Abstract
Rice is a primary food source for nearly half of the global population. In Northeast China, paddy soils are mainly classified into two distinct types: fertile mollisol and nutrient-deficient saline–sodic soil. Soil microbial communities play a critical role in maintaining the stability of rice agroecosystems; however, comparative studies on microbial diversity and functional systems across these soil types remain limited. This study aimed to systematically investigate the bacterial diversity, community structure, and functional characteristics of mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils during the rice heading and harvest stages and to elucidate the differences between them. High-throughput sequencing technology was used to delineate the differences in bacterial communities and their functional attributes between these soil types. The results indicated that distinct variations occur in the alpha diversity and community structures of bacterial populations in both soil types during the rice heading and harvest stages. Typically, the alpha diversity indices were higher in mollisol paddy soil than that in saline–sodic soil. Notably, Actinomycetota showed a significantly higher relative abundance in saline–sodic paddy soil at the harvest stage, whereas Bacteroidota were more abundant in saline–sodic soil at both stages examined. A functional gene analysis via KEGG pathways revealed that carbon fixation pathways were more prevalent in mollisol paddy soil during the rice heading stage. Conversely, genes related to nitrogen metabolism were more abundant under saline–sodic conditions, suggesting a greater need for nitrogen in nutrient absorption by rice in these soils. Overall, bacteria in mollisol paddy soil appear to play more pivotal roles than those in saline–sodic paddy soil. This study not only sheds light on the functional dynamics of bacterial communities but also holds practical implications for soil management strategies in these contrasting environments.
1. Introduction
As a staple food source for more than half of the world’s population, rice is undoubtedly one of the most important food crops [1]. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO, 2023), global rice production exceeded 510 million metric tons in recent years, with Asia accounting for more than 90% of global production and consumption. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China in 2022, as the world’s largest producer and consumer of rice, with an annual rice production of more than 200 million tons in 2022, China plays a key role in national food security and the rural economy. Situated within one of the world’s three major cold mollisol belts, Jilin boasts fertile soils rich in organic matter and nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it a premier site for high-quality rice production in China [2]. It is also globally recognized as a high-quality agricultural resource with excellent characteristics for farming and potential for increased production [3]. Conversely, the Songnen Plain in northwest Jilin, another significant grain-producing area, is increasingly affected by the expansion of saline–sodic soil [4]. This soil type, characterized by high salinity and exchangeable Na+ content, imposes osmotic stress and ionic poisoning on plants, leading to severe agricultural challenges [5]. The heavy, colloidal texture of saline–sodic soil, which expands and disperses easily, becomes muddy when wet and hardens when dry, resulting in a structurally weak and poor soil that hinders effective salt leaching and crop growth [6]. As key drivers of soil ecosystems, soil microorganisms mediate biogeochemical cycles through organic matter decomposition (e.g., cellulose breakdown), nutrient transformations, and contaminant degradation via enzymatic and redox processes [7]. The structure and diversity of the soil microbial community are widely recognized as vital indicators of soil health, as they sensitively reflect shifts in soil fertility, nutrient status, and environmental stress, thus providing important ecological insights for assessing soil quality and sustainability [8]. Environmental factors such as pH, carbon content, and climate significantly influence these microbial communities [9]. A study by A.M. Bossio revealed that soil type impacts soil microorganisms more significantly than agricultural management practices [10]. In addition, the soil type markedly affects the structure and activity of soil microorganisms [11], which in turn influences nutrient uptake, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. Extensive research into soil microbial diversity, employing techniques such as PCR-DGGE and high-throughput sequencing, has delved into the species abundance, community structure, and dynamics at the genetic level [12]. These studies not only elucidate the patterns of microbial diversity but also provide a scientific foundation for enhancing and protecting soil health.
Despite their importance, research on the variations in soil bacterial diversity and the factors influencing these differences in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils remains limited. Previous studies have shown that rice paddies in mollisol are dominated by the phyla Pseudomonadota, Acidobacteria, and Chloroflexi [13], with genera such as Bradyrhizobium and Sphingomonas contributing to organic matter decomposition [14,15]. In contrast, saline–sodic soils are enriched with Bacteroidota and Firmicutes [16], including salt-tolerant genera such as Halomonas, Stenotrophomonas, and Bacillus [17,18]. At present, most studies on mollisol or saline–sodic paddy soils have focused on a single soil type, investigating the characteristics of microbial communities and their effects on crop growth separately. However, systematic comparative studies of bacterial communities in these two typical paddy soil types remain limited, and our understanding of the differences in microbial community across soil types is still inadequate. Thus, a detailed investigation into the bacterial diversity of mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils, alongside the influence of soil properties and environmental factors on these communities, holds significant scientific and practical value. In this study, we utilized high-throughput sequencing technology to identify the differences in bacterial diversity between mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils and to delineate the core microbial community. We hypothesize that the significant variances of the bacterial community in the two soil types contribute to the unique formation processes of mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils. The findings from this research are expected to provide a scientific basis for optimizing soil management strategies and enhancing rice yields.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Sample collection for this study was conducted at four sample plots [19]: two in Mishazi Town (mollisol, M1 and M2 plots), one in Da’an City (DA plot), and one in Qian’an County (QA plot) in 2023. These collections took place during the rice heading period at the end of August and the harvest period in November. Mishazi (125°28′ E, 44°08′ N), located in north-central Jilin Province, northeastern China, features fifty-year-old paddy soil rich in mollisol formed by a unique combination of climate, soil properties, and river scouring. The two soil samples from this area, M1 (125°16′45″ E, 44°6′32″ N) and M2 (125°18′22′ E, 44°4′33″ N), were collected here. Da’an City (DA) (123°58′45″ E, 45°9′53″ N) and Qian’an County (QA) (123°57′8″ E, 45°18′0″ N), situated on the Songnen Plain in the northwest of Jilin Province, experience severe land salinization due to cold climatic conditions, high alkalinity, and salinity in surface and groundwater, respectively, alongside unsustainable agricultural practices and changes in the water table. Despite geographic differences in the sampling locations, all sample sites had a long history of rice cultivation as well as similar farming systems and climatic backgrounds, and samples were selected to represent typical mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils to ensure that microbiological differences originated primarily from the soil types themselves rather than the sampling locations. In summary, the samples included saline–sodic soil at the rice heading stage (QAC, DAC); mollisol at the rice heading stage (MC1, MC2); saline–sodic soil at the rice heading stage (QA, DA); and mollisol at the rice harvest stage (M1, M2). Each soil sample was replicated five times, stored in a refrigerated box, transported to the laboratory, sieved through a 2 mm sieve after root removal, and refrigerated at 4 °C for subsequent analysis.
2.2. Environmental Parameters
The soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were assessed using a soil temperature moisture salinity pH tachymeter (H-WSYP, Shandong Hengmei Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Weifang, China). Soil total nitrogen (TN), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) levels were quantified following the continuous flow analyzer method outlined in ‘Nitrogen determination methods of forest soils’ (LY/T1228-2015, State Forestry Administration of China, Beijing, China, 2015). Soil total phosphorus (TP) and available phosphorus (AP) levels were determined using the continuous flow analyzer method of ‘Phosphorus determination methods of forest soils’ (LY/T1232-2015, State Forestry Administration of China, Beijing, China, 2015). Available potassium (AK) content was measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES) using the method from ‘Determination of available potassium in forest soil’ (LY/T1236-1999, State Forestry Administration of China, Beijing, China, 1999). The soil organic matter (OM) content was analyzed via the external heating-potassium dichromate titration method specified in ‘Determination of organic matter in forest soil and calculation carbon-nitrogen ratio’ (LYT1237-1999, State Forestry Administration of China, Beijing, China, 1999).
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing of Soil
Approximately 0.5 g of sieved soil samples were used for DNA extraction, adhering to the manufacturer’s protocol provided with the Fast DNA SPIN Kit (Catalog No. 6560-220, Mpbio, Irvine, CA, USA). The V3–V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene were targeted for amplification using the primers 341F (sequence 5′-ACTCCTACGGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and 806R (sequence 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). The resulting amplicons were used to construct a sequencing library. The raw sequences generated were then subjected to denoising and clustering using the DADA2 method within the QIIME2 framework. This process included quality control, denoising, merging, and de-chimerization of sequences. Depending on the analysis requirements, the sequence denoising or operational taxonomic unit (OTU) clustering followed either the QIIME2 dada2 analysis protocol [20] or the Vsearch software version 2.26.1 analysis process [21].
2.4. Metagenomic Data Analysis
The DNA extracted was also subjected to metagenomic sequencing. The DNA was randomly sheared into fragments ranging from 200 to 500 bp, which were subsequently sequenced using the Illumina X Ten platform (San Diego, CA, USA). The raw metagenomic data were quality-controlled with fastp (https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp, accessed on 21 May 2022). Following the approach described by Tian et al. (2022), assembled and predicted genes were analyzed for gene expression levels [22]. The abundance of these predicted genes was quantified using Salmon version 0.7.2 [23] (https://combine-lab.github.io/salmon/, accessed on 21 May 2022), which mapped the contigs of predicted genes against the cleaned metagenomic sequencing reads. Gene expressions were represented by transcripts per million reads (TPM). The bacterial functional potential and annotated genes were explored by querying the microbial gene sequences in KAAS (KEGG Automatic Annotation Server) (https://www.genome.jp/tools/kaas/, accessed on 21 May 2022) to obtain KEGG orthology (KO) numbers [24]. Differentially abundant genes (DEGs) between saline–sodic and mollisol paddy soils were identified using TPM data through one-way ANOVA and Student’s t-tests (p < 0.01) in R v.3.3.1 [25] (https://www.r-project.org/, accessed on 21 May 2022). KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was then performed to discern which microbial genes were more abundant in saline–sodic versus mollisol paddy soil, utilizing the GOstats package in Bioconductor within R v.3.3.1.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
A principal component analysis (PCA) based on the TPM data of the genes was conducted using the PCA function in the FactoMineR package in R v.3.3.1. A bubble chart depicting the enriched KEGG pathways of microbial genes in saline–sodic versus mollisol paddy soil was generated using the ggplot2 package in R v.3.3.1. The statistical significance of the differences between soil types was determined through one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s tests (p < 0.05).
3. Result
3.1. Raw Sequencing Data
High-throughput sequencing data from the soil samples collected at the rice harvest stage (Table S1) yielded a total of 782,272 paired reads after substandard sequences were excluded. The average reads per sample were 39,114, with the lowest read count for a single sample being 28,606 (Table S1). At the rice heading stage, a total of 851,408 paired reads were obtained after removing failed sequences, with an average of 42,570 reads per sample and a minimum count of 28,606 in one sample (Table S1). The rarefaction curve, illustrating the relationship between the number of reads and the number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs), indicated an overall upward trend. All sample curves eventually reached a stable plateau, suggesting sequencing depth adequacy (Figure S1). This saturation of the curve confirms the validity of the captured OTUs. With sequences covering at least 96.74% of the OTUs, it is evident that the sequenced data adequately represent the bacterial diversity in the samples and are suitable for further analysis.
3.2. Alpha Diversity of Bacterial Communities
The alpha diversity indices measured include the Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Simpson index. The Chao1 index assesses the difference between the observed and estimated microbial species richness within a sample, while the Shannon and Simpson indices estimate the overall microbial diversity. The results indicated significant variation in the Chao1 index among the groups. Specifically, the Chao1 indices for M1 and M2 were notably higher than those for QA and DA at the harvest stage (Figure 1a). Similarly, the Chao1 indices for MC1 and MC2 were significantly higher than those for QCA and DCA at the heading stage (Figure 1a). The Shannon indices for M1 and M2 exceeded those for QA and DA (Figure 1b), and this pattern was also observed for MC1 and MC2 compared to QAC and DAC (Figure 1b). Conversely, the Simpson indices for M1 and M2 were significantly higher than those for QA and DA (Figure 1c), whereas no significant differences were found between MC1, MC2, QAC, and DAC (Figure 1c).
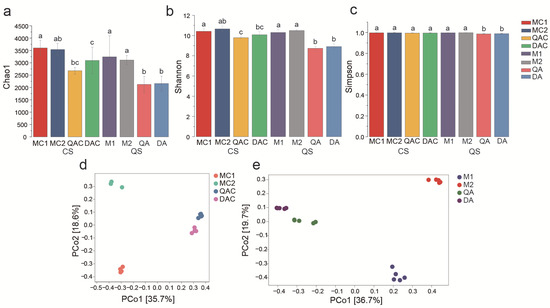
Figure 1.
Alpha diversity analysis of bacterial communities in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at the rice heading (CS) and harvest (QS) stages. (a) presents the Chao1 index analysis, (b) displays the Shannon index analysis, (c) shows the Simpson index analysis, (d) illustrates the Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) at the rice heading stage, (e) depicts the PCoA at the harvest stage. Sample labels: MC1 and MC2 represent mollisol paddy soils at the heading stage; QAC and DAC represent saline–sodic paddy soils at the heading stage; M1 and M2 denote mollisol paddy soils at the harvest stage; QA and DA denote saline–sodic paddy soils at the harvest stage. Significant differences between samples at p < 0.05 are indicated by different letters above the error bars. Each group consists of 5 replicates.
3.3. Beta Diversity of Bacterial Communities
Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) was utilized to examine changes in bacterial compositions among the samples. A significant difference (p < 0.05) in community composition was observed between mollisol paddy soil and saline–sodic paddy soil samples (Figure 1d). This observation was corroborated by the results of the hierarchical clustering analysis, confirming distinct community compositions between the two soil types.
The PCoA analysis further revealed that bacterial community structures in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils were distinct; five replicates of each treatment clustered separately, indicating consistency within each soil type. In order to compare spatial differences between soil types more clearly within each stage and to minimize disturbances due to temporal variables, we analyzed the samples separately by heading and harvest stage. Specifically, bacterial communities in M1 and M2 at the harvest stage, and MS1 and MS2 at the heading stage, differed markedly from those in DA and QA at the harvest stage and DAC and QAC at the heading stage (Figure 1d,e).
Hierarchical clustering of the OTUs from the two soil types at different stages was also performed (Figure S2). The clustering showed that all five replicates from each soil type grouped together, with mollisol paddy soil samples (M1 and M2, MC1 and MC2) depicted by red and blue lines (Figure S2b) and saline–sodic paddy soil samples (QA and DA, QAC and DAC) by green and purple lines (Figure S2a,b). This indicates a greater similarity within bacterial compositions of mollisol samples compared to those from saline–sodic soil at both rice heading and harvest stages.
3.4. Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Structure
The composition of the bacterial communities across all samples was analyzed (Figure 2). The discussion of changes in bacterial community composition was based on the varying relative abundances at the phylum and genus levels in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at both the heading and harvest stages. The dominant phyla in these soils included Pseudomonadota, Actinomycetota, Bacteroidota, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Firmicutes, Desulfobacterota, Mucor, and Verrucomicrobia (Figure 2).
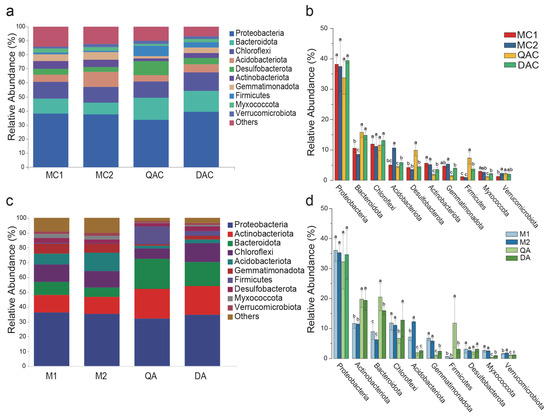
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of bacteria at the phylum level in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils. (a,b) correspond to the rice heading stage, while (c,d) correspond to the harvest stage. Sample labels: MC1 and MC2 for mollisol paddy soils at the heading stage; QAC and DAC for saline–sodic paddy soils at the heading stage; M1 and M2 for mollisol paddy soils at the harvest stage; QA and DA for saline–sodic paddy soils at the harvest stage. Significant differences between samples (p < 0.05) are denoted by different letters above the error bars. Each group comprises 5 replicates.
Significantly higher relative abundances of Actinomycetota and Bacteroidota were noted in QA and DA compared to M1 and M2 (Figure 2d), and higher levels of Bacteroidota were observed in QAC and DAC than in MC1 and MC2 (Figure 2b). Conversely, Actinomycetota and Gemmatimonadota showed significantly greater abundance in MC1 and MC2 than in QAC and DAC (Figure 2b), while Gemmatimonadota, Verrucomicrobiota, Myxococcota, and Acidobacteriota were more abundant in M1 and M2 than in QA and DA at the harvest stage (Figure 2d). Meanwhile, the full-level LEfSe analysis further confirmed that Bacteroidota were significantly enriched in saline–sodic paddy soils, while Gemmatimonadota were significantly enriched in mollisol paddy soils (Table S2).
At the genus level, KD4-96, Ellin6067, and Subgroup_7 were more abundant in MC1 and MC2 than in QAC and DAC (Figure 3b), whereas Lysobacter and Antarcticibacterium were more prevalent in QA and DA than in M1 and M2 (Figure 3d). The abundance of KD4-96, Ellin6067, and Subgroup_7 was also significantly higher in M1 and M2 than in QA and DA (Figure 3d). Meanwhile, the STAMP analysis showed that the abundances of Antarcticibacterium and Lysobacter were significantly higher in saline–sodic paddy soils than in mollisol paddy soils, whereas Sphingomonas was significantly more abundant in mollisol paddy soils compared to saline–sodic soils (Figure S4).
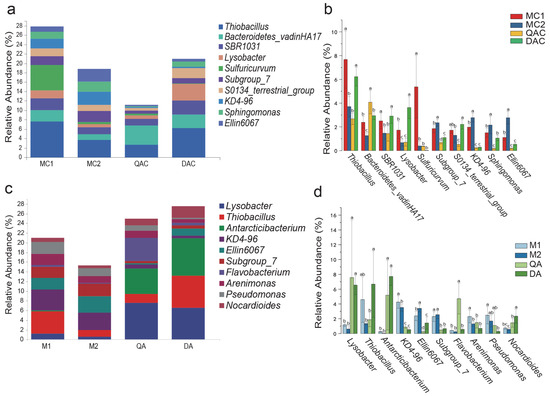
Figure 3.
Relative abundance of bacteria at the genus level in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at the rice heading and harvest stages. (a,b) represent the heading stage, while (c,d) depict the harvest stage. Sample labels: MC1 and MC2 for mollisol paddy soils at the heading stage; QAC and DAC for saline–sodic paddy soils at the heading stage; M1 and M2 for mollisol paddy soils at the harvest stage; QA and DA for saline–sodic paddy soils at the harvest stage. Differences between samples with statistical significance (p < 0.05) are highlighted by different letters above the error bars. Each group includes 5 replicates.
The microbial covariance network analysis based on the relative abundance of bacteria indicated that the keystone taxa of mollisol paddy soil at the heading stage (CS) included Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, Acidobacteria, and Chloroflexi (Figure 4a); those of saline–sodic paddy soil were dominated by Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, and Desulfobacterota (Figure 4b). The keystone taxa in mollisol paddy soil during the late fall harvest (QS) were Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, Chloroflexi, Actinomycetota, and Acidobacteria (Figure 4c); in saline–sodic paddy soil, they included Pseudomonadota, Bacteroidota, Actinomycetota, and Chloroflexi (Figure 4d).
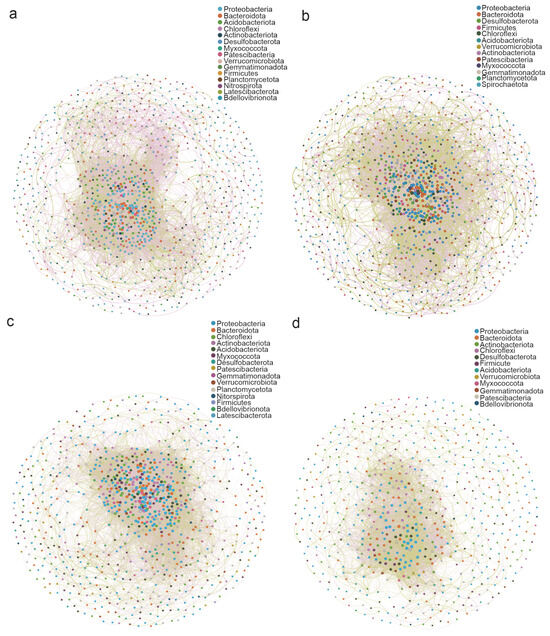
Figure 4.
Covariance network analysis of bacteria in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils. (a,b) depict microbial network analysis plots for mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at the rice heading stage, respectively. (c,d) display microbial network analysis plots for mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at the rice harvest stage, respectively.
3.5. Metagenomic Data Analysis
The metagenomic data were utilized to examine differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between saline–sodic and mollisol paddy soils. The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of these DEGs highlighted distinct biological pathways differentially active in the two soil types at both the harvest and heading stages (Figure 5). Pathways associated with “Nitrogen metabolism” were significantly more enriched in saline–sodic paddy soil than in mollisol paddy soil at the rice heading stage (Figure 5a). Conversely, pathways linked to the “Two-component system” and “Carbon fixation pathways in prokaryotes” were notably more enriched in mollisol paddy soil (Figure 5b). Additionally, pathways related to “Peroxisome” and “Proteasome” were more prevalent in saline–sodic paddy soil (Figure 5c), while the same “Two-component system” pathways showed greater enrichment in mollisol paddy soil at this stage (Figure 5d).
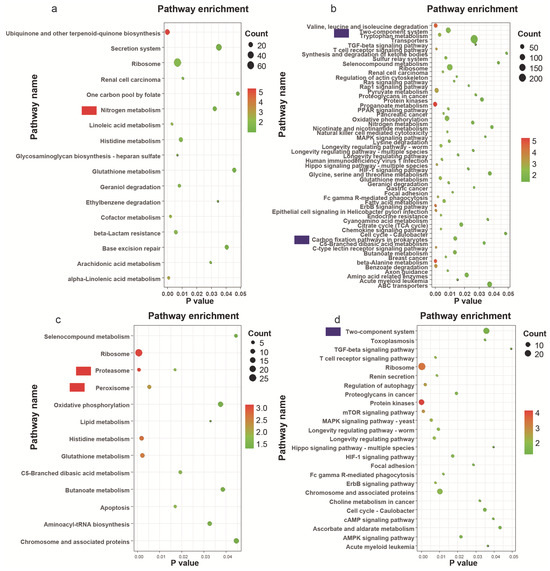
Figure 5.
KEGG enrichment analysis of metagenomic data comparing saline–sodic and mollisol paddy soils across two developmental stages. (a,c) depict the up-regulated genes in KEGG enrichments, while (b,d) show the down-regulated genes during the heading and harvest stages, respectively.
In terms of gene-specific activity, 36 genes were upregulated in mollisol paddy soil within the “Carbon fixation pathways in prokaryotes,” including K01938 (formate–tetrahydrofolate ligase), K00626 (acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase), K01849, K01963, K00244, K01895, among others (Table S3b). Notably, K01938, K00626, and K00925 (acetate kinase) are pivotal for carbon fixation processes (Table S3b). In the saline–sodic soil, 16 genes were upregulated in the “nitrogen metabolism” pathway, including K01673, K04561 (nitric oxide reductase), K00262, K00459, K02567, K15864 (nitrite reductase), K01673, K01915, K15576, and K15371, highlighting their roles in bacterial denitrification (Table S3a).
3.6. RDA Analysis of the Influence of Soil Physicochemical Properties on Bacterial Community Diversity
Soil microorganisms are profoundly influenced by nutrient content and physicochemical properties, leading to significant variations in the compositional structure of microbial communities across different soil types. Detailed physicochemical data for mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils at both the heading and harvest stages are provided in Table S4. Typically, the content of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), available potassium (AK), available phosphorus (AP), and organic matter (OM) in mollisol paddy fields consistently exceeded that in saline–sodic soil paddy fields during both the heading stage and the late fall harvest. Conversely, electrical conductivity (EC) and pH values presented inverse trends.
Notably, the nitrate nitrogen (NO3−) content surpassed that of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+) in mollisol paddy soils during the spike stage, whereas the reverse was true during the fall harvest. The Redundancy Analysis (RDA) indicated close similarities within each soil type, suggesting a greater community similarity among the mollisol paddy soils compared to the saline–sodic paddy soils (Figure 6). At the rice heading stage, RDA1 accounted for 15.34% of the variation, RDA2 for 14.24%, with a cumulative explanatory power of 29.58%. This analysis underscored that the diversity of the soil bacterial community structure was predominantly influenced by a combination of environmental factors (Figure 6a). Significant correlations were observed between the soil’s physicochemical properties—such as TP, OM, AK, pH, AP, NH4+-N, yield nitrogen (YN), and EC—and the structural diversity of the bacterial community, highlighting their substantial impact (p < 0.01). These factors crucially affect the diversity of soil bacterial microorganisms in paddy fields. During the late autumn harvest, RDA1 and RDA2 explained 20.28% and 16.82% of the variation, respectively, cumulating to 37.1%. This further indicates that environmental and multiple factors significantly shape the structural diversity of soil bacterial communities (Figure 6b). The physical and chemical properties of the soil exerted a highly significant influence on the bacterial community structure (p < 0.01), reaffirming their pivotal role in determining the diversity of soil bacteria in paddy fields.
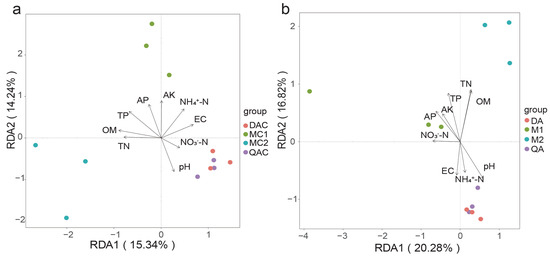
Figure 6.
RDA analysis of the influence of soil physicochemical properties on bacterial community diversity in mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils. (a) covers the rice heading stage and (b) the rice harvest stage. MC1, MC2 represent mollisol paddy soils; QAC, DAC denote saline–sodic paddy soils at the heading stage; M1, M2 represent mollisol paddy soils; QA, DA denote saline–sodic paddy soils at the harvest stage. Significant differences between samples (p < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above the error bars. Five replicates were used in each group.
4. Discussion
The structure of soil bacterial communities is influenced by interactive and synergistic effects with natural conditions, soil physicochemical properties, soil type, enzyme activity, aeration, temperature, and pH [26]. These factors significantly impact soil microbial diversity. The variety and vitality of soil bacteria are primary indicators of microbial health, influencing nutrient composition and transformation, as well as the physical and chemical properties of the soil. These characteristics are also key indicators of soil fertility. Moreover, the diversity of soil microorganisms regulates soil abiotic indicators, which are critical for soil health and fertility [27].
The alpha diversity indices, including Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson, were used to evaluate the differences in bacterial diversity across soil types and stages. At both the rice heading and harvest stages, the Chao1 index, which emphasizes species richness, was significantly higher in mollisol paddy soils compared to saline–sodic soils; the Shannon index showed a higher average in mollisol soils, though without statistical significance; the Simpson index, which places greater weight on dominant taxa and evenness, exhibited the smallest variation among the three indices and also did not reach significance. However, both the Shannon and Simpson indices followed the same trend as the Chao1 index, consistently indicating higher diversity in mollisol samples. This suggests that the observed lack of statistical significance in the Shannon and Simpson indices may be due to relatively small differences in community evenness or greater within-group variability, rather than an absence of ecological difference. Together, the combined results from all three indices support the conclusion that mollisol paddy soils harbor more diverse bacterial communities than saline–sodic soils. This disparity could be attributed to differences in soil physicochemical properties affecting diversity indices, revealing that bacterial community diversity was superior in mollisol paddy soil. Additionally, the results indicated that bacterial diversity varies with different stages of the same soil, being higher at the heading stage (CS) than at the harvest stage (QS).
Meng et al. identified soil properties as a principal driving factor for the formation of understory vegetation diversity [28]. In paddy soils, the barrenness or fertility of nutrients directly impacts the activity and composition of soil microorganisms. Xu et al. [29] pointed out that soil properties—including nutrient status, moisture content, and pH—can collectively regulate soil microbial communities. Among these, the composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities largely depend on soil nutrient levels, such as soil organic carbon (SOC), soil total nitrogen (STN), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), ammonium nitrogen (SAN), and nitrate nitrogen (SNN). Studies have shown that under different vegetation restoration patterns, changes in soil properties exert varying effects on microbial communities. For example, compared with grasslands, higher nutrient levels in plantation forests can promote greater bacterial diversity and community complexity. This highlights that soil nutrients are one of the key factors influencing the structure of microbial communities. The abundance and diversity of bacterial communities were significantly higher in mollisol than in saline–sodic soils, underscoring the inferior conditions of saline–sodic soils. Across various periods, the Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson indices were consistently lower in saline–sodic paddy soil compared to mollisol paddy soil. This suggests that bacterial communities in saline–sodic soils are less abundant and diverse than in mollisol, possibly because high salinity and pH reduce nutrient availability, thereby limiting microbial and plant growth [30].
The spatial analysis revealed a greater distance between samples from saline–sodic paddy soil than those from mollisol paddy soil (Figure S2), indicating higher microbial community similarity within saline–sodic samples. This suggests that certain keystone bacteria in saline–sodic paddy soil may be commonly enriched, adapting to adverse conditions. However, this current phased PCoA analysis has some limitations; it is not possible to directly observe the dynamics of microbial communities at the same site during different growth stage. Future studies may consider integrating all growth stages into the same graph to more fully characterize the changes in soil microbial communities.
The distinct characteristics of saline–sodic and mollisol paddy soils are significant factors influencing the populations of dominant microorganisms [31]. This study found that the relative abundance of Antarcticibacterium was found to be significantly higher at both the rice heading and harvest stages, and STAMP analysis at the genus level revealed that the relative abundance of Antarcticibacterium was significantly higher in saline–sodic than in mollisol paddy soil. Studies have indicated that Antarcticibacterium, as a denitrifying bacterial genus, may play a role in soil nitrogen transformation and has the potential to be involved in nitrogen cycling processes such as denitrification or nitrogen utilization [32].Although Antarcticibacterium started out as a marine bacterium found in sediments, it has also been found to survive in highly saline environments [33], and the genus Antarcticibacterium was detected by Bi et al. in the treatment of saline soils using microbial agents [34], suggesting that it is salt-tolerant, and it may be involved in soil conditioning as an auxiliary strain. This may be due to the properties of the genus Antarcticibacterium, such as salt tolerance, cold tolerance, and tolerance to organic matter, which are adapted to the microecology of rice paddies, and the promotion of human agricultural activities (e.g., the use of marine organic fertilizers), which have led to the emergence of Antarcticibacterium in paddy soils. The relative abundance of Lysobacter, a genus within the Pseudomonadota known for its robust survivability and minimal survival requirements, was markedly higher in saline–sodic soil at the rice harvest stage. Lysobacter produces phosphatases that not only degrade the phospholipids in the cell membranes of plant pathogens, leading to the death of these microorganisms, but also mineralize organic phosphorus in the soil, thereby enhancing phosphorus availability and promoting plant growth [35]. Sphingomonas was significantly enriched in mollisol paddy soils at both sampling stages. This may be attributed to the ability of Sphingomonas to enhance plant nutrient uptake efficiency [36] and its known sensitivity to water availability [37]. The higher water-holding capacity of mollisol soils likely supports the growth of Sphingomonas, whereas saline–sodic soils often impose osmotic stress due to high salinity, which may inhibit its proliferation. Moreover, Sphingomonas can produce extracellular polysaccharides (EPSs) [38], enhancing its tolerance to drought and environmental stress. The enrichment of Sphingomonas in the rice rhizosphere may also be promoted by root exudates, ultimately contributing to improved rice growth. Thiobacillus was found to be abundant in both mollisol and saline–sodic paddy soils, indicating a strong capacity for environmental tolerance. Previous studies have reported that Thiobacillus can adapt to diverse environments by dynamically regulating its biochemical metabolic pathways, and this metabolic plasticity enables its survival across soils with varying physicochemical properties [39]. In this study, the widespread presence of Thiobacillus in both soil types further supports the diversity of its adaptive mechanisms. Moreover, it has been reported that Thiobacillus is capable of oxidizing inorganic sulfur compounds in the soil, converting them into forms such as sulfate, which can be utilized in the physiological metabolism and growth of rice [40]. Actinomycetota are known for their capacity to produce a wide range of antibiotics, contribute to nitrogen fixation, and facilitate the cycling of organic matter. These bacteria promote the decomposition of plant and animal residues, thus influencing the ecological balance of soil microorganisms [41]. The abundance of Actinomycetota in soil has been closely linked to pH levels, with optimal abundance occurring at pH 6.8–8.5 [42]. In this study, the pH of saline–sodic paddy soil was less conducive to their growth, yet the relative abundance of Actinomycetota was higher than in mollisol paddy soil. This study also found that Bacteroidota were significantly enriched in saline–sodic paddy soils, while Gemmatimonadota showed higher abundance in mollisol paddy soils. These contrasting distributions are closely related to the environmental preferences and ecological functions of these two phyla. Previous studies have reported their enrichment in saline, alkaline, and arid soils, where their metabolic versatility and halotolerance confer ecological advantages [43,44]. The saline–sodic soils in our study, characterized by high pH, elevated electrical conductivity, and low organic matter and nutrient content, likely provided favorable conditions for the proliferation of Bacteroidota. Bacteroidota are widely recognized for their ability to degrade complex organic compounds and adapt to extreme or nutrient-limited environments [45]. Bacteroidota are capable of degrading complex organic compounds in soil, such as polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids, thereby releasing nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium that are available for plant uptake. This process enhances soil fertility and supplies essential nutrients for rice growth [46]. In saline–sodic soils, this function is particularly critical, as nutrient availability is generally limited. The degradative activity of Bacteroidota can facilitate the release of nutrients that are otherwise immobilized or difficult for plants to access, thereby promoting rice growth. Gemmatimonadota is usually more abundant in well-structured soils with high fertility and is involved in key processes such as organic matter transformation and long-term nutrient cycling [47], They can convert organic nitrogen into ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3−) [48], making nitrogen available for rice uptake. In this study, their higher abundance in mollisol paddy soils can be attributed to the greater availability of organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus, as well as to more favorable moisture and soil texture conditions. In addition, they are capable of synthesizing and secreting plant growth hormones such as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and gibberellins (GA). These phytohormones can stimulate the growth and development of rice roots, increasing root length, the number of root hairs, and root activity, thereby enhancing the plant’s capacity to absorb water and nutrients [49].
Metagenomic data are typically utilized to analyze bacterial functions relative to their environmental conditions [22]. Pathways related to “nitrogen metabolism” were more enriched in saline–sodic paddy soil than in mollisol paddy soil at the rice heading stage. Conversely, “carbon fixation pathways in prokaryotes” were more enriched in mollisol paddy soil. These observations suggest a higher abundance of carbon fixation pathways in mollisol soils, suggesting that microbial communities in fertile black soils have greater potential for autotrophic carbon assimilation, which may contribute to organic matter accumulation and soil productivity, providing superior nutrient conditions for rice growth and contributing to robust rice growth and high yields. In contrast, the enrichment of nitrogen metabolism pathways in saline–sodic soils may represent an adaptive microbial response to nitrogen-limited, high-salinity conditions, mitigating the adverse effects of salinization on rice and supporting its growth in saline–sodic soils. Additionally, genes such as K01938 (formate--tetrahydrofolate ligase), K00626 (acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase), and K00925 (acetate kinase), which are key for carbon fixation, were predominantly expressed in mollisol paddy soil at the rice heading stage (Table S3b). Conversely, K04561 (nitric oxide reductase) and K15864 (nitrite reductase), crucial for denitrification, were highlighted in saline–sodic paddy soil (Table S3a). These findings underscore the differential roles of specific genes in metabolic processes across different soil types. Although this study did not directly measure rice growth parameters such as yield, plant height, or biomass, the functional characterization of microbial communities provides important ecological insights. In particular, mollisol paddy soils exhibited a higher abundance of bacterial taxa and functional genes associated with carbon fixation (e.g., formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase, acetate kinase), which are known to enhance soil carbon cycling and plant productivity [50]. Conversely, nitrogen metabolism and denitrification related genes were more enriched in saline–sodic paddy soils than mollisol paddy soil, indicating nutrient limitations and stress adaptation strategies in saline–sodic soil [51,52].
Soil physicochemical factors typically influence both the bacterial community and its functions, which in turn are implicated in bacterial metabolism [53]. This study found that differences in soil nutrient profiles, including higher levels of total nitrogen, nitrate, and organic matter in mollisol soils, may indirectly reflect better conditions for rice growth. Organic matter (OM) and total phosphorus (TP) were the primary factors positively influencing the bacterial communities of mollisol paddy soil at both the rice harvest and heading stages, whereas these factors negatively influenced the bacterial communities of the saline–sodic paddy soil at these stages. Conversely, pH and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) were the primary factors positively affecting the bacterial communities of saline–sodic paddy soil at the rice heading stage; similarly, pH and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) were influential at the rice harvest stage. Considering the metagenomic data, this suggests that OM and carbon fixation-related bacteria are positively correlated in mollisol paddy soil at the rice heading stage; meanwhile, NO3−-N and bacteria with denitrification functions are positively correlated in saline–sodic paddy soil at the rice harvest stage. Soil physicochemical properties are key factors influencing rice growth and plant physiological traits. Studies have shown that soil physical and chemical characteristics—such as texture, organic matter, and nutrient contents including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—significantly affect rice yield and grain quality, including the physical characteristics and chemical composition of grains, as well as the physicochemical properties of starch [54]. Therefore, soil microorganisms may influence rice physiology and yield by regulating nutrient availability and mediating plant–microbe interactions. Future studies will incorporate rice phenotypic and yield-related agronomic traits to further validate the actual contributions of core microbial taxa to rice growth under different soil conditions.
5. Conclusion
This study established several key findings regarding soil microbial communities: (1) the diversity of the bacterial community in mollisol paddy soil was found to be significantly higher than in saline–sodic paddy soil at both the rice heading and harvest stages; (2) the relative abundance of Bacteroidota was significantly higher in saline–sodic paddy soil compared to mollisol paddy soil. Conversely, the relative abundance of Gemmatimonadota was significantly higher in mollisol paddy soil than in saline–sodic paddy soil; (3) bacteria in mollisol paddy soil were found to play more significant roles in carbon fixation, whereas nitrogen metabolism was more critical in saline–sodic soil, essential for rice nutrient absorption at the rice heading stage; and (4) Antarcticibacterium may play a pivotal role in the denitrification processes within saline–sodic paddy soil.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15121261/s1, Figure S1: a is the sparse curve of paddy soil at the rice heading stage, and b is the sparse curve of paddy soil at the rice harvest stage; Figure S2: otu hierarchical clustering tree analysis. a, at the rice heading stage; b, at the rice harvest stage; Figure S3: LEfSe analysis of bacterial communities in mollisol and saline-sodic paddy soils. (a) illustrates analysis results for MC1 and MC2 from mollisol paddy soils, and DAS and QAS from saline-sodic paddy soil at the rice heading stage. (b) shows results for M1 and M2 from mollisol paddy soils, and DA and QA from saline-sodic paddy soil at the rice harvest stage. Labels: MC1, MC2 are mollisol paddy soils at heading stage; QAC, DAC are saline-sodic paddy soil at heading stage; M1, M2 are mollisol paddy soils at harvest stage; QA, DA are saline-sodic paddy soil at harvest stage. Each group consisted of 5 replicates; Figure S4: STAMP analysis displaying differences in relative abundance at specific taxonomic levels with 95% confidence intervals (p < 0.05). (a) corresponds to the rice heading stage, (b) relates to the rice harvest stage. BS represents mollisol paddy soil; SAS denotes saline-sodic paddy soil; Table S1: Sequences of bacterial samples read from black soil paddy soils and saline-sodic soil paddy soils at heading stage MC1, MC2, black soil paddy soils; QAC, DAC, saline-sodic soil paddy soils; Table S2: Sequences of bacterial samples read from black soil paddy soils and saline-sodic soil paddy soils at harvest stage M1, M2, black soil paddy soils; QA, DA, saline-sodic soil paddy soils; Table S3a: KEGG analysis of the related genes with nitrogen metabolism in the comparison of saline-sodic versus mollisol paddy soils; Table S3b: KEGG analysis of the related genes with carbon fixation in the comparison of saline-sodic versus mollisol paddy soils; Table S4: Physicochemical indexes of black soil paddy soils and saline-sodic soil paddy soils: M1 and M2 for black soil paddy soils at harvest stage, MC1 and MC2 for black soil paddy soils at heading stage, QA and DA for saline-sodic soil paddy soils at harvest stage, and QAC and DAC for saline-sodic soil paddy soils at heading stage.
Author Contributions
L.T. and L.H. designed the experiment. J.Z., Y.Y., S.H., D.J. and H.M. conducted the experiments. J.Z. and Y.Y. analyzed and visualized the data. The original manuscript was written by J.Z. and Y.Y., with input from L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Key Research and Development Program, China (No. 2022YFD1500201), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Black Soil Granary, China (No. XDA28020400 and XDA28080200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42007043 and 41920104008), the National Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province, China (No. YDZJ202201ZYTS472), and the Innovation Team Project of Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2023CXTD02).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chang, J.; Shi, S.; Tian, L.; Leite, M.F.; Chang, C.; Ji, L.; Ma, L.; Tian, C.; Kuramae, E.E. Self-crossing leads to weak co-variation of the bacterial and fungal communities in the rice rhizosphere. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.X.; Wang, Z.Q. Influence of Soil Erosion to Soil Enzyme Activities in the Black Soil Area in Northeast China. Soil Water Conserv. China 2018, 9, 47–51+67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.J.; Yu, X.F.; Gao, J.L.; Zhao, Y.P. The Bottleneck and Breakthrough path of the Conservation Tillage Development in Black Soil of Northeast China. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 2, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qu, Y. Relationships between temporal and spatial changes in lakes and climate change in the saline-alkali concentrated distribution area in the Southwest of Songnen Plain, Northeast China, from 1985 to 2015. Water 2020, 12, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Nie, S.; Wang, R.; Wan, H.; Liu, C. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater for irrigation use in central and eastern Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Ma, X. Additional application of aluminum sulfate with different fertilizers ameliorates saline-sodic soil of Songnen Plain in Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3521–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-Jimenez, B.; Schilder, M.T.; Nijhuis, E.H.; Te Beest, D.E.; Bloem, J.; Visser, J.H.; van Os, G.; Brolsma, K.; de Boer, W.; Postma, J. Chitin-and keratin-rich soil amendments suppress Rhizoctonia solani disease via changes to the soil microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00318–e00321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreo-Jimenez, B.; Te Beest, D.E.; Kruijer, W.; Vannier, N.; Kadam, N.N.; Melandri, G.; Jagadish, S.K.; Van Der Linden, G.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. Genetic mapping of the root mycobiota in rice and its role in drought tolerance. Rice 2023, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, C.; Cai, Y.; Mao, L.; Ge, Z.; Yang, N. Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.; Scow, K.; Gunapala, N.; Graham, K. Determinants of soil microbial communities: Effects of agricultural management, season, and soil type on phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Qiao, C.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Cao, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q. Rhizosphere bacterial community is mainly determined by soil environmental factors, but the active bacterial diversity is mainly shaped by plant selection. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F. Impact of Tree Species Mixture on Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Soil Aggregates of Castanopsis hystrix Plantations. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, F. Biochar application reduces saline–alkali stress by improving soil functions and regulating the diversity and abundance of soil bacterial community in highly saline–alkali paddy field. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.J.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, Z.H.; Wei, D.; Zhou, B.K.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, G.H. Response of nirS-type denitrifier community and network structures tolong-term application of chemical fertilizers in a black soil of northeast China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.Y.; Shao, Y.X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.D.; Zhou, N.Y.; Yan, L. Research advances of carbon-fixing microorganisms in the black soil of northeast China. Microbiol. China 2024, 51, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhai, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Microbial diversity and functions in saline soils: A review from a biogeochemical perspective. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Takano, T.; Liu, S. Isolation and characterization of novel bacterial taxa from extreme alkali-saline soil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Leng, X.Y.; Shi, C.F. Research Progress on Bacterial Communities in Saline-alkali Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Huangfu, S.; Sun, Y.; Sun, C.; Huang, L.; Tian, L. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Play More Important Roles in Saline–Sodic Soil than in Black Soil of the Paddy Field in Northeast China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Chang, J.; Shi, S.; Ji, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Cai, Y.; et al. Comparison of methane metabolism in the rhizomicrobiomes of wild and related cultivated rice accessions reveals a strong impact of crop domestication. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Qiu, Q.; Yan, C.; Xiong, J. Structure, acquisition, assembly, and function of the root-associated microbiomes in Japonica rice and hybrid rice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 373, 109122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassán, F.; Diaz-Zorita, M. Azospirillum sp. in current agriculture: From the laboratory to the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Y.; Fan, S.X.; Dong, L.; Li, K.; Li, X.L. Response of Understory Plant Diversity to Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Urban Forests in Beijing, China. Forests 2023, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.P.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Han, X.H.; Ren, C.J.; Yang, G.H. Plant Biomass and Soil Nutrients Mainly Explain the Variation of Soil Microbial Communities During Secondary Succession on the Loess Plateau. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehtaiwesh, A.F. The effect of salinity on nutrient availability and uptake in crop plants. Sci. J. Appl. Sci. Sabratha Univ. 2022, 9, 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, M.; Mathur, P. Restoration of Saline and Sodic Soil Through Using Halophytes as Agroforestry Components. In Sustainable Management and Conservation of Environmental Resources in India; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 311–354. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chun, L.; Ji, L.; Na, R.; Wei, Z.; Han, W. Investigating the diversity and influencing factors of the rhizosphere bacterial community associated with Salicornia europaea L. populations in semi-arid grassland. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awagul, T.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yuan, F.Z.; Zhu, Y.B.; Zhang, L.; Du, W.J.; Ma, Z.H. Analysis of soil microbial diversity and influencing factors in Hemaquan New District in Urumqi. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, Y. Bacillus halophilus BH-8 Combined with Coal Gangue as a Composite Microbial Agent for the Rehabilitation of Saline-Alkali Land. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Huang, J.; Yuan, L. A new function of the biocontrol bacterium Lysobacter enzymogenes LE16 in the mineralization of soil organic phosphorus. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.F.; Jiang, R.H.; Zhu, C.Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.X.; Hou, X.L. Effects of Phosphate-solubilizing Bacteria on Maize Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Structure. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2025, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Gu, Y.T.; Liu, L.; Li, G.H.; Guo, H.C.; Li, J. Growth promotion effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on potato under water deficit by combining microbiome and metabolome. South. Agric. 2023, 54, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Biopolymers Produced by Sphingomonas Strains and Their Potential Applications in Petroleum Production. Polymers 2022, 14, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, S.; Hu, S.; dela Cruz, T.E.E.; Veen, G. Protists as catalyzers of microbial litter breakdown and carbon cycling at different temperature regimes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gerrity, S.; Collins, G.; Chen, T.; Li, R.; Xie, S.; Zhan, X. Enrichment and characterization of autotrophic Thiobacillus denitrifiers from anaerobic sludge for nitrate removal. Process Biochem. 2018, 68, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.A.; Haq, S.; Bhat, R.A. Actinomycetes benefaction role in soil and plant health. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Guo, X.; Ma, L.Z.; Dong, H.; Huang, Y. Iron reduction by diverse actinobacteria under oxic and pH-neutral conditions and the formation of secondary minerals. Chem. Geol. 2019, 525, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Wang, Z.; Teng, X.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Lian, B. Rhizosphere bacterial diversity and environmental function prediction of wild salt-tolerant plants in coastal silt soil. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mohamed, O.A.A.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Ma, J. Bacterial community structure and potential microbial coexistence mechanism associated with three halophytes adapting to the extremely hypersaline environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Guo, F. Comparative analysis of the endophytic bacterial diversity of Populus euphratica oliv. in environments of different salinity intensities. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00500–e00522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Jin, T.; Zhang, H.; Peng, J.; Zuo, N.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.; Tian, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, K.; et al. Deciphering the diversity and functions of plastisphere bacterial communities in plastic-mulching croplands of subtropical China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yu, S. Impacts of Land Use on Soil Nitrogen-Cycling Microbial Communities: Insights from Community Structure, Functional Gene Abundance, and Network Complexity. Life 2025, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Kumar, S.D.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Impa, S.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.J.A.; et al. Dynamic interplay among soil nutrients, rhizosphere metabolites, and microbes shape drought and heat stress responses in summer maize. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Guo, E.Q.; Tan, J.H.; Kang, F.Y. Influence of rotation fallow mode on bacterial community in soil. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2020, 38, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Begmatov, S.; Beletsky, A.V.; Dedysh, S.N.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V. Genome analysis of the candidate phylum MBNT15 bacterium from a boreal peatland predicted its respiratory versatility and dissimilatory iron metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 951761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, H.; Min, W. Saline and alkaline stresses alter soil properties and composition and structure of gene-based nitrifier and denitrifier communities in a calcareous desert soil. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Li, H.B.; Li, Z.J.; Quan, W.C.; Kan, S.M.; Luo, P.; Zhou, D.P.; Zheng, L. Effects of PAM water retention improvement on soil properties and microbial characteristics in dry-hot valley loamy soils. Environ. Ecol. 2025, 7, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Leite, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, L.; Chang, J.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; van Veen, J.; Tian, C.; Kuramae, E. Facilitation in the soil microbiome does not necessarily lead to niche expansion. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwongchai, W.; Tananuwong, K.; Krusong, K.; Thitisaksakul, M. Yield, Grain Quality, and Starch Physicochemical Properties of 2 Elite Thai Rice Cultivars Grown under Varying Production Systems and Soil Characteristics. Foods 2021, 10, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).