Pre-Exercise Factors Associated with the Magnitude of Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Cross-Sectional, Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample Size
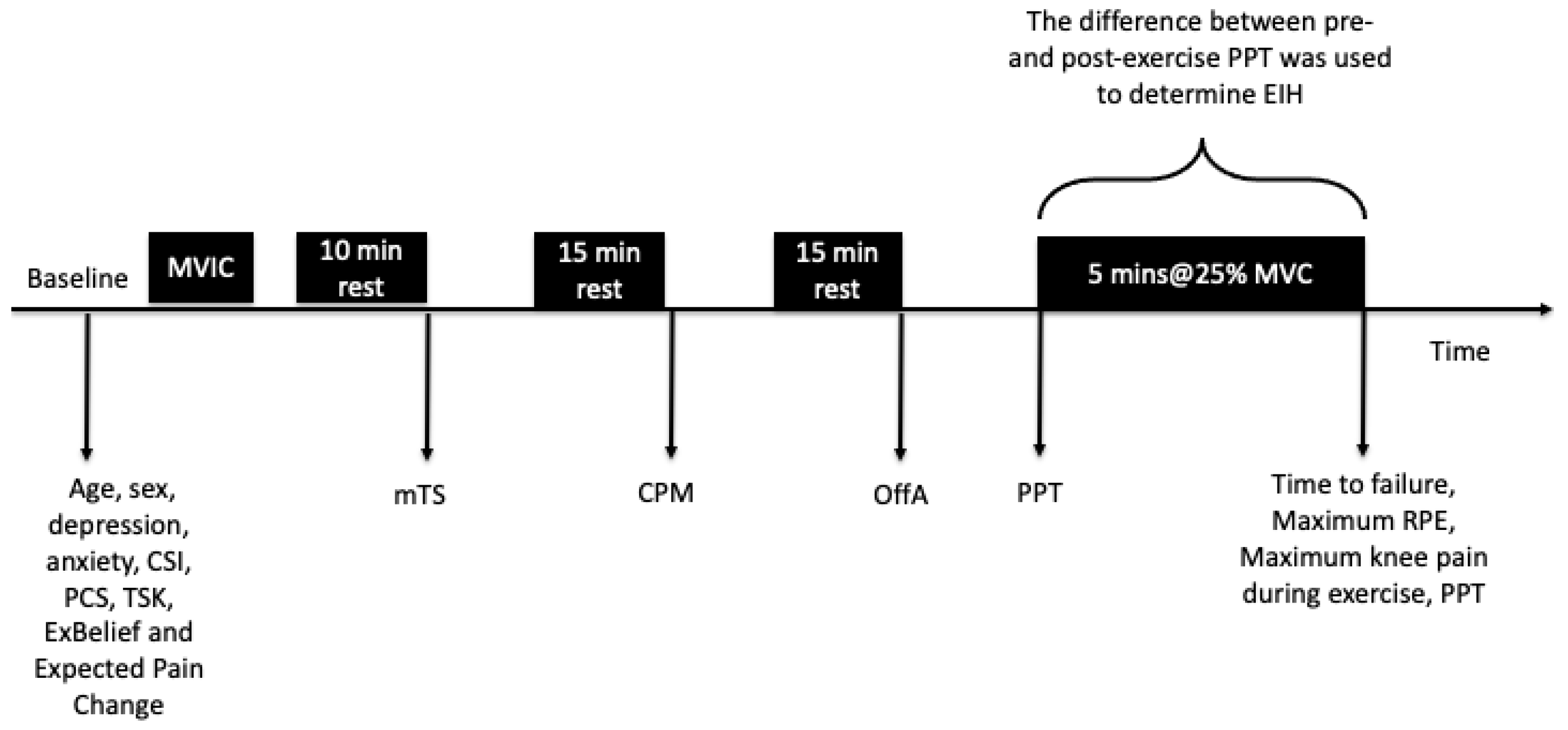
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Dependent Variables
Isometric Exercise Protocol
2.5. Independent Variables
2.5.1. Clinical Variables
Age and Sex
Order of PPT Testing
Time to Failure (Seconds)
Maximum Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
Maximum Knee Pain During Exercise
2.5.2. Neurophysiological Variables
Conditioned Pain Modulation
Offset Analgesia
Mechanical Temporal Summation
Central Sensitisation Inventory (CSI)
2.5.3. Psychological Variables
Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS)
The Pain Catastrophising Scale (PCS)
The Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia (TSK)
Beliefs About Exercise and Pain (ExBelief)
Expected Pain Change
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Factors Associated with EIH Magnitude at the Knee and Forearm
3.2.1. Relationships Between Independent Variables and Absolute EIH
3.2.2. Relationships Between Independent Variables and Relative EIH
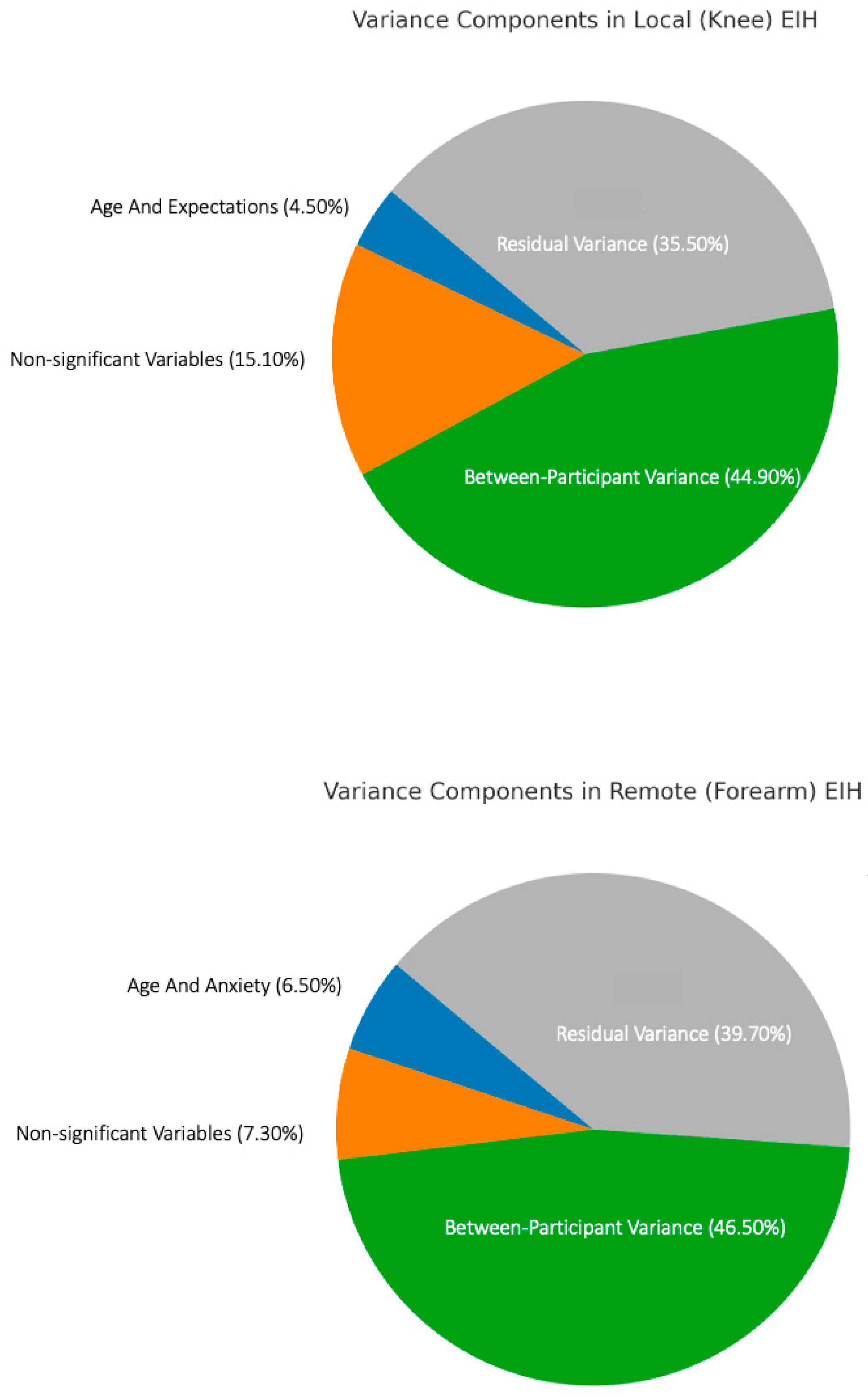
3.2.3. Sources of Variance in EIH Magnitude at the Knee and Forearm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BPI | Brief Pain Inventory |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CCK | Cholecystokinin |
| CPM | Conditioned Pain Modulation |
| CSI | Central Sensitisation Inventory |
| DNIC | Diffuse Noxious Inhibitory Control |
| EIH | Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia |
| EIHabs | Absolute Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia |
| EIHrel | Relative Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia |
| eVAS | Electronic Visual Analogue Scale |
| ExBelief | Exercise Belief (Pain can be reduced from just a single session of exercise) |
| HADS | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| ISI | Inter-Stimulus Interval |
| LLTQ | Lower Limb Task Questionnaire |
| mTS | Mechanical Temporal Summation |
| MVIC | Maximum Voluntary Isometric Contraction |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| NPRS | Numerical Pain Rating Scale |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| OffA | Offset Analgesia |
| PPT | Pressure Pain Threshold |
| PPTpre | Pre-Exercise Pressure Pain Threshold |
| PPTpost | Post-Exercise Pressure Pain Threshold |
| PCS | Pain Catastrophising Scale |
| RPE | Rating of Perceived Exertion |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TSK | Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia |
| TS | Temporal Summation |
References
- Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Judge, A.; Javaid, M.K.; Cooper, C.; Diez-Perez, A.; Arden, N.K. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: Influences of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiński, R.; Prus, A.; Baj, J.; Radej, S.; Prządka, M.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, K. Articular Cartilage: Structure, Biomechanics, and the Potential of Conventional and Advanced Diagnostics. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.J.; Gray, B.; Wallis, J.A.; Taylor, N.F.; Kemp, J.L.; Hunter, D.J.; Barton, C.J. Recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte Access Economics. The economic cost of arthritis in New Zealand in 2018. In Analysis & Policy Observatory; Deloitte Access Economics: Sydney, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Skou, S.T.; Rasmussen, S.; Laursen, M.B.; Rathleff, M.S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Simonsen, O.; Roos, E.M. The efficacy of 12 weeks non-surgical treatment for patients not eligible for total knee replacement: A randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skou, S.T.; Roos, E.M. Good Life with osteoArthritis in Denmark (GLA:D): Evidence-based education and supervised neuromuscular exercise delivered by certified physiotherapists nationwide. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, E.M.; Grønne, D.T.; Skou, S.T.; Zywiel, M.G.; McGlasson, R.; Barton, C.J.; Kemp, J.L.; Crossley, K.M.; Davis, A.M. Immediate outcomes following the GLA:D(R) program in Denmark, Canada and Australia. A longitudinal analysis including 28,370 patients with symptomatic knee or hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.; Harvey, W.F.; Han, X.; Price, L.L.; Driban, J.B.; Bannuru, R.R.; Wang, C. Pain and functional trajectories in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis over up to 12 weeks of exercise exposure. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinman, R.S.; Jones, S.E.; Nelligan, R.K.; Campbell, P.K.; Hall, M.; Foster, N.E.; Russell, T.; Bennell, K.L. Absence of Improvement With Exercise in Some Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Qualitative Study of Responders and Nonresponders. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, F.; Bennell, K.L.; French, S.D.; Nicolson, P.J.; Klaasman, R.N.; Holden, M.A.; Atkins, L.; Hinman, R.S. Barriers and Facilitators to Exercise Participation in People with Hip and/or Knee Osteoarthritis: Synthesis of the Literature Using Behavior Change Theory. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.M.; Fillingim, R.B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. A meta-analytic review of the hypoalgesic effects of exercise. J. Pain 2012, 13, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.; Nijs, J.; Kosek, E.; Wideman, T.; Hasenbring, M.I.; Koltyn, K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Polli, A. Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Pain-Free and Chronic Pain Populations: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2019, 20, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapala, R.Y.; Nayak, S.; Sivalanka, S.; Cornelio, R.; Prajapati, M. Influence of isometric exercise on pressure pain sensitivity in knee osteoarthritis. J. Pain Manag. 2018, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kosek, E.; Roos, E.M.; Ageberg, E.; Nilsdotter, A. Increased pain sensitivity but normal function of exercise induced analgesia in hip and knee osteoarthritis—Treatment effects of neuromuscular exercise and total joint replacement. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaegter, H.B.; Handberg, G.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Hypoalgesia After Exercise and the Cold Pressor Test is Reduced in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Patients with High Pain Sensitivity. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, C.; Smart, K.M.; Doody, C.M. Exercise-induced Hypoalgesia in People with Knee Osteoarthritis with Normal and Abnormal Conditioned Pain Modulation. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germanou, E.I.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Malliou, P.; Beneka, A.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Bikos, C.; Tsoukas, D.; Theodorou, A.; Katrabasas, I.; Margonis, K.; et al. Oxidative stress and inflammatory responses following an acute bout of isokinetic exercise in obese women with knee osteoarthritis. Knee 2013, 20, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, S.; Jayabalan, P.; Gustafson, J.A.; Klatt, B.A.; Sowa, G.A.; Piva, S.R. The influence of continuous versus interval walking exercise on knee joint loading and pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture 2017, 56, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, N.J.; Booth, J.; Sturnieks, D.L.; Barry, B.K. Acute resistance exercise and pressure pain sensitivity in knee osteoarthritis: A randomised crossover trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.L.; Kjaer, M.; Søgaard, K.; Hansen, L.; Kryger, A.I.; Sjøgaard, G. Effect of two contrasting types of physical exercise on chronic neck muscle pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.T.; Light, A.R.; Hughen, R.W.; Bateman, L.; Martins, T.B.; Hill, H.R.; Light, K.C. Severity of symptom flare after moderate exercise is linked to cytokine activity in chronic fatigue syndrome. Psychophysiology 2010, 47, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, T.H.; Finan, P.H.; Edwards, R.R.; Quartana, P.J.; Buenaver, L.F.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Smith, M.T. Increased sensitivity to physical activity among individuals with knee osteoarthritis: Relation to pain outcomes, psychological factors, and responses to quantitative sensory testing. Pain 2014, 155, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Vaegter, H.B.; Petersen, K.K. Pretreatment Exercise-induced Hypoalgesia is Associated With Change in Pain and Function After Standardized Exercise Therapy in Painful Knee Osteoarthritis. Clin. J. Pain 2020, 36, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brellenthin, A.G.; Crombie, K.M.; Cook, D.B.; Sehgal, N.; Koltyn, K.F. Psychosocial Influences on Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munneke, W.; Ickmans, K.; Voogt, L. The Association of Psychosocial Factors and Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Healthy People and People with Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review. Pain Pract. 2020, 20, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlman, T.; Miller, L.; Naugle, K.E.; Naugle, K.M. Physical Activity Levels Predict Exercise-induced Hypoalgesia in Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13 (Suppl. S1), S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.B. How Many Subjects Does It Take To Do A Regression Analysis. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1991, 26, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNair, P.J.; Prapavessis, H.; Collier, J.; Bassett, S.; Bryant, A.; Larmer, P. The lower-limb tasks questionnaire: An assessment of validity, reliability, responsiveness, and minimal important differences. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleeland, C.S.; Ryan, K.M. Pain assessment: Global use of the Brief Pain Inventory. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 1994, 23, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kosek, E.; Ekholm, J.; Hansson, P. Modulation of pressure pain thresholds during and following isometric contraction in patients with fibromyalgia and in healthy controls. Pain 1996, 64, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N. The Borg rating of perceived exertion (RPE) scale. Occup. Med. 2017, 67, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Karoly, P.; Braver, S. The measurement of clinical pain intensity: A comparison of six methods. Pain 1986, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pud, D.; Granovsky, Y.; Yarnitsky, D. The methodology of experimentally induced diffuse noxious inhibitory control (DNIC)-like effect in humans. Pain 2009, 144, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Granot, M.; Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Khamaisi, M.; Granovsky, Y. Conditioned pain modulation predicts duloxetine efficacy in painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 2012, 153, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, J.D.; Coghill, R.C. Transient analgesia evoked by noxious stimulus offset. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2205–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Spatial and temporal summation of pain evoked by mechanical pressure stimulation. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregel, J.; Vuijk, P.J.; Descheemaeker, F.; Keizer, D.; van der Noord, R.; Nijs, J.; Cagnie, B.; Meeus, M.; van Wilgen, P. The Dutch Central Sensitization Inventory (CSI): Factor Analysis, Discriminative Power, and Test-Retest Reliability. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scerbo, T.; Colasurdo, J.; Dunn, S.; Unger, J.; Nijs, J.; Cook, C. Measurement Properties of the Central Sensitization Inventory: A Systematic Review. Pain Pract. 2018, 18, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, T.G.; Neblett, R.; Cohen, H.; Howard, K.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Williams, M.J.; Perez, Y.; Gatchel, R.J. The Development and Psychometric Validation of the Central Sensitization Inventory. Pain Pract. 2012, 12, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neblett, R.; Hartzell, M.M.; Mayer, T.G.; Cohen, H.; Gatchel, R.J. Establishing Clinically Relevant Severity Levels for the Central Sensitization Inventory. Pain Pract. Off. J. World Inst. Pain 2017, 17, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axford, J.; Butt, A.; Heron, C.; Hammond, J.; Morgan, J.; Alavi, A.; Boltno, J.; Bland, M. Prevalence of anxiety and depression in osteoarthritis: Use of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale as a screening tool. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, V.; Verdilos, A.; Pereira, B.; Boisgard, S.; Costes, F.; Coudeyre, E. Core Outcome Measuremepnt Instruments for Clinical Trials of Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinhoven, P.; Ormel, J.; Sloekers, P.P.; Kempen, G.I.; Speckens, A.E.; Van Hemert, A.M. A validation study of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) in different groups of Dutch subjects. Psychol. Med. 1997, 27, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Bishop, S.R.; Pivik, J. The pain catastrophizing scale: Development and validation. Psychol. Assess. 1995, 7, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, S.; Crombez, G.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Goubert, L.; Van den Broeck, A.; Van Houdenhove, B. De Pain Catastrophizing Scale: Psychometrische karakteristieken en normering. Gedragstherapie 2000, 33, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lamé, I.E.; Peters, M.L.; Kessels, A.G.; Van Kleef, M.; Patijn, J. Test-retest stability of the Pain Catastrophizing Scale and the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia in chronic pain over a longer period of time. J. Health Psychol. 2008, 13, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeudomwong, P.; Buttagat, V. Reliability and Validity of the Cross-Culturally Adapted Thai Version of the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.D.; Valenzuela, T.; Booth, J.; Taylor, J.L.; Barry, B.K. Explicit Education About Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia Influences Pain Responses to Acute Exercise in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pain 2017, 18, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.; Patil, I.; Waggoner, P.; Makowski, D. performance: An R Package for Assessment, Comparison and Testing of Statistical Models. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdecke, D.; Waggoner, P.; Makowski, D. insight: A Unified Interface to Access Information from Model Objects in R. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- McElreath, R. Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vaegter, H.B.; Handberg, G.; Emmeluth, C.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Preoperative Hypoalgesia After Cold Pressor Test and Aerobic Exercise is Associated With Pain Relief 6 Months After Total Knee Replacement. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaegter, H.B.; Handberg, G.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Similarities between exercise-induced hypoalgesia and conditioned pain modulation in humans. Pain 2014, 155, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.M.; Naugle, K.E.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. Reduced Modulation of Pain in Older Adults After Isometric and Aerobic Exercise. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2016, 17, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tumi, H.; Johnson, M.I.; Dantas, P.B.F.; Maynard, M.J.; Tashani, O.A. Age-related changes in pain sensitivity in healthy humans: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; O’Connor, P.J.; Boyd, C.M.; Dishman, R.K. Low intensity pain reported during elicitation of the H-reflex: No effects of trait anxiety and high intensity cycling exercise. Brain Res. 2002, 951, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemley, K.J.; Hunter, S.K.; Bement, M.K. Conditioned pain modulation predicts exercise-induced hypoalgesia in healthy adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugle, K.M.; Naugle, K.E.; Fillingim, R.B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. Isometric exercise as a test of pain modulation: Effects of experimental pain test, psychological variables, and sex. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger Bement, M.K.; Weyer, A.; Hartley, S.; Drewek, B.; Harkins, A.L.; Hunter, S.K. Pain perception after isometric exercise in women with fibromyalgia. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricio, P.; Mailloux, C.; Wideman, T.H.; Langevin, P.; Descarreaux, M.; Beaulieu, L.D.; Massé-Alarie, H. Assessment of exercise-induced hypoalgesia in chronic low back pain and potential associations with psychological factors and central sensitization symptoms: A case-control study. Pain Pract. Off. J. World Inst. Pain 2023, 23, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.; Owen, P.J.; Tagliaferri, S.D.; Van Oosterwijck, J.; Fitzgibbon, B.M.; Ford, J.J.; Belacvy, D.; Miller, C. The Interaction Between Psychosocial Factors and Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Pain-Free Nurses. J. Pain Res. 2023, 16, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.M.; Naugle, K.E.; Fillingim, R.B.; Samuels, B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd. Intensity thresholds for aerobic exercise-induced hypoalgesia. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzangs, N.; de Jonge, P.; Smit, J.H.; Bahn, S.; Penninx, B.W. Cytokine production capacity in depression and anxiety. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Nir, R.-R.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Psychological Factors and Conditioned Pain Modulation A Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijkers, J.T.W.; van den Oever, W.; Weerts, Z.; Vork, L.; Mujagic, Z.; Leue, C.; Hesselink, M.A.M.; Kruimel, J.W.; Muris, J.W.M.; Bogie, R.M.M.; et al. Examining the optimal cutoff values of HADS, PHQ-9 and GAD-7 as screening instruments for depression and anxiety in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaegter, H.B.; Thinggaard, P.; Madsen, C.H.; Hasenbring, M.; Thorlund, J.B. Power of Words: Influence of Preexercise Information on Hypoalgesia after Exercise-Randomized Controlled Trial. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Ugidos, A.; Vázquez-Millán, A.; Samartin-Veiga, N.; Carrillo-de-la-Peña, M.T. Conditioned pain modulation (CPM) paradigm type affects its sensitivity as a biomarker of fibromyalgia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaegter, H.B.; Petersen, K.K.; Mørch, C.D.; Imai, Y.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Assessment of CPM reliability: Quantification of the within-subject reliability of 10 different protocols. Scand. J. Pain 2018, 18, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, P.; Itter, A.; Wach, K.; Ruscheweyh, R. Inter-Individual Differences Explain More Variance in Conditioned Pain Modulation Than Age, Sex and Conditioning Stimulus Intensity Combined. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossenger, N.R.; Lewis, G.N.; Rice, D.A.; Shepherd, D. The autonomic and nociceptive response to acute exercise is impaired in people with knee osteoarthritis. Neurobiol. Pain 2023, 13, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaeli Izak, E.; Kodesh, E.; Weissman-Fogel, I. Vagal tone, pain sensitivity and exercise-induced hypoalgesia: The effect of physical activity level. Eur. J. Pain 2024, 28, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tour, J.; Löfgren, M.; Mannerkorpi, K.; Gerdle, B.; Larsson, A.; Palstam, A.; Bileviciute–Ljungar, I.; Bjersing, J.; Martin, I.; Ernberg, M.; et al. Gene-to-gene interactions regulate endogenous pain modulation in fibromyalgia patients and healthy controls—Antagonistic effects between opioid and serotonin-related genes. Pain 2017, 158, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ouyang, H.; Dass, C.R.; Xu, J. Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 15040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age (y) | 68 | (10) |
| Sex (females (%)) | 53 | (45%) |
| Height (cm) | 170 | (10) |
| Weight (kg) | 82 | (16) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28 | (25–31) |
| Ethnicity: frequency/percentage | ||
| New Zealand European | 101 | (85%) |
| New Zealand Māori | 7 | (6%) |
| Tongan | 1 | (1%) |
| Chinese | 2 | (2%) |
| Indian | 2 | (2%) |
| Other | 6 | (5%) |
| Duration of knee pain (months) | 48 | (24–120) |
| LLTQ (0–100) | 26 | (6) |
| HADS-Depression (0–21) | 4 | (2–6) |
| HADS-Anxiety (0–21) | 5 | (3–7) |
| TSK-11 (11–44) | 25 | (5.1) |
| PCS (0–52) | 10 | (5–17) |
| BPI-Ave (0–10) | 4 | (3–5) |
| BPI-Worst (0–10) | 8 | (4–10) |
| BPI-Least (0–10) | 3 | (1.5–4) |
| BPI-Interference (0–10) | 4 | (2) |
| CSI (0–100) | 45 | (20–60) |
| mTS | 30 | (10) |
| CPM | −4 | (−15–3) |
| Peak pain conditioning stimulus (0–100) | 58 | (45–70) |
| OffA | −19 | (17) |
| Peak Torque (Nm) | 117 | (91–116) |
| EIH testing order (knee first (%)) | 57 | (48%) |
| Expected change in knee pain (0–100) | 45 | (20–60) |
| Actual change in knee pain (0–100) | 0 | (0–2) |
| Maximum knee pain during contraction (0–100) | 10 | (0–50) |
| Time to failure (s) | 300 | (246–300) |
| Max RPE (6–20) | 19 | (17–20) |
| Test Site | PPT Pre-Exercise | PPT Post-Exercise | EIHabs (kPa) | EIHrel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knee | 252 (176–353) | 293 (190–413) * | 28 (1–93) | 1.12 (1.01–1.35) |
| Forearm | 249 (188–356) | 251 (199–388) * | 12 (−19–58) | 1.06 (0.91–1.22) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toomey, D.; Lewis, G.; Nijs, J.; Rashid, U.; Tuck, N.; Rice, D. Pre-Exercise Factors Associated with the Magnitude of Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Cross-Sectional, Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228086
Toomey D, Lewis G, Nijs J, Rashid U, Tuck N, Rice D. Pre-Exercise Factors Associated with the Magnitude of Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Cross-Sectional, Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228086
Chicago/Turabian StyleToomey, David, Gwyn Lewis, Jo Nijs, Usman Rashid, Natalie Tuck, and David Rice. 2025. "Pre-Exercise Factors Associated with the Magnitude of Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Cross-Sectional, Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228086
APA StyleToomey, D., Lewis, G., Nijs, J., Rashid, U., Tuck, N., & Rice, D. (2025). Pre-Exercise Factors Associated with the Magnitude of Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Cross-Sectional, Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228086








