Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency and Endoscopic Piriformis Release for Refractory Piriformis Syndrome: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Interventions
2.2.1. Pulsed Radiofrequency (PRF)
2.2.2. Endoscopic Piriformis Release (EPR)
2.2.3. Standardized Physical Therapy Program
2.3. Outcomes
- Patient satisfaction, measured on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = very dissatisfied, 5 = very satisfied), with ≥4 considered satisfactory.
- Reintervention rate within 6 months (e.g., repeat procedure, alternative therapy, or surgery).
- Procedure-related complications (e.g., infection, hematoma, nerve injury, classified as minor or major as per Clavien–Dindo criteria).
- Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores (0–100%, higher indicating greater disability) at baseline and 6 months, analyzed in a subgroup with complete data (n = 90) as an exploratory endpoint [2,4,7]. Baseline ODI data were incomplete for the full cohort, limiting its inclusion in PSM; subset values are reported in Table 1 and Table 2.
2.4. Propensity Score Matching and Balance Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
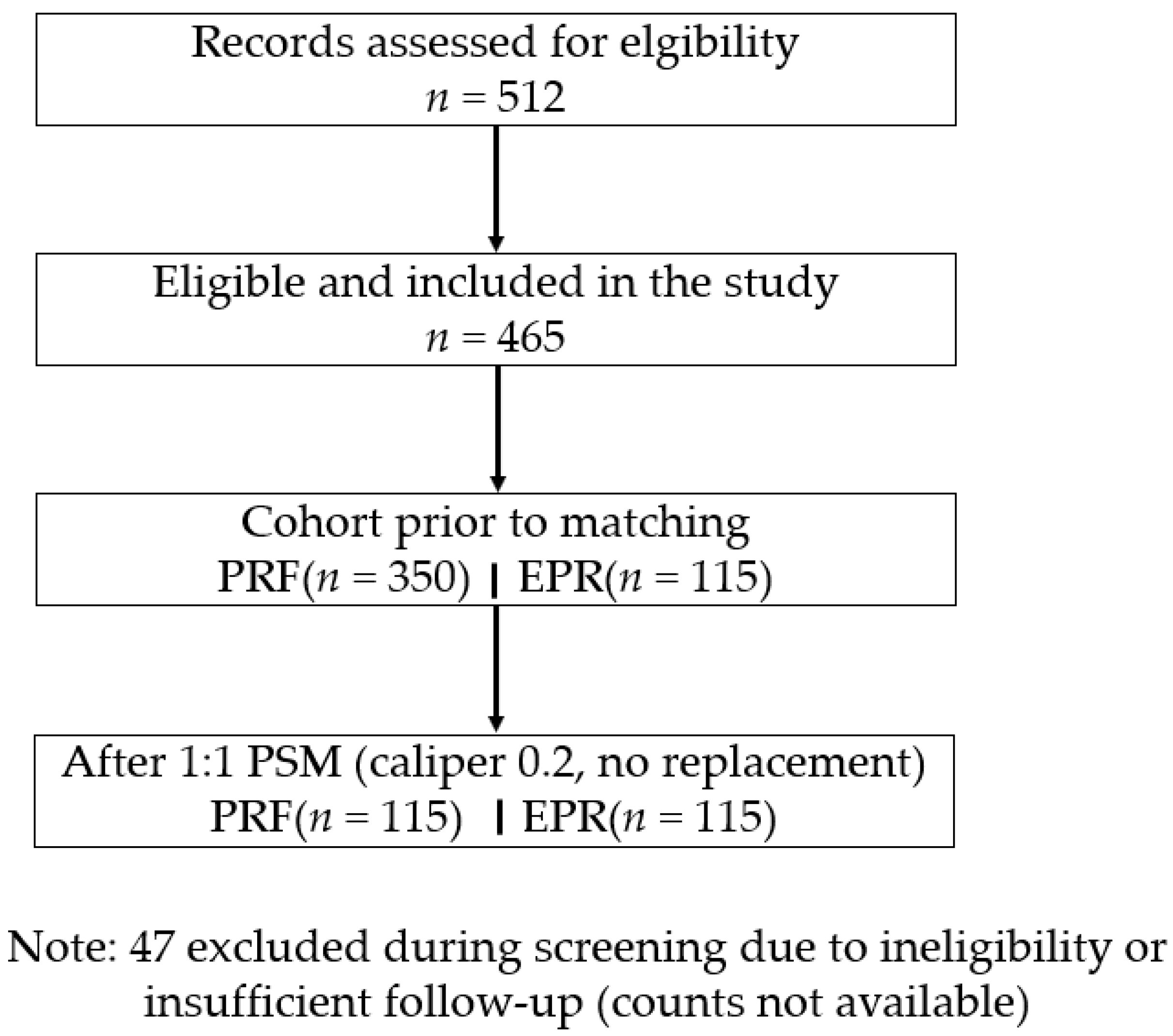
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | PRF (n = 350) | EPR (n = 115) | p-Value | PRF (n = 115) | EPR (n = 115) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 51.9 ± 12.3 | 53.4 ± 12.2 | 0.231 | 52.8 ± 11.9 | 53.4 ± 12.2 | 0.672 |
| Sex (M/F) | 142/208 (59.4% F) | 49/66 (57.4% F) | 0.701 | 48/67 (58.3% F) | 49/66 (57.4% F) | 0.881 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.2 ± 4.1 | 26.5 ± 4.2 | 0.184 | 26.5 ± 4.2 | 26.5 ± 4.2 | 1.000 |
| Symptom duration (months) | 19.1 ± 8.7 | 18.4 ± 8.2 | 0.435 | 18.6 ± 8.5 | 18.4 ± 8.2 | 0.842 |
| Baseline NRS | 7.3 ± 1.4 | 7.5 ± 1.3 | 0.199 | 7.4 ± 1.4 | 7.5 ± 1.3 | 0.586 |
| Diabetes (%) | 14.3 | 15.7 | 0.698 | 14.8 | 15.7 | 0.851 |
| Hypertension (%) | 22.6 | 24.3 | 0.696 | 23.5 | 24.3 | 0.879 |
3.1.1. Primary Outcome
3.1.2. Secondary Outcomes
| Variable | PRF (n = 115) | EPR (n = 115) | p-Value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRS at 3 months | 3.2 ± 1.6 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 0.032 | Primary outcome (difference −0.6, 95% CI −1.1 to −0.1) |
| NRS at 6 months | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 0.018 | Primary outcome (difference −0.7, 95% CI −1.1 to −0.3) |
| ≥50% NRS reduction at 6 months (%) | 65 (75/115) | 78 (90/115) | 0.041 | OR 1.92, 95% CI 1.03–3.57 |
| Satisfaction (Likert ≥ 4) (%) | 82 (94/115) | 90 (104/115) | 0.092 | |
| Complications (%) | 1.7 (2/115) | 7.8 (9/115) | 0.053 | |
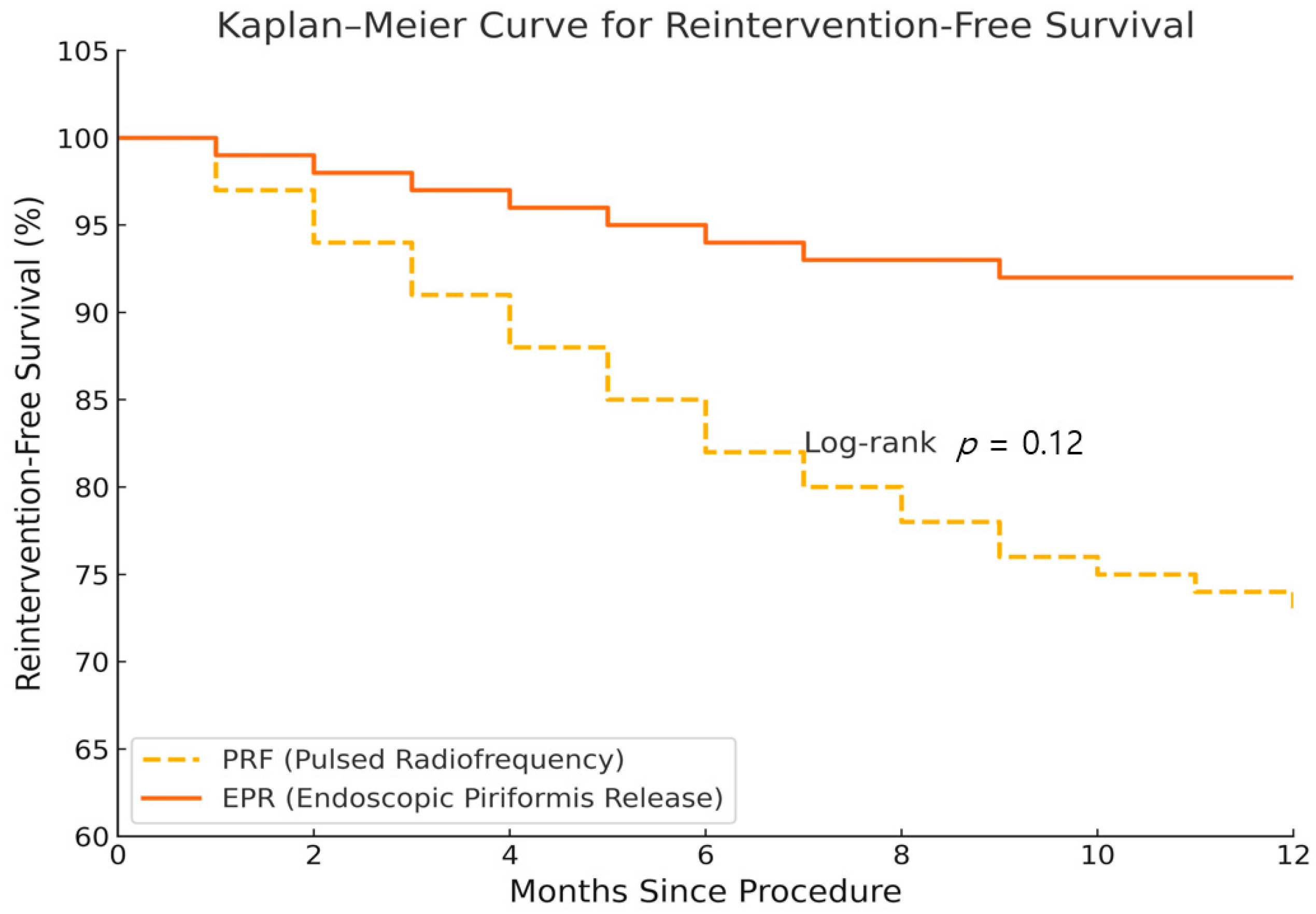
| Reintervention rate (%) | 12 (14/115) | 6 (7/115) | 0.134 | |
| ODI baseline (subset) | 42.3 ± 12.1 | 43.1 ± 11.8 | 0.71 | (n = 90) |
| ODI at 6 months (subset) | 28.5 ± 10.4 | 26.2 ± 9.7 | 0.29 | (n = 90) |
| ODI change (subset) | −13.8 ± 8.2 | −16.9 ± 7.5 | 0.198 | (n = 90) |
3.2. Time to Reinnervation
3.3. Multivariate Logistic Regression
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PS | Piriformis Syndrome |
| PRF | Pulsed Radiofrequency |
| EPR | Endoscopic Piriformis Release |
| PSM | Propensity Score Matching |
| NRS | Numeric Rating Scale (0–10 scale for pain) |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| FAIR test | Flexion, Adduction, and Internal Rotation Test |
| MCID | Minimal Clinically Important Difference |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| PRP | Platelet-Rich Plasma |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
References
- Hicks, B.L.; Lam, J.C.; Varacallo, M.A. Piriformis Syndrome. [Updated 4 August 2023]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448172/ (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Probst, D.; Stout, A.; Hunt, D. Piriformis Syndrome: A Narrative Review of the Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment. PMR 2019, 11 (Suppl. S1), S54–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopayian, K.; Danielyan, A. Four Symptoms Define the Piriformis Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review of Its Clinical Features. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018, 28, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, L.M.; Hosseini, M. Piriformis Syndrome—A Diagnosis Comes into Its Own. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, H.; Verma, N.; Adhya, B. Looking beyond Piriformis Syndrome: Is It Really the Piriformis? Hip Pelvis 2023, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, J.; de Sa, D.; Morrison, L.; Fejtek, E.; Simunovic, N.; Martin, H.D.; Ayeni, O.R. Surgical Management of Deep Gluteal Syndrome Causing Sciatic Nerve Entrapment: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy 2017, 33, 2263–2278.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larionov, A.; Yotovski, P.; Filgueira, L. Novel Anatomical Findings with Implications on the Etiology of the Piriformis Syndrome. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2022, 44, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Park, H.B.; Kim, Y.U. Diagnosis of Piriformis Syndrome Based on the Piriformis Muscle Cross-Sectional Area on Hip MRI. Medicine 2025, 104, e41689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siahaan, Y.M.T.; Tiffani, P.; Tanasia, A. Ultrasound-Guided Measurement of Piriformis Muscle Thickness to Diagnose Piriformis Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 721966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudin, A.L.; Shomakhov, M.A.; Yumatova, E.A.; Abovich, Y.A. Piriformis Syndrome. Treatment under Control of CT Fluoroscopy. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova 2020, 120, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, N.; Kiernan, H.; Bisht, R.; Singleton, I.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D.; Imani, F.; Varrassi, G.; Pourbahri, M.; Viswanath, O.; et al. Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Piriformis Syndrome: A Literature Review. Anesth. Pain Med. 2021, 11, e112825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanermen, F.; Van Melkebeek, J. Endoscopic Treatment of Piriformis Syndrome Results in a Significant Improvement in Pain Visual Analog Scale Scores. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2022, 4, e309–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Stancati, A.; Silvestri, C.A.; Ciapetti, A.; Grassi, W. Minimal Clinically Important Changes in Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Intensity Measured on a Numerical Rating Scale. Eur. J. Pain 2004, 8, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardowski, E.A.; Byrd, J.W.T. Piriformis Injection: An Ultrasound-Guided Technique. Arthrosc. Tech. 2019, 8, e1457–e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Xiong, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Z.; Tang, G. Little Needle-Scalpel for Piriformis Syndrome: A Protocol for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, G.T.; Erden, E.; Erden, E.; Ulaşlı, A.M. Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Platelet Rich Plasma Injection in Patients with Piriformis Syndrome. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2022, 35, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bağcıer, F.; Tufanoğlu, F.H. A New Treatment Modality in Piriformis Syndrome: Ultrasound Guided Dry Needling Treatment. Agri 2020, 32, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Jimenez, R.; Kahana-Rojkind, A.H.; Kingham, Y.E.; Kuhns, B.D.; McCarroll, T.R.; Domb, B.G. Endoscopic Technique: Sciatic Neurolysis and Piriformis Tendon Release for Treating Piriformis Syndrome. Arthrosc. Tech. 2024, 13, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Siraj, S.; Dadgal, R. Physiotherapy for Piriformis Syndrome Using Sciatic Nerve Mobilization and Piriformis Release. Cureus 2022, 14, e32952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, S.; Tunç, M.; Aksay, U.C.; Sönmez, E.; Özşahin, E.; Göker, P. Assessment of the Piriformis Muscle and Piriformis Syndrome via Web of Science Database: A Bibliometric Analysis. Medicine 2024, 103, e40416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention (EPR vs. PRF) | 2.15 | 1.12–4.13 | 0.021 |
| Age (per years) | 0.99 | 0.97–1.02 | 0.612 |
| Sex (F vs. M) | 1.14 | 0.62–2.09 | 0.674 |
| BMI (per kg/m2) | 1.03 | 0.96–1.11 | 0.401 |
| Symptom duration (per years) | 0.87 | 0.76–0.99 | 0.038 |
| Baseline NRS (per unit) | 1.32 | 1.08–1.61 | 0.007 |
| Diabetes (Yes vs. No) | 0.82 | 0.39–1.73 | 0.601 |
| Variable | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline NRS | r = 0.42 (Pearson) | <0.001 |
| Symptom duration | ρ = −0.19 (Spearman) | 0.004 |
| Age | r = −0.06 (Pearson) | 0.372 |
| BMI | r = 0.04 (Pearson) | 0.551 |
| Intervention (EPR vs. PRF) | ρ = 0.22 (Spearman) | 0.001 |
| Model | Key Covariates | EPR Effect (Direction vs. Primary) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary model | Age, sex, BMI, symptom duration, baseline NRS, diabetes, hypertension | References |
| Residual-imbalance model | Primary + any covariate with post-match SMD ≥ 0.10 | Similar |
| ODI-subset model | Primary + baseline ODI (subset n = 90) | Similar |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, E.; Choi, D.; Lee, C. Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency and Endoscopic Piriformis Release for Refractory Piriformis Syndrome: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165908
Park E, Choi D, Lee C. Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency and Endoscopic Piriformis Release for Refractory Piriformis Syndrome: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165908
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Eunsung, Duyoung Choi, and Cheol Lee. 2025. "Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency and Endoscopic Piriformis Release for Refractory Piriformis Syndrome: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165908
APA StylePark, E., Choi, D., & Lee, C. (2025). Comparison of Pulsed Radiofrequency and Endoscopic Piriformis Release for Refractory Piriformis Syndrome: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5908. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165908






