Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized primarily by symmetrical small joint inflammation and damage, often accompanied by anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity. While conventional imaging modalities such as plain radiographs, ultrasound (US), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are widely used to assess articular and some extra-articular manifestations, each presents limitations in terms of accessibility, comprehensiveness, and diagnostic scope. Nuclear imaging techniques, including positron emission tomography (PET), scintigraphy, and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), offer whole-body imaging capabilities and the potential to simultaneously detect multi-system involvement, making them uniquely suited to the complex, systemic nature of RA. This review explores the current and potential roles of nuclear imaging in RA, highlighting its advantages in detecting both articular and extra-articular disease and its emerging promise as a routine tool in RA management.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disorder, typically presenting with symmetrical small joint polyarthritis and early morning stiffness alongside anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity [1]. Although extra-capsular tendon disease and articular and manifestations are the most prominent feature particularly in early disease, patients can develop extra-articular manifestations such as interstitial lung disease, rheumatoid-related myocarditis, and vasculitis, and are at higher risk of conditions including cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis [2,3,4,5,6].
Plain film radiographs (XR), ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are commonly used in imaging of RA joint disease [7,8]. Radiographs are helpful in the identification of bone erosions and large joint effusions, and US and MRI can confirm the presence of synovitis, tenosynovitis and subclinical synovitis, and can elucidate the degree of underlying bone damage [9]. Imaging can be particularly helpful for joints that are more difficult to assess clinically such as large joints and joints within the spine and pelvis, and it also forms an essential part of the assessment of extra-articular disease [10].
There are limitations and compromises when using any imaging technique—XR is not able to easily visualise soft tissue, and US depends on a skilled sonographer and is time-consuming, usually focused on symptomatic joints in clinical practice [11]. Similarly, obtaining MR images is a lengthy process, whole-body MRI is not widely available outside research centres and takes around 1.5 h per patient acquisition [12]. Additionally, MRI is not appropriate for all patients, for example those with claustrophobia, pacemakers, or an unsuitable body habitus, and gadolinium contrast agents can be associated with allergy or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis particularly in those with sub-optimal renal function [13].
Nuclear imaging techniques can offer rapid whole-body assessment and can visualise multi-system pathology simultaneously. It stands to reason that for multi-joint and multi-system diseases like RA, nuclear imaging techniques are uniquely exciting [14]. Here we look at how nuclear imaging can be effectively used for our RA patients and why it may form a more routine part of care for these patients in the future.
2. A Summary of Nuclear Imaging Techniques
Molecular imaging techniques use tracers that are introduced into the body and interact with tissues according to their biochemical properties. Nuclear imaging is a subset of molecular imaging that uses radiopharmaceuticals (radiotracers). Radiotracers are compounds tagged with a radionuclide whose emissions can be detected allowing visualization of where these compounds are sequestered, metabolised, and excreted throughout the body. Tagged compounds include analogues to natural compounds like glucose or can be engineered molecules that bind specific ligands of interest [15]. Imaging modalities using radiotracers include scintigraphy, positron emission tomography (PET), and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), features of each are summarised in Table 1 [15].

Table 1.
An overview of features of different nuclear imaging techniques.
3. Identification and Quantification of Inflammation Using Nuclear Imaging
Tracer uptake in a particular area helps determine disease activity there. Tracer uptake is affected by variables including time between administration and scanning and physiological differences in uptake of tracers within different tissues. These factors can be taken into account and imaging data can be analysed using semi-quantitative assessments to evaluate disease activity in a specific joint or globally [19].
To analyse nuclear medicine images, a common technique is to define a volume of interest (VOI) if 3D and a region of interest (ROI) if 2D. In rheumatology, a volume of interest might be the knee joint, for example. Areas can be mapped using fixed sized regions, manual mapping, or algorithms. ‘Standardised uptake value’ (SUV) is the most commonly used uptake measure and refers to tracer uptake for each pixel or voxel (3D pixel) within the VOI or ROI compared to the average uptake through the whole body. A high SUV infers that that area has a higher concentration of radioactivity than we would expect if the tracer had distributed equally throughout the body. SUVmax refers to the pixel or voxel within the VOI or ROI with the highest SUV [20,21,22,23].
Scintigraphy was the first nuclear imaging technique used to quantify RA disease activity, it is highly sensitive for joint inflammation and outperforms clinical examination in the identification of histologically confirmed synovitis [24,25,26]. Over decades and with various tracers, scintigraphy has been shown to correlate with markers of disease activity; tender and swollen joint counts, biochemical markers such as CRP and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and composite scores DAS-28-CRP and DAS-28-ESR [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. The same is true for SPECT imaging [15,36,37,38,39].
PET was first used in RA assessment in the 1990s. Since then, several studies have confirmed correlation between PET activity and clinical joint swelling and tenderness, but not with patient reported outcomes indicating additional factors above joint inflammation affect patient experience [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Additionally, 18F-FDG PET has been shown to demonstrate uptake in tendon sheaths and bursae [50].
In some studies, 18F-FDG PET was less successful in low disease activity groups [51,52]. This may be due to FDG imaging having lower specificity for joint inflammation meaning that joints with low level inflammatory change may be missed [53,54,55].
Several studies using PET to assess treatment responses in RA have shown that changes in tracer uptake reflects improvement in disease control, demonstrating its utility in quantification of disease activity [40,41,44,49,50,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. PET is useful in assessing larger joints, the atlanto-axial joint, and the sacro-iliac joints, where it is more difficult to differentiate non-inflammatory and inflammatory pain clinically [67,68,69,70]. Notably, there are lower rates of intra-observer variability when evaluating disease using PET imaging compared to clinical examination [41].
Lee et al. developed a composite score assessing disease activity taking in account PET28 counts (i.e., PET positivity or negativity in joints involved in DAS28 calculations). This correlates well with DAS28-ESR [43]. They completed similar work using bone scintigraphy, and again demonstrated good correlation of BSS28 (bone scintigraphy score) with TJC28, SJC28, DAS28-ESR, and PET28 counts. Using BSS28 in addition to ESR and patient global assessment, the team created a composite score that strongly correlated with DAS28-ESR. Given the lower cost and wider availability of scintigraphy compared to PET, this has clear benefit [29].
4. How Do Nuclear Imaging Techniques Compare to Conventional Imaging?
Scintigraphy is comparable to conventional MRI and US imaging in identifying inflamed joints in RA [24,25,71,72,73,74]. 18F-FDG and 11C-choline PET tracer uptake strongly correlates with MRI synovitis with areas of highest uptake corresponding with synovial thickening on MRI [48,49,75]. 18F-FDG PET has a higher detection rate for inflammation within the ischial tuberosities and sacroiliac joints compared to MRI in RA, polymyalgia rheumatica, and axial spondyloarthropathy patients [69].
Scintigraphy produces rapid whole-body images with ~30 min image acquisition time, compared to 90 min required for whole-body or robust joint set images with MRI and US [12,14]. However, a delay is required between tracer injection and image acquisition to allow for adequate tracer distribution, this delay varies between tracers. Compared to an MRI scanner, the scintigraphy scanner is more open and easier to tolerate. Articular views produced by scintigraphy are easy to interpret, and analysis of these images is rapid and can be done using automated algorithms, though they do not provide the same level of anatomical detail as can be demonstrated with MRI and US. Figure 1 shows examples of each.
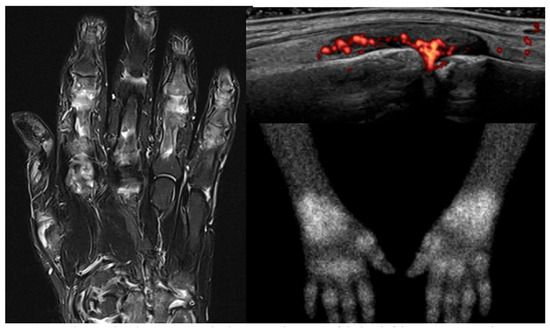
Figure 1.
MRI, ultrasound, and 99mTc-Maraciclatide scintigraphy images of the hand(s) of the same patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
PET is considerably more expensive compared to scintigraphy, MRI, and US, and is less widely available, though shows excellent utility in identification of joint inflammation. Beckers et al. scanned a limited joint set in 21 RA patients using 18F-FDG PET and ultrasonography. Of the joints assessed 75% were swollen, 63% were PET positive, and 56% were USS positive, indicating that PET scanning was able to detect more clinically swollen joints compared to ultrasound. Joints were PET positive in 96% of joints where ultrasound power Doppler was present, and 83% of ultrasound positive joints with hypoechoic or anechoic areas within the joint space but without power doppler. There was also good correlation between SUV levels on PET scanning and synovial thickness on ultrasound in all joints except the first MTP [41].
18F-FDG and 11C-choline PET tracer uptake strongly correlates with MRI synovitis and clinical swelling, and areas of highest uptake correspond with synovial thickening on MRI [48,49,75]. 18F-FDG PET has been shown to have a higher detection rate for inflammation within ischial tuberosities and sacroiliac joints compared to MRI in RA, polymyalgia rheumatica, and axial spondyloarthropathy patients [69].
Limitations of nuclear imaging techniques include radiation exposure, potential for tracer allergy or extravasation, and logistical challenges such as varying time scales required between injection and image acquisition depending on tracer used, and advice to avoid young children and pregnant people for several hours following tracer injection and abstain from having blood tests for a few days owing to radioactivity of bodily fluids. It is important to note the difference in radiation exposure between nuclear imaging scan types, with exposure from PET-CT scanning being five times higher than scintigraphy, this is an important consideration particularly in regard to serial scanning [16,18].
Currently there are no contemporaneous cost effectiveness analyses for the use of nuclear imaging techniques for inflammatory arthritis, and this is certainly an area that requires further investigation.
5. Novel Tracers
As suggested in Table 2, one of the benefits of nuclear techniques in RA imaging is the scope to develop radiotracers targeted towards specific cells and pathways involved in the inflammatory process, this is a major area of development and has the potential to improve specificity of these techniques for rheumatoid-related inflammation. To date, tracers targeting fibroblasts, macrophages, and activated vascular endothelium have all been used experimentally and are discussed below.

Table 2.
Comparison of some of the pros and cons of MRI, USS, and scintigraphy/SPECT/PET imaging.
5.1. Fibroblast-Targeting Tracers
Fibroblasts are key players in synovial inflammation development, depletion of fibroblast activation protein (FAP)-expressing fibroblasts is associated with lower levels of arthritis [76,77]. PET uptake of tracers such as 18F-FAPI, 68Ga-FAPI which bind FAP correlates with DAS28-CRP scores [78,79,80]. Interestingly, a lack of uptake of 68Ga-FAPI within clinically inflamed or swollen joints on PET/CT was associated with a lower likelihood of response to csDMARD and bDMARD treatment. This could be due to fibroblast imaging differentiating between tenderness and swelling due to previous damage as opposed to active inflammation [80].
FAP imaging is able to differentiate between active inflammation and fibrosis in IgG4 related disease and has also been able to demonstrate fibrosis in interstitial lung disease secondary to systemic sclerosis [81,82]. The potential to image both articular and lung disease simultaneously has huge benefits in RA.
5.2. Macrophage-Targeting Tracers
Macrophages are polarised towards an M1 or M2 phenotype; the M1 phenotype is pro-inflammatory where the M2 phenotype is anti-inflammatory [83]. High numbers of macrophages within the RA synovium are associated with more severe joint damage and higher disease activity scores, and although numbers of both M1 and M2 macrophages are raised in active rheumatoid joints, there is a higher proportion of M1-types [84,85]. M2 macrophages predominate in healthy joints, and the joints of RA patients in remission [83,86,87]. Macrophage imaging has therefore been suggested as a potentially more specific tracer for joint inflammation compared to 18F-FDG [88].
Tracers such as (R)-[11C]PK11195, 18F-DPA-714, and 18F-DPA-713 bind to peripheral benzodiazepine receptors, types of translocator proteins (TSPOs), predominantly found on macrophages and monocytes. Imaging using (R)-[11C]PK11195 is helpful in predicting future flare of RA in patients in remission as well as in assessing disease activity [53,54,55,89,90].
Additionally, folate receptor beta, a plasma membrane protein strongly expressed on M2 macrophages is a potential macrophage tracer target [91]. 18F-fluoro-PEG-folate uptake on PET/CT correlates well with clinically active joints, but with lower background uptake compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT meaning that subtle arthritis was more easily visualised [92]. 99mTc-EC20—folic acid conjugated with 99mTc—has been utilised to image the folate receptor though using scintigraphy rather than PET and showed 47% sensitivity and 85% specificity for joint swelling identified on clinical examination, uptake correlated well with ESR and CRP, and subclinical inflammation was detected in 180 joints from 40 RA patients [93].
5.3. Activated Vascular Endothelium-Targeted Tracers
Vascular endothelial dysfunction is seen in both large and small vessels in RA, it is implicated in the increased prevalence of atherosclerotic disease in RA cohorts, and in synovitis-associated neo-angiogenesis respectively [94,95].
Integrin aVB3 is involved in neo angiogenesis in RA, macrophage-dependent inflammation, and bone homeostasis [96]. 99mTc-Maraciclatide binds this integrin with high affinity, and scintigraphy imaging uptake correlated strongly with ultrasonographic and clinical findings in 100 RA patients with low, moderate, and high disease activity [97]. 99mTc-Maraciatide scintigraphy findings strongly correlate with ultrasound findings in RA, an example of Maraciclatide scintigraphy imaging can be seen below in Figure 2 [97]. Further studies using this tracer are ongoing, comparing it to MRI and ultrasonography in RA and psoriatic arthritis, assessing its utility in prediction of successful TNF inhibitor tapering in RA, and also in identification of interstitial lung disease [98,99,100].
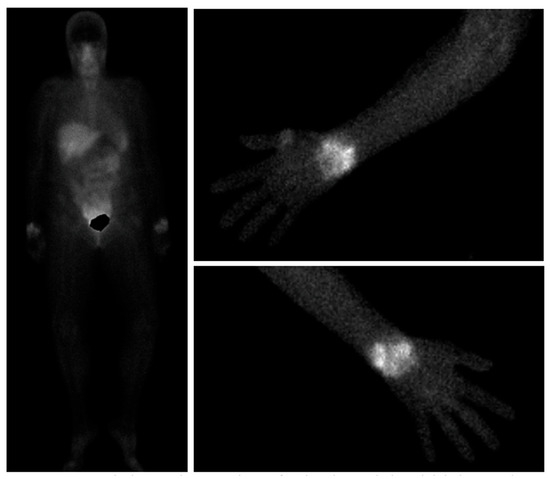
Figure 2.
99mTc-Maraciclatide images showing visualisation of uptake in the wrists both on whole-body views and dedicated upper limb views in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
5.4. Radiolabelled Biologics
Biologic medications have been a hugely important breakthrough in RA treatment. By using radioactive isotopes to tag biologic medications to create tracers such as 123I-IL-1ra, 99mTc-human-anti-TNF-mAb, 99mTc-labelled certolizumab pegol, 99mTc-infliximab, and 124I-labelled-rituximab, we can show where these drugs are concentrated within the body [73,101,102,103,104,105,106]. This is beneficial in drug selection. It has been demonstrated that increased uptake of 99mTc-lableled certolizumab-pegol within a joint is correlated with resolution of pain following certolizumab treatment, compared to in painful joints without uptake [101]. Additionally, 99mTc-infliximab can be useful in identifying persistent mono-arthritis in RA that would be responsive to intra-articular infliximab injection [104]. There is clear potential here in pre-determining biologic treatment success without exposing patients to potential adverse effects of these medications and allowing patient-specific drug selection.
6. Subclinical Synovitis
Subclinical synovitis refers to inflammation that is not detectable on physical examination. At the joint level it has been shown to be associated with progressive bone erosion and can help predict development of RA in at-risk individuals [107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114].
Gent et al. reviewed MCPs, PIPJs, and wrists of patients with RA in clinical remission using a macrophage-targeting tracer, 11C-(R)-PK11195; the definition of remission was not specified. They demonstrated that subclinical inflammation was seen in 55% of patients (n = 16) and 8% of imaged joints (n = 50) on 11C-(R)-PK11195 PET/CT [89,115].
Verweij et al. utilised the same technique in active early arthritis patients pre-treatment [116]. 35 patients had 11C-(R)-PK11195 PET/CT scanning and DAS44 scoring. PET positivity or negativity corresponded with presence or absence of tenderness or swelling in 74 and 75% of joints respectively. They found that 83 out of 1400 joints (5.9%) assessed were PK11195 PET/CT positive but clinically not swollen. 12.1% of clinically non-swollen large joints (shoulders, wrists, knees, and ankles) were PET positive. This may indicate a benefit in the use of PET imaging to assess subclinical disease in larger joints, perhaps indicating low volume inflammation that is clinically imperceptible [116].
99mTc-pyrophosphate scintigraphy scanning has shown that radionuclide activity can precede synovitis and or radiographic changes at the joint level [117]. Subclinical disease detected by scintigraphy may be predictive of flare, with evidence showing that a high proportion of joints found to be sub-clinically active on scintigraphy scanning become clinically synovitic with follow up [28].
7. Differentiation Between RA and Other Types of Arthritis
In some cases, it is difficult to differentiate types of arthritis as well as active inflammation versus previous damage. This is an important factor when considering treatment escalation, particularly in the polyrefractory and EULAR described ‘difficult to treat’ RA cohorts, where higher disease activity scores may be driven by previous damage rather than ongoing active inflammation [118,119]. Radiotracer uptake on scintigraphy or PET/CT scanning is attenuated or absent in non-inflammatory joints, including joints with erosions, and is also helpful in the assessment of larger joints, where it can be more difficult to identify swelling and synovitis clinically [27,67].
Tender or painful joints in patients with fibromyalgia and osteoarthritic joints without secondary synovitis do not show tracer uptake on 18F-FDG PET scanning, though as with other imaging techniques, uptake in a synovitic osteoarthritic joint is indistinguishable from a synovitic rheumatoid joint, particularly in PIP joints [120]. Multi-pinhole single photon emission computer tomography (MPH-SPECT) has shown a difference in the appearance of uptake, with a higher proportion of eccentric uptake in inflammatory osteoarthritic joints and central uptake in inflammatory rheumatoid joints [121].
Synovitic joints in seronegative spondyloarthropathy patients differ in 18F-FDG PET appearance compared to synovitic RA joints, which are more homogenous, higher grade, and symmetrical [122]. RA patients can also have increased uptake in lymph nodes surrounding inflamed areas, and this phenomenon is not seen in spondyloarthropathy patients [122]. Uptake in entheses, spine, and sacroiliac joints have also been successfully demonstrated using 18F-FDG PET imaging in patients with seronegative spondyloarthropathies, including psoriatic arthritis, where nail matrix abnormalities can also be demonstrated [47,122,123,124,125].
For all nuclear imaging modalities, tracer uptake generally reflects the classical distribution of disease as demonstrated in Figure 3 [120]. When comparing uptake patterns in RA, spondyloarthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica patients higher SUVmax levels are seen at sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis patients, and higher levels at greater trochanters in polymyalgia rheumatica patients [69].
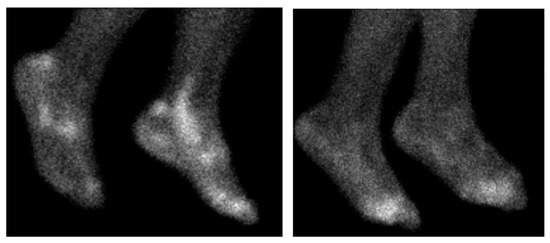
Figure 3.
99mTc-Maraciclatide scintigraphy scans of the feet. The left showing a patient with psoriatic arthritis, with characteristic uptake within the achilles enthesis and peroneal tendons. The right showing a RA patient with metatarsophalangeal joint uptake.
One group has used 18F-FDG PET imaging to develop a composite score encorporating SUVmax, metabolically active volume, and total lesional glycolysis, to differentiate between rheumatoid (n = 18) and non-RA (n = 17) [126]. The non-RA group comprised patients with undifferentiated arthritis, SAPHO syndrome, IgG4 arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Scores were significantly higher in the RA group. The study was limited by low participant numbers, and there was no comparison of disease activity between groups on a clinical level [126].
These findings highlight the potential of nuclear imaging not only in detecting inflammatory activity but also in distinguishing RA from other rheumatological conditions, supporting its growing role in diagnostic refinement and personalised treatment strategies.
8. Prediction of Disease Course
RA is a heterogenous condition, some patients obtain excellent early disease control with csDMARD monotherapy, where others experience prolonged inflammation and become ‘difficult to treat’ or ‘poly-refractory’ [119]. Smoking is positively associated with development of polyrefractory RA [118]. Other variables including disease duration, DAS28-CRP, and tender and swollen joint counts were not found to be predictive [118]. Nuclear imaging techniques are helpful in predicting flare or development of erosions, but to our knowledge, there have been no studies looking at whether nuclear imaging techniques can predict development of a more difficult to manage rheumatoid phenotype [27,127].
Thirteen patients with active RA were prospectively assessed by Möttönen et al. in 1988 [27]. They had 99mTc-methylenediphosphonate scintigraphy scanning at baseline, 6 and 12 months alongside clinical assessment of tenderness. X-rays were also completed at 0, 6, 12, 18, and 24 months. All 6/6 hand joints and 21/22 foot joints that developed radiographic erosions at 12 months were scintigraphically active at baseline. In the feet, positive scintigraphy at baseline had a sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 95% in prediction of erosion development at 12 months, this compared to clinical activity score of 3 or higher, which had a sensitivity of 86% but a low specificity of 46%. Clinical activity scores considered tenderness within a joint only and graded this on a scale of 0–3. Similar sensitivity was seen using 99mTc-IgG scintigraphy, though with inferior specificity [33].
Using PET, higher levels of 18F-FDG uptake in large joints is highly correlated with later radiographic erosions, in that joint. Additionally, higher SUVmax levels pre-treatment are a significant predictor for progressive bone erosion after 3 years [62,128,129].
Elzinga et al. used 18F-FDG PET/CT at baseline and after 2 weeks of treatment with infliximab and followed patients for 22 weeks. Changes in SUVmean between baseline and 2 weeks correlated significantly with DAS28 outcomes at 14 and 22 weeks. This indicates that very early treatment response is a predictor of outcomes, if we can accurately determine within just a few weeks which patients will and will not respond well to treatment, it may allow for accelerated decision making regarding medications [130].
Regarding prediction of flares, a single study using 11C-PK11195 PET has shown promise in predicting development of flare for patients in remission or with low disease activity within the next 3 years with those who flare having higher cumulative PET scores whilst in remission [53,89].
Remission is the goal for RA patients, and once in stable remission, minimising patient exposure to anti-rheumatic drugs by tapering these medications is preferable [127,131,132,133]. There are several factors that have been found predictive of flare versus successful tapering and cessation of biological therapy, factors include lower disease activity at baseline, absence of imaging detected inflammation, longer remission duration, better patient-reported outcomes, and lower CRP and ESR levels at baseline [134,135,136,137].
Bouman et al. assessed whether inflammation detected using FDG-PET imaging could have utility in prediction of successful TNFi tapering and cessation. Of 79 patients enrolled, 47% of patients (n = 37) had successfully reduced TNFi doses at 18 months, and 20% (n = 16) had successfully discontinued. SUVmax and SUVmean at baseline between those who weren’t able to taper at all, those who were able to taper partially, and those who were able to taper to cessation were not significantly different and the team were not able to demonstrate that 18F-FDG PET/CT scores were able to assist in prediction of successful tapering or discontinuation of TNFis [52]. This is reflective of earlier remission work using ultrasound imaging [135,136]. This could indicate that subclinical joint inflammation is predictive of flare within the short-term only, serial imaging during tapering may be beneficial in elucidating this further.
A drug tapering study using scintigraphic imaging and a 99m-Tc labelled molecule that binds with high affinity to avB3 integrin expressed on angiogenic blood vessels is in progress [98]. Further work in this area is required.
9. Prediction of Future Arthritis Development in at Risk Individuals
The definition of ‘at risk’ of RA has not been universally defined and can take the form of ACPA and or RF positivity alongside musculoskeletal symptoms including early morning stiffness and arthralgia, particularly when involving small joints of the hands, others define undifferentiated arthritis as an at risk population [110].
Conventional imaging findings using MRI and ultrasound correlate with future development of inflammatory arthritis in these at risk cohorts [111,138,139,140,141]. Nuclear imaging techniques have also been shown to have predictive value; 11C-PK11195 tracer uptake on PET imaging is associated with arthritis development within 2 years in at risk ACPA positive patients [142]. Gent et al. assessed 29 ACPA positive patients with arthralgia with clinical examination and 11C-PK11195 PET of the hands and wrists. Four patients had tracer uptake in at least 1 joint and all 4 of these patients progressed to clinical arthritis by 24 months. Those without tracer uptake within the joints did not progress within the follow up period, this prognostic information could be extremely valuable in reassuring patients by identifying patients at very low risk of progression despite other risk factors [142].
Nuclear imaging techniques have also been shown to be helpful in more heterogenous cohorts including both at risk with arthralgia and undifferentiated arthritis patients. Duer et al. compared contrast enhanced MRI of the wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints of the most symptomatic hand and whole-body bone scintigraphy in 41 patients with undifferentiated arthritis. Patients were tentatively labelled as RA if MRI and scintigraphic images showed subclinical joint inflammation in the hands that reflected a classical rheumatoid arthritis distribution (n = 13). Within 2 years, 11/13 of these patients fulfilled the 2010 ACR classification criteria for RA diagnosis. The remaining 28 undifferentiated arthritis patients whose scintigraphy imaging was not in keeping with RA did not progress to RA at 2 years [143].
A cohort of 51 patients with symptoms including pain, swelling, or <30 min morning stiffness who did not meet criteria for RA were reviewed by Ozgul et al., again this cohort included both undifferentiated arthritis and at risk arthralgia patients [71]. Participants had ultrasonography and whole-body bone scintigraphy scanning at baseline and were followed up for 2 years. Thirty-three patients met 2010 ACR classification criteria for RA by 2 years. Although both imaging modalities correlated with development of RA, there was a higher predictive value for ultrasound detected synovitis at baseline and progression compared to bone scintigraphy [24].
De Bois et al. identified 47 patients with arthralgia in multiple joints and no clinical evidence of synovitis alongside at least one of the following features: joint stiffness, limited joint motion, tenderness on palpation. Patients received 99mTc-IgG scintigraphy scanning at baseline and were followed up for 12 months. Over the follow up period, 8 patients progressed to RA and 7 of these patients had tracer uptake within their joints at baseline. Of the remaining patients who did not progress, only 1 patient had tracer uptake in any joint [144].
Whole body imaging in the context of the pre-RA disease state where symptoms are less well defined and localised offers potential for early detection detection and opportunity to intervene to prevent or delay development of RA. There is significant scope to use nuclear medicine techniques to help identify those at the highest risk (Table 3).

Table 3.
Summary of findings surrounding topic of “at-risk” individuals and nuclear imaging.
10. Extra-Articular Disease
Extra-articular manifestations such as myocarditis, interstitial lung disease, and vasculitis, affect around 40% of RA patients at some point during the disease course [145]. In addition, patients with RA are at higher risk of conditions including cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis [146].
Nuclear imaging techniques can demonstrate inflammatory pathology at the whole-body level which is helpful in assessing whole-body disease burden. 18F-FDG PET CT can visualise synovial and vascular inflammation simultaneously [65], vascular inflammation being an integral part of atherosclerotic disease as well as rheumatoid vasculitis, rheumatoid nodules, and associated thyroiditis [122].
PET can be used to assess coronary blood flow and subclinical atherosclerosis [147,148]. The TARGET study assessed RA patients who had failed methotrexate monotherapy and who were randomised to receive either TNFi therapy or triple therapy with methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine. Participants had 18F-FDG PET scanning at baseline and at study completion after 24 weeks, FDG uptake was assessed in the aorta and carotid arteries. The results demonstrated significant reduction in arterial uptake between baseline and follow-up, independent of treatment regime [149]. The study did not report on differing uptake at the articular level, but extrapolating from other studies which have shown reduction in 18F-FDG uptake at the joints with treatment, we can surmise that 18F-FDG PET imaging can be used to visualise multi-organ inflammation simultaneously [58,60,62,63,64,65]. Although 18F-FDG PET is useful in imaging vascular inflammation, it is not able to differentiate blood vessel calcification, an important factor in the development of cardiovascular disease, other PET tracers such as 18F-Na-F are more successful in imaging vascular calcification [150].
Nuclear imaging also has a role in the evaluation of lung fibrosis which can be seen more frequently in RA patients, and although there is literature describing 18F-FDG PET activity in the lungs in scleroderma patients, this has not yet been assessed in RA patients to our knowledge [151,152].
In any case, caution must be exercised when using whole-body imaging due to the potential for promoting over-investigation of benign lesions when up to 50% of RA patients having 18F-FDG PET CT can be found to have extra-articular abnormalities with only a small proportion of these being clinically concerning on further investigation [153]. Nuclear imaging techniques are not able to differentiate easily between rheumatoid manifestations such as rheumatoid nodules and malignancy and so could increase investigative and diagnostic procedures unnecessarily [154].
11. Next Steps for Nuclear Imaging in RA
Radiopharmaceuticals tailored to detect disease targets fundamental to the pathophysiology of RA clearly have potential in sensitively and specifically imaging RA-related inflammation. Further exploration of their utility in prediction, diagnosis, and prognosis in RA is required. In particular, the development of tracers that can identify RA-related inflammation in multiple organ systems offers an exciting opportunity to evaluate and manage RA, not as a solely articular disease, but a systemic inflammatory disorder. Nuclear imaging could be integral in assessing response of extra-articular disease to treatments, and subsequently in optimising of preventing and managing inflammatory sequelae and comorbidity, though the associated radiation exposure must be considered. Patients with established systemic disease have the highest levels of healthcare burden, improving detection and prevention is extremely valuable both financially and at the patient level.
Within nano-therapeutics, radiopharmaceutical tracers that can be specifically concentrated in areas of active inflammation via chemically engineered binding motifs would allow optimisation of localised drug delivery to areas of high disease burden, potentially reducing the likelihood of adverse effects and improving drug efficacy. Nuclear imaging can visually demonstrate the success of these binding motifs in promoting sequestration of a labelled molecule in areas of inflammation [155,156].
On a practical level, images produced by nuclear techniques are easy to interpret for both non-specialist physicians and lay-people alike and so can form a uniquely important part of a clinician-patient interaction. Being able to clearly and easily see inflammation within the joints on screen can motivate treatment adherence, where being able to clearly see a lack of inflammation for those patients in remission may bolster confidence in medication tapering. Excitingly, artificial intelligence can be used to rapidly interpret scintigraphy images with similar performance to a clinician. Thus, there is potential both for rapid whole-body imaging with automatic assessment of joint inflammation [157].
12. Conclusions
Nuclear imaging is comparable to both MRI and ultrasonography in demonstrating articular inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis but has other wide-ranging advantages.
Further research is required to assess the capacity of newer, targeted radiotracers to predict RA development in patients deemed at risk, as well as in prediction of successful drug tapering. A robust comparison between scintigraphy and PET/CT would be beneficial to determine whether there are any significant benefits in using PET given the increased cost and radiation exposure. Additionally, whether nuclear imaging can demonstrate extra-articular and articular inflammation simultaneously requires further exploration, as this offers the potential to show a true reflection of whole-body inflammatory burden in RA and a chance to intervene to prevent extra-articular complications of RA at an early stage.
Author Contributions
H.S. manuscript ideation and preparation, A.D.M. and K.M. manuscript revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Helen Sugden’s Doctorate in Philosophy is part-funded by Serac Healthcare Ltd., Dr Andrea Di Matteo has received speaking fees from Janssen and AstraZeneca, and research grant fees from Alfasigma outside the submitted work, Professor Kulveer Mankia has received grants from Gilead, Lilly, Serac Healthcare Ltd., AstraZeneca, Deepcure, and Alfasigma, and consultancy fees/honoraria from Abbvie, ALLin Bio, AstraZeneca, Engitix, UCB, Lilly, Galapagos, Serac Healthcare Ltd., Zura Bio, Deepcure, and Ventus Therapeutics.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ACPA | Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| US | Ultrasound |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| SPECT | Single-photon emission computed tomography |
| XR | Plain film radiograph |
| USS | Ultrasound scan |
| VOI | Volume of interest |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SUV | Standardised uptake value |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| DAS | Disease activity score |
| FDG | Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| BSS | Bone scintigraphy score |
| TJC | Tender joint count |
| SJC | Swollen joint count |
| FAP | Fibroblast activation protein |
| csDMARD | Conventional synthetic disease modifying drug |
| bDMARD | Biologic disease modifying drug |
| TSPO | Translocator protein |
| TNF | Tumour necrosis factor |
| MCP | Metacarpophalangeal |
| MTP | Metatarsophalangeal |
| PIPJ | Proximal interphalangeal joint |
| EULAR | European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology |
| MPH | Multi-pinhole |
| SAPHO | Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| TNFi | Tumour necrosis factor inhibitor |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
References
- Kay, J.; Upchurch, K.S. ACR/EULAR 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria. Rheumatology 2012, 51 (Suppl. 6), vi5–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadura, S.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease: Manifestations and current concepts in pathogenesis and management. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210011. Available online: https://publications.ersnet.org/content/errev/30/160/210011 (accessed on 10 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.M.; Bridges, A.J. Rheumatoid vasculitis: Vanishing menace or target for new treatments? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2010, 12, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Fassio, A.; Rossini, M.; Caimmi, C.; Giollo, A.; Orsolini, G.; Viapiana, O.; Gatti, D. Osteoporosis in Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, B.R.; Thiele, G.M.; Anderson, D.R.; Mikuls, T.R. Increased cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanisms and implications. BMJ 2018, 361, k1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breed, E.R.; Binstadt, B.A. Autoimmune valvular carditis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, A.; Mankia, K.; Azukizawa, M.; Wakefield, R.J. The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Continuum. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Ash, Z.R.; Hodgson, R.J.; Emery, P.; Radjenovic, A. MRI for the assessment and monitoring of RA–what can it tell us? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, D.A.; Morris, N.T.; Lee, S.M.; Baker, J.F.; Chu, P.; Ranganath, V.K.; Kaeley, G.S.; Yang, H.H. Clinical utility of ultrasound and MRI in rheumatoid arthritis: An expert review. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 39, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figus, F.A.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoenacker, F.M.; Bosmans, F. Radiographic/MR Imaging Correlation of Soft Tissues. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2019, 27, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, K.; Sidhu, N.; Rowbotham, E.; Duquenne, L.; Sharrack, S.; Howell, K.; Bertham, D.; Abacar, K.; Emery, P.; McGonagle, D.; et al. Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Arthralgia or Inflammatory Arthritis After Exposure to Immune Checkpoint In-Hibitors: A Single-Centre Prospective Imaging Study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, E697–E707. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(25)00061-X/fulltext#supplementary-material (accessed on 10 July 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamam, Y.M.; Hashmi, M.F.; De Jesus, O. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567754/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Davenport, M.S.; Brown, R.K.J.; Frey, K.A. Utility of delayed whole-body bone scintigraphy after directed three-phase scintigraphy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crișan, G.; Moldovean-Cioroianu, N.S.; Timaru, D.-G.; Andrieș, G.; Căinap, C.; Chiș, V. Radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT Imaging: A Literature Review over the Last Decade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Banks, K.P. Bone Scan. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531486/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Rausch, I.; Füchsel, F.G.; Kuderer, C.; Hentschel, M.; Beyer, T. Radiation exposure levels of routine SPECT/CT imaging protocols. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, M.; Takenaka, M.; Monzen, H.; Tamura, M.; Kudo, M.; Nishimura, Y. Cumulative radiation doses from recurrent PET–CT examinations. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinahan, P.E.; Fletcher, J.W. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography standardized uptake values in clinical practice and assessing response to therapy. Semin. Ultrasound. CT MR 2010, 31, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijzer, K.; Niezink, A.G.H.; de Boer, J.W.; van Doesum, J.A.; Noordzij, W.; van Meerten, T.; van Dijk, L.V. Semi-automated 18F-FDG PET segmentation methods for tumor volume determination in Non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients: A literature review, implementation and multi-threshold evaluation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasadny, K.R.; Wahl, R.L. Standardized uptake values of normal tissues at PET with 2-[fluorine-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose: Variations with body weight and a method for correction. Radiology 1993, 189, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R. Standards for PET image acquisition and quantitative data analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50 (Suppl. S1), 11S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wei, C. Glycolysis and rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 14, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, M.; Kamradt, T.; Sandrock, D.; Loreck, D.; Fritz, J.; Wolf, K.J.; Raber, H.; Hamm, B.; Burmester, G.R.; Bollow, M. Arthritis of the finger joints: A comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, M.; Burmester, G.R.; Sandrock, D.; Loreck, D.; Hess, D.; Scholz, A.; Blind, S.; Hamm, B.; Bollow, M. Prospective two year follow up study comparing novel and conventional imaging procedures in patients with arthritic finger joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bois, M.H.; Tak, P.P.; Arndt, J.W.; Kluin, P.M.; Pauwels, E.K.; Breedveld, F.C. Joint scintigraphy for quantification of synovitis with 99mTc-labelled human immunoglobulin G compared to histological examination. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1995, 13, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Möttönen, T.T.; Hannonen, P.; Toivanen, J.; Rekonen, A.; Oka, M. Value of joint scintigraphy in the prediction of erosiveness in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1988, 47, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimou, G.; Moralidis, E.; Papanastasiou, E.; Liaros, G.; Aggelopoulou, T.; Triantafyllidou, E.; Lytras, N.; Settas, L.; Gotzamani-Psarrakou, A. Radionuclide imaging with human polyclonal immunoglobulin (99mTc-HIG) and bone scan in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and serum-negative polyarthritis. Hippokratia 2011, 15, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Hong, C.M.; Cho, I.; Ahn, B.-C.; Eun, J.S.; Kim, N.R.; Kang, J.W.; Kang, Y.M. Reappraisal of bone scintigraphy as a new tool for the evaluation of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Sung, Y.-K.; Yoo, D.-H. Bone Scintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is There Additional Value of Bone Scintigraphy with Blood Pool Phase over Conventional Bone Scintigraphy? J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamar, F.; Houssiau, F.A.; Devogelaer, J.-P.; Chapman, P.T.; Haskard, D.O.; Beaujean, V.; Beckers, C.; Manicourt, D.-H.; Peters, A.M. Scintigraphy using a technetium 99m-labelled anti-E-selectin Fab fragment in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamar, F.; Chapman, P.T.; Manicourt, D.H.; Glass, D.M.; Haskard, D.O.; Peters, A.M. A comparison between 111In-anti-E-selectin mAb and 99Tcm-labelled human non-specific immunoglobulin in radionuclide imaging of rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Radiol. 1997, 70, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bois, M.H.; Westedt, M.L.; Arndt, J.W.; Wiarda, K.S.; van der Velde, E.A.; Pauwels, E.K.; Breedveld, F.C. Value of 99mTc-IgG scintigraphy in the prediction of joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of recent onset. Rheumatol. Int. 1995, 15, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, R.; Grau, K.; Puille, M.; Matter, H.P.; Lange, U.; Steiner, D.; Bauer, R. Comparison of HIG scintigraphy and bloodpool scintigraphy using HDP in arthritic joint disease. Nuklearmedizin 2000, 39, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cindaş, A.; Gökçe-Kustal, Y.; Kirth, P.O.; Caner, B. Scintigraphic evaluation of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis with (99m)technetium-labelled human polyclonal immunoglobulin G. Rheumatol. Int. 2001, 20, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhong, J.; Wu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, K.; Lin, J. SPECT imaging and highly efficient therapy of rheumatoid arthritis based on hyperbranched semiconducting polymer nanoparticles. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Godinez, F.; Sood, K.; Hagge, R.J.; Boutin, R.D.; Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Badawi, R.D.; Chaudhari, A.J. Feasibility of dual-phase 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT imaging in rheumatoid arthritis evaluation. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbender, C.; Ostendorf, B.; Mattes-György, K.; Miese, F.; Wittsack, H.-J.; Quentin, M.; Specker, C.; Schneider, M.; Antoch, G.; Müller, H.-W.; et al. Synovitis and bone inflammation in early rheumatoid arthritis: High-resolution multi-pinhole SPECT versus MRI. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. Ank. Turk. 2013, 19, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbender, C.; Sewerin, P.; Mattes-György, K.; Miese, F.; Wittsack, H.-J.; Specker, C.; Antoch, G.; Müller, H.-W.; Schneider, M.; Scherer, A.; et al. Utility of combined high-resolution bone SPECT and MRI for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis patients with high-risk for erosive progression. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polisson, R.P.; Schoenberg, O.I.; Fischman, A.; Rubin, R.; Simon, L.S.; Rosenthal, D.; Palmer, W.E. Use of magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography in the assessment of synovial volume and glucose metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, C.; Ribbens, C.; André, B.; Marcelis, S.; Kaye, O.; Mathy, L.; Kaiser, M.-J.; Hustinx, R.; Foidart, J.; Malaise, M.G. Assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with (18)F-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miese, F.; Scherer, A.; Ostendorf, B.; Heinzel, A.; Lanzman, R.S.; Kröpil, P.; Blondin, D.; Hautzel, H.; Wittsack, H.-J.; Schneider, M.; et al. Hybrid 18F-FDG PET-MRI of the hand in rheumatoid arthritis: Initial results. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, C.-H.; Ahn, B.-C.; Eun, J.S.; Kim, N.R.; Kang, J.W.; Nam, E.J.; Kang, Y.M. Development and Validation of an 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography-Based Tool for the Evaluation of Joint Counts and Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikanth, R.; Singh, J.K. Semi-quantitative analysis of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the assessment of disease activity and therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis: An institutional experience. World J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 19, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, W.Y.; Jonnakuti, V.S.; Zirakchian Zadeh, M.; Werner, T.J.; Cheng, G.; Zhuang, H.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A.; Baker, J.F. Comparison of methods of quantifying global synovial metabolic activity with FDG-PET/CT in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Chang, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.M. Clinical utility of F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT for estimating disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.J.; Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Nardo, L.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. EXPLORing Arthritis with Total-body Positron Emission Tomography. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2023, 27, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roivainen, A.; Parkkola, R.; Yli-Kerttula, T.; Lehikoinen, P.; Viljanen, T.; Möttönen, T.; Nuutila, P.; Minn, H. Use of positron emission tomography with methyl-11C-choline and 2-18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of inflammatory proliferation of synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.E.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Schoenberg, O.I.; Fischman, A.J.; Simon, L.S.; Rubin, R.H.; Polisson, R.P. Quantification of inflammation in the wrist with gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging and PET with 2-[F-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Radiology 1995, 196, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerres, G.W.; Forster, A.; Uebelhart, D.; Seifert, B.; Treyer, V.; Michel, B.; von Schulthess, G.K.; Kaim, A.H. F-18 FDG whole-body PET for the assessment of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 31, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkin, C.; Fosse, P.; Malaise, O.; Chapelier, N.; Horrion, J.; Seidel, L.; Albert, A.; Hustinx, R.; Malaise, M.G. Dissociation between 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission computed tomography, ultrasound and clinical assessments in patients with non-severe rheumatoid arthritis, including remission. BMC Rheumatol. 2021, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, C.A.M.; van Herwaarden, N.; Blanken, A.B.; Van der Laken, C.J.; Gotthardt, M.; Oyen, W.J.G.; den Broeder, A.A.; van der Maas, A.; van den Ende, C.H. 18F-FDG PET-CT in rheumatoid arthritis patients tapering TNFi: Reliability, validity and predictive value. Rheumatology 2022, 61, SI6–SI13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Ter Wee, M.M.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Den Uyl, D.; Ahmadi, N.; Dowling, C.; Van Kuijk, C.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; et al. Subclinical synovitis detected by macrophage PET, but not MRI, is related to short-term flare of clinical disease activity in early RA patients: An exploratory study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Laken, C.J.; Elzinga, E.H.; Kropholler, M.A.; Molthoff, C.F.M.; van der Heijden, J.W.; Maruyama, K.; Boellaard, R.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Voskuyl, A.E. Noninvasive imaging of macrophages in rheumatoid synovitis using 11C-(R)-PK11195 and positron emission tomography. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 3350–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijnen, S.T.G.; Verweij, N.J.F.; Gent, Y.Y.J.; Huisman, M.C.; Windhorst, A.D.; Kassiou, M.; van de Ven, P.M.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Voskuyl, A.E.; et al. Imaging disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis by macrophage targeting using second generation translocator protein positron emission tomography tracers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danfors, T.; Bergström, M.; Feltelius, N.; Ahlström, H.; Westerberg, G.; Långström, B. Positron emission tomography with 11C-D-deprenyl in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evaluation of knee joint inflammation before and after intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 26, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Inubushi, M.; Shiga, T.; Hirata, K.; Okamoto, S.; Kamibayashi, T.; Tanimura, K.; Tamaki, N. Therapeutic effects of acupuncture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective study using (18)F-FDG-PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2009, 23, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.J.; Bowen, S.L.; Burkett, G.W.; Packard, N.J.; Godinez, F.; Joshi, A.A.; Naguwa, S.M.; Shelton, D.K.; Hunter, J.C.; Boone, J.M.; et al. High-resolution (18)F-FDG PET with MRI for monitoring response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisaka, Y.; Oriuchi, N.; Higuchi, T.; Amanuma, M.; Endo, K. Clinical implication of F-18-FDG-PET and MRI for assessing therapeutic effect of anti TNFα antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51 (Suppl. 2), 1644. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, K.; Yonemoto, Y.; Arisaka, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Oriuchi, N.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. The assessment of biologic treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using FDG-PET/CT. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roivainen, A.; Hautaniemi, S.; Möttönen, T.; Nuutila, P.; Oikonen, V.; Parkkola, R.; Pricop, L.; Ress, R.; Seneca, N.; Seppänen, M.; et al. Correlation of 18F-FDG PET/CT assessments with disease activity and markers of inflammation in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis following the initiation of combination therapy with triple oral antirheumatic drugs. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, T.; Okamura, K.; Yonemoto, Y.; Okura, C.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. Prediction of Large Joint Destruction in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and Disease Activity Score. Medicine 2016, 95, e2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.S.; Shejul, Y.; Asopa, R.; Basu, S. Quantitative Metabolic Volumetric Product on 18Fluorine-2fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Assessing Treatment Response to Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Multiparametric Analysis Integrating American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Criteria. World J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 16, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosse, P.; Kaiser, M.-J.; Namur, G.; de Seny, D.; Malaise, M.G.; Hustinx, R. 18F-FDG PET/CT joint assessment of early therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with rituximab. Eur. J. Hybrid Imaging 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamar, A.; Hascsi, Z.; Pusztai, A.; Czókolyová, M.; Végh, E.; Pethő, Z.; Gulyás, K.; Soós, B.; Kerekes, G.; Szekanecz, É.; et al. Prospective, simultaneous assessment of joint and vascular inflammation by PET/CT in tofacitinib-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Associations with vascular and bone status. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, N.; Zwezerijnen, G.; Ter Wee, M.; de Jongh, J.; Yaqub, M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Lammertsma, A.; Voskuyl, A.; Lems, W.; Boers, M.; et al. Early prediction of treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis by quantitative macrophage PET. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Ito, K.; Morooka, M.; Mitsumoto, T.; Kurihara, K.; Yamashita, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Mimori, A. Whole-body FDG-PET/CT on rheumatoid arthritis of large joints. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2009, 23, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, W.V.; van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Oyen, W.J.G. FDG-PET/CT can visualise the extent of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis of the tarsus. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Kubota, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Minamimoto, R.; Morooka, M.; Kaneko, H.; Kano, T.; Mimori, A. Similarities and differences in fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography findings in spondyloarthropathy, polymyalgia rheumatica and rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Ihata, A.; Kunishita, Y.; Kishimoto, D.; Kamiyama, R.; Hama, M.; Yoshimi, R.; Kirino, Y.; Asami, Y.; et al. (18)F-FDG and (18)F-NaF PET/CT demonstrate coupling of inflammation and accelerated bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgul, A.; Yasar, E.; Arslan, N.; Balaban, B.; Taskaynatan, M.A.; Tezel, K.; Baklaci, K.; Özgüven, M.A.; Kalyon, T.A. The comparison of ultrasonographic and scintigraphic findings of early arthritis in revealing rheumatoid arthritis according to criteria of American College of Rheumatology. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palosaari, K.; Vuotila, J.; Takalo, R.; Jartti, A.; Niemelä, R.; Haapea, M.; Soini, I.; Tervonen, O.; Hakala, M. Contrast-enhanced dynamic and static MRI correlates with quantitative 99Tcm-labelled nanocolloid scintigraphy. Study of early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roimicher, L.; Lopes, F.P.P.L.; de Souza, S.A.L.; Mendes, L.F.; Domingues, R.C.; da Fonseca, L.M.B.; Gutfilen, B. 99mTc-anti-TNF-α scintigraphy in RA: A comparison pilot study with MRI and clinical examination. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, D.J.A.; Carmo, C.C.M.; Romeiro, L.D.; Gutfilen-Schlesinger, G.; Amarante, J.L.M.J.; de Souza, S.A.L.; Gutfilen, B. 99mTc-antitumor necrosis factor-alpha scintigraphy for the detection of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2021, 42, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M.; Patel, N.; Manavaki, R.; Janiczek, R.L.; Bergstrom, M.; Östör, A.; Gerlag, D.; Roberts, A.; Graves, M.J.; Karkera, Y.; et al. Quantifying disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with the TSPO PET ligand 18F-GE-180 and comparison with 18F-FDG and DCE-MRI. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mo, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Inhibition of fibroblast activation protein ameliorates cartilage matrix degradation and osteoarthritis progression. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, A.P.; Campos, J.; Jansen, K.; Turner, J.D.; Marshall, J.; Attar, M.; Savary, L.; Wehmeyer, C.; Naylor, A.J.; Kemble, S.; et al. Distinct fibroblast subsets drive inflammation and damage in arthritis. Nature 2019, 570, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, M.; Lu, L.; Mo, B.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Fu, W. Fibroblast activation imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: Evaluating disease activity and treatment response using [18F]FAPI PET/CT. Eur. Radiol. 2025, 35, 6104–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, F. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Study. Radiology 2023, 307, e222052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Li, M. [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT may be a predictor for early treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis. EJNMMI Res. 2024, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidkonz, C.; Rauber, S.; Atzinger, A.; Agarwal, R.; Götz, T.I.; Soare, A.; Cordes, M.; Prante, O.; Bergmann, C.; Kleyer, A.; et al. Disentangling inflammatory from fibrotic disease activity by fibroblast activation protein imaging. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, C.; Distler, J.H.W.; Treutlein, C.; Tascilar, K.; Müller, A.-T.; Atzinger, A.; Matei, A.-E.; Knitza, J.; Györfi, A.-H.; Lück, A.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET-CT for molecular assessment of fibroblast activation and risk evaluation in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: A single-centre, pilot study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e185–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Campitiello, R.; Gotelli, E.; Soldano, S. The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 867260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Alivernini, S. Synovial tissue macrophages in joint homeostasis, rheumatoid arthritis and disease remission. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrouk, N.; Alcraft, R.; Hall, B.A.; Augé, F.; Niarakis, A. Large-scale computational modelling of the M1 and M2 synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2024, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivernini, S.; MacDonald, L.; Elmesmari, A.; Finlay, S.; Tolusso, B.; Gigante, M.R.; Petricca, L.; Di Mario, C.; Bui, L.; Perniola, S.; et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wei, K.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, J.; Shan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; et al. Macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: Signaling pathways, metabolic reprogramming, and crosstalk with synovial fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1394108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulherin, D.; Fitzgerald, O.; Bresnihan, B. Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Ahmadi, N.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Hoetjes, N.; van Kuijk, C.; Britsemmer, K.; Turkstra, F.; Boers, M.; Hoekstra, O.S.; van der Laken, C.J. Detection of subclinical synovitis with macrophage targeting and positron emission tomography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis without clinical arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqub, M.; Verweij, N.J.; Pieplenbosch, S.; Boellaard, R.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Laken, C.J. van der Quantitative Assessment of Arthritis Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Using [11C]DPA-713 Positron Emission Tomography. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, J.W.; Oerlemans, R.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Qi, H.; Laken, C.J.V.D.; Lems, W.F.; Jackman, A.L.; Kraan, M.C.; Tak, P.P.; Ratnam, M.; et al. Folate receptor β as a potential delivery route for novel folate antagonists to macrophages in the synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, N.J.F.; Yaqub, M.; Bruijnen, S.T.G.; Pieplenbosch, S.; Ter Wee, M.M.; Jansen, G.; Chen, Q.; Low, P.S.; Windhorst, A.D.; Lammertsma, A.A.; et al. First in man study of [18F]fluoro-PEG-folate PET: A novel macrophage imaging technique to visualize rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, E.L.; Lowe, V.J.; Prendergast, F.G.; Crowson, C.S.; Moder, K.G.; Morgenstern, D.E.; Messmann, R.A.; Low, P.S. Assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis using a novel folate targeted radiopharmaceutical FolatescanTM. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bordy, R.; Totoson, P.; Prati, C.; Marie, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Chen, Z.; Volin, M.V.; Ravella, S.; Virupannavar, S.; Shahrara, S. The Pathogenic Role of Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, R. Integrin alpha V beta 3 as a target for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and related rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61 (Suppl. 2), ii96–ii99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaging Neoangiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis II (INIRA II): Whole-Body Synovial Uptake of 99mTc-Maraciclatide Correlates with Power Doppler Ultrasound and Serum Neoangiogenic Biomarkers-ACR Meeting Abstracts. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ii-inira-ii-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-99mtc-maraciclatide-correlates-with-power-doppler-ultrasound-and-serum-neoangiogenic-biomarkers/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust. An Observational Study Exploring the Value 99mMaracticaltide Imaging for Predicting Outcomes for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Undergoing Tapering of Therapy. Report No.: NCT05983848. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05983848 (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- University of Exeter. PRospective Evaluation of Interstitial Lung DIsease Progression with Quantitative CT. Report No.: NCT05609201. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05609201 (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- IMAGE-IA. Health Research Authority. Available online: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/image-ia/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Carron, P.; Lambert, B.; Praet, L.V.; Vos, F.D.; Varkas, G.; Jans, L.; Elewaut, D.; Bosch, F.V. den Scintigraphic detection of TNF-driven inflammation by radiolabelled certolizumab pegol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, P.; van der Laken, C.J.; Boerman, O.C.; Oyen, W.J.G.; van de Ven, M.T.P.; van Lent, P.L.E.M.; van de Putte, L.B.A.; Corstens, F.H.M. Radiolabelled interleukin-1 receptor antagonist for detection of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, P.; Oyen, W.; Boerman, O.; Riel, P.L.C.M. van Scintigraphic detection of tumour necrosis factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, F.; Malviya, G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Priori, R.; Iagnocco, A.; Valesini, G.; Signore, A. Role of Scintigraphy with 99mTc-Infliximab in Predicting the Response of Intraarticular Infliximab Treatment in Patients with Refractory Monoarthritis. 2012. Available online: https://iris.unito.it/handle/2318/1613200 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Tran, L.; Huitema, A.D.R.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; Dinant, H.J.; Baars, J.W.; Beijnen, J.H.; Vogel, W.V. CD20 antigen imaging with 124I-rituximab PET/CT in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Antibodies 2011, 20, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, G.; Anzola, K.L.; Podestà, E.; Laganà, B.; Del Mastro, C.; Dierckx, R.A.; Scopinaro, F.; Signore, A. (99m)Tc-labeled rituximab for imaging B lymphocyte infiltration in inflammatory autoimmune disease patients. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Montoya, L.; Kang, J.; Duquenne, L.; Di Matteo, A.; Nam, J.L.; Harnden, K.; Chowdhury, R.; Mankia, K.; Emery, P. Factors associated with resolution of ultrasound subclinical synovitis in anti-CCP-positive individuals with musculoskeletal symptoms: A UK prospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 6, e72–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashiri, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Horai, Y.; Okada, A.; Iwamoto, N.; Ichinose, K.; Tamai, M.; Arima, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Ultrasonographic examination of rheumatoid arthritis patients who are free of physical synovitis: Power Doppler subclinical synovitis is associated with bone erosion. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Geng, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Subclinical Synovitis Assessed by Ultrasound Predicts Flare and Progressive Bone Erosion in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Clinical Remission: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 2010–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquenne, L.; Hensor, E.M.; Wilson, M.; Garcia-Montoya, L.; Nam, J.L.; Wu, J.; Harnden, K.; Anioke, I.C.; Di Matteo, A.; Chowdhury, R.; et al. Predicting Inflammatory Arthritis in At-Risk Persons: Development of Scores for Risk Stratification. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakieh, C.; Nam, J.L.; Hunt, L.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Das, S.; Bissell, L.-A.; Villeneuve, E.; McGonagle, D.; Hodgson, R.; Grainger, A.; et al. Predicting the development of clinical arthritis in anti-CCP positive individuals with non-specific musculoskeletal symptoms: A prospective observational cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarlund, M.; Østergaard, M.; Jensen, K.E.; Madsen, J.L.; Skjødt, H.; Lorenzen, I. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: One year follow up of patients with early arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Matteo, A.; Duquenne, L.; Cipolletta, E.; Nam, J.L.; Garcia-Montoya, L.; Wakefield, R.J.; Mahler, M.; Mankia, K.; Emery, P. Ultrasound subclinical synovitis in anti-CCP-positive at-risk individuals with musculoskeletal symptoms: An important and predictable stage in the rheumatoid arthritis continuum. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3192–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, A.; De Lorenzis, E.; Duquenne, L.; Nam, J.L.; Garcia-Montoya, L.; Harnden, K.; Chowdhury, R.; Wakefield, R.J.; Emery, P.; Mankia, K. Ultrasound in anti-CCP+ at-risk individuals without clinical synovitis: Development of a novel 6-joint protocol for feasible risk prediction. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Han, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Presence of power Doppler synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients with synthetic and/or biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug-induced clinical remission: Experience from a Chinese cohort. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, N.J.F.; Ter Wee, M.; De Jongh, J.; Zwezerijnen, G.C.J.; Yaqub, M.; Boers, M.; Voskuyl, A.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Lems, W.; Van der Laken, C.J. SAT0551 Whole Body Macrophage Pet Imaging That Includes the Feet Can Provide Additional Information to Clinical Assessment in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissberg, D.; Resnick, D.; Taylor, A.; Becker, M.; Alazraki, N. Rheumatoid arthritis and its variants: Analysis of scintiphotographic, radiographic, and clinical examinations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1978, 131, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Di Matteo, A.; Hen, O.; Dass, S.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Wakefield, R.J.; Bissell, L.-A.; Nam, J.; Mankia, K.; Emery, P.; et al. Poly-Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Uncommon Subset of Difficult to Treat Disease with Distinct Inflammatory and Noninflammatory Phenotypes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EULAR Definition of Difficult-To-Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis|Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Available online: https://ard.bmj.com/content/80/1/31 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Elzinga, E.H.; van der Laken, C.J.; Comans, E.F.I.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Dijkmans, B.a.C.; Voskuyl, A.E. 2-Deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-D-glucose Joint Uptake on Positron Emission Tomography Images: Rheumatoid Arthritis Versus Osteoarthritis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2007, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ostendorf, B.; Mattes-György, K.; Reichelt, D.C.; Blondin, D.; Wirrwar, A.; Lanzman, R.; Müller, H.W.; Schneider, M.; Mödder, U.; Scherer, A. Early detection of bony alterations in rheumatoid and erosive arthritis of finger joints with high-resolution single photon emission computed tomography, and differentiation between them. Skeletal Radiol. 2010, 39, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayant, V.; Sarma, M.; Aurangabadkar, H.; Bichile, L.; Basu, S. Potential of (18)F-FDG-PET as a valuable adjunct to clinical and response assessment in rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative spondyloarthropathies. World J. Radiol. 2012, 4, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.J.; Ferrero, A.; Godinez, F.; Yang, K.; Shelton, D.K.; Hunter, J.C.; Naguwa, S.M.; Boone, J.M.; Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Badawi, R.D. High-resolution 18F-FDG PET/CT for assessing disease activity in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: Findings of a prospective pilot study. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20160138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Shejul, Y. Regional Lymph node hypermetabolism corresponding to the involved joints on FDG-PET in newly diagnosed patients of rheumatoid arthritis: Observation and illustration in symmetrical and asymmetric joint involvement. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldin, D.W.; Habib, I.; Soudry, G. Axillary Lymph Node Visualization on F-18 FDG PET Body Scans in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2007, 32, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, A.; Nakajima, T.; Sapkota, S.; Arisaka, Y.; Tokue, A.; Yonemoto, Y.; Tsushima, Y. Diagnostic value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake parameters to differentiate rheumatoid arthritis from other types of arthritis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, C.A.; van Herwaarden, N.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; Fransen, J.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van der Maas, A.; den Broeder, A.A. Long-term outcomes after disease activity-guided dose reduction of TNF inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis: 3-year data of the DRESS study-a randomised controlled pragmatic non-inferiority strategy trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, T.; Yonemoto, Y.; Okamura, K.; Okura, C.; Kaneko, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Tachibana, M.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. Predictive factors associated with the progression of large-joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after biologic therapy: A post-hoc analysis using FDG-PET/CT and the ARASHI (assessment of rheumatoid arthritis by scoring of large-joint destruction and healing in radiographic imaging) scoring method. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solymossy, C.; Dixey, J.; Utley, M.; Gallivan, S.; Young, A.; Cox, N.; Davies, P.; Emery, P.; Gough, A.; James, D.; et al. Larsen scoring of digitized X-ray images. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elzinga, E.H.; van der Laken, C.J.; Comans, E.F.I.; Boellaard, R.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Voskuyl, A.E. 18F-FDG PET as a Tool to Predict the Clinical Outcome of Infliximab Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Explorative Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.F.; Rajesh, D.A.; Jannat-Khah, D.P.; Jivanelli, B.; Bykerk, V.P. Can Patients with Controlled Rheumatoid Arthritis Taper Methotrexate from Targeted Therapy and Sustain Remission? A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maassen, J.M.; van Ouwerkerk, L.; Allaart, C.F. Tapering of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: An overview for daily practice. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e659–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoef, L.M.; van den Bemt, B.J.; van der Maas, A.; Vriezekolk, J.E.; Hulscher, M.E.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; Jacobs, W.C.; van Herwaarden, N.; den Broeder, A.A. Down-titration and discontinuation strategies of tumour necrosis factor-blocking agents for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with low disease activity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 5, CD010455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlager, L.; Loiskandl, M.; Aletaha, D.; Radner, H. Predictors of successful discontinuation of biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in remission or low disease activity: A systematic literature review. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, H.; Di Matteo, A.; Anioke, I.; Shuweidhi, F.; Mankia, K.; Ponchel, F.; Emery, P. Predicting Flare in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Biologic Induced Remission, on Tapering, and on Stable Therapy. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024, 6, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, B.; Brown, A.K.; Quinn, M.; Karim, Z.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Conaghan, P.; Peterfy, C.; Wakefield, R.J.; Emery, P. Can flare be predicted in DMARD treated RA patients in remission, and is it important? A cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naredo, E.; Valor, L.; De la Torre, I.; Montoro, M.; Bello, N.; Martínez-Barrio, J.; Martínez-Estupiñán, L.; Nieto, J.C.; Ovalles-Bonilla, J.G.; Hernández-Flórez, D.; et al. Predictive value of Doppler ultrasound-detected synovitis in relation to failed tapering of biologic therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankia, K.; Siddle, H.; Di Matteo, A.; Alpízar-Rodríguez, D.; Kerry, J.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Aletaha, D.; Emery, P. A core set of risk factors in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review informing the EULAR points to consider for conducting clinical trials and observational studies in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.L.; Hensor, E.M.A.; Hunt, L.; Conaghan, P.G.; Wakefield, R.J.; Emery, P. Ultrasound findings predict progression to inflammatory arthritis in anti-CCP antibody-positive patients without clinical synovitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, A.; Mankia, K.; Duquenne, L.; Cipolletta, E.; Wakefield, R.J.; Garcia-Montoya, L.; Nam, J.L.; Emery, P. Ultrasound erosions in the feet best predict progression to inflammatory arthritis in anti-CCP positive at-risk individuals without clinical synovitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnden, K.; Di Matteo, A.; Mankia, K. When and how should we use imaging in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis? Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1058510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gent, Y.Y.J.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Kloet, R.W.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Lammertsma, A.A.; van der Laken, C.J. Macrophage positron emission tomography imaging as a biomarker for preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: Findings of a prospective pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duer, A.; Østergaard, M.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Vallø, J. Magnetic resonance imaging and bone scintigraphy in the differential diagnosis of unclassified arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bois, M.H.W.; Arndt, J.W.; Speyer, I.; Pauwels, E.K.J.; and Breedveld, F.C. Technetium-99m Labelled Human Immunoglobulin Scintigraphy Predicts Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients with Arthralgia. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 25, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, M.; Cojocaru, I.M.; Silosi, I.; Vrabie, C.D.; Tanasescu, R. Extra-articular Manifestations in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mædica 2010, 5, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Crowson, C.S.; Liao, K.P.; Davis, J.M., III; Solomon, D.H.; Matteson, E.L.; Knutson, K.L.; Hlatky, M.A.; Gabriel, S.E. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. Heart J. 2013, 166, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, G.; Soltész, P.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Turiel, M.; Végh, E.; Shoenfeld, Y.; McInnes, I.; Szekanecz, Z. Validated methods for assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatology. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucerius, J.; Hyafil, F.; Verberne, H.J.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Lindner, O.; Sciagra, R.; Agostini, D.; Übleis, C.; Gimelli, A.; Hacker, M.; et al. Position paper of the Cardiovascular Committee of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) on PET imaging of atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Giles, J.T.; Liao, K.P.; Ridker, P.M.; Rist, P.M.; Glynn, R.J.; Broderick, R.; Lu, F.; Murray, M.T.; Vanni, K.; et al. Reducing cardiovascular risk with immunomodulators: A randomised active comparator trial among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraj, S.M.; Raynor, W.Y.; Revheim, M.-E.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Zadeh, M.Z.; Arani, L.S.; Rojulpote, C.; Werner, T.J.; Gerke, O.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; et al. Assessing the feasibility of NaF-PET/CT versus FDG-PET/CT to detect abdominal aortic calcification or inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ha, S.; Ryu, J.-S.; Song, J.W. The Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Evaluating Disease Severity and Prognosis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broens, B.; Nossent, E.J.; Meijboom, L.J.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; Spierings, J.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.K.; van Laar, J.M.; van der Laken, C.J.; Voskuyl, A.E. Quantitative 18F-FDG PET-CT can assess presence and extent of interstitial lung disease in early severe diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulijn, E.; den Broeder, A.A.; Boers, N.; Gotthardt, M.; Bouman, C.A.M.; Landewé, R.; den Broeder, N.; van Herwaarden, N. Extra-articular findings with FDG-PET/CT in rheumatoid arthritis patients: More harm than benefit. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2022, 6, rkac014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhakchhuak, C.L.; Khosravi, M.; Lohr, K.M. Role of 18F-FDG PET Scan in Rheumatoid Lung Nodule: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2013, 2013, 621340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, T.; Dave, N.; Basu, K.; Sonawane, P.; Gawas, T.; Ravindran, S. Nano-Radiopharmaceuticals as Therapeutic Agents. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1355058. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1355058/full (accessed on 30 May 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Medina, C.; Teunissen, A.J.P.; Kluza, E.; Mulder, W.J.M.; van der Meel, R. Nuclear imaging approaches facilitating nanomedicine translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, R.; Cook, G.J.R.; Reader, A.J. Deep Learned Segmentations of Inflammation for Novel 99mTc-maraciclatide Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).