Neurosensory Disturbances Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Relocation and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
- 1.
- Population:
- 2.
- Intervention:
- 3.
- Comparison:
- 4.
- Outcomes:
- ○
- Primary Outcome: Incidence of neurosensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesia, hypoesthesia, or dysesthesia) following IAN repositioning.
- ○
- Secondary Outcome: Rate and extent of spontaneous recovery from neurosensory disturbances following IAN repositioning.
- 5.
- Study Design:
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Prospective cohort studies, observational studies, and RCTs reporting altered sensation following implant placement.
- Studies providing data on the onset and duration of neurosensory disturbances postoperatively.
- Studies published between 2009 and 2024 to capture advancements in techniques.
- Articles written in English.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Case reports, cross-sectional studies, and literature reviews.
- In vitro studies, finite element analyses, and animal studies.
- Studies not meeting the focus on neurosensory disturbance or inferior alveolar nerve repositioning.
2.3. Search Strategy
- PubMed;
- Cochrane Library;
- Science Direct;
- Google Scholar;
- Ovid;
- Embase;
- Open Gray (for gray literature).
2.4. Keywords and Search Terms
- Altered sensation;
- Dental implant;
- Dysesthesia;
- Hyperalgesia;
- Implant placement
- Inferior alveolar nerve;
- Mandibular nerve;
- Nerve injury;
- Nerve lateralization;
- Nerve repositioning;
- Neurosensory disturbance;
- Paresthesia;
- Sensory disturbance;
- Transposition.
2.5. Selection Process
2.6. Data Collection Process
- Author and year;
- Study design;
- Sample size;
- Statistical analysis methods;
- Radiographic method;
- Method of nerve repositioning/surgical technique;
- Number of patients with altered sensation;
- Method of evaluation of altered sensation;
- Nature of altered sensation;
- Recovery rate and intervals;
- Implant survival rate.
2.7. Data Items
2.8. Effect Measures
2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
2.12. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
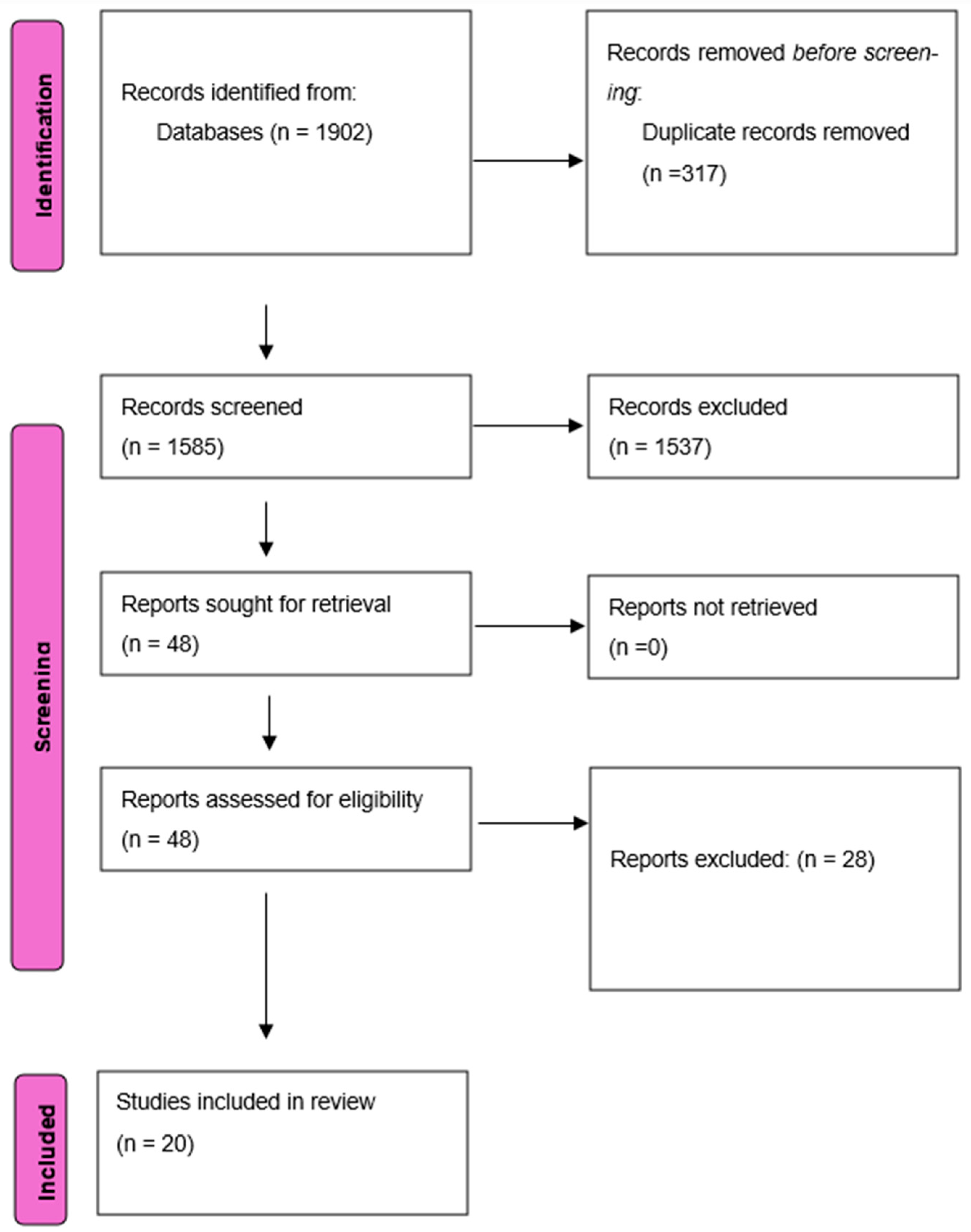
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies and Reporting Biases
3.3.1. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
3.3.2. Retrospective Studies
3.3.3. Non-Randomized Studies
3.4. Results of Syntheses
- -
- -
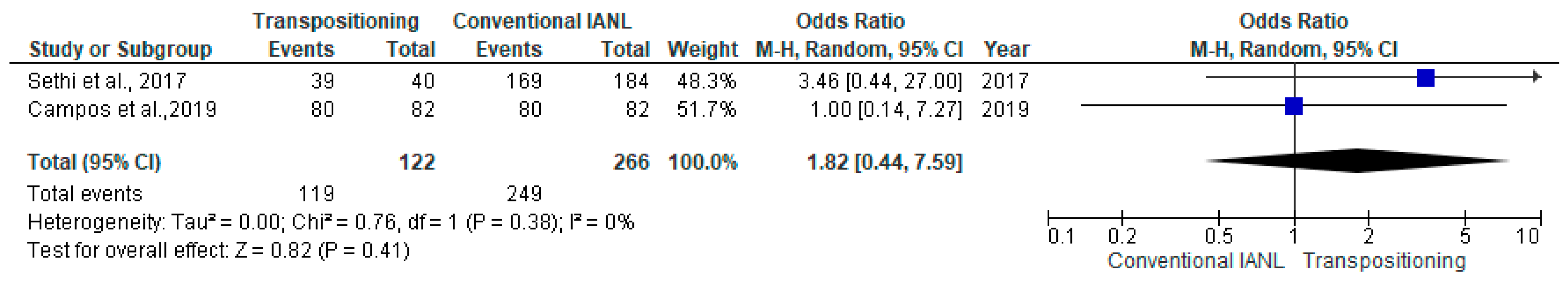
3.5. Incidence of Neurosensory Disturbances in Lateralization and Transposition Techniques
- -
- -
3.6. Recovery Timelines Were as Follows:
- -
- -
- -
3.7. Piezo Surgery vs. Rotary Instruments
3.8. Key Findings
3.9. Implant Success Rate
3.10. Influence of Bone Grafts and Interface Materials
- -
- -
- Interface Materials: PRF and collagen membranes were used to protect nerves from direct implant contact and promote regeneration through the release of growth factors such as the following:
- ○
- Platelet-derived growth factor;
- ○
- Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β).
3.11. Certainty of Evidence
3.12. Meta-Analysis
3.12.1. Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ)
3.12.2. Marginal Bone Loss
3.12.3. Implant Success Rate
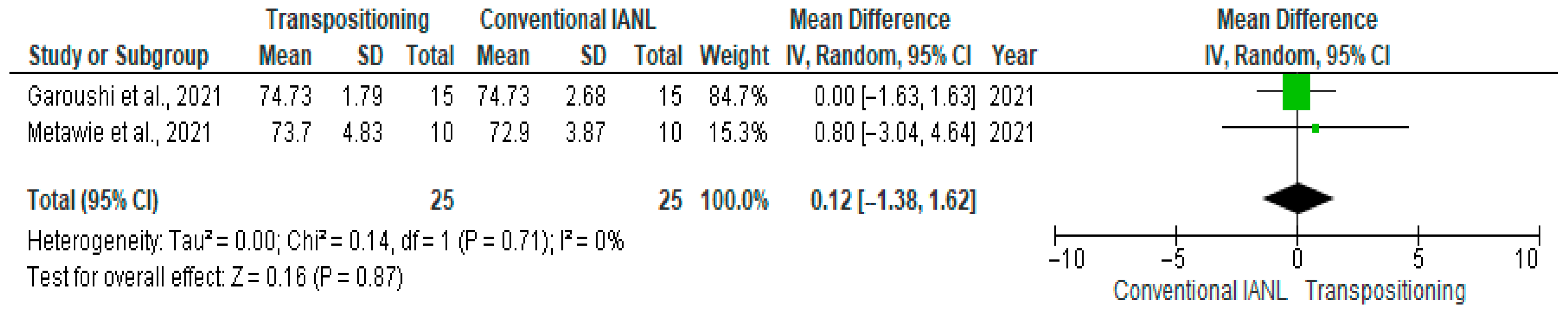
3.12.4. Neurosensory Disturbances at 3 Months
4. Discussion
4.1. Atrophic Mandibular Rehabilitation
4.2. Challenges in Atrophic Mandibular Rehabilitation
4.3. Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ)
4.4. Marginal Bone Loss
4.5. Success Rate
4.6. Neurosensory Disturbances at 3 Months
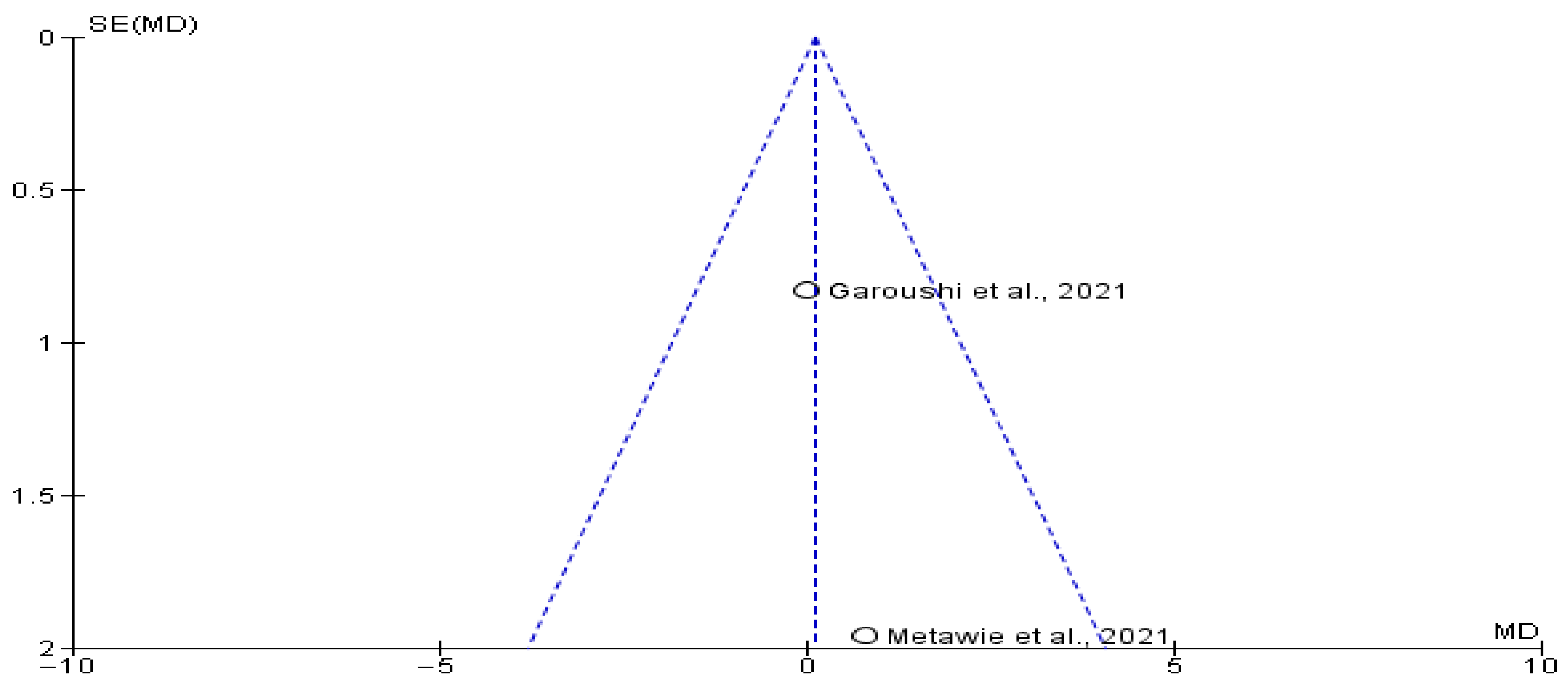
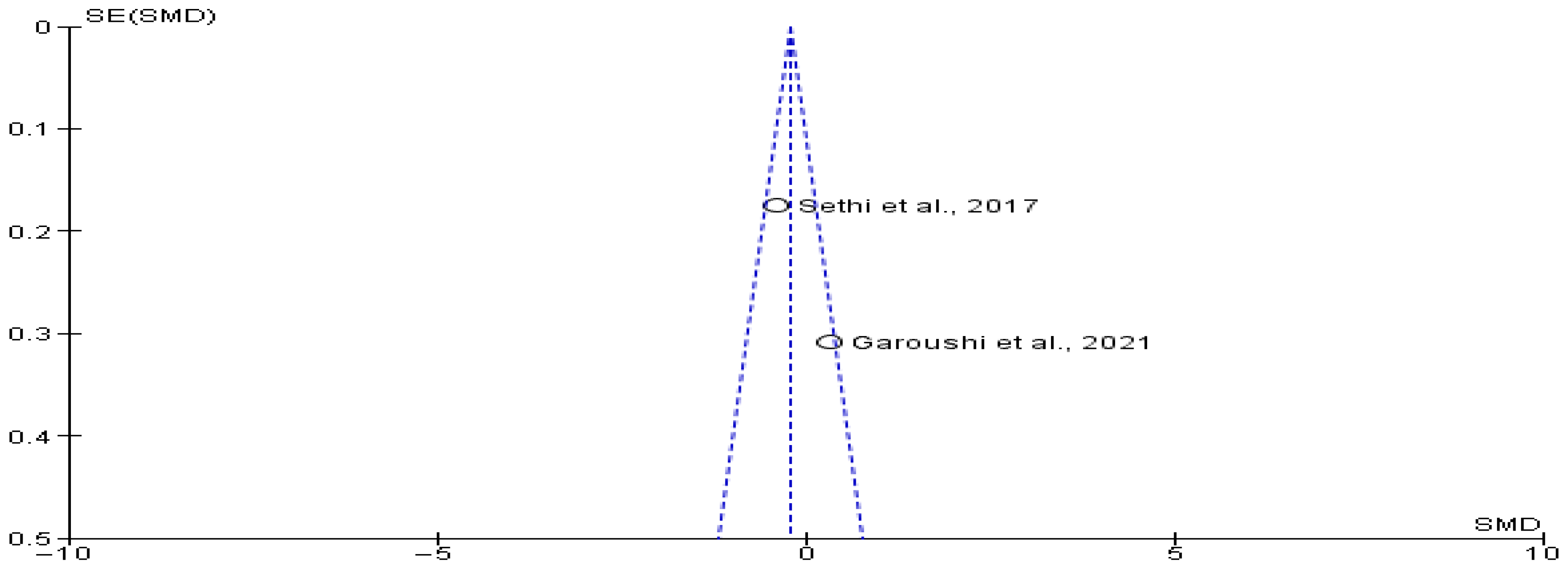
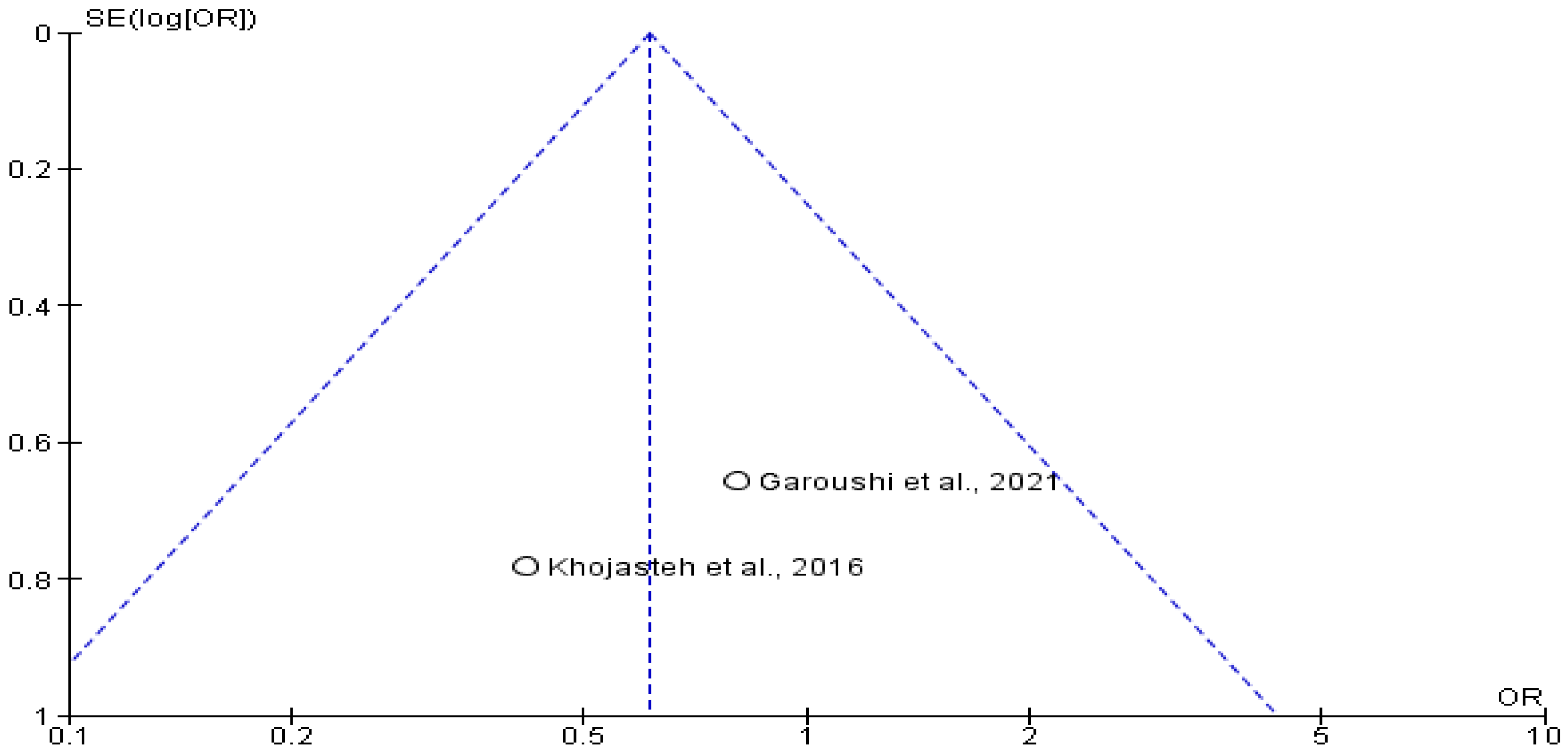
4.7. Heterogeneity and Publication Bias
4.8. Techniques for Mandibular Nerve Management
4.8.1. Nerve Lateralization
4.8.2. Nerve Transposition
4.9. Comparison of Techniques
4.10. Lateralization vs. Transposition
4.11. Technological Advances in Mandibular Rehabilitation
4.12. Neurosensory Disturbances
4.13. Adjunctive Measures
4.14. Feasibility of the Techniques
4.15. Clinical Implications
4.16. Alternative Strategies and Future Perspectives
4.17. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Vicente, J.C.; Peña, I.; Braña, P.; Hernández-Vallejo, G. The use of piezoelectric surgery to lateralize the inferior alveolar nerve with simultaneous implant placement and immediate buccal cortical bone repositioning: A prospective clinical study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehata, I.; Abdelmonim, G. Piezosurgery versus conventional rotary instrument for Inferior Alveolar Nerve lateralization prior to implant placement: (Comparative Clinical Study). Egypt. Dent. J. 2021, 67, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, G.; Boniello, R.; Saponaro, G.; Marianetti, T.M.; Foresta, E.; Torroni, A.; Longo, G.; Azzuni, C.; Cervelli, D.; Pelo, S. Long term follow-up in inferior alveolar nerve transposition: Our experience. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 170602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorean, A.; Kablan, F.; Mazor, Z.; Mijiritsky, E.; Russe, P.; Barbu, H.; Levin, L. Inferior alveolar nerve transposition and reposition for dental implant placement in edentulous or partially edentulous mandibles: A multicenter retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, A.; Hosseinpour, S.; Nazeman, P.; Dehghan, M. The effect of a platelet-rich fibrin conduit on neurosensory recovery following inferior alveolar nerve lateralization: A preliminary clinical study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryabin, G.; Grybauskas, S. Dental implant placement with inferior alveolar nerve repositioning in severely resorbed mandibles: A retrospective multicenter study of implant success and survival rates, and lower lip sensory disturbances. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2021, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. Available online: https://www.bmj.com/content/372/bmj.n71 (accessed on 20 December 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RoB 2: A Revised Cochrane Risk-of-Bias Tool for Randomized Trials|Cochrane Bias. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/bias/resources/rob-2-revised-cochrane-risk-bias-tool-randomized-trials (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- ROBINS-I Tool|Cochrane Methods. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/robins-i (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, J.Y.; Lozada, J.L.; Goodacre, C.J.; Davis, W.H.; Hanisch, O. Endosseous implant placement in conjunction with inferior alveolar nerve transposition: An evaluation of neurosensory disturbance. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1997, 12, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Abdo, A.E.; Abd-Elhakam, H.; Abd-Elmonim, G. Evaluation of neurosensory deficits following the use of computer assisted surgical guide for inferior alveolar nerve bypass versus inferior alveolar nerve lateralization (randomized controlled trial). Indian. J. Public. Health Res. Dev. 2021, 12, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- de Campos, C.; Francischone, C.; Assis, N.; Devito, K.; Sotto-Maior, B. Neurosensory Function and Implant Survival Rate Following Implant Placement With or Without an Interposed Bone Graft Between the Implant and Nerve: Prospective Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metawie, D.; El Prince, N.; Fahmy, M.; El Dibany, R.; Ibrahim, I. Computer guided inferior alveolar nerve larteralization after repositioning of the bone window versus sticky bone augmentation (a randomized clinical trial). Alex. Dent. J. 2022, 47, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoushi, I.H.; Elbeialy, R.R.; Gibaly, A.; Atef, M. Evaluation of the effect of the lateralized inferior alveolar nerve isolation and bone grafting on the nerve function and implant stability. (Randomized Clinical Trial). Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, A.; Banerji, S.; Kaus, T. Inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle repositioning: A retrospective analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göçmen, G.; Bayram, F. Evaluating the influence of the mandibular canal trajectory on the duration of postoperative paraesthesia in patients undergoing inferior alveolar nerve lateralisation: A prospective cohort study. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 61, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, E.; Keceli, H.G.; Uysal, S.; Güngör, H.; Muhtarogullari, M.; Tözüm, T.F. Management of limited vertical bone height in the posterior mandible: Short dental implants versus nerve lateralization with standard length implants. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2016, 27, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Díaz, J.Ó.; Naval Gías, L. Rehabilitation of edentulous posterior atrophic mandible: Inferior alveolar nerve lateralization by piezotome and immediate implant placement. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.M. Neurosensory function following mandibular nerve lateralization for placement of implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, N.; Barona-Dorado, C.; Cortes-Breton Brinkmann, J.; Martín-Ares, M.; Leco-Berrocal, M.; Prados-Frutos, J.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Martínez-González, J.M. Implant survival and complications in cases of inferior alveolar nerve lateralization and atrophied mandibles with 5-year follow-up. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, M.; Kshirsagar, R.A.; Joshi, S.; Pawar, S.; Tapadiya, V.; Gupta, S.; Mahajan, V. Evaluation of Neurosensory Function Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Lateralization for Implant Placement. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2019, 18, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Almaie, S.; Kavarodi, A.; Al Faidhi, A.; Alorf, A.; Alzahrani, S. Incidence of neurosensory disturbance and success rates of solid-screw implants placed in conjunction with inferior alveolar nerve transposition. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 10, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano-Navarro, J.M.; Castellano-Reyes, J.J.; Hirdina-Castilla, M.; Suárez-Soto, A.; Bocanegra-Pérez, S.; Vicente-Barrero, M. Neurosensory issues after lateralisation of the inferior alveolar nerve and simultaneous placement of osseointegrated implants. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 57, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimaki, F.; Kurita, H.; Tozawa, S.; Teramoto, Y.; Nishizawa, R.; Yamada, S.I. Subjective and qualitative assessment of neural disturbance after inferior alveolar nerve transposition for dental implant placement. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2016, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.A.; Bagheri, S.C. Letters to editor a bioabsorbable collagen nerve cuff (NeuraGen) for repair of lingual and inferior alveolar nerve injuries a case series. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 67, 2550–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.C.; Williams, C.W. Documentation method for inferior alveolar and lingual nerve paresthesias. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1986, 62, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.M.; Branemark, P.I. Fixture stability and nerve function after transposition and lateralization of the inferior alveolar nerve and fixture installation. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1995, 33, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio García-Ochoa, A.; Pérez-González, F.; Negrillo Moreno, A.; Sánchez-Labrador, L.; Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J.; Martínez-González, J.M.; López-Quiles Martínez, J. Complications associated with inferior alveolar nerve reposition technique for simultaneous implant-based rehabilitation of atrophic mandibles. A systematic literature review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 121, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Cannizzaro, G.; Barausse, C.; Pistilli, R.; Esposito, M. Short implants versus longer implants in vertically augmented posterior mandibles: A randomised controlled trial with 5-year after loading follow-up. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 7, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Allavéna, J.; Nicot, R.; Majoufre, C.; Schlund, M. Inferior alveolar nerve repositioning surgical techniques and outcomes—A systematic review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.J.; Cariseo, C.; Gold, M.; Díaz, D.; Orellana, M.; Iwanaga, J. Anatomical variations of the mandibular canal and their clinical implications in dental practice: A literature review. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2021, 43, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayev, B.; Juodzbalys, G. Inferior Alveolar Nerve Lateralization and Transposition for Dental Implant Placement. Part II: A Systematic Review of Neurosensory Complications. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2015, 6, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ravidà, A.; Serroni, M.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Romandini, M.; Wang, I.C.; Arena, C.; Annunziata, M.; Cecoro, G.; Saleh, M.H. Short (≤ 6 mm) compared with ≥10-mm dental implants in different clinical scenarios: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials with meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis and quality of evidence grading. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2024, 51, 936–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.P.; Sutariya, P.V.; Pathan, M.R.; Upadhyay, H.H.; Patel, S.R.; Kantharia, N.D. Clinical success between tilted and axial implants in edentulous maxilla: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2021, 21, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiuto, R.; Barbieri, C.; Garcovich, D.; Dioguardi, M.; Redaelli, M.; De, M.i. cheli L. Rehabilitation of Edentulous Jaws with Full-Arch Fixed Implant-Supported Prostheses: An Approach with Short and Ultrashort Implants and Metal-Free Materials. Case Rep. Dent. 2020, 2020, 8890833. [Google Scholar]
- Vetromilla, B.M.; Moura, L.B.; Sonego, C.L.; Torriani, M.A.; Chagas, O.L., Jr. Complications associated with inferior alveolar nerve repositioning for dental implant placement: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Marques, G.B.; Andrade, M.; Shinohara, E.H. Inferior Alveolar Nerve Lateralization Surgery for Implant Installation in Atrophic Posterior Mandible with Accessory Mental Foramen: A Challenge for the Usual Technique. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2022, 33, e255–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhani, D.; Ohlmeier, K.H.; Sutter, W.; Kielbassa, A.M. Undesirable course of an oral implant rehabilitation in a patient with a long history of bulimia nervosa: Case report and review of the literature. Quintessence Int. 2019, 50, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vo, N.; Nguyen, T.; Ta, Q.D.; Truong, B.C. Contralateral Inferior Alveolar Nerve Transposition for Simultaneous Dental Implant Placement on a Unilateral Reconstructed Mandible: A Case Report with a 7-Year Follow-Up. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 813.e1–813.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.J. Inferior alveolar nerve repositioning. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 9, 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatteroni, E.; Covani, U.; Fabris, G.B.M. The New Generation of Subperiosteal Implants for Patient-Specific Treatment of Atrophic Dental Arches: Literature Review and Two Case Reports. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2023, 43, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libertucci, M.; Cosola, S.; Covani, U. A single overturning of ridge for horizontal bone augmentation in maxilla with immediate implant placement: 18-years follow-up. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Cases 2021, 7, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, P.; Marchionni, S.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Marconcini, S.; Covani, U.; Barone, A. Surgical techniques used in the rehabilitation of partially edentulous patients with atrophic posterior mandibles: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, N.A.; Marchio, V.; Troiano, G.; Gasparro, R.; Balice, P.; Marenzi, G.; Laino, L.; Sammartino, G.; Iezzi, G.; Barone, A. Narrow-diameter versus standard-diameter implants placed in horizontally regenerated bone in the rehabilitation of partially and completely edentulous patients: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2022, 15, 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti, T.; Troiano, G.; Oreglia, F.; Lombardi, T.; Gregorig, G.; Morella, E.; Rapani, A.; Stacchi, C. Wedge-Shaped Implants for Minimally Invasive Treatment of Narrow Ridges: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, R.; Manacorda, M.; Abundo, R.; Lucchina, A.G.; Scarano, A.; Crocetta, C.; Muzio, L.L.; Gherlone, E.F.; Mastrangelo, F. Accuracy of Edentulous Computer-Aided Implant Surgery as Compared to Virtual Planning: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchuk, S.; Ivanov, S.Y.; Sukharev, V. Inferior alveolar nerve preservation during resection and reconstruction of the mandible for benign tumors as a factor improving patient’s quality of life. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2022, 50, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Saadat, S.; Moshiri, R.; Shahmirzad, S.; Hassani, A. Nerve Retraction During Inferior Alveolar Nerve Repositioning Procedure: A New Simple Method and Review of the Literature. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E. Severe Atrophy of the Posterior Mandible and Inferior Alveolar Nerve Transposition. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2021, 41, e199–e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Bassi, A.P.; Lee, H.J.; Alcântara, P.R.; de Sartori, I.M.; Luvizuto, E.R.; Faco, E.F.; Faot, F. Inferior alveolar nerve lateralization and implant placement in atrophic posterior mandible. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, e347–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.; Chiarot, M.; Kirby, S. Mental nerve function after inferior alveolar nerve transposition for placement of dental implants. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2002, 68, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zandi, M.; Heidari, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Aminzadeh, A.; Rajaei, S.; Mousavi, M.; Mohammad Gholi Mezerji, N. Histological evaluation of inferior alveolar nerve injury after osteotomy of mandibular buccal cortex using piezoelectric versus conventional rotary devices: A split-mouth randomised study in rabbits. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iezzi, G.; Perrotti, V.; Felice, P.; Barausse, C.; Piattelli, A.; Del Fabbro, M. Are <7-mm long implants in native bone as effective as longer implants in augmented bone for the rehabilitation of posterior atrophic jaws? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 552–566. [Google Scholar]
- Vinci, R.; Cosola, S.; Borsi, A.; Speroni, S.; Esposito, M. Immediate loading after implant placement with relocation of the inferior alveolar nerve in atrophic mandibles: A 1-year retrospective case series. Clin. Trials Dent. 2024, 06, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zizzari, V.L.; Zara, S.; Tetè, G.; Vinci, R.; Gherlone, E.; Cataldi, A. Biologic and clinical aspects of integration of different bone substitutes in oral surgery: A literature review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, R.; Teté, G.; Lucchetti, F.R.; Capparé, P.; Gherlone, E.F. Implant survival rate in calvarial bone grafts: A retrospective clinical study with 10 year follow-up. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Zarchini, R.; Ozkan, B.T.; Majdi, S. Dental Implant Survival after Postoperative Infection. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.H. Peri-Implantitis and Concomitant Perigraftitis of an Implant Placed in a Site That Had Alveolar Ridge Preservation Three Decades Earlier: A Case Report with Human Histology. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2022, 12, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, R. Less is more. Clin. Trials Dent. 2024, 6, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, S.K.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Alqarni, A.; Alarabi, S.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alshamrani, A.; Covani, U.; Cosola, S. Insights into the Current Management Techniques for Peri-Implant Gaps: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatteroni, E.; Toti, P.; Covani, U.; Crespi, R.; Cosola, S.; Menchini-Fabris, G.B. A Retrospective Radiological and Clinical Survey of Full-Arch Immediate Fixed Prostheses Supported by Custom-Made Three- Dimensional Printed Subperiosteal Titanium Implants in Patients with Severe Atrophic Jaws: Implant Success Code. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author and Year | Study Design | Sample Size | Statistical Analysis Used | Radiographic Method | Method of Nerve Repositioning/Surgical Technique | Number of Patients with Altered Sensation | Method of Evaluation of Altered Sensation | Nature of Altered Sensation | Recovery Rate and Intervals | Implant Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdo et al., 2021 [14] | RCT | 26 patients | Chi-square, t-test | CBCT | IAN lateralization vs. nerve bypass using computer-guided stent and conventional rotary method | 26 patients | Subjective (questionnaire, light touch [LT], brush direction detection [BDD]), objective (TSEP) | Temporary sensory disturbance | Full recovery by 24 weeks | Not explicitly mentioned |
| Campos et al., 2019 [15] | RCT | 34 patients, 82 implants | Student’s t-test, ANOVA | CBCT | IAN lateralization with/without bone graft | 34 patients | Questionnaire, periodic follow-up | Temporary hypoesthesia, paresthesia | Mean recovery: 118.6 days (control), 123.5 days (bone graft) | 97.56% |
| Metawie et al., 2022 [16] | RCT | 20 patients (10 per group) | ANOVA, t-test | CBCT | IAN lateralization with sticky bone vs. bone block repositioning | 20 patients | Subjective and objective testing, Modified Nerve Block Recovery (MNBR) scale | Temporary disturbance | 100% recovery at 6 months | 100% |
| Garoushi et al., 2021 [17] | Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial | 18 patients (30 ridges) | Chi-square, GEE model, t-test | CBCT | IAN lateralization with/without collagen membrane and bone graft | All patients initially | Medical Research Council (MRC) scale, sensory tests | Temporary disturbance | 100% recovery at 6 months | 100% |
| chehata et al., 2021 [2] | Comparative Clinical Study | 24 patients (12 per group) | t-test, ANOVA | CBCT | IAN lateralization with Piezosurgery vs. rotary instruments | 24 patients | Transcutaneous electrical stimulation potential (TSEP), Visual Analog Scale (VAS) | Temporary disturbance | Full recovery by 24 weeks | 95% |
| Sethi et al., 2017 [18] | Retrospective Analysis | 78 patients, 308 implants | Kaplan–Meier survival curve | CBCT | IAN lateralization/transposition | All initially; 5 patients with residual altered sensation | Wisp test, sharp test, discriminatory distance test | Residual altered sensation in 5 patients | Recovery varied between 24 h and 6 months | 97.8% |
| Bayram et al., 2023 [19] | Prospective Cohort Study | 20 patients, 50 implants | Shapiro–Wilk, ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc | CBCT | IAN lateralization | 20 patients initially | Westermark’s subjective method, Von Frey hair test | Temporary paresthesia | Median duration 120 days, no permanent issues at 12 months | 100% |
| De Vicente et al., 2016 [1] | Prospective Clinical Study | 13 patients, 27 implants | Mann–Whitney, Fisher’s exact test, Spearman’s correlation | CT scans | IAN lateralization with buccal cortical bone repositioning | All patients initially | Light touch (LT), pain threshold, Two-point discrimination (TPD) tests | Temporary hypoesthesia | 11 fully recovered at 3 months, 1 patient had residual sensation at 12 months | 100% |
| Dursun et al., 2016 [20] | Prospective Comparative Study | 15 patients (25 implants in IANL group) | ANOVA, Pearson Chi-square test | CBCT, Panoramic X-rays | IAN lateralization with Piezosurgery vs. short implant conventional methods | 2 patients | Two-point discrimination, pin-prick tests | Temporary paresthesia | Resolved in 1 week | 100% |
| Fernández et al., 2013 [21] | Prospective Cohort Study | 15 patients (19 procedures) | Descriptive statistics | Panoramic X-rays | IAN lateralization with Piezosurgery | All patients initially | Two-point discrimination test | Temporary hypoesthesia | 93.33% recovered at 8 weeks | 97.36% |
| Hashemi et al., 2010 [22] | Prospective Cohort Study | 87 patients (110 sites) | Descriptive statistics | Panoramic X-rays, CT scans | IAN lateralization using hand instruments | All patients initially | Questionnaire (subjective reporting of sensory disturbances) | Temporary hypoesthesia, tickling in 3% at 6 months | 97% normal neurosensory function by 1 year | 100% |
| Martínez-Rodríguez et al., 2016 [23] | Prospective Cohort Study | 27 patients, 74 implants | Descriptive statistics | Panoramic radiographs, CT scans | IAN lateralization with Piezosurgery | 27 patients initially | Two-point discrimination test | Temporary hypoesthesia | 74.1% recovery at 3 months; 96.3% recovery at 18 months | 98.6% preloading, 100% post-loading |
| Rathod et al., 2018 [24] | Prospective Clinical Study | 10 patients, 20 implants | Descriptive statistics | CBCT, Panoramic radiographs | IAN lateralization | All patients initially | Semmes–Weinstein monofilaments (SWMs) | Temporary hypoesthesia | Minimum recovery time: 2 months; maximum: 4 months | Not reported |
| Saad Al-Almaie et al., 2020 [25] | Prospective Study | 8 patients, 20 implants | Life-table analysis | Panoramic radiographs | IAN transposition | 6 patients initially | Light touch test, pain test, two-point discrimination test | Temporary neurosensory disturbances in 20% of cases | Complete recovery in 3 patients within 1 month | 100% |
| Castellano-Navarro et al., 2019 [26] | Retrospective Case Series | 123 patients, 337 implants | Descriptive statistics | Panoramic X-rays | IAN lateralization and transposition | All patients initially | Light touch test, sensitivity mapping | Temporary hypoesthesia in all patients | 81% recovery within 6 months, 100% by 1 year | Not reported |
| Gasparini et al., 2014 [3] | Retrospective Cohort Study | 35 patients, 49 IANTs | Fisher’s exact test | CT dentascan | IAN transposition | 6 patients with complications | Two-point discrimination test, painful stimulus, thermal sensitivity | Transient hypoesthesia (14.3%) and anesthesia (2.8%) | All symptoms resolved by 6 months | Not reported |
| Deryabin et al., 2021 [6] | Retrospective Multicenter Study | 15 patients, 48 implants | Descriptive statistics | CBCT | IAN lateralization and transposition | All patients initially | Subjective assessment using a modified questionnaire | Transient numbness in all patients; weak hypoesthesia in 2 patients by 3 years | Transient numbness resolved in most cases by 3 months; weak hypoesthesia persisted in 2 patients at 3 and 5 years | 95.8% |
| Khojasteh et al., 2016 [5] | Retrospective Cohort Study | 14 patients, 51 implants | Descriptive statistics | CBCT, Panoramic X-rays | Modified IAN lateralization with PRF conduit | All patients initially | Static light touch (SLT) and two-point discrimination (TPD) tests | Numbness, tingling; transient hypoesthesia | Normal sensation at 6 months in 42.9% (modified) and 28.6% (conventional); full recovery in most by 12 months | Not explicitly reported |
| Lorean et al., 2013 [4] | Multicenter Retrospective Study | 57 patients, 232 implants | Descriptive statistics | CT scans | IAN transposition/reposition | 4 patients (5%) | Von Frey test, two-point discrimination, pin-prick tests | Prolonged transient neural disturbance (1–6 months) | No permanent neural damage; full recovery by 6 months in most cases | 99.57% |
| Nishimaki et al., 2016 [27] | Retrospective Assessment | 7 patients, 22 implants | Descriptive statistics | CBCT, Panoramic X-rays | IAN transposition | All patients initially | Modified SW perception test, highest grading | Transient numbness, moderate hypoesthesia, severe hypoesthesia | Full recovery on 2 sides; weak hypoesthesia in 2 sides; moderate in 2 sides; severe in 1 side | 100% |
| Study | Bias from Randomization | Bias from Interventions | Bias from Missing Data | Bias from Outcome Measurement | Bias from Reported Results | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdo et al. [14] | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Campos et al. [15] | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Metawie et al. [16] | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Garoushi et al. [17] | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| chehata et al. [2] | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk | Low Risk |
| Study | Selection (4) | Comparability (2) | Outcome (3) | Total (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lorean et al. (2013) [4] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9/9 (Low Risk) |
| Sethi et al. (2017) [18] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9/9 (Low Risk) |
| Castellano et al. (2019) [26] | ★★★★ | ★ | ★★★ | 8/9 (Low Risk) |
| Gasparini et al. (2014) [3] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8/9 (Low Risk) |
| Nishimaki et al. (2016) [27] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 8/9 (Low Risk) |
| George Deryabin et al. (2021) [6] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6/9 (Moderate Risk) |
| Khojasteh et al. (2016) [5] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6/9 (Moderate Risk) |
| Study | Confounding Bias | Selection Bias | Intervention Classification Bias | Deviation Bias | Missing Data Bias | Measurement Bias | Reporting Bias | Overall Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayram et al. [19] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| De Vicente et al. [1] | Moderate | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Erhan Dursun et al. [20] | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Fernandez Diaz et al. [21] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Hashemi et al. [22] | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Martínez-Rodríguez et al. [23] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Rathod et al. [24] | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Saad Al-Almaie et al. [25] | Moderate | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Article citation | Reason for Exclusion |
| Meyer et al. [28] | Letters to editor |
| Robinson et al. [29] | No comparison between lateralization and transposition |
| Hirsch et al. [30] | Year of publications |
| Palacio García-Ochoa et al. [31] | |
| Felice et al. [32] | Only evaluated short implants and bone augmentation, no nerve relocation |
| Allavéna et al. [33] | Narrative review, not original data |
| Valenzuela-Fuenzalida et al. [34] | Narrative review |
| Abayev et al. [35] | |
| Ravid et al. [36] | Systematic review and no nerve technique evaluated |
| Mehta et al. [37] | Systematic review and no nerve technique evaluated |
| Aiuto et al. [38] | Study on alternative procedures |
| Vetromilla et al. [39] | No comparison between lateralization and transposition |
| Yoshimoto et al. [40] | Technology report, no clinical outcomes |
| Turhani et al. [41] | Narrative review with case report |
| Van Vo et al. [42] | Case report |
| Louis et al. [43] | No implant placement |
| Vatteroni et al. [44] | Review article of alternative procedures |
| Libertucci et al. [45] | No nerve relocation data |
| Toti et al. [46] | Clinical article of alternative procedures |
| Valente et al. [47] | Clinical article of alternative procedures |
| Vercellotti et al. [48] | Clinical article of alternative procedures |
| Vinci et al. [49] | Technical review without clinical data related to relocation of the nerve |
| Tereshchuk et al. [50] | No implant placement |
| Hassani et al. [51] | Technical method description |
| Romanos et al. [52] | Technical method description |
| Suzuki et al. [53] | Case report |
| Morrison et al. [54] | It has not been published between 2009 and 2024 |
| Zandi et al. [55] | Animal study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinci, R.; Cosola, S.; Varkey M, K.; Gunasekaran, S.; George, J.; Covani, U. Neurosensory Disturbances Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Relocation and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165741
Vinci R, Cosola S, Varkey M K, Gunasekaran S, George J, Covani U. Neurosensory Disturbances Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Relocation and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165741
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinci, Raffaele, Saverio Cosola, Korath Varkey M, Sowndarya Gunasekaran, Jaibin George, and Ugo Covani. 2025. "Neurosensory Disturbances Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Relocation and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165741
APA StyleVinci, R., Cosola, S., Varkey M, K., Gunasekaran, S., George, J., & Covani, U. (2025). Neurosensory Disturbances Following Inferior Alveolar Nerve Relocation and Implant Placement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165741








