Evidence for a Common Genetic Origin of Classic and Milder Adult-Onset Forms of Isolated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Editorial Policies and Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Assays
2.4. Genetic Analyses by Targeted Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
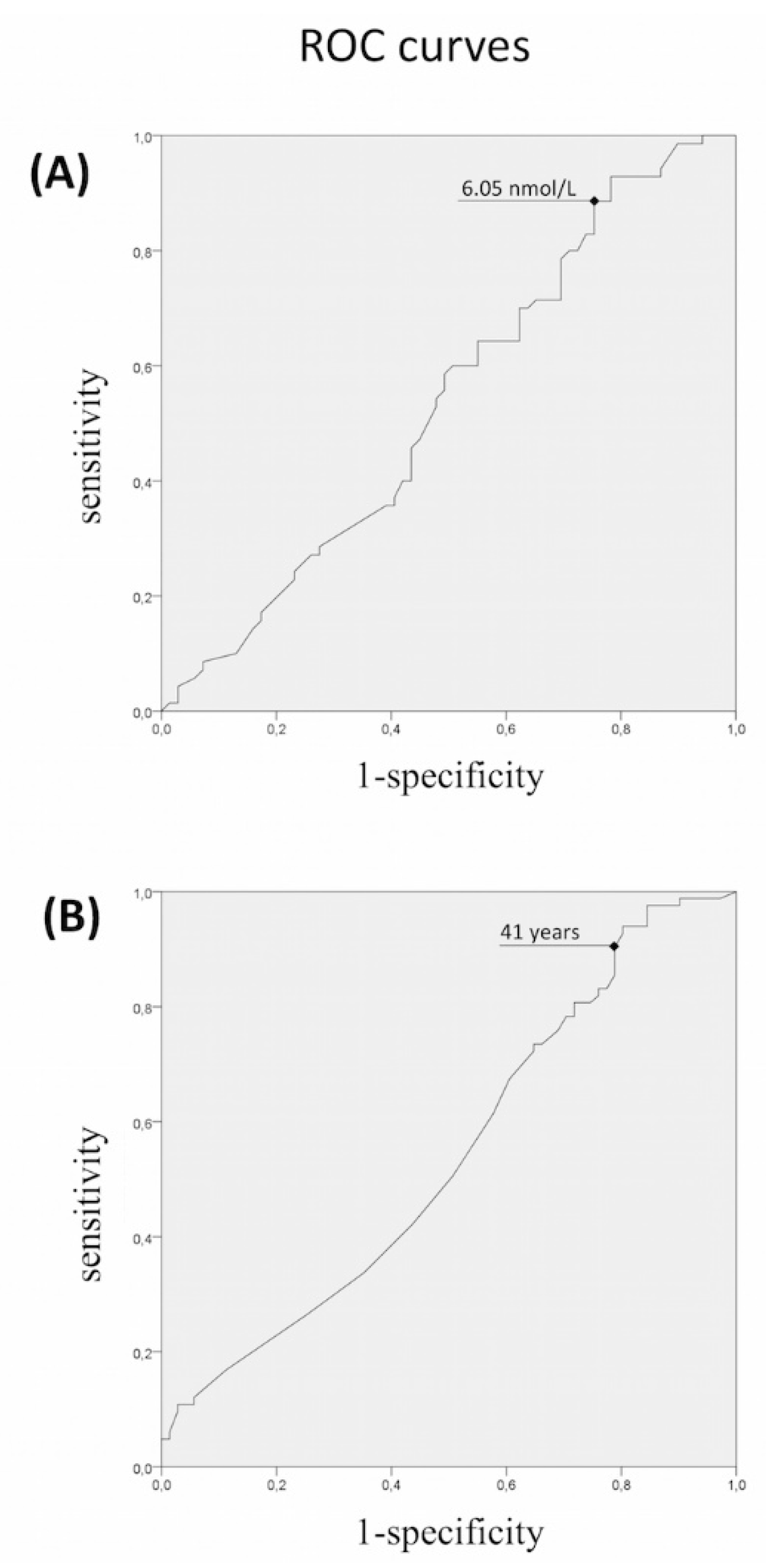
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
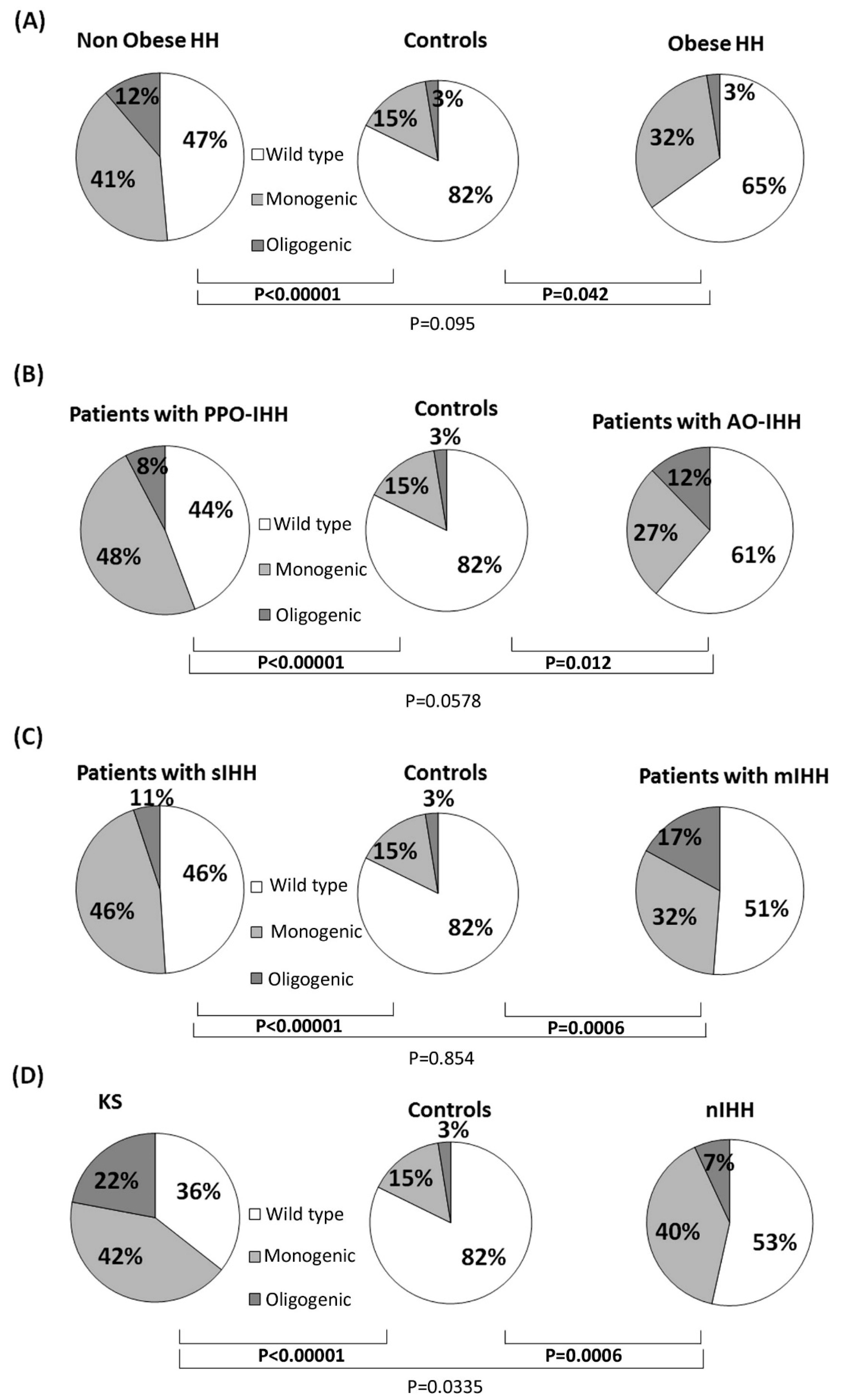
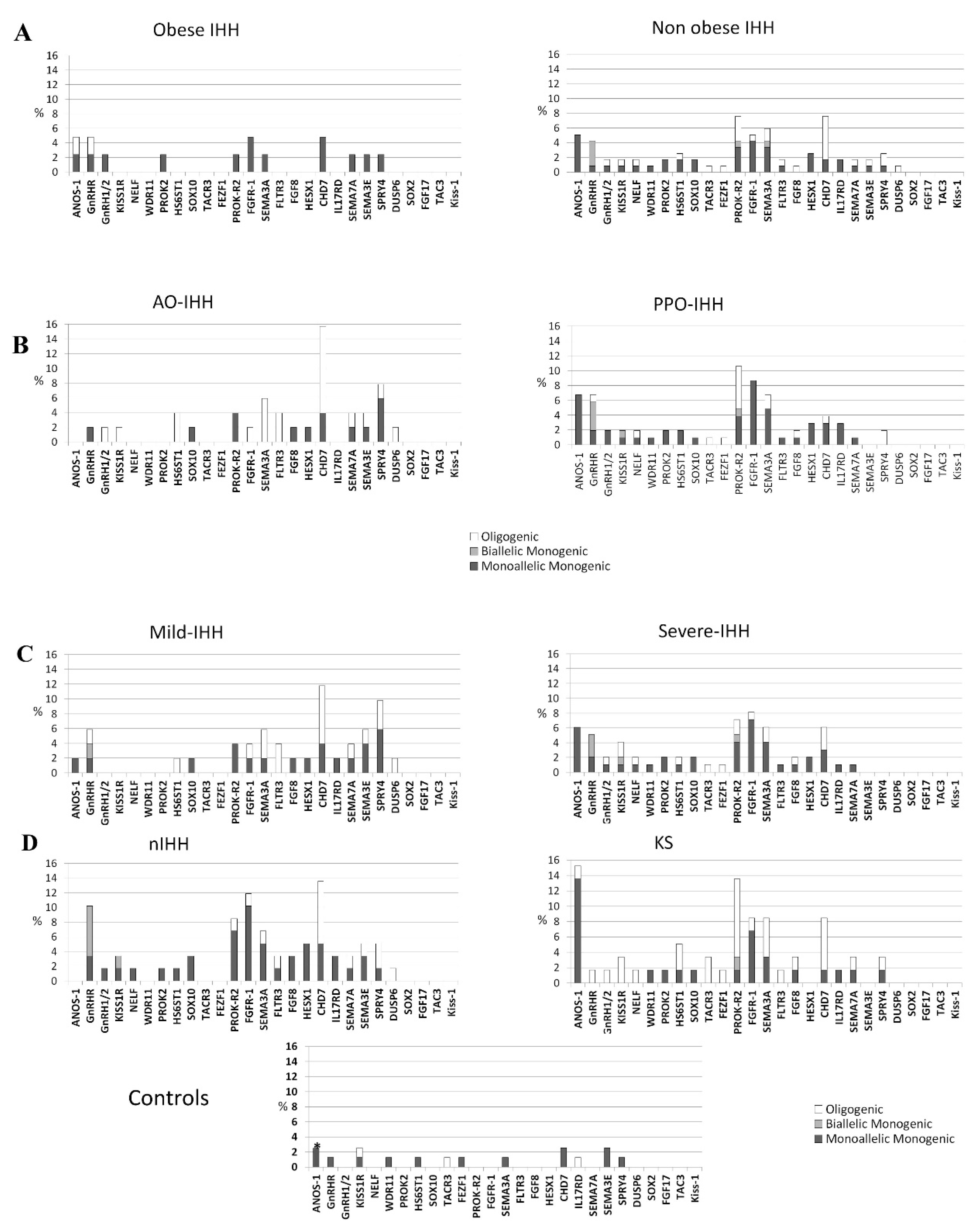
3.1. Rare Allelic Gene Variants Enrichment According to TTe Levels, IHH Onset, Obesity, Olfactory Defects
3.2. Differences in Gene Involvement According to Testosterone Level, IHH Onset, Obesity, Olfactory Defects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Financial Support
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boehm, U.; Bouloux, P.-M.; Dattani, M.T.; de Roux, N.; Dodé, C.; Dunkel, L.; Dwyer, A.A.; Giacobini, P.; Hardelin, J.-P.; Juul, A.; et al. European Consensus Statement on congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism—Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminara, S.B.; Hayes, F.J.; Crowley, W.F. Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Deficiency in the Human (Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Kallmann’s Syndrome): Pathophysiological and Genetic Considerations. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, M.; Vezzoli, V.; Krausz, C.; Guizzardi, F.; Vezzani, S.; Simoni, M.; Bassi, I.; Duminuco, P.; Di Iorgi, N.; Giavoli, C.; et al. Characteristics of a nationwide cohort of patients presenting with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, E.-M.; Vaaralahti, K.; Tommiska, J.; Eklund, E.; Tervaniemi, M.; Valanne, L.; Raivio, T. Incidence, Phenotypic Features and Molecular Genetics of Kallmann Syndrome in Finland. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzoli, V.; Duminuco, P.; Bassi, I.; Guizzardi, F.; Persani, L.; Bonomi, M. The complex genetic basis of congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Minerva Endocrinol. 2016, 41, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quinton, R.; Duke, V.M.; Robertson, A.; Kirk, J.M.; Matfin, G.; de Zoysa, P.A.; Azcona, C.; MacColl, G.S.; Jacobs, H.S.; Conway, G.S.; et al. Idiopathic gonadotrophin deficiency: Genetic questions addressed through phenotypic characterization. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf). 2001, 55, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavath, B.; Podolsky, R.H.; Ozata, M.; Bolu, E.; Bick, D.P.; Kulharya, A.; Sherins, R.J.; Layman, L.C. Clinical and molecular characterization of a large sample of patients with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 85, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykiotis, G.P.; Plummer, L.; Hughes, V.A.; Au, M.; Durrani, S.; Nayak-Young, S.; Dwyer, A.A.; Quinton, R.; Hall, J.E.; Gusella, J.F.; et al. Oligogenic basis of isolated gonadotropin-releasing hormone deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15140–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitteloud, N.; Hayes, F.J.; Dwyer, A.; Boepple, P.A.; Lee, H.; Crowley, W.F. Predictors of Outcome of Long-Term GnRH Therapy in Men with Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4128–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitteloud, N.; Hayes, F.J.; Boepple, P.A.; DeCruz, S.; Seminara, S.B.; MacLaughlin, D.T.; Crowley, W.F. The Role of Prior Pubertal Development, Biochemical Markers of Testicular Maturation, and Genetics in Elucidating the Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraoui, H.; Dwyer, A.A.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Plummer, L.; Chung, W.; Feng, B.; Beenken, A.; Clarke, J.; Pers, T.H.; Dworzynski, P.; et al. Mutations in FGF17, IL17RD, DUSP6, SPRY4, and FLRT3 are identified in individuals with congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, A.A.; Hayes, F.J.; Plummer, L.; Pitteloud, N.; Crowley, W.F. The Long-Term Clinical Follow-Up and Natural History of Men with Adult-Onset Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4235–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, L.B.; Boepple, P.A.; Pralong, F.P.; Crowley, W.F. Adult-Onset Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism—A Treatable Form of Male Infertility. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of All-Cause Mortality With Overweight and Obesity Using Standard Body Mass Index Categories. JAMA 2013, 309, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, T.; Gelmini, G.; Paraboschi, E.; Vigone, M.C.; Di Frenna, M.; Marelli, F.; Bonomi, M.; Cassio, A.; Larizza, D.; Moro, M.; et al. A frequent oligogenic involvement in congenital hypothyroidism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanchate, N.K.; Giacobini, P.; Lhuillier, P.; Parkash, J.; Espy, C.; Fouveaut, C.; Leroy, C.; Baron, S.; Campagne, C.; Vanacker, C.; et al. SEMA3A, a Gene Involved in Axonal Pathfinding, Is Mutated in Patients with Kallmann Syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roux, N.; Young, J.; Brailly-Tabard, S.; Misrahi, M.; Milgrom, E.; Schaison, G. The Same Molecular Defects of the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Determine a Variable Degree of Hypogonadism in Affected Kindred. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, S.B.; Beranova, M.; Oliveira, L.M.B.; Martin, K.A.; Crowley, W.F.; Hall, J.E. Successful Use of Pulsatile Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) for Ovulation Induction and Pregnancy in a Patient with GnRH Receptor Mutations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitteloud, N.; Quinton, R.; Pearce, S.; Raivio, T.; Acierno, J.; Dwyer, A.; Plummer, L.; Hughes, V.; Seminara, S.; Cheng, Y.-Z.; et al. Digenic mutations account for variable phenotypes in idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottler, M.-L.; Chauvin, S.; Lahlou, N.; Harris, C.E.; Johnston, C.J.; Lagarde, J.-P.; Bouchard, P.; Farid, N.R.; Counis, R. A New Compound Heterozygous Mutation of the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor (L314X, Q106R) in a Woman with Complete Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Chronic Estrogen Administration Amplifies the Gonadotropin Defect. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3002–3008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitteloud, N.; Boepple, P.A.; DeCruz, S.; Valkenburgh, S.B.; Crowley, W.F.; Hayes, F.J. The Fertile Eunuch Variant of Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Spontaneous Reversal Associated with a Homozygous Mutation in the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2470–2475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Roux, N.; Young, J.; Misrahi, M.; Genet, R.; Chanson, P.; Schaison, G.; Milgrom, E. A Family with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Mutations in the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.M.F.; Bedecarrats, G.Y.; Mendonca, B.B.; Arnhold, I.J.P.; Kaiser, U.B.; Latronico, A.C. Two Novel Mutations in the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Gene in Brazilian Patients with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Normal Olfaction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2680–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, B.; Karges, W.; Mine, M.; Ludwig, L.; Kühne, R.; Milgrom, E.; de Roux, N. Mutation Ala 171 Thr Stabilizes the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor in Its Inactive Conformation, Causing Familial Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodé, C.; Teixeira, L.; Levilliers, J.; Fouveaut, C.; Bouchard, P.; Kottler, M.-L.; Lespinasse, J.; Lienhardt-Roussie, A.; Mathieu, M.; Moerman, A.; et al. Kallmann Syndrome: Mutations in the Genes Encoding Prokineticin-2 and Prokineticin Receptor-2. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnier, C.; Dodé, C.; Fabre, L.; Teixeira, L.; Labesse, G.; Pin, J.-P.; Hardelin, J.-P.; Rondard, P. PROKR2 missense mutations associated with Kallmann syndrome impair receptor signalling activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Balasubramanian, R.; Lee, P.H.; Shaw, N.D.; Hall, J.E.; Plummer, L.; Buck, C.L.; Kottler, M.-L.; Jarzabek, K.; Wołczynski, S.; et al. Expanding the Spectrum of Founder Mutations Causing Isolated Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1378–E1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbai, O.; Monnier, C.; Dodé, C.; Pin, J.-P.; Hardelin, J.-P.; Rondard, P. Biased signaling through G-protein-coupled PROKR2 receptors harboring missense mutations. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3734–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.P.; Noel, S.D.; Xu, S.; Carroll, R.S.; Latronico, A.C.; Kaiser, U.B. Evidence of the Importance of the First Intracellular Loop of Prokineticin Receptor 2 in Receptor Function. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raivio, T.; Avbelj, M.; McCabe, M.J.; Romero, C.J.; Dwyer, A.A.; Tommiska, J.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Gregory, L.C.; Diaczok, D.; Tziaferi, V.; et al. Genetic Overlap in Kallmann Syndrome, Combined Pituitary Hormone Deficiency, and Septo-Optic Dysplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E694–E699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caronia, L.M.; Martin, C.; Welt, C.K.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Quinton, R.; Thambundit, A.; Avbelj, M.; Dhruvakumar, S.; Plummer, L.; Hughes, V.A.; et al. A Genetic Basis for Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falardeau, J.; Chung, W.C.J.; Beenken, A.; Raivio, T.; Plummer, L.; Sidis, Y.; Jacobson-Dickman, E.E.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Ma, J.; Dwyer, A.; et al. Decreased FGF8 signaling causes deficiency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in humans and mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2822–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, M.; Quinton, R. Congenital GnRH deficiency: A complex and genetically heterogeneous disease affecting human fertility and sexual development. Minerva Endocrinol. 2016, 41, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Sub-Groups | n (%) | Mean LH U/L (SD) | Mean FSH U/L (SD) | Mean Total Testosterone nmol/L (SD) | Mean Age at Diagnosis Years (SD) | Mean Bitesticular mL at Diagnosis (SD) | Mean BMI at Diagnosis (SD) | Hearing Defects | Renal Agenesia | Familiarity | Synkinesias | Midline Defects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPO-IHH | 109 (68%) | 0.7 (±0.8) | 1.1 (±1) | 1.4 (±1.5) | 17.4 (±6.4) | 5.6 (±3.3) | 24.7 (±5.3) | 2% | 2% | 30% | 9% | 15% |
| AO-IHH | 51 (32%) | 1.7 (±1.2) | 2.8 (±2.1) | 5 (±2.3) | 37.7 (±13.9) | 35.9 (±8.2) | 28.9 (±5.8) | 0% | 0% | 2% | 2% | 0% |
| sIHH | 110 (69%) | 0.7 (±0.8) | 1 (±0.9) | 1 (±0.8) | 18 (±6.9) | 7.7 (±7.9) | 24.4 (±4.8) | 2% | 2% | 30% | 9% | 13% |
| mIHH | 50 (31%) | 1.7 (±1.2) | 2.9 (±2) | 5.8 (±1.5) | 36.9 (±14.9) | 32 (±13.7) | 29.7 (±6) | 0% | 0% | 3% | 3% | 3% |
| Obese | 42 (26%) | 1.1 (±1.1) | 2 (±2.1) | 3.6 (±2.5) | 29.1 (±14.9) | 21.4 (±16) | 34 (±3.7) | 0% | 0% | 2% | 5% | 5% |
| non Obese | 118 (73%) | 0.95 (±1) | 1.5 (±1.4) | 2.2 (±2.4) | 22.1 (±12.3) | 13.1 (±14.2) | 23.2 (±3.1) | 2% | 2% | 30% | 7% | 10% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cangiano, B.; Duminuco, P.; Vezzoli, V.; Guizzardi, F.; Chiodini, I.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M.; Persani, L.; Bonomi, M. Evidence for a Common Genetic Origin of Classic and Milder Adult-Onset Forms of Isolated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010126
Cangiano B, Duminuco P, Vezzoli V, Guizzardi F, Chiodini I, Corona G, Maggi M, Persani L, Bonomi M. Evidence for a Common Genetic Origin of Classic and Milder Adult-Onset Forms of Isolated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleCangiano, Biagio, Paolo Duminuco, Valeria Vezzoli, Fabiana Guizzardi, Iacopo Chiodini, Giovanni Corona, Mario Maggi, Luca Persani, and Marco Bonomi. 2019. "Evidence for a Common Genetic Origin of Classic and Milder Adult-Onset Forms of Isolated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010126
APA StyleCangiano, B., Duminuco, P., Vezzoli, V., Guizzardi, F., Chiodini, I., Corona, G., Maggi, M., Persani, L., & Bonomi, M. (2019). Evidence for a Common Genetic Origin of Classic and Milder Adult-Onset Forms of Isolated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010126






