNguyen, T., Kim, D., Li, Y., Emrich, C. T., Crook, J., Thiamwong, L., & Xie, R. (2025). Effect of Elevated Temperature on Physical Activity and Falls in Low-Income Older Adults Using Zero-Inflated Poisson and Graphical Models. Information, 16(6), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060442







