Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part II—Intraspecific Variation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Radular Elemental Composition and Morphometry
3.2. Valve Morphometrics
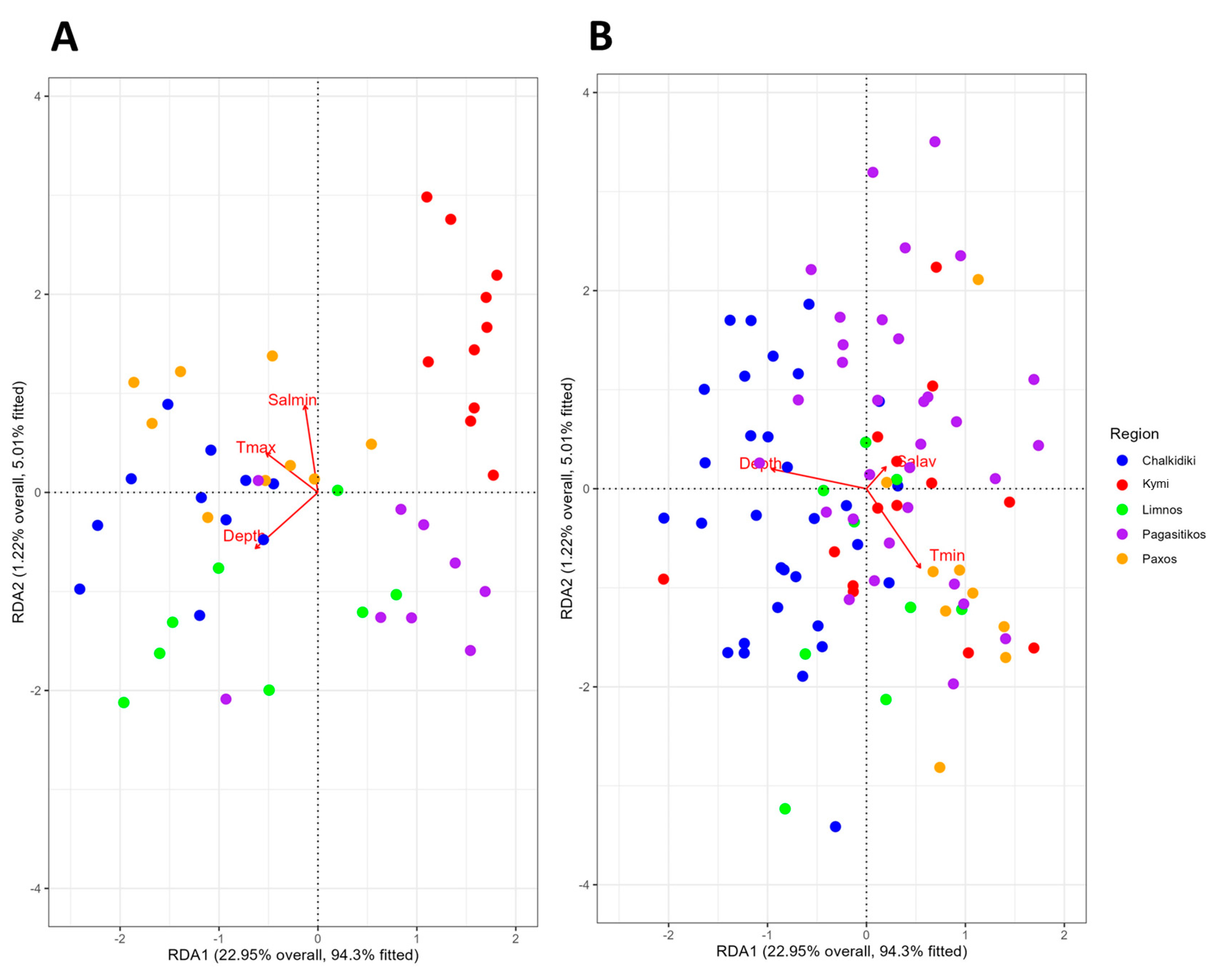
3.3. Influence of Abiotic Variables
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sirenko, B. New Outlook on the System of Chitons (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). Venus 2006, 65, 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sigwart, J.D.; Green, P.A.; Crofts, S.B. Functional Morphology in Chitons (Mollusca, Polyplacophora): Influences of Environment and Ocean Acidification. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, C.; Gorb, S.N.; Glaubrecht, M.; Krings, W. Not Just Scratching the Surface: Distinct Radular Motion Patterns in Mollusca. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio055699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigwart, J.D.; Schwabe, E. Anatomy of the Many Feeding Types in Polyplacophoran Molluscs. Invertebr. Zool. 2017, 14, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschvink, J.L.; Lowenstam, H.A. Mineralization and Magnetization of Chiton Teeth: Paleomagnetic, Sedimentologic, and Biologic Implications of Organic Magnetite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 44, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, W.; Brütt, J.-O.; Gorb, S.N. Elemental Analyses Reveal Distinct Mineralization Patterns in Radular Teeth of Various Molluscan Taxa. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paaby, A.B.; Testa, N.D. Developmental Plasticity and Evolution. In Evolutionary Developmental Biology: A Reference Guide; Nuño de la Rosa, L., Müller, G.B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1073–1086. ISBN 978-3-319-32979-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-P, R.; Benítez, H.A.; Ornelas-García, C.P.; Correa, M.; Suazo, M.J.; Piñero, D. Bergmann’s Rule under Rocks: Testing the Influence of Latitude and Temperature on a Chiton from Mexican Marine Ecoregions. Biology 2023, 12, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Angelo, B.; Smriglio, C. Living Chitons of the Mediterranean; Evolver: Rome, Italy, 2001; ISBN 978-88-8299-007-7. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Karachle, P. The Polyplacophoran (Eumollusca, Mollusca) Fauna of the Aegean Sea with the Description of a New Species, and Comparison with Those of the Neighbouring Seas. J. Biol. Res. 2004, 3, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Varkoulis, A.; Voulgaris, K.; Zachos, D.S.; Vafidis, D. Population Dynamics of Three Polyplacophora Species from the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Diversity 2023, 15, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mygdalias, T.; Voulgaris, K.; Varkoulis, A.; Zachos, D.S.; Vafidis, D. Short-Term Effect of Extreme Storms on Population Characteristics of a Common Mediterranean Chiton. In Proceedings of the HydroMediT 2024, Mytilene, Greece, 30 May–2 June 2024; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Intergouvernemental Panel on Climate Change (Ed.) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mygdalias, T.; Varkoulis, A.; Voulgaris, K.; Zaoutsos, S.; Vafidis, D. Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part I—Radula and Valves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, B.B. A Novel Approach for the High-Resolution Interpolation of In Situ Sea Surface Salinity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Droghei, R.; Santoleri, R. Multi-Dimensional Interpolation of SMOS Sea Surface Salinity with Surface Temperature and in Situ Salinity Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droghei, R.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Santoleri, R. A New Global Sea Surface Salinity and Density Dataset from Multivariate Observations (1993–2016). Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, F.; Le, S.; Pagès, J. Exploratory Multivariate Analysis by Example Using R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-429-19003-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F. The Analysis of Vegetation-Environment Relationships by Canonical Correspondence Analysis. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package Version 2.0-10; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.; Codd, C.; Hebbert, D.; Vink, S.; Burt, J. The Functional Significance of the Relative Size of Aristotle’s Lantern in the Sea Urchin Echinometramathaei (de Blainville). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 77, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.C.; Wang, Q.; Miserez, A.; Tantuccio, A.; Stromberg, R.; Bozhilov, K.N.; Maxwell, P.; Nay, R.; Heier, S.T.; DiMasi, E.; et al. Analysis of an Ultra Hard Magnetic Biomineral in Chiton Radular Teeth. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunenfelder, L.K.; de Obaldia, E.E.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Weden, B.; Salinas, C.; Wuhrer, R.; Zavattieri, P.; Kisailus, D. Stress and Damage Mitigation from Oriented Nanostructures within the Radular Teeth of Cryptochiton stelleri. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6093–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.H.; Lu, D.; Pugno, N.M. Extreme Strength Observed in Limpet Teeth. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Nemoto, M.; Li, D.; Weaver, J.C.; Weden, B.; Stegemeier, J.; Bozhilov, K.N.; Wood, L.R.; Milliron, G.W.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Phase Transformations and Structural Developments in the Radular Teeth of Cryptochiton stelleri. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.L. Adaptations of the Chiton Sypharochiton pelliserpentis to Rocky and Estuarine Habitats. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1982, 16, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, P.M.; Santure, A.W.; Lavery, S.D.; de Villemereuil, P. Finding the Adaptive Needles in a Population-Structured Haystack: A Case Study in a New Zealand Mollusc. J. Anim. Ecol. 2022, 91, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R. Adaptive Value of Shell Variation in Thais Lamellosa: Effect of Thick Shells on Vulnerability to and Preference by Crabs. Veliger 1985, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, K.O.; Carlson, R.L.; Shulman, M.J.; Ellis, J.C. Why Are Intertidal Snails Rare in the Subtidal? Predation, Growth and the Vertical Distribution of Littorina littorea (L.) in the Gulf of Maine. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 369, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafidis, D.; Varkoulis, A.; Zaoutsos, S.; Voulgaris, K. Tooth Mg/Ca Ratios and Aristotle’s Lantern Morphometrics Reflect Trophic Types in Echinoids. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, C.L.; Ormondroyd, G.A.; Curling, S.F.; Ball, R.J.; Whiteley, N.M.; Malham, S.K. Ocean Warming, More than Acidification, Reduces Shell Strength in a Commercial Shellfish Species during Food Limitation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Poupin, M.J.; Lagos, N.A.; Broitman, B.R.; Lardies, M.A. Physiological Resilience of Intertidal Chitons in a Persistent Upwelling Coastal Region. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.S.; Peck, L.S.; Arivalagan, J.; Backeljau, T.; Berland, S.; Cardoso, J.C.R.; Caurcel, C.; Chapelle, G.; De Noia, M.; Dupont, S.; et al. Deciphering Mollusc Shell Production: The Roles of Genetic Mechanisms through to Ecology, Aquaculture and Biomimetics. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1812–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, F.; Caccia, M.G.; Simoncini, G.A.; Mancuso, A.; Reggi, M.; Fermani, S.; Brizi, L.; Fantazzini, P.; Stagioni, M.; Falini, G.; et al. Shell Properties of Commercial Clam Chamelea Gallina Are Influenced by Temperature and Solar Radiation along a Wide Latitudinal Gradient. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschino, V.; Marin, M.G. Seasonal Changes in Physiological Responses and Evaluation of “Well-Being” in the Venus Clam Chamelea gallina from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 145, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Indicator Domains | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental composition | SiL1 | Silicon Lateral I |
| SiL2 | Silicon Lateral II | |
| SiM | Silicon Marginal | |
| SiC | Silicon Central | |
| PL1 | Phosphorus Lateral I | |
| PL2 | Phosphorus Lateral II | |
| PM | Phosphorus Marginal | |
| PC | Phosphorus Central | |
| KL1 | Potassium Lateral I | |
| KL2 | Potassium Lateral II | |
| KM | Potassium Marginal | |
| KC | Potassium Central | |
| FeL1 | Iron Lateral I | |
| FeL2 | Iron Lateral II | |
| FeM | Iron Marginal | |
| FeC | Iron Central | |
| MgL1 | Magnesium Lateral I | |
| MgL2 | Magnesium Lateral II | |
| MgM | Magnesium Marginal | |
| MgC | Magnesium Central | |
| Standardized morphometrics for head (I), intermediate (IV) and tail (VIII) valves and radula | STIL | Length of I |
| STIW | Width of I | |
| STIT | Thickness of I | |
| STIVL | Length of IV | |
| STIVW | Width of IV | |
| STIVT | Thickness of IV | |
| STVIIIL | Length of VIII | |
| STVIIIW | Width of VIII | |
| STVIIIT | Thickness of VIII | |
| STRL | Radula Length | |
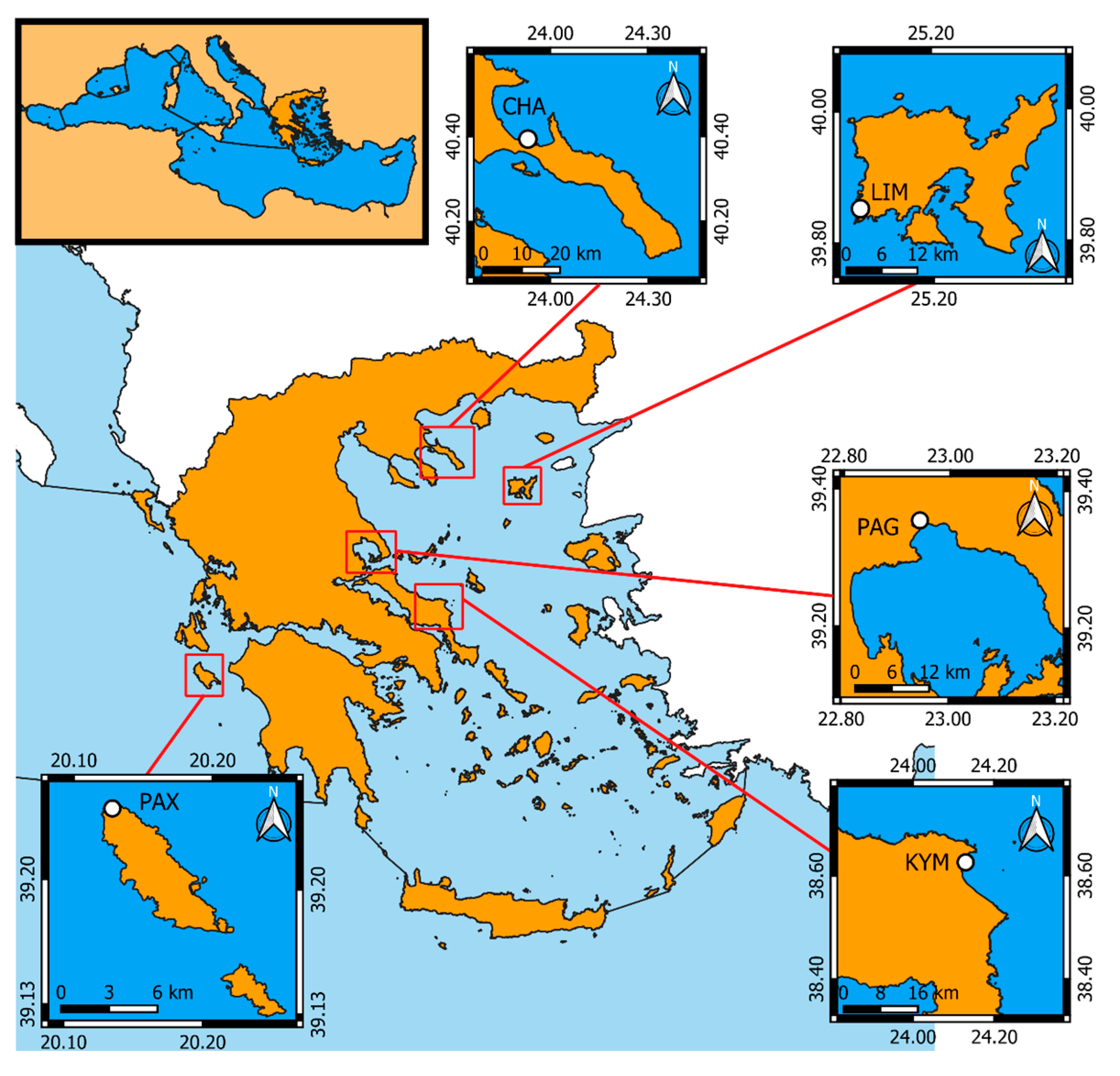
| Regional abbreviations | CHA | Chalkidiki Peninsula |
| LIM | Limnos Island | |
| PAG | Pagasitikos Gulf | |
| KYM | Kymi (Evoia Island) | |
| PAX | Paxos Island | |
| Abiotic factors | Depth | Sampling Depth |
| Tmin | Minimum Annual Temperature | |
| Tmax | Maximum Annual Temperature | |
| Salav | Average Annual Salinity | |
| Salmin | Minimum Annual Salinity |
| Clusters | Principal Components | Variables | v.test | Mean | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PC2 | 3.05 | 1.57 | 0.002 | |
| PC1 | −4.93 | −3.75 | 0.000 | ||
| SiL1 | 5.75 | 1.73 | 0.000 | ||
| SiM | 5.56 | 1.68 | 0.000 | ||
| SiC | 4.55 | 1.37 | 0.000 | ||
| PC | −3.02 | −0.91 | 0.003 | ||
| PL2 | −3.13 | −0.94 | 0.002 | ||
| KL1 | −3.14 | −0.95 | 0.002 | ||
| KM | −3.48 | −1.05 | 0.001 | ||
| PM | −3.50 | −1.06 | 0.000 | ||
| 2 | PC2 | −4.72 | −1.66 | 0.000 | |
| FeL1 | 3.47 | 0.71 | 0.001 | ||
| FeM | 3.30 | 0.68 | 0.001 | ||
| MgL2 | −3.01 | −0.62 | 0.003 | ||
| MgL1 | −3.48 | −0.71 | 0.001 | ||
| 3 | PC1 | 5.76 | 2.12 | 0.000 | |
| PC | 5.01 | 0.73 | 0.000 | ||
| PL1 | 4.75 | 0.69 | 0.000 | ||
| MgL2 | 4.53 | 0.66 | 0.000 | ||
| KL1 | 4.11 | 0.60 | 0.000 | ||
| PL2 | 4.08 | 0.59 | 0.000 | ||
| KC | 3.96 | 0.58 | 0.000 | ||
| MgL1 | 3.85 | 0.56 | 0.000 | ||
| PM | 3.22 | 0.47 | 0.001 | ||
| FeM | −3.34 | −0.49 | 0.001 | ||
| STRL | −4.26 | −0.62 | 0.000 | ||
| FeL1 | −4.40 | −0.64 | 0.000 |
| Clusters | Principal Components | Variables | v.test | Mean | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PC1 | −7.42 | −2.71 | 0.000 | |
| STVIIIT | −3.30032 | −0.51313 | 0.001 | ||
| STIVT | −4.53104 | −0.70448 | 0.000 | ||
| STIT | −5.11977 | −0.79601 | 0.000 | ||
| STVIIIL | −5.68382 | −0.88371 | 0.000 | ||
| STVIIIW | −6.07251 | −0.94414 | 0.000 | ||
| STIVL | −6.07471 | −0.94449 | 0.000 | ||
| STIL | −6.61804 | −1.02896 | 0.000 | ||
| STIVW | −6.69796 | −1.04139 | 0.000 | ||
| STIW | −6.96144 | −1.08235 | 0.000 | ||
| 2 | |||||
| 3 | PC1 | 7.73 | 2.89 | 0.000 | |
| STIW | 7.044249 | 1.122779 | 0.000 | ||
| STIL | 6.870369 | 1.095065 | 0.000 | ||
| STIVW | 6.750648 | 1.075982 | 0.000 | ||
| STVIIIL | 6.380709 | 1.017018 | 0.000 | ||
| STIVL | 6.126409 | 0.976485 | 0.000 | ||
| STVIIIW | 5.862777 | 0.934465 | 0.000 | ||
| STIT | 5.681176 | 0.90552 | 0.000 | ||
| STIVT | 5.078662 | 0.809485 | 0.000 | ||
| STVIIIT | 3.627933 | 0.578254 | 0.000 |
| Component | Elemental Composition | Morphometrics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term | F | p-Value | Term | F | p-Value | |
| Variables | Tmax | 2.6861 | 0.008 | Tmin | 9.3686 | 0.001 |
| Salmin | 3.5596 | 0.002 | Depth | 19.5992 | 0.001 | |
| Depth | 3.3753 | 0.003 | Salav | 0.9543 | 0.366 | |
| Axes | CCA1 | 4.7559 | 0.002 | CCA1 | 28.2158 | 0.001 |
| CCA2 | 3.3794 | 0.005 | CCA2 | 1.4999 | 0.421 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voulgaris, K.; Varkoulis, A.; Mygdalias, T.; Zaoutsos, S.; Vafidis, D. Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part II—Intraspecific Variation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122230
Voulgaris K, Varkoulis A, Mygdalias T, Zaoutsos S, Vafidis D. Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part II—Intraspecific Variation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122230
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoulgaris, Konstantinos, Anastasios Varkoulis, Thomas Mygdalias, Stefanos Zaoutsos, and Dimitris Vafidis. 2024. "Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part II—Intraspecific Variation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122230
APA StyleVoulgaris, K., Varkoulis, A., Mygdalias, T., Zaoutsos, S., & Vafidis, D. (2024). Elemental Composition and Morphometry of Rhyssoplax olivacea (Polyplacophora): Part II—Intraspecific Variation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122230








