PDO-Modulated ENSO Impact on Southern South China Sea Winter SST: Multi-Anticyclone Synergy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
3. Results
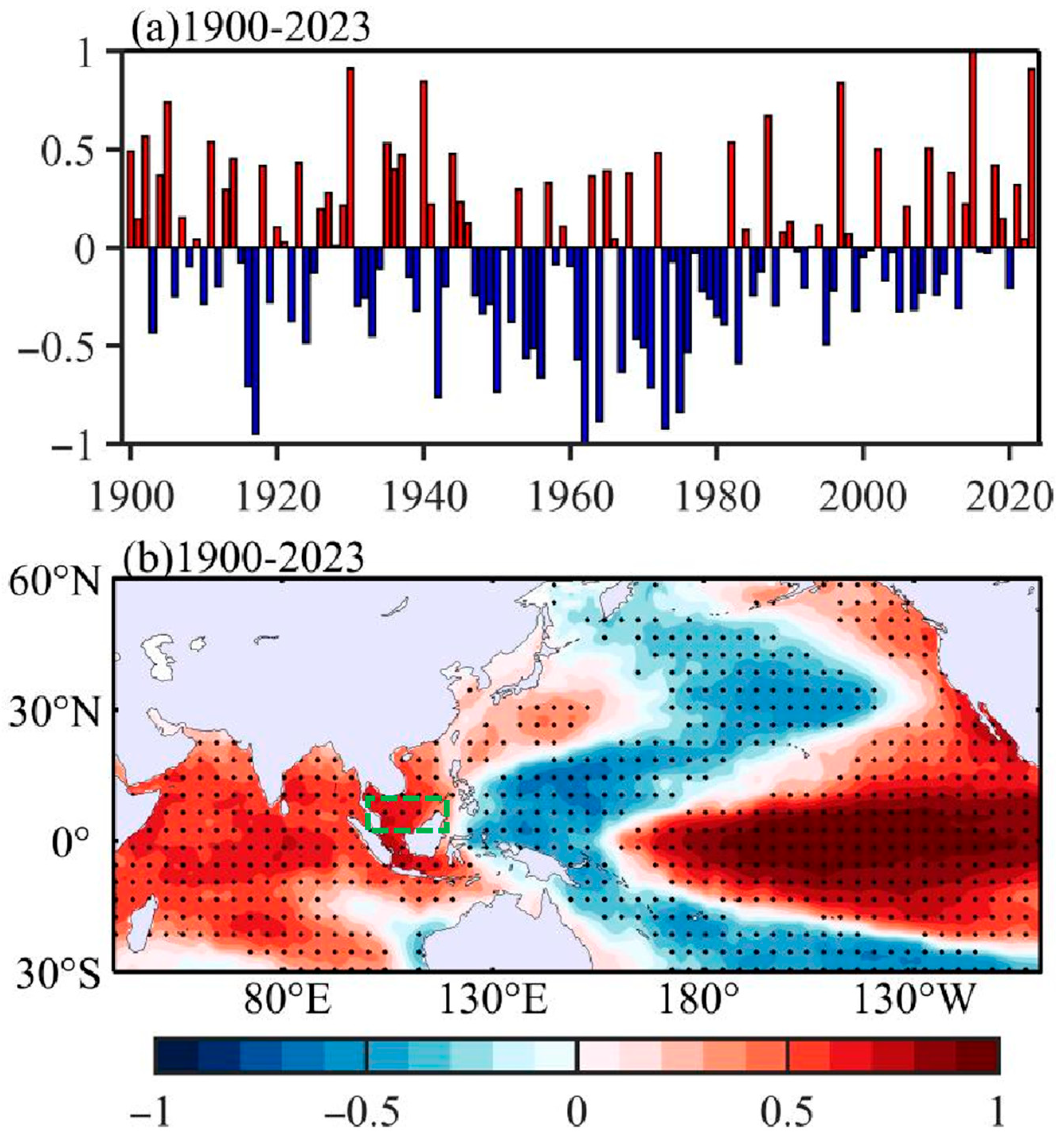
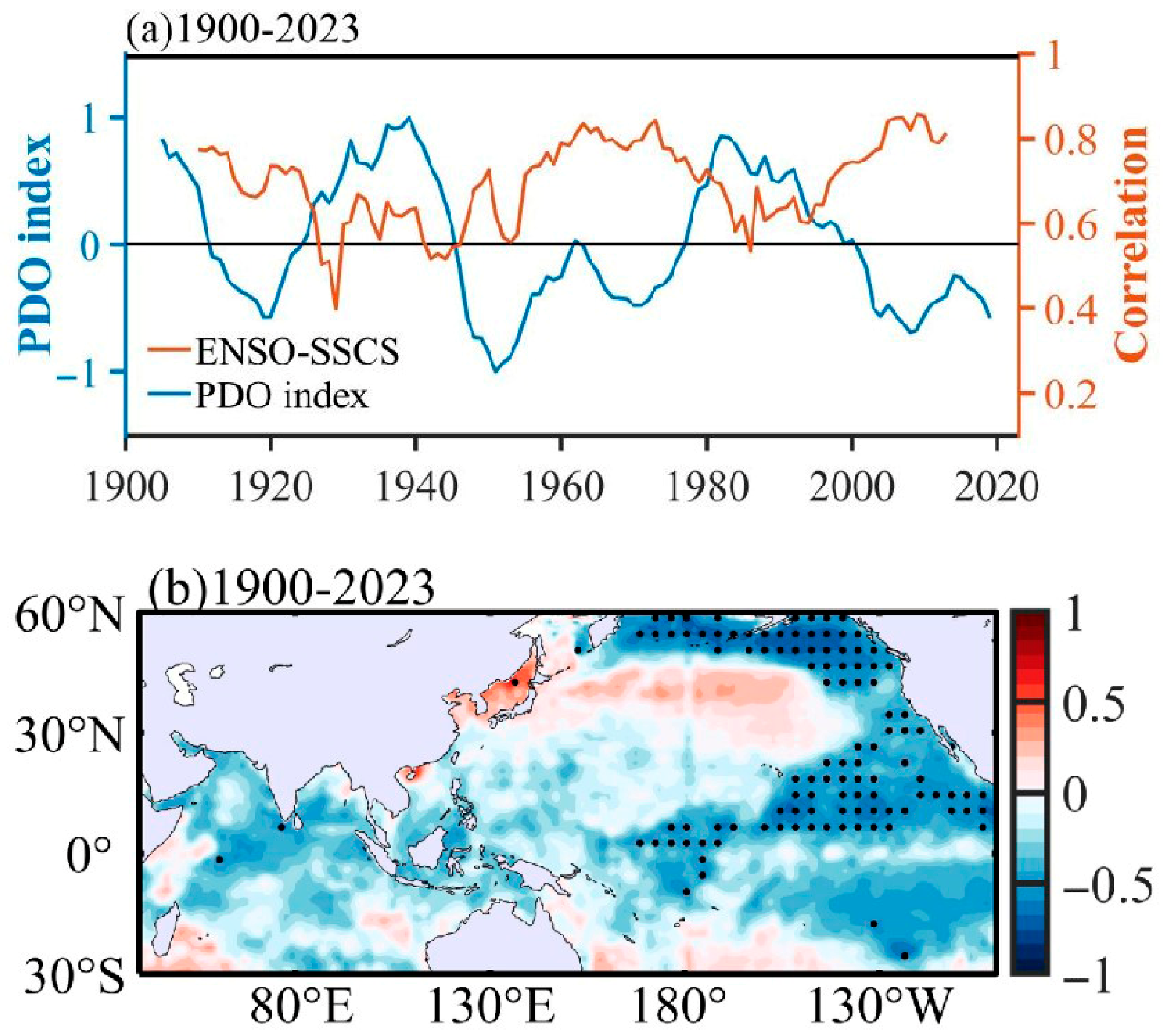
3.1. Relationship Between El Niño and SST in the Southern SCS
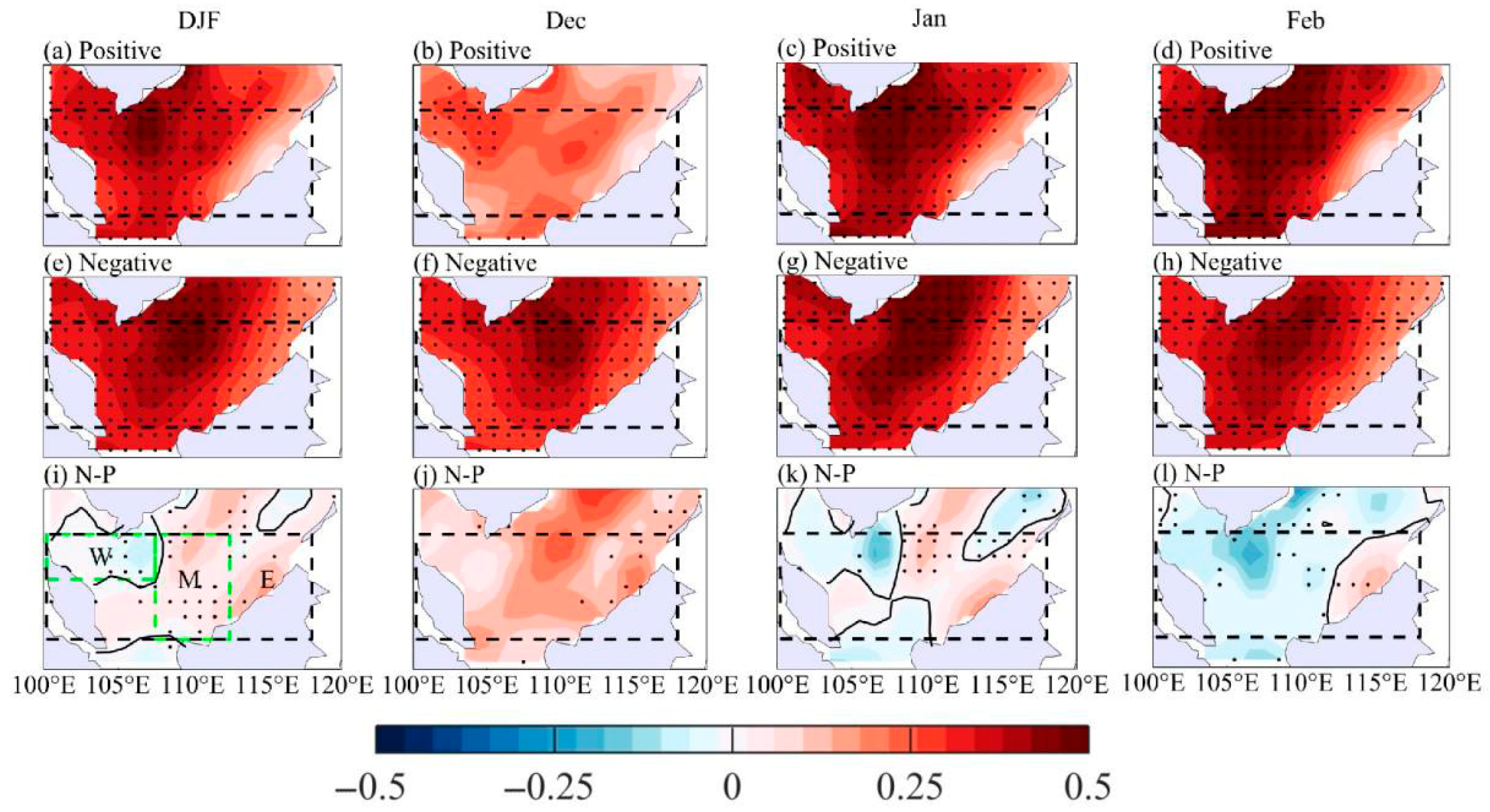
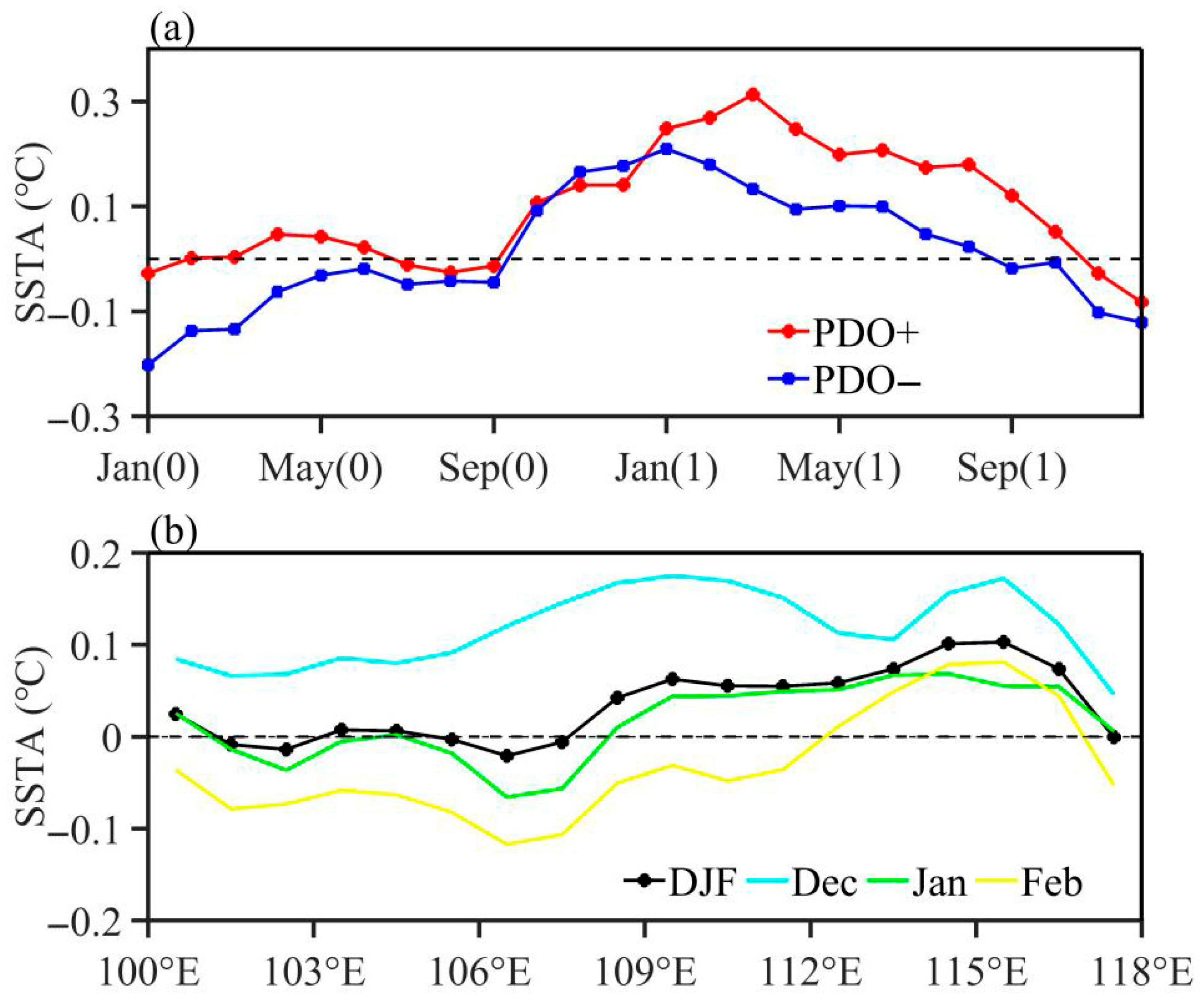
3.2. Thermodynamic Processes
3.3. Synergy of the Multi-Anticyclone Systems
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyrtki, K. Physical Oceanography of the Southeast Asian Waters; Naga Report; University of California, Scripps Institution of Oceanography: San Diego, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Huang, R.X.; Su, J.L.; Chen, D. The effects of thermohaline circulation on wind-driven circulation in the south china sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 12, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasatriya, A.; Hosoda, K.; Setiawan, J.D.; Susanto, R.D. Variability of diurnal sea surface temperature during short term and high SST event in the western equatorial pacific as revealed by satellite data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.G.; Chen, Z. Intraseasonal SST variations in the South China Sea during boreal winter and impacts of the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5863–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Tam, C.Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, W. Extremely long-lived marine heatwave in South China Sea during 1981 summer 2020: Combined effects of the seasonal and intraseasonal variations. Glob. Planet. Change. 2023, 230, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Jiang, X.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, W.T. A Gap in the Indo-Pacific Warm Pool over the SCS in Boreal Winter: Seasonal Development and Interannual Variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2004, 109, C07012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, D.; Leung, M.Y.T. Early and Extreme Warming in the South China Sea During 2015/2016: Role of an Unusual Indian Ocean Dipole Event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Q.; Peng, Q.; Wang, D. Interpretation of interannual variability of the zonal contrasting thermal conditions in the winter South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 58, 1439–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.W.; Liu, Q.Y.; Chen, X.Y. Summer surface warming driven by the strong El Niño in the South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 1407–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.; Tkalich, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P. Regime shift of the South China Sea SST in the late 1990s. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Q.; Jin, Q.; Wei, J.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Gordon, A.L.; Li, M. A Reduction in the Sea Surface Warming Rate in the SCS During 1999–2010. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 2093–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.A.; Soden, B.J.; Lau, N.C. Remote Sea Surface Temperature Variations During ENSO: Evidence for a Tropical Atmospheric Bridge. Clim. Dyn. 1999, 12, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, M.; Enomoto, T.; Takaya, K. Disparate Midlatitude Responses to the Eastern Pacific El Niño. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some Simple Solutions for Heat-Induced Tropical Circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Fu, X. Pacific-East Asian Teleconnection: How Does ENSO Affect East Asian Climate? J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Yung, H.L.; Feng, C.S. Impacts of two different types of El Niño on the thermal variability in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.A.; Wang, D.X.; Wu, Q.Y.; Song, W. Discrepant effects of oceanic advection in the evolution of SST anomalies in the South China Sea during El Niño of different intensities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 871458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, D.X.; Wang, X.; Shu, Y.Q.; Xie, Q.; Chen, J. Thermal variations in the South China Sea associated with the eastern and central Pacific El Niño events and their mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2014, 119, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gan, J.; Cai, Z.; Quan, Q.; Zu, T.; Liu, Z. Coherent Interannual–Decadal Potential Temperature Variability in the Tropical-North Pacific Ocean and Deep South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Gao, J. The modeled atmospheric and oceanic response to the South China Sea SST anomaly. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2016, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Fang, J.B.; Sun, X.G. PDO-Related Wintertime Atmospheric Anomalies over the Midlatitude North Pacific: Local versus Remote SST Forcing. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 6989–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.A.; Wang, D.X.; Yang, L. Can Tropical Pacific Winds Enhance the Footprint of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on the Upper-Ocean Heat Content in the South China Sea? J. Clim. 2020, 33, 4419–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Luo, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Yamagata, T. ENSO–IOD inter-basin connection is controlled by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL101571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H. PDO modulation of ENSO effect on tropical cyclone rapid intensification in the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.T.; Chen, W.; Huang, P.; Huang, P.; Yang, X.K. Weakened influence of ENSO on the East Asian summer monsoon since the early 2000s. npj Clim Atmos Sci. 2025, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Meng, X.F.; Xie, R.H. Interdecadal modulation of ENSO asymmetry by the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and its mechanism. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lin, W.; Dong, L.; Song, F.; Yang, S.; Lu, Z.; Hu, X. Role of SST in Seasonal Western North Pacific Anomalous Anticyclone: Insights From AMIP Simulations in CMIP6. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tao, W.; Huang, G.; Hu, K.; Qu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S. Ongoing intensification of anomalous Western North Pacific anticyclone during post-El Niño summer with achieved carbon neutrality. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, Q.; Wang, H.; Ma, J. Strengthened Western North Pacific Anomalous Anticyclone in an El Niño–Decaying Summer across the Last Interglacial. J. Clim. 2025, 38, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Jin, F.F. Role of Indian Ocean warming in the development of Philippine Sea anticyclone during ENSO. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Physics-Based Predictions of the Month-by-Month Summer Western North Pacific Anomalous Anticyclone. J. Clim. 2025, 38, 2187–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carton, J.A.; Giese, B.S. A Reanalysis of Ocean Climate Using Simple Ocean Data Assimilation (SODA). Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 138, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, W.; Jin, F.; Hu, S. Decadal Modulation of the ENSO–Indian Ocean Basin Warming Relationship during the Decaying Summer by the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 2685–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ren, R.; Xia, X.; Shi, C.; Guo, D. Combined Impact of El Niño–Southern Oscillation and Pacific Decadal Oscillation on the Northern Winter Stratosphere. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, E.; Jiang, Y. ENSO and PDO-Related Interannual and Interdecadal Variations in the Wintertime Sea Surface Temperature in a Typical Subtropical Strait. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 3359–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Kucharski, F.; Li, J.P.; Jin, F.F.; Kang, I.S.; Ding, R.Q. Western tropical Pacific multidecadal variability forced by the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, B.J.; Vecchi, G.A. The vertical distribution of cloud feedback in coupled ocean-atmosphere models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Hartmann, D.L. Why is longwave cloud feedback positive? J Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Mochizuki, T. Decadal modulation of ENSO and IOD impacts on the Indian Ocean upwelling. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1212421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.K.; Varikoden, H.; Babu, C.; Reshma, T. Influence of PDO and ENSO with Indian summer monsoon rainfall and its changing relationship before and after 1976 climate shift. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 61, 5465–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, P.; Weller, E.; Young, I.R. Positive relationship between seasonal Indo-Pacific Ocean wave power and SST. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 17419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Balmaseda, M.; Tietsche, S.; Mogensen, K.; Mayer, M. The ECMWF Operational Ensemble Reanalysis-Analysis System for Ocean and Sea-Ice: A Description of the System and Assessment. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 779–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, A. Evaluation of the GECCO2 ocean synthesis: Transports of volume, heat and freshwater in the Atlantic. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.S.; Jin, X.Z.; Robber, W. Multidecade Global Flux Datasets from the Objectively Analyzed Air-Sea Fluxes (OAFlux) Project: Latent and Sensible Heat Fluxes, Ocean Evaporation, and Related Surface Meteorological Variables; OAFlux Project Technical Report. OA-2008-01; Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2008; p. 64. [Google Scholar]

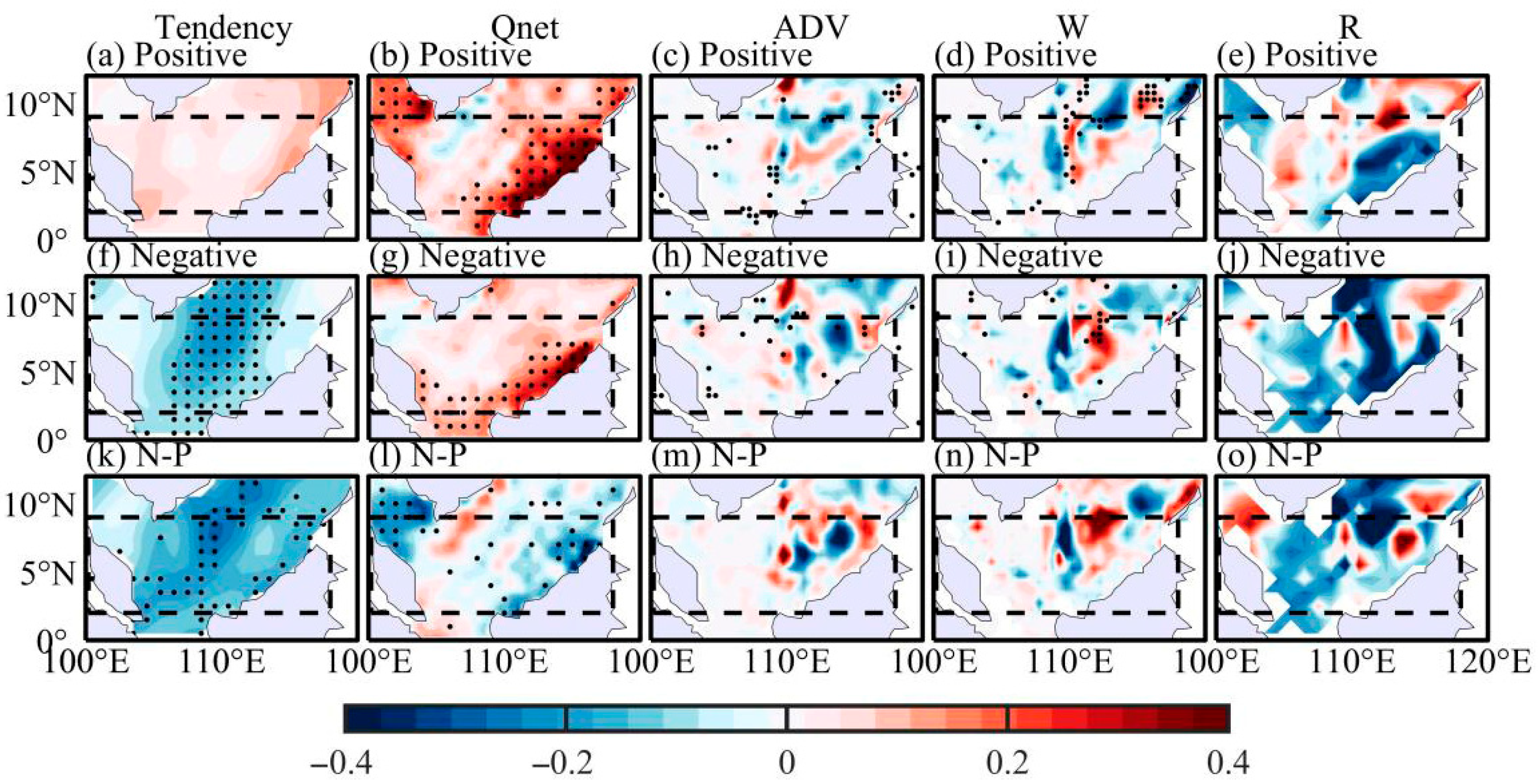
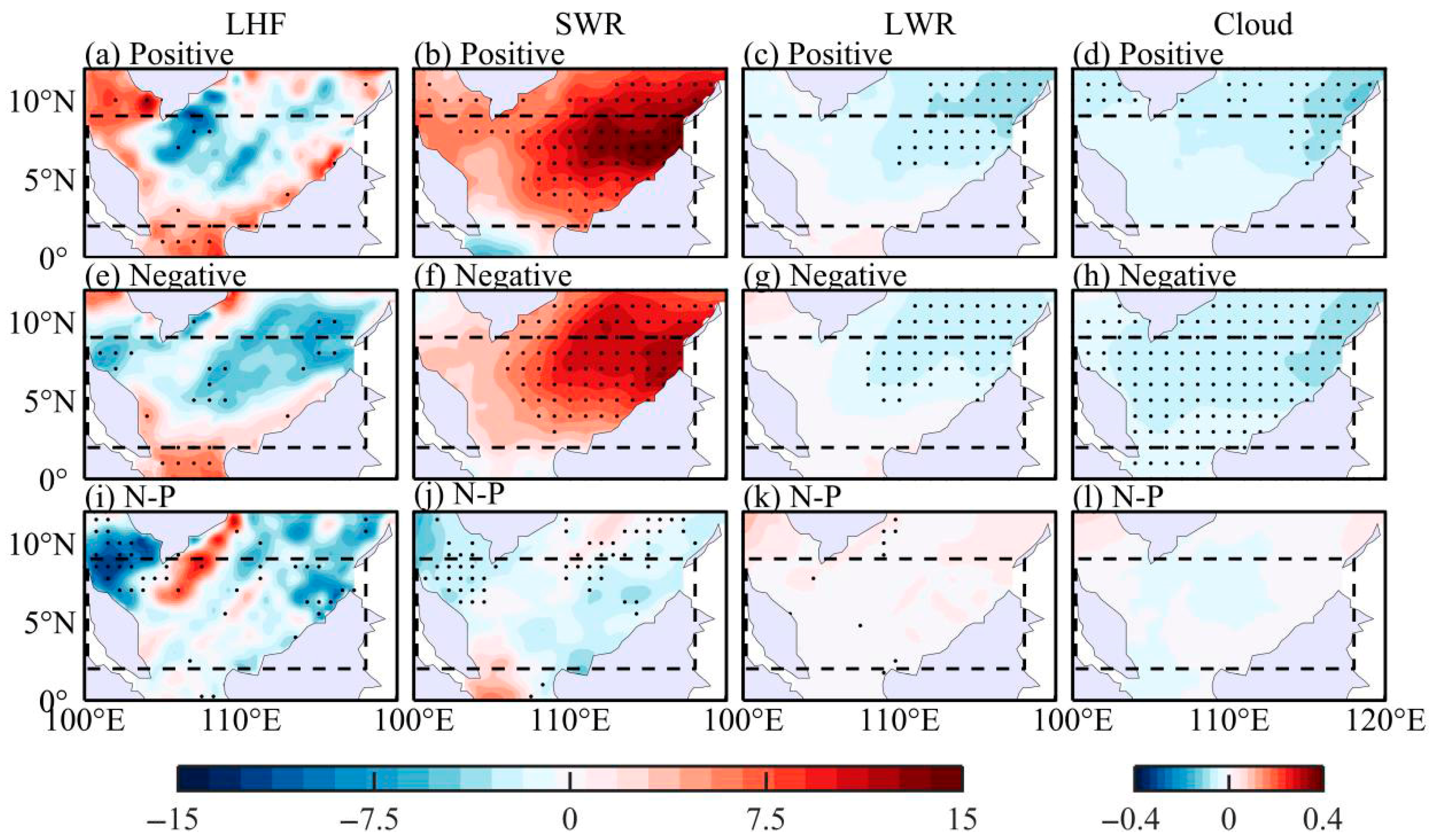

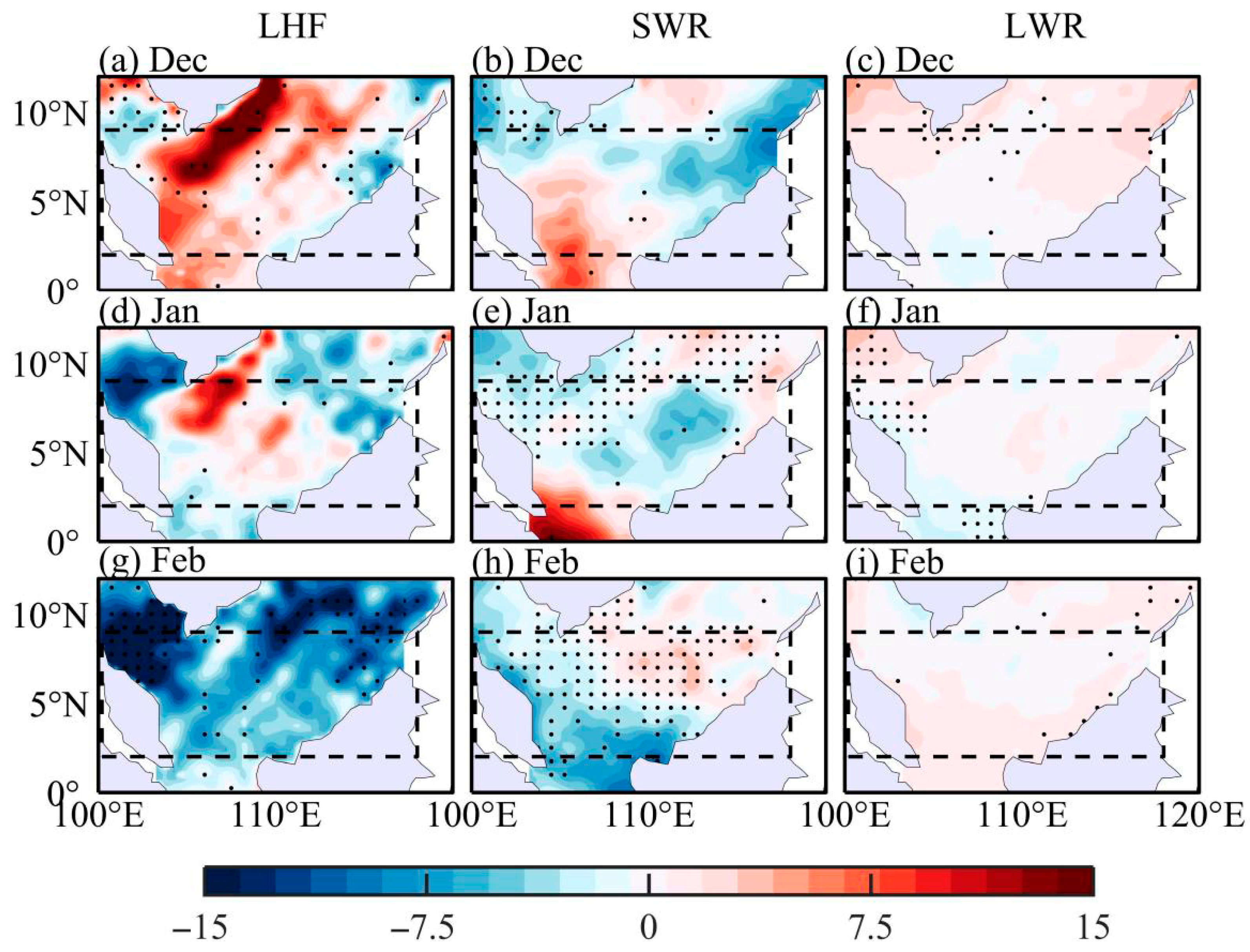
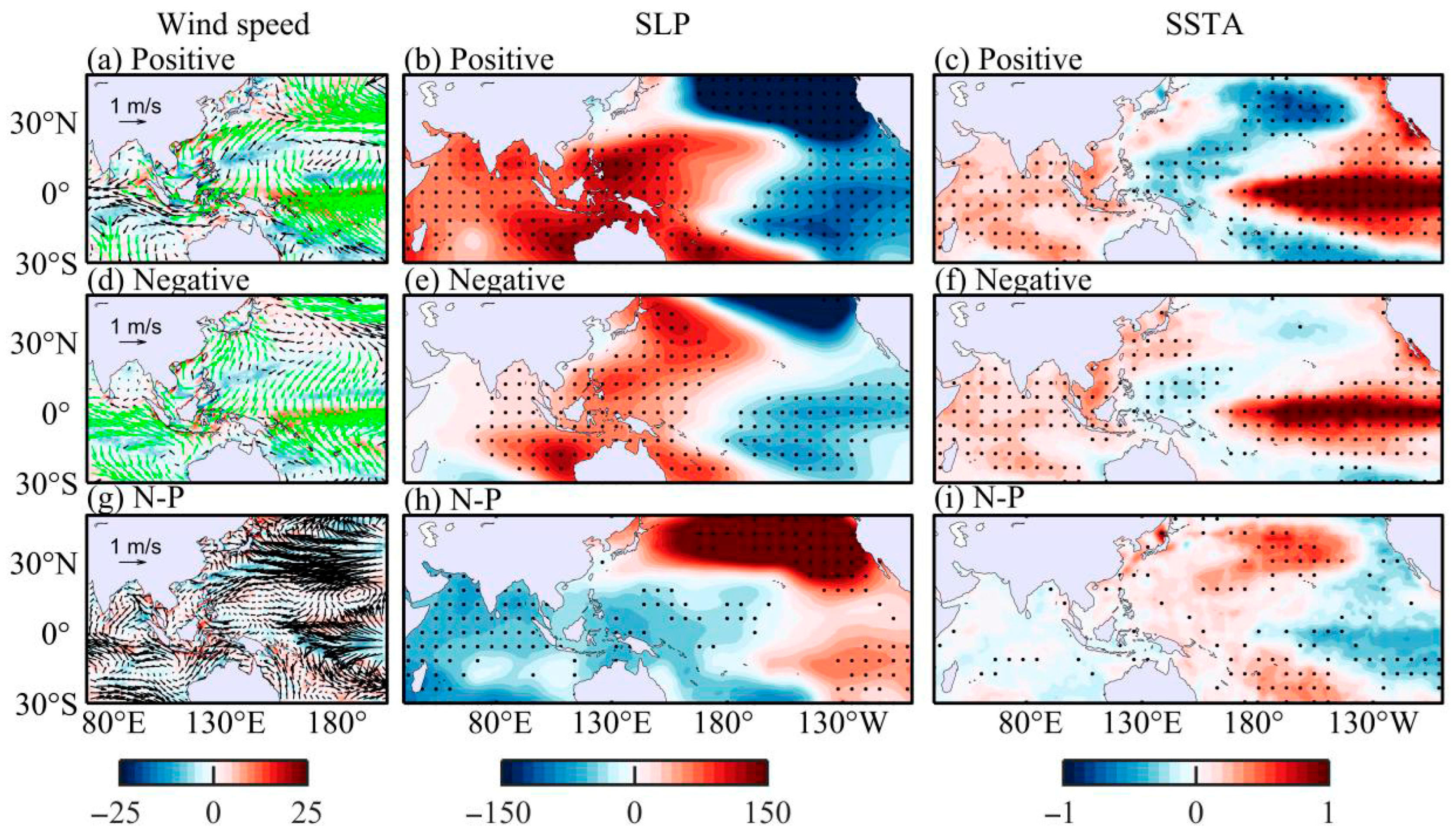
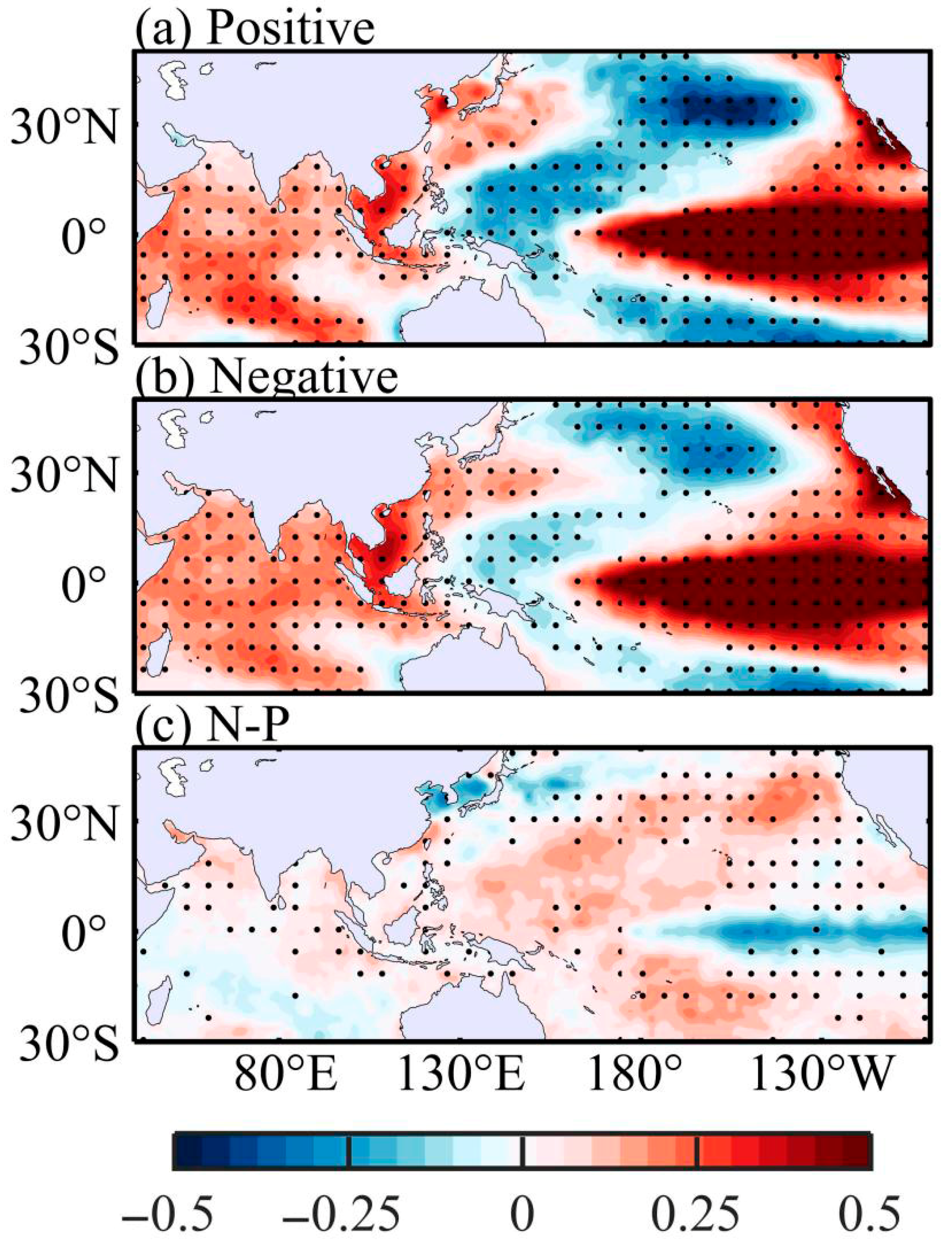
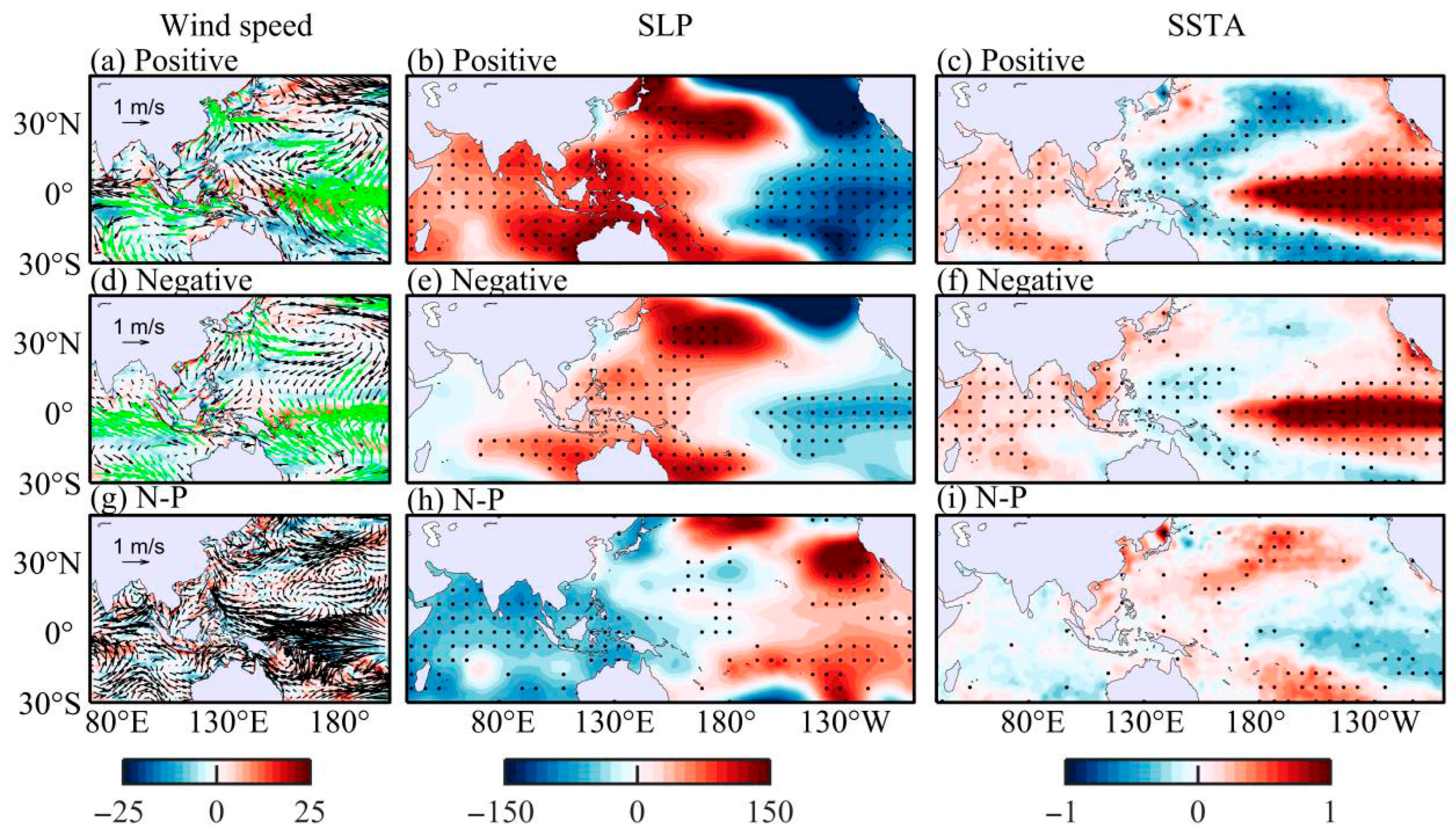
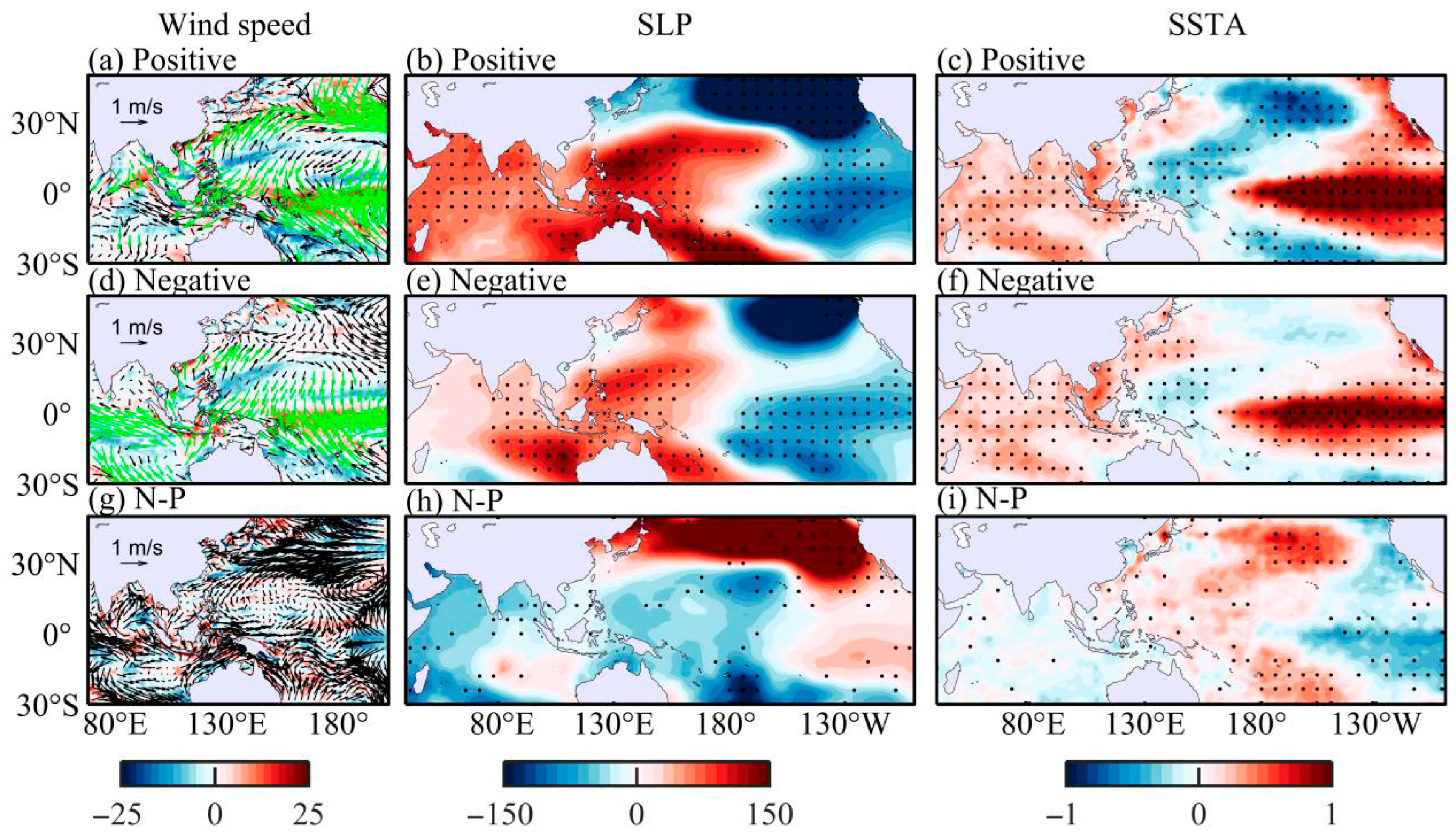

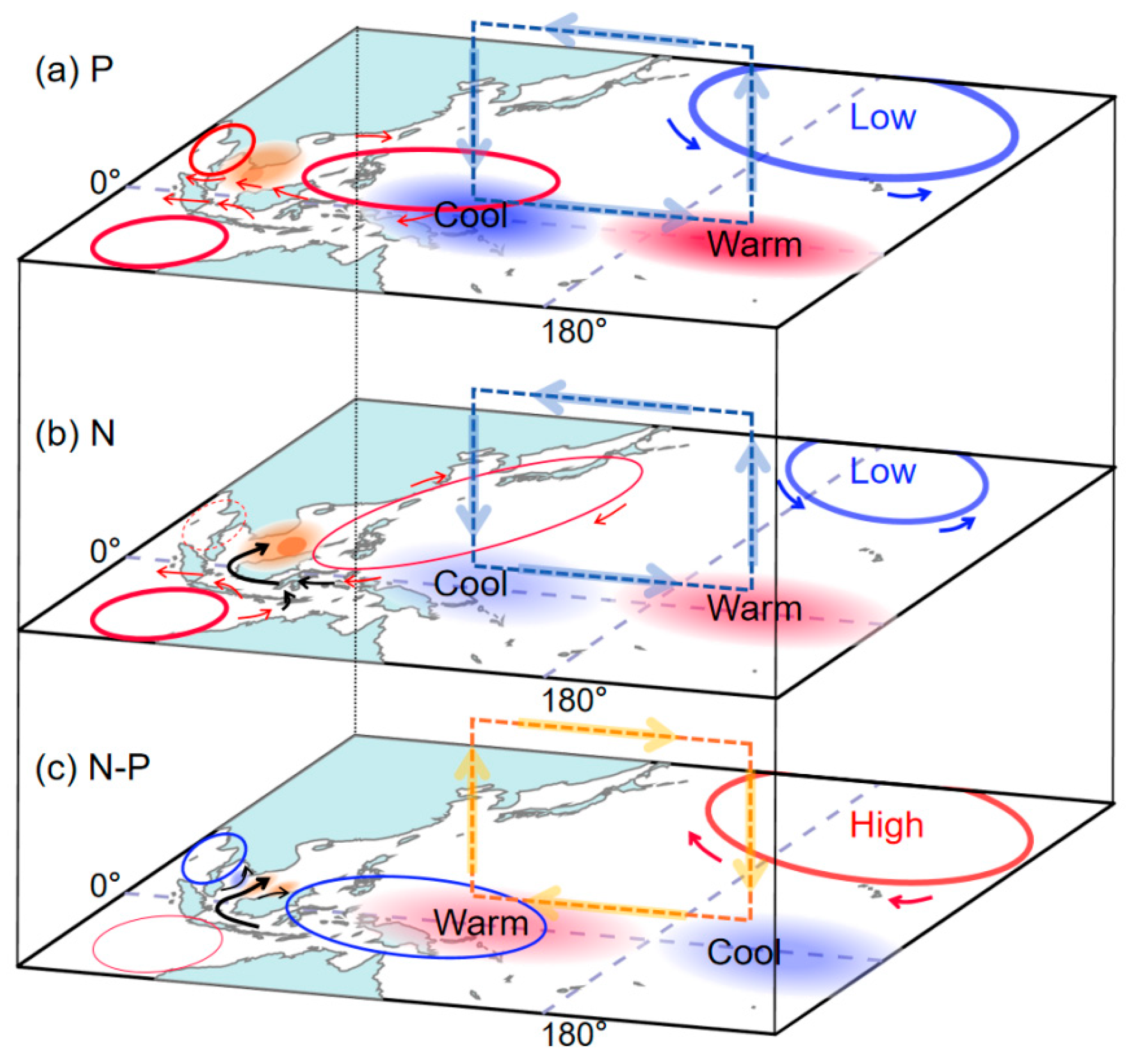
| PDO Phase | El Niño Events |
|---|---|
| Positive | 1925/26, 1930/31, 1940/41, 1941/42 |
| 1977/78, 1979/80, 1982/82, 1986/87, 1987/88, 1990/91, 1991/92, 1994/95, 1997/98 | |
| Negative | 1902/03, 1905/06, 1911/12, 1913/14, 1914/15, 1918/19, 1923/24 |
| 1951/52, 1953/53, 1957/58, 1963/64, 1965/66, 1968/69, 1969/70, 1972/73, 1976/77 | |
| 2002/03, 2003/04, 2004/05, 2006/07, 2009/10, 2014/15, 2015/16, 2018/19, 2019/20, 2023/24 |
| dSST | Qnet | ADV | W | R | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJF | West | −0.0954 | −0.0515 * | 0.0023 | 0.0074 | −0.0536 |
| Middle | −0.1717 | −0.0407 | −0.0077 | −0.0229 | −0.1004 * | |
| East | −0.1291 | −0.0937 * | −0.0098 | −0.0057 | −0.0199 | |
| Dec | West | −0.1164 | 0.0768 | −0.0091 | −0.0035 | −0.1806 * |
| Middle | −0.1254 | 0.0348 | −0.0292 | −0.1227 * | −0.0083 | |
| East | −0.0434 | −0.1001 * | 0.093 | −0.0076 | −0.0287 | |
| Jan | West | −0.0553 | −0.0243 | −0.0034 | 0.0196 | −0.0472 * |
| Middle | −0.0632 | −0.0226 | 0.0154 | −0.0541 * | −0.0019 | |
| East | −0.0260 | −0.0870 * | −0.0153 | 0.0338 | 0.0425 | |
| Feb | West | −0.0521 | −0.2071 * | 0.0044 | −0.0015 | 0.1521 |
| Middle | −0.1295 | −0.1345 * | 0.0301 | 0.0058 | −0.0309 | |
| East | −0.1120 | −0.0939 * | −0.078 * | −0.0383 | 0.0982 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Dong, W. PDO-Modulated ENSO Impact on Southern South China Sea Winter SST: Multi-Anticyclone Synergy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091741
Wang Z, Wang Y, Qiu M, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Dong W. PDO-Modulated ENSO Impact on Southern South China Sea Winter SST: Multi-Anticyclone Synergy. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091741
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhaoyun, Yanyan Wang, Mingpan Qiu, Yimin Zhang, Guosheng Zhang, and Wenjing Dong. 2025. "PDO-Modulated ENSO Impact on Southern South China Sea Winter SST: Multi-Anticyclone Synergy" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091741
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, Y., Qiu, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, G., & Dong, W. (2025). PDO-Modulated ENSO Impact on Southern South China Sea Winter SST: Multi-Anticyclone Synergy. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091741







